UNIT 1: INTERPRETATION OF PHOTOGRAPHS AND VIDEO IMAGES
Key Unit competence:
By the end of this unit, I should be able to interpret photographs, video andimages.
Introductory activity
In the previous units, it was shown that maps are very important tools to
indicate and to describe physical and human features. Identify and describe
other techniques used in geography to locate and display physical andhuman features.
1.1. Definition and types of photographs
Learning activity 1.1Describe the difference between the two photographs provided below:
1.1.1. Definition
A photograph is a picture of an object or environment taken by a camera at
a particular time in a given place. Photographs are techniques of recording
geographical information. They enhance the understanding of reality. However,
when a photograph is taken, some parts of the object or environment are seen
while others may not appear clearly. A hidden ground or area which cannot beseen by a camera when a photograph is taken is called a dead ground.
1.1.2. Major types of photographs
There are two major types of photographs: Terrestrial / close or ground
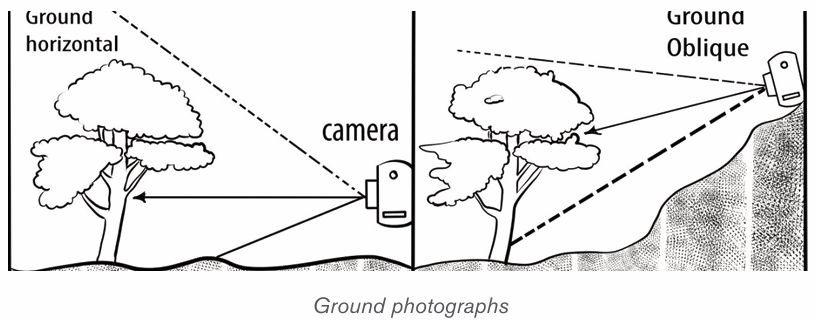
photographs and Aerial photographs.1) Ground Photographs
Also called terrestrial or close photographs, ground photographs are
photographs taken from the ground level. They record targets exactly what a
person would see if he or she was standing on the ground level. A ground
photograph gives a horizontal view, great details of the landscape and covers asmall area.
There are two types of ground photographs:
i) Ground horizontal photograph: This is a photograph taken when a
camera is held horizontally to the ground.
ii) Ground oblique photograph: This is a photograph taken when thecamera is titled at an angle facing the ground.
2) Aerial Photographs
Aerial photographs are images taken from aerial station such as aircrafts,
satellites and other flying objects. They cover a wide area where features are
greatly reduced. They show the top of the object and do not view objects in a
perfect horizontal perspective.
There are two categories of aerial photographs:
i) Vertical aerial photographs are images taken when the camera is
directly located above or overheading the target objects, or when it isperpendicular to the ground.
ii) Oblique aerial photographs: These are photographs taken when the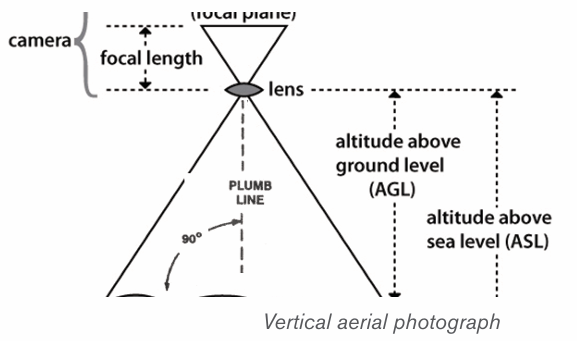
camera is titled at an angle below 90 degrees.
Application activity 1.1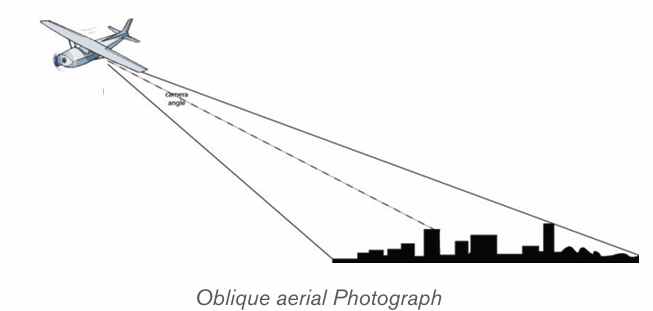
Identify the types of the photographs A and B below and describe them
1.2. Sections of a photograph and interpretation of
physical and human aspects
Learning activity 1.2
Observe the photograph below and answer the following questions:
1) Identify the physical and human features shown on the below
photograph.
2) Indicate the respective parts where these features are found in thebelow photograph.
1.2.1. Sections of a photograph
From a horizontal perspective, photographs have three parts described below:
• The foreground: It is the part of the photograph located nearest to
the camera.
• The middle ground: It is the central part of the photograph.
• The back ground: It is the farthest part of the photograph that includes
the horizon.
From a vertical perspective, photographs are also divided in three parts: left,
centre and right.
Combining both horizontal and vertical perspectives, the photographs can beput into the following categories:
1.2.2. Interpretation of physical and human aspects on
photographs and video images
Physical and human aspects on photographs and video images can beinterpreted as follows:
A. Interpretation of physical aspects
i) Climate: Climate in a photograph is indicated by rainfall and temperature.
Heavy rainfall can be observed by presence of dense forests and crops
like sugar cane, rice and tea while high temperature may be observed by
the presence of poor vegetation, people wearing light clothes etc.
ii) Relief: The landforms depicted on a photograph include mountains,
hills, valleys, escarpments, plateaus and plains. A hilly or mountainous
landscape is indicated by the presence of steep slopes, presence of
terraces, snow and glaciers on the top. Plateaus and plains are identified
by a uniformly flat land with sloping edges and pools of water or irrigated
land. Wide valleys with meanders and flood plains also suggest thepresence of plain land.
Relief on vertical aerial photographs can be interpreted by observing the
following:
• Flat areas can be identifiable by the presence of meandering rivers,
straight roads and gentle bends.
• Plateaus can be indicated by presence of flat topped hills.
iii) Vegetation: This is the plant life that covers the earth surface; it is both
natural and artificial. When describing vegetation on a photograph, the
aspects to consider are the type of vegetation whether grassland, scrub
or thicket; the tree species such as baobab, acacia, eucalyptus; the
density of the vegetation whether trees are close together or scattered;
and the nature of the vegetation whether human made or natural.
iv) Drainage: Drainage is shown by the presence of water bodies on a
photograph, such as streams, rivers, lakes, swamps, seas, and oceans.
Others are man-made water features like wells, ponds, valley dams and
boreholes. In photographs, drainage is interpreted in the following ways:
• Rivers appear with meandering channels with swampy vegetation along
them.
• Swamps appear with luxuriant vegetation dominated by papyrus reeds.
v) Soils: The types of soils can be identified by observing the types of
crops grown there because there are crops that grow well in specific
types of soils, for example, tea and coffee grow well in fertile volcanicsoils. Where erosion took place, the soils are exposed.
B. Interpretation of human aspects
Photographs and video images can be very useful in the interpretation of human
activities such as:
i) Forestry: A forest is evidenced by the presence of both artificial and
natural forests.
ii) Agriculture: Agricultural activities can be observed by the presence of
food crops and cash crops as well as animals like cattle both exotic and
traditional breeds.
iii) Transport and communication: Both transport and communication
networks are evidenced by presence of motor vehicles, bicycles, roads,
ships, airports, and communication facilities such as telephone lines and
masts.
iv) Mining: This is shown by Open pits, people undertaking mining or a
mineral processing plant show that there is mining taking place in that
area.
v) Industry: Industrialization is shown by the presence of industries emitting
smoke from huge chimneys.
vi) Trade or commerce: the commerce is evidenced by trading centers
with congested buildings and at times presence of markets.
vii) Settlement: It is evidenced by the presence of houses in differentpatterns.
Application activity 1.2
Observe the photograph below and describe the physical and humanaspects represented on it.
1.3. Relationship between physical and human aspects on
photographs and video images
Learning activity 1.3
Describe the relationship between physical and human features representedon the photograph below:
Photograph showing physical features (down-left) and human
features (up-right): the arrow indicates the position of a river whichdrains the valley that appears on the photograph.
Some photographs and video images help in illustrating the relationship
between human and physical aspects. Basing on the figure provided above, the
relationship between human and physical aspects can be explained as follows:
i) Relief and transport: Transport routes occur on gentle slopes and
avoid steep slopes and valleys since it is very expensive to construct
roads in hilly areas.
ii) Relief and agriculture: On steep slopes, less agriculture takes place
while on gentle slopes most agricultural practices are observed. The low
lands are usually reserved for growing of vegetables, sugar cane, rice,
and other crops that need enough water.
iii) Relief and settlement: Settlements are commonly found in gentle
slopes and are few in steep slopes and valleys because of the problem
of severe soil erosion and flooding in valleys.
iv) Drainage patterns and settlement: Settlement occurs in well
drained areas and avoids lake shores or river banks because of floods
and associated problems.
v) Drainage and transport: Transport routes are usually found in well
drained areas. For example, roads cannot be constructed in swampy
areas due to excessive water. Water transport occurs on water bodieslike rivers, lakes, oceans and seas.
Application activity 1.3
Observe the photograph below and describe how physical features haveinfluenced human activities in the area.
Skills Lab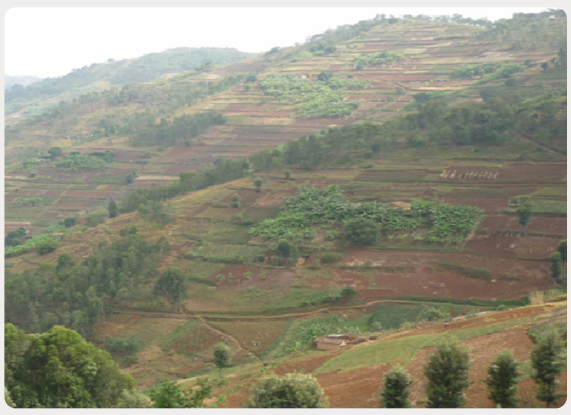
With help of the knowledge, skills, attitudes and values acquired in this unit,
suggest ways of conserving the physical features and promoting economicactivities in your school environment for sustainable development.
End unit assessmentStudy the photograph provided below and answer the following questions:
1) Identify the economic activities taking place and describe their
importance to the people living in the area.
2) Suggest ways of conserving the area in the background of the
photograph for environmental sustainability.
3) Identify the human features which are predominant in the foregroundof the above photograph
