UNIT 2: FOOTBALL
2.1. Key unit competence:
Perform various individual skills and team tactics needed to play effective football.2.2. Prerequisite (knowledge, skills, attitudes and values)
Students of senior five will learn better football if they have developed basic
techniques of playing football in Ordinary Level and in senior four.2.3. Cross-cutting issues to be addressed
Gender
In teaching and learning process of football, the teacher must prepare and provide
physical activities that engage both girls and boys equally to exploit their full
potential and talents without any discrimination or prejudice.Inclusive education
The teacher as a facilitator he/she must consider different special education needs
and select Football activities to adapt his teaching approaches to students. This
creates a positive attitude and helps all students to participate actively and develop
their competence levels.Financial education
The teacher should integrate Financial Education into his teaching/learning
activities by providing the local and no cost teaching material where is possible. He/
she must encourage students to make their own materials that can help them to
develop competences not only in sport at school but also in their life. The teacher
must explain the financial implication of some sports.Standardization culture
The teacher must choose and select the standardized materials to use in his/her
teaching/learning process of football.
It is necessary to provide appropriate materials required to the levels of learners and
help them to develop culture of checking and using the qualityof sport materials for
the competitions before using them in order to prevent injuries and other accident.Environment and sustainability
The teacher should provide materials and deliver the lesson by encouraging
learners to protect the environment and well use of materials. The teacher helps
them to develop the spirit of keeping safe the environment in which they use in
sports activities by avoiding waste on the playground.Peace and values education
The teacher helps students to develop fair play and social values by avoiding violence
and conflict in the football game and by setting clear and relevant instructions. He/
she should provide the activities that help students to develop their competence
peacefully.Comprehensive sexuality education
The teacher provides football exercises and sets instructions that prevent sexual
harassment or any kind of gender-based violence like sexual abuse and physical
contacts oriented to the sexuality intention.Genocide studies
While conducting football exercises a teacher should take a time to explain to
student show sports should be used to fight against Genocide ideology and how to
prevent it. For example, to organize Genocide memorial tournaments at school and
give the message related to the Genocide.2.4. Guidance on introductory activity
Before introducing the lesson one of this unit, you must introduce the whole unit.
The teacher as a guide, facilitator and expert, ask questions or give activity related
to tactics used in playing football in order to help them to predict what to be learned
in the whole unit.2.5. List of lessons/sub-heading

Lesson 1: Playing positions and general offensive and defensive tactics
a) Learning objectives
The students of senior five will master football playing positions and develop general
tactics in attack in football.b) Teaching resources
– Playground of football
– Stopwatch / Watch
– Whistle
– Chasubles
– Football balls
– Cones
– Movable goalposts (additional
goalposts)
– Ballsc) Prerequisites/Revision/Introduction:
Students of senior five will perform better in playing positions and offensive tactics if
they can execute basics techniques of playing football learned in in ordinary level and
senior four and have developed basic physical conditions for an athlete.d) Learning activities
Opening discussions
– Ask questions about playing positions in football learned in senior four and in
ordinary level.
– Let students present their findings.
– Invite students to start warm up exercises.Warm up exercises
– Let students perform general warm up exercises and specific warm up based
on the most body’s parts to use in football and stretch their muscles properly.
Emphasize exercises like jogging around the playground progressively,
sideways facing to a marked point, sideways back to back to the marked
point, forwards and backwards to the marked point, high knees, heel flicks,
inside and outside leg lunges, jog and sprints and header at the marked point.
– Guide them while performing warm up and stretching exercises Lesson body
– Ask the students to recall the playing positions in football. Guide them while
practicing the exercises.
– Tell students that in football, basic positions are based on each position
assigned a number and involve the following positions/roles that correspond
to the number assigned to them as follow:
Remind students that:
– Every position has a specific task to accomplish which corresponding to its
name and its position number even though formations should vary based on
the strategy of the coach/teacher /trainer.
– Let students take different positions on the football court individually.ACTIVITY 1
– Select 11 students to be ready to take any position on the court.
– Tell other s t u d e n t s to be attentive in order to checkout his/her teammate
has taken the right position (goalkeeper, defenders, midfielders, attackers).
– Request one student to take any position of your choice, ask other students to
confirm whether the position taken is right or wrong.
– Continue in such ways until all positions finish.General offensive and defensive tactics
Tell students that even though there are playing posts seem to offensiveor defensive,
in modern football every player can be offensive or defensive at any time during the
game situation based on playing actions.Explain five attacking principles used in playing football which are:
– Penetration,
– Support,
– Mobility,
– Widening the playground,
– Creativity or improvisation.Tell student that general principles of attacking during playing football
game are:– All players must help their teammates.
– Everyone participates in attack.
– Everyone participates in defense.
– Remember that defense starts as soon as the ball is lost.Tell student that main individual tactics for attacking during playing
football game are:– Always try to be in an unmarked position (free).
– Pass and get into position that enable to help a teammate.Avoid unnecessary confrontations.Remind students that when faced by an
opponent while attacking, they should:– Take the ball to the opposite side from your opponent.
– Shake off your opponent by quick bursts, feints and sudden changes of
direction.
– Take the ball to the left and then pass to the right and vice versa.
– Do not carry the ball too far; short and long passes should make progress.
– Use cross-pitch balls to a teammate in a good position.
– Avoid playing down the center in their own half; if the ball is lost, it could be
dangerous.
– Do not pass the ball into crowded areas, play it to a teammate who is in free
space.
– Always support a teammate who has the ball.
– Run to meet the ball; do not wait for it to come to you.
– Do not let the ball go past without controlling it.
– Do not waste time with fancy footwork.
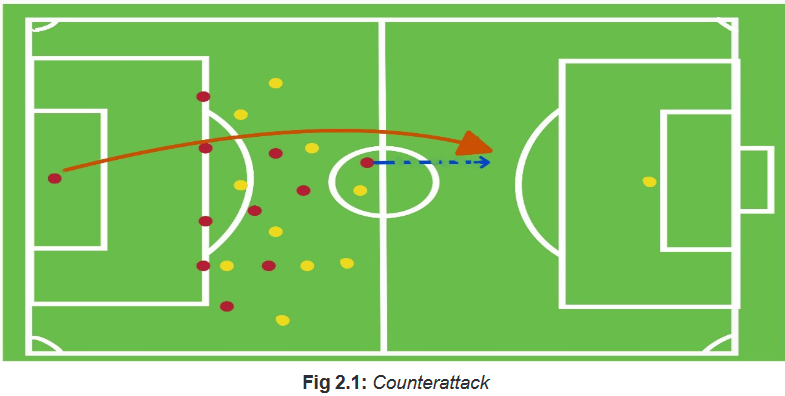
– Play in a sensible, simple, useful manner.Remind students that counter attacks may be used while offensive tactics.
ACTIVITY 2
4 vs 2 to 2 vs 2
Activity organization
Play in a total area of 18m x 27m or two areas of 18m x 14m.Description of the activity
Play starts with a 4 vs 2 possession game. When the two inside players win the ball,
they play 2 vs 2 in the other half to try and score. Should the two defenders (black)
win the ball, they quickly play the ball back to the original grid, and the two original
defenders return to the grid defend.Variations
– Limit touches to attacking team.
– If waiting defenders (black) allows a goal, they become defenders in the first
zone.Teaching points to consider
– Possession team (red) maintain possession of the ball by offeringgood support.
– Defending (black) defend as unit. Limit penetrating passes. Once the ball is
won, transition quickly try to score.
ACTIVITY 3
(8 vs 5 to counter goals)
Organization of the activity
7 + Goalkeeper Vs 5 on a field 23 x 45 m.Description of the activity
White team attacks the goal. Red team plays to the small goals at midfield. Red
Team must transition to goal within four touches, and Red team must play two
touches to small goals.Variations
Adjust touch limits to suit age/skills level of the students.Teaching points to consider
Constant transition and awareness. Defenders become attackers and attackers
becoming defenders.
ACTIVITY 4
Organization of the activity
Three even numbered teams, two goals with keepers, with the field set up into three
zones.Description of the activity
Team 1 will attack, Team 2 will defend, and Team 3 will wait. Team 1 attacks the
goal and if Team 2 wins the ball, they attack team 3. Teams may regroup in the
middle zone. If attacking team scores, theymaintain possession and attack the third
team.Variations
Attacking team in the middle zone is allowed no time to gain their shape.Teaching Points to consider
– Possession when the attack is not on.
– When possession is lost, transition into defense.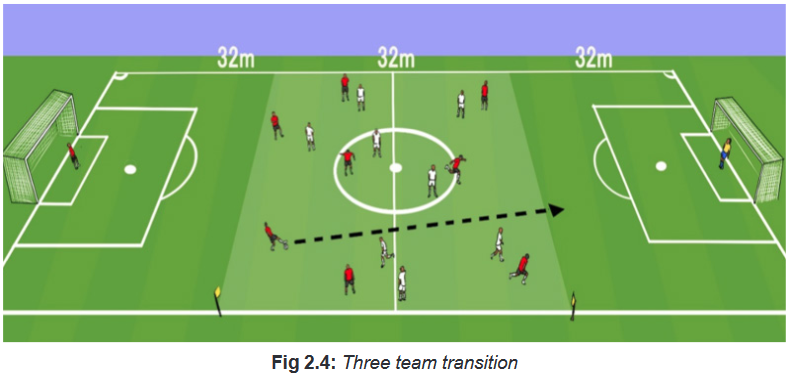
Attacking formations in football
• 4-3-3 formation
The most popular attacking formation in football is 4-3-3 and it is used by most of
the teams during football matches. Four defenders, three midfielders and three
attackers compose it. The 4-3-3 formation is the most used formation during the
matches. This is because it is a good attacking formation, which also has a solid
back-four defense. The job of the four defenders is to keep it tight, secure at the
back, and get the ball forward to the midfielders as quickly as possible.During a soccer game, the three midfielders (who will play through the center) will
look to get the ball to the three front players.The three attacking players can be used in different ways. For example, you could
have three strikers playing close together.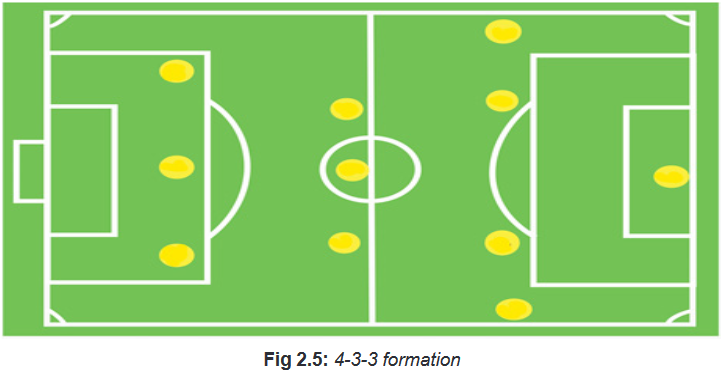
• 3-4-3 formation
The key to this formation is to ensure your team has three attributes.They are:
A. 3 strong central defenders.
B. 3 competent attacking players.
C. 2 good wingbacks who can run and intervene in attacking and defending.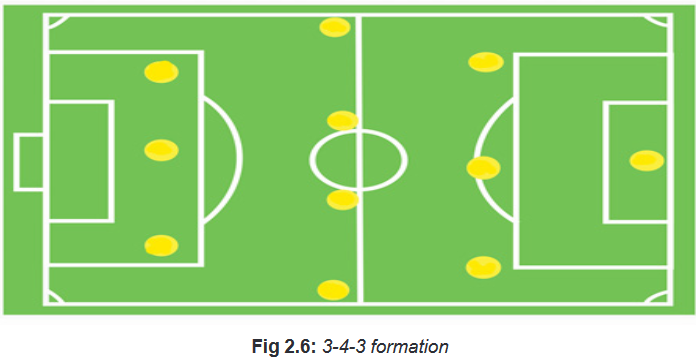
• 4-4-2 formation
In this attacking system
– 4 stands for 4 defenders.
– 4 stands for 4 midfielders.
– 2 stands for 2 forwards (strikers).
Let students apply formation systems learned in a normal football game.
APPLICATION ACTIVITY
Counter attack
One team for 4 students another for 2 students. Instructions
– Put your students in teams as indicated.
– Allow everyone to have an experience on the exercises.
– Help them to manage well their time.
– If you have many balls you can work in more teams and use the whole pitch
divided into parts according to the measures given in instructions.
– Play in a total area of 13m X 18m- two areas of 13mx 15m.Description of the activity
Play starts with a 4 Vs 2 possession game. When the two inside players win the
ball, they play 2 Vs 2 in the other half, to try and score. Should the two defenders
win the ball, they quickly play the ball back to the original grid, and the two original
defenders return to the grid to defend.Variations
– Limit touches to attacking team.
– If waiting defenders allows a goal, they become defenders in the first zone.Teaching points to consider
– Possession team maintains possession of the ball by offering good support.
– Defending team defends as unit. Limit penetrating passes. Once the ball is
won, transition quickly try to score.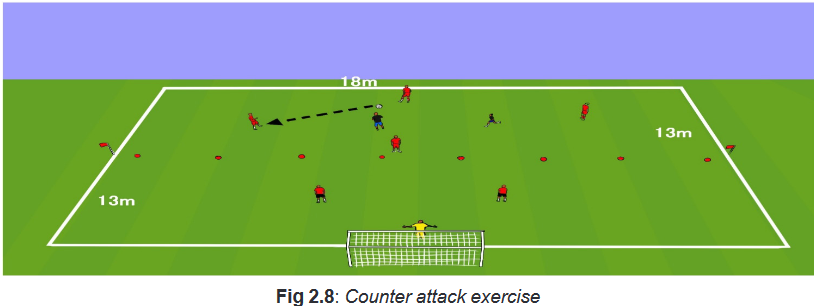
Cool down exercises
Let students do light exercises and stretch their group of muscles by insisting on
most used parts.
– Randomly, one of students leads cool down exercises.
– Guide them while stretching their muscles systematically.
– Help them/demonstrate/correct where is necessary.Some exercises after this intense workout may include:
– Easy jogging or walking around the playground
– Deep breathing during the exercise to help oxygenate the system
– Static stretching of all the body partsClosing discussions
• Reflect
– Which challenges did you face while initiating counter attack in football
exercises?
– What went well during the workout?• Connect
– What are the skills do you need in order to play an offensive game
tactically?• Apply
– What is the usefulness of offensive play mind-set in football?
– How will you use the learned offensive tactics in football in next days?Lesson 2: Set pieces used in offensive tactics
a. Learning objectives
To develop offensive tactics during set pieces in football.b. Teaching resources
– Playground of football
– Whistle
– Football balls
– Watch/Stopwatch
– Cones
– Balls
– Chasubles
– Additional goalpostsc. Prerequisites/Revision/Introduction:
Students of senior five will learn better offensive tactics in set pieces if they can
execute basics techniques of playing football learned in ordinary level and in senior
four and have developed basic physical conditions for an athlete. These basic
techniques include heading, kicking the ball, blocking, dribbling, and stopping the
ball.d. Learning activities
Opening discussions
– Ask the students the questions about set pieces in football game learned in
senior four and in ordinary level.
– Invite students to start warm up exercises.Warm up exercises
– Let students perform general warm up exercises and specific warm up
based on the body’s parts to be used in playing football and stretch their
muscles properly. Emphasize exercises like jogging around the playground
by increasing the speed after each series, sideways facing to a marked point,
sideways back to back to the marked point, forwards and backwards to the
marked point, high knees, heel flicks, inside and outside lunges, jog and
sprints and header at the marked point.
– Guide them while performing warm up and stretching exercises.e. Lesson body
Explain to the students set pieces and their importance in playing football game.• Description of set pieces
Set pieces in football
A set piece is the action of putting the ball back into play when the ball is out of play
(the ball is dead). Set pieces involve:
• Importance of set pieces in football game
Set pieces can give to a team an opportunity to score. Some teams are said to
be good at set pieces when it comes to be offensive. The other ones are bad in
defending against balls from set pieces. A good coach knows how to use these
opportunities to create chances to score from set pieces by using different tactical
systems. One of the ways of scoring from set pieces is to play very quickly without
giving the opponent the time to position well in defense.ACTIVITY 1
During the practical lesson, help the l students to do many repetitions on executing
ball from set pieces, the teacher will guide, demonstrate and correct where
necessary. You can use videos from youtube.com to illustrate some complicated
tactics if you are not able to do demonstrations or to understand.Free kicks
Explain students that while executing free kicks, they can use two types of free
kicks: direct and indirect kick.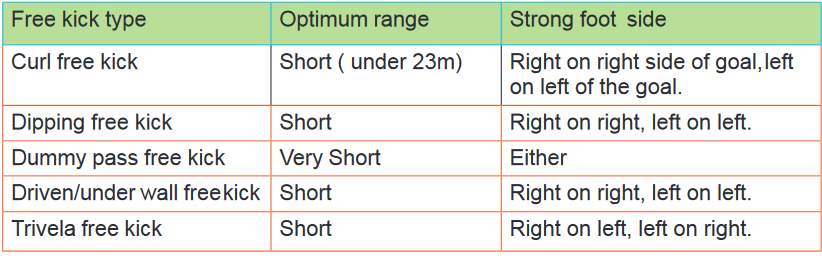
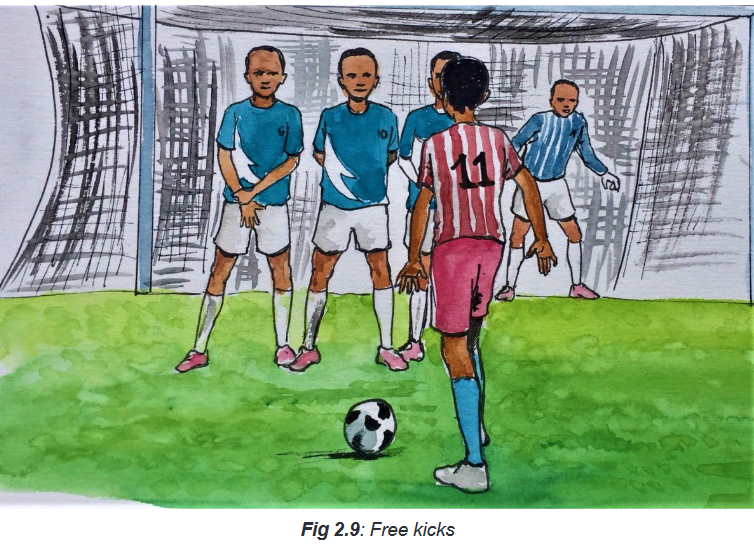

Penalty kick
While teaching tactics of taking a penalty, emphasize that the research has showed
that:
– Targeting to the upper third of the goal will maximize the chances to score.
– The kicks to the middle third of the goal will decrease the chances to score
– The kicks to the lower third will decrease the chances to score.Remind students that:
They must train themselves to kick targeting the upper third of the goal. It is better to
remember that from there is also a risk that the ball may be kick out of the goalpost.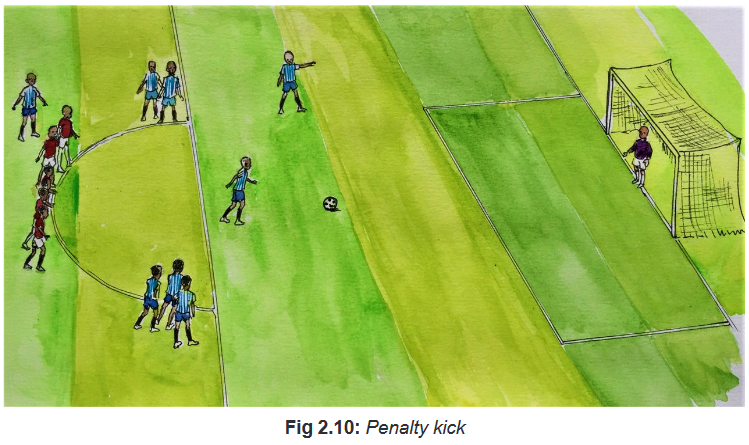
Corner kick
Explain students that there are four types of corner kick according to the area they
are kicked to. In teaching, you will ask the students to try each type and to score
from these different balls.
– The back post corner kick.
– The front post corner kick.
– The penalty spot corner kick.
– The short lay-off.
The kick off
A team can initiate a powerful attack from the kick off. From the kick off you can
initiate a counter attack from a long ball, you can retain ball position and attack. A
more direct strategy when kicking off is to progress up the pitch straight away in order
to threaten the opposition goal or to shift into the opposition half withthe whole team.Application activity
The students form teams according to the personal ability (strengths and weaknesses
of the students) and the resources available
Students are asked to:
– Play balls from set pieces.
– Execute the balls in set pieces.
– Create tactical moves in set pieces’ balls.
– Create different offensive tactical exercises in set pieces.
– Create scoring opportunities from set pieces’ balls.Cool down exercises
– Let students do light exercises and stretch their group of muscles by insisting
on most used parts. Some exercises after this intense workout may include
easy jogging or walking around the playground, deep breathing during the
exercise to help oxygenate the system, Static stretching of all the body parts.
– Guide students while stretching their muscles systematically.
Closing discussions• Reflect
– Which challenges did you face while executing set pieces (free kicks,
– corner kick, and penalty kick) in football?
– What went well during the workout?• Connect
– What are the skills do you need in order to score from set pieces during the
game tactically?• Apply
– What is the usefulness of set pieces in football?
– How will you use these learned tactics in football in next days?Lesson 3: General defensive tactics and defending at set pieces
a. Learning objectives
The students of s e n i o r f i v e will develop defensive tactics during set pieces in
football.b. Teaching resources
– Playground of football
– Cones
– Whistle
– Chasubles
– Football balls
– Additional goal posts
– Watch/ Stopwatch
– Ballsc. Prerequisites/Revision/Introduction
Students of senior five will learn better defensive tactics in set pieces if they
can execute basics techniques (heading, kicking the ball, blocking, dribbling, and
stopping the ball) of playing football learned in senior four and in ordinary level and
have developed basic physical conditions for an athlete.d. Learning activities
Opening discussions
– Ask the students the questions about set pieces in football game learned in
senior four and in the previous lesson.
– Introduce the lesson of the day.
– Invite students to start warm up exercises.Warm up exercises
– Let students perform general warm up exercises and specific warm up based
on the most used body’s parts in football and stretch their muscles properly.
Emphasize exercises like jogging around the playground by increasing the
speed after each series, sideways facing to a marked point, sideways back to
back to the marked point, forwards and backwards to the marked point, high
knees, heel flicks, inside and outside leg lunges, jog and sprint and header at
the marked point.
– Guide them while performing warm up and stretching exercises .e. Lesson body
Explain students that set pieces can give to a team an opportunity to score, but also
it can help a defending team to initiate a counter attack if well organized in defense
and with good defending tactics.• Defending a ball from a corner kick
Tell students that tactics of defending a ball from the corner kick to teach to the
students are:• Man marking defence
In man marking defence, a player must make sure to be at the right side of him/her
and the goal. When you are on the wrong side, it makes it harder to defend and it will
be easy for the opponent to score the goal.Remind students to be sure to communicate with their teammates, to make sure that
the right player is marking the right player and no confusion happens.• Zonal marking
In zonal marking defence tactics, during defending the corner kick, all players have
their own defensive zone in which they are supposed to defend the ball when it
comes to their zone. It is better to position at the edge of the 5.5 m box because
that is the most frequent and most dangerous position for an offensive player to head
a ball into the goal. Tell students never clear a ball to the middle. There will always
be an opponent at the edge of the area and you do not want him to get an easy shot
on goal. When clearing the ball, play it to the side of the field. It also makes it a lot
easier to counter-attack since there will most likely be no opposing players there.
Remind students that most teams use a mix, with more players defending zone
than defending the man. Teams do this to try to benefit from both types of marking
and concede as fewer goals from corner kicks as possible.• Defending a ball from a free kick
Tell students that the most used and real defending tactic against the balls from free
kick is to build the wall.• How to build the wall?
The first player in the wall should position him/herself about eight paces from
the ball in a direct line between it and the near post, facing the goal. The remaining
players build a wall towards the opposite post. The players follow the first player’s
lead as the goalkeeper repositions him. The goalkeeper might position this player
up correctly based on where the ball is and the side or position he/she wishes to be
covered by the wall. If the player standing over the ball is supposed to be in the wall,
they should call for a replacement. Remind students that the referee should have
informed everyone that the taker must wait for the whistle, allowing the player to take
up his or her position in the wall. If a player that forms part of the wall is substituted,
they must tell their replacement what number they are to take in the wall.
The aspects to be taught by the teacher during the practical lesson
– When a free kick is conceded the player who committed the fault must stay
nearest the ball to prevent the opponent to play very quickly and allow his/her
teammates to position well in defending positions.
– The goalkeeper must be sure that the free kick cannot be taken quickly
– Once the goalkeeper is sure that the free kick cannot be taken quickly, he/ she
calls players to build the wall (in general not exceeding four players).
– Once he/she has positioned the wall, the goalkeeper should position him/
herself in the unprotected part of the goal. Make sure he/she knows which part
of the goal he/she is defending and where he/she should stand when the kick
is taken.Remind students that defending tactics in other set pieces rather than the corner
kick and the free kicks, requires only the ability to read the game and to react quickly
according to the opponent actions.B. General defending tactics in football
Explain students that generally the purpose of defending in footballis to regain the
possession of the ball once you have lost it and to prevent the opponent to score.
Those defending tactics are as the follows:
– Man to man making.
– Zone marking.
– Stealing the ball by a block.
– Tackling
– Clearing the ball by a kick or by a header.
– Protecting the ball.
– Committing a tactical foul.Tell students general defending tactics for a good defender
– Giving no time to react.
– Correct Positioning.
– Patience waiting for mistakes.
– Anticipating their next move.
– Using your body correctly.
– The eyes on the ball and the player.
– Always play to the outside.
– No risking of leaving the ball behind.
– Impose yourself with security.– Always on your toes.
– Covering the ball.
– Perfect slide tackles.
– Intimidating attackers and prevent them from using their strengths.
– Using your strengths.
– Moving attackers into congested areas.
– Tactical fouls are needed where is necessary.In details, explain defensive tactics and demonstrate how to apply them on thecourt.
• Protecting the ballRules to follow while protecting the ball in football:
– The first rule of protecting the ball is to avoid turning your back on the
– incoming defender if possible.
– The second rule of protecting the ball is to take control of the situation
yourself.
– The third rule of protecting the ball is to be aggressive in holding onto the ball.Remind students that the basic protecting posture in football:
– Knees bent and bottom down to lower centre of gravity.
– Turn sideways with weight balanced on both feet.
– Arm/elbow of side, which will make contact tucked well in to protect ribs.
– Keep other arm spread out for balance.
– Time the step across so that shoulder aggressively makes contact with
opponent, transferring weight to front foot so that back foot is free to pass/
control the ball.
TASK / ACTIVITY
In pairs, students perform the following exercise.
– One student has a ball another has the task of stealing the ball.
– If a player with the ball is approaching the stealer, he/she must be in ball
protection position.Teaching point to consider
– Keep head up and be aware of coming stealers.
– Keep the ball from sharks by accelerating into space.Variation
– Switch roles of students.
– The stealers have four seconds to try to get the ball.Tackling in football
Tackling is an important skill in football regardless of your playing position. Tackles
are used to regain possession of the ball for your team and are sometimes seen as
critical particularly in defensive positions when the opponent are in an offensively
advantageous position.Tell students that there are two types of tackles:
– A standing/block tackle as its name implies is one where you remain on your
feet.
– The other tackle is when you are off your feet, also known as the sliding
tackle.Explain
students that tackling should be made by:
Front block tackle
• Position of the ball
Tell students to ask themselves how far the ball away is. This allows you to assess
the timing to stick their foot out and dispossess their opponent by taking the ball
away from them with minimal physical contact.• Position of their own feet
Ask them to lead them with their non-primary foot. Their weaker foot will be in front
while their primary foot will be behind. This allows them to dispossess the opponent
or quickly begin running after them.• Position of their body
Ask them to keep their body low, and always slightly bending their knees, as it will
lower their Centre of gravity. This will give them additional balance and allow them
to turn the other ways more easily.• Lead with the inside of their foot
This will allow more control and can pull back their foot remind them to pull back the
ball to draw a foul from them. This ensures they are not fully committed to a tackle like
a toe-poke, and be able to still give chase if they manage to get past them.Side block tackle
The side block tackle is used when the opponent is in full flight or has managed to
move pass them, resulting in themselves no longer facing them directly. They now
have to attempt to chase them down and make the tackle from the side.• Position of the ball
Similar to the front block tackle, gauge the distance between the ball, their feet and
the speed at which their opponent is travelling to time their tackle.• Position of your own feet
Once they are beside their opponent, they will have to drop their nearest shoulder
to them and lean into them to exert pressure.• Position of your body
Keep their body low once again to lower their center of gravity, allowing more
stability and strength.Remind students that during tackling:
It is extremely important to remain on your feet because if you fall down and the ball
breaks free, your opponent will regain control of the ball and there is an immediate
gap in your team’s shape which the opposition team can exploit. The fact that you
remain on your feet is the main reason why standing and block tackles are preferred
over slide tackles. As with all other techniques in football, always lock your ankle
before performing any action. Football injuries can be avoided and keeping ankles
locked is one of the best ways to avoid picking up unnecessary injuries.Let students apply tackling tactics during game play situation.
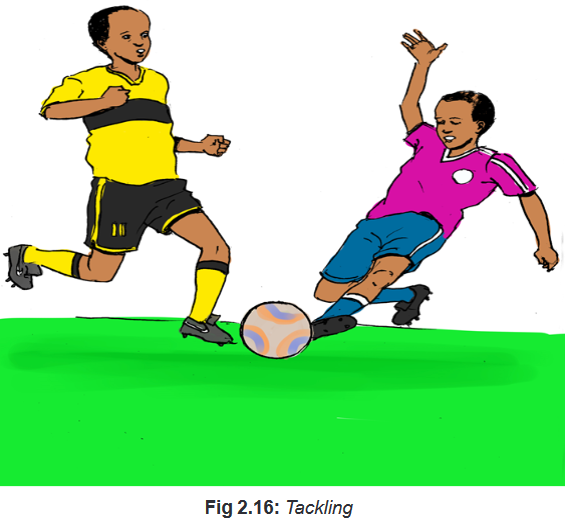

C. Man to man defence
Man to man, marking simply means that all your teammates are responsible for keeping an ey
on a particular opponent.D. Zonal marking defence
Every midfielder and defender is given a particular zone on the field to cover. It is crucial th
each one of your teammates fulfil their duties with 100 % concentration.
Remind students that while defending, they should:
– Always keep between the opponent and your goal.
– Always watch the opponent and the ball.
– Try to counter the opponents’ attacking build-up as soon as possible by marking.
– Do not give their opponent space.
– Slow the opponent down when they run with the ball (shutting down).
– Try to get to the ball before the opponent, or otherwise hinder them when they receive th
ball.– Mark the opponent on the side of the ball, in other words the side where he/
she will make the pass.
– When a high ball comes in, jump a moment earlier than the opponent
(timing of the ball).
– Do not dribble in their penalty area.
– Avoid cross-pitch passes from the outside to the inside.
– Play on the outside along the touchline.
– If he/she loses the ball, strive to recover it.
– Avoid ineffective tackles; do not throw yourself at an opponent who has the
ball.
– Never turn your back on an attacker
– Push the opponent towards the touchline.
– Carefully follow play, even if the ball is far away.
– A good defender never gives up.
APPLICATION ACTIVITY
– Composing teams among the students according to their number and the
resources available.
– Setting exercises of different types of defending tactics in football.
– Create different defensive tactical exercises in set pieces.
– Students are asked to execute the balls in set pieces.
– Students are asked to defend balls from set pieces.
– Be familiar with the defensive tactics in set pieces.
– Evaluate individual students. Progress/performance.
Cool down exercises
– Let students do light exercises and stretch their group of muscles by insisting
on most used parts. Some exercises after this intense workout may include
easy jogging or walking around the playground, deep breathing during the
exercise to help oxygenate the system, static stretching of all the body parts.
– Guide students while stretching their muscles systematically.Closing discussions
• Reflect
– Which challenges did you face while defending a ball from a corner kick/ free
kick?
– What are the qualities of a good defender?• Connect
– What are the skills do you need in order to avoid to concede a goal from set
pieces during the game tactically?
• Apply
– What is the usefulness of the learned tactics of defending set pieces in
football?Lesson 4: Safe play in short football match to apply themastered tactics
a. Learning objectives
The students will apply the learned tactics in game situation with confidence.b. Teaching resources
– Playground of football
– Cones
– Whistle
– Chasubles
– Football balls
– Goalposts
– Watch/ Stopwatchc. Prerequisites/Revision/Introduction:
Students of senior five will perform better safe play in a short football match to apply
the mastered tactics if they are able to remember and use learned defending and
offensive tactics learned whether in set pieces or during the game situation.d. Learning activities Opening discussions
– Ask the students to brainstorm different offensive and defending tactics learned
in the previous lesson.
– Introduce the topic of the day.
– Invite students to start warm up exercises.Warm up exercises
– Let students perform general warm up exercises and specific warm up based
on the most used body’s parts in football and stretch their muscles properly.
Emphasize exercises like jogging around the playground by increasing the
speed after each series, sideways facing to a marked point, sideways back to
back to the marked point, forwards and backwards to the marked point, high
knees, heel flicks, inside and outside leg lunges, jog and sprint and header at
the marked point.
– Randomly one student to lead the stretching and guide him/her where
necessary.e. Lesson body
GAME SITUATION
Teacher avails materials to be used during this safe play including balls (at least
2) chasubles (11 for each team), whistle, watch, chronometer, flags and cards
(optional). Request students to form two balanced teams (balance between
defenders, attackers and midfielders). Let all students participate in a play as either
a court player or substitute. Manage well the time in order to give every student
the chance to play. Correct students mistakes where is necessary. Within this game
situation students are requested to play by avoiding any unwanted risks or dangers
with caution and prudence.Description of the activity
– Students will play a football game where they will be asked to play a normal
game by using offensive tactics (counter attack, penetration, and set pieces)
and defensive tactics (tackling, covering/protecting the ball, man to man
and zonal marking) learned and they are requested to create more often set
pieces’ situations so as the teacher can evaluate how they have mastered the
tactics of defending and offending in set pieces. Here the teacher will observe
how the defending team defends a ball from a corner, a free kick, and how
attacking team tries to score from this ball.
– The teacher will observe that the students take good positions during the
game and keep good attitudes (emphasis on positioning during set pieces for
both defenders and attackers).
– Once attackers loose the ball they become defenders and defenders become
attackers (change of game situation).
– The teacher has to take notes of what is going well and what is not going
well to help him/her during the final discussion.
– The teacher may give correction immediately during the play when it is
necessary.
– The teacher will evaluate individual student progress/performance during the
safe play and provide feedback after the game situation.Cool down exercises
– Let learners students do light exercises and stretch their group of muscles
by insisting on most used parts. Some exercises after this intense workout
may include easy jogging or walking around the playground, deep breathing
during the exercise to help oxygenate the system, static stretching of all the
body parts.
– Guide them while stretching their muscles systematically.
– Help them/demonstrate/correct where is necessary.Closing discussions
• Reflect
– Which challenges did you face in applying the mastered tactics in game
situation?
– What went well during the safe play applying the mastered offensive and
defending tactics?• Connect
– What are the skills do you need in order to play safely with confidence and
applying correct defending and offensive tactics?• Apply
– What is the usefulness of the learned tactics in football?
2.6. Summary of the unit
Playing positions and general offensive tactics
In football, there are different formations that are used during the matches, but
there is no ideal formation. Adopting a given formation depends on the qualities of
your players and that of your opponent. A given system also may depend on the
game philosophy of the players and of the coach. In modern football, every player
can score a goal and every player can defend. Overall, we can say that the roles of
players are summarized as in the playing positions below.• Goalkeeper: The main aim of a goalkeeper is to stop the opposing team from
scoring a goal.
• Defenders: The defenders are positioned in front of the goalkeeper and their
aim is to stop the opposing team from entering into their goal area.
• Outside fullback/winger back: They play on the left and right flanks and
• see that the ball does not pass over them.
• Central Defenders (Central back and the sweeper): They are positioned in
the center of the field and are supposed to cover the leading goal scorer of the
opposition’s team.
• Midfielders (Central midfielders, defensives midfielders, attacking
midfielders, wide midfielders): They are the link between the defenders and
attackers. They need to be fit and physically very strong than other players on
the field as they are the players who run maximum time of the game all around
the field. Their responsibility is to enter the opposing team’s area and see that
they defend them when the opposing team retains the ball.
• Forwards/attackers (Center forwards, second strikers, winger attackers):
Their main aim is to score goals or to create an easy situation for their
teammates to score a goal.• Center Forward: The most tactful, dangerous and strong player of the game.
He/she is also called a striker. Strikers are the leading goal scorers in the
game.Offensive tactics in set pieces
Set pieces refer to a situation when the ball is returned to open play after the ball
was dead.These are corner kick, free kicks; kick off, goal kick, penalty and throw-ins. All these
set pieces when they are well used they may result into a powerful goal scoring
opportunities.General defensive tactics and defending at set pieces
In set pieces there, some positions to take in defense in order to avoid con- ceding
a goal from set pieces’ ball. Some of tactics involve man mark and zone marking,
tackling, building a wall, blocking etc.Safe play in short football match to apply the mastered tactics
After studying different tactics of defending and attacking, the students can now
apply in game situations the learned tactics whether in defense or in attack by using
individual and team tactics in order to win the game.2.7. Additional information for teachers
Terminologies used in offensive tactics in football• Tactics
Those are plans, which are set up for a specific purpose during a match. Essentially,
the tactics in football involves dropping deep, allowing the opposition to have the
ball and come forward with it, committing players forward and leaving gaps in behind
as they go. The aim is to take the ball off the opposition, exploiting the space left to
attack and score.Applying different tactics in football needs some important skills to master which
include ball control, passing, dribbling, shooting and defending.Tactical awareness is the ability to know your role and have positional awareness
on the field, and possessing the ability to make good decisions.• Counter attacking
Series of actions involves a team withdrawing players into their own half but
ensuring that one or two players are committed to the attack. The idea is to try to get
strikers isolated from the defenders by remaining hidden on the halfway line, and to
create space for a quick break.• Game intelligence
A player’s ability to make smart decisions on the pitch and make them quickly.
Game intelligence requires three skills: spatial awareness (ability to see space
clearly across the entire pitch and utilize it to his/her advantage), tactical knowledge
(knowledge of the nature and structure of the game) and the risk assessment (having
in mind that certain aggressive decisions could lead to loss of ball possession).• Creating free spaces
When an attacker beats one defender or more defenders, it gives him/her and
teammates a free space to play and create chances to score.• Individual tactics
Those are simple principles that a player learns in order to make the best decisions
during a particular passage of play.• Plan of a football training sessions
As teacher of physical education and sports subject, the first thing to teach your
students is to know how to plan a football training session.
Have in mind that failing to plan is planning to fail. One and important thing in
teaching physical education and sport subject is to plan practice in writing.• Factors to consider in planning football training sessions:
– Capabilities of the players
– Number of players
– Length of the training session
– Field space available
– Weather conditions
– Objective of each activity
– Approximate time per activity
– Weekly cycle
– Include on the Plan
– Topic
– Age group
– Training equipment
– Activity description
– Activity diagram
– Key coaching points
– Guided discovery• Guidelines for the length of a training session based on age:
– U6 = 45 minutes
– U8 = 45 to 60 minutes
– U10 = 60 to 75 minutes
– U12 = 75 minutes
– U14 = 75 to 90 minutes
– U16 = 90 minutes
– U19 = 90 to 120 minutes• Key activities to plan for in advance some of them must be shown in the
steps of your lesson plan:
– Define learning objectives
– Organize materials to use
– Plan demonstrations
– Focus on timing
– Cooling down exercises
– Warm up drills
– Stretching drills
– Techniques and tactics to teach
– Include evaluation2.8. End unit assessment
– Set different exercises that help you to evaluate how the students apply
playing positions and general offensive tactics.
– Set different exercises that help you to evaluate how the students apply
offensive tactics in set pieces.
– Set exercises on general defensive tactics and defending at set pieces and
evaluate individual student performance.
– Organize a competition and evaluate how the students are playing respecting
the learned tactics during the game situation.2.9. Additional activities
2.9.1. Remedial activities
The students form teams according to their abilities and based on the resources
available. Students are asked to:
– Play balls from set pieces.
– Execute the balls in set pieces.
– Create scoring opportunities from set pieces’ balls.2.9.2. Consolidation activities
Form two teams of 11 players including goalkeepers and let play a normal game by
taking learned position. In case students are above 22, create more than two teams
to let all students to participate in the game. This exercise should be done not
more than 10 minutes. Select a student who is able to lead the game and be there
to support him/her and giving instructions, reminders or orientations to the students
while performing an activity.2.9.3. Extended activities
Organization of the activity
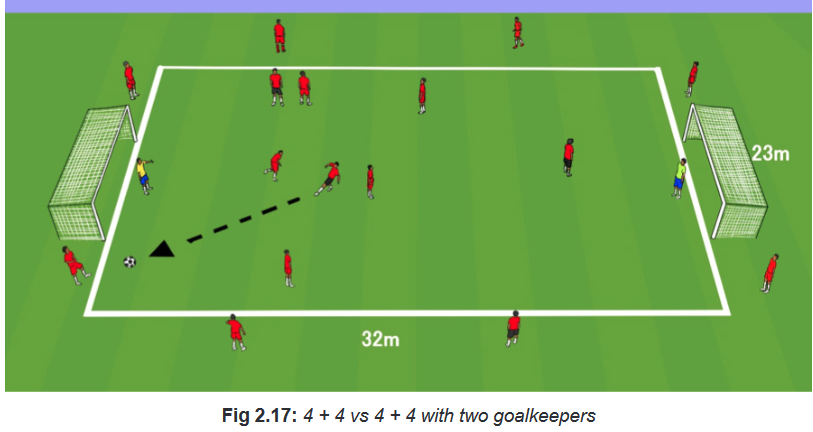
4 + 4 vs 4 + 4 with two goalkeepers in 30 x 22m areaDescription of the activity
Fast paced 4 Vs 4 game utilizing four neutrals on the outside of the playing fieldVariations
– Inside Players, two touch limit.
– Outside Players one touch limit.
– After winning the ball, must playing an outside player before scoring.Teaching Points to consider
– Shooting technique.
– Following up shots.
– Constant transition and awareness. Defenders become attackers and
attackers becoming defenders.