UNIT 11:PERFORM PHYSICAL FITNESS EXERCISES
Key unit competence: Perform successfully physical fitness test and result
interpretation
11.1 Prerequisite (Knowledge, skills, attitudes and values)
Students of senior six will learn better physical fitness exercises if they can perform
basic physical exercises learnt in senior four and in previous levels
11.2 Cross-cutting issues to be addressed
Gender: In teaching and learning of physical fitness exercises, the teacher must
prepare and provide activities that engage both girls and boys equally to exploit
their full potential and talents without any discrimination or prejudice.
Inclusive education: The teacher as a facilitator he/she must consider
different special education needs and select physical activities to adapt his
teaching approaches to all students. This creates a positive attitude and helps
all students to participate actively and develop their competence levels.
Financial education: The teacher should integrate Financial Education into
his/her teaching/learning activities by providing the local and no cost teaching
material where is possible. He/she must encourage students to make their own
materials which can help them to develop competences not only in sports at
school but also in their daily life.
Standardization culture: The teacher must choose and select the standardized
materials to use in his/her teaching/learning process. It is necessary to provide
appropriate materials required to the levels of students and help them to
develop culture of checking and using the quality of sport materials for the
competitions before using them in order to prevent injuries and other accidents.
Environment and sustainability: The teacher should provide materials and
deliver the lesson with encouraging students to protect the environment and
well use of materials. The teacher helps them to develop the spirit of keeping
safe the environment they use in sports activities.
Peace and values education: The teacher helps students to develop fair play
and social values by planning physical activities that avoid violence and conflict
in the game and by setting clear and relevant instructions. He/she should
provide the activities that help students to develop their competence peacefully.
Comprehensive sexuality education: The teacher provides physical activities
and sets instructions that prevent sexual harassment, any kind of gender based
violence like sexual abuse and physical contacts oriented to the sexuality
intention.
Genocide studies: While conducting physical fitness lesson a teacher should
take a time to explain students how sports should be used to fight against
Genocide ideology and how to prevent it. For example, to organize Genocide
memorial tournaments at school and give the message related to the Genocide.
11.3 Guidance on introductory activity
Before introducing the lesson one of this unit, the teacher must introduce the
whole unit. The teacher as a guide, facilitator and expert, asks questions or give
activity related to physical fitness exercises in order to help them to predict
what to be learnt in the whole unit.
Introductory activity
Scenario:
Mugabo is a 19 years old. He is a secondary school student of senior six. He has
been attending his local gymnasium for the past 2 weeks going through cardio
exercises and he also practices running exercise for 30 minutes every morning
before going to school. Two years ago, he used to play football in his Ordinary
level in secondary school team but he stopped due to the lack of enough time at
his new school. Since then, he has not been involved in any team activity. Today
he has finished his last trimester at his school and he is looking for a training
program that will help him to build his body. Mugabo is 1.83 m tall and tips that
scale with 78 kg.
In groups discuss the following points:
a) Is Mugabo physically fit?
– if yes, what criteria are you referring too?
– If no, why?
b) Suggest exercises that he can perform in order to achieve his dreams.11.4 List of lessons/sub-heading
Lesson 1: Components of Physical fitness test
a) Learning objectiveIdentify and explain the component of physical fitness test
b) Teaching resourcesBooks, Laptop, Projector, Internet, Photos and video of exercises
c) Prerequisites/Revision/Introduction
Students of senior six will learn better components of Physical fitness test ifthey have developed physical exercises learnt in previous levels.
d) Learning activities
Opening discussions
– Ask students different types of basic physical exercises they have learnt in
previous levels
– Introduce the new lesson by asking students to brainstorm the components
of physical fitness test. Guide and facilitate them where it is necessary.
e) Lesson body
Activity 11.1
Divide students into 5 groups, ask them to discuss the following componentsof physical fitness test, how we measure and how to improve each component.
– Pass though groups and help them where is necessary. Request students
to choose a secretary to record findings and group representative who will
present their findings.
– Request group representative to present their findings and group members.
– Teacher may support where is necessary. After presentation of all groups,use a projector to recap presentations.
Application Activity 10.3
Assess Aerobic Fitness
Explain and ask students to perform the exercise of assessing aerobic fitness
test.
Explication:
Counting the number of beats of the resting heart rate (RHR). It is the useful
way of indicating the fitness progress. It should reduce according to theaerobic fitness improvements.
Your resting heart rate (RHR) represents the number of times your heart
beats each minute when you are at rest. Since a strong cardiovascular system
allows your heart to pump more blood with every beat, a lower RHR tends to
correspond with higher aerobic fitness. Some athletes have recorded a RHRof 40.
How to do this exercise
To measure your RHR, place two fingers either on your neck, just below your
jawline (carotid artery), or on your wrist (radial artery), and then count the
number of beats you feel in 60 seconds. You should count the first beat as‘zero’
Results of this exercise test:
– 60 or less = Good
– 61 to 80 = Average
– 81 to 100 = High, but still considered acceptable
– 101 or more = Abnormally high (not good!)
Your resting heart rate is a useful marker of your fitness progress, as it will drop
as you get fitter. It is often thought that the best time to take our RHR is first thingin the morning.



Closing discussions / Conclusion
Together, teacher and students summarize the lesson of the day, and students
record the summary in their note books.
Lesson 2: Perform different exercises used in physical fitnesstest
a) Learning objective
– Perform physical fitness exercises– Interpret the result of physical fitness test.
b) Teaching resources
– Cones
– Whistle
– Laptop
– Field/playground
– watch/ Chronometer– decameter
c) Prerequisites/Revision/Introduction
Students of senior six will perform better different exercises used in physical
fitness test and interpret the result if they have developed basic physicalexercises.
d) Learning activities
Opening discussions
– Ask questions related to different component of physical fitness test learnt
in lesson one of this unit.
– Introduce the lesson of the day by asking questions on measuring physical
fitness.– Invite students to start warm up exercises.
Warm up exercises and stretching exercises
Let students perform general warm up exercises and specific warm up based on
the most body’s parts to be used while performing techniques of discus throw
and stretch their muscles properly.
e) Lesson body
Activity 11.2
In groups or individually, students perform different exercises used in physical
fitness test and they can interpret the result according the types of exercises they
perform. All of them perform cardiovascular endurance exercises in physical
fitness test. They interpret their physical fitness by appreciating their ability to
perform and the use of physical fitness exercises to develop and keep their bodyhealthy.
Activity 11.3
In groups or individually, students perform different exercises used in physical
fitness test and they can interpret the result according the types of exercises they
perform. All of them perform body composition exercises in physical fitness
test. They interpret their physical fitness by appreciating their ability to performand the use of physical fitness exercises to develop and keep their body healthy.
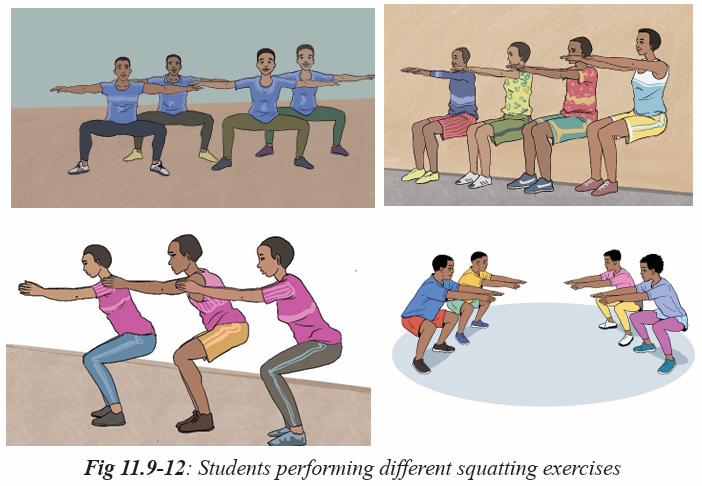

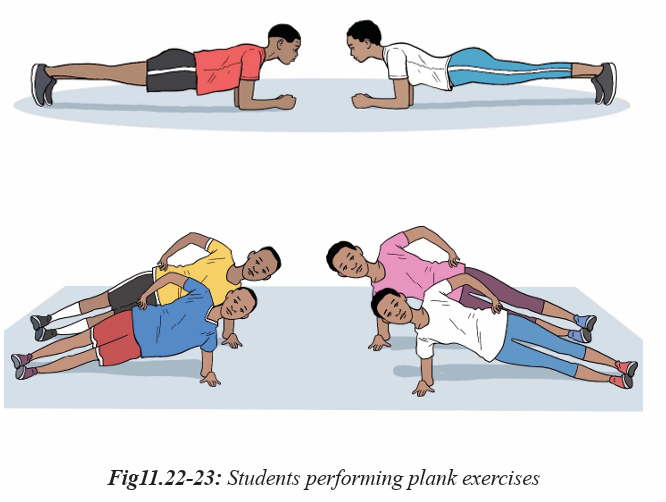
Activity 11.4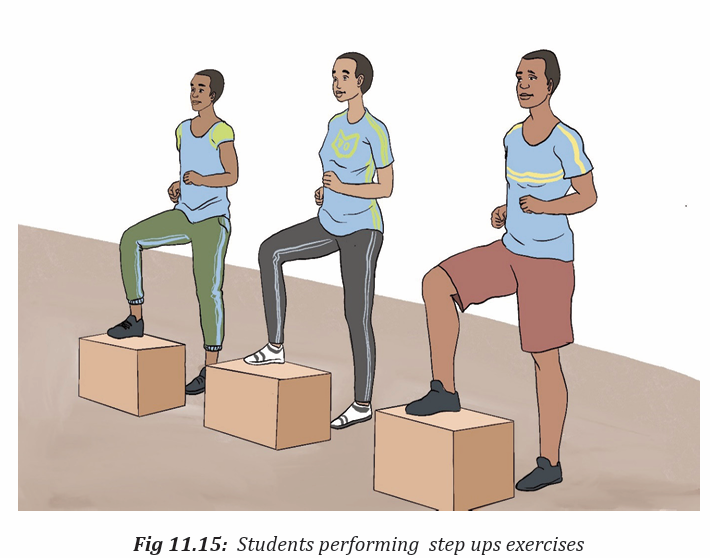
In groups or individually, students perform different exercises used in physical
fitness test and they can interpret the result according the types of exercises they
perform. All of them perform muscular strength exercises in physical fitness
test. They interpret their physical fitness by appreciating their ability to performand the use of physical fitness exercises to develop and keep their body healthy.
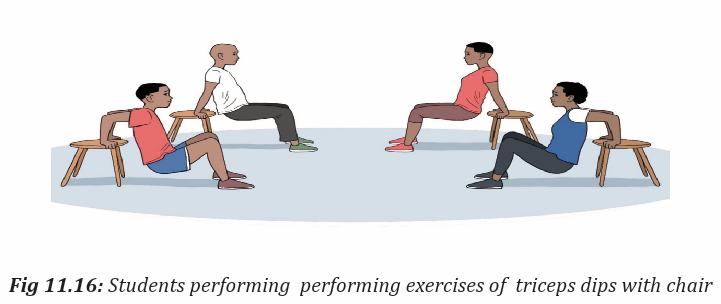
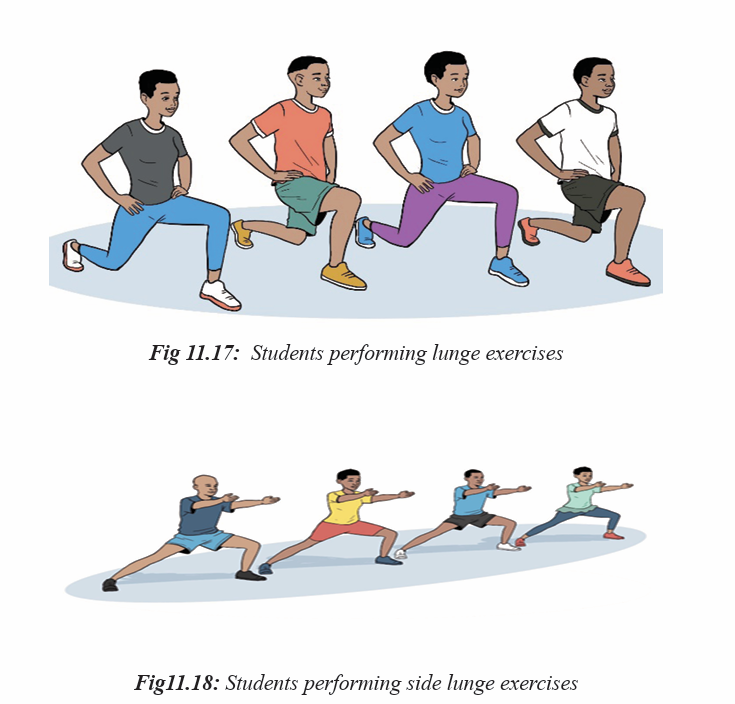
Activity 11.5
In groups or individually, students perform different exercises used in physical fit
ness test and they can interpret the result according the types of exercises they per
form. All of them perform muscular endurance exercises in physical fitness test.
They interpret their physical fitness by appreciating their ability to perform and theuse of physical fitness exercises to develop and keep their body healthy.
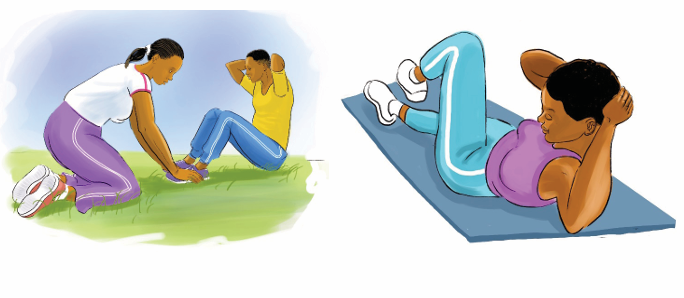
Activity 11.6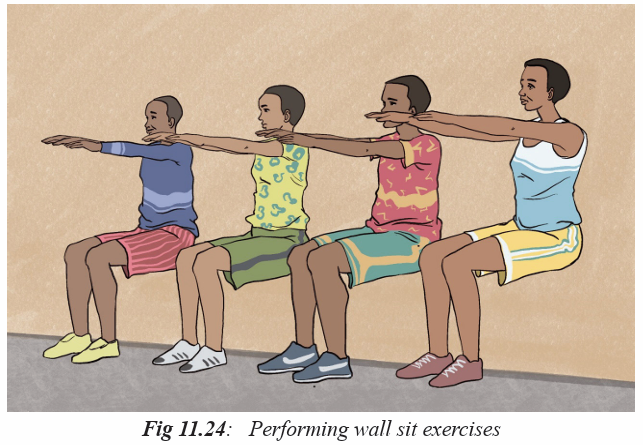
In groups or individually, students perform different exercises used in physical
fitness test and they can interpret the result according the types of exercises they
perform. All of them perform flexibility exercises in physical fitness test. They
interpret their physical fitness by appreciating their ability to perform and the useof physical fitness exercises to develop and keep their body healthy.

Application Activity 11.2
Let students perform shuttle run exercises by dividing them in 5 groups, each
group will have its own area of practicing.
Steps of practicing shuttle run exercises:
– Set up markers such as cones about 25 meter apart.
– Sprint from one marker to the other and back. That is 1 repetition.
– Do 3 repetitions as fast as you can (150 m total).
– Time your result for the entire 6 repetitions.
Let students perform standing jump exercises by respecting the following
steps:
– The student must stand behind a line marked on the ground with feet
slightly apart.
– A two-foot takeoff and landing is used, with swinging of the arms and
bending of the knees to provide forward drive.
– The subject attempts to jump as far as possible, landing on both feetwithout falling backwards.
Cool down exercises
Let students do light exercises and stretch their group of muscles by insisting
on most used parts. Guide them while stretching their muscles systematically.Help them/demonstrate/correct where is necessary.
Closing discussion
Reflect
– What are challenges/advantages did you face while performing different
exercises used in physical fitness test.
– How did you proceed to perform those exercises?
– How do you feel in your body fitness after performing those exercises?
Connect
– In which conditions do you need exercises used in physical fitness test
Apply
– How will you use different exercises used in physical fitness test in yourdaily life to maintain your physical fitness?
Summary of the unit
Physical Fitness is a measure of the body’s ability to function efficiently and
effectively in work and leisure activities, resist hypokinetic diseases (diseasesfrom sedentary lifestyles), and to meet emergency situations.
Components of Physical Fitness
The 5 components of physical fitness are often used in our school systems,
health clubs and fitness centers to gauge how good a shape we are truly in. The
5 components that make up total fitness are:
– Cardiovascular Endurance
– Muscular Strength
– Muscular endurance
– Flexibility
– Body Composition
These are the 5 components of fitness. But if you are an athlete, you have to step
up your game. Here are a few extra components of fitness that you should take
care of.
Other Components of Fitness for Athletes
a) Agility
b) Power
c) Balance
d) Coordinatione) Reaction time/ speed
11.5. Additional information for teacher
– Cardiovascular endurance is the ability of the heart and lungs to work together
to provide the needed oxygen and fuel to the body during sustained workloads.
Examples would be jogging, cycling and swimming. The Cooper Run is used
most often to test cardiovascular endurance.
– Muscular strength is the amount of force a muscle can produce. Examples
would be the bench press, leg press or bicep curl. The push up test is most often
used to test muscular strength.
– Muscular endurance is the ability of the muscles to perform continuous
without fatiguing. Examples would be cycling, step machines and elliptical
machines. The sit up test is most often used to test muscular endurance.
– Flexibility is the ability of each joint to move through the available range of
motion for a specific joint. Examples would be stretching individual muscles or
the ability to perform certain functional movements such as the lunge. The sit
and reach test is most often used to test flexibility.
– Body composition is the amount of fat mass compared to lean muscle mass,
bone and organs. This can be measured using underwater weighing, Skinfold
readings, and bioelectrical impedance. Underwater weighing is considered the
“gold standard” for body fat measurement, however because of the size and
expense of the equipment needed very few places are set up to do this kind of
measurement.
– Manual muscle testing is the most popular way to test strength. Your
physical therapist will push on your body in specific directions while you
resist the pressure. A score or grade is then assigned, depending on howmuch you were able to resist the pressure.
11.6 End of unit assessment
Let students perform regularly cardiorespiratory endurance exercises, body
composition exercises, muscular strength exercises, muscular endurance
performance.exercises, and flexibility exercises and analyze and interpret the results their
11.7 Additional activities
Remedial activities
Explain the following components of physical fitness:
a) Cardiorespiratory endurance
b) Body composition
c) Muscular strength
d) Muscular endurance
e) Flexibility
Consolidation activities
Let students perform regularly cardiorespiratory endurance exercises, body com
position exercises, muscular strength exercises, muscular endurance exercises,and flexibility exercises and analyze their performance.
Extended activities Encourage learners:
Let students participate regularly in competition of cardiorespiratory endurance
exercises, body composition exercises, muscular strength exercises, muscularendurance exercises, and flexibility exercises in their villages or sector.
REFERENCES
1. Dave Carnell, John Ireland, Claire Jones, Ken Mackreth, Sarah van Wely (2002),
Advanced PE for OCR, Oxford U.K
3. FIFA. (2018). Coaching manual
2. ELIAS, A. HILGERS, W. JETTER, M. RASHDORFF. J. WINTERMEIIER, D.
WOLFARTH Education Physique et Sportive pour les Ecoles Primaire et les
CERAI, F, Kigali.
4. Goldberger, M. and Howarth, K. (1990). The National Curriculum in Physical
Education and the Spectrum of Teaching Styles. British Journal of Physical
Education.
5. Ken Jones and Pat Welton (1979) Soccer Skills and Tactics, Crown Publishers.
6. Ministry of Education. (1998). Physical and Sports Training Programme in
Ordinary Level. National Curriculum Development Centre.
7. Peter J L Thomson (2009) The Official IAAF Guide to Teaching Athletics
8. REB (2019). The Teacher Training Colleges (TTCS) COMPETENCE BASED
CURRICULUM ORIENTATION MANUAL, Kigali.
9. REB. (2015). Ordinary level Physical Education syllabus
10.REB (2019). TTCs Physical Education and Sports syllabus
11.REB. (2016), Physical Education for Rwandan Schools. Teacher’s Guide,
Ordinary level 1, MK Publishers, Kigali, Rwanda.
12.REB. (2016), Physical Education for Rwandan Schools. Teacher’s Guide,
Ordinary level 2, MK Publishers. Kigali, Rwanda.
13.Right to Play, (2007). Football for development. Coaching manual
14.Williams, A. (1993). Aspects of Teaching and Learning in Gymnastics. British
Journal of Physical Education.
15.St John Ambulance (2019) saving lives REFERENCE GUIDE, Fourth Edition,
Canada.
16.Gina M. Piazza, DO, FACEP (2014) First Aid Manual, fifth Edition, New York.
17.AL JUFAILI Mahmood S. Dr (all) (2015) Football Emergency MedicineManual, 2nd Edition, Zurich.
