PART I: GENERAL INTRODUCTION
1.1 The structure of the guide
This section presents the overall structure of this guide,
the unit and lesson structure to help teachers to understand
different sections of this teacher’s guide.
Overall structure
The whole guide has three main parts as follows:
General Introduction:
This part provides general guidance on:
– How to develop the generic competences;
– How to integrate cross cutting issues;
– How to cater for students with special educational needs, active
methods and techniques of teaching Physical Education and Sports
and guidance on assessment.
Sample lesson plan:
This part provides a sample lesson plan developed and designed to
help the tutors to develop their own lesson plans.
Unit development:
This is the core part of the guide. Each unit is developed by following the structure below.
Structure of a unit
Each unit is made of the following sections:
– Unit title: From the syllabus.
– Key unit competence: From the syllabus.
– Prerequisites (knowledge, skills, attitudes and values): This section
indicates knowledge, skills and attitudes required for the success of the unit.
The competence-based approach calls for connections between units/topics within
a subject and interconnections between different subjects.
The teacher will find an indication of those prerequisites and guidance on
how to establish connections.
– Cross-cutting issues to be addressed: This section suggests cross
cutting issues that can be integrated depending on the unit content.
It provides guidance on how to come up with the integration of theissue. Note that the issue indicated is a suggestion; teachers are free to
take another crosscutting issue taking into consideration the learning environment.
– List of lessons/sub-heading: This section presents in a table
suggestion on the list of lessons, lesson objectives copied or adapted from the syllabus
and duration for each lesson. Each lesson /subheading is then developed.
– Summary of the unit: This section summarizes what students have been learned in the whole unit.
– End of each unit: At the end of each unit, the teacher’s guide provides the following sections:
Additional Information
This section gives further information that may help him/her to plan
and conduct Physical Education and Sports lesson.
End unit assessment
This part provides guidance on how to conduct the end unit assessment in a practical way.
It suggests activities/games as well as guidance on criteria to be considered such as:
– Cognitive skills: (E.g.: Increase of the level of capacity of anticipation,
problem solving during sports activities, know rules of the game,
know techniques and tactics to use different sports activities,
know the importance of practice etc.).
– Technical competences: (E.g.: to receive the ball, to pass the ball to the teammates,
to throw a javelin, to score the goal, to dribble the ball etc.).
– Strong emotional points: Such as self-confidence and feeling, secure.
– Social competences: Such as cooperation and solidarity.
– Attitudes and values: E.g.: optimism, confidence, respect, fair play,
teamwork spirit, self-confidence, determination, courage, impartiality,
avoid doping in sport activities etc.
Additional activities
This section provides additional games/exercises for the teacher to have a
wide range of activities/games related to the unit.
– Consolidation activities: Additional activities to students with special educational needs.
– Remedial Activities: Additional activities for students who need more time
and exercises to achieve a certain level of performance.
– Extended activities: Additional activities for talented students.
The guide ends with references.
Structure of each lesson
Each lesson/sub-heading is made of the following sections:
– Lesson title: It shows the title of the lesson.
– Introduction: This section gives a clear instruction to the teacher on
how to start the lesson.
– Teaching resources: This section suggests the teaching aids or other
resources needed in line with the activities to achieve the learning objectives.
Teachers are encouraged to replace the suggested teaching aids by the available
ones in their respective schools and based on learning environment.
– Steps of the lesson: This section provides activities/games/exercises and
guidance step by step: Opening discussions, warm up, lesson body, cool down
and closing discussions (R-C-A): Reflect, Connect and Apply.
1.2 Methodological guidance
1.2.1 Developing competences
Since 2015, Rwanda shifted from a knowledge based to a competency based
curriculum for pre-primary, primary and general secondary education.
This called for changing the way of learning by shifting from teacher-centered to
the Learner-centered approach. Teachers are not only responsible for knowledge
transfer but also for fostering students’ learning achievement, and creating safe
and supportive learning environment. It implies also that a student has to
demonstrate what he/she is able to do using the knowledge, skills, values and
attitude acquired in a new or different or given situation.
The competence-based curriculum employs an approach of teaching and
learning based on discrete skills. It focuses on what students can do rather
than what students know. Students develop basic competences through
specific subject unit competences with specific learning objectives broken
down into knowledge, skills and attitudes. These competences are developed
through learning activities disseminated in learner-centered rather than the
traditional didactic approach. The students are evaluated against set standards
to achieve before moving on.
In addition to specific subject competences, students also develop generic
competences that are transferable throughout a range of learning areas and situations in life.
Below are examples of how generic competences can be developed in Physical
Education and Sports:
Generic competence
Examples of activities that develop generic competences
Communication
– Organize and present in writing and verbally a complete and clear
report of a training session, a match for a given sports or any organized sport event;
– Select and use a set of verbal and nonverbal channels of communication during a
game situation or sport activities (a voice, facial expressions and bodily movements);
– Observe and interpret different game situations, sport events and react accordingly;
– Argue verbally or in writing about any given performance/results in
sports activities.
Cooperation, Personal and Interpersonal management and life skills
– Playing in Pairs;
– Playing in small groups/teams;
– Playing in large team and/or a club.
Critical thinking
- Demonstrate advantages of Sports activities to the schools where sports is
valued contrary to a school or institution where sport is neglected.
Innovation and creativity
– Create a set of physical activities of a training session for a given sport;
– Leading a given activity in sport training session with objectives,
methodology, observations, results and conclusions;
– Design a sketch map of some techniques and tactics used in different games;
– Create a chart of the main steps in a performing a given tactic in
different sports/games;
– Create and organize sport event.
Intra and interpersonal skill
(Intra skills refer to the skills of knowing and living with oneself while Inter personal
skills deals with knowing and living with others)
- Ability in facilitating interaction and communication with others.
Lifelong learning
- Exploit all opportunities available to improve on knowledge and skills.
- Reading sports journals, listening to sports news and following different
games and sport events on TV or on playgrounds/ stadium.
Research and Problem solving
- Research using internet or books from the library and develop tactics or
strategies to be used in performing sports activities;
- Fabricate sports materials from local materials (e.g. making a soccer ball,
making a shot putting using sand and sacs, etc.).
1.2.2 Addressing cross-cutting issues
Among the changes in the competence, based curriculum is the integration of
cross cutting issues as an integral part of the teaching learning process as they
relate to and must be considered within all subjects to be appropriately addressed.
The eight cross cutting issues identified in the national curriculum framework are:
– Comprehensive Sexuality Education (CSE);
– Environment and sustainability;
– Financial Education;
– Gender;
– Genocide studies;
– Inclusive Education;
– Peace and Values Education;
– Standardization Culture.
Some cross cutting issues may seem specific to particular learning areas or
subjects but the teacher need to address all of them whenever an opportunity arises.
In addition, students should always be given an opportunity during the learning
process to address these cross cutting issues both within and out of the classroom to
progressively develop related attitudes and values.
Below are examples on how crosscutting issues can be addressed and how to
integrate them in Physical Education and Sports lessons.
Comprehensive sexuality education
A teacher provides physical activities. A teacher sets instructions that prevent
any sexual harassment, any kind of gender-based violence like sexual abuse and
physical contacts oriented to the sexuality intention physical and sports activities.
Environment and sustainability
In teaching and learning process environment and sustainability are addressed when:
The teacher explains to students the importance of a safe and clean environment for
safe physical and sport activities.
– Students avoid throwing away used materials before, during and after exercises.
– There are rules set for cleaning the playgrounds before and after
exercises.
– Students avoid spitting or blowing the nose in pitch, field, and court during exercises.
Financial Education
In teaching and learning process, financial education may be addressed when:
– Students are able to find themselves local grown solutions as regards to sports
equipment and sport materials where there is shortage;
– Students are good managers of sports infrastructures and sports
materials, knowing that some of them are costly.
Gender
Teachers should ensure equal participation of both girls and boys during physical
activities and equal participation in open discussion and in refereeing.
Genocide studies
While conducting Physical Education and Sports activities a teacher should take a time
to explain students how sports should be used to fight against Genocide against Tutsi ideology
and how to prevent it or organizing Genocide against Tutsi memorial tournaments at
school and giving the message related to the Genocide against Tutsi.
Inclusive education
Involve all students in all activities without bias. E.g., allow a student with physical
disability to be a referee, a coach, an assistant, a judge. Modify activities so they suit the
abilities and attention span of the students.
Peace and Values Education
In teaching and learning process, the teacher must encourage tolerance, patience,
cooperation, teamwork spirit, mutual help, and respect of opinions of colleagues,
obeisance (respect) of rules and creation of a more peaceful game situation.
Standardization culture
– In teaching and learning process, the students must use standardized materials in
prevention of injuries and accidents.
– The teacher also must help students to know how to choose and use safe sports
clothing for their health (e.g. safe sports shoes), safe physical exercises
(avoid bad body postures and forbidden body exercises, adapted physical activities).
1.2.3 Attention to special educational needs
Currently we are convinced that games and sports are very beneficial to people with
physical, mental, emotional and psychological disabilities.
What attitude to adopt to promote the integration of students with disabilities during
recreational and sports activities?
To promote the integration of students with disabilities during recreational and sports
activities, the following tips may help teachers/educators in the training of these students:
– Adopt an approach of sports and game which is based on skills, you focus on what
students are capable of doing. In this respect, you can introduce small changes in
games and activities for students with disabilities.
– Be relaxed and natural when you are with people with disabilities. Do not treat them
as if they need your pity or your charity. Do not think they necessarily need help.
Let them do and say things themselves.
– Avoid keeping students with disabilities out of the game: in a regular class,
let them participate in other’s games. However, avoid being too demanding about
the level of their performance.
What can we modify to promote the integration of students with disabilities during
recreational and sports activities?
Within the framework of integration of students in games, according to the nature
and the gravity of impairment, students can participate in games designed for all students.
In other cases, the teacher or educator should think about changes he/she could
make to meet the special needs of teachers he/she has in the group.
He/she should also think about adaptation of the game, the playground, equipment
and duration of the game.
Below are some examples of adaptation to initiate:
i) Adapt roles and rules
– Make the game easier or harder by changing some rules.
– Let students play different roles and in different positions.
– Allow students to play in different ways, for example, sitting instead of standing.
– Simplify expectations of the game.
– Simplify instructions.
ii) Adapt the playground
– Change the size of the playground. Enlarge or reduce the playground.
– Change the distance: for example, put a target closer.
– Change the height of a target.
– Allow more or less space between students.
– Let students move from different spaces.
iii) Adapt the materials
– Reduce the size or weight of materials.
– Choose balls of various textures, bright colours or balls, which make noise.
iv) Adapt the duration of the activity
– Reduce or extend the time allotted to the activity.
Aspects to consider when you want to modify an activity
Ask yourself the following questions:
– Does the modification affect negatively the activity? This should not be the case.
– Does the modification correspond to the ability and duration of
students’ attention?
– Will the students with disability be able to play with others?
– Is the activity proportional to ages of participants?
– Does the activity respond to the needs of all participants?
Strategies to help students with physical disabilities or mobility difficulties
– Adapt activities so that students, who use wheelchairs, use other
mobility aids, have difficulty in moving can participate.
– Ask for adaptation of furniture. E.g., the height of a table may need to be changed to
make it easier for a student to reach it or fit their legs or wheelchair.
Encourage peer support between students. Get advice from parents or a health
professional about assistive devices.
Strategies to help students with hearing disabilities or communication difficulties
– Always get the student’s attention before you begin to speak.
– Encourage the students to look at your face.
– Use gestures, body language and facial expressions.
– Use pictures and objects as much as possible.
– Ask the parents/caregivers to show you the signs they use at home
for communication (use the same signs yourself and encourage other students to also use them).
– Keep background noise to a minimum.
Strategies to help students with visual disabilities
– Help students to use their other senses (hearing, touch, smell and
taste) to play and carry out activities that will promote their learning
and development.
– Use simple, clear and consistent language.
– Use tactile objects to help in explaining a concept.
– For students with some sight, ask them what they can see. Get
information from parents/caregivers on how the students manage
their remaining sight at home.
– Make sure that the students have a group of friends who are helpful and who
allow the student to be as independent as possible.
– Plan activities so that students work in pairs or groups whenever
possible.
1.2.4 Guidance on assessment
Assessment in PES must be a continuing process that arises out of interaction
during teaching and learning process. It includes lesson evaluation during R-C-A
after each session and end of unit assessment.
This formative assessment should play a big role in teaching and learning process.
The teacher should encourage individual, peer and group evaluation of the activity done.
In this step, the teacher sets exercise to assess abilities, skills, knowledge and
attitudes of individual students basing on unit or lesson objectives.
During assessment activity, students perform exercises individually
or work in teams. The teacher avoids intervening directly. In fact, results from this
assessment inform the teacher on next steps for the whole class and individuals.
In some cases, the teacher can end up with giving remedial and extra activities.
1.2.5 Students’ learning styles and strategies to conduct teaching and learning process
There are different teaching styles and techniques that should be catered for.
The selection of teaching method should be done with the greatest care and some
of the factors to be considered that are:
– The uniqueness of Physical Education and Sports.
– The type of lessons to be learned.
– The particular learning objectives to be achieved.
– The allocated time to achieve the objective.
– Available instructional Sports materials, equipment and Sports
infrastructure.
– Individual students’ needs.
– Abilities of students’ and learning styles.
There are different learning styles to use while teaching Physical Education and
Sports depending on students’ abilities. The teacher should use a wide range of
techniques and tools to cater for different specificity of students’.
1.2.6 Teaching methods and techniques that promote the active
learning
A. Suitable Methods / techniques to teach PES
Physical Education and Sports is taught:
– In the classrooms (e.g. using a projector and videos to teach steps of performing
a technique, a system of game play and using a chalk board to teach rules of the game).
– In the playgrounds/courts for teaching different games (e.g.: football playground for
teaching football game, volleyball court for teaching volleyball game, handball
playground for teaching handball game, basketball court for teaching basketball game,
netball court for teaching netball game).
– On the athletic track, fields, roads and hills for teaching athletics
activities (racing, jumps and throws).
– In Gymnasiums for teaching gymnastics and indoor sports.
In the process of teaching and learning Physical Education and Sports,
the following methods should be used:
Demonstration method
A teacher makes him/herself a demonstration or asks an able student to do a demonstration.
The teacher is advised not to do a demonstration if he/she is not sure to do it better than
every individual student can do it.
Verbal Explanation
A teacher describes/explains activities he/she wants students to perform.
Practice session
Students are given time to practice exercises intended to develop the desired skills.
Supervision
During a PES lesson, the teacher plays a role of supervising where he/she must move
around in field and make corrections for individual students during exercises.
Correction
While making corrections starting by group correction to individual correction.
Corrections for inaccuracy in performing given techniques are done immediately.
Evaluation
Let students do their own evaluation for each other, then help them by giving some
advice using encouraging words. Evaluation is a continued activity
throughout the physical exercises.
Discussion
Discussions are used before and after teaching and learning activities in open
talks to motivate and develop attitude and values in students.
Application
Use of learned Physical Education and Sports skills in different situations to solve a given problem.
Physical Education and Sports in small schools or schools with limited facilities
Where schools have specific problems related to a lack of indoor and outdoor space,
consideration might be given to:
– The use of the classrooms, corridors and available school grounds for orienteering exercises.
– The provision of markings on the playground for athletic activities and small- sided games.
– The use of local facilities, e.g. Local grounds, community centres, parish halls, youth clubs,
colleges, higher learning institutions etc.
– Co-operation with other primary or secondary schools in sharing
facilities.
– Allocating more time to Physical Education and Sports in good weather.
– Visiting an outdoor education centre providing facilities for many
worthwhile activities.
– Use possible available space, which should be used to facilitate teaching and learning of
Physical Education and Sports.
– Use local materials by making for example: goal posts for Football,
Netball and Handball, posts for supporting net in Volleyball.
– Try to create their own playgrounds by using space available.
B. Steps of a PES lesson
While teaching a Physical Education and Sports lesson by using play based approach,
a teacher follows these steps:
Step 1: Opening discussions.
Step 2: Warm-up activities.
Step 3: Lesson body.
Step 4: Cool down.
Step 5: Closing discussions focusing on Reflect, Connect and Apply (R-C-A).
Step 1: Opening discussions
The Opening discussions prepare students for the learning experience.
Discussions encourage them to think about the learning objective of the play.
Opening discussions include quick questions to stimulate students’ curiosity and engagement.
Strategies for good discussions:
– Set appropriate arrangement for good discussions: e.g. semi-circle,
circle, U-shape.
– Set ground rules, which create a safe atmosphere for students.
– Prepare students for discussions.
– Ensure interactive and inclusive discussions.
– Acknowledge each student’s contribution.
– Ensure classroom management and control.
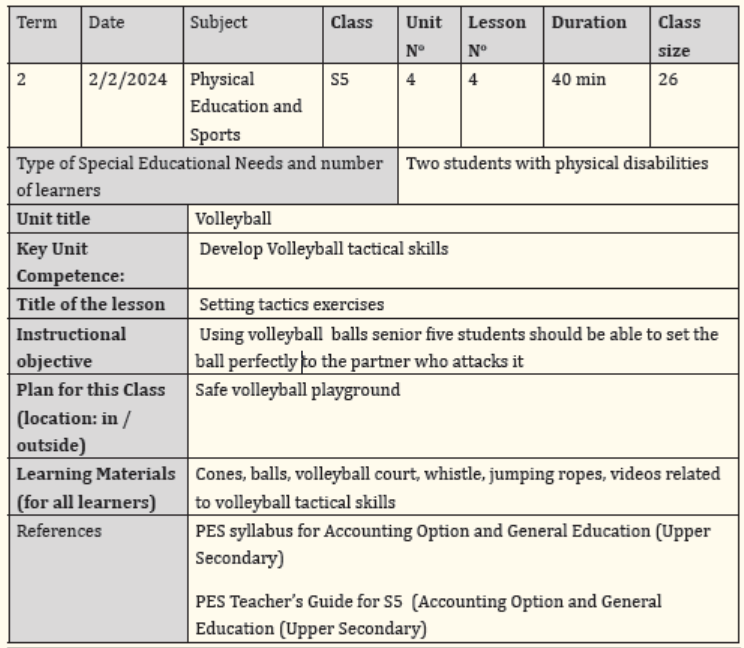
Step 2: Warm-up activities
A warm-up is performed before a game/play/practice of technique.
It helps the body activation, prepares itself for a physical exercise, and reduces the risk of injury.
The warm-up should be a combination of rhythmic exercises,
which begin to raise the heart rate and raise muscle temperature, and
static stretching through a full range of motion. The use balls while warm up activities help
students to master previous skills, which should help them to perform new skills.
Step 3: Lesson body
A game/play/exercise is selected according to the topic to be taught/age of
students/ability of students/available materials and skills you want to develop.
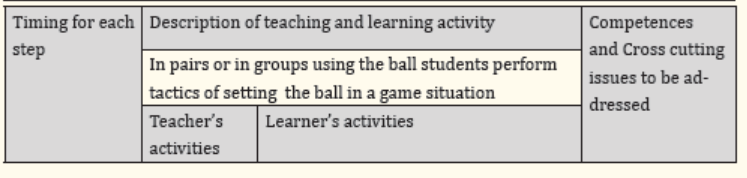
Step 4: Cool down
A cool down activity is an easy exercise that allows the body to gradually
transition to a resting or near-resting state. It is done after the main activity or lesson body.
Step 5: R-C-A discussions
Assessment in PES lesson is done when students are performing exercises/ activities/games.
At this level, through the R-C-A discussions the teacher allows students to
do their self-evaluation and provide the feedback from learned lesson.
Reflect-Connect-Apply is a teaching and learning strategy that leads students
through a 3-steps discussion about their experience:
Reflect
Ask questions, which help student to reflect on the game/ play/skill learned.
The teacher asks questions about their experience and feelings during the
game/exercise/activity.
The teacher asks questions like:
– What was interesting?
– What was easy?
– What was challenging?
– What strategies have you used to win?
– How did you feel in case of success or failure?
Connect
Ask questions, which help students to connect what they have learned to
life experiences and lesson content.
The teacher asks questions like:
– How this game/exercise/activity is connected to what you already
know, believe or feel?
– Does it reinforce or expand your view?
– The teacher also asks questions, which connect the game/exercise/
activity to lesson content.
Apply
Ask questions, which help student to apply acquired experience to another situation.
The teacher asks questions like:
– How could you use what you have learned from this experience?
– How could you use your new learning to benefit yourself, others, your community?
RCA is based on the work of educationalists such as Freire, Brown, Piaget,
Brantford and others who support the concept of an educational process that is
active, relevant, reflective, collaborative and applied, and has its roots in
experiential learning theory (Kolb, 1984). Play-based learning technique is
closely linked to the Experiential Learning Cycle. It starts with a game or play-based
activity and ends with a closing Reflect, Connect and Apply (RCA)
discussion linked to the subject matter.
Experiential Learning Cycle (David A. Kolb, 1984 – Experiential Learning Theory).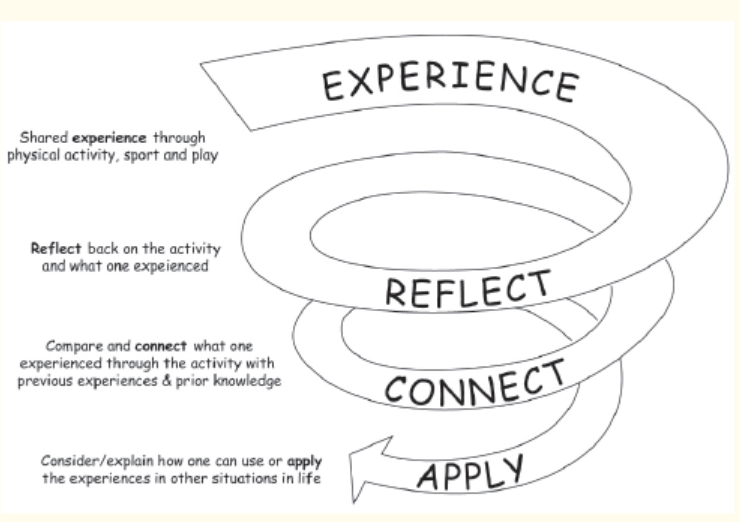
PART II: SAMPLE LESSON PLAN
School Name: ………………
Teacher’s name: ……………………………