UNIT 8: FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Key Unit Competence: To be able to recognize the value of accounting in
managing the business.
Introductory activity
Financial Statements “The language of business decision making.”
James is a local entrepreneur in Huye town, he is so passionate and
committed to solve community problems in his home town and country, he
started a crafts business in Huye town, he moves to villages and collect crafts
from women groups and put them in his shop which is strategically placed
to target tourist heading to Nyungwe forest and Akanyaru Centre. He had
a book where he instructed his workers to be recording all sales for each
day, supplies and operating expenses. He believed that this is the best way to
keep track of all business transactions and a sure way to growth.
He wanted to expand the business and felt that 5 million Francs would be
enough. He was advised by his sister Uwera a student of entrepreneurship,
to approach investors and bankers and pitch his business and convince them
to provide funding to enable him to meet the business growth needs.
The investors only gave him 10 minutes to explain the profitability of his
business, the net financial position and the financial projection he needed
for the next 2 years, but this challenged him because the book he kept could
not easily provide this information in the given time, so he failed to convince
the investors and missed the funding.
James realized that he needed to have organized the financial information he
was keeping in a certain order that would enable him to make quick decisionsand make it more presentable and easy to explain to external stakeholders.
Questions:
1. What kind of documents James would have used to organize his
business’s financial information before presenting to investors?
2. What do you understand by financial statements?
3. What is the difference between financial statements and the books of
accounts? Give examples of each.
4. Why is financial information important to any business?
5. What is the purpose of financial statements in business?6. Distinguish between income statement and balance sheet
8.1. Meaning and importance of Financial Statements
Activity 8.1
Study the quote below and respond to the questions that follow.
1.What does the quote above mean to you as a student of
entrepreneurship?
2. Why does the author of the quote emphasize the reliability of the
financial statements?
3. What is the meaning of financial statements?
4. What financial statements should every entrepreneur use tocommunicate and manage businesses effectively? Why?
8.1.1. Meaning of Financial Statements
Financial statements are reports prepared by a company’s management to
present the financial performance and position of a business at a point in time.
Financial statements consist of four statements namely:
1. Income statement
2. Balance sheet
3. Statement of owner’s equity and
4. Cash flow statement
Generally, the most important financial statements are:
(i) The income statement / Financial performance statement or Trading, profit
and loss account.(ii) Balance sheet or the Financial position statement.
8.1.2. Importance of Financial Statements
Evaluation
It’s possible to assess future cash flows, and compare economic and financial
results year by year.
Internal Decision Making
The management can use all the information to guide and lead the company
through future performances.
Planning
Financial Report can be the basis to plan the activity, allocate resources, scheduleActivities etc.
External Decision MakingExternal users can evaluate the possibility to invest in the business or company
Application Activity 8.1
With clear examples, explain the reasons why the following people may
be interested in looking at the financial statements of any business?
-Employees
-Business Manager
-Entrepreneur
-Government-Investors
8.2 Income statement (Trading, Profit & Loss Account)
Activity 8.2
“An income statement is mostly important for well established companies
like Bralirwa, Rwandair, among others, a developing entrepreneur only
needs a book to record day to day transactions”
a. Do you agree with the above assertion? Explain your decision.b. What is an income statement?
Main elements of Income Statement
Income statement is a financial statement that reports a company’s financial
performance over a specific accounting period. Financial performance is
assessed by giving a summary of how the business incurs its revenues and
expenses through both operating and non-operating activities. The income
statement is made of two accounts:
• Trading account where the value of the gross profit is determined bydeducting the cost of goods sold from net sales i.e.
1) Trading account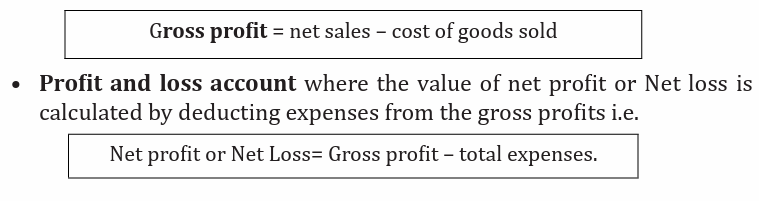
Trading account is an account which is prepared to determine the gross profit
or gross loss of the business concern. It shows the revenues from sales, the cost
of those sales or goods sold and the gross profit or loss from the specific period
ended. It is prepared after the preparation of the trial balance.
Items found in a trading account:
a) Sales: Refer to the value of goods which were bought for resale and have
been sold by the business. It is revenue earned from goods sold. They are
entered in the trading account for the purpose of calculating gross profit or loss.
b) Sales return: Roods that were previously sold but have been returned to the
business due to different reasons including but not limited to poor quality/defects, wrong pricing and delayed delivery.
c) Opening stock: Unsold goods in the business available at the beginning of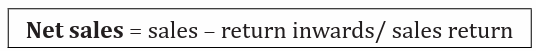
the new trading period.
d) Purchases: Goods bought by the business for resale.
e) Purchases return: Goods previously bought by the business for sale but
have been sent back to the suppliers. This value is treated in the tradingaccount and its subtracted from the purchases to get the net purchases i.e.
f) Carriage inwards: Refers to the cost of transporting the goods or bringing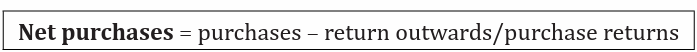
the goods up to the premises. It forms part of the goods bought hence addedto purchases in the trading account.
g) Closing stock: Goods not sold by the business at the end of a trading period.
It’s included in the trading account and it is subtracted from the goodsavailable for sale to get cost of sales. i.e:
h) Drawings of goods: Sometimes an entrepreneur may take physical items
out of the business for private use. This must be subtracted from the goods
available for sale in the trading account. It should be noted that “only
drawings in form of goods” must be treated in the trading account.
i) Gross profit: Excess of net sales over the cost of goods sold or cost of sales. It
also refers to the total profit obtained by an enterprise before paying off the
operating expenses. Thus
Gross profit = net sales – cost of salesj) Gross loss: This is excess of cost of sales over the net sales of the business.
Format of a trading account
There are basically two formats that are used to prepare a trading account. i.e
a) Horizontal
b) Vertical formatHorizontal format / T - Format
Note: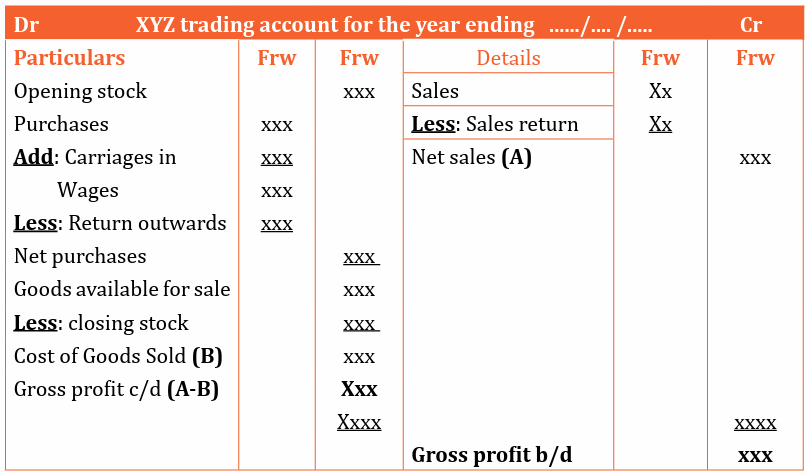
• Goods available for sale (GAS) = Opening stock + Net purchases
• Cost of Goods Sold (COS) = Goods Available for Sale – Closing stock.
• Gross profit = Net sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Vertical format of an Income statement
Income statement for the yearended. date



b) Notice use of brackets on the amounts mean deduction of the amount. The
other option would be to use the word ‘Less’ before the item concerned.
Profit and Loss account:
As seen in the above vertical format of an income statement, you will realize
that Profit and Loss account part represent the company’s NET PROFIT or
NET LOSS which is determine by deducting operating expenses (these includeselling and distribution expenses and administrative expenses) from the Gross income.
Application Activity 8.2
KUNDUMURIMO Enterprise showed the following balances as on 31stDecember 2012
Required: Prepared an income statement for KUNDUMURIMO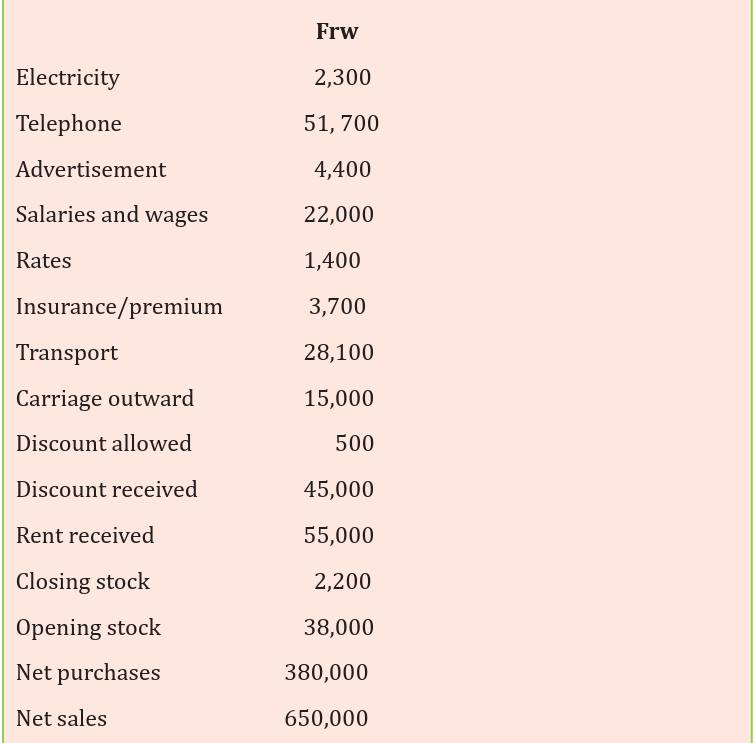
Enterprise for the period ended 31st December 2012.
8.3. Balance sheet
Activity 8.3
A balance sheet is a statement of assets and liabilities of a business organization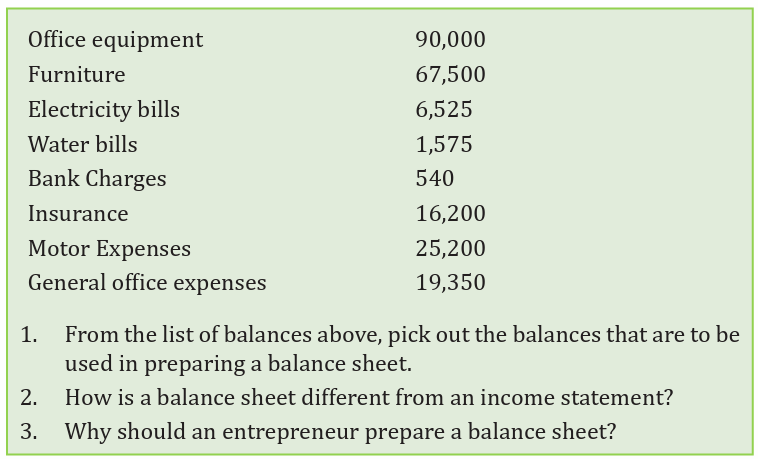
at a given period of time. It is a statement that shows what you own, what youowe, and what you are worth at the end of each accounting period.
A balance sheet is not an account therefore, not part of the double entry but
it is prepared based on the ACCOUNTING EQUATION, which states that: Assets
=capital + liabilities. That is why a balance sheet is also defined as “a statementin which the business accounting equation is expressed”
Parts of a balance sheet:
There are three major parts of a balance sheet;
• Assets
• Liabilities• Capital / Owner’s equity
Assets
These are possessions owned by the business and have got money value.
They are grouped into two;
• Fixed assets
• Current assets
a) Fixed assets: These are the possessions of the business which are of a
durable nature bought for use in the business for a long period of time
usually above one year. E.g. land, equipment, machinery, fixtures and fittings,motor vehicle etc.
b) Current assets: Possessions or properties of the business which lasts for
a short time and usually easily changed into cash. Current assets keep on
being converted from one form to another e.g. stock of goods, debtors, cash
at hand , prepaid expenses or expenses paid for in advance, outstandingincome etc.
Liabilities
These are debts or amount of money that the business owes the outsiders.
They are claims of outsiders on the business’ assets. They are also properties/
possessions that are used by the business and which must be paid back in the
future. There are 2 types of liabilities:
• Long term liabilities
• Short term liabilities
a) Long term liabilities: These are debts of the business that are expected to
be paid after a long time usually after one-year e.g. bank loans, debentures.
b) Short term liabilities/current liabilities: These are debts of the business
which are to be paid within a short time usually within a year. They are claims
by outsiders of the business that are repaid within one accounting year e.g.
trade creditors, bank overdraft, outstanding expenses, prepaid income etc.
Capital
These are the resources invested by the owner or the entrepreneur in the
business. Capital is also known as owner’s equity. To start any business a person
requires capital; which can be in the form of money or other physical resources.
The balance sheet can be reported in two different formats: Horizontal format
referred as account form and Vertical format referred to as report form.
• The Horizontal format consists of two columns displaying assets
on the left column of the report and liabilities and equity on the rightcolumn.
An example of the balance sheet in horizontal format:BALANCE SHEET AS AT ……/………/……….
• The Vertical format, on the other hand, has only one column. This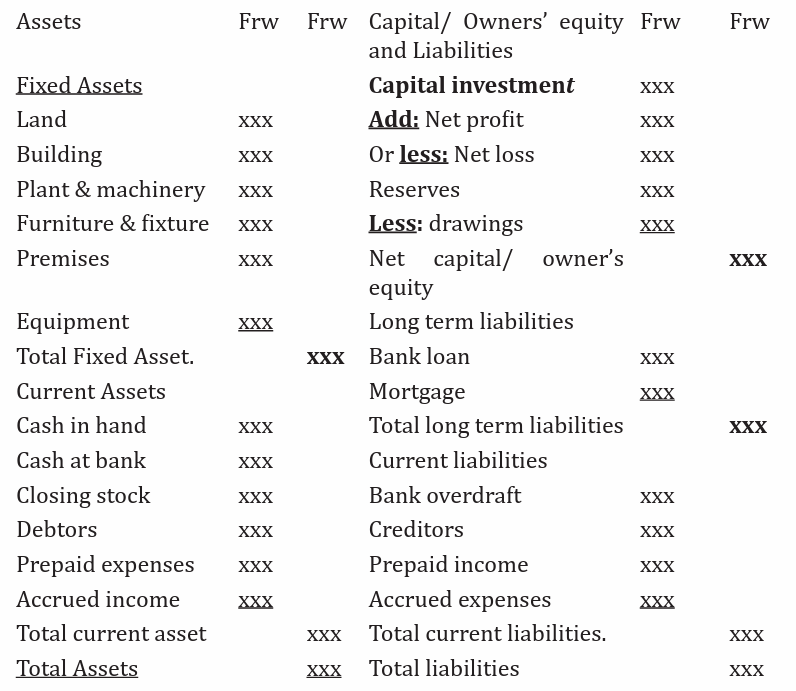
form is one of the most widely used today. Assets are always presentedfirst, followed by liabilities and equity.
An example of the balance sheet in Vertical format:
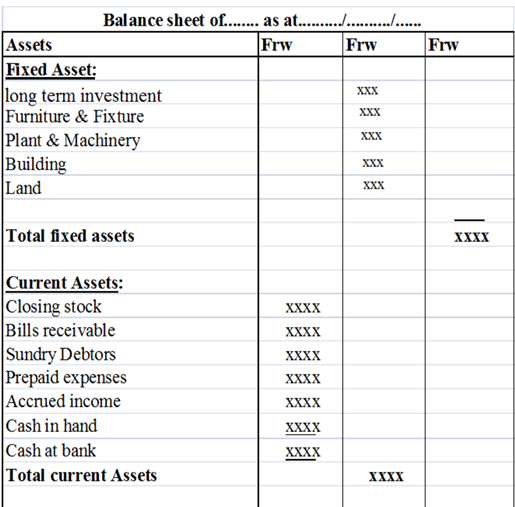
Also assets and liabilities can be arranged according to their realization and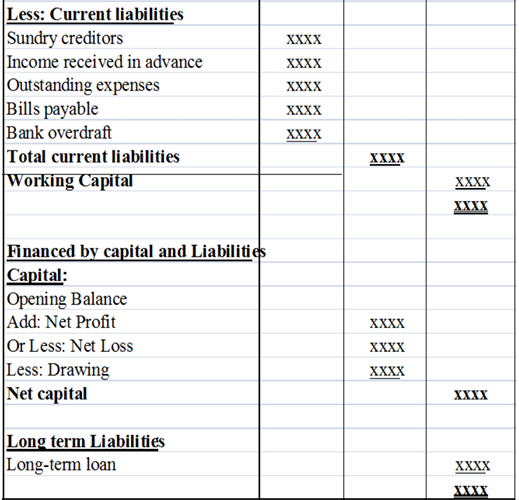
payment preference, which is called liquidity order basis or on the assumption
that these will be sold and paid only on the liquidation of business which is
called the permanence/fixity basis.
Application Activity 8.3
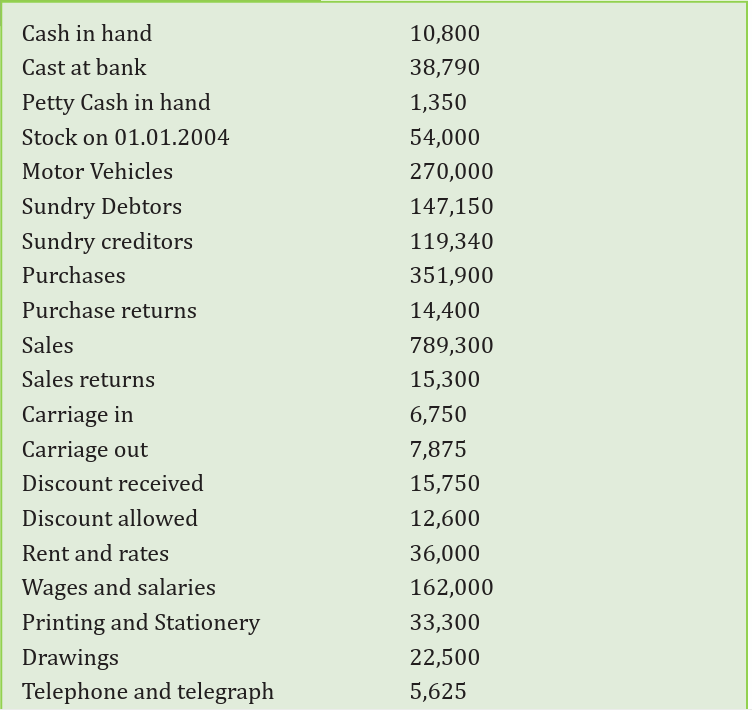
Analyse the accounting information below in the trial balance anddiscuss the questions that follow.
Required: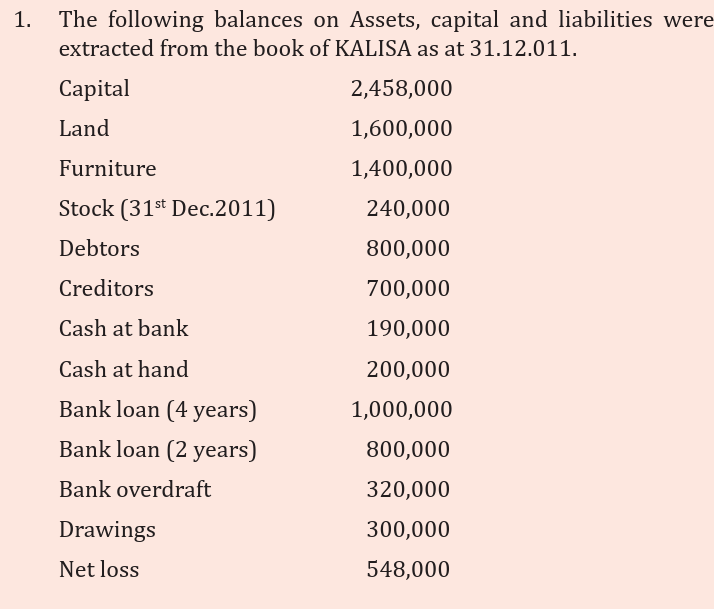
a) Prepare KALISA’s Balance sheet as at 31st Dec. 2011
b) What advice would you give KALISA to improve on his business’sfinancial position?
Skills lab 8
Use the current financial data you have so far in the business club and
prepare an income statement and a balance sheet (or projected income
statement & Balance sheet) for your business club. Analyse the Income
statement and Balance sheet, describe the net financial position of the
business club. Basing on the financial position, suggest action steps to
improve the financial life of your Business club.
End of unit 8 Assessment
1) The following information was obtained from the books of Kanezaand Kamali Ltd Company as at 31 March 2010.
You are required to: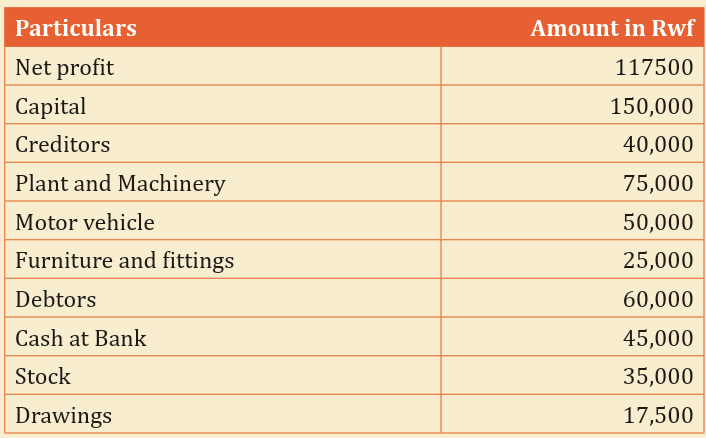
a) Prepare the business balance sheet as at 31 March 2010 in both
formats (Horizontal and vertical).
b) How do you describe the financial status of Kaneza and Kamali
Ltd Company given their balance sheet status?
2) The following was extracted from the books of Alexis traders Ltd asat 31st December 2011

Additional Information: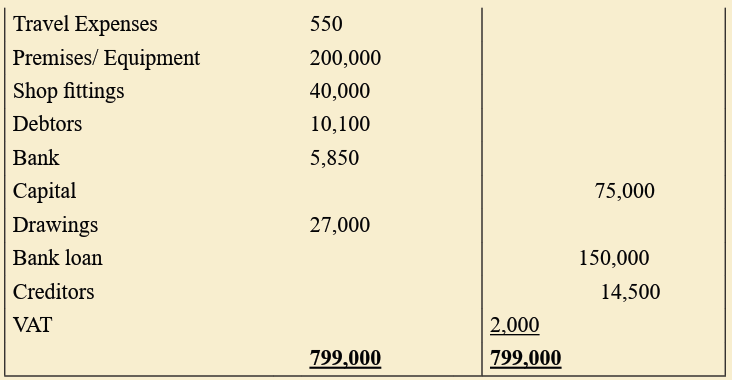
• Stock at 31st December 2011 was valued at 42,000Rwf.
Required:
Using a Vertical format, Prepare Alexis traders’ Ltd trading, profit and
Loss account for the year ended 31st December 2011.
What advice would you give to the business operators given the natureof the profit and loss account?
