UNIT 3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS TOOLS
3.0 Introductory Activity
3.1. Introduction to Computer Graphics
Modifying a hard drawing can be hard, swapping colors or resizing a picture on such
a drawing is more complicated. That’s why it is more efficient to draw a picture on a
computer screen and the drawing is now a piece of digital information which is easyto modify.
Computer Graphics involves the ways in which images can be displayed, manipulatedand stored using a computer.
Computer graphics provides the software and hardware techniques or methods forgenerating images.
3.1.1. Definitions of Different Terms
Computer graphic: This is the use of a computer and specialized programs to produce
and manipulate pictorial images.
Pixel: is the smallest unit of a digital image or graphic that can be displayed and
represented on a digital displayed device. Is also known as a picture element. A pixel
can have different colors produced by mixing the three colors RGB (Red, Green and
Blue) and each of the three colors can take values ranging from 0 to 256.
2D (2Dimensional) images are objects that are rendered visually on paper, film or on
screen in two planes representing width and height (X and Y). Two-dimensionalstructures are also used in the construction of 3D objects.
3D computer graphics or three-dimensional computer graphics, (in contrast to 2D
computer graphics) are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of
geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for the purposes ofperforming calculations and rendering 2D image.
Morphing: is a technique which involves using a computer to make an image on film
or television appear to change shape or change into something else. For example a
human face may be transformed into a lion one and the human eye will find it
unbelievable how the human has changed him/herself.
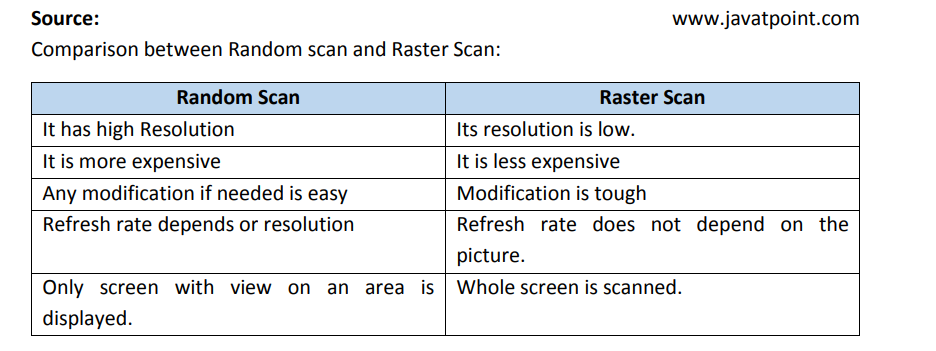
Random scan:
Random Scan System uses an electron beam which operates like a pencil to create a
line image on the CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) screen. The picture is constructed out of a
sequence of straight-line segments. Each line segment is drawn on the screen by
directing the beam to move from one point on the screen to the next, where its x & y
coordinates define each point. After drawing the picture. The system cycles back to
the first line and design all the lines of the image 30 to 60 time each second.
The process is shown in figure: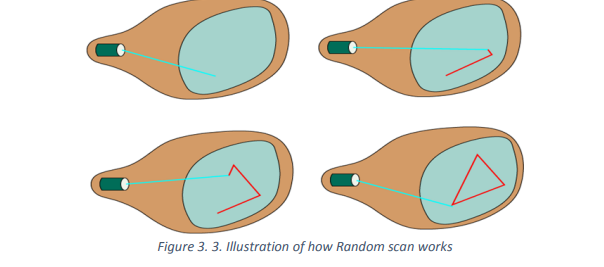
Source: : https://www.javatpoint.com/
Raster scan
A raster scan display is based on intensity control of pixels in the form of a rectangular
box called Raster on the screen. Information about On and Off pixels is stored in a
refresh buffer or Frame buffer. Televisions in homes are based on Raster Scan
Method. The raster scan system can store information of each pixel position, so it is
suitable for realistic display of objects. Raster Scan provides a refresh rate of 60 to 80
frames per second.
Frame Buffer is also known as Raster or bit map. In Frame Buffer the positions are
called picture elements or pixels. Beam refreshing is of two types. First is horizontal
retracing and second is vertical retracing. When the beam starts from the top left
corner and reaches the bottom right scale, it will again return to the top left side called
at vertical retrace. Then it will again more horizontally from top to bottom. The figure
below illustrates the process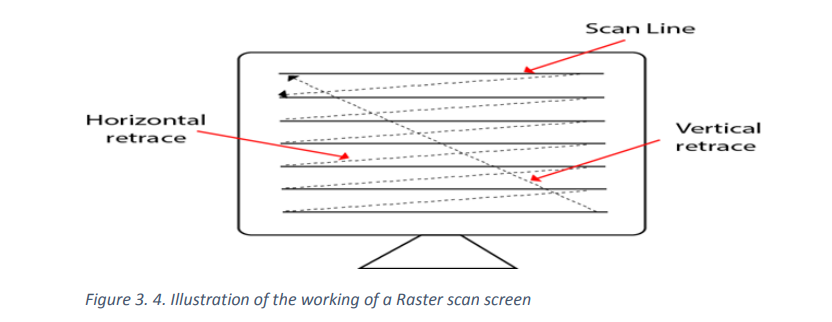

3.2.1. DEFINITION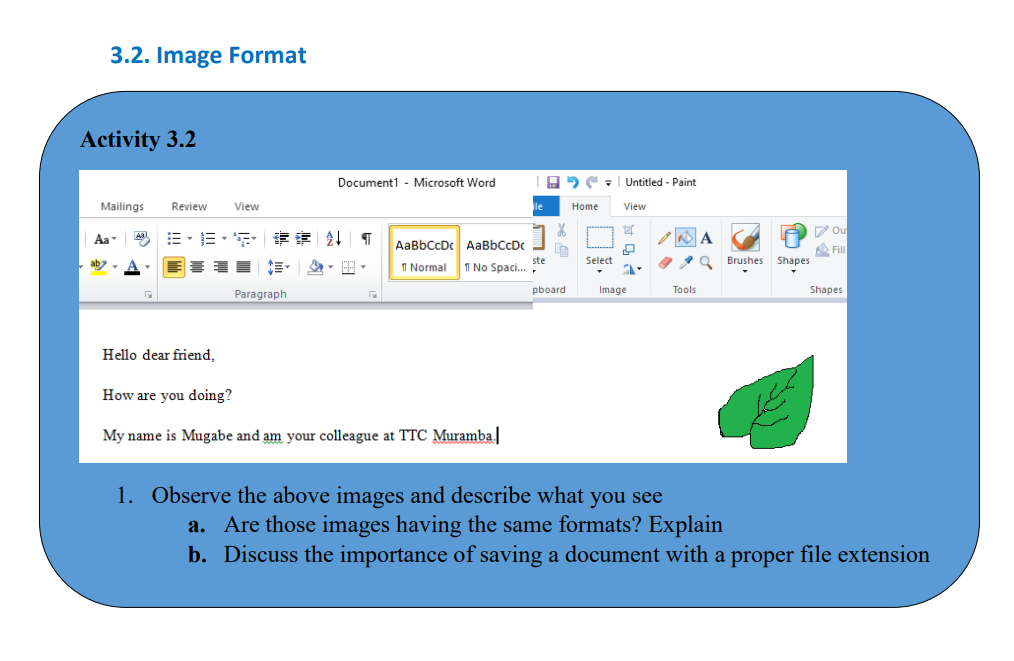
Image file formats are standardized means of organizing and storing digital images.
Image files are composed of digital data in one of the formats that can be rasterized
for use on a computer display or printer.
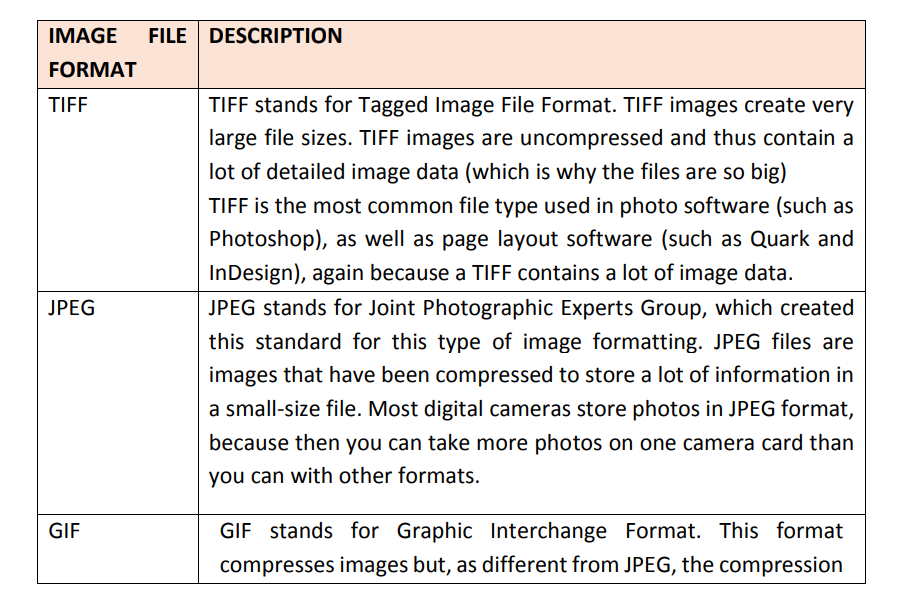
There are 4 main formats in which to store images including TIFF, JPEG, GIF and PNG.Their differences are given in the table below:
3.2.2 Image compression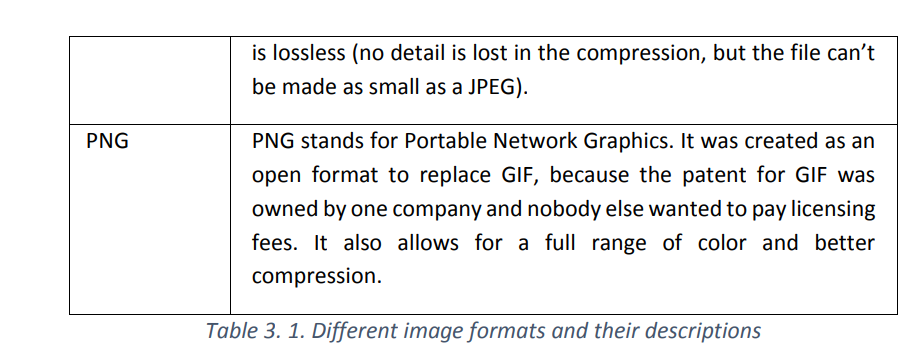
Image compression is minimizing the size in bytes of a graphic file without degrading
the quality of the image to an unacceptable level. The reduction in file size allows
more images to be stored in a given amount of disk or memory space. It also reduces
the time required for images to be sent over the Internet or downloaded from web
pages. Know an image’s file size and dimensions before or after uploading it into theLibrary
Image compression techniques Lossy and Lossless
Lossless: The compression technique where compressed data (byte) will be the same
replica of actual data. In this case, compressed file is required to be reproduced
exactly when get decompressed again.
Lossy: File compression results in lost data and quality from the original version. Lossycompression is typically associated with image files.
3.2.3 Viewing an image’s file size and dimensions
The determination of an image’s file size and dimensions depends on an Operating
System being used.
Open the image in Windows Explorer to check dimensions and file size by clicking the
Windows Start button on the taskbar.
Right clicking the icon of the image file,
In the pop up menu, click on property and details.
The result will look like below. The wanted information are circled with red line.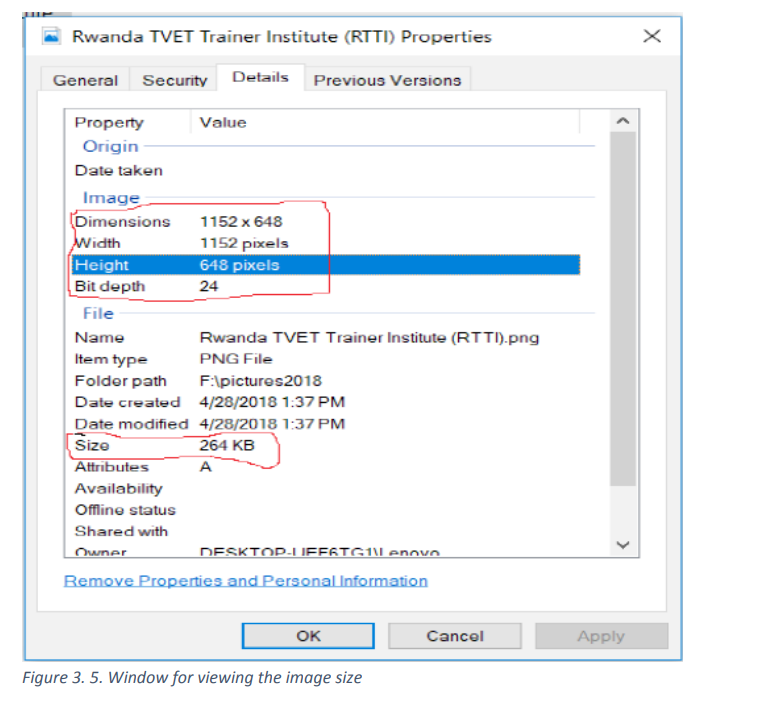
3.2.4 Calculating size of an uncompressed image file
Computer storage and memory is measured in Megabytes (MB) and Gigabytes (GB).
A bit is the smallest unit of measurement used to quantify computer data and byte is
a group of 8 binary digits.
Unit of memory size.
1Byte= 8bits
1KB= 1024Bytes
1MB = 1024 KB
1GB=1024 MB
1TB=1024 GB
It takes 2 to 3 bytes to store one pixel of a color image. The pixels in an image store a
color at a given point in the image, but it takes 2 to 3 bytes of storage to record this
value. If we consider 3 bytes of storage, the file size of a color image is equivalent to:
width * height * 3
Example: Let‘s consider an image whose Width is 1152 and height is 648.
If we consider 3 bytes of storage, the file size of a color image is equivalent to: width
* height * 3 which is =1152*648*3 = 2,239,458 which gives the file size in bytes. This
file size number is so big, it needs to be converted in Kilobytes or even megabytes.
There are 1,024 bytes in a kilobyte and 1,024 kilobytes in a megabyte which makes
this file have the size of 2.187 Kilobytes.
3.3 Image Capturing Tools
The process of obtaining a digital Image from a vision sensor, such as camera usually
entails a hardware interface known as a frame grabber, which captures single frames
of video, converts the analogue values to digital, and feeds the results into thecomputer memory.
3.3.1. Digital Camera
The first digital camera was invented by STEVEN SASSON in 1975. Digital cameras are
normally used to capture pictures or video through the use of an electronic image
sensor.
There are two types:
3.3.1. Digital Camera
The first digital camera was invented by STEVEN SASSON in 1975. Digital cameras are
normally used to capture pictures or video through the use of an electronic image
sensor.There are two types:
a. Definition
A digital camera is a camera which produces digital images that can be stored in a
computer and displayed on screen. It records and stores photographic images in
digital format.
These stored images can be uploaded to a computer immediately or stored in the
camera to be uploaded into a computer or printed later.Digital cameras use an image sensor instead of photographic film.
Digital camera parts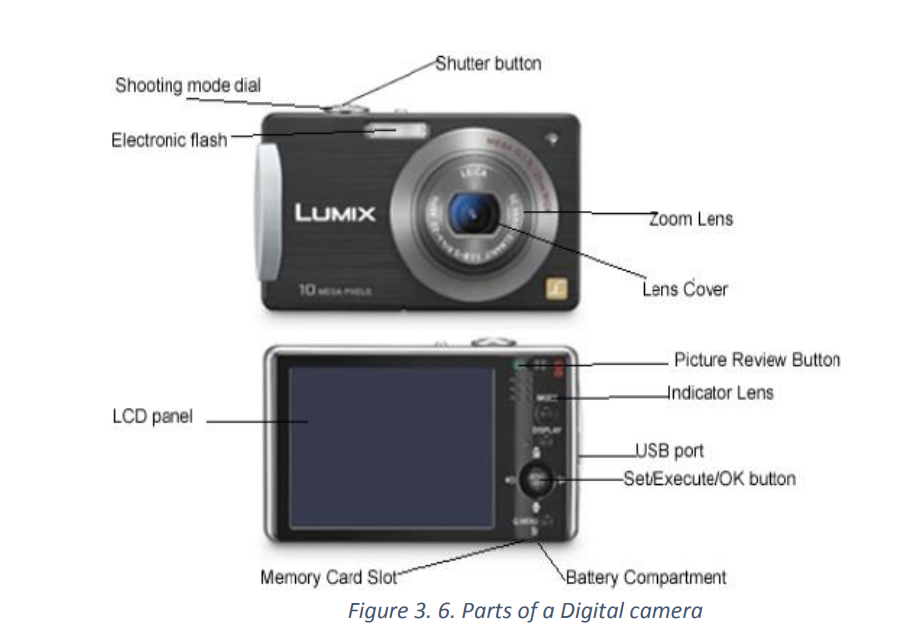
There are 10 basic camera parts to identify in today’s digital world. These parts will
inevitably be found on most cameras being digital compact or single-lens reflex
camera (SLR)
Lens
The lens is one of the most vital parts of a camera. The light enters through the lens,
and this is where the photo process begins. Lenses can be either fixed permanently to
the body or interchangeable. They can also vary in focal length, aperture, and other
details.
Viewfinder
The viewfinder can be found on all digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLR) and some
models of digital compacts. On DSLRs, it will be the main visual source for image taking,
but many of today’s digital compacts have replaced the typical viewfinder with
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) screen.
Body
The body is the main portion of the camera, and bodies can be in different shapes and
sizes. DSLRs tend to be larger bodied and a bit heavier, while there are other consumercameras that are a conveniently smaller size and even able to fit into a pocket.
Shutter Release
The shutter release button is the mechanism that “releases” the shutter and therefore
enables the ability to capture the image. The length of time the shutter is left open
Aperture
The aperture affects the image’s exposure by changing the diameter of the lens
opening, which controls the amount of light reaching the image sensor. Some digital
compacts will have a fixed aperture lens, but most of today’s compact cameras have
at least a small aperture range.
Image Sensor
The image sensor converts the optical image to an electronic signal, which is then sent
to the memory card. There are two main types of image sensors that are used in most
digital cameras: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) and Charge
Coupled Device (CCD) Both forms of the sensor accomplish the same task, but each
has a different method of performance.
Memory Card
The memory card stores all of the image information, and they range in different size
and speed capacity. Memory cards can be taken out of the camera and inserted in a
computer memory card bay for reading.LCD Screen
The LCD screen is found on the back of the body and can vary in size. On digital
compact cameras, the LCD has typically begun to replace the viewfinder completely.
On DSLRs, the LCD is mainly for viewing photos after shooting, but some cameras dohave a “live mode” as well.
Flash
The on-board flash will be available on all cameras except some professional grade
DSLRs. It can sometimes be useful to provide a bit of extra light during dim, low light
situations.
User Controls
The controls on each camera will vary depending on the model and type. The basic
digital compacts may only have auto settings that can be used for different
environments, while a DSLR will have numerous controls for auto and manualshooting along with custom settings.
c. Importing pictures using USB cable
The images taken by using a camera are stored automatically in its memory. However,
for different purposes, the images can be printed or inserted in documents for
illustrations. The camera is then connected to the printer or the computer by using a
USB cable appropriately designed for such action. The fact of taking pictures from thecamera to the computer is called importing pictures.
The following steps are followed to successfully import a picture from camera to
computer by using a USB cable.
Step 1: Connect one end of the USB cable to the port in your camera.
Step 2: Connect the other end of the USB cable to the USB port in the computer. This
may be in the front or back of the computer.
Step 3: Turn on the camera
Step 4: A dialog box may appear on the screen. If it does, select “View Files” or “Open
Folder.” If the dialog does not appear, click the Windows “Start” menu, select“Computer” and then choose the drive labeled for the connected camera.
The pictures are probably located in a particular photo folder on the camera. Open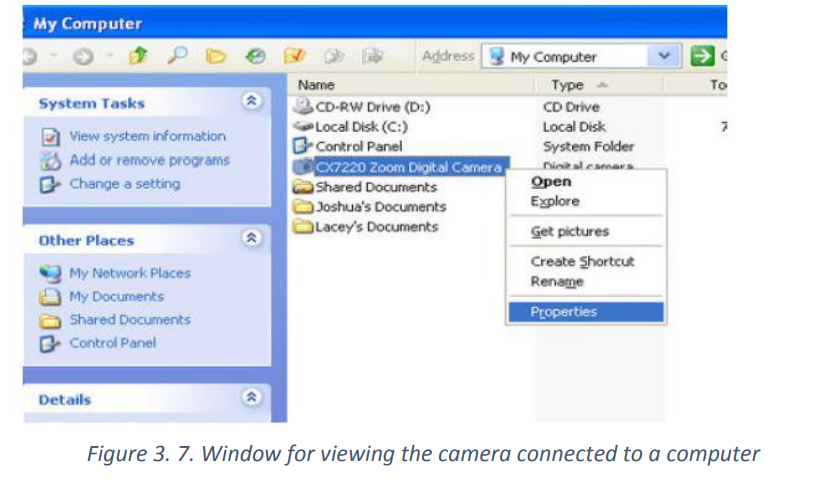
that folder. Drag individual photos from the folder to the desktop or some other folder
on the computer. All the photos can be selected by pressing “Ctrl-A” and then pastedinto a folder on the computer by pressing “Ctrl-V
3.3.2 Scanner
A scanner is an electronic device which can capture images from physical items
(printed text, handwriting, photographic prints, posters, magazine pages, and similar
sources) and convert them into digital formats, which in turn can be stored in a
computer and viewed or modified using software applications.
Very high resolution scanners are used for scanning for high-resolution printing, butlower resolution scanners are adequate for capturing images for computer display.
b. The different parts of scanner
A scanner has the following five parts visible externally:
(1)Start button, (2) Copy button, (3) Scan to E-mail button, (4) Scan to Web button, (5)Scanner cover
Note: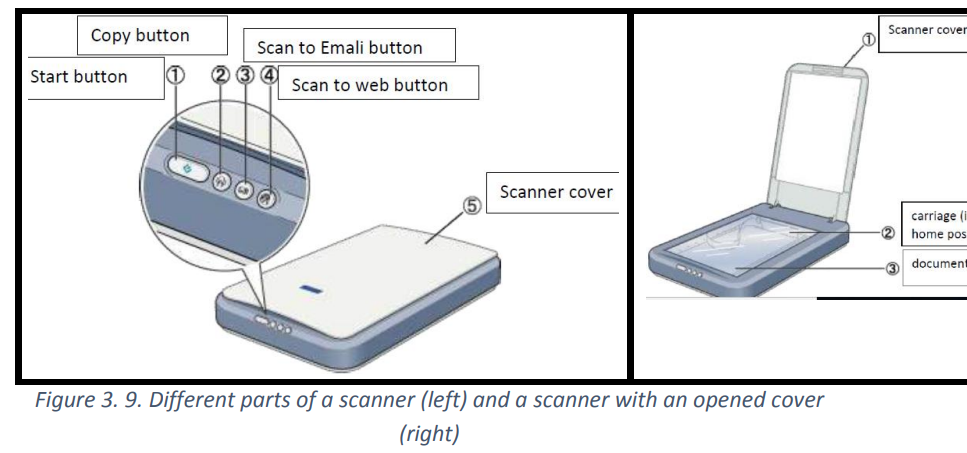
Parts, size and looks of scanners vary depending on the type of scanner and some scanning
and photocopying functionalities are combined in one physical device therefore some of the
parts mat not be visible
Some scanners have touch screen capabilities therefore they may not have some of thebuttons

3.4 Screenshots Capturing
A screenshot is an image of a computer desktop that can be saved as a graphic file. (The mouse
cursor is not included in the image). The main ways used to get the screen of computer is to
use the Print Screen key (PrtSc) or the Snipping Tool3.4.1. Use of Print Screen Key
A print screen is a computer key which is used to copy to the clipboard an image of the screen
and paste it in any other application for saving or manipulation
Steps to follow in screen shot capturing using Print screen key:
Open the screen that is going to be copied.
Press the Print Screen key
Paste (CTRL+V) the image into an Office program or any other application.
The taken image can be edited depending on the options provided by the program in which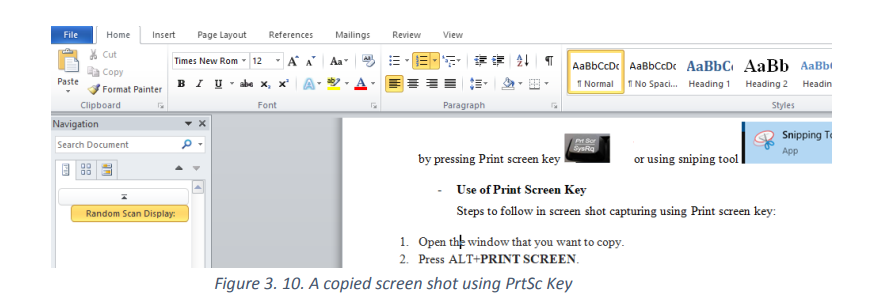
it is pasted.
3.4.2 Use of Snipping tool
Snipping Tool is a Microsoft Windows screenshot utility included in Windows Vista and in
later versions. It can take still screenshots of an open window, rectangular areas, a free-formarea, or the entire screen.
To open the Sniping tool:
Click on Start
Write Snipping Tool in the search box and once found click on it to launch or click on All
Programs then click on Accessories and click on the snipping tool
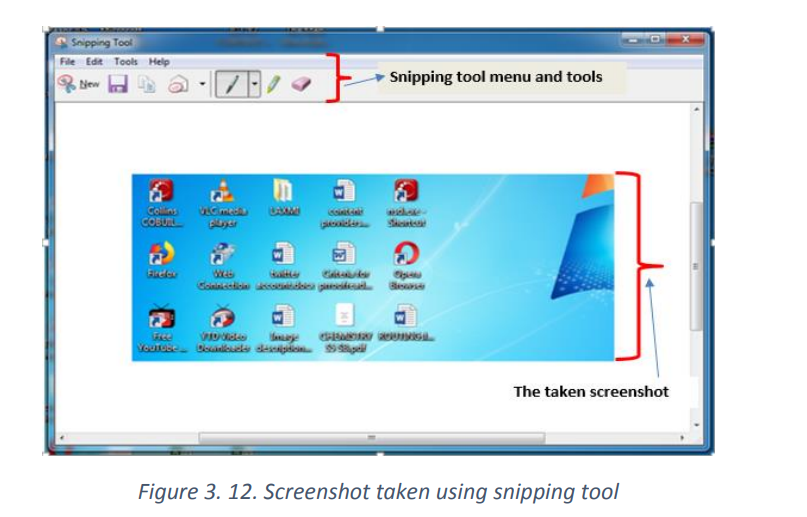
An opened Sniping tool will look like in the image below:
To take a screenshot using Snipping tool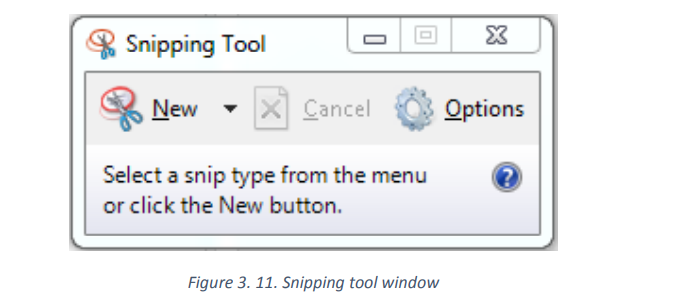
To take a screenshot in the opened Snipping tool

3.5. Graphic Software-Paint
In computer graphics, graphics software refers to a program or a collection of
programs that enable a person to manipulate images on a computer.Examples of such programs include Adobe Photoshop, Microsoft Publisher, Paint, Etc.
3.5.1. Starting and saving a Paint file
A paint program is a software graphics program that allows the user to draw or paint
bitmapped images on a computer.To start Paint go through the following steps:

Understand the canvas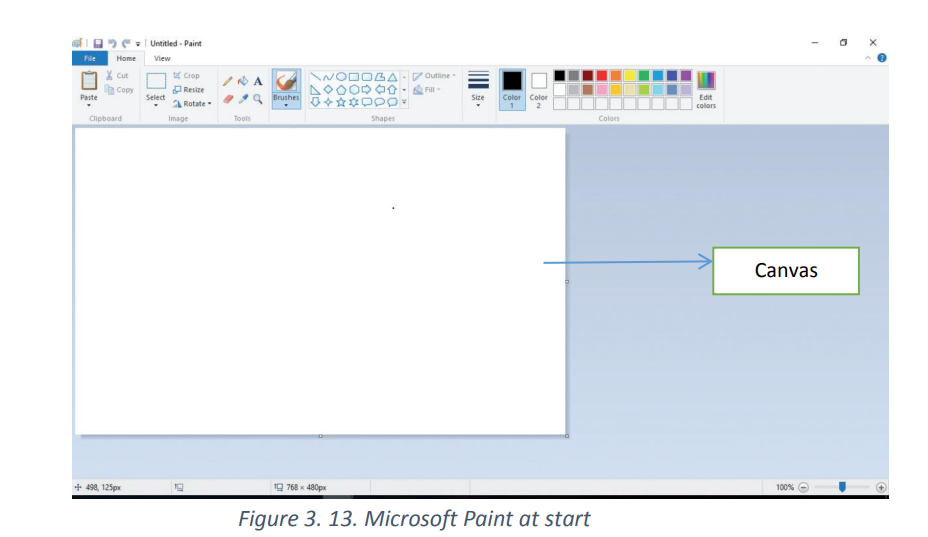
When Paint launches, the white “canvas” will appear on the screen. Imagine this
canvas as a piece of paper to draw or write on. The size of the canvas can be adjustedbefore starting to create images.
The flower above has been drawn using the Pencil tool which was used to draw lines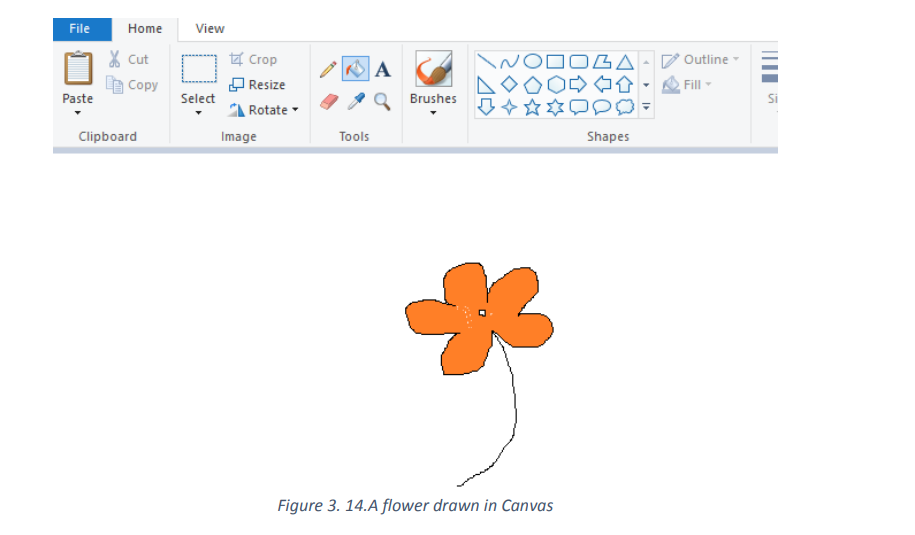
and the Fill with color tools was used to fill the red color on the leafy part of the flower.
Saving a paint file
 From File menu, choose Save as.
From File menu, choose Save as. From a dialog box, choose PNG picture or any other image file format
From a dialog box, choose PNG picture or any other image file format
In the next window type the file name, choose file format then click on save button.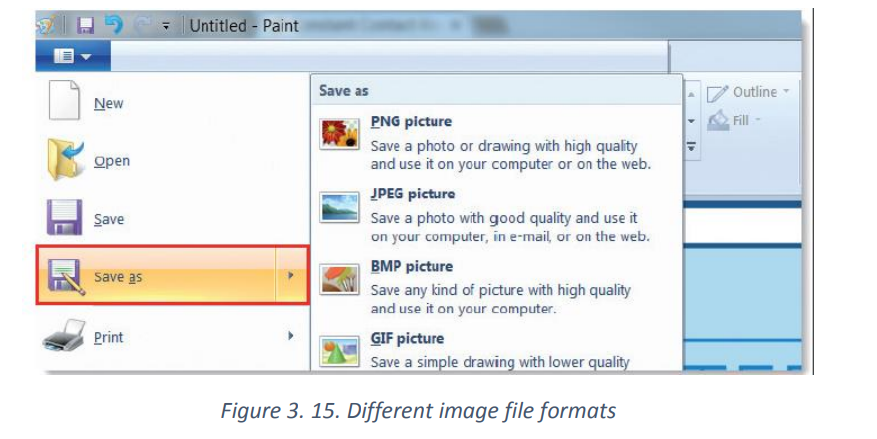
3.5.2. Paint tools
The paint program has got many tools which help its user manipulate images and do
any activity Paint is supposed to do. Some of the Paint tools are shown in the imagebelow:
Text tool: The tool allows text to be typed onto the current layer using the primary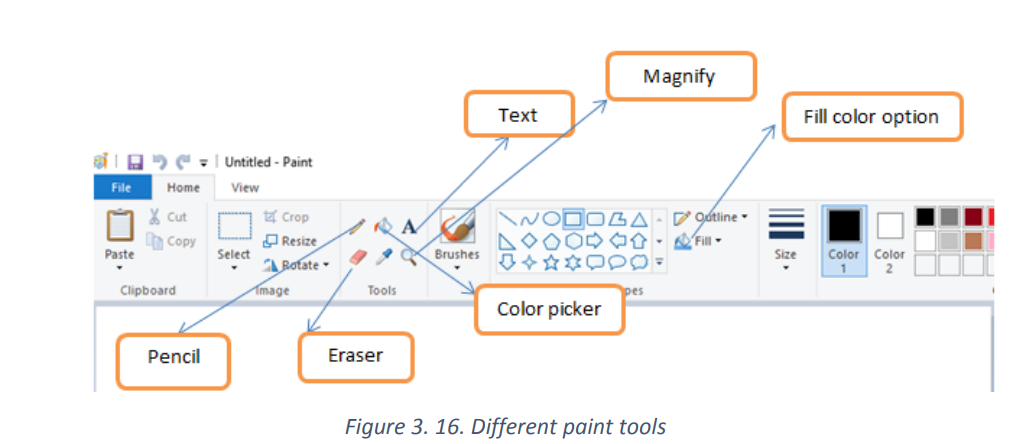
color. The text controls in the Toll Bar can be used to change the font, the size of thefont, formatting.
The pencil tool: is a freehand drawing tool, much like an actual pencil. The width of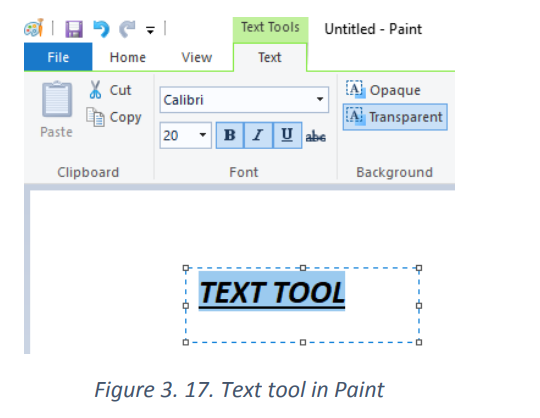
the line can be adjusted by clicking the Size menu and selecting a different line width.To draw, simply press the mouse button as you move the mouse on the canvas.
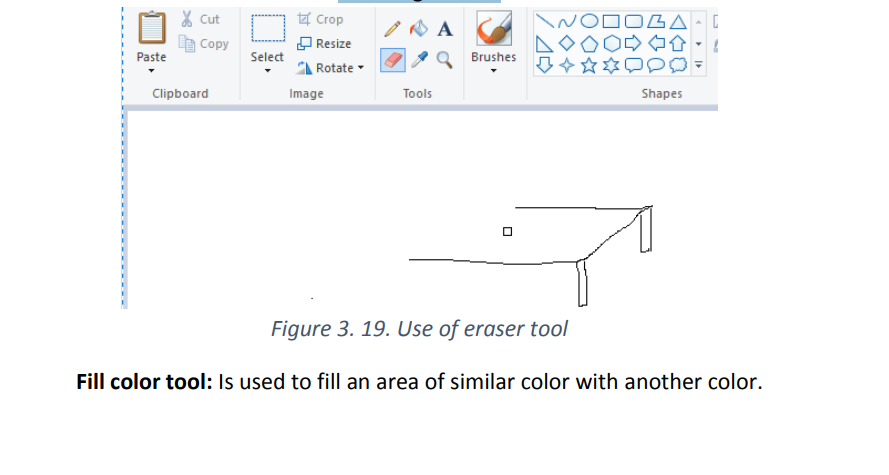
Eraser tool: This tool is used to remove parts of the active layer or selection like in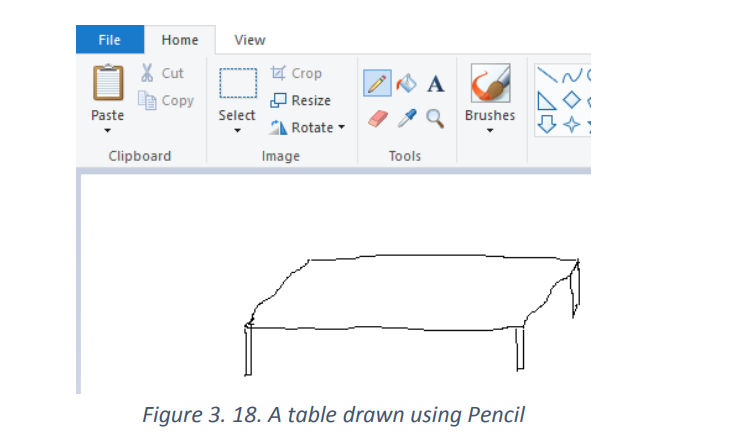
the image below
Color picker tool: is used to select a color on the active layer. By clicking a point on a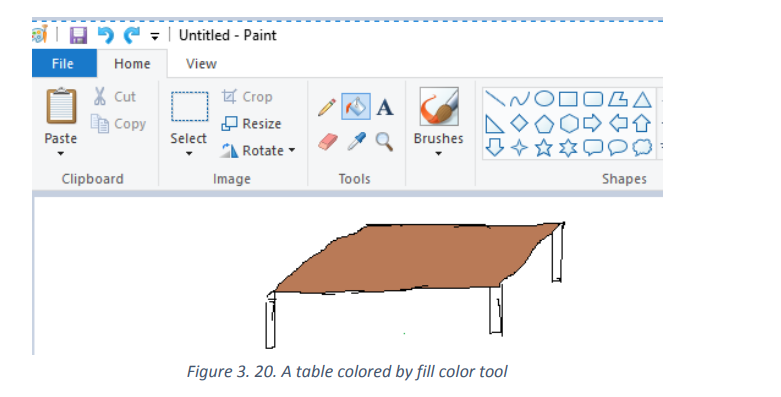
layer,
You can change the active color to that which is located under the pointer.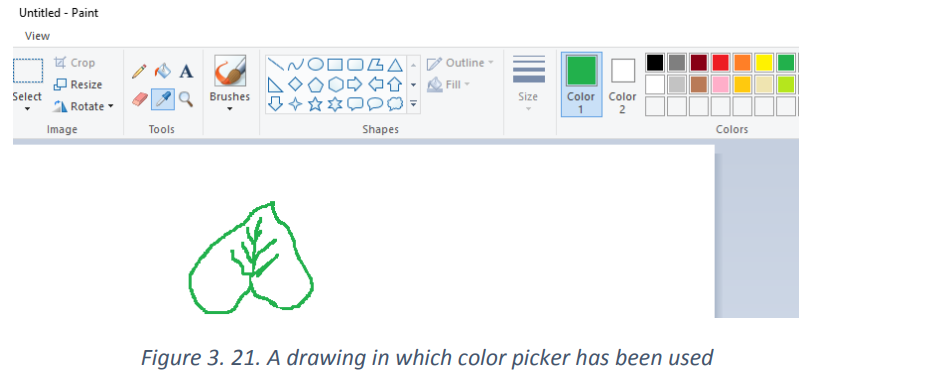
Magnifier: next to the “Pick color” button is the “Magnifier” button, which looks like
a magnifying glass. Selecting this tool will allow the user to zoom in and out of animage.
3.5.3. Insertion of Shapes
A shape is a geometric figure such as square, triangle or rectangle. Using illustrator’s
shape to draw can be an effective way to create smooth paths and predictable results.Below are different shapes in Paint:
Select any shape from the toolbar to draw that shape. Once you’ve chosen a shape,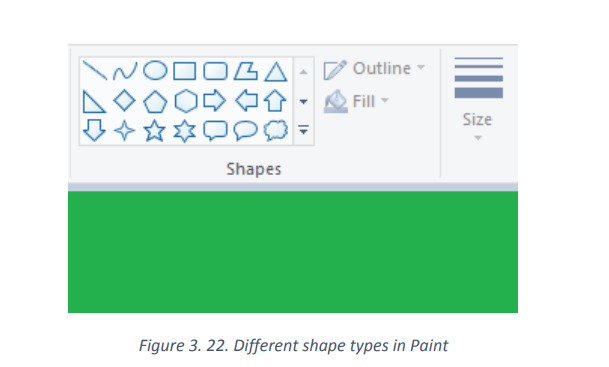
you’ll notice some options for the shape’s appearance.
Click the “Outline” and “Fill” menus to view your options.
Select your preferred outline and fill options,
Then, click the canvas where you’d like to place your shape.
Hold down the mouse button as you drag the cursor to enlarge the shape.
Let go of the mouse button when reach the desired shape size.
After choosing a shape with an outline, the color of the outline will be the current
foreground color. If the shape has a solid filling, the fill color will be the background
color.
3.5.4. Select, Cut, Copy, Paste and Crop
a. Copy and Paste
Press and hold down the left mouse button inside the selection box and move the
picture to relocate the image.If you wish to copy the image:
 Right-click inside the selection box
Right-click inside the selection box And click "Copy."
And click "Copy." An image can be pasted to another paint document or in another program
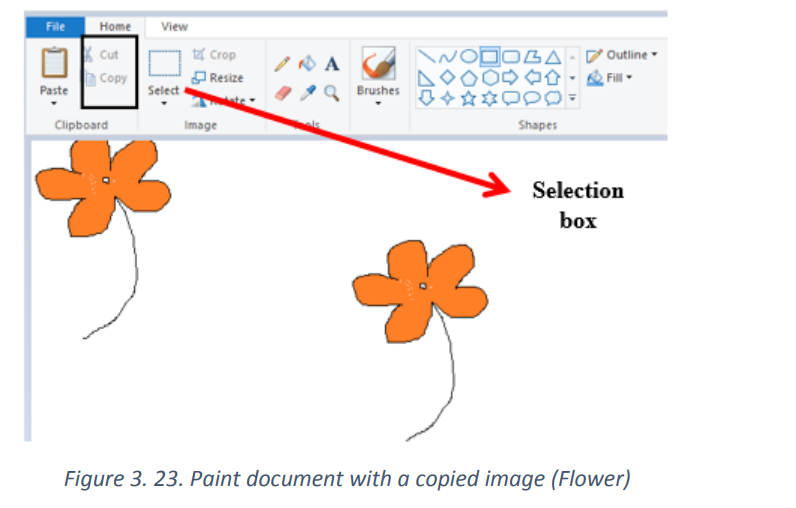
b. Cut and Paste
Click on the area of an image you want removed, click and hold the mouse to dragthe box as far down and over as needed
 Press and hold "Ctrl" and "X" to cut the selection.
Press and hold "Ctrl" and "X" to cut the selection. Press and hold "Ctrl and "V" to paste the selection, either elsewhere in the
Press and hold "Ctrl and "V" to paste the selection, either elsewhere in the
same document or in a separate document.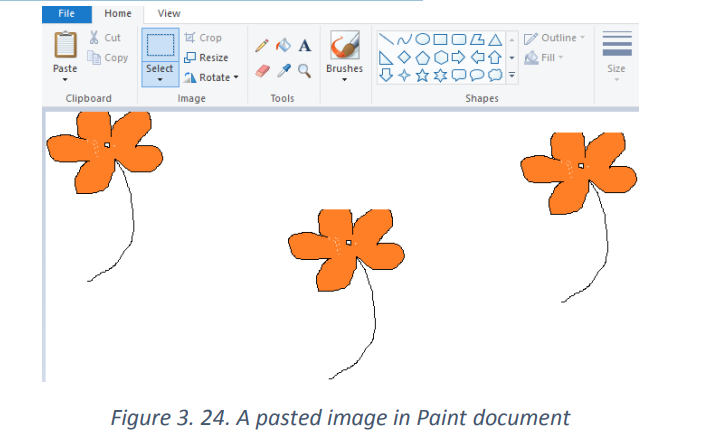
 Paste in Ms Office word
Paste in Ms Office word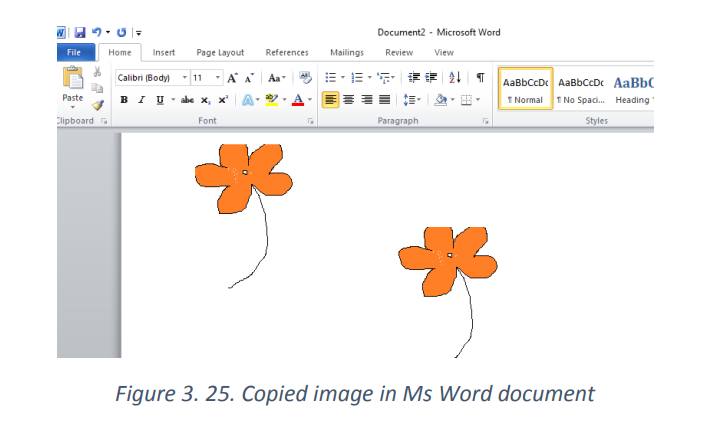
After cutting in Paint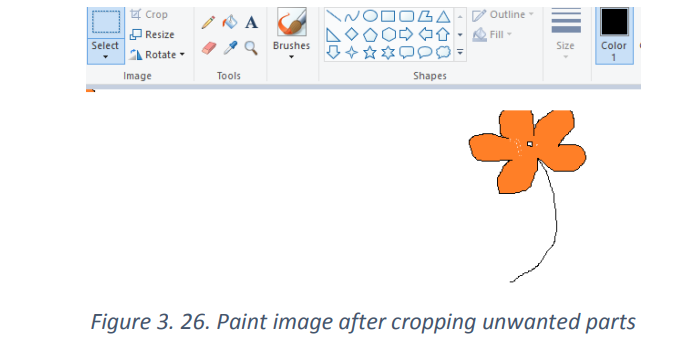
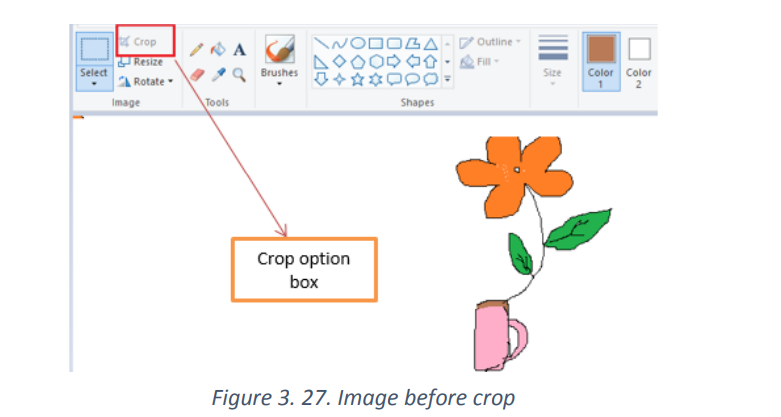
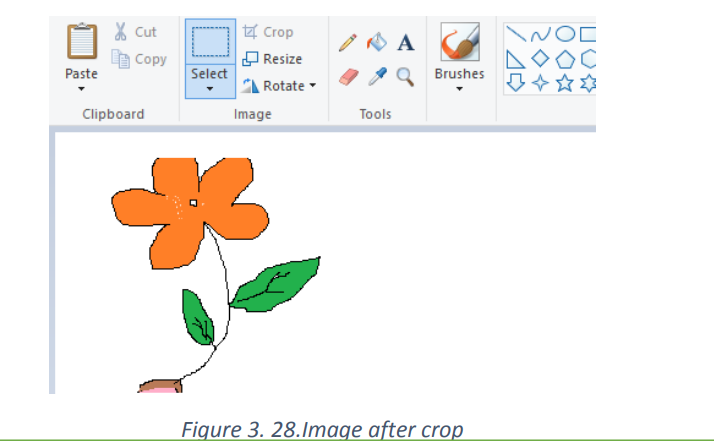
c. Crop
Select the portion of the image you want to crop using the Select tool.
Once selected right-click with the mouse anywhere in the image selection andselect Crop or go to Crop in tools bar.


The test contains 15 questions and there is no time limit
At the end of the Test, your total score will be displayed and the Maximum score is 30 points.CLICK Here to start NETWORK EVALUATION QUIZ
