UNIT 5: EXPLORATION OF AFRICA
Key unit competence: By the end of this unit, the learner should be
able to explain the causes and consequences of
exploration of Africa. Think of a new place that you recently visited. It should be a place that
Think of a new place that you recently visited. It should be a place that
you had never visited before.
1. Why did you visit the place?
2. What was the impact of your visit to the place you visited on
you?
Now, get a dictionary to find out the meaning of the word ‘exploration.
From the above activity, it is clear that you visited the place for a reason.
That act of travelling to that place can be referred to as exploration. The
European explorers in Africa had come as visitors. Exploration can be
defined as travelling to a place or through an unfamiliar area in order to
learn about it.5.1. Different European explorers and their routes 1. Use the map of Africa to identify the main routes used by1. Infante Henrique of Portugal, Duke of Viseu (Henry the Navigator).
1. Use the map of Africa to identify the main routes used by1. Infante Henrique of Portugal, Duke of Viseu (Henry the Navigator).
different European explorers.
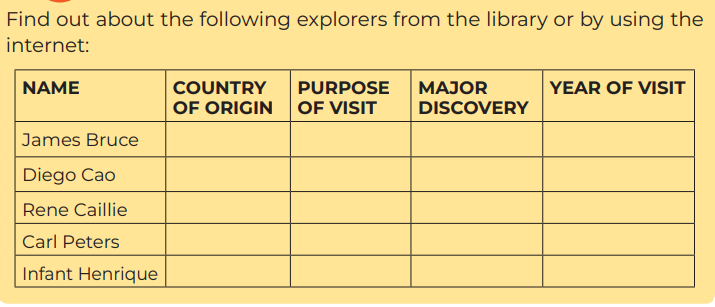
2. Carry out research using different History books in the library
and from the Internet to find out explorers who visited Africa in
the 15th and 19th Centuries.
3. Prepare a comprehensive report for class presentation. Include
a map showing the routes each explorer followed.
4. Let us discuss some of the European explorers and the routesthey followed.

2. Bartolomeu Dias.
Together with his crew, they reached Kwaaihoek near the mouth of the
Bushman’s River. He wanted to continue to India, but his crew refused to
go further. He was forced to turn back. It was only on the return voyagethat he discovered the Cape of Good Hope in May 1488.
 \
\
On 1st July 1796, he escaped alone with nothing but his horse and a pocket
compass. On 21st July 1796, he reached the long-sought Niger River at
Segu. He thus became the first European to do so. Mungo Park died in1806 in Bussa, Nigeria.

During this time, he lost touch with Europe. Fearing that he might have
died, Henry Morton Stanley was sent to find him, dead or alive. Stanley
met Livingstone at Ujiji. Livingstone’s meeting with H.M Stanley on
10th November 1871 gave rise to the popular quotation “Dr Livingstone,
I presume?”. They stayed together and even explored Lake Tanganyika.
However, Stanley failed to convince Livingstone to return to Europe. Theyparted ways on 14th March 1872.
In August 1872, Livingstone resumed his search for the source of River
Nile. However, he was found dead on 1st May,1873 due to exhaustion and
illness. He was one of the most popular heroes of the late 19th Century in
Victorian Britain. He had a mythical status which operated on a number
of interconnected levels. These were:• Protestant missionary martyr
• Imperial reformer
• Scientific investigator and an explorer
• Anti-slavery crusader• Advocate of commercial empire.

8. Sir Richard Francis Burton.
9. Sir Samuel Baker.
10. John Hanning Speke.
11.Sir Henry Morton Stanley.


14. Mary Henrietta Kingsley.
15.Oscar Baumann.
16. Count Gustav Adolf von Gotzen

5.2. Different causes of exploration
Research on the reasons why Europeans were interested in the African
continent in 15th and 19th centuries. Present the findings.
The following are different causes of Exploration:
a) Geostrategic interests.
The desire for respect and prestige attracted many European explorers to
Africa. This was because those who would discover new things were given
titles such as sir and many other rewards. A country with many colonies
was also highly respected, hence the exploration of Africa. For example,
France regarded the acquisition of colonies in Africa as prestigious and
as a way of strengthening her supremacy in Europe. After 1870, European
rivalry spread to Africa, Asia and the Pacific and colonies were increasingly
regarded as symbols of national prestige.
b) To discover more about Africa.
Most of the explorers were scientists and geographers who desired to
research about African societies and their organisation, for example,
Thomas Fowel Buxton. Africa was also long believed to be dark and
undomesticated continent to many Europeans. It was this, among other
reasons, which made the Europeans come to Africa for exploration.
c) Humanitarian reasons.
Some of the explorers had humanitarian reasons and feelings. They
wanted to stop slave trade and cure various diseases such as malaria that
were affecting lives of Africans. The best example in this case was Dr DavidLivingstone.
d) To spread Christianity.
Some explorers such as Rebmann were Christian missionaries. They came
partly to spread Christianity to Africa. They believed that Africans wereprimitive. They also wanted to counter the influence of Islam in Africa.\
e) Agents of colonialism.
Explorers are also believed to have been sent by their home countries to
prepare Africa for colonisation. This explains why they did the mappingand tracing minerals and fertile soils.
f) To discover the sources of African rivers.
The source of this longest African river (River Nile) was unknown to all. This
created the need to come and find its source. It influenced the coming
of explorers such as Richard Burton and Speke. Other sources of riversdiscovered by explorers are, River Niger and River Zambezi.
g) Love for adventure.
Some other explorers were full of excitement to travel to new places
beyond their continent, especially Africa. They believed that Africa wasdark and uninhabited.
h) The effects of the industrial revolution.
By 1750s, European changed from agriculture to industrial economy.
This required raw materials and spices such as nutmeg, ginger, cloves,
cinnamon and pepper. It also required and luxury goods such as silk,
gold, silver, jewels, ivory, porcelains and tea from Africa and the East. Theyneeded a market for their industrial output.
i) To find new trade routes.
The explorers were looking for an alternative safe trade route this was
due to political tensions and frequent fights on the way from European
countries to India (in Asia). Usual path passing through Suez Canal
was clouded with political instabilities and frequent fights. It was alsobecoming less and less safe for trade purposes.
j) Improvements in technology.
Europeans began to build stronger and faster sailing ships such as a
caravel. A caravel was a ship with two sails on each side. This was required
for running with the wind and for sailing into the wind. The Europeans
also came up with better navigational instruments which could tell north
and south of the equator by the position of the stars. An example was themagnetic compass.

Find out on internet other motives for exploration. Present in class
5.3. Consequences of exploration of Africa.
Use textbooks and explain the consequences of exploration of Africa.
Present your findings in class.
The following are some of the consequences of exploration of Africa:1. Exploration of Africa led to the introduction of Christianity. Some
explorers were missionaries. For example, Dr. Livingstone and
Rebman. This ushered in European missionary activity in Africa and
the final spread of the gospel.
2. The exploration led to the drawing of the map of Africa. Explorers
drew more accurate maps of Africa on paper which eased the
coming of many more Europeans in Africa due to the geographical
discoveries made by their predecessors.
3. It led to the discovery of the sea route to India by Vasco da Gama
(1497- 1499). This increased trade links between Europe and the East.
4. It contributed to the stopping of slave trade. The explorers reported
evils of slave trade in Europe and campaigned against this inhuman
trade. They insisted that slave trade be replaced with legitimate
trade which was more profitable and acceptable in Africa.
5. Exploration opened the interior of Africa to the Europeans. Many
feared to come due to the belief in the Dark Continent theory.
However, with exploration, many got information about the interior
which enticed them to come.6. Africans adopted a new culture. Aspects of thi his culture includedlanguage, dressing, feeding and religion. This was responsible
for the weakening or disappearing of the traditions among the
communities that interacted with the Europeans.
7. Explorers led to the colonisation of Africa. This was through a number
of activities such as signing misleading treaties with local African
chiefs and cooperating with other colonial agents like missionaries.
Africa was finally colonised by Europe.
8. It made Europeans to increase their political ambitions to create
colonial empires for prestige. For example, Britain was able to
expand her wealth and power.9. It turned Africa to be a source of raw materials and market for
European manufactured goods such as clothes and guns.
10. Exploration led to the production of a new race of people known
as the Mulattos. These came as a result of intermarriages between
Africans and European explorers.
11. It led to introduction of plantation agriculture and keeping of
exotic breeds of livestock. The Portuguese introduced maize which
was grown in large plantations. Other crops that were introduced
by Europeans were sugarcane, tea, cocoa and tobacco. Livestock
breeds that were introduced were those of among others, pigs,
horses, sheep and cattle.
12. Many trading posts in West Africa and in many other parts of Africa
developed. For example, Timbuktu in Mali, South of the Sahara.
13. Exploration led to the rise of capitalism. Rise of capitalism resulted
from the growth of town and city life and the expansion of trade.14. It led to the rise of mercantilism. This rose from economic growth
and expanding royal power. Joint stock companies such as the
English East India Company and Dutch East India Company were
formed. It also led to rivalries at sea.
15. Exploration led to introduction of commercial revolution because
it ushered in trade involving Asia, America and Europe. Europebecame the centre of world trade
16. Shifts in population occurred. Europeans migrated to Asia and
America and Africa.
17. Knowledge about the earth increased. This made a significant
impact on Geography. Explorers were able to learn more about areas
in Africa and America. In learning more about such places, explorers
were able to bring knowledge of a larger world back to Europe.
In addition, methods of navigation and mapping also improved as
a result of the travels of people such as Prince Henry the Navigator.
Prior to his expeditions, navigators used traditional charts which
kept them tied to the shoreline. Among the many goals of his
expeditions were to develop a new nautical chart so future sailors
could sail out of sight of land. All in all, the Age of Exploration
served as a steppingstone for geographic knowledge. It allowed
more people to see and study various areas around the world. This
increased geographic study, giving us the basis for much of theknowledge we have today.
 Discuss in groups the economic consequences of exploration of Africa
Discuss in groups the economic consequences of exploration of Africaby Europeans. Make a presentation in class.
5.4. Problems faced by explorers in Africa.
 In Activity 5.1, you explained your visit to a place you had never visited
In Activity 5.1, you explained your visit to a place you had never visited
before. Using that information explain the challenges you are likely to
face when you visit a new place.The explorers faced a number of challenges during the exploration. Some
of them have been discussed below:
a) Poor communication and transport.
Generally, the whole of pre-colonial Africa had no established railways and
water canals. Most rivers and lakes were not navigable. There were also
physical barriers such as forests, mountains and rift valleys. The European
explorers were not familiar with such. They could get lost in forests. Thisslowed their work for some time.
b) Harsh climatic conditions.Africa had different climatic conditions as compared to what the
explorers were used to in Europe. It was sometimes too hot or too cold.
Tropical diseases such as malaria and yellow fever killed a large number
of European explorers. Due to such conditions, West Africa was regardedas a white man’s graveyard.
c) Hostility from slave dealers.
Most Europeans explorers claimed to have come to stop slave trade on
African soil. This drew them into hostility with Arab slave dealers who
disliked missionary explorers for attacking their business. This led toconstant attacks and alliances with resistors to frustrate Europeans.
d) Limited manpower.The explorers lacked enough manpower. This was due to coming in of
few professionals compared to the big tasks they had. Some also died or
were sick and unable to work. Africans were ignorant and had no requiredskills. This led to overworking leaving many places unattended.
e) The problem of language barrier.
This was another challenge that was faced by the European explores. They
spoke European languages that were not known in Africa. Europeans
spoke languages such as English, German and French. In Africa, there
was no uniform language because even Swahili was not known to all. This
hampered communication as there were no even interpreters.
hampered communication as there were no even interpreters.
f) The threat of Islam.
Islam had long been introduced in most places of Africa. It spread especially
at the coast of West Africa and East Africa where Arab traders lived. Many
people had embraced Islam, yet missionary explorers wanted to stop it.
They wanted to replace it with Christianity. This led to wars where manyperished, consequently slowing down the work of explorers.
g) Hostile tribes.This was another challenge that was faced by European explorers in
Africa. Most tribes stopped explorers from passing through their land.
The Turkana, Nandi and Maasai from Kenya were among the hostile
communities that attacked and killed explorers. This was in addition totribal wars that affected the work of European explorers in Africa.
h) Presence of wild animals.These included animals such as lions, reptiles and wild beast in the tropics.
Most explorers passed through forests and national parks due to lack of
geographical maps and compasses. They were later eaten up and killed
by lions, for example, in Tsavo National Park in Kenya. This threatenedtheir mission in Africa.
i) Lack of home support.Most explorers lacked enough support from home. This was due to long
geographical separation between Europe and Africa. This led to limited
supplies in form of food, medicine and clothes. It crippled their work
alongside registering a lot of failures. For example, Dr David Livingstone
died before completing his work.
j) Getting lost.
One big problem was faced was that they were lost in Africa due to lack
of geographical maps and compasses. They either relied on local guides
or just gut feelings. This was catastrophic in the sense that if they got lostnobody could help them.
k) Diseases.
When explorers encountered new people, they exchanged diseases
as well as goods. Diseases such as malaria, dysentery and yellow fever
caused many deaths among ship crews. Some of these, especially yellow
fever, were spread to other ports that the sailors visited. This left most ofthem sickly and unable to do the work effectively.!
 Touring new places is indeed very important. It enables one to discover,
Touring new places is indeed very important. It enables one to discover,
have fun and be exposed to new areas. However, travelling without
taking precaution is risky. Remember the following:
1. Do not travel alone to places you do not know very well.
2. Avoid walking on foot in national parks for animals can easily kill
you.
3. Travel once in a while but not always to minimise costs and toavoid bankruptcy.

Discuss the main problems faced by explorers. Present in class.
 1. Define the term ‘exploration’.
1. Define the term ‘exploration’.
2. Identify different European explorers who visited the African
continent.
3. Give reasons why European explorers were interested in the
African continent.
4. Discuss the challenges faced by early explorers in Africa.
5. Explain the impact of the European exploration of the African
continent.
