UNIT1: ADVANCED SPREADSHEET II
 The If function takes as arguments the logical test, checks if it evaluates to true and ifA condition is an expression that either evaluatesto true orfalse. The expression couldbe a function that determines if the value entered in a cell is of numeric or text datatype, if a value is greater than, equal to or less than a specified value, etcLogical Function is a feature in Excel that allows excel users to introduceautomated decision-making when executing formulas and functions.The role of functionsin thisisto check if a condition istrue orfalse. It combines multipleconditions together and comes up with a result depending on the result of theevaluation of the condition.a. IF FunctionThe If function checks whether data in a cell meets a certain condition and returnsone value which can be True or False• Syntax: = IF(Logical_test, Value_If_True, Value_If_False )
The If function takes as arguments the logical test, checks if it evaluates to true and ifA condition is an expression that either evaluatesto true orfalse. The expression couldbe a function that determines if the value entered in a cell is of numeric or text datatype, if a value is greater than, equal to or less than a specified value, etcLogical Function is a feature in Excel that allows excel users to introduceautomated decision-making when executing formulas and functions.The role of functionsin thisisto check if a condition istrue orfalse. It combines multipleconditions together and comes up with a result depending on the result of theevaluation of the condition.a. IF FunctionThe If function checks whether data in a cell meets a certain condition and returnsone value which can be True or False• Syntax: = IF(Logical_test, Value_If_True, Value_If_False )
so returns as a result the content of the second argument and if false the content ofthird argument is returned
• Example 1:
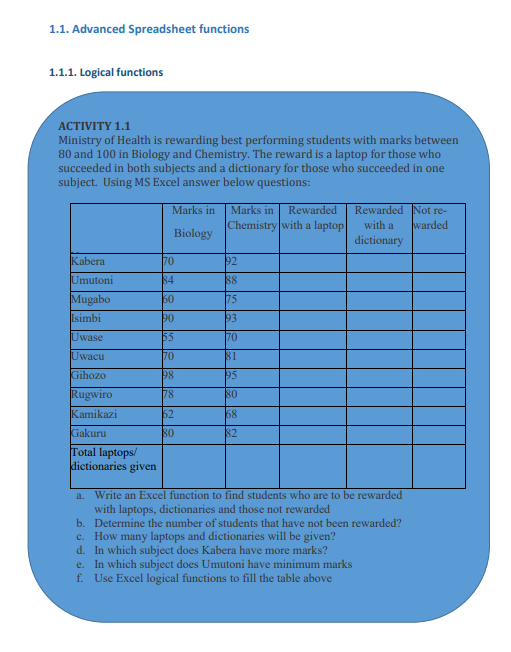
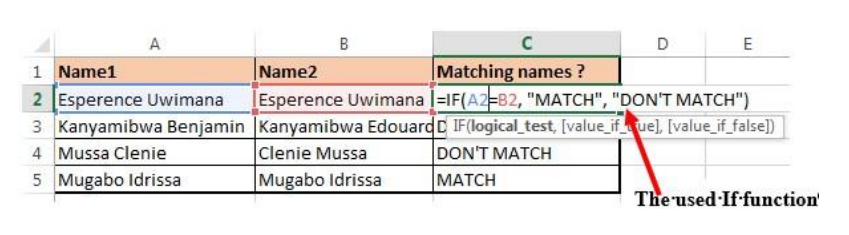 Figure 1. 1. The use of If function to compare namesIn the above example the If function with its arguments is entered in the cell wherethe result is to appear.To apply that function in other cells proceed like this:1. Place the cursor in the bottom corner of the cell2. Hold down the left key, scroll down to other cells and release the leftbuttonThe If function in the above examples checks if the two names are alike and if yes,the function writes MATCH in the cell, if not the function writes DON’T MATCH• Example 2:Considering the marks obtained by Irasubiza, Karenzi, Byukusenge and Shyaka in ICT,Maths and English. The If function checks if the marks are greater than87 and gives to the candidate the Very Good note else the Good note is given.
Figure 1. 1. The use of If function to compare namesIn the above example the If function with its arguments is entered in the cell wherethe result is to appear.To apply that function in other cells proceed like this:1. Place the cursor in the bottom corner of the cell2. Hold down the left key, scroll down to other cells and release the leftbuttonThe If function in the above examples checks if the two names are alike and if yes,the function writes MATCH in the cell, if not the function writes DON’T MATCH• Example 2:Considering the marks obtained by Irasubiza, Karenzi, Byukusenge and Shyaka in ICT,Maths and English. The If function checks if the marks are greater than87 and gives to the candidate the Very Good note else the Good note is given.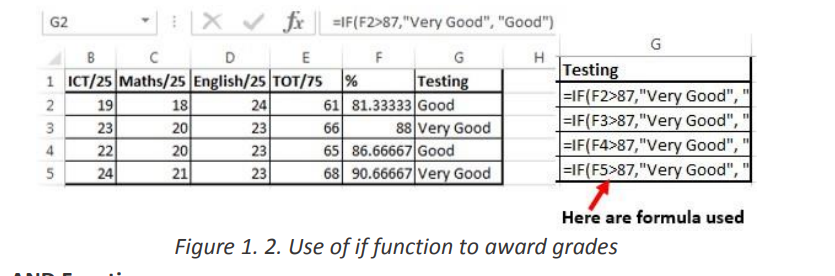 Interpretation of the results:b. AND FunctionThe Excel AND function is a logical function used to test if two or many conditions aretrue. The result is TRUE if all the conditions are true else the result is FALSE• Syntax: =AND (Logical1, Logical2, logical3,…)• Example:In the table below the And function checks if people in the table studiedEducation and that their age is greater than 18
Interpretation of the results:b. AND FunctionThe Excel AND function is a logical function used to test if two or many conditions aretrue. The result is TRUE if all the conditions are true else the result is FALSE• Syntax: =AND (Logical1, Logical2, logical3,…)• Example:In the table below the And function checks if people in the table studiedEducation and that their age is greater than 18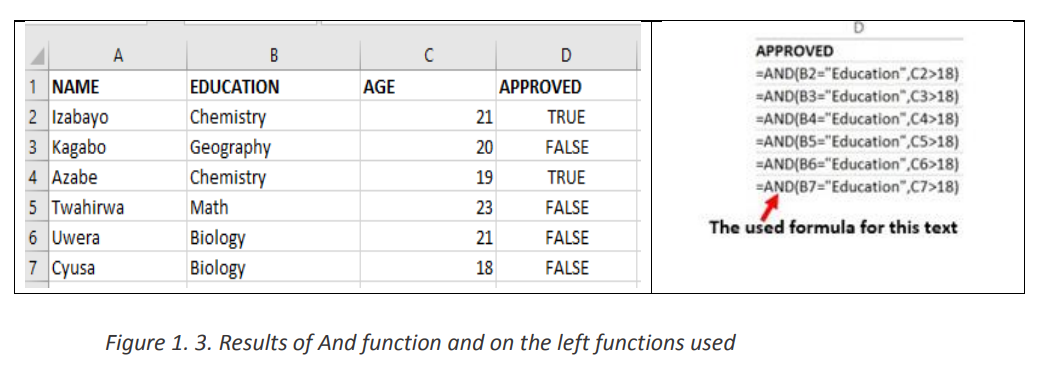 Note: the And function may have more than two arguments and for the results to beTrue all the arguments must evaluate to TRUE and if one of the arguments is false allthe result is FALSE
Note: the And function may have more than two arguments and for the results to beTrue all the arguments must evaluate to TRUE and if one of the arguments is false allthe result is FALSE
The second, fourth, fifth and seventh rows evaluate to True as the education for all
those rows is Education and the age is greater than 18 while the remaining rowsc. FALSE Functionevaluate to FALSE as they don’t meet the two criteria.
The FALSE function takes no arguments and generates the Boolean value FALSE. It is
used to compare the results of a condition or function that either returns true or false
• Syntax: =False
The false function takes no argument but just returns the logical value False
•Example: The False function used in the example below returns FALSE if the ageInterpretation:entered in C2 is less than 20 (C2<10)
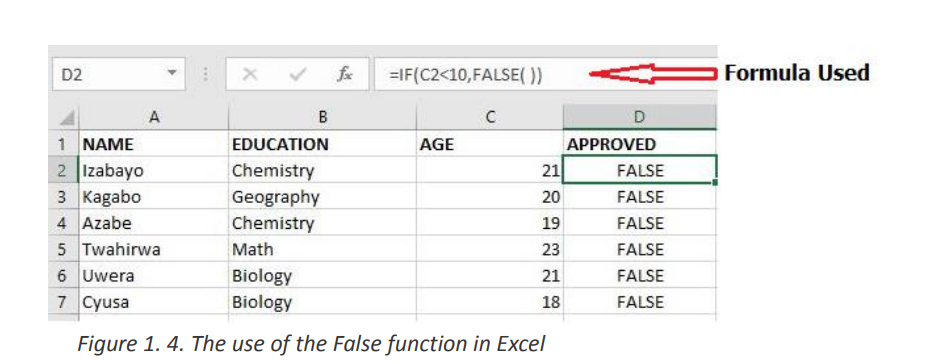
The used function “=IF(C2<10,FALSE)” will check if the C2 cell data is less than 10, if
so it will return False as a result else it will return True. The same function will bed. NOT Functionapplied to other cells by changing the cell position
The Excel NOT function returns the opposite of a given logical or Boolean value. When
given TRUE, NOT returns FALSE. When given FALSE, NOT returns TRUE. Use the NOT
function to reverse a logical value.
• Syntax: =NOT(Logical)
The not function takes one logical expression as an argument. It returns an error if• Examplemore than one argument is used.
The table below will have all its content returned to True by the use of the NOT
function. If the results to reverse were got by using a formula the Not function can be
put in front of the function/formula to make the latter an argument of the NotNote: If the results in column D2 were got by using the function “=IF(C2<10,FALSEfunction.
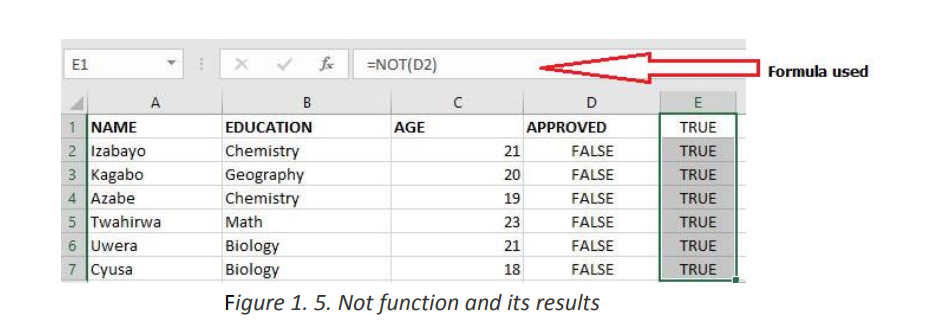
)”
the result in column E2 can be got by using the function “=NOT(IF(C2<10,FALSE))”.
As always the formula/function in one cell can be applied to other cells by pasting it in
those cells
e. The OR function
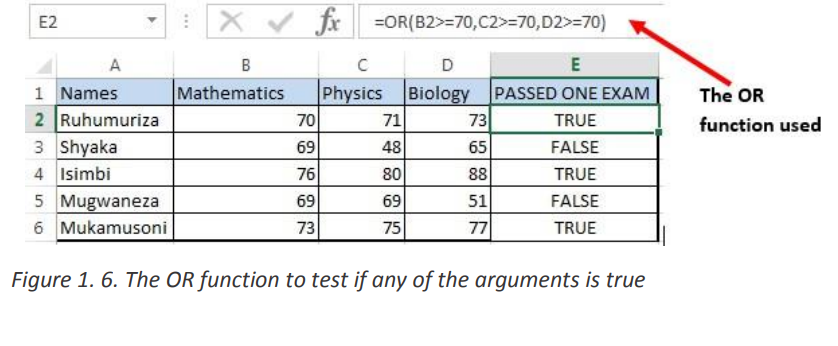
The OR function is a logical function to test multiple conditions at the same time. OR• Syntax: = OR(logical1, Logical2, …)returns either TRUE or FALSE.
• Example:
The OR function in the screenshot below checks for students who got more than 70%Mathematical functions are used to calculate values basing on what is in cells, performas the Pass mark in anyone of the three tests.

operations on a cell content, fetch values after an operation based on the search
criteria and much more. Some of the functions to be seen here are Abs, Arabic
,
a. ABSRoman
, Base
, Mod
and Sqrt
The Excel ABS function returns the absolute value of any provided number.Where the numerical argument is the positive or negative numeric value for whichThe syntax of the function is: ABS (number)
the absolute value is to be calculated.
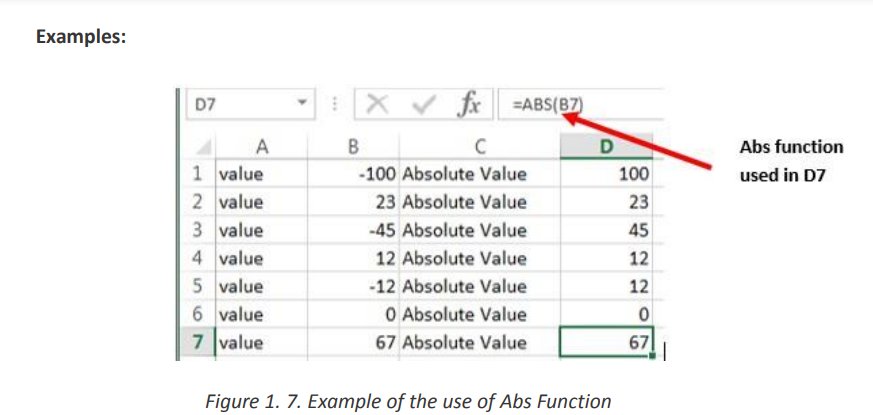 b. ARABIC
b. ARABIC
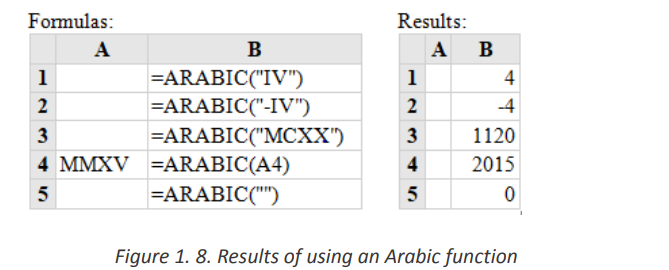
The Excel Arabic function converts a Roman numeral into an Arabic numeral. The
syntax of the function is: ARABIC (text)
Where the text argument is a text representation of a Roman numeral not
exceeding 255 characters.
Note that:
• If supplied directly to the function, the text argument must be encased in
quotation marks;
• If an empty textstring is supplied, the Arabic function returnsthe value 0;
• The Arabic function was only introduced in Excel 2013 and so is not
available in earlier versions of Excel.c. ROMANBelow are five examples of converting ARABIC to NUMBERS
The Excel ROMAN function converts an Arabic number to a Roman number. This
means that if a function is supplied with an integer, the function returns a text string
showing the Roman numeral form of the number.
The syntax of the function is: ROMAN (Number, [form])
• Where Number is any Arabic number and the form specifies the presentation
format of the Roman number to be calculated. The formats to choose from are
displayed after writing the number to convert and writing the comma but the default
(classic) is used.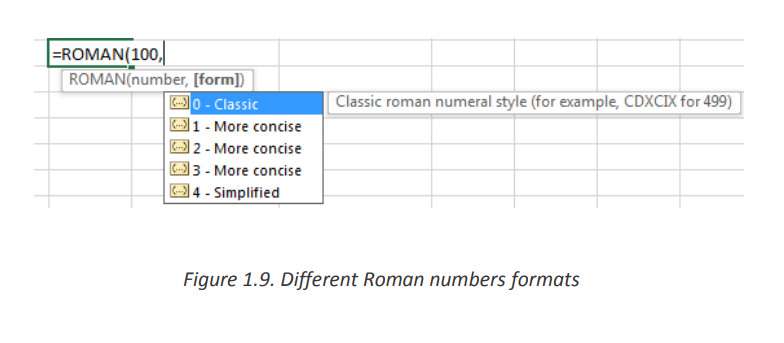
• Roman Function use examples
In the following spreadsheet, the Excel Roman function is used to convert thenumber 1999 to different forms of Roman numerals.
d. BASE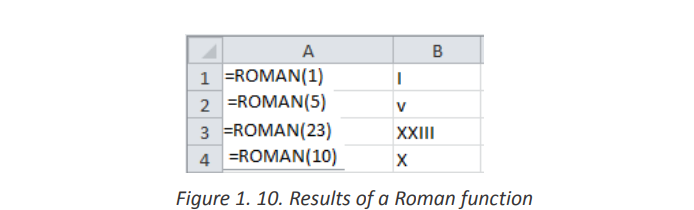
The Excel Base function converts a number into a supplied base and returns a text
representation of the calculated value. The Base function was introduced in Ms Excel
2013 and therefore, it is not available in earlier versions of Excel.
The spreadsheet below shows three examples of the Excel Base Function.
e. MOD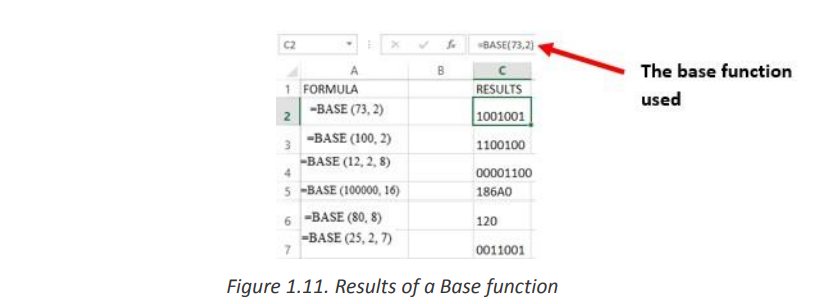
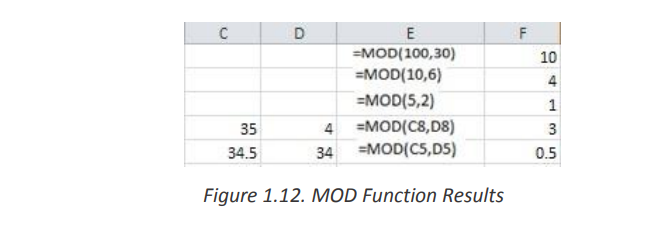
The Excel MOD function returns the remainder of a division between two
supplied numbers.
The syntax of the function is: =MOD (number, divisor)f. SQRTThe spreadsheet below shows four simple examples of the Excel Mod function.
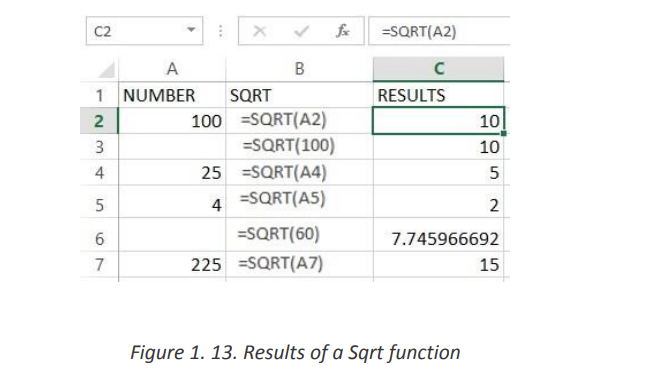
The Excel SQRT Function calculates the positive square root of a supplied• Where the number argument is the numeric value for which the squarenumber.
The syntax of the function is: SQRT (number)
root is to be found.• Excel Sqrt Function ExamplesIf the supplied number is negative, the Sqrt function returns the #NUM! Error.
The following spreadsheet shows three simple examples of the Excel Sqrta. AVERAGEfunction.

The AVERAGE function in Excel returns the arithmetic mean of a list of supplied
numbers, where the number arguments are a set of one or more numeric values, or• Syntax of AVERAGE Function in Excelarrays of numeric values, for which the average is to be calculated.
= Average (Number1, Number2, …)b. AVERAGEIFAn example of how Average function is used is displayed in the screenshot below:
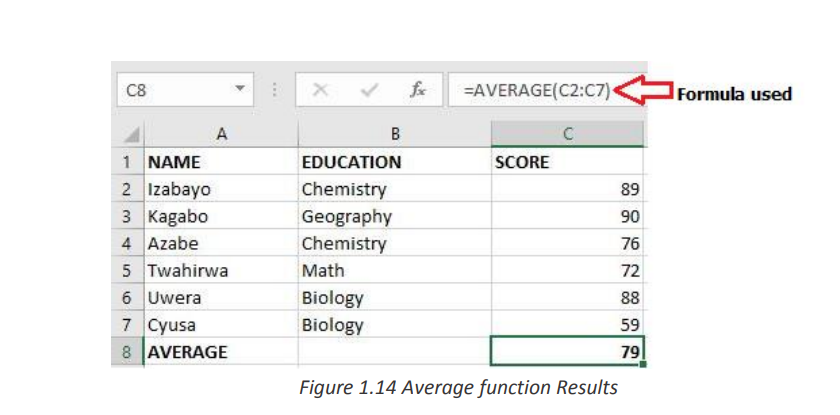
AVERAGEIF Function in Excel finds and returns the average of array that meets the
specific condition. The AVERAGEIF function in Excel supports logical operators (>, <,• Syntax of AVERAGEIF Function in Excel:<>, =)
=AVERAGEIF (range, criteria, [average_range]) Where:
• Range: An Array of range to be tested against the supplied criteria.
• Criteria: The criteria or condition on which average has to be calculated.
• [average_range]: An optional array of numeric values for which the
average is to be calculated.
Example of AVERAGEIF Function in Excel
In the Excel screenshot below the averages of cells meeting certain conditions have
been calculated. Those conditions are: cells with scores greater than 70, average for
Irasubiza and average for science courses.c. LARGE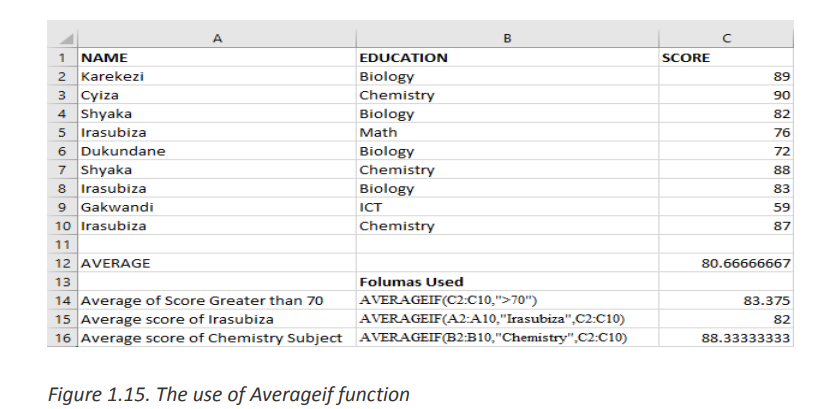
The LARGE Function in Excel returns the largest value from an array of numeric values.
• The syntax of LARGE Function isWhere:=LARGE (array, k)
• Array – An array of numeric values from which to find the Kth largest
value.
• K- The index. Value of K that is passed to find the Kth largest value.Interpretation:Example of LARGE Function in Excel:
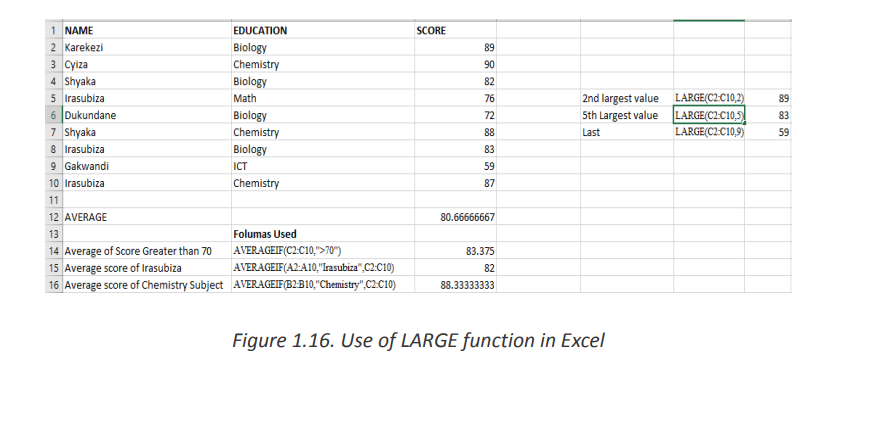
• First Example finds the 2nd Largest Value as 89
• Second Example finds the 5th Largest Value as 72
• Third Example finds the 7th Largest Value as 55
d. MEDIAN
MEDIAN function in Excel returns the statistical median or middle value of a list of
supplied numbers.
Syntax of MEDIAN Function in Excel is: = MEDIAN (number1, [number2], …) Where
the number arguments are a set of one or more numeric values forAn example of how the Median function is used in Excel is shown in the tablewhich to calculate the median
below:
• When the total number of supplied values is odd, the median is calculated as the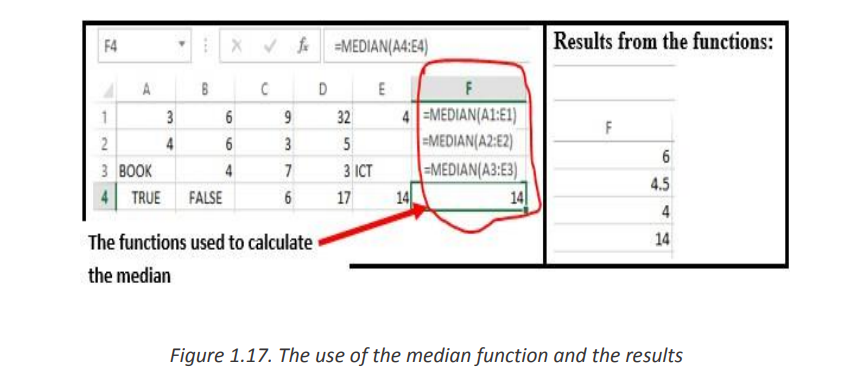
middle number in the group.
• When the total number of supplied values is even, the median is calculated
as the average of the two numbers in the middle.e. MODE Function• Cells containing Text values, logical values, or no value are ignored.
MODE function in Excel returns the mode which is themost frequently occurring
number in a group of supplied arguments.
The Syntax of MODE Function in Excel is =MODE (number1, [number2],…)
Where the number of arguments are a set of one or more numeric values forCells containing Text values, logical values, or no value are ignored.which you want to calculate the mode.
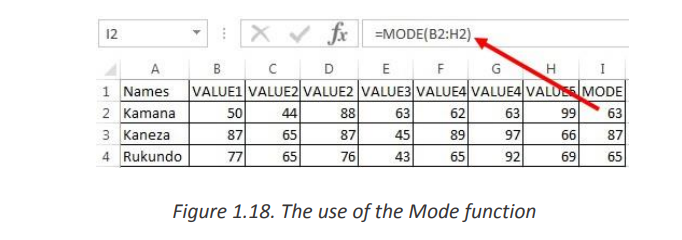
• Mode (most frequently occurring value) is calculated row wise in above example.
 Excel has functions which facilitate an automatic manipulation of text which would
Excel has functions which facilitate an automatic manipulation of text which would For example in the case presented in the activity above if one has to combine data
For example in the case presented in the activity above if one has to combine datatake too much time if it was done manually.
from two rows into one for a total of 1000 rows by copying data from one row and
pasting it next to data in the other row and if one can do one row in
2 seconds, the whole exercise would take up to 33 minutes. Considering that some
names which are in upper case must be in lower case and some in lower must be in
upper which would require rewriting the names the whole exercise can take up to anThat is where Excel ingeniosity comes in by providing functions which can allow onehour.
to do this in less than one minute. The section below explore the functions that cana. CHARbe used to do such a task
The CHAR function returns the character based on the ASCII value. The CHAR function
is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a String/Text Function.The ASCII value is used to retrieve the character.The syntax for the CHAR function is:

Example: Explore how to use the CHAR function as a worksheet function inMicrosoft Excel:
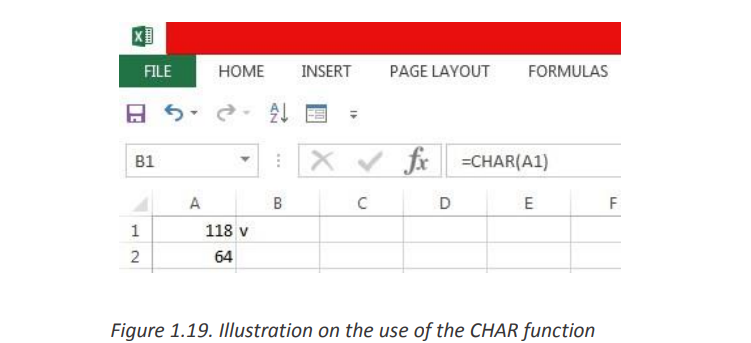 Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following use of the CHAR function
Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following use of the CHAR function
would return:
=CHAR(A1) : Gives Result: “v”
=CHAR(A2) : Gives Result: “@”
=CHAR(72) : Gives Result: “H”b. CONCATENATE=CHAR(109) : Gives Result: “m”
The CONCATENATE function in Excel is designed to join different pieces of text
together or combine values from several cells into one cell.
The syntax of Excel CONCATENATE is as follows:Where text is a text string, cell reference or formula-driven value.CONCATENATE (text1, [text2], …)
Below is an example of using the CONCATENATE function in Excel in which data
from two cells has been combined.
The simplest CONCATENATE formula to combine the values of cells A1 and B1 is as
follows:c. UPPER=CONCATENATE(A1, B1)
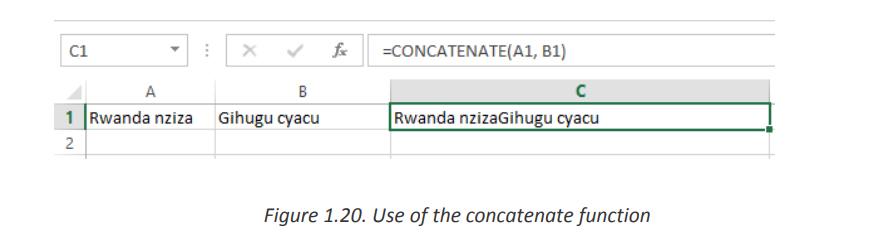
Figure 1.20. Use of the concatenate function
The UPPER function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a String/ Text
Function. It converts a text (String) into uppercase
Example:
A1==” better technology for the best future”
=UPPER(A1)d. LOWERResult: “BETTER TECHNOLOGY FOR THE BEST FUTURE”
The LOWER function is used to convert text (String) into small cap text
Example: B1=”EXCEL SCIENCES THROUGH TECHNOLOGY”
=LOWER (B1)When the workbook has many sheets there is a possibility to get data from one sheetResult: excel sciences through technology


into another by using formula or functions.
Example 1:
Consider the example below which are data from two different sheets named Sheet1
and Sheet2. These sheets contain marks for ICT and for Biology. The teacher wants to
make totals for each student for the two subjects and keep those totals in a separatesheet “Sheet3”
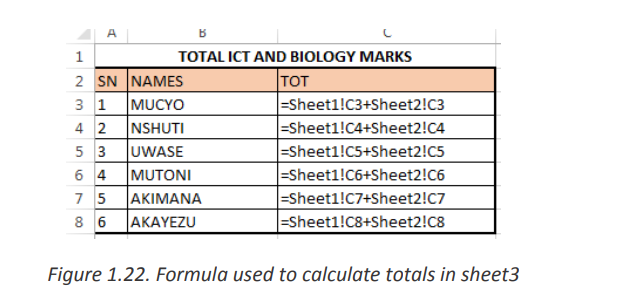
To achieve this go to the table in Sheet3 where totals of data from the two sheets has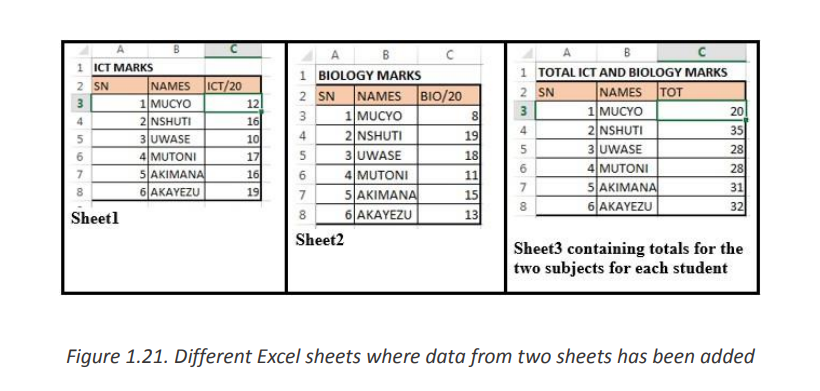
to be done then in the TOT column cell C3 write the formula to use which is
=Sheet1!C3+Sheet2!C3
Meaning that data from cell C3 of Sheet1 is added to data from cell C3 of sheet2
You can do this by writing formula from scratch or by:
• Writing the equal sign in the cell where total is to be written
• Going to the cell containing the first data to be added and selecting it
• Writing the + sign
• Selecting second data to be added by going to the sheet containing that data
and selecting the right cell and lastly hitting enter
The formulas used to calculate the totals for the example above are in the imageExample 2:below:
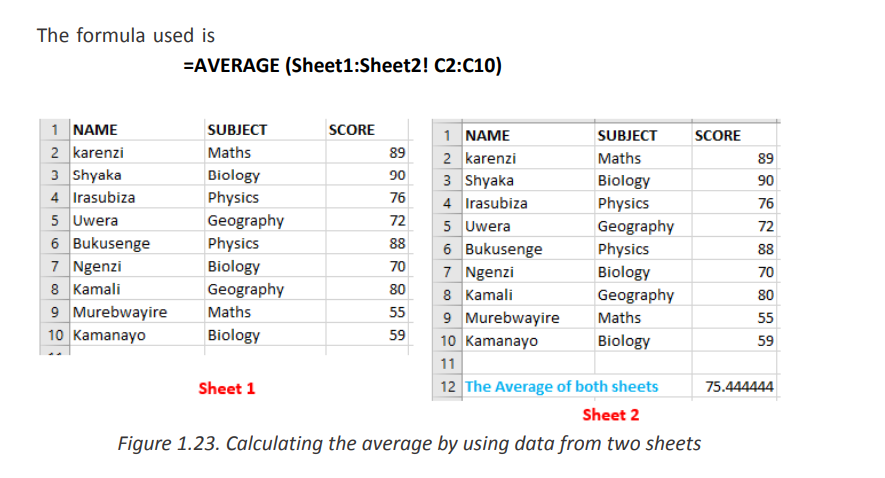
Consider another example in which two sheets Sheet1 and Sheet2 contains data
(score) on different subjects. The average of marks contained in the two sheetsis going to be calculated and kept in Sheet1.
 Worksheet protection is to prevent other users from accidentally or deliberately
Worksheet protection is to prevent other users from accidentally or deliberately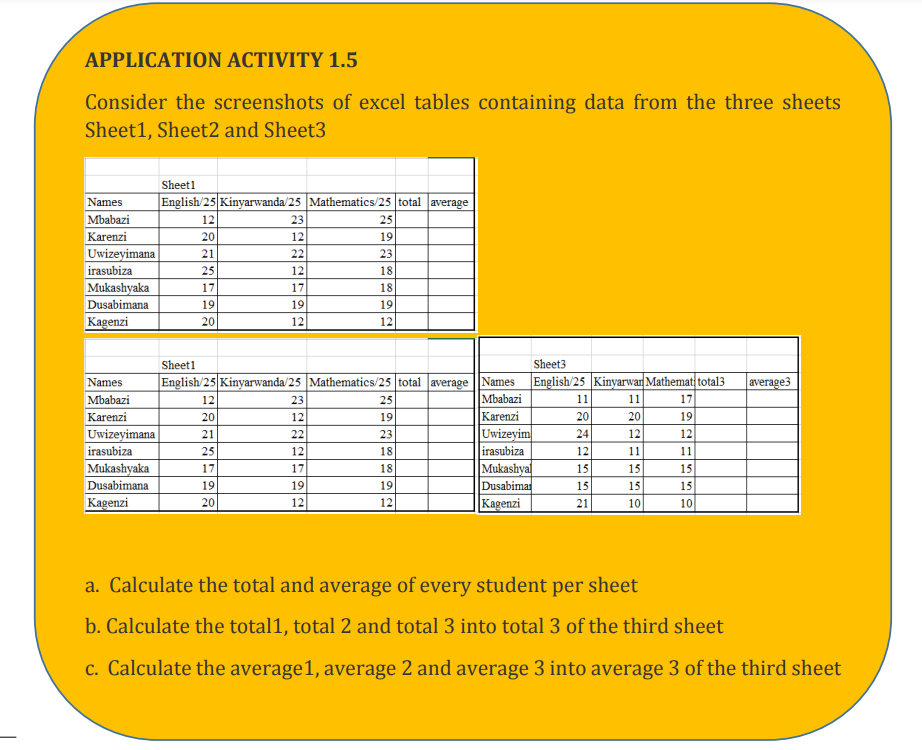

changing, moving, or deleting data in a worksheet, you can lock the cells on your Excel
worksheet and then protect the sheet with a password.
With worksheet protection, you can make only certain parts of the sheet editable and
users will not be able to modify data in any other region in the sheet.
Rules to follow for protecting worksheets with strong protectiona. Protect your sheets with strong passwords that include different types of
alpha numeric characters and special symbols. At that, try to make passwords
as random as possible
b. Protect the workbook structure to prevent other people from adding, moving,
renaming or deleting the sheets.
c. For workbook-level security, encrypt the workbook with different passwords
from opening and modifying. If possible, store your Excel files with sensitiveinformation in a secure location, e.g. on an encrypted hard drive.
To protect a sheet in Excel 2019, 2016, 2013 and 2010, perform the following steps.When a sheet is protected, anyone will be able to read data but will not be able to
a. Under the Review tab click on Protect Sheet.
b. Type the password and click on Okc. Reenter password and click on Ok
modify it and once data in that sheet is modified this message below will be displayed1.3.2. Lock &unlock cells, style, contents and other elements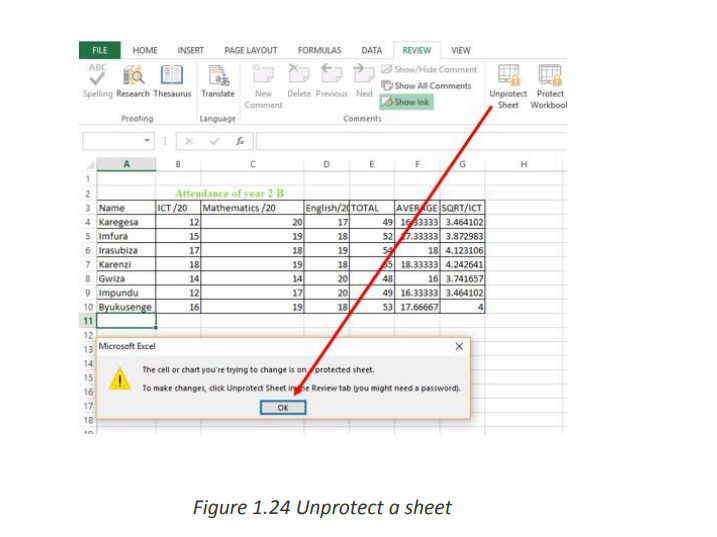
a. How to Lock Cells for Editing and Protect Formulas
When a sheet is shared while some sheet cells must not be modified some rules have
to be set so that data can be modified by anyone who wants it but not modified by
someone who does not have the right to do so. In the table below a list of products
will be sent to the customers. Customers will be able to modify some product records.The great news is that you can lock cell, or a whole range of cells, to keep your work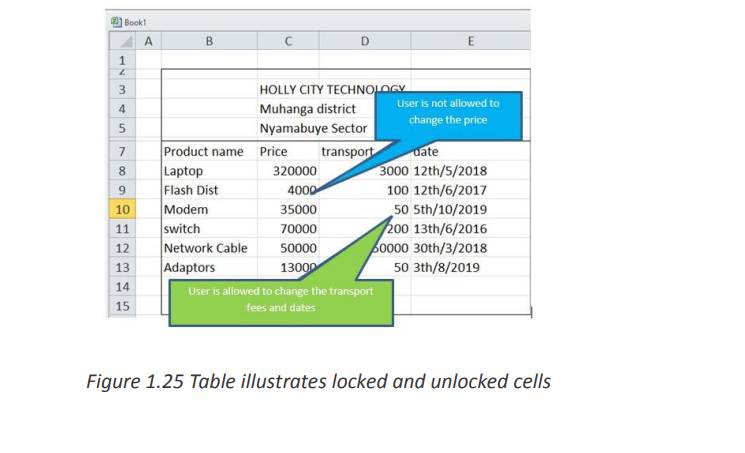
protected.Here’s how to prevent users from changing some cells. Type a password in the corresponding field.
Type a password in the corresponding field. Be sure to remember the password or store it in a safe location because you
Be sure to remember the password or store it in a safe location because you
will need it later to unprotect the sheet.
Select locked cells .
If only these two options are selected, the users of your sheet, including yourself, will
be able only to select cells (both locked and unlocked).If the worksheet protection is nothing more than a precaution against accidental
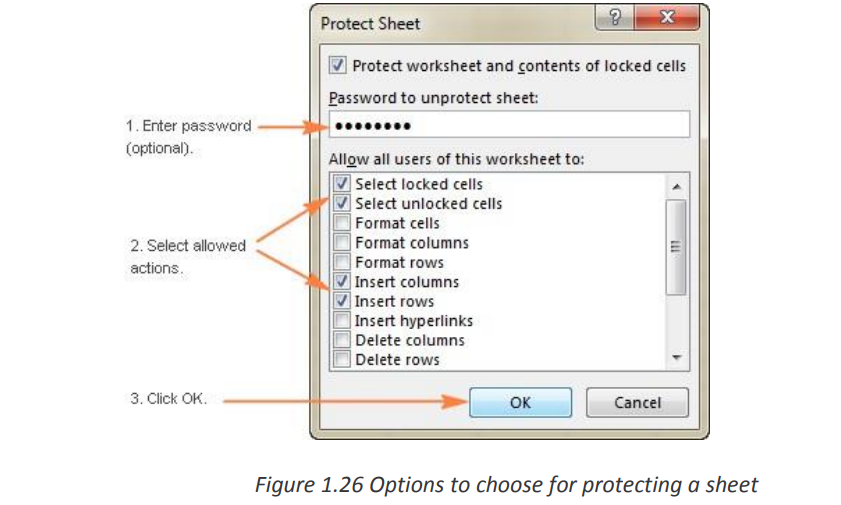
modification of the sheet contents by yourself or by the members of your local team,you may not want to bother about memorizing the password and leave the password
field empty
Select the actions you allow the users to perform.
b. How to unprotect Excel sheet with password
To lock only specific cells and ranges in a protected worksheet
Follow these steps:1. Select the cells you want to lock.
2. On the Home tab, in the Alignment group, click the small arrow to
open the Format Cells popup window.
3. On the Protection tab, select the Locked check box, and then click
OK to close the popup.
4. Right-click the sheet tab, and select Unprotect Sheet from the
context menu.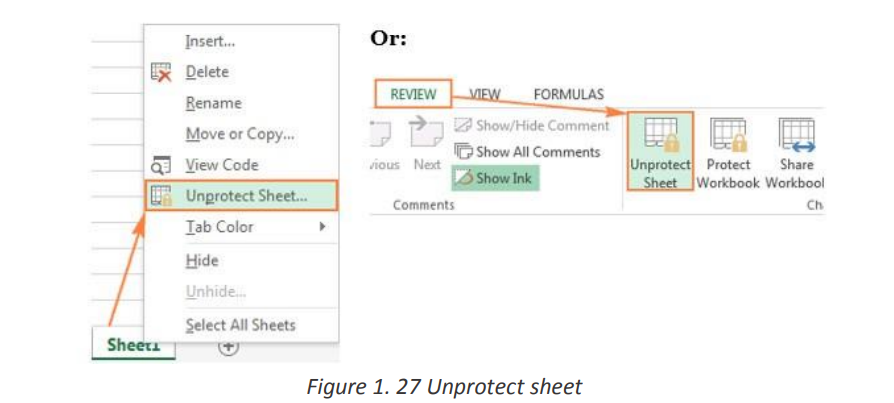 On the Review tab, in the Changes group, click Unprotect Sheet.
On the Review tab, in the Changes group, click Unprotect Sheet.
• On the Home tab, in the Cells group, click Format, and select Unprotect
Sheet from the drop-down menu.Excel Data Validation is a feature that restricts (validates) user input to a worksheet.

Technically, you create a validation rule that controls what kind of data can be enteredinto a certain cell.
Here are just a few examples of what Excel’s data validation can do:• Allow only numeric or text values in a cell.
• Allow only numbers within a specified range.• Allow data entries of a specific length.
• Restrict dates and times outside a given time frame.
• Restrict entries to a selection from a drop-down list.
• Validate an entry based on another cell.
• Show an input message when the user selects a cell.
• Show a warning message when incorrect data has been entered.
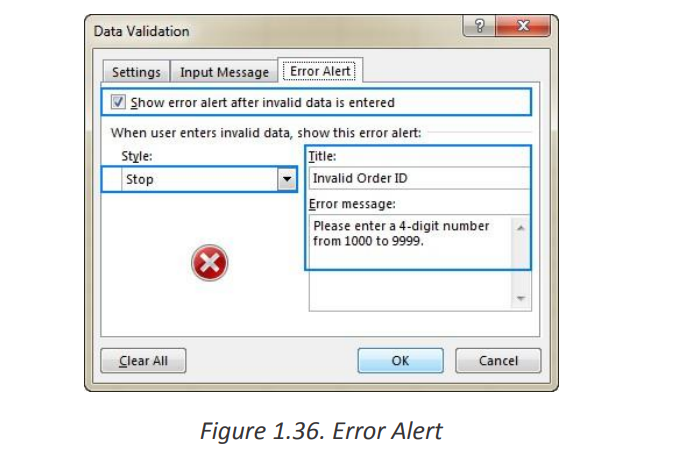
• Find incorrect entries in validated cells.For instance, you can set up a rule that limits data entry to 4-digit numbers between
1000 and 9999. If the user types something different, Excel will show an error alert
explaining what they have done wrong. The window below shows a warning message
that appears when data outside of the range (1000-9999) is entered.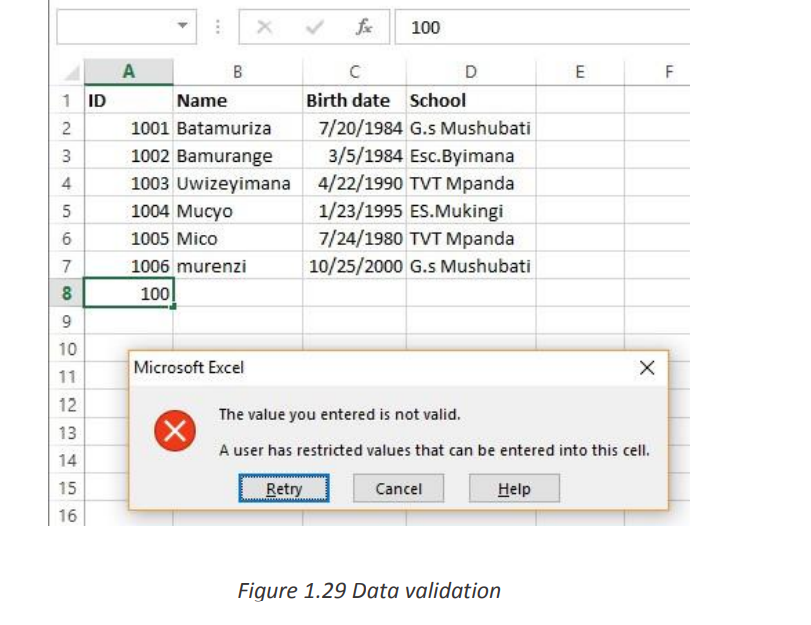
283. On the Settings tab, under Allow, select an option.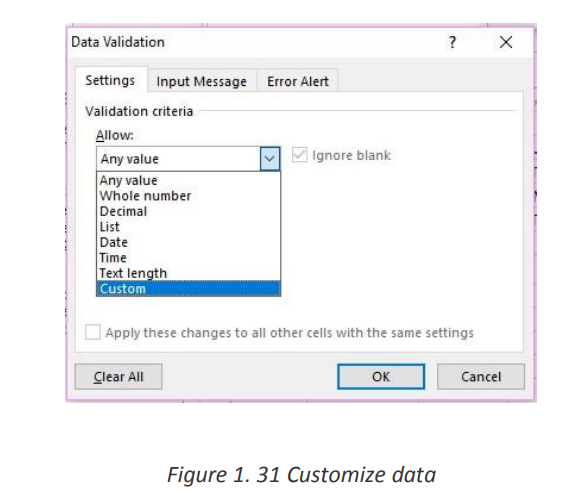
4. Under Data, select a condition:
5. On the Settings tab, under Allow, select an option: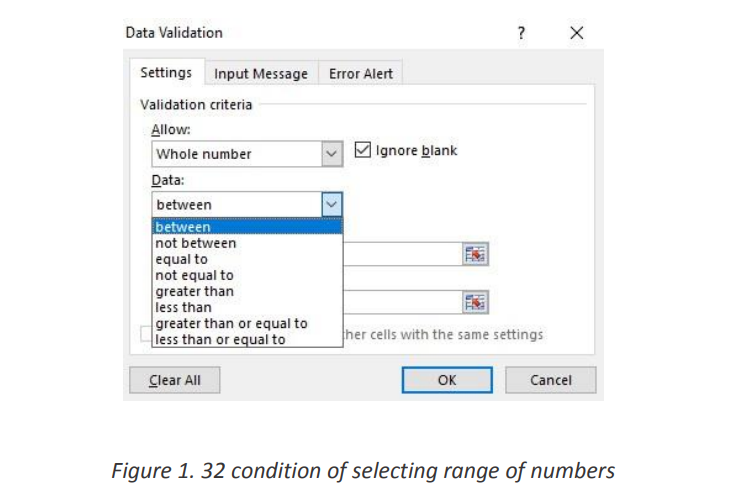
6. Set the other required values, based on what you chose for Allow and Data.
For example, if you select between, then select the Minimum: and maximum:
values for the cell(s)
7. Select the Ignore blank checkbox if you want to ignore blank spaces.
8. If you want to add a Title and message for your rule, select the Input
Message tab, and then type a title and input message.
9. Select the Show input message when cell is selected checkbox to display the
message when the user selects or hovers over the selected cell(s).
10. Select OK.
As an example, let’s make a rule that restricts users to entering a whole numberbetween 1000 and 9999:
With the validation rule configured, either click OK to close the Data Validation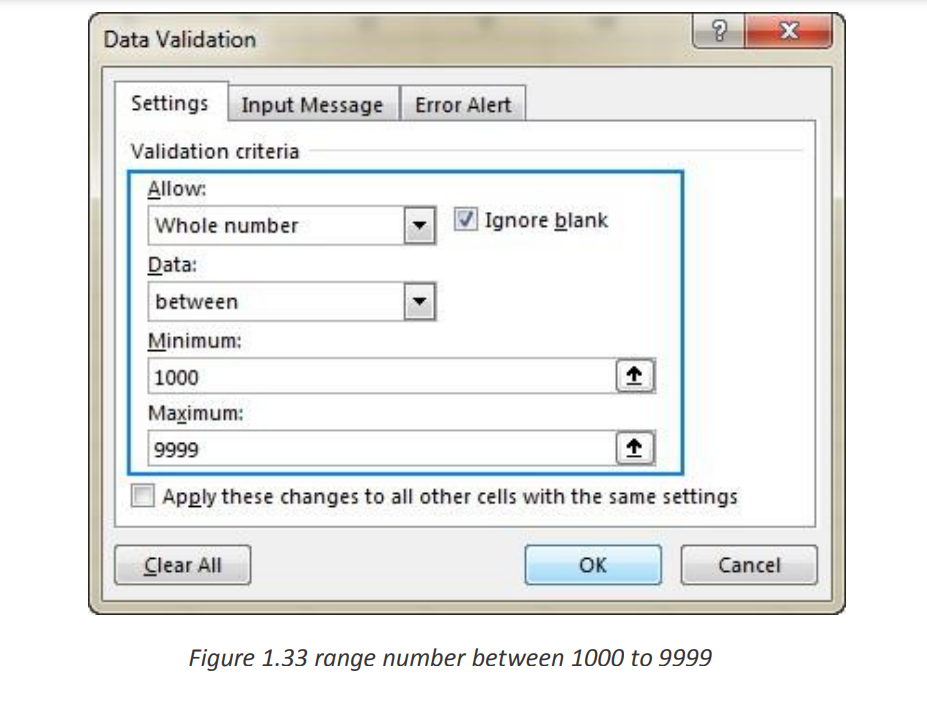
window or switch to another tab to add an input message or/and error alert.
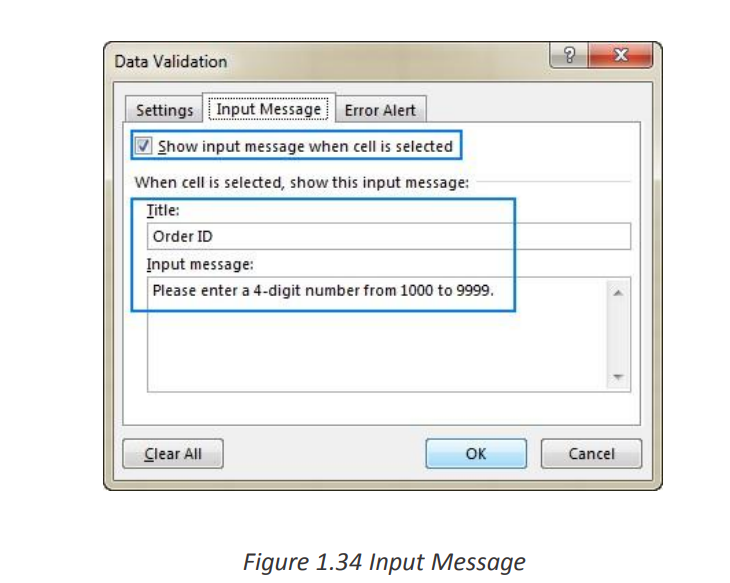
3. Add an input message (optional)
If you want to display a message that explains to the user what data is allowed in a
given cell, open the Input Message tab and do the following:
• Make sure the Show input message when cell is selected box is checked.
• Enter the title and text of your message into the corresponding fields.• Click OK to close the dialog window.
As soon as the user selects the validated cell, the following message will show up:
4. Display an error alert (optional)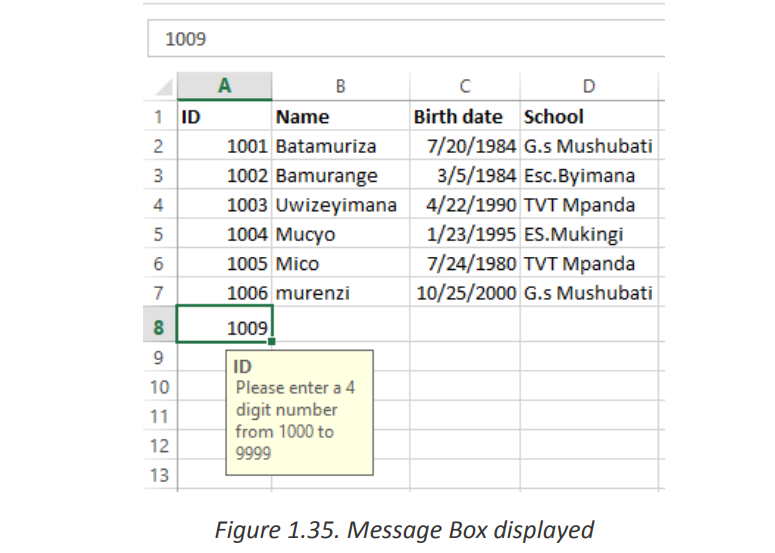
To configure a custom error message, go to the Error Alert tab and define the
following parameters:
• Check the Show error alert after invalid data is entered box (usually
selected by default).
• In the Style box, select the desired alert type.
• Enter the title and text of the error message into the corresponding boxes.• Click OK.
21.5. Using other Excel templates

Microsoft Excel templates are a powerful part of Excel experience and a great way to
save time. Excel templates can also help you create consistent and attractive
documents that will impress your colleagues or supervisors.
Templates are especially valuable for frequently used document types such asExcel calendars, budget planners, invoices, inventories and dashboards.
a. Creating a workbook from an existing Excel template
Instead of starting with a blank sheet, you can quickly create a new workbook based
on an Excel template. The right template can really simplify your life since it makes the
most of tricky formulas, sophisticated styles and other features of Microsoft Excel that
you might not be even familiar with.
To make a new workbook based on an existing Excel template, perform the following
steps.
• Switch to the File tab• Click New
Templates provided by Microsoft displayed.
1.Topreviewa certaintemplate,simply clickonit.Apreviewoftheselected template will
show up along with the publisher’s name and additional details on how to use the
template.
2. If you like the template’s preview, click the Create button to download it.For example, I’ve chosen a nice mini calendar template for Excel:
b. Finding more templates
To get a bigger selection of templates for your Excel, type a corresponding
keyword in the search bar:
That’s it - the selected template is downloaded and a new workbook is created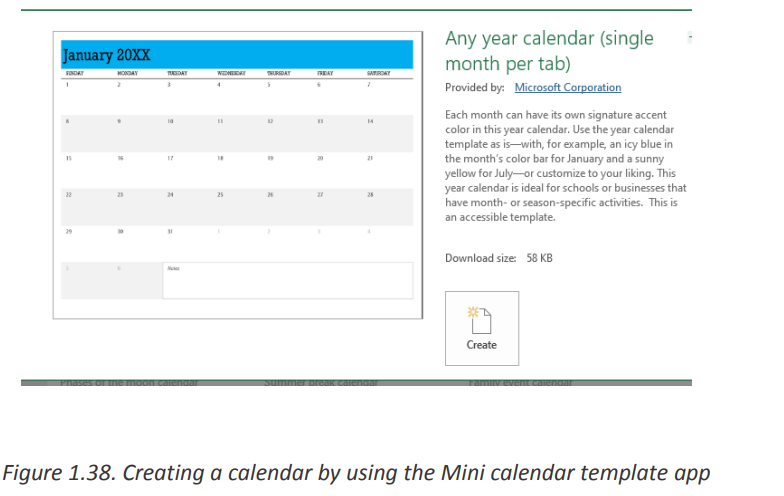
based on this template right away.
b. Finding more templates
To get a bigger selection of templates for your Excel, type a correspondingkeyword in the search bar:
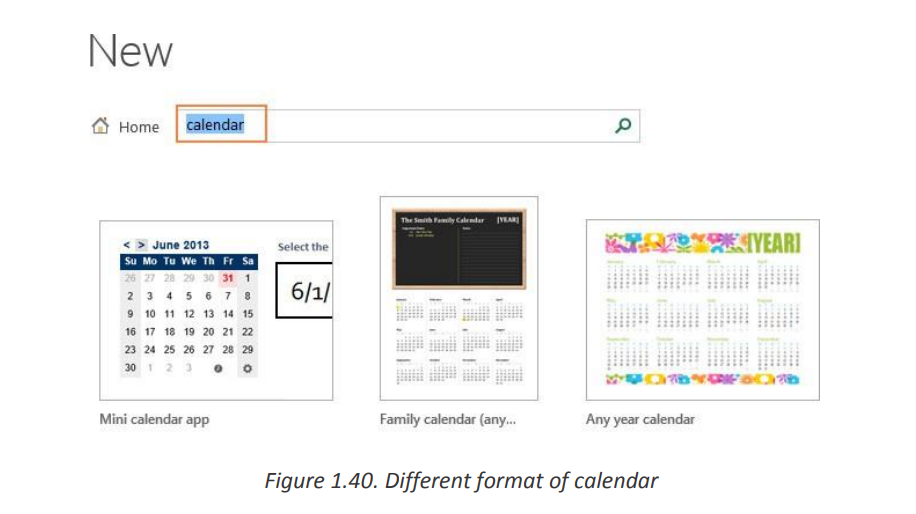
Note. When you are searching for a certain template, Microsoft Excel displays
all relevant templates that are available on the Office Store.
c. Making a custom Excel template
Making your own templates in Excel is easy. You start by creating a workbook in the
usual way, and the most challenging part is to make it look exactly the way you want.
It is definitely worth investing some time and effort both in the design and contents,
because all formatting, styles, text and graphics you use in the workbook will appear
on all new workbooks based on this template.
In an Excel template, you can use save the following settings:• The number and type of sheetsNote: Once you’ve created the workbook, you just need to save it as a .xlt or .xltx
• Cell styles and formats
• Page layout and print areas for each sheet
• Hidden areas to make certain sheets, rows, columns or cells invisible
• Protected areas to prevent changes in certain cells
• Text that you want to appear in all workbooks created based on a given
template, such as column labels or page headers
• Formulas, hyperlinks, charts, images and other graphics
• Excel Data validation options such as drop-down lists, validation messages
or alerts, etc.
• Calculation options and window view options.
• Macros and ActiveX controls on custom formsfile (depending on which Excel version you use) instead of usual .xls or .xlsx.
If you need the detailed steps, here you go:
• In Excel 2019,2016,2013, click File
• In the Save As dialogue, in the File name box, type a template name.
• Under Save as type, select Excel Template (*.xltx) if you are using Excel
2019,2016,2013, 2010 or 2007. In earlier Excel versions, select Excel 97-2003Template (*.xlt).
If your workbook contains a macro, then choose Excel Macro-EnabledTemplate (*.xltm).
When you select one of the above template types, the file extension in the File
Name field changes to the corresponding extension.
1.Click the Save button to save your newly created Excel template. Where to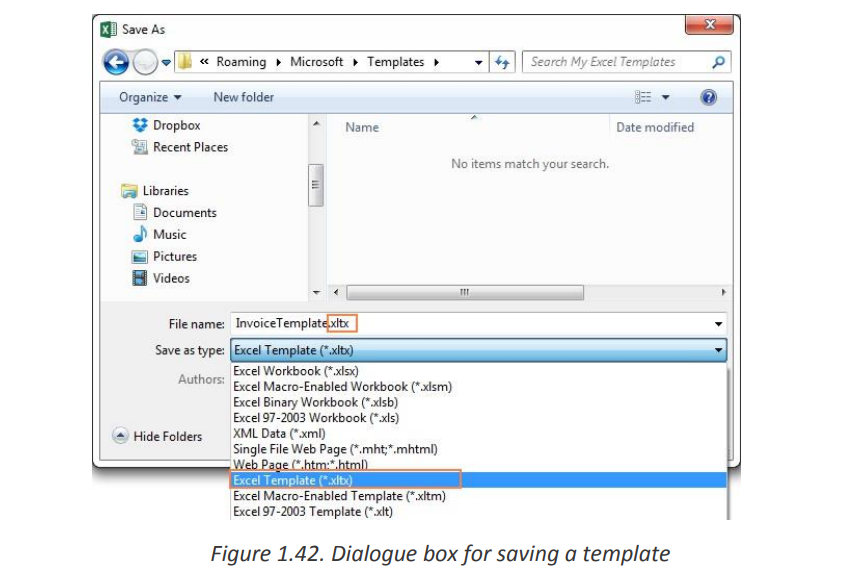
download Excel templates
As you probably know, the best place to look for Excel templates from Microsoft
Office website ( w w w . Office. com). Here you can find a great lot of free Excel
templates grouped by different categories such as calendar templates, budget
templates, invoices, timelines, inventory templates, project management templatesand much more.
Figure 1.45. Download a template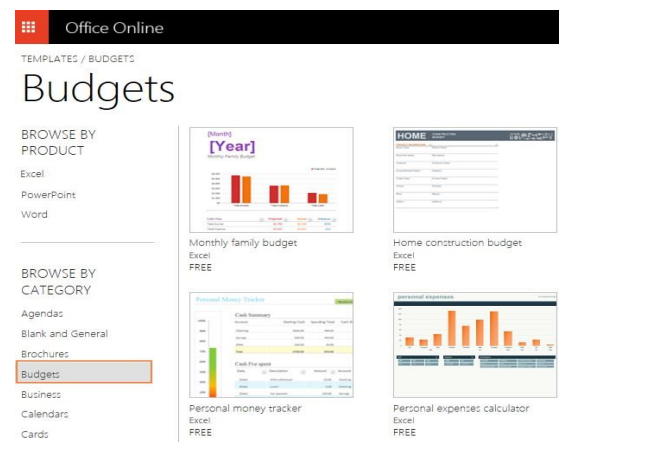
To download a particular Excel template, simply click on it. This will display a briefdescription of the template as well as the Open in Excel Online button

please click here to learn more about network device
- Opened: Friday, 26 February 2021, 1:00 AMDue: Friday, 5 March 2021, 1:00 AM
please submit this work before deadline
- Opened: Friday, 26 February 2021, 12:16 PMClosed: Friday, 26 March 2021, 12:16 PMRead carefully the questions before answering it
- Opened: Sunday, 11 April 2021, 9:51 AMDue: Monday, 12 April 2021, 6:00 PM
plz make sure you submit the work before deadline
- Opened: Saturday, 10 April 2021, 9:00 AMClosed: Sunday, 11 April 2021, 9:40 AM
