UNIT 1: THE STRUCTURE OF COSTING SYSTEM WITHIN AN ORGANIZATION
Key Unit Competence: Explain the structure of costing system within anorganization
Introductory activity
The Brothers Ltd Co. is a hospitality company operating in Huye District. It
has been hired by its potential customer Neza to serve her wedding ceremony.
The company has been requested to perform different activities: decoration,
meal provision and soft drinks to host such an event, transport facilities from
the beginning to the end of the ceremony, as well as the coordination of
ceremony and to entertain guests. Before signing a contract, The Brothers Ltd
co. exhorted its accountant to firstly assess various costs that will occur for
activities to be performed in order to set affordable price, but the company
was not well informed about the number of people to be hosted for proper
financial valuation of resources to be used in the job completion. Later the
client informed the company that 750 people were approved to attend the
wedding. The company policy is to compute the cost based on material
used, skills required, direct expenses, overhead and the quality of service.
However, accountant has revealed that the amount of money to be spent for
individual item was structured as follows: meal as a product: FRW 3500 and
soft drinks FRW 1,400 per person; decoration and transport as services were
FRW 650,000 and FRW 300,000 respectively as fixed cost; and FRW 150,000
to Master of Ceremony (MC) for his coordinating and organizing role duringthe event.
Question:
1. Basing on the above case study, what is about the scenario?
2. Outline different activities that require cost.
3. Define costing?4. Explain the main costing methods as used in product costing
1.1 Introduction to costing systemLearning Activity 1.1
Ruberwa is soler trader producing and selling bread, juice and biscuits.
Ruberwa as an entrepreneur does not have sufficient skills and necessary
information to compute the cost of each product; he estimates the cost of
product based only on ingredients recorded during the production process.
While selling, he gets many customers due to the lower price resulting
from wrong costing system comparatively to surroundings business.
Considering high sales and getting a lot of money in the pocket, he thinks
that really, he will get high profit; unfortunately, he gets loss at the end of
the year in his financial statement. He decided to hire an accountant for
monitoring and controlling exist costs so as to know the main cause of this
problem. The accountant revealed that information used in computation
of the cost of product was incomplete for each product because the owner
only considered the portion of direct material cost recorded and did not
consider labor cost, direct expenses and overhead incurred during andafter the production process.
RUBERWA was surprised by the cost review report provided by
accountant, the later has been requested to calculate the cost of each
product appropriately. In next accounting period, RUBERWA recognized a
significant profit resulting from good computation of the production costand setting affordable price.
Questions
1. From the above scenario, what do you understand by a costing
system?
2. Identify the lesson you learnt from this case study.
3. As an accountant of Ruberwa, explain he main advantages forinstalling a good costing system in your organization.
1.1.1. Definition of key concepts
Today different business and industry needs different methods for calculating,
monitoring and controlling cost to meet their individual requirements. It
is not possible to devise a single costing system to fulfill everybody’s needs.
Different methods of costing for different industries depending upon the type
of manufacturing and their nature have been developed. Various methods
of ascertaining costs are available to suit the business needs. But the basic
principles are the same in every method.
• Product cost
Product cost refers to the costs incurred to make or produce a product. These
costs include direct labor, direct materials, direct expenses and overhead cost.
• costing
Costing’ refers to the methods and processes of determining costs of a product
manufactured or services rendered. or costing is the technique and process of
ascertaining costs.
• Costing system
Costing system is that system in which we calculate different cost with different
methods and also monitor cost for reducing wastages and misuse of resources.
Costing system comprises of a set of forms, processes, controls and reports that
are designed to aggregate and report to the management about revenue, costs
and profitability. It ascertains product profitability and helps management in
planning and control of business operations.
1.1.2. Characteristics of a good costing system
A good Costing System will consist of the following characteristics:
• The Costing System adopted in a particular organization must suit its
nature and size of business and its information needs.
• The Costing System must be economical to the organization and the benefits
derived from the system should be more than its cost of installation and
operation.
• The system should be more flexible enough to take care of changing
business situations and information needs of the organization.
• The system should be simple to understand and easy to operate. The users
of costing data should be convinced of the Costing System from which the
data is derived.
• The Costing System should ensure proper accounting for materials, labour
and overheads and proper classification of transactions should be done at
the level of recording.
• The Costing System should clearly mention the details of records to be
maintained and the degree of accuracy of data required.
• Since the Costing System is for internal control purpose, it should meet the
requirements of management and its information needs.
• The costing system should fix up the duties and responsibilities of costing
department staff and the cooperation that can be sought from other
departments.
1.1.3. Effective conditions for a good costing system installation
As a system designer, the cost accountant should be able to perceive the needs
of the management at various levels and design such a system as will meet
those needs promptly, effectively and efficiently. The following conditions and
factors must be taken into account when designing a costing system:• Preliminary investigations must be made before a system is installed. ThisThe following factors must be taken into account before finalising the cost
help to discover weaknesses and inefficiencies
• For accuracy of cost records, a system of material cost, labour cost and
production overhead cost is essential
• Nature of business enterprise must be put into consideration when
designing a cost system accounting system. the system developed should
be practical and must suit the business.
• The system must be cost effective in that the benefits derived from the
system must be greater than the cost of running it.
management system• The system must be designed in such a way as to meet managerial1.1.4. Advantages of installation a costing system.
information needs. There should be no duplication in reporting.
• The factory layout and production sequence. This is important for the
identification of the sequence of production.
• The nature of material used affect the system adopted. This is because it
affects the recording and issue of raw materials and method of pricing.
• Control exercise over production: the cost data must focus on specific
areas of control so that any variance between actual and standard cost can
be identified by the individual department.
• The deployment of workers, who may work as a team or as individuals.
This affects the method of remuneration and analysis of time worked.
• Key personnel and office staff, their cooperation is vital for success of the
system. In addition, the system needs to be simple and easy to understand
to enhance acceptability.
• Need for uniformity; a business needs to observe the industrial norms and
thus follow the industrial practices as regards the accounting.
• The cost benefit analysis should be carried out and it is only reasonable to
run a system which has more benefits than cost.
• The system should be capable of adapting to changing conditions.• It should be logical and simple.
Cost accounting has now become the norm in most industries and firms.
Almost all businesses rely on cost accounting information to supplement
the information provided by financial accounting. In fact, cost accounting is
essential not only to businessmen and the management but also to the economy
as a whole.
a. Measuring and Improving efficiency
Cost accounting allows for data that enables the firm to measure efficiency.
This isefficiency in respect to cost, time, expenses etc. Standard costing is then
used to compare actual outcomes with the industry or economy standards to
indicate changes in efficiency.
b. Identification of Unprofitable Activities:
Just because a firm is making overall profits, it does not mean all activities
are profitable. Cost accounting system will help us identify the profitable and
unprofitable activities of the firm. Activities that cause the firm losses can be
made profitable or eliminated. This can happen due to the cost ascertainment
done in cost accounting.
c. Fixing the price
Costing system makes the distinction between fixed and variable cost, which
allows the firm to fix prices in different economic scenario. prices that we fix
without the help of costing system can be too high or too Low and both cause
losses to the business.
c. Control over Stock
Costing system helps with restocking and control over materials. Cost accounting
system will help us determine the most ideal and economic re-order level and
quantities. This will ensure that the firm is never overstocked or understocked.
e. Evaluates the Reasons for Losses
Every firm has to deal with periods of profits and losses, hence they must
always evaluate or investigate the reasons for the losses suffered. This will help
to tackle the problem or overcome the cause by some other means necessary. if
the cause can not be eliminated then at least minimize the losses.
f. Aids Future Planning
One of the biggest advantages of cost accounting system is that it will help the
management with future plans they may have. For any production or selling
plans, it is important to have detailed data about the machines, the labour
capacity, output levels, levels of efficiency of each process.
1.1.5. Challenges in installing of costing system
There are different challenges facing the business at the time of installation a
Costing System:
a. Lack of Support from Top Management
The basic objective of Cost Accounting System is to provide necessary
information to the internal management for the purpose of problem solving,
decision making and control. Without support and recognition from the top
management, the very purpose of Cost System is insignificant.
b. Resistance from Existing Accounting Staff
The existing accounting staff may resist the introduction of Cost Accounting
System in the organization due to fear of loosing job recognition and importance
after the implementation of the system.
c. Lack of Cooperation from other Departments
The employees of other departments may not cooperate for the installation of
Cost Accounting System due to fear of increase in workload as it brings-out
inefficiency etc.
d. Resistance from Operating Level Workers
The foremen, supervisors, workers and other operating level staff may resent
the introduction of cost system on the ground that it will increase their job
responsibilities and paperwork and may fear that it may cause change in wage
structure.
e. Shortage of Trained Staff
The installation and implementation of cost system requires trained, qualified
and experienced staff which may not be available.
1.1.6. Overcoming challenges to costing system
The management of business after finding the above challenges should set
strategies to overcome them. The following are the proposed solutions:
• The management should be convinced of the benefits which can be derived
by installation and operation of a Costing System.
• Non-cooperation and resistance can be overcome by explaining the
simplicity and use of the system and should be assured that the system will
benefit the organization and increase its profitability. They should be given
assurance that the system will not reduce the importance of existing staff.
• To overcome resistance, the existing staff should be properly trained to
take up the responsibilities in the Costing System
• All levels of staff and managers in the organization should be properly
trained and made familiar with the Costing Procedures.
• The system should be simple to understand and easy to operate.
• The benefits derived from Costing System should be more than the costs
incurred on its installation and operation.
• A qualified and experienced cost accountant should be assigned with
responsibility to achieve the desired objectives of the Costing System. He
should be capable of coordinating with other departments.
• The Costing System designed and installed should meet specific
requirements of the concern and it should reduce unnecessary paperwork
of the organization.
• Regular meetings with accounting staff and user departments will clarify
all doubts about the system and eliminate ambiguity.
1.1.7. Steps for installing a good costing system
The steps to be taken into consideration in installing a costing system are given
below:
a. Objective to be achieved through the Costing System
The costing system will be simple if the objective is only to determine cost, but
it will have to be elaborated if the objective is to have information which will
help management in exercising control and taking decisions.
b. Studying the Existing Organisation and Routine
In this connection the points to be noted are the nature of the business and
of the operations or process carried on, extent of responsibility and authority
attached to the various functions, the methods of dealing with wastage of
materials, the system of time recording and the methods of computing and
paying wage.
c. Deciding the Structure of Cost Accounts:
The structure of cost accounts should follow the natural production line; the
sequence can be simple, analytical or synthetic.
d. Determining the Cost Rates
This entails a thorough study of factory conditions and decisions are to be made
about classification of cost into direct and indirect, grouping of indirect costs
into production, selling, administration etc., treatment of wastes of all kinds,
methods of pricing issues, methods of recovering overheads and calculation of
overhead rates.
e. Introducing the System
No costing system can be expected to function effectively unless co-operation
of all the officials could be obtained. Before the system is implemented, the
implications of the system should be explained to all indicating to them the
benefits that will accrue to each and to the business as a whole.
f. Organising the Cost Office
It is always better that the cost office is situated adjacent to the factory so that
delay in routing out documents or in clearing up discrepancies and doubts, is
avoided. The costing staff must be allowed to have access to the works if they
are to perform their duties properly.
1.1.8. Factors to consider for installation of a good costing
system
It is necessary that the costing system is properly installed in an organization.
Costing system installed in an organization should be simple to understand,
easy to operate, highly reliable and suitable to the organization. In designing
and installation of a good costing system, the following factors should be given
due consideration:
a. Size of the firm
Size of the firm is an extremely important factor in designing a cost accounting
system. As the size of the firm and its business grows, the volume and complexity
of the cost data also grows. In such situation, the cost accounting system should
be capable of supplying such information.
b. Manufacturing Process:
Process of manufacturing changes from industry to industry. In some industries,
there may be a continuous process of production while in some batch or job
type of production may be in operation. A cost accounting system should be
such that the manufacturing process is taken into consideration and cost data
is collected accordingly.
c. Nature and Number of Products
If a single product is produced, all costs like material, labor and indirect
expenses can be directly allocated to that product. But if more than one
product is manufactured, the question of allocation and apportionment as
well as absorption of indirect expenses (Overheads) arises and hence the cost
accounting system should be designed accordingly as more complex data will
be required.
d. Management Control Needs: The designing of a cost accounting system in
a business organization is guided by the management control requirements.
The costing system should supply data to persons at different levels in the
organization to take suitable action in their respective areas.
e. Raw Materials: The designing of a cost accounting system in a business is
also guided by the raw materials required for production. The nature of raw
materials and the degree of waste therein influence the designing of costing
system. There are some materials which have a high degree of spoilage.
The costing system should be such that identification of spoilage, keeping
records of materials, pricing of the issues etc are taken into consideration.
f. Organization Structure: The structure of the organization also plays a vital
role in designing a costing system. The system should correspond to thehierarchy of the organization.
Application activity 1.1
1. What are the main characteristics of a good costing system?
2. Complete the following sentences by given terms :
I. Costing refers to the techniques and processes of __________
A. ascertainment of costs.
B. allocation of costs.
C. apportionment of costs.
D. distribution of costs.
II. Cost of sales plus profit is __________.
A. selling price.
B. value of finished product.
C. value of goods produced.D. value of stocks
1.2. Information required in costing systemLearning Activity 1.2
RAVIM Ltd is a manufacturing business which produces high-quality
Soaps compared to existing soap market. The management is not able
to determine the cost of one soap and it sets soap price in reference to
the price of similar soap. At the end of six months, the company prepared
interim financial statement and finds that it made a loss. The management
hired an accountant for installation of a good costing system which could
help the company to determine the cost of the product but the accountant
has not found necessary data to install a good costing system and prepares
a cost sheet which indicates the data needed in his exercise such as cost
of material used, number of employees used , processing cost, number of
hours available per day and overhead absorption cost , the wasted materials
cost during the production process , water and electricity cost, pay rate per
day, packaging cost, overhead cost and the quantity produced during this
period . Accountant decides to meet with different business managers
to collect necessary data related to production process and delivery. After
this exercise he/ she gets necessary data that could allow him/her to
determine the cost of each soap produced and get the opportunity to advise
the managers on the strategies that they can use to reduce the cost of each
department as well as the cost of the soap. This may include reducing theduplication use of resources and reusing existing resources.
Questions
Identify information that an accountant needs to design a good costing system
1.2.1 Identify information required in costing system.
A costing system should collect statistical data for significant operations, analyse
the data, and make it available to the management to support managerial
decision making.
Businesses or industries need sufficient information for installation of costing
system in organization but the type of information required depends on
whether you are a service, trading or manufacturing organization and how you
have structured your cost system. Business needs the following information,
including: volume, material quantities, expected output or yield, scrap factor,
standard time, business capacity, labor hours available, material cost, labor
cost and overhead etc
1.2.2. Explain information required in costing system
The availability of information is the lifeblood of any cost and management
accounting system. It is vital that input information is properly controlled in
order that output information is useful. Such information must be relevant
for management‘s planning, control and decision-making purposes. The
information used in cost and management accounting may be quantitative or
qualitative.
• Quantitative information is information which may be measured in
monetary terms or other physical units eg material may be expressed as
FRW 200 or 500 Kilos. It is easily objectively expressed.
• Qualitative information: is that information which cannot be objectively
expressed. It is therefore very difficult to quantify such information and
for this reason, it is largely subjective. The management accounting mainly
utilizes mixture of the two but mainly quantitative information.
The information required for installation a good costing system are:
• Volume
The volume levels usually drive the number of resources required or consumed
by the organization. It is the starting point for any budgeting or forecasting
exercise and is a critical element to determine capacity utilization and its
impact on the cost structure of the organization.
• Materials quantities
This information is important for business organizations and will generally
be found in the bill of materials. It provides the quantities required of each
component or ingredient that is used to manufacture the product. In some
service organizations, materials may also represent significant costs, for
example, a power generation facility typically consumes a significant amount
of carbon or fuel in the production of electricity.
• Expected output or yield
For process manufacturers, each product should have an expected or theoretical
output for each process based on the key ingredient. In service organizations,
the expected yield represents the expected output of a process based on a fixed
level of input.
• Scrap factor
This factor will reflect how much materials are lost as a normal part of the
process. Discrete manufacturers commonly use the scrap factor to recognize
expected materials losses resulting from breakage, spillage, equipment failures,
and operator errors.
• Process parameters.
Process parameters are used to determine the time standards, particularly
for machine-paced operations. They generally describe the cycle time of the
process such as bottles or capsules per minute and the number of workers
required to run the operation. Process parameters vary significantly from
industry to industry.
• Business process Capacity.
The team should determine the practical and available capacity of each
major business process and how much of this capacity is being utilized. This
information can help identify improvements in capacity utilization and is used
to isolate the cost of excess capacity in the unit cost.
• Materials costs.
This cost represents the actual, standard, forecasted, or estimated cost of
the material components or ingredients that are consumed by the product or
service. The materials costs usually includes the purchase price of the goods
plus other costs such as freight, insurance, royalty payments, tax, brokerage
fees, and duties. In organizations that have high materials costs, focusing on
this area can produce significant cost savings.
• Labor and overhead costs.
This information is necessary to calculate the labor and overhead rate that will
be used to assign these costs to the items being measured. Usually organizations
budget and collect labor and overhead costs by work areas or departments. The
team should ensure that the way the organization is currently collecting actual
costs is consistent with the system design.
Application activity 1.2
1. Explain the information needed to design a good costing system in
organization
2. Matching questionMatch up the following services with their typical cost units
1.3. Types of costing system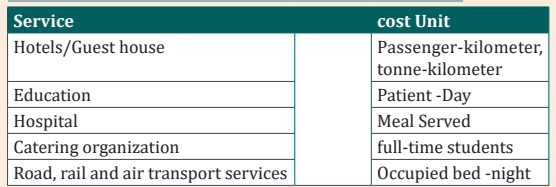
Learning Activity 1.3
PIKU co. is a company which produces and provide different products
such as manufacturing of modern plastic bucket, manufacturing motor
vehicles, construction services and road maintenance, it receives two
purchase orders, one for 2000 plastic buckets and second 5 motor vehicles
and winning two tenders, one for construction a mega building house and
second for road maintenance. The main problem in this company is to
know the method that should be used to calculate the cost of each product.
Purchase order 1: For manufacturing plastic bucket, Kaneza requests 2000
plastic bucket of 10 liters with the following specification: 1000 plastic
bucket should be in a yellow color and the remaining should be in a white
color and the purchase order should be delivered within 15 days. And the
payment will be made on condition that the company supplies all quantity
required in time.
Purchase order 2: For manufacturing the motor vehicle, Muzika Ltd in
its purchase order requests motor vehicle materials that can be used to
manufacture 5 motor vehicle (V6 Tesla) and assembling will be done in
its premises after physical testing; and the payment will be done based on
batch tested.
Tender 1. Rwanda Housing Authority requests PIKU in its bidding
documents to construct a mega Building in Kigali City and the payment will
be done after completing this activity.
Tender 2. Road maintenance: Rwanda Housing Authority has contracted
PIKU Co. to maintain the Huye – Kigali Road of 154 kilometers in a period
of 1 year and the payment will be done on quarterly basis based on workdone. Consider that the maintenance cost of 1 kilometer is FRW 3000,000.
Question
1. What do you understand by costing methods?
2. Explain costing methods that can be used on
a) purchase order one and twob) tender one and two
1.3.1. Job Costing
Job Costing: This method is used in Industries or businesses where the
production is per the requirements of the customer. In Job Order, the production
is not on continuous basis, rather it is only when order from customers is
received and made as per the specifications of the customers. Consequently,
each job is different from the other one. Method used in such type of business
organizations is the Job Costing or Job Order Costing.
A costing system is designed to suit the way goods are processed or
manufactured or the way services are provided. Each organisation’s costing
method will therefore have unique features but costing methods of firms in the
same line of business will more than likely have common aspects.
The objective of this method of costing is to determine the cost of each job by
preparing a Job Cost Sheet. A job may be a product, unit, batch, sales order,
project, contract, service, specific program or any other cost objective that is
distinguishable clearly and unique in terms of materials and other services
used. The cost of completed job will be the materials used for the job, the
direct labor employed for the same and the production overheads and other
overheads if any charged to the job
1.3.2. Batch Costing
Batch Costing: In the job costing, we have seen that the production is as per the
orders of the
customers and according to the specifications mentioned by them. On the
other hand, batch costing is used where units of a product are manufactured
in batches and used in the assembly of the final product. Thus, components of
products like television, radio sets, motor vehicle and other consumer goods
are manufactured in batches to maintain uniformity in all respects.
It is not possible here to manufacture as per the requirements of customers and
hence rather than manufacturing a single unit, several units of the component are
manufactured as group. For example, rather than manufacturing a single unit, it
will be always beneficial to manufacture say, 75,000 units of the component as
it will reduce the cost of production substantially and bring standardization in
the quality and other aspects of the product. The finished units are held in stock
and normal inventory control techniques are used for controlling the inventory.
Batch number is given to each batch manufactured and accordingly the cost isdetermined.
1.3.3. Service Costing
Cost Accounting has been traditionally associated with manufacturing
companies. However, in the modern competitive market, cost accounting has
been increasingly applied in service industries like banks, insurance companies,
transportation organizations, electricity generating companies, hospitals,
road transport and railway transport, hotels, road maintenance, educational
institutions, road lighting, canteens, port trusts and several other service
organizations. The costing method applied in these industries is known as
‘Operating Costing’. operating costing is, ‘that form of operating costing which
applies where standardized services are provided either by an undertaking or
by a service cost center within an undertaking’.
• Nature of Operating Costing:
The main objective of operating costing is to compute the cost of the services
offered by the organization. For doing this, it is necessary to decide the cost
unitin such cases. The cost units vary from industry to industry. For example,
in goods transport industry, cost per tonnne perkilometer is to be ascertained
while in case of passenger transport, cost per passenger per kilometer is to be
computed
1.3.4. Contract Costing
Contract Costing: Contract Costing is a method used in construction industry
to find out the cost and profit of a particular construction assignment.
The principles of job costing are also applicable in contract costing. Contract
Costing can be termed as an extension of Job Costing as each contract is nothing
but a job completed. Contract Costing is used by concerns like construction
firms, civil engineering contractors, and engineering firms. One of the important
features of contract costing is that most of the expenses can be traced to a
particular contract. Those expenses that cannot be traced to a particularcontract are apportioned to the contract on some suitable basis.
Application activity 1.3
1. Differentiate costing method from costing technique.
2. Choose the best alternative.
A. Which of the following organizations should not be advised to
use service costing?
a) Freight rail company
b) IT department company
c) Catering company
d) Clothing company
B. Operating costing is suitable for ___________.
a) job order business.
b) contractors.
c) sugar industries.
d) service industries.
C. Process costing is suitable for _________.
a) hospitals.
b) oil reefing firms.
c) transport firms.d) brick laying firms.
Skills Lab 1
Imagine in your school, students need to consume bread every day and no
one produces bread near the school. Your business club members bring the
idea of bakery but none among the club members has information on what
it requires to produce bread (ingredients, equipments, required skills etc),
As club members research on:
1) Ingredients
2) Equipments3) Skills required in producing bread.
End unit assessment 1
1. Differentiate costing and costing system?
2. complete the following sentence with appropriate words
A. Job costing is used in ..........
a) a) furniture making
b) b) repair shoes
c) c)press printing
d) d) all the above
B. In a job cost system, costs are accumulated
a) On a monthly basis
b) By specific job
c) By department or process
d) By kind of material used
C. Operating costing is suitable for ___________.
a) job order business.
b) contractors.
c) sugar industries.
d) service industries.
1. Suggest the challenges faced during installation of a good costing
system and propose the possible solution for each challenge.
2. BAHO is a profit oriented business which produces and sells
different products such as jeans clothing, Television Manufacturing,
transport services and civil engineering contractors services , its
sales and marketing department has the task to search for themarket of its products.
On 1 January 2023 the company received a purchase order for 1000 jeans
for men and 1000 jeans for women from Terimbere and each jeans should
be delivered at 15000FRW.
On 1 January 2023 the company received a purchase order of 1200
Televisions from AGAHOZO TV shop and each television should be
delivered at 200,000FRW and the payment will be done based on batchdelivered.
15 January 2023 the management was contracted by REB for transporting
students from their homes to their schools and payment was to be made
when all students reached to their schools.
On 20th January 2023 won a tender of constructing model village in
Nyamagabe. The contract specify the terms of payment, first term the
company will receive a half of total amount and the remaining half will be
paid after official handover
Required
a) As cost accountant, some costing method are appropriate to the
above case, highlight at least four and propose a brief explanation
on the Indicator / activities for each costing method using BAHOcase.
