UNIT 4: GRAPHIC DESIGN
Key Unit competence:
To be able to create various designs with illustrations and different lettersstyles using digital devices
4.1. The Elements of Graphic Design
4.1. Aspects and elements of design.
1. Lines
Lines are used as roadmaps to direct the viewer’s eye movements. They can
exist on their own or be employed to create texture and movement to connect
information, to demarcate space or even to create a desired mood. Lines can bevertical, horizontal, diagonal, circular, patterned, free form or solid/bold.
2. Shape
Shapes can be geometric, abstract, stylized or as they occur in nature. They
give volume to the forms in a design. You can make use of texture, lines, colorsand alterations in value to discern shapes.
3. Texture
Texture is a powerful graphic design tool used to enhance design with details
necessary for creating visual impact. It delivers a sense of feel, especially with
two-dimensional images. In graphic design, texture can take the form of layers
or gradation of text, lines or shapes.
4. Space
In design expression; white space is called negative space. It can be used to
connect, separate or maximize the relationship between the elements making
up the design. Negative space creates groupings, enhances expressions and
emphasizes hierarchies. Space can also be used to give the illusion of depth ormulti-dimension.
5. Size
The functionality of a graphic design layout hinges heavily on size. Use size to
draw attention to the most important element in the design; typically, a larger
size invites the most attention. Different sizes within the same graphic design
or layout creates a hierarchy of dominance. Use variations in size to guide theviewer’s eye through the path you want it to take.
6. Value
This refers to how dark or light (in terms of color) something is. In a monochromatic
image, value is used to define the shape and texture of a design element. Value
comes in handy when you want to convey the illusion of movement or bring oneelement into sharp focus while another recedes into the background.
7. Color
People process color subconsciously. To establish mood, create appeal,
generate interest and get a message across, color is the most potent tool inyour graphic design arsenal.
• Aspects/qualities of design
Layout in graphic design deals with the arrangement of visual elements so as
to achieve specific communication objectives.
When designing, the graphic designers should rely on the required information
to present the layout properly, such as rotating and resizing the images, which
requires time and efforts. In order to be able to design quickly, it is necessary
to plan the layout in advance to save time and create a consistent look for your
design.
Legibility: the artist should choose the kind of lettering that will be easy to read
at a glance. It should not be too congested or condensed. The words should
have proper spacing, a good background color and illustrations should be seen
clearly.
Placement: don’t overlap your images over your font, but make sure they are
next to any wording that helps explain them. You shouldn’t be using these just
to fill a giant empty space. All of your images should have purpose.
Illustration: are those images or pictures that accompany the text to explain
it, illustrations help the viewer to understand well and quickly the message. On
a poster it is better when the illustration takes a big place at least 60% of thewhole place.

1.2. Different letter styles with digital tools and software.
Generally letter styles are classified into two main font styles which are serif and
san serif letter styles. Around 19th century the author categorized letters into the
following types of letter styles.
Sans serif, Serif, Cursive / Script, Vintage, Gothic – Black letter
calligraphy, Graffiti, Creative lettering and
Other sub-lettering styles
• Sans serif letters
Sans serif letters are letters that doesn’t have tailor hock at the bottom and
at the top. When creating sans serif lettering you need to pay close attention
to the letter forms where nature of line that are made letters are valued while
tracing letters
• Serifs
The serifs – small decorative strokes added at the end of the letterformsThe different thickness in the strokes – not every stroke has the same thickness.
• Cursive
Cursive lettering also known as script, cursive is about hand lettering
Vintage
It is letter style which is recognizable on a few different aspects Decorations(flourishes/embellishments)Serifs, Textures and Colors
Gothic / black letter calligraphy
 Black letter calligraphy is one of many scripts created using a flat
Black letter calligraphy is one of many scripts created using a flat
style with digitalGraffiti
CREATIVE LETTERING
Creative lettering it the type of lettering that incorporates some different elements
besides just the letters.This could be illustrations, textures, play on words, perspective etc.
In our days all the letter styles can be manipulated with digital tools to produce
digital artworks it only requires the font style installed in digital tool. Let’s takethis example on how to design the word creativity in Micro soft world processer


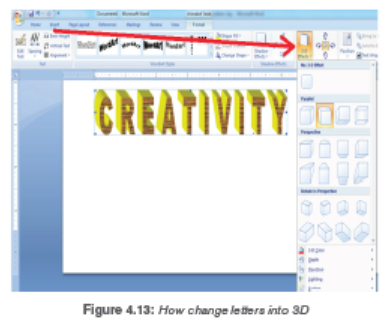
• Poster making using digital tools
A poster is a large notice or picture that you stick on a wall or board, often
in order to advertise something. Synonyms: notice, bill, announcement and
advertisement
Steps for designing a professional poster
Determine you poster format
Brainstorm the content
Pick a suitable template
Use colours to grab attention
Choose graphics and typography
Clean up any clutterExample of a poster with machine software design
After select drawing tools you can start sketching your ideas by taking care of
element and principles of design






