UNIT 1 COMPUTER MAINTENANCE
Introductory activity 1.0
1. Observe the image below and answer related questions:
a. What is the task being accomplished by the person in the image above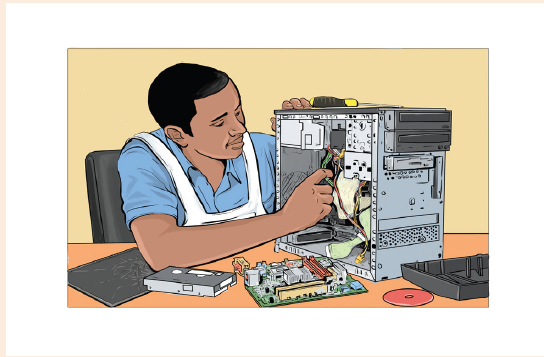
b. List out any five names of devices found on the figure above
1.1. HARDWARE:
Hardware refers to any physical or tangible part of a computer. The computer
hardware consist of internal and external parts.
A.Internal computer components
Those are all components that are found inside the system unit such as disk drives,
motherboard, processor, power supply, memory, etc.
B.External computer components
External components of a computer also known as peripherals refer to all externals
devices connected to central housing known as the system unit. They can be input
devices, output devices such as the monitor or storage devices such as a hard
drive or flash drive, memory card. Peripherals devices are connected to the systemunit through different ports found on the computer.
1.1.1. Elements of the computer system unit and their roles:
Activity 1.1
1. Open the system unit cover to expose the internal components as shownin Figure below.
a. Identify various components inside the system unit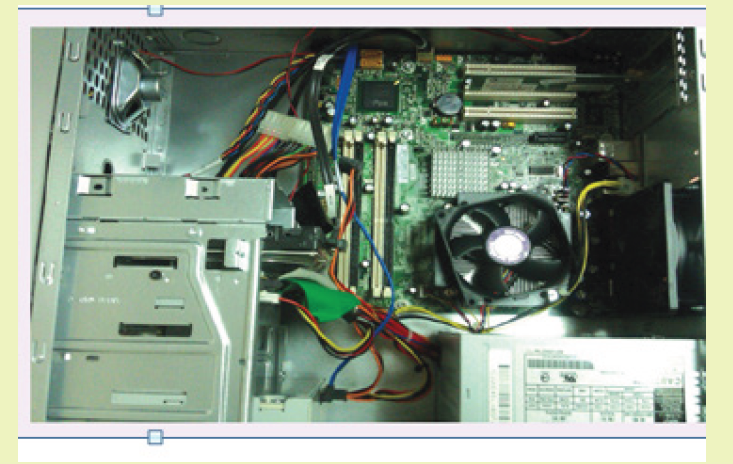
b. Briefly state the role of each component identified in a)
Activity 1.1
The system unit, which houses all the internal components of a computer, has a
number of components inside it such as the power supply and the motherboard on
which are connected other parts like microprocessor (or CPU) disk drives, adapter
cards and memory.
Different components of the computer case and their roles are elaborated in the
content to follow.
A. Power supply
The power supply is unit is the one which is directly connected to the power outlet
through the power cable. The Power Supply Unit (PSU) converts alternating current
(AC) from the power outlet to direct current (DC) required by internal computercomponents.
B. Motherboard
A motherboard also known as circuit board is the main printed circuit board onto
which all components of the computer interconnect into one another. It also allows
communication of those different parts as it has routes from/to those parts.
Motherboard size varies depending on whether a computer is a desktop or a laptop
and the size also varies depending on manufacturers but the devices found on
each and their functions don’t vary. A particular desktop computer looks like in theimage below:
On the motherboard are connected different devices which are CPU, hard disk,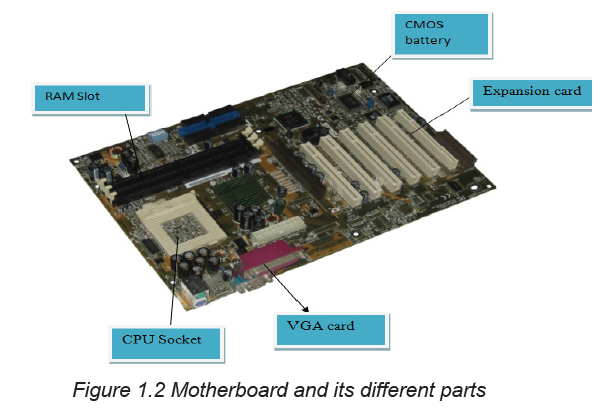
video card, RAM, ROM, expansion slots, data buses, etc.
B.1. Central processing unit (CPU)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU), also known as the processor or microprocessor,
is the most important part of the computer which is considered as the “brain” of the
computer because all processing activities are carried out inside it.
The processor controls the retrieval, interpretation, and execution of instructions in
a computer. It consists of three components namely the Arithmetic and Logic Unit
(ALU), the Control Unit (CU) and the memory units, known as registers.
i. The Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
It is the part of the CPU that performs two main functions, namely arithmetic
operations such as addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication and logical
operations such as OR, AND, and NOT among others. These two functions are
necessary in the execution of different instructions by the CPU.
ii. The control unit (CU)
The control unit coordinates all processing activities in the CPU as well as input,
storage and output operations. It also performs tasks like controlling, supervising,
and overseeing all the activities of the computer. It oversees fetching instructions
from the main memory, decoding the instructions in a format the computer can
understand, executes the instructions by issuing commands to respective
components where action is supposed to be taken and controlling the transfer of
data and information within the available storage space.
iii. Registers
Registers are temporary storage locations located inside the processor that are
used to hold data, instructions or information waiting processing or output. There
are four types of registers namely: instruction register, accumulator register, address
register, and storage register. All the four types of registers store information that
is temporarily needed for program execution. The Instruction register holds an
instruction before it is converted to machine readable format, the Address register
stores the address of the next instruction to be processed, the Accumulator
register holds the last processing step of the Arithmetic Logic Unit and the Storage
register holds information waiting to be outputted.
B.2. Hard disk
A hard disk also known as hard disk drive (HDD) is a non-volatile computer storage
device containing magnetic disks or platters with high speed. It is a secondary
storage device used to store data and program permanently, the term Non-volatilemeans data and program are retained even when the computer is turned off.
B.3. Video card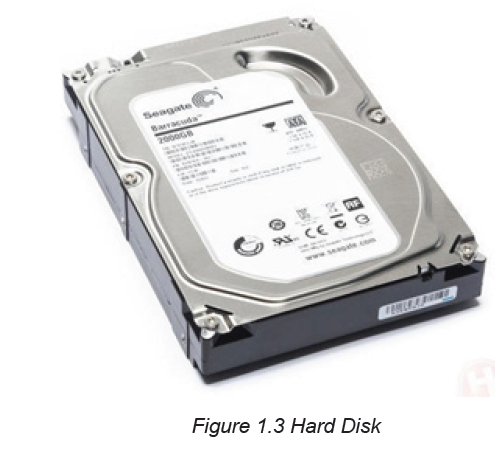
Video cards also referred to as graphic cards are components that are connected
to the motherboard of a computer system and generates the quality of images
on output devices such as screen. Graphic cards have processors or a graphic
processing unit and are directly connected to the motherboard which allows it toaccept information from the CPU and send output to the monitor.
B.4. Random Access Memory (RAM)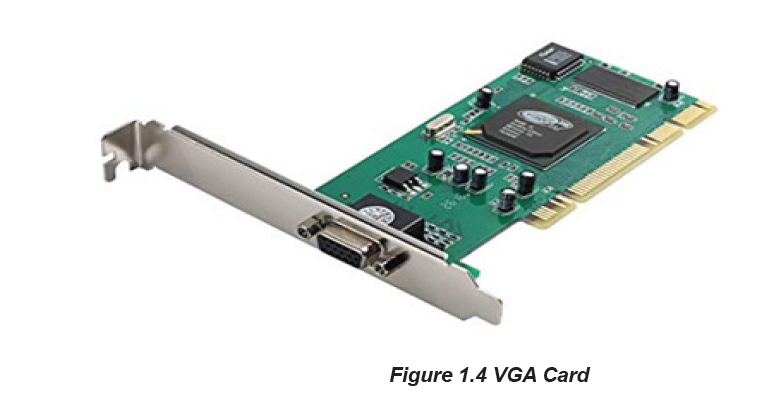
Random access memory (RAM) also known as working storage is used to hold
instructions and data needed by the currently running programs. It is referred to as
random access because its content can be read directly regardless of the sequence
in which it was stored.
RAM is a temporary or volatile storage because its content disappears when the
computer is switched off. Therefore, before switching off the computer, it is importantto save the work in a device that offers relatively permanent storage facility.
B.5. ROM
Read-Only Memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and
other electronic devices. As the name indicates; data stored in ROM may only be
read and cannot be electronically modified after the manufacturer of the memory
device. Unlike RAM (Random Access Memory), ROM is non-volatile, which meansit keeps its contents regardless of whether or not it has power.
B.6. Expansion slot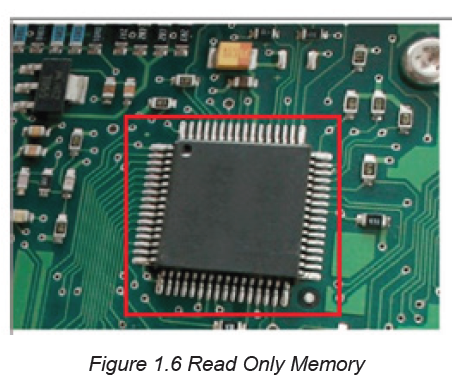
Expansion slot alternatively referred to as bus slot or port is a connection on the
motherboard to which an expansion card can be plugged in order to expand thefunctionalities of a computer.
B.7. Data buses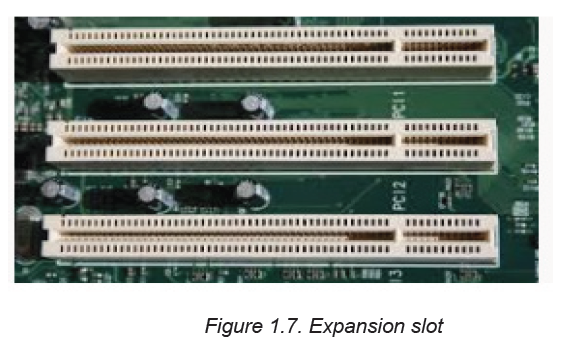
Data buses are those used to transfer data and instructions between componentsinside the computer.
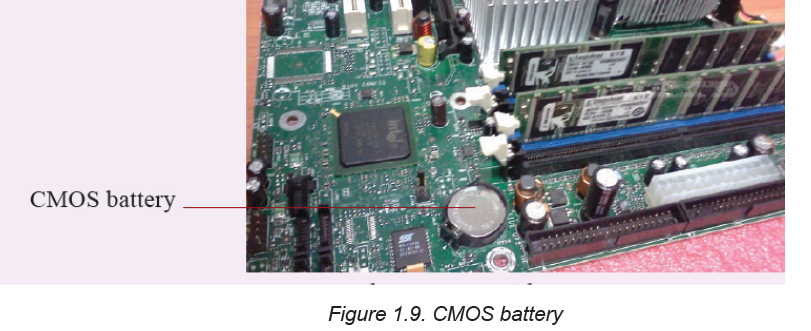
B.8 Complementary Metal- Oxide Semi-Conductor (CMOS) Battery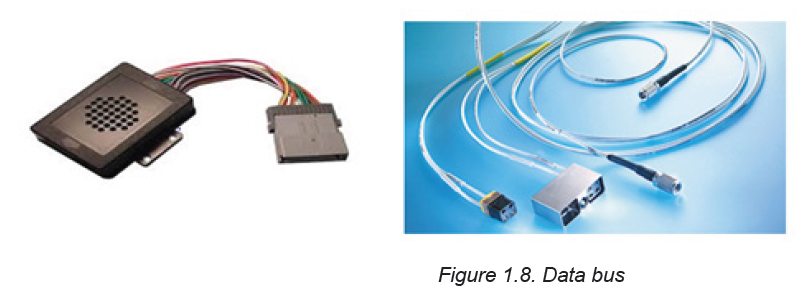
Complementary Metal- Oxide Semi-Conductor (CMOS) is the term usually used to
describe the small amount of memory on a computer motherboard that stores the
BIOS settings. The basic activities carried out by CMOS is to test the availability
of computer basic input and output devices (POST) and make sure no errors existbefore loading the operating system.
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.1
1. Explain three types of ports available on a desktop or laptop computer.
2. Research on the internet about primary, secondary and tertiary memory
and answer the questions below:
a. Which devices are referred to as primary,secondary or tertiary storage
devices?b. Why are some of these devices referred to as mass storage devices?
1.1.2. Computer maintenance principles
Activity 1.2
1. Identify five factors that need to be considered in order to minimize health
risks such as RSI (Repetitive Strain Injuries) and eye strain while using
computer.
2. Explain why it is not advisable to take food substances and drinks in the
computer lab.Computers are expensive to acquire. They are also useful to human being because
they carry out tasks that are sometimes so difficult. As an important tool in the life
of a human, a computer needs to be in good working conditions. Some computer
components can easily get damaged hence need to be handled with care. To
protect computers, certain rules, precautions and practices must be obeyed while
using computers and their components. This would help to avoid damage to the
computers.
Computer maintenance is the practice of keeping computers in a good state.
Computer maintenance can be carried out on the hardware or software. The
principles of software maintenance can be updates firmware, operating system,
application and data security such as encryption, cache clearing, and secure
deletion. On the hardware side of maintenance there can be cleaning and properly
connecting hardware components, monitoring peripherals, maintaining cooling and
testing individual components for integrity such as power supplies, RAM modules
and the hard disk. On the software side there is running different tools and software
aimed at optimizing the working of a computer.
Below are principles to be followed for computer maintenance:
A. Hardware:
1. Clean dust from the computer.
Computers are some of the most efficient dust collectors. Apart from looking gross
and possibly being an allergy hazard, a dusty computer will trap heat, which can
reduce its performance and lifespan.
2. Clean up the cabling and everything else
Cables may collect a lot of dust as they are sometimes on the floor. If there are
many peripherals consider cleaning them regularly.
3. Organize the installation disks
Keep memories for different software organized. Don’t mix CDs with memory
sticks or external memories and separate each memory depending on the type of
software stored. Installation software can be Operating systems, application and
utility software.
4. Properly interconnects components
Electronic device components are designed to fit into one another without using
mechanical force, when interconnecting a component into another requires force
this may be an indication of connecting it wrongly and it can result in the breaking
of pins making the whole device unusable.
B. Software
1. Properly switch on/off the computer
To properly switch off the computer gives time for the whole process required to
unload running programs. Switch off the computer when all programs are closed
and use the available computer menu (click on Start then on Shut down). Never
press the power button for switching off the computer. When programs fail to close
use the combination key Ctlr + Alt + Delete to open the task manager which will
help in closing those stubborn programs.
2. Delete unused files and programs
Unused Files and empty folders occupy space and make the computer run slowly.
Delete temporary files, old audios and videos as these occupy bigger space. Delete
also programs that are not used and don’t keep two versions of the same program
if they are not both needed.
3. Back up the data.
A data backup is the result of copying or archiving files and folders for the purpose
of being able to restore them in case of data loss. Data backup should be done
regularly in order to avoid total catastrophe in case there is a problem with the
computer.
4. Run antivirus and scans regularly
Antivirus software is a type of utility software used for scanning and removing
viruses from a computer. Scan so as to avoid computer being infested.
5. Clean up the OS
Disk cleanup is a maintenance utility used to free up space on a hard disk by
deleting unnecessary files and Windows components that are no longer in use.
This includes temporary internet files, downloaded program files and files in the
recycle bin. The disk cleans up procedure will be discussed later.
6. Clean up the software.
Every few months, look through the ‘Add or Remove Programs’ interface that is
found in the control panel. If there’s a software that is no longer needed, it must be
deleted.
7. Update everything
Check for updates for the hardware and software. This includes running Windows
Updates, checking for updated drivers, and checking for software patches.
8. Defragment
Defragmentation is the process of moving file fragments to contiguous clusters tooptimize the storage space and performance.
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.2
1. Explain the importance of computer maintenance
2. Highlighting some routine maintenance practices that need to be carriedout in a computer laboratory.
1.1.3. Computer capacityActivity 1.3
One day, Josiane wanted to borrow films from Paul who had many but when she
went to Paul’s home with her flash disk to borrow, the flash was able to keep
only two.
a. What should Josiane do so as to get all the films?
b. The two films stored on the flash were of equal size and the flash dish’ssize is 1GB. What is the size of each film?
A. Storage size
In digital computers, data is represented using a sequence of bits, bytes and words.
A bit is a short form for binary digit referring to a single digit which can be either
0 or 1 used to represent any data in digital computers. In other words, a bit is the
smallest unit used to represent data in digital computers.
A byte is a storage unit capable of representing a single character, such as a
letter, number or symbol. Technically, computers represent any type of data using a
sequence of 8 bits. A byte can store 28 or 256 different values, which is sufficient to
represent standard ASCII characters (letters, numbers and symbols)
A word is a unit of data used by a particular processor
Storage capacity also known as storage size refers to the amount of data a storage
device can hold. It is measured in kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes
(GB) and terabytes (TB). Since most files contain thousands of bytes, file sizes
are often measured in kilobytes. Larger files, such as images, videos, and audio
files, contain millions of bytes and therefore are measured in megabytes. Modern
storage devices can store thousands of these files, that is why storage capacity is
typically measured in gigabytes or even terabytes for larger memories.Standard units of measurement used for data storage are in the table below:
A.1. Reading memory/storage size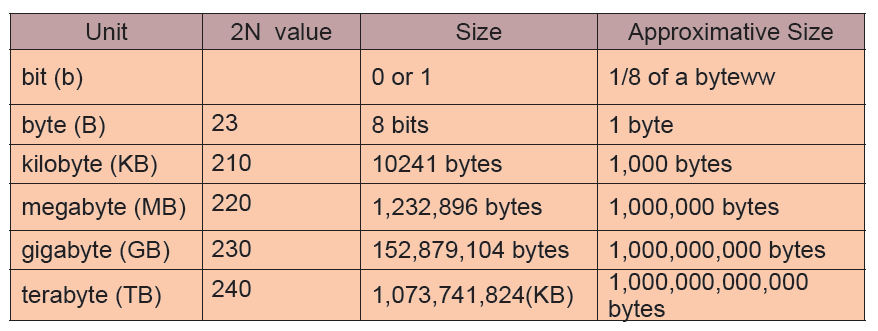
It is possible to know the size of the memory plugged in a computer or found inside
it.
I. Hard disk size
The hard disk size and its different disks can be viewed by going to the Computer
or This PC icon depending on the operating system. These icons can be found onthe desktop or on the startup menu. The window below will appear:
The window above shows that the computer has three disks each disk having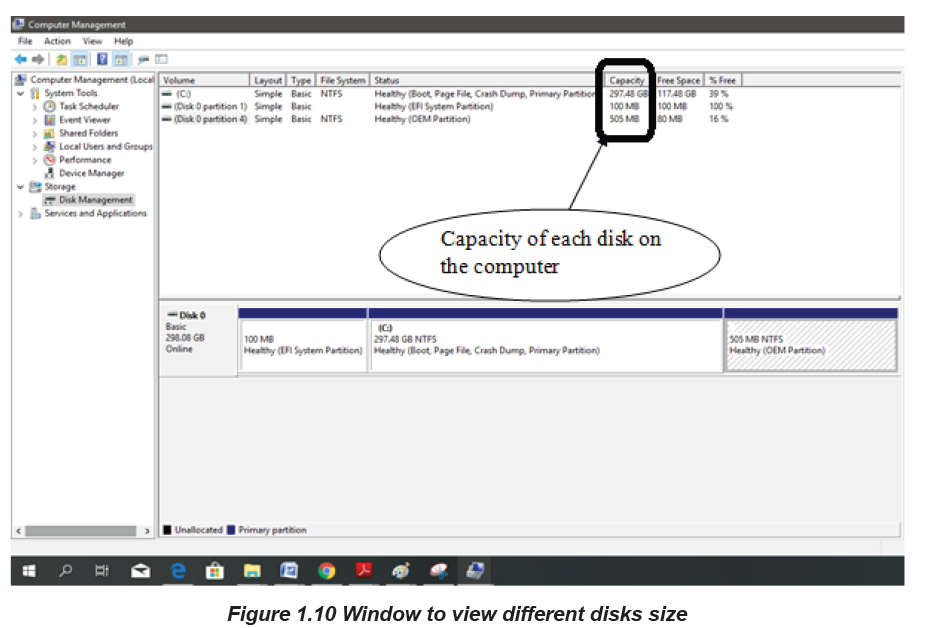
respectively 297.48GB, 100 MB and 500 MB of size. The size of the hard disk is
obtained by summing up the size of all the individual disks.
NB: When there is an external memory mounted on the computer, the name of that
memory will be displayed in the window used to view the hard disk’s size and the
size of that memory can also be viewed in the same window.
ii. RAM size
Proceed through the following steps to obtain basic information regarding the
capacity of primary memory (RAM) installed in the computer
Press control panel icon
Through all Control Panel Items select System.
A shortcut can also be used by using Right click on this PC icon and select properties.The figure below showing information of installed RAM will appear.
B. Processing speed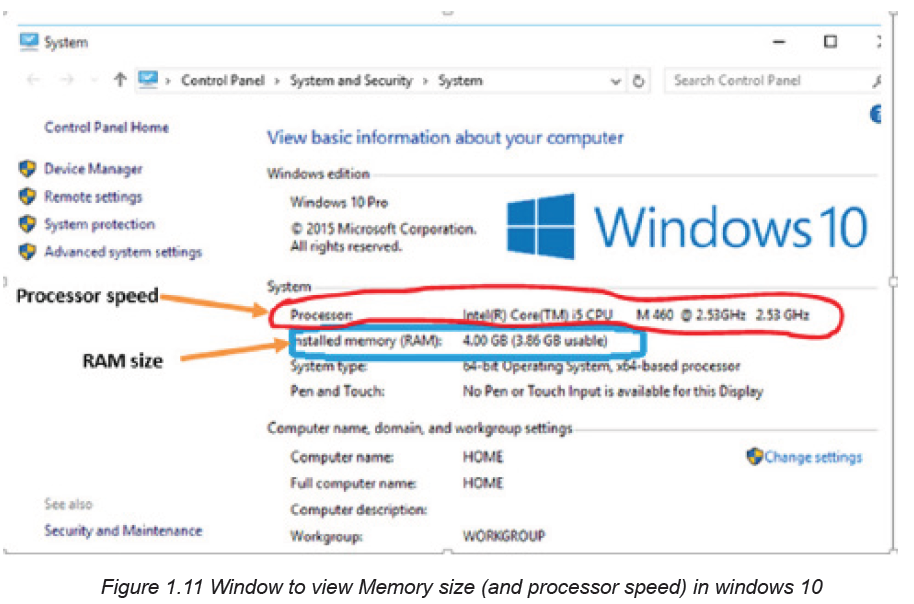
Processing speed is defined as the number of cycles per second at which the central
processing unit (CPU) of a computer operates and is able to process information.
It is measured in megahertz and is essential to the ability of a computer to run
applications.
The processing speed is measured in terms of Clock Speed which is measured in
gigahertz (GHz), with a higher number equating to a higher clock speed. Faster
clock speeds mean that tasks ordered from CPU are completed quicker, making
the computer user experience seamless. The processor speed can be viewed usingthe same window as the one used to view the RAM size.
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.3
1. If a CD contains 700 MB, how many number of CDs a DVD of 4,7 GB can
contain ?
2. If a 4MB document is downloaded within 6 seconds, what time (in hours)is required to download a 4GB movie?
1.1.4. Identifying and addressing hardware issuesActivity 1.4
a. Explain how you would connect both projector and monitor to a single
computer.
Computers are built with all security to protect sensitive components and hardware
housed inside a casing against any form of dust and other harsh elements. However,
some common computer hardware problems occur despite the protection. It’s very
crucial to identify and recognize such problems. The following are some of the
commonly found hardware related problems on computers.
1.1.4.1. Common hardware related problems
A. The Check POST test fails
POST stands for “Power on Self-Test”. This is part of a computer’s startup program
used to diagnose the keyboard, random access memory (RAM), disk drives and
other hardware to make sure they are working properly. If the POST detects any
errors in the hardware, it will either display a text error message on the screen or a
series of short and long beeps.
If an error message appears as the computer is booted, read careful the error
message and correct it or type the exact error message into a search engine to find
more information about it.
B. Blank monitors
A blank monitor is the most common computer problem. Most people who work
with computers might have dealt with such non-working blank monitor at least
once. In such cases, first and foremost check the supply cord and power systems.
Sometimes, the video cable might be loosened. Just push the video cable and
place it again.
C. Mouse Problems
The mouse is used for a variety of purposes, such as playing games or opening files
and moreover, it facilitates easy navigation. The most common problems related to
the mouse include failure to move, connection problems, freezing on the screen or
damage to the mouse. Mouse with PS/2 connection are prone to damages in its
pins, once such a mouse is not functioning its pins must be checked for blockage
or bending.
D. Jumpy Mouse
A jumpy mouse is just a muted mouse that cannot be scrolled. In case of a track
and ball mouse the problem can be solved by opening the ball container, removing
the excess debris and cleaning the dirt that lines the rollers. For an optical mouse,
eliminate the dust that has collected around the optical sensor.
E. Computer does not recognize USB
In this case, even when the USB is connected, the computer might not be able to
recognize it and hence displaying errors like “Device not recognized” This might
be due to the USB connector problems or the software malfunctions.
F. Keyboard Problems
Keyboard is a vital part of any computer. It not only allows typing, but also gives
commands. Common potential problems with the keyboard include keyboards that
will not connect to the computer, stuck keys, broken keyboards or keyboards where
the letters end up jumbled.
G. Power Cord Problems
Whether it is a laptop or a desktop, power cords are a vital part of any computer. A
laptop can run on batteries for a limited amount of time but then needs the power
cord for recharging. The most common problem with the power cord is an improper
connection.
H. Motherboard Problems
The motherboard has several parts of the computer including the RAM, BIOS system,
mass storage and CPU. The computer motherboard contains several devices,
which can create numerous potential problems. Problems with the motherboard
range from too little RAM to BIOS problems. Fixing the problems will depend on
the specific problem and, in the worst case scenario will require purchasing a new
motherboard to fix the problems.
I. Insufficient Memory
Processor-intensive programs also demand a lot of memory. Random access
memory (RAM) aides the central processing unit (CPU) by storing instructions linked
to common operations. Without enough RAM, software crashes and slowdowns
can occur.
1.1.4.2. Checking for hardware problems
Many computer problems are caused by hardware failures or problems with
hardware drivers. Windows will usually notify about devices that have problems.
Device Manager can be used to check the status of different hardware devices. The
Device Manager which is the Control Panel extension of Microsoft Management
Console, provides users an organized, central view of the Windows-recognized
hardware attached to a computer. This includes devices like keyboards, hard disk
drives, USB devices etc. It sorts out all hardware, listing them on the basis of various
criteria and when a device malfunctions or stops working altogether, it immediately
notifies the user. Thus, it can be used to control devices, enable or disable them,
configure them, identify conflicts between devices, and so forth.
To check for window hardware problem using device manager go through
this process:
Open Control Panel
Click on the Hardware and Sound link for Windows 8 or 10 or Click System and
Security for Windows 7.
Check under Devices and Printers in Windows 8 and 10, and under System in
Windows 7, to find Device Manager.
Once Device Manager is open, user can view device status, update device drivers,
enable or disable devices or do hardware management as shown in the figurebelow:
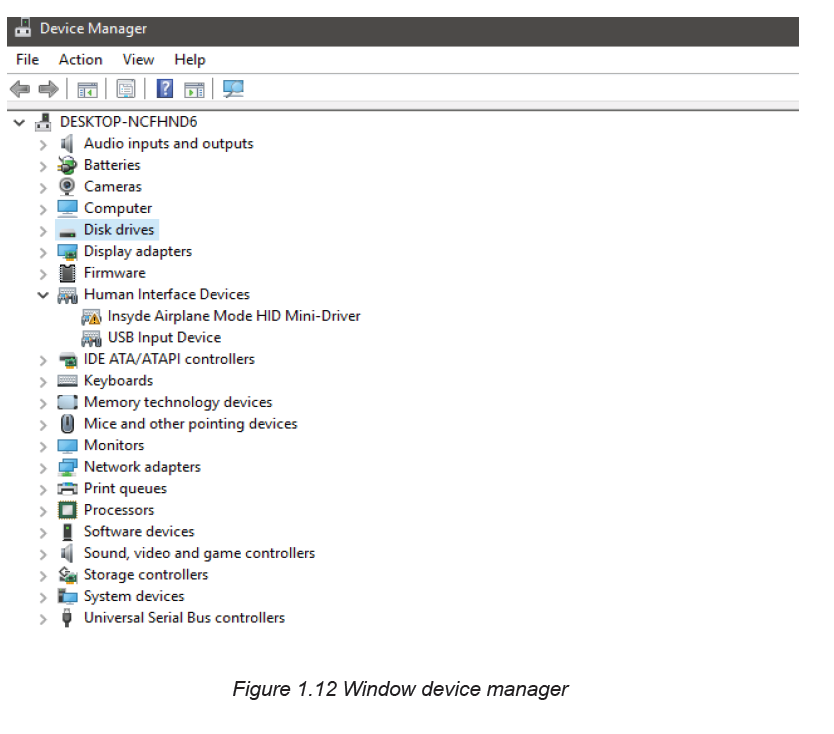
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.4
1. a. Identify the common hardware problems that you used to
face with while using computerb. How can you proceed to solve the problem above?
Note: Depending on version of Windows, Control Panel is usually available from
the Start Menu or the Apps screen.1.1.5. Assembling a computer & disassembling a computer
Activity 1.5
1. By searching the internet identify tools used in assembling and
disassembling a computer
2. Explain the reasons that may prompt a technician to remove any internalpart of a computer
A. Assembling a computer
Assembling a computer is putting together the computer components mainly the
internal ones so that they get interconnected and work together. Assembling acomputer can take 20 to 40 minutes provided all parts to assemble are available.
Steps to assemble a computer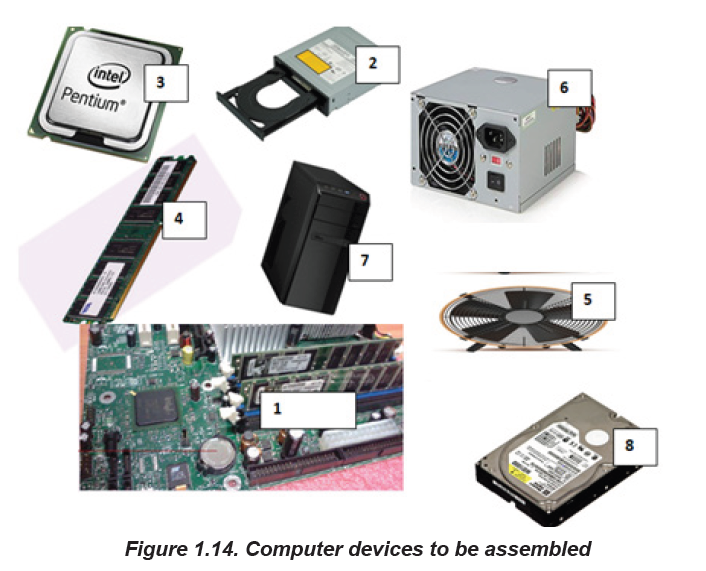
Step 1: Gather Tools and Supplies
Some tools such as Screwdriver, Wire cutters and strippers, Needle-nosed pliers,
Small flashlight, Small container to hold screws, Grounding Strap are helpful to
open or fix the screw and need to be made ready before. Also make sure all parts
are available and are organized in a way to facilitate identification of which part to
fit in the computer case first.
Step 2: Prepare the Case for Assembly
There are three things that need to be considered before assembly
Before assembling consider removing the cover for the optical drive and make note
of the cables pre-installed in the case. These should be front panel connections for
features such as the power switch, audio jacks and USB ports.
Step 3: Install the Motherboard
During motherboard mounting all standoffs need to be installed in the case. After
installation of standoffs it is necessary to check for screw hole locations on the
motherboard for exact placement. The next stage requires lowering the motherboard
into the case and aligning with the I/O bezel and installing the screws. The standoffs
and screws are installed in order to prevent damage to the motherboard.
Step 4: Install Hard Drive
Hard disk drives are usually connected to the motherboard through Enhanced
Integrated Drive Electronics (EIDE), Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) or
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) cable interface. Because with the
SATA technology a drive can be detached or attached to the motherboard while the
computer is switched on
The following steps are used to mount the drive into its hole:
1. Find drive bay to install the drive in. If there is a trouble finding a place to
mount the drive consult the case documentation for suggestions.
2. Slide the drive into place until the screw holes on the sides are lined up with
the holes in the case and put/tighten the screws in place.3. Connect wires that need to be connected
Step 5: Install Optical Drive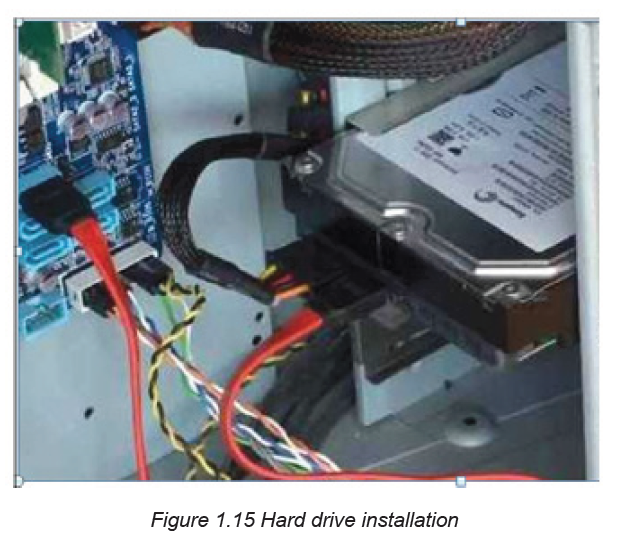
The optical drive is installed in the drive bay. The following steps are used to mount
the optical drive into its hole:
1. Slide the drive into the drive bay until the screw holes are lined up and the
front of the drive is flush with the front of the case. Make sure that it is
orientated correctly.
2. Install the screws and install wires to the right places
Step 6: Install the CPU
The CPU is the brain of the computer. It is installed on the motherboard’s appropriatesocket.
To install the CPU, first locate the corner marking that designates pins of the CPU.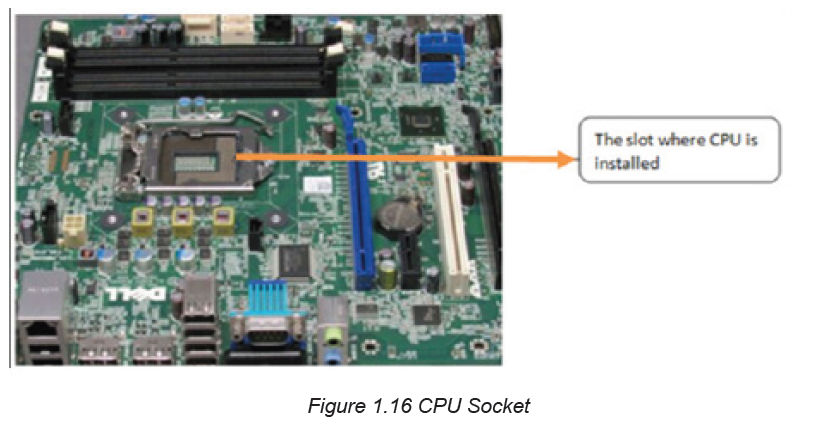
The second stage require to lift the small metal rod next to the socket and then
find the corresponding marking on the CPU socket to insert the CPU so that the
markings are lined up. Last push the rod down to lock the processor in place.
Step 7: Install RAM
The RAM is the temporary memory location that the processor works from.
Permanently stored data is pulled from disks and stored in RAM while the processor
works with it
The following steps are gone through to mount RAM into its exact position:
Set the RAM board in the socket. Check to see that the notch in the board is in the
correct location
Press firmly on both ends of the board to set it into the socket. Make sure the tabs
lock into place and press the board only when the tab is aligned as not doing so candamage the RAM or even the motherboard.
Step 8: Install the CPU Fan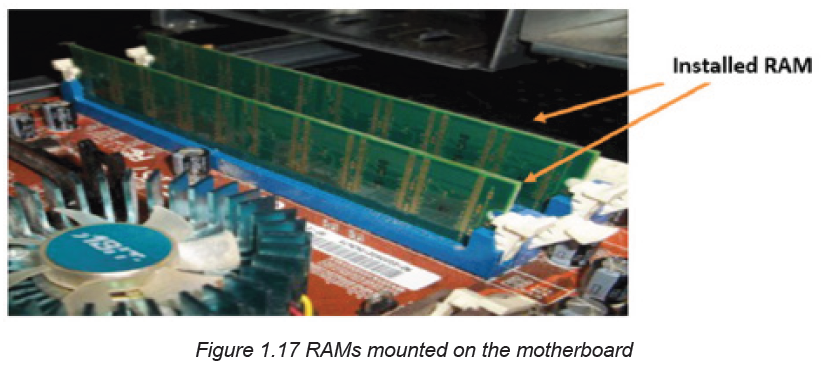
The CPU fan is a combination of a heat sink and fan together. The unit draws heat
away from the CPU. To install the fan the following steps are followed:
Firstly, Place thermal compound to the CPU following the instructions provided with
the compound,
Secondly, set the fan assembly on the CPU with mounting tabs aligned,
Pull the locking rod down on the fan assembly to lock into place,
Connect the fan assembly’s power connector to the motherboard.
Note: Failure to apply thermal compound results in insufficient cooling and cancause damage to the CPU or motherboard.
Step 9: Install Case Fan
The case fan is usually installed on the back panel of the case. To mount the fan
do the following:
1. Align the mounting holes by holding the fan to the mounting pad on the
inside of the case. The fan needs to be mounted so that it blows air out of
the case.
2. Insert the screws from the outside of the case and tighten them
Step 10: Install Power Supply
The following steps are followed to install power supply:
1. Align the mounting holes in the case and power supply.
2. Insert screws and tighten.Step 11: Connect Cables
When all of the components installed in the case, it may be possible that there are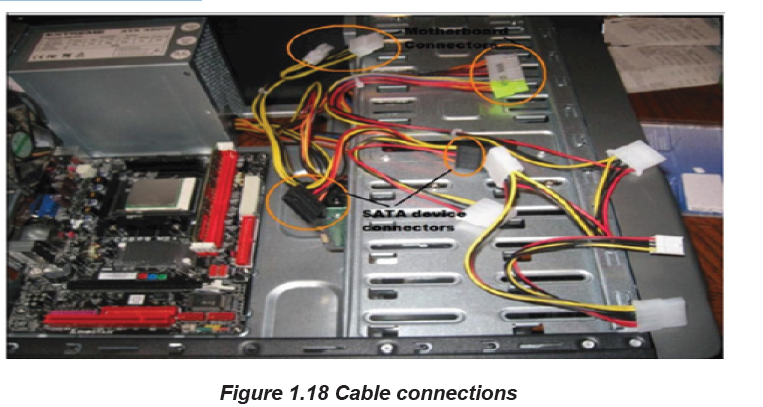
some parts which may not be supplied with the power. It is important to consult the
motherboard manual in order to make sure proper connections are made. There
are two kinds of connections, power and data.
About power connectors, every device installed needs power. The motherboard
has two power connections, connectors specifically for SATA devices (drives) other
connectors for running fans and or non-SATA devices. While data cables connect
drives and front panel devices to the motherboard. Incorrect connections can
damage components.
Step 12: Wrap-up
Now that the components are completely installed, the last thing to do is to
reinstall the side panels on the case. The computer is now ready to be turned
on. If the computer has problems starting up, check all component connections
and mounting to make sure that everything has been attached correctly. Otherwise
consult individual component manuals for specific troubleshooting information if
problems persist.
B. Disassembling a desktop computer
Disassembling a computer means disconnecting external and internal components
from the system unit. This process involves unplugging,
unscrewing and sliding out components depending on the mechanism used
to connect to the system unit or mount it onto motherboard. To disassemble a
computer, the following process is followed:
1. Disconnect the computer from the power source by unplugging the power
cable from power supply unit.
2. Unplug peripheral devices attached to the system unit such as monitor,
keyboard, mouse and printer.
3. Open the outer cover of the system unit by unscrewing or sliding it out.
4. Remove the adapter cards by first unscrewing them and gently unplug them
off the motherboard
5. Remove the fixed drives such as hard disk and optical (CD/DVD) drives by
unscrewing and disconnecting them from power supply unit. Next, disconnect
the IDE or SATA interface cable that connects the drive to the motherboard.
6. Remove memory (RAM) modules by pressing the tabs located on both ends
down away from the memory slot. Carefully hold the slightly lifted module by
the edges and remove it from the motherboard.
7. Remove the power supply unit starting with the power connector to the
motherboard, CPU fan, cabinet fan, power buttons and drives if any. Next,
unscrew the unit to disconnect it from the system casing
8. Remove the CPU and its fan by first unscrewing the cooler fan from the
motherboard.
9. Finally, unscrew the motherboard to unplug it from the system unit casing soas to have an empty shell of the casing
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.5
1. Demonstrate how to mount a motherboard using the following guidelines:
• Line it up properly on the chassis, screw and fit it into place.
• Mount the processor, RAM modules and any expansion cards separately.
• Plug in the power cable connector from the power supply unit.
• Connect other internal components onto the board, and then connect the
monitor, keyboard and mouse to the system unit.
• Test for power and ensure that internal and external components are
initializing correctly during POST (Power-On Self-Test).
2. Do a research and explain five types of expansion cards used on desktopcomputers.
1.2. SOFTWARE1.2.1. Software installation principles
Activity 1.6
1. Explain the importance of reading the user manual before installing new
software.
2. State three factors you would consider before purchasing application
software.
3. State three hardware requirements to be considered when installing
application software.
Software is another part of a computer. It is the invisible part which consists of
instructions which operates a computer and executes specific tasks. Software can
be classified into two main categories namely system software and application
software.
System software is the one that performs a variety of fundamental operations that
helps to make computer resources available to the user. It can be divided into
Operating systems, Utility software, Firmware and Networking software.
Application software is the one used in a computer in order to perform tasks,
functions for the benefits to the user. Application software available in a specific
computer depends on the needs of the computer user. For example
one may have VLC to play videos while another may not have it depending on the
needs.
The number of computer software or programs installed on a computer is only limited
to hardware specifications such as processor type, memory and storage capacity.
Once a computer meets recommended specifications, software installations is
automatically carried out.
A.System requirement
Before installing computer program whether operating system or application
software, there are minimum system specifications that have to be considered in
terms of: Memory (RAM) capacity, Free hard disk space, Processor type with
speed and Graphics display.
For example, the following are the minimum and recommended system requirements
for the installation of Windows 10 operating system:
• Memory capacity: 1 Gigabyte (GB) of RAM on a 32-bit or 2 GB on 64-bit
machine
• Storage space: 16 GB free-disk space on 32-bit or 20 GB on 64-bit machine
• Processor type and speed: 1 Gigahertz (GHz) of CPU Speed
• Graphics card: Microsoft DirectX 9 graphics controller with WDDM driver
(Windows Display Driver Model)
B. Application software goes with specific operating system
An operating system has specific application software that it is designed to accept,
that is due to the fact that an application software needs a working environment
that is made ready by an operating system and while developing a program, the
developer considers the environment provided by that specific operating system.
For example, Windows operating system cannot accept application programsdeveloped for Linux.
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.6
1. Discuss various categories of software installed in the computers found in
the computer lab of your school.
2. Research on the internet minimum and recommended specification for
installing the following software:
a. Latest version of Microsoft Office
b. Latest release of Kaspersky Antivirusc. latest Ubuntu Linux
1.2.2. Computer software issues:Activity 1.7
At the end of the school term when students were using computers in the school
computer lab, every computer worked well but at the beginning of next term they
brought from outside different storage devices such as flash disks and other
external disks used to copy various documents to the computers. One day when
their teacher switched on the computers so as to install some software most of
the computers displayed suspected messages.
a. Discuss what may be the cause of such behaviors.
b. How the problem can be addressed in the laboratory?
A. Operating System issues
Being the one that directly interacts with the computer hardware through the
Operating system kernel, an operating system issue is a serious problem that may
make even accessing the computer’s different applications impossible. The various
operating system issues are elaborated in the subsequent content.
i. The computer won’t start
Operating system has the function of managing hardware and other application
software resources. A complete damage of an operating system leads a computer
to do not start even not function.
ii. Abnormally Functioning Operating System
If the operating system or other software is misbehaving, close it forcefully and
reopen it. A virus scan can also help if a reliable anti-virus software is installed.
iii. Operating system is not booting up
When the operating system is not loading, it is a serious problem that requires a
fresh reinstall of an OS.
iv. Operating system blue screen of death
A blue screen of death pops up when Windows encounter a critical error and
indicates a serious error with a computer device. Incase this occurs, users are
prone to losing important data since regular apps don’t normally have a right to
save their open data. The main reasons for this issue are:
• Crashing of a low-level software or drivers
• Drivers updates going wrong
• A faulty hardware
• A virus attack on a system
How to fix the blue screen of death issue:
• Do a system restore which will help undo any recent installed driver.
• Update device drivers since as time goes by some drivers become incompatible
with the regular OS updates which could cause the computer drivers to crash
more frequently.
• Start PC in Safe Mode and troubleshoot any problem from the blue screen
details and scan it for viruses since some viruses are known to cause the
Blue Screen of death.
• Reinstall the Windows OS if none of the above works.
v. Windows freezes or stops responding
The operating system may sometimes stop responding and freeze. In this case
a cursor may not move, an application may not respond or just a computer
user gets stuck on a certain action. Potential causes of the random freeze and
unresponsiveness on a PC may include:
• Software related issue including malicious software, virus attack and driver
related issues,
• Running too many programs at the same time,
• Memory issues and general hardware failure
• Solutions to windows freezing or stopping to respond
• The best solution is to give the computer some time to process, since it might
be handling a complex task that could be taking most of its CPU and RAM
If giving it more time does not work, then force end the task or program that is not
responding by pressing Ctrl + Alt + Del to open the Task Manager. After the Task
Manager opens highlight the non-responding program or process and choose “End
Task”.
• Reboot the PC by pressing down on the power button until the computer turns
off and restart it after a few seconds
• If after rebooting the computer still freezes then reboot the PC in Safe Mode
and uninstall any recent driver that might be causing the computer to freeze.
• Determine if there is a defective piece of hardware that might be causing the
device to freeze and replace it immediately. Also check on the computer’s
memory such as RAM to know if it needs upgrading.
• When none of the above solutions work a clean install of the Windows
Operating System can be considered.
vi. Less free storage than before after an operating system upgrade
This happens because files from the previous operating system are still left in the
system in a folder known as “Windows Old “the “Disk Clean-up” tool can be used
to prevent the computer from running slowly.
Steps to delete unnecessary files after an operating system upgrade
• Irrespective of the operating system used, either Windows 7, 8, 8.1, or 10 go
to the start then search and type Disk Cleanup
• The disk cleanup app shows, click on it to launch
• From the Apps interface, select the drive on which the OS is installed which
is usually C by default in many PCs.
• After selecting the drive click Ok and the disk cleanup app will scan for theunnecessary files that can be deleted and present them as a list.
• The disk cleanup then does another search and gives another list now with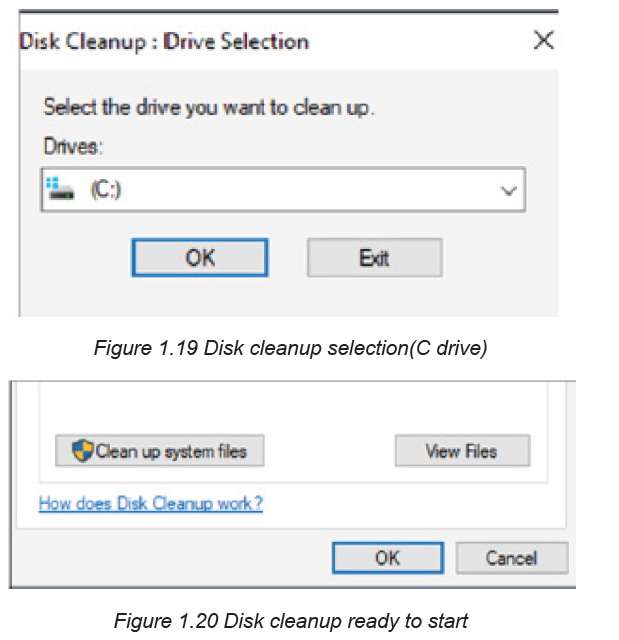
all the necessary files to delete. From the list select all the unnecessary files
taking up on the space including “Previous Windows installations”
• Click OK and a box asking whether to permanently delete these files will pop
up. Click Delete Files.
There are thousands of problems an operating system might encounter. However
most of those problems are rare and the existing few have been documented.
The various common issue and how they can be solved has been looked at in theabove content.
B. Applications issues
Common computer software issues or fault can include the following:
Inadequate software performance: This refers to slow system response time and
transaction throughput rates.
1. Obsolete software: Software that no longer works due to new hardware or
support software changes
2. Inconsistent processing: Software that only works correctly in one
environment. This refers to software that has been designed for only
one environment and cannot be easily transported and used in another
environment.
3. Unreliable results or performance: This means that the software does not
deliver consistently correct results and cannot work correctly each time it is
used.
4. Incorrect software version being installed on a computer
5. Virus and malware infection on a computer, etc.
The most common way to rectify software issues include uninstalling and reinstalling
a software, upgrading the software, running a virus and malware scan. It is also a
good practice to check for the manufacturers’ website for patches
C. Malware
Malware are harmful programs or malicious software that are specifically designed
to gain access or damage a computer without the user’s knowledge. They affect
the smooth running of a computer system or carry out illegal activities such ascollecting information from the infected user’s computer.
The categories of harmful programs include viruses, worms, Trojan horses, rootkits,spyware, crimeware, and adware. In this section we will discuss on viruses.
a) Virus
A virus is a self-duplicating computer program or piece of code that is loaded into
a computer without the user’s knowledge. Viruses can spread themselves from
computer to computer, interfering with data and software.
The source of computer viruses is the internet and storage devices or media.
To Prevent Harmful Programs the following measures can be taken:
i. Install an antivirus program
An antivirus will check for suspicious files and disinfect them or delete them. Make
sure the antivirus is up to date so that it can detect even newly created viruses.
ii. Avoid non-secure sites
Avoid visiting unfamiliar suspicion sites and block special sites that should not be
accessed using the computer browser.
iii. Scan emails for viruses
Do not open email attachments unless they are from legitimate known source.
iv. Install anti-spyware software
This is a type of program designed to prevent and detect unwanted spyware
program installations.
b) Trojan
Trojan or Trojan Horse is a malicious software that is disguised as legitimate. Trojan
misrepresents itself as useful, routine, or interesting in order to persuade a victim to
install it on a computer. Trojans do not replicate themselves and appear harmless
but in fact malicious.
c) Worms
A worm is a computer program that sits in the computer memory, duplicates itself
continuously until the system runs out of memory and crashes. Worms infect
networks by replicating themselves and transmitting their multiple copies to all the
nodes connected on the network
d) Rootkit
A rootkit is software used by a hacker to gain constant administrator-level access
to a computer or network. It is installed through a stolen password or by exploiting
system vulnerabilities without the victim’s consent or knowledge.
Rootkits primarily aim at user-mode applications. Rootkits can completely deactivateor destroy the anti-malware software installed in an infected computer, thus making
a rootkit attack difficult to track and eliminate. When done well, the intrusion can be
carefully hidden so that even system administrators are unaware of it.
e) Spyware
Spyware is a software code installed on a computer without user’s knowledge to
monitor or supervise user activities.
Spyware can do the following:
• Gather personal information and can transmit it without user’s knowledge,
• Change computer settings,
• Corrupt windows Registry files,
• Slow down internet connection speeds and the computer itself by taking up
memory and space on the computer,
• Can make a computer to malfunction or totally crash.
f) Adware
The term adware is used to describe a form of malicious software which presents
unwanted advertisements to the user of a computer. The advertisements produced
by adware are sometimes in the form of a pop-ups or in a window that cannot be
closed.
Adware is considered a dangerous program, its main objective is to collect information
about the user, to remove the browser ‘s restrictions, settings and default search
engine. When data collection is complete, the current opened program starts to be
active, and user gets low-quality sites in response to any request.
g) Crimeware
Crimeware is distinct from spyware and adware. It is designed to commit identity
theft through social engineering in order to access a computer user’s financial and
retail accounts for the purpose of taking funds from those accounts or completing
unauthorized transactions.
Crimeware can have the following impact:
• Install keystroke loggers to collect sensitive data login and password
information for online bank accounts.
• Redirect a user’s web browser to a counterfeit website controlled by the thief
even when the user types the website’s proper domain name in the address bar.
• Steal passwords cached on a user’s system.
• Enable remote access into applications, thus allowing a break into networksfor malicious purposes
• Encrypt all data on a computer and require the user to pay a ransom to decrypt it
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.7
1. Using internet and brainstorming, search any other common sources of
computer virus infection
2. Discuss the various ways a user can acquire a software to use.3. Demonstrate how to start disk cleanup utility.
1.2.3. Computer software installation
1.2.3.1. Installation of an OS
Activity 1.8
Suppose your school receives 30 new computers with no installed programs.
a. What is the first program the school ICT teacher or lab technician should
firstly install?
b. Explain why?
The term Software Installation means the process of copying installation files of
a given program onto the hard disk in a format that allows the computer to run the
program. It means putting a computer program on a computer and make it ready
to use. Before installing any software read the manufacturer’s installation manual
to correctly install programs. This manual describes all the procedures and the
necessary system requirements for successful installation.
Most programs are installed by downloading the program from online sources.
Programs can be installed from an external storage medium such as a DVD or USB
stick. If a program is being installed from the disk, the installer will automatically start
when a memory is inserted in the DVD drive. What the one doing the installation will
have to do is just follow the instructions.
Installation of an Operating System is a fundamental process that starts with
identifying minimum or recommended system specifications.
Installation of Windows 10
Like other versions of Microsoft Windows, installation of Window 10 is a threephase
process consisting of: copying files from either bootable USB or CD/
DVD, installing features and drivers and configuring settings.
a. Copying files,
At this first stage of installation the all files are moved from either bootable USB or
CD/DVD to computer which require installation
b. Installing features and drivers,
At this stage the copied files with respect to their features start to be installed
together with the drivers, recall that the role of drivers is to provide a software
interface to hardware devices, enabling operating systems and other computer
programs to access hardware functions without needing to know precise details
about the hardware being used.
c. Configuring settings
This is where installer is asked to choose from available options. This stage of
configuration requires to be taken carefully as some of the settings once disabled
may lead to the malfunctioning of the computer
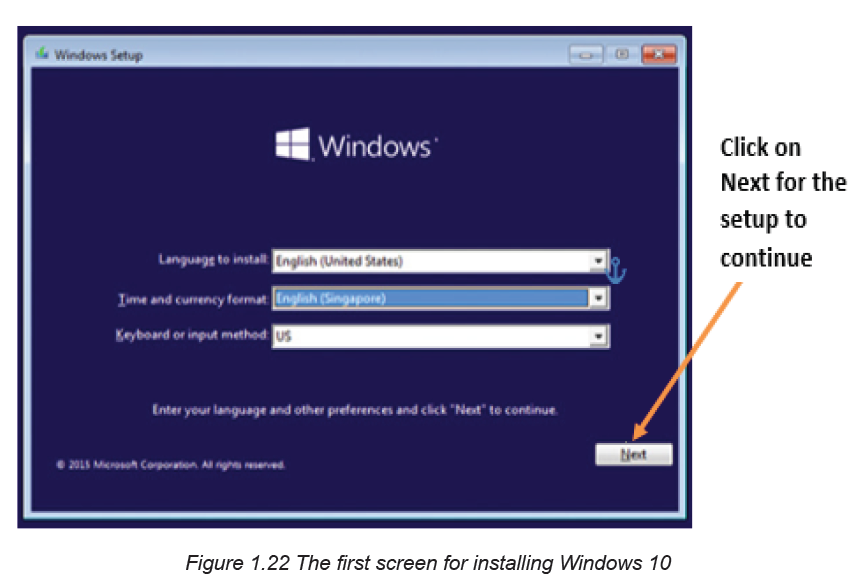
Step 1: This is the first screen to see while installing Windows 10 using a bootable
USB flash drive or DVD. Here’s where to choose the Operating System’s language,
time and currency format, and input method. Once everything is chosen appropriatelychoose Next to continue
Step 2: In the new window that appears click on Install now
Note: If the repair option is chosen, the Troubleshoot screen where to choose to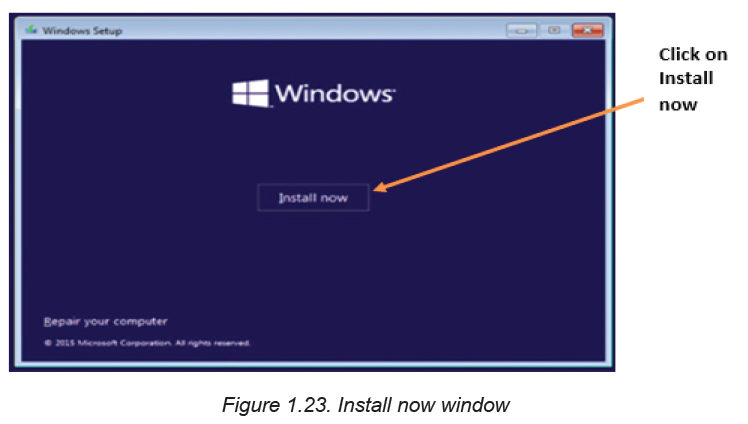
reset the PC and re-install windows will appear. Therefore, keep or remove the files
Step 3: In the window that appear next enter the Windows product key. This can
be found online, in the confirmation email so that they can be purchased, or on theDVD packaging.
Step 4: Accept the license terms. This stage deals with reading software license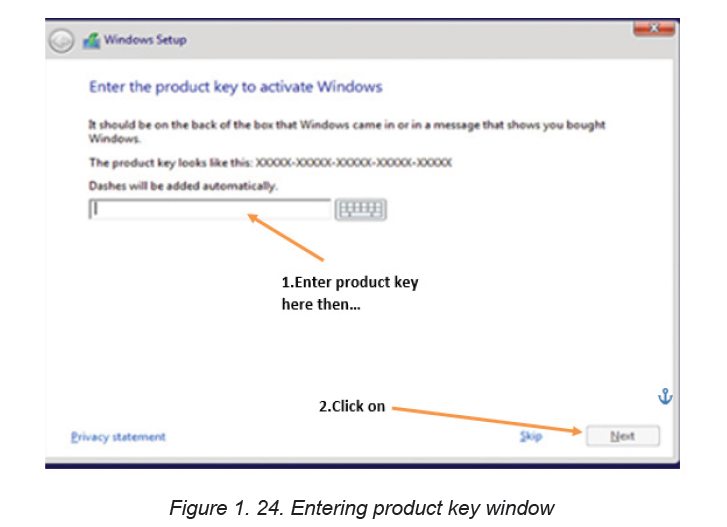
terms and condition to install window 10.
Step 5: In the next image, one can choose to upgrade or custom install windows.
In the upgrade option, files, settings and apps are moved to Windows while in
custom option these are not moved. The choice to make will depend on the oneinstalling Windows and what is the needed outcome at the end of the installation.
Step 6: Select the drive to install Windows 10 on. At this step an existing drive can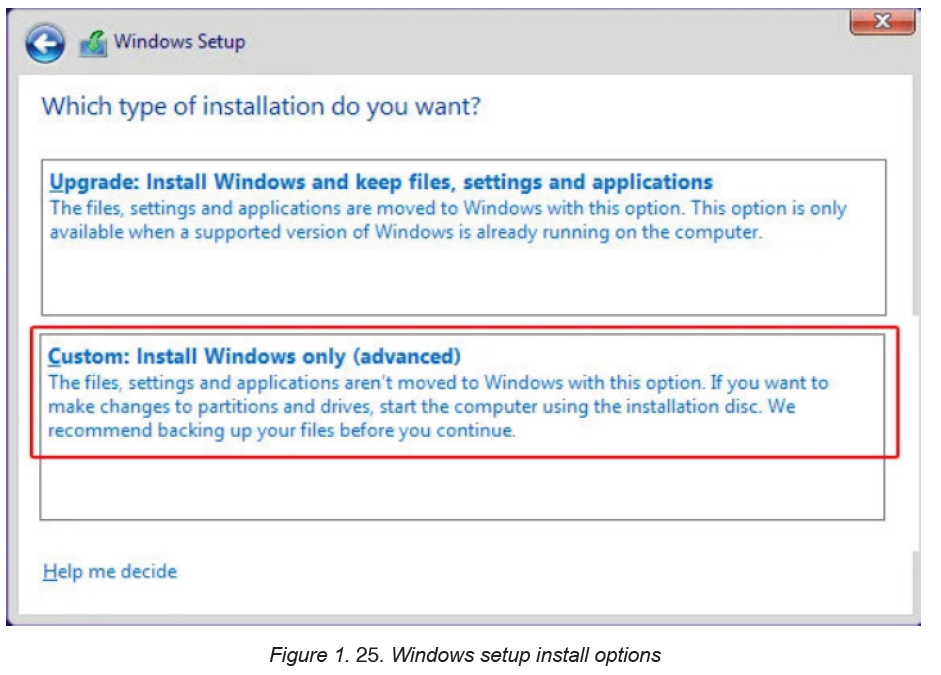
be formatted and used for installation like a new drive can be used for that purpose.Partition is also done.
Step 7: Once the partition in which Windows will resides specified, clicking the Next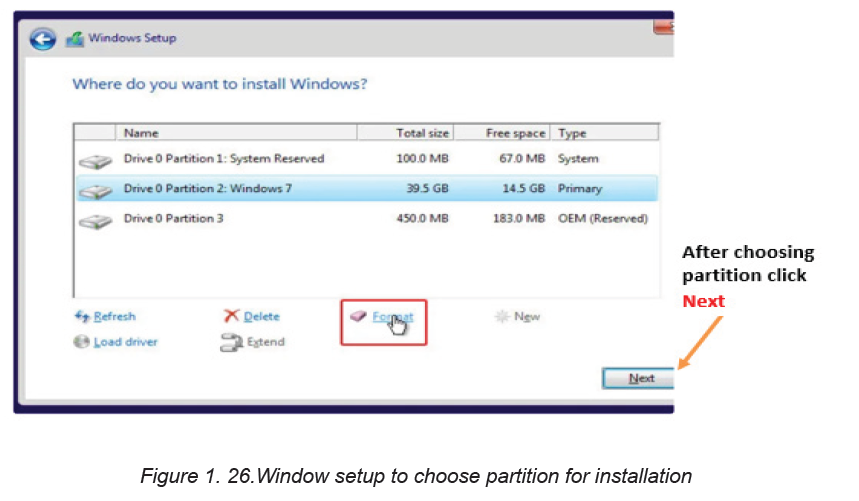
button moves the installation to the next phase of copying Windows 10 files ontothe partition as shown in Figure below:
At this stage after files have been copied configuration is started. During drivers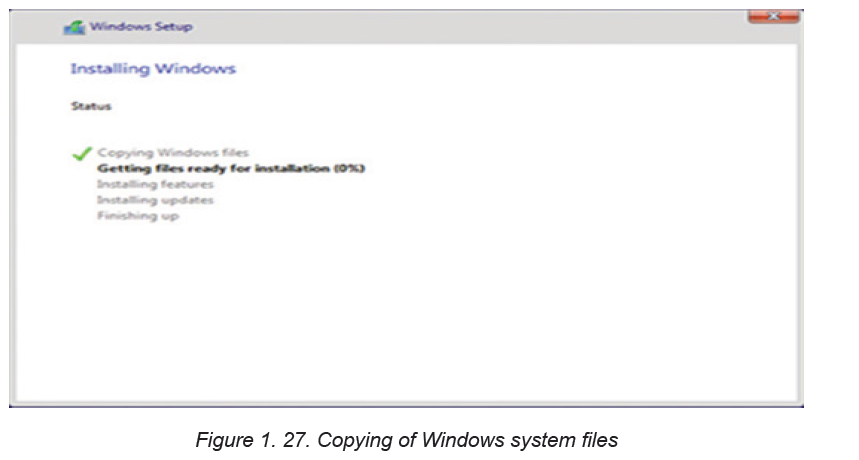
and features configuration stage, the PC restarts several times.Step 8: Do personalization of installed Windows
Read the settings to customize carefully before turning them on or off
Step 9: Sign in or create a Microsoft account when prompted to do so as shown inthe figure below.
Microsoft account is important as it allows the user to access Windows 10 resources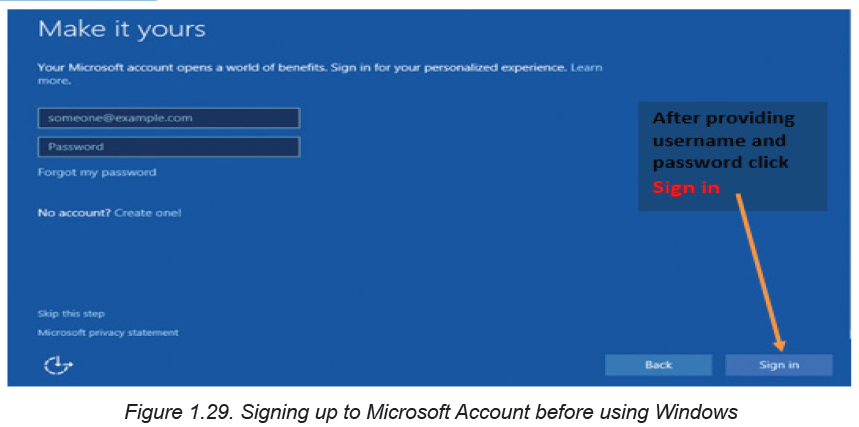
like online emails, cloud and Apps.
Step 10: Let the installer configure Apps before the desktop shown in the figurebelow is displayed.
Now Windows 10 is ready to be used. The newly installed window will have on
desktop three main items: This PC, Network and Recycle bin
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.8
Demonstrate and outline steps on how to install various versions of Microsoft
Window operating systems such as window 7,8, etc..
1.2.3.2. Installation of Application software
Activity 1.9
John bought a computer and connected a flash disk on it to play some music,
unfortunately the computer refused to either play the music or open some
documents stored on the flash disk but once the flash was connected to the
friend’s computer it played and opened the document. After reading this scenario:
a. Suggest what should be the problem with John’s computer
b. How to handle the issue seen in a?
In order to have a computer accomplish a specific task that the computer user want,
instead of having only the operating system, a specific software to accomplish a
specific task is installed. That software to install is an application software.
A. General guidelines procedure to install application software on the
Computer
The first most important step in software installation is to check whether the
target system meets the general hardware requirements of the application. It is
also necessary to make sure that the version of the application to be installed
corresponds to the Operating System platform running on the computer.
Some computer programs also have software requirements prior to installation.
Once all the initial requirements have been met, make sure that there are no
unnecessary programs running before beginning the installation procedure.
Software installation can be done directly from the Internet or from an installation
media
A.1. Installation from media
To install from the disk, insert the CD/DVD drive. Once A setup wizard is running
simply follow the prompts until the installation process is completed. In case there
is no setup wizard window, open the Explorer and navigate to the optical drive.
Double click on either the Autorun or Setup file. For novice users, accept the defaultvalues to minimize potential problems during the procedure.
A.2. For installation from the Web
Launch the browser application and download the setup file to the hard drive.
After completion of the downloading process, run the setup program which is found
in the Downloads folder to execute the setup wizard that will handle the automatic
installation of the software.
After the installation procedure has been completed and the setup wizard has
terminated, reboot the computer before launching the newly installed software.
A.3. Installation of Microsoft office 2013
Most software developers package several programs into a suite with good example
being Microsoft Office 2013. Go through the following steps:
Step4: Insert Microsoft Office 2013 DVD or USB installation media into the
computer. In the license agreement screen that appears, click the check box withthe text “I accept the terms of this agreement”.
Step 2: Once the Microsoft terms of agreement are accepted, choose whether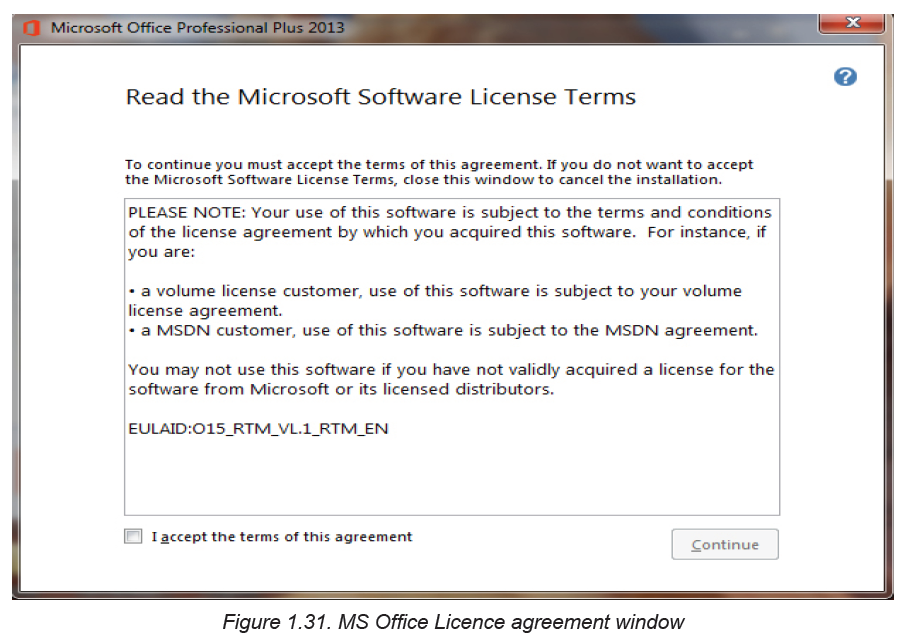
to upgrade an existing version or custom install a new copy. install new copy asshown in Figure below:
If an old version of office is already installed there is an option to upgrade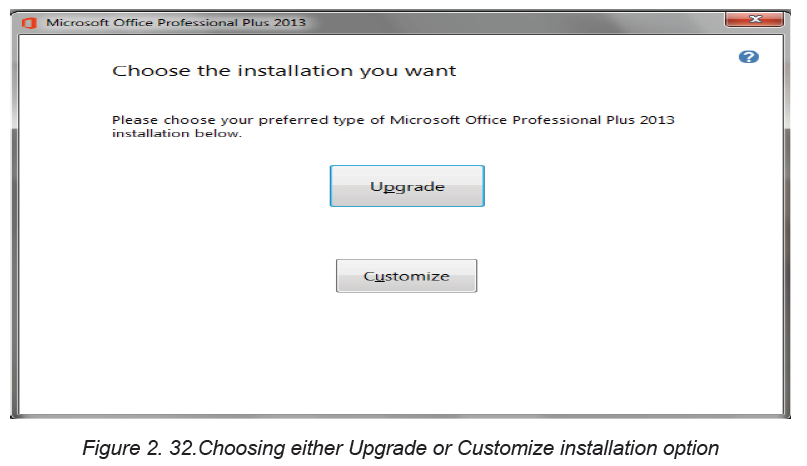
it to a newer version but both the new and the old versions can be kept
depending on the user’s choice.
Step 3: To upgrade an existing version of Microsoft Office, click Upgrade. Make
sure the radio button “Remove all previous versions” is selected, and then clickNext. The installation progress screen shown in the figure fellow.
Step 4: Once the installation process is complete, sign in for Microsoft account to
get online access to the Microsoft resources like the screen shown in the figurebelow is displayed to confirm that Office 2013 has successfully been installed.
Step 5: Open Office 2013 by clicking on the Start button then All apps. The list of
installed Microsoft Office 2013 apps is displayed.
Note:
To install application software successfully there is a need to use an administrator
login because with other types of accounts with limited privileges such an installation
is not possible.
Sometime once a program is installed into a computer there may be a need for
removing them from the computer for different reasons. The process or removing
installed application software from computer is known as uninstallation. Here below
are the procedures followed to uninstall some programs in window 10:
• Open the Start menu
• Select control panel
• Click on uninstall program
• Select the program to remove
• Click Uninstall• Click on the program to uninstall
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 1.9
You are provided with Microsoft Office 2019 Installation on DVD or on flash disk.
Uninstall the current running Microsoft office and Install this provided application
on your computer.End unit assessment
1. Compare safety precautions applied in scientific laboratories such as
chemistry, physics and those observed in computer laboratory
2. Study the motherboard of a computer and perform the following:
a. Identify the CMOS cell battery and RAM mounted on the motherboard
b. Detach and re-attach a CMOS battery and RAM
3. a. Explain briefly the meaning of operating system in the computer system.
b. Explain three phases taken by operating system during its installation
c. Discuss any five functions performed by the operating system residing
on a computer.
4. State four factors to consider before purchasing application software.
5. Explain why motherboard is the first element to be installed in the process
of assembling but the last one to be removed during the process ofdisassembling?
