UNIT 1:GENERAL INTRODUCTION
Skills lab based education practice in healthcare has been defined as any
educational activity that utilizes simulative aides to replicate clinical scenarios.
In skills lab setting students use variety equipment such as manikins, medical
equipment, consumables and checklists of procedures, but also, they can watch
videos on healthcare professional education. The acquisition of hands-on clinicalskills in a long education way is a key to protect patient safety.
1.1.Goal of skills laboratory
The goal for clinical skills laboratory is to create an artificial replication of the real
world situation in which students can gain knowledge and psychomotor skills and
be able to critically think through complex scenarios in a safe and non-threatening
environment. This approach to experiential learning is a ‘learner centric’ educational
method, which integrates the cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains in a
non-threatening and safe environment thus ensuring accuracy and competency ofskills before the student enters the clinical environment.
1.2.Purpose of Skills lab
Maintain state-of-the-art laboratories that are equipped with human patient
simulators, digitalized video, and electronic supply and static mannequins. These
laboratories were designed to reproduce realistic practice settings, including the
basic hospital unit, critical care, surgical/operating suite, pediatrics neonatal nursery,
maternity, home care, health assessment and diagnostic laboratory. All laboratory
spaces are also outfitted with tables and chairs for reflective thinking exercises that
allow the students time to review their decisions and actions with the instructor andtheir classmates.
The Clinical Skill Laboratories exist primarily to serve the students, faculty and staff
of Nursing department
The clinical skill laboratories provide a clinical learning environment utilizing task
trainers and human patient simulation technology, as specified by the curriculum
and on recommendation by the faculty, and facilitate optimum and efficient utilizationof those resources.
1.3.Purpose of this teacher’s guide
To facilitate the teacher in teaching activities, the content of this teacher`s guide isself-explanatory so that you can easily use it.
1.3.1.Purpose
The purpose of the rules and regulations of skills lab is to guide teachers, students
and other health care professionals to use the available facilities for the development
of clinical competencies required in a skills lab environment before translating them
to the real clinical settings for the provision of safe and quality health care services toclients.
1.4. Structure of the guide
The guide has two main parts
1.4.1.Part I: General guidelines
This part provides general guidance on:
• Rules and regulation for skills lab
• Methodological principles to be used in skills lab• Guidance on assessment
1.4.2.Part II: Development of Checklist
This is the most important part of the guide. It includes Checklist of fundamental of
Nursing for senior 4, 5 and 6, and Checklist of Maternal and Child health for Senior4, 5 and 6.
Each checklist is developed in the following structure:- - -
Checklist title: this title is taken from course units; it contains the theory that need
to be translated into practices.
Procedure: each checklist is divided into different procedures; technique and all
steps composed each checklist.Aims of techniques(procedures).
1.5.Objectives of the Nursing Skills Laboratory
1. The objective of the Nursing Skills Laboratory is to provide realistic and quality
clinical learning experience to associate nursing students through various
clinical learning opportunities in the Nursing Skills Laboratory and serve as a
provision for the students to become associate nurses. It specifically aims to:
2. Build the students’ basic skills by providing definite connections between the
theoretical and clinical learning of the students through definite and adept
clinical learning experiences in the laboratory.
3. Develop the students’ associate nurse in providing nursing care in accordance
with the norms and values.
4. Foster the students’ ability to utilize the nursing process in performing nursingprocedures.
1.6. Duties and Student Nurse responsibilities in skills laboratory
Students are expected to come to skills laboratory prepared by having reviewed the
skill(s) to be practiced and/or demonstrated as well as having read the assigned
topics/chapters (if any) by his/her instructor prior to laboratory demonstration. Theyare advised to take advantage of every opportunity to enhance their nursing skills.
1. Log in on arrival to the attendance sheet provided by the laboratory instructor
and log out before leaving.
2. Inform the laboratory instructor of any particular learning needs.
3. Gather and return the equipment used for skill performance.
4. Approach situations and scenarios as if they are actual client interactions.
5. Follow safety measures at all time.
6. Maintain cleanliness of the laboratory area.
7. Dispose of sharps appropriately.
8. Demonstrate respect and consideration for self and others. All students
should display professional, courteous conduct.
9. Alert the laboratory instructor of allergies and injuries including latex allergy.
10. Any damage or malfunction of mannequins or equipment should be reported
to the laboratory instructor immediately.
11. Students should at all times observe the safety precautions and appropriate
techniques while learning and practicing skills in the lab. If not sure where to
locate equipment, supplies or resources, ask.
12. Students should be knowledgeable of the care, handling, and proper use of
equipment prior to using it in the laboratory.
13. The Identification card or ID should be always surrender when borrowingequipment
1.7.Skills lab Technician responsibilities
1. Conduct monthly inventory of the existing laboratory equipment and supplies and
submit semestral report to the program coordinator. It should include utilization,
losses, and breakages/damages on all laboratory rooms, laboratory equipment
and supplies.
2. Catalog and maintain security for audio visual and other media resources.
3. Check that the number of borrowed materials is complete and in good condition
when returned.
4. Prepare laboratory equipment and supplies for each skills laboratory class based
from the laboratory instructor or demonstrator’s requests.
5. Oversee maintenance of laboratory equipment and supplies, and computer
technology equipment for simulation; responsible in monitoring all equipment for
optimum performance and also for the certification.
6. Initiate processes on ensuring repairs of damaged laboratory equipment.
7. Coordinate with the laboratory coordinator in the procurement/requisition of
equipment and supplies.
8. Directly responsible on the documentation of usage of laboratory, laboratory
equipment and supplies.
9. Ensure that the laboratory rooms are clean, safe, and organized.
10. Accomplishes the Daily Nursing Skills Lab Follow-Up Sheet.
11. Promote safe laboratory practices.
12. Ensure the completeness of the first aid kit everyday. He/she will replace supplies
as needed.
13. Responsible for the Nursing skills laboratory lock/key.
1.8. Physical safety guidelines
1. Students should perform proper body mechanics during practice and return
demonstration especially in moving, lifting, and transferring skills.
2. Equipment used for body mechanics practice (bed, wheelchairs, stretcher,
etc.) should be used only if in good working condition. Any malfunction in
the equipment should be reported immediately to the laboratory technician
using the incident/injury form.
3. The wheels of all equipment (wheelchairs, stretchers, and beds) should be
locked during practice and return demonstration.
1.8. Managing hazardous waste:
1. Batteries which are not functioning should be disposed properly.
2. Contaminated supplies used during laboratory activities are collected,
singed as hazardous waste material and stored in designated area of the
skills laboratory.3. All biohazard wastes will be taken by a designated transporter.
2. RULES AND REGULATION FOR SKILLS LAB
2.1.Users of skills lab
Skills lab can be used by:
– Individual student,
– Individual instructor for his/her preparation before practice session,
– Group of students accompanied by a teacher,
– Group of students for peer tutoring,
– Group of instructors for continuous professional development,– People from outside the institution upon request
2.2.Main consideration during a skills lab
1. In accordance with humanistic education, all manikins and models are to be
treated with respect as though they are real clients. Models and manikins
are to be handled gently and carefully, draped appropriately when used, and
covered when not in use.
2. All skills lab users shall dress for skills lab as if attending the real clinical
setting among others name badges and uniform (or clinical coat), tied up
hair, close-toe shoes wear.
3. Tutors are responsible for supervising all students brought to the lab for
tutor-led sessions. He/she must prepare and rehearsal the practical sessions
before they start.
4. The tutor should not exceed a group of 8 students for session demonstration
and the student should not have more than 3 practical sessions for one day.
5. English as a medium language of instruction is recommended in all teaching
sessions including demonstration of procedures in skills lab.
6. Anybody who wants to practice in skills lab must make a booking for practical
rooms and equipment.
7. If the program permits students/tutors/other users to check out equipment
from the simulation lab, all procedures for signing out and returning equipment
are to be followed. Failure to responsibly adhere to the policy may mean loss
of check-out privileges.
8. Attendance and logbook for students should be signed after each simulation
teaching/learning session.
9. If the material(s)/equipment(s) are lost or damaged the person responsible,
signs the form of accepting the act and submit to the skills lab Technician
within 24 hours of the incidence in working days, then the procedure of
replacing it/them starts.
10. Clean-Up of the Area after Sessions: Upon completion of practice session,
it is the responsibility of the users to ensure that they tidy up the room
(furniture, trolleys,…) and leave the lab as they found it.
11. Coats, backpacks, and other personal belongings are not allowed in skills
lab rooms.
12. Food and drinks are prohibited in the skills lab rooms.
13. Universal precautions are to be followed at all times as are all safety
guidelines used in the clinical setting. Sharps and syringes are to be disposed
in appropriate containers.
14. Incident report: In case of any incidence during session, the responsible
person should report it in writing to the skills lab Technician within 24 hoursof the incidence in working days.
2.3.Attendance & evaluation skills lab
1. The signed attendance sheet is used in skill lab sessions as proof.
2. The module leader communicates the date of evaluation (OSCE) to be done
in skills lab to the students and any change is communicated at least two
weeks before.
3. OSCE should be prepared and rehearsed one day before by teachers.
4. Student must practice individually at least three times each procedure
taught, before the OSCE.
5. The student who hasn’t regularly attended the skills lab as indicated is not
allowed to sit for OSCE.
6. The average pass mark of OSCE is 60% and the results should be
communicated to the students within 48 hours of working days.
7. Debriefing is mandatory for all students within 2 working days after OSCE
and HoD should be informed of the process.
8. The evaluator should turn off his/her phone during OSCE, and follow each
step of the procedure done by student.
9. The student who missed the OSCE without sound justification is awarded a
zero mark. The justification has to be notified to the head of department at
the latest within 48 hours after the OSCE.
10. No teacher shall accept a justification which is not countersigned by thehead of the department.
2.4.Methodological principles to be used in skills lab
2.4.1.Techniques to be used in skills lab
Skills lab is an opportunity for a student to apply practically what he/she
learned theoretical. Even if there are different techniques to be used, one of the
recommendable techniques is Scaffolding.
Scaffolding is supporting new learning by building new concepts on previously
learnt concepts. There are various ways teachers can do this. One way is by
reminding the learners about concepts they have previously learned. Another is to
display previously learned concepts so that learners can focus on the new learning.
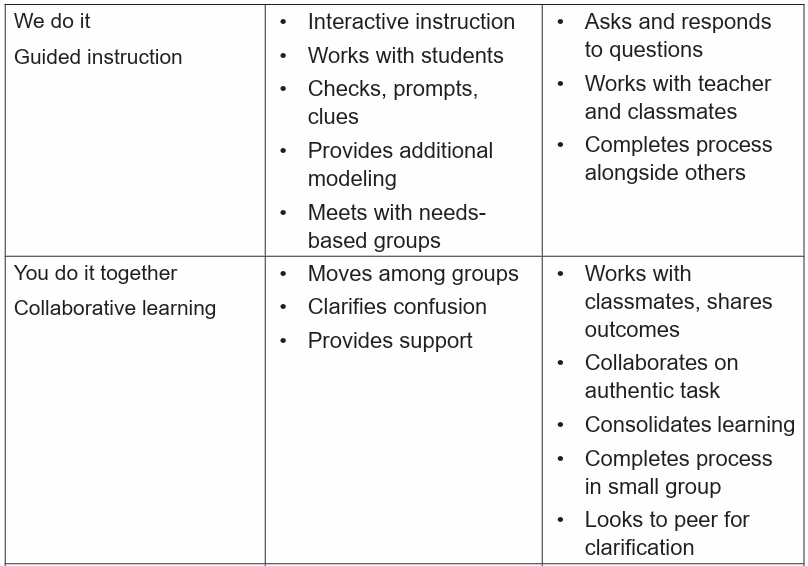
This gradual release of responsibility is sometimes called “I do, We do, You do”.
This model proposes a plan of instruction that includes demonstration, prompt, andpractice.
At the beginning of a procedure or when new material is being introduced, the
teacher has a prominent role in the delivery of the content. This is the “I do” phase.
But as the student acquires the new information and skills, the responsibility of
learning shifts from teacher-directed instruction to student processing activities. In
the “We do” phase of learning, the teacher continues to model, question, prompt
and cue students, but as student move into the “You do” phases, they rely more onthemselves and less on the teacher to complete the learning task.
2.4.1.1.The roles and responsibilities of teacher and student at every phase.
The table below shows the roles and responsibilities of teacher and student atevery phase.

2.4.2. Attention to special educational needs specific to skills lab practice
Teachers need to:
• Pair a student who has a disability with a friend. Let them do things together and
learn from each other. Make sure the friend is not over protective and does not do
everything for the student. Both students will benefit from this strategy.
Below are strategies related to each main category of disabilities and how to deal
with every situation that may arise. However, the list is not exhaustive becauseeach student is unique with different needs that should be handled differently.
2.4.3.Strategies to help student with physical disabilities:
• Do activities together with the student.
• Be patient! If you find that the student takes longer than others to learn or to
do an activity, allow more time.
• Gradually give the student less help.
• Let the student do the activity with other students and encourage them to help
each other.
• Divide the activity into small achievable steps.
• Remember to praise and say ‘Well done’ when the student learns somethingnew or makes a strong effort.
2.5.Guidance on assessment
The various assessment will be undertaken to assess students in skills laboratory :
OSCE:
The objective structured clinical examination (OSCE), is designed to assess the
student ability to competently apply the professional nursing or midwifery skills and
knowledge into real practice. It is set at the level expected of nurses and midwives
as they enter the profession. This means that you must show that you are capable
of applying knowledge to the care of patients.
The examination is testing the student ability to apply knowledge to the care of
patients rather than how well you can remember and recite facts. All of the scenarios
and any questions relate to current best practice and you should answer them in
relation to published evidence and not according to local arrangements.
Time for OSCE: The OSCE will be scheduled at the end of each unit theory,
organized to assethe students competencies using different stations according to
the course units.
Equipment : All equipment needed to complete the station successfully,accordingto the station requirements.
