UNIT 6: LASER AND ITS EFFECTS.
Key Unit Competence:Point out effects of LASER beam.
Introductory activity
Man has tried all forms of advancements from traditional methods of solving
problems to advanced methods by use of different technologies. Among other
technological advancements, discovery of Laser that is a part of visible light
under electromagnetic waves has had a great impact in solving many of our
problems. In the picture above a doctor is examining internal part of a patient
using LASER beam. This work has been made easy by use of strong radiationslike LASER beam.
Note: LASER stands for Light Amplifier by Stimulated Emission of
Radiation.
a) From the diagram, what is the nature of LASER light?
b) What do you think are characteristics of a LASER beam as observed
from the figure above?
c) LASER beam is used in different fields. These include, industry,
Agriculture, Medicine and Scientific research. Can you explain how these
radiations are useful to these fields?
d) Though these radiations are useful in real life, but they are also dangerous
if miss-used. Can you guess some of the dangers of LASER beam?
e) With relevant examples, what do you think are dangers caused by theseLASER beam radiations if not well controlled?
6.1 PRODUCTION OF LASER
Activity 6.1
The laser is a special device that uses the ability of some substances to
absorb electromagnetic energy and re-radiate it, as a highly focused beam
of monochromatic and synchronized wavelength radiation. Laser has to be
produced in laboratory so that people benefit from its uses.
a) From your own understanding, explain how a LASER light can be
produced.
b) Does its production, need source of energy like electricity? Explain your
reasoning.
c) In energy levels, particles are either in ground or excited states. Is laser
formed when particles or electrons are in ground or excited states?
Explain your reasoning.
d) From question in c) it is clearly indicated that particles are either in
ground state or excited state. Explain the changes in number of particles(electrons) in each level as they energy is absorbed.
The acronym LASER stands for Light Amplifier by Stimulated Emission of
Radiation. This expression means that the light is formed by stimulating a material’selectrons to give out the laser light or radiation.
In 1953 Charles H. Townes, with graduate students James P. and Herbert
J., produced the first Microwave Amplifier by Stimulated Emission of
Radiation (MASER), as a device operating in the same way as a laser, but
amplifying microwave radiations. This system could release stimulated emissions
without falling to the ground state, and thus maintaining a population inversion. A
laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based
on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. That is, the laser is a light
source that produces a beam of highly coherent and very nearly monochromaticlight because of cooperative emission from many atoms.
6.1.1 Absorption, Spontaneous emission and Stimulatedemission
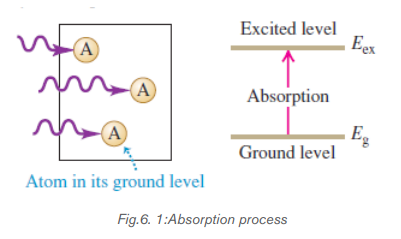
a. Absorption
During the process of absorption, a photon from the source is losingits entire
energy to the atom which was at the ground state and then the atom is promotedto the excited state.
b. Spontaneous emission.
An atom or an electron can move from one energy level to another. A photon is
released when an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower energy level.
The release of photon (a particle of light) is called spontaneous emission.
At the excited state, an atom will drop to a lower level by emitting a photon of radiation
in a process called spontaneous emission. It emits the photon spontaneously
after an average time τ called the spontaneous lifetime of the level. This
time depends on the atomic species; some levels have long lifetime measured in
seconds, whereas others are relatively short on the order of nanoseconds or less.
This lifetime determines the ability of the emitting atom to store energy and willaffect the efficiency of sources.

When an excited atom, depending on its lifetime at the higher energy level, comes
down to lower energy level, a photon is emitted, corresponding to the equation,
c. Stimulated emission
Stimulated emission occurs when a photon strikes an atom that is in excited state
and makes the atom emit another photon
In stimulated emission (Fig. 6.3), each incident photon encounters a previously
excited atom. A kind of resonance effect induces each atom to emit a second
photon with the same frequency, direction, phase, and polarization as the incident
photon, which is not changed by the process. For each atom there is one photon
before a stimulated emission and two photons afterthus the name light amplification.
Because the two photons have the same phase, they emerge together as coherentradiation.
6.1.2 Population inversion
Population inversion: This is the process of increasing excited electrons inhigher energy levels.
Normally, most atoms are in ground state, so most of the incident energy or photon
will be absorbed. To achieve a coherent light from stimulated emission, there are
some conditions that should be satisfied.
In the first case, the atoms must be excited to the higher state and so an inverted
population is produced. One in which more atoms are in upper state than in lower
one.
The emission of photons will dominate over absorption.
In the second case, the higher state must be a metastable state. This is a state
in which the electrons remain longer than usual so that transition to the lower stateoccurs by stimulated emission rather than spontaneously.
This is the redistribution of atomic energy levels that takes place in a system so that
laser action can occur.
There are different methods of achieving population inversion in atomic states that
is essential requirement to produce laser beam.
Normally, most of the atoms in a medium are in the ground state of energy There
There
are four different methods of making these atoms to get to excited states:
i) Excitation with the help of photons: If the atoms are exposed to an
electromagnetic radiation of high frequency, then there is selective absorption
of energy and thus atoms are raised to excited state.
ii) Excitation by using electrons: This method is used in some gas lasers.
Electrons are released from the atoms due to high voltage electric discharge
through a gas. These electrons are then accelerated to high velocities due to
high electric field inside a discharge tube. When they collide with neutral gasatoms, a fraction of these atoms are raised to excited state.
iii) Inelastic collision between atoms: If a gas contains two different kinds
of atoms X and Y, then during electric discharge through the gas some of the
atoms are raised to excited state.
iv) Excitation by chemical energy: Sometimes, an atom or a molecule can
be a product of a chemical reaction and can be produced in its excited state.
An example is hydrogen combining with fluorine to form hydrogen fluoride HFthat is in excited state.
6.1.3 Laser structure
In general case laser system consists of three important parts: Active medium or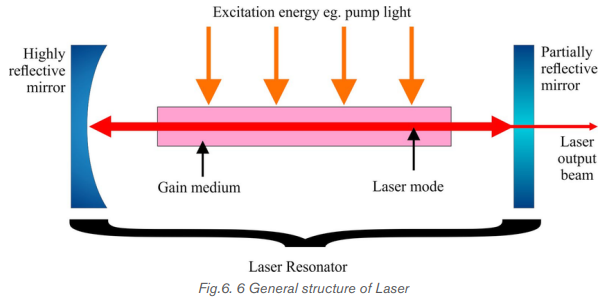
amplifying medium, the energy source referred as the pump or pump source
and the optical resonator consisting of mirrors or system of mirrors.
Pumping Mechanism
Pumping is the process of supplying energy to the laser medium to excite to the
upper energy levels. To have this mechanism, it depends on the existence of
interactions between light from pump source to constituents of active medium.
Usually, pump sources can be: electrical discharges, flash lamps, arc lamps, light
from another laser, chemical reactions and even explosive devices. Most common
lasers use electrical or optical pumping. The type of pump source used dependsessentially on the gain medium.
Active Medium
The active medium is the major determining factor of the wavelength of operation,
and other properties of the laser. The gain medium is excited by the pump source
to produce a population inversion, and it is where the spontaneous and stimulated
emission of photons take place, leading to the phenomenon of optical gain or
amplification. The gain medium may be a solid crystal like a ruby, a liquid dye, gases
like CO2 or He-Ne or semiconductors. The gain medium for some lasers like gas
lasers is closed by a window under the Brewster’s angle to allow the beam to leave
the laser tube.
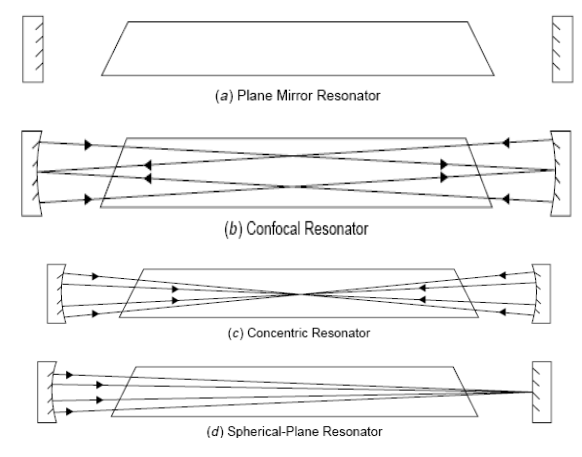
Optical resonator or Optical cavity
The optical resonator or optical cavity is a system of two parallel mirrors placed
around the gain medium that provide reflection of the light beam. Light from the
medium produced by the spontaneous emission is reflected by the mirrors back
into the medium where it may be amplified by the stimulated emission. Mirrors are
required for most lasers to increase the circulating power within the cavity to the
point where gains exceed losses, and to increase the rate of stimulated emission.
One of the mirrors reflects essentially 100% of the light, while the other less than
100% and transmits the remainder. Mirrors can be plane, spherical or a combinationof both. Here represented are the common cavities configuration that can be used:
Application activity 6.
1. Write in full the acronym L.A.S.E.R
2. What do you understand by the term LASER?
3. In your own words, explain how laser light is produced.
4. Explain the meaning of population inversion and discuss how an atom
can be put into excited state.
5. a) What are the three major components of laser?
b) Using diagrams, explain all the types of optical cavity.
6. With the aid of diagrams explain the meaning of the following terms as
applied in LASERs
i) Stimulated Absorption
ii) Stimulated Emission
iii) Spontaneous Emissioniv) Population inversion
6.2 PROPERTIES OF LASER BEAM
Activity 6.2
Lasers emit light that is highly directional. Laser light is emitted as a relatively
narrow beam in a specific direction. Ordinary light, such as coming from the
sun, a light bulb, or a candle, is emitted in many directions away from the
source.
a) By analyzing how a laser pointer works, discuss characteristics of laser
light?
b) Do you think all different kinds of laser light have the same properties?Give reasons to support your answer.
The laser light is not like any other light emitted by usual sources found in nature. This
special light emitted by the laser, has three properties according to its usefulness inmany applications: Coherence, Monochromaticity and Collimation or Directionality.

6.2.1 Coherence
Coherence is the most interesting property of laser light. All photons emitted, are
exactly in the same phase, they are all crest and valley at the same time. It is
brought about by the mechanism of the laser itself in which photons are essentially
copied.
The good temporal coherence is essentially for Interferometry like in Holography.
Coherence is not trivial and is brought about by the amplification mechanism of the
laser.
6.2.2 Monochromaticity
Monochromaticity is the ability of the laser to produce light that is at one wavelength
λ. It is a requirement for coherence since photons of different wavelengths cannot
be coherent. When white light is dispersed through a prism, you note that it is
composed of an infinite number of wavelengths of light covering the entire visible
spectrum as well as into the UV and IR regions. However, no light source is perfectly
monochromatic. Lasers tend to be relatively monochromatic and this depends on
the type of laser. Monochromatic output, or high frequency stability, is of great
importance for lasers being used in Interferometry.
6.2.3 Collimation or Directionality
Collimation or directionality is the property of laser light that allows it to stay in one
direction at the strait line, confined beam for large distances. This property makes
it possible to use the laser as a level in construction or to pinpoint speeders on a
highway. This highly directional laser light is determined by the mechanism of thelaser itself.
Application activity 6.2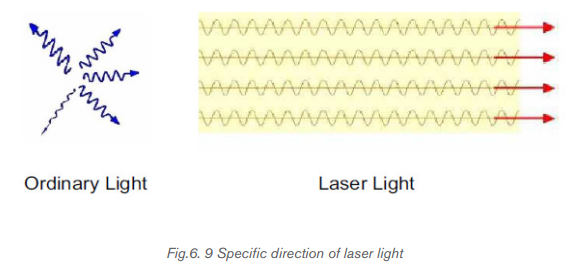
1. Choose the correct group of terms that are properties of laser light.
A. Coherent, unpolarized, monochromatic, high divergence
B. Monochromatic, low divergence, polarized, coherent
C. Polychromatic, diffuse, coherent, focused
D. Monochromatic, birefringent, nonpolarized, coherent
2. Which of the following properties of laser light enables us to use it to
measure distances with great precision?
A. All the light waves emitted by the laser have the same direction
B. The light waves are coherent
C. The light waves are monochromatic
D. The individual waves effectively work like a single wave with very
large amplitude.
3. Explain how coherence, monochromatic and collimation are
interconnected.
4. All light in laser light are produced and found to be in the same phase.
How does this help in the formation of 3D images?
5. Laser light can be used as a level. Which special feature that makes it
be used as a level. Explain your answer
6. Explain the meaning of the following properties of LASERS
i) Monochromaticity
ii) Coherenceiii) Directional/collimation.
6.3 APPLICATIONS AND DANGERS OF MISUSE OF LASER
Activity 6.3
You can use the figure above to answer the following questions
a) Starting from the figure indicated above, where do you think in real life
LASERS are helpful?
b) From your experience, have you ever used LASER light?
c) Other than using it by yourself, what are other places where laser light isapplied
6.3.1 Applications of lasers.
There are many interesting uses for lasers, depending on the special characteristic
being applied. Laser Diodes are used in a wide range of applications. Partial lists of
those applications include:
i) They are used in common consumer devices such as DVD players, bar code
scanners; CD ROM drivers; laser disc and other optical storage drivers; laser
printers and laser fax machines; sighting and alignment scopes; measurement
equipment; free space communication systems; pump source for other
lasers; high performance imagers; and typesetters. CD players have lasers.
Light from the laser in CD player reflects off patterns on CD’s surface. The
reflected light is converted to a sound wave.
ii) Laser beams can be used in diverse fields of science and technology. Like in
the control of motion of moving objects like aircrafts or missiles. This method
thus makes it possible for a missile to hit a certain target.
iii) Because of high directional property, lasers are used to measure distances
accurately. A laser beam is sent, and the time taken for it to be reflected back
is measured. Using this idea, the distance can thus be measured.
iv) Because laser beam can be focused into a small spot, it can thus be used to
cut minute holes onto a material.
v) The very high intensity of laser beam means that the amplitude of the
corresponding electromagnetic wave is very large. So it is possible to
investigate the nonlinear optical properties of different materials with the help
of laser light.
vi) Lasers are also used in industry for cutting materials such as metal and cloths.
and welding materials
vii) Doctors use lasers for surgery and various skin treatments
viii) They are used in military and law enforcement devices for marking targets
and measuring range and speed.
ix) Laser lighting displays use laser light as an entertainment medium.
x) Lasers also have many important applications in scientific research
In a tabular way, we can have a summary of different types of lasers and their
applications.The following are types of lasers and their applications
a. Gas Lasers:
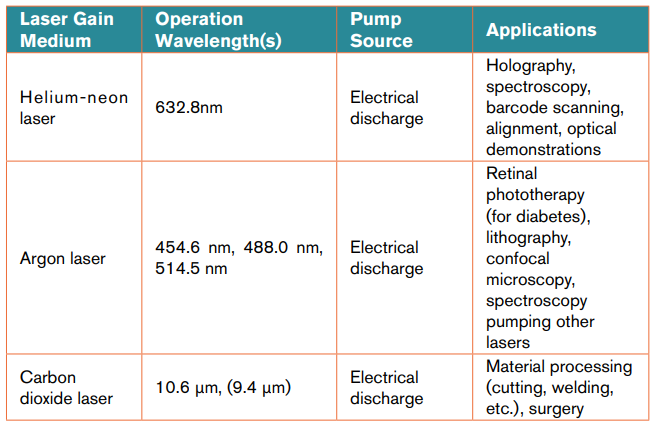

b. Solid State Lasers:

c. Metal-vapor Lasers:
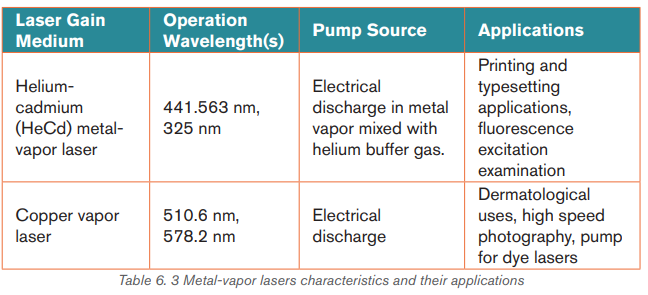
d. Other types of lasers:
6.3.2 Dangers of lasers
You should be careful when dealing with lasers, because they can have a negative
impact when exposed to your body. Among other negative effects, some of them
are discussed below
i) If directly exposed to our skin, it burns the skin
ii) When absorbed by skin, Laser light reacts with body cells causing cancer.
iii) Because of their high energy, it affects eyes if exposed to them
iv) Lasers can affect cells of a human being. This leads to mutation
Because of the negative effects of lasers, care must be taken to avoid all the risks
of being affected by lasers.
6.3.3 Precaution measures to avoid negative effects of lasers
The following are some of the measures one can take to avoid the negative effects
of lasers.
i) For any one working in places where there are incidences of being exposed
to laser light, one should wear protective clothes, glasses and shoes so that
there is no direct exposure of these radiations on to the body.
ii) One should minimize the time of working with lasers.
iii) Areas that are exposed to these radiations should be warning signs and labels
so that one can be aware of places/areas where laser light is used.
iv) Safe measures like Use of remote control should be used to avoid direct
exposure of these radiations (LASER light).
v) People should be given trainings on how to handle lasers.vi) There should also access restrictions to laboratories that use laser
Application activity 6.3
1. i) Discuss applications of Laser Light in daily life
ii) Though LASER light is important in day today life but if miss-used it
can be dangerous to our lives. Discuss dangers that may arise if it is
miss-used.
iii Using your personal judgment, which side outweighs the other? Give
scientific reasons.
3. Depending on your judgment in (2) do you think man should continue
using laser light?
4. Lasers are classified depending on either how they are produced or the
material that makes up laser. Discuss
i) Types of lasersii) Examples of lasers.
Skills Lab 6
This activity intends to make you analyze how LASER light is produced and
used.
What to do?
Visit a nearby hospital Laboratory where they do LASER surgery.
Note: Before you make a visit make sure that you inform them like a week
before through class leaders or your physics tutor.
In your visit focus on the following:
a. How laser light is produced
b. How LASER beam is used to do surgery.
c. Why do they adopt using this type of surgery but not other forms?For each case compile out your findings and a full report about lasers.
End of unit 6 assessment
Copy the questions below to your exercise books and chose the best
alternative that answers the question.
1) What does the acronym LASER stand for?
A. Light Absorption by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
B. Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
C. Light Alteration by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
2) The acronym MASER stands for?
A. Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
B. Molecular Absorption by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
C. Molecular Alteration by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
D. Microwave amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radio waves
3) Which of the following is true about population inversion
A. Number of electrons in excited levels reduces
B. Number of electrons in excited levels increase
C. Number of electrons in ground levels reduces
D. Electrons remain completely in ground state
4) Which of the following determines the color of light?
A. its intensity
B. its wavelength
C. its source
D. Some information missing
5) Among the three examples of laser listed below, which one is considered
“eye safe”?
A. Laser bar-code scanners
B. The excimer laser
C. Communications lasers
D. YAG
6) Why are lasers used in fiber optic communications systems?
A. The government has mandated it
B. They can be pulsed with high speed data
C. They are very inexpensive
D. They are not harmful
7) Lasers are used in CDs and DVDs. What type of laser is used in these
players?
A. Semiconductor
B. YAG
C. Alexandrite
D. All the above
8) The best reason why lasers used in “Laser Printers” is
A. They can be focused down to very small spot sizes for high resolution
B. They are cheap
C. They are impossible to damage
D. They are locally available
9) As wavelength gets longer, the laser light can be focused to…
A. Larger spot sizes
B. Smaller spot sizes
C. Large and small spot sizes
D. None of the above
10) Among the following, which color of laser has the shortest wavelength?
A. Yellow C. Blue
B. Red D. Green
11) What property of laser light is used to measure strain in roadways?
A. Intensity
B. Power
C. Coherence
D. All the above
12) What is the type of laser used most widely in industrial materials
processing applications?
A. Dye Laser C. YAG laser
B. Ruby Laser D. Carbon Dioxide Laser
13) Why are lasers used for cutting materials?
A. It never gets dull D. It has a small “heat affected zone”
B. Accuracy E. Smoother cuts
C. Repeatability F. All of the above
14) The Excimer laser produces light with what wavelength?
A. Visible
B. Ultraviolet
C. Infrared
D. All the above.
15) Most lasers are electrically inefficient devices.
A. True
B. False
16) Chemical lasers use………………. to produce their beams.
A. Excessive amounts of electrical power
B. Small amounts of electrical power
C. No electrical power
D. Other lasers
17) What type of laser could cause skin cancer if not used properly?
A. Red semiconductor laser C. Blue semiconductor
B. Excimer laser D. YAG laser.
18) a) what do you understand by term LASER?
b) Depending on the nature and what laser is made of, Laser is classified
into different types. Discuss at least 5 types of lasers
19) a) Laser light have been employed in different areas. This has helped
man in solving different problems. What are some of the areas where
laser light is employed?
b) Though laser light is very important in different activities, it can alsocause harm if miss-used in what ways is laser light harmful?
