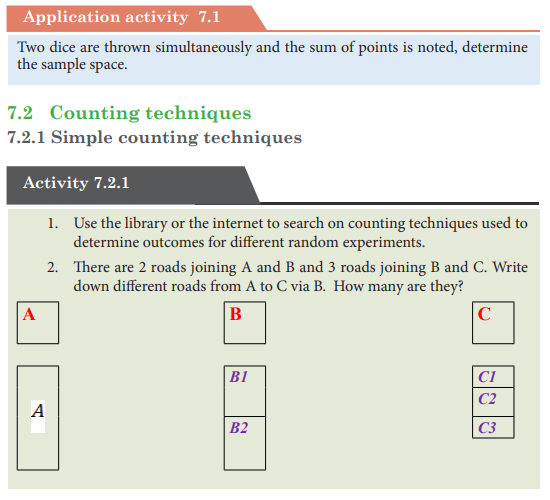
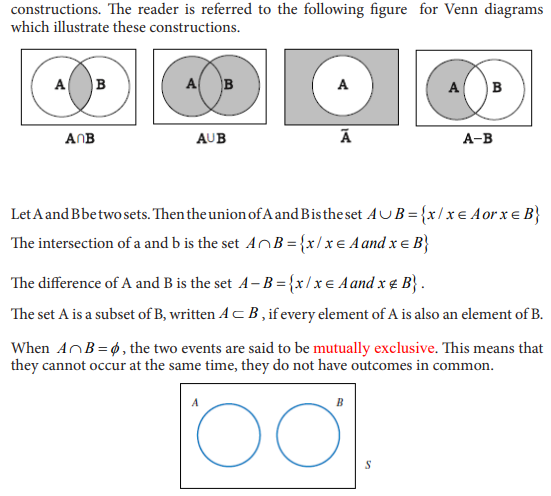
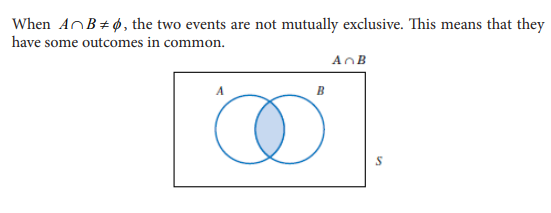
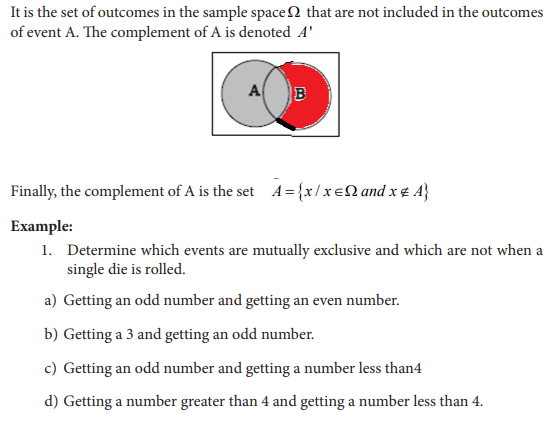
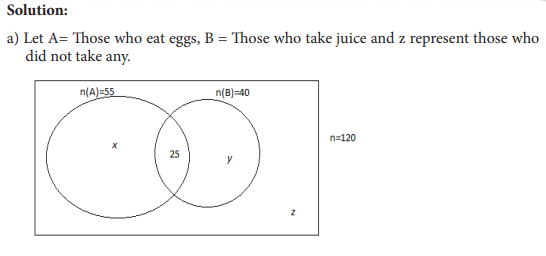
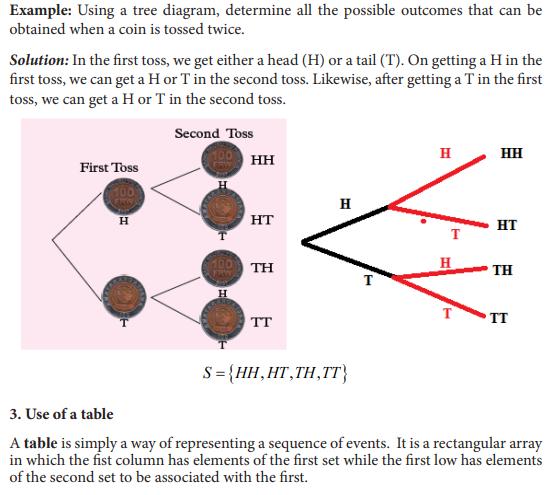
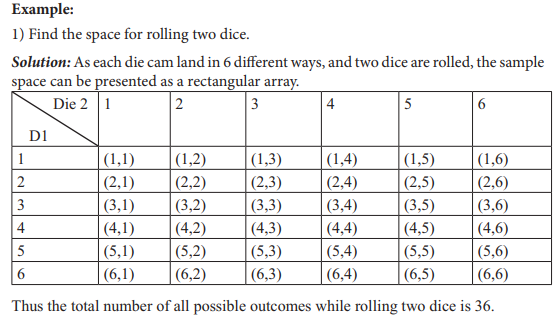
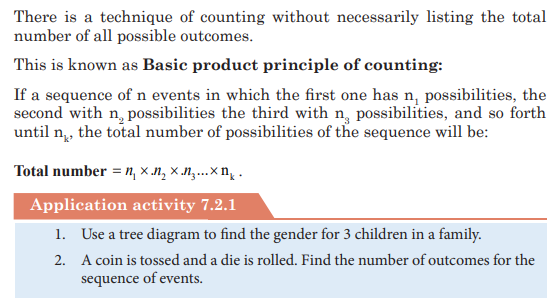
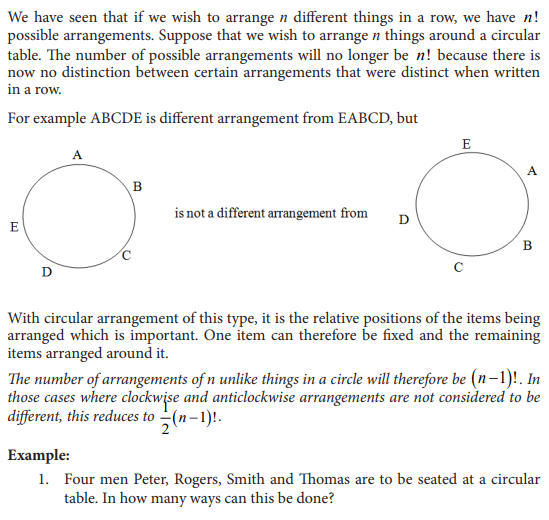
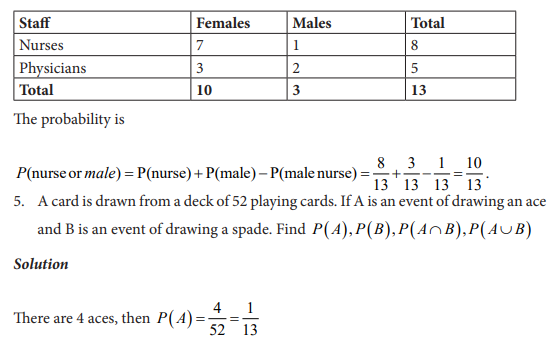
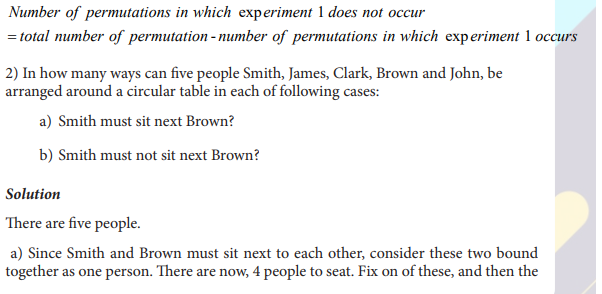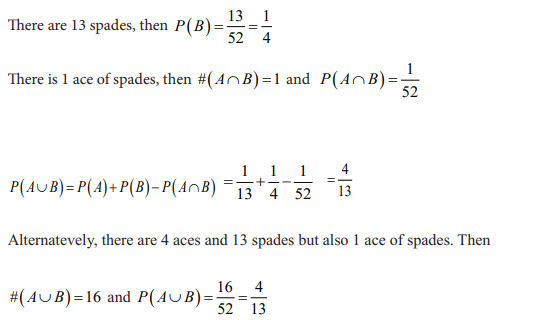UNIT 7:ELEMENTARY PROBABILITY

7.0. Introductory Activity
A woman applying the family planning program considers the assumption that
one boy or one girl can be born at each delivery. If she wishes to have 3 children
including two girls and one boy, she knows that this is a case among other cases
which can happen for the 3 children she can have. Discuss all these cases and
deduce the chance the woman has for having a girl at the first and the second
delivery and a boy at the third delivery.
Activity 7.

Probability is the chance that something will happen.
The concept of probability can be illustrated in the context of a game of 52 playing
cards. In a park of deck of 52 playing cards, cards are divided into four suits of 13
cards each. If a player selects a card at random (by simple random sampling), then
each card has the same chance or same probability of being selected.
When a coin is tossed, it may show Head (H- face with logos) or Tail (T-face with
another symbol).

We cannot say beforehand whether it will show head up or tail up. That depends on
chance. The same, a card drawn from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards can be red or
black. That depends on chance. Such phenomena are called probabilistic. The theory
of probability is concerned with this type of phenomena.
Probability is a concept which numerically measures the degree of uncertainty and
therefore, of certainty of occurrence of events.
In most sampling situations we are generally not concerned with
sampling a specific individual but instead we concern ourselves with the
probability of sampling certain types of individuals.
Random experiments and Events
A random experiment is an experiment whose outcome cannot be predicted or
determined in advance.
Example of experiments:
– Tossing a coin,
– Throwing a dice
– Selecting a card from a pack of paying cards, etc.
In all these cases there are a number of possible results (outcomes) which can occur
but there is an uncertainty as to which one of them will actually occur.
Each performance in a random experiment is called a trial. The result of a trial in
a random experiment is called an outcome, an elementary event, or a sample point.
The totality of all possible outcome (or sample points) of a random experiment
constitutes the sample space which is denoted by Ω . Sample space may be discrete
or continuous.
Discrete sample space:
• Firstly, the number of possible outcomes is finite.
• Secondly, the number of possible outcomes is countably infinite, which means
that there is an infinite number of possible outcomes, but the outcomes can be