Topic outline
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
This textbook is part of school curriculum reform in Rwanda in particular how
the curriculum is taught. It is hoped that this change will make what you learn
in school more useful both at school and when you leave school.
In the past, the main reason for schooling was to obtain knowledge – that is
facts and ideas about each subject. But nowadays the main reason due to
changes that are happening in the environment and the job market is becoming
more competitive therefore you should be able to use the knowledge you
will obtain from this text book to develop competencies. These competencies
include, ability to think for yourself, ability to communicate with others and to
explain what you have learnt, as well as being creative in developing your own
ideas, not just following those of the Tutor and the textbook. In this textbook,
different approaches are used to help you to develop competences and make
this textbook user friendly. Among these approaches are the following:
Activity-based learning
These activities present you with instructions to follow that will help you to
learn and discover others for yourself. You already have knowledge and many
ideas based on the experiences you have had and your life within community.
Some of the activities, therefore, require you to use the knowledge and ideas
you already have.
In using this book, therefore, it is essential that you do all the activities and
follow all the instructions. You will not learn very well unless you complete
these activities provided. They are the most important part of the Textbook.
In some ways this makes learning more of a challenge. It is usually challenging
to think for yourself than to copy what the Tutor tells you. But if you take up
this challenge you will become a better person and become more productive
and successful in your life.
Group work
You can also learn a lot from other people in your class. If you have a problem,
it can often be solved by sharing it with others. Many of the activities in the
book, therefore, involve discussion. Your tutor will help to form and organize
these groups in a conducive learning environment facing each other. You cannot
discuss properly unless you are facing each other.
Research
One of the objectives of the new curriculum is to help you discover for yourself.
Some activities, therefore, require you to do research using Textbooks in
the library, the internet if your school has access, or any other source such
as newspapers and magazines etc. This means that you will develop skills
of learning for yourself that can help you both when still in school and after
school. Your tutor will help in case your school does not have a fully equipped
library or internet.
Skills lab
Entrepreneurship subject is more practical than theoretical that is why it
requires time for skills lab which is a regular time on normal time table when
student-teachers are required to complete learning activities working in
manageable groups.
During skills lab activity student-teachers are given an opportunity to talk
more and get more involved in the lesson than tutors. Student-teachers receive
constructive feedback on work done (Tutor gives quality feedback on student
presentations).
The Skills Lab prepares student-teachers to complete portfolio assignments on
their own after classes. So, classroom activity should connect directly to the
portfolio assignment and during the skills lab the tutor makes sure that he/
she links the unit with the portfolio assignment, student’s business club and
back home projects.
Icons
To guide you, each activity in the book is marked by a symbol or icon to show
you what kind of activity it is. The icons are as follows:
This indicates thinking for yourself or groups discussion. You are expected to
use your own knowledge or experience, or think about what you have read in
the book, and answer questions individually or as a group activity.
Thinking icon/Learning activity icon
This icon reminds you to link your previous knowledge with the topic you
are going to learn. As a student feel free to express what you already know
about the topic. What is most important is not giving the right answer but the
contribution you are making towards what you are going to learn.
Application Activity icon
Some activities require you to complete them in your exercise book or any other
book. It is time for you to show if you have understood the lesson by answering
the questions provided.
Skills lab icon
This icon indicates a practical activity, such as a role play to solve a problem or
complete an activity, participating in a debate and following the instructions
provided by the teacher. These activities will help you to obtain practical skills
which you can use even after school.
End unit Assessment icon
This icon requires you to write down the responses to activities including
experiments, case studies and other activities which assess the attainment
of the competences. Tutors are expected to observe the changes in you as astudent teacher.
UNIT 1 : BUSINESS IDEAS AND OPPORTUNITIES
Key Unit Competence: To be able to generate viable business ideas.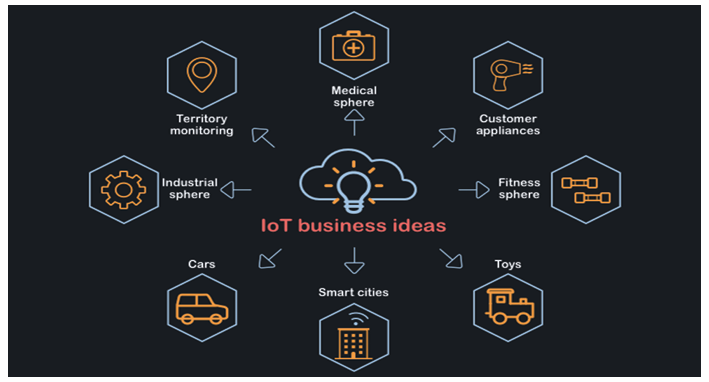
Introductory activityAnalyze the photo below and answer the following questions
Observe the picture above and identify different sources of business
ideas.
1. Generate different business ideas from the above environment.
2. Notall business ideas are business opportunities. Is this statement true or
false? Give reasons to justify your response.
1.1 Business, business idea and a business opportunity
1.1.1. Meaning of a business idea
Business refers to any economic activity that involves the production, selling
of goods and services, covering risks with the aim of getting profits.
An idea is called an opportunity if there is evidence that the entrepreneur’s
idea can be turned into reality.
A business idea simply refers to any thought that the entrepreneur may
come up with as a result of scanning the environment with the possibility
of developing it into a business opportunity. It requires the entrepreneur to
exercise creativity and innovativeness in order to come up with the successful
business ideas for the environment.
Examples of business ideas in Rwanda include; Real estate, clothing and
textiles, food processing, E-Commerce, technology products.
1.1.2. Meaning of a business opportunity
A business opportunity can be defined as an identified situation or chance
that can be turned into a real and profitable business.
An opportunity is a favorable set of circumstances that creates a need for a new
product, service, or business. Such opportunities are determined by customer
requirements and lead to the provision of a product or service which creates or
adds value for its buyers or end-users.
A business opportunity is any situation that can be turned into a possible and
profitable business activity.
An opportunity is a situation in which it is possible for you to do something
that you want to do. A business opportunity is said to be viable, when it has the
ability to grow and expand.
Examples of business opportunity and their business idea
-Lack of sufficient safe water in your community is a business opportunity.
Provision of JIBU, NIL, AKANDI or INYANGE water can be a business ideas.
-High demand for charcoal as a source of energy in your community is
business opportunity. For that opportunity, many business ideas can be
generated like provision cooking gas, making charcoal in wastes, planting
trees, buying big vehicle to transport charcoal from far forest…
A business idea may not necessarily be a profitable business opportunity; one
needs to filter and sift through these ideas to realize whether they are realopportunities.
Application Activity 1.1Case study: A reality T.V. Show
Rwiyemeza is a prominent entrepreneur dealing in growing and
processing of Mushrooms in Kicukiro district. One day she was invited
to give an interview on Rwanda Broadcasting Agency (RBA) about her
business to the whole nation by Mr. Makuru.
Read through the excerpts from the interview
Makuru: How did you decide to get into mushroom growing and
processing? How did you start?
Rwiyemeza: It was during my school time when I joined a school
business club. I got the idea when our club mentor told us that we canstart a backhome.
business, we used to call it a ‘BHB’. I introduced the idea to my parents
and I was lucky that they supported me. It was not a very easy task with
everyone telling me different things about growing mushrooms. Actually
many people that I talked to focused on the challenges but about three
people told me that I can overcome the challenges if I plan in advance.
I therefore decided to take on the business of Mushroom growing and
processing.
Makuru: What was the biggest challenge while starting your Mushroom
business? How did you overcome it?
Rwiyemeza: There were so many challenges such as unsure market,
competition, pests, but deciding on turning my business idea into a
profitable business was most challenging. I had to make a lot of research
from existing entrepreneurs, sector offices, and financial institutions.
I also had to do personal evaluation. I found that I could market my
product very widely to beat the market problem, and ensure much
cleanliness and timely watering to avoid pests.
Makuru: What are the benefits of your business to the community?
Rwiyemeza: Apart from earning a living for me and my family, my
business employs three ladies and 2 gentlemen who earn a monthly
salary. Important to note also, is that I have inspired a lot of other young
entrepreneurs especially women to start their own businesses.
Makuru: What advice would you give to the young people who may
want to start businesses?
Rwiyemeza: My advice would be that all around us are opportunities
of business ideas but one has to be careful because NOT all business
ideas can be turned into profitable businesses. Before I finally decided
to start mushroom growing and processing, I had tried a number of
business ideas which failed because they were not viable. So, I again
advise the young people to take time and research about the business
ideas before investing money since “Not all business ideas are businessopportunities”.
Questions:
Referring to the case study (A reality T.V. Show) above, answer the
following questions:
a) What do you understand by a business and what is Rwiyemeza’s
business?
b) Explain what you understand by a business idea. Mention any
sources of business ideas for Rwiyemeza’s business activity.
c) Rwiyemeza says it was not easy for her to start up the business
activity. Explain what you understand by a business opportunity
and identify some challenges Rwiyemeza faced.
d) Why do you think it is very important to do a research and personal
evaluation before deciding to start a business activity?
e) Looking at the situation at school and in your home community,
what two best business ideas can you possibly take on? Why doyou think those two are the most viable ones?
1.2. Reasons for generating business ideas
Activity 1.2
1) Why do you think that it is important to generate business ideas?
2) In your own words, explain why the following Entreprises Urwibutso,Inyange, Mara phone, Volkswagen have been generated.
The simplest purpose of business is to solve a customer’s problem or meet
the customers’ needs. By providing the goods and services that meet the
customer’s needs, the business owner may realize profits. Businesses exist to
impact on people’s lives. This happens by businesses providing people with
goods and services they desire to meet their needs. While the people buying the
business’ products (goods and services) are meeting their needs, the business
owners expect to realize profits. Businesses serve as conductors of economicactivity and development.
Business may be done by private individuals, government, companies, cooperatives or non-governmental organizations (popularly known as NGOs).
Hereafter are many reasons why entrepreneurs would need to generatebusiness ideas:
To start a sustainable business: a good idea is essential for a successful
business venture – both when starting a new business or expanding it.
To respond to market needs: markets are made up essentially of
customers who have needs and wants waiting to be satisfied.
To meet changing fashions and requirements: provide opportunities
for entrepreneurs to respond to demand with new ideas, products and
services.
To stay ahead of the competition: Remember, if you do not come up
with new ideas, products and services, a competitor will. So the challenge
is to be different or better than others.
To exploit technology – do things better: Technology has become a major
competitive tool in today’s markets and for one to be better with changing
technology, generation of business ideas is crucial.
Because of product life cycle: All products have a finite life. The firm’s
prosperity and growth depends on its ability to introduce new products
and to manage their growth.
To diversify risks and overcome failure: It is necessary for firms to try
to diversify their risks and overcome failures that may occur from time totime by constantly generating new ideas.
Application Activity 1.2
Identify a number of different needs and wants in your community
that are not yet being met by the existing businesses and suggest the
business you would come up with.
1.3 Sources of Business Ideas.
Activity 1.3
Referring to your community and beyond, explain at least 5 business
ideas that you can generate from the different sources.
The following are some of the sources of business ideas:
-Looking within you and examining skills, talent and passion: The very
first place to start looking for business ideas and opportunities is to look
within yourself. Self-examination is an important thing that can help in
reaching to different decisions. It is important to examine your own skills,
talent or passion that can fit into the business. Therefore, such businesses,
which corresponds according to your skills is the most appropriate andare expected to be successful in the future.
-Inventing a new product or service: Another great source of business
opportunity is inventing a new product or service. Different people are
creative with a mindset of thinking out of the box and solving problems
with the best appropriate solution. One needs to think like great
entrepreneurs such as SINA Gerald of Urwibutso enterprise, Zulphat
Mukarubega proprietor of Rwanda Tourism University College, etc.
However, for winning ideas you need to be specific on your target marketand analyse the problem.
-Adding value to an existing product(Innovation): Rather than inventing
a product, one can also add value to existing products. These kinds of
innovations can be proved as a great source of business opportunities.
Since most of the inventions have already taken place, so it is prevailingas innovation.
-Franchising: A continuing relationship in which a franchisor provides a
licensed privilege to the franchisee to do business and offers assistance
in organizing, training, merchandising, marketing and managing in
return for a monetary consideration. Franchising is a form of business
by which the owner (franchisor) of a product, service or method obtainsdistribution through affiliated dealer (franchisees).
By looking on the demographics and the need for a particular service or
product, one can also start a franchising business. It can be really profitable
since much of business modeling is not required because a person usesthe rights of another retailer.
Mass Media: Mass media has become comprehensive from past few
years. Magazines, TV, Newspapers etc. are a great source of ideas and
opportunities. Different businesses are on sale and different commercial
advertisements are available to choose from.
Attending Exhibitions: Trade shows and Expos helps to develop a strongbusiness network.
Industrial Survey: Another important source for a business ideas can
be industrial surveys. Since, the main point of a business is to fulfill the
needs of a customer. Therefore, surveying and analyzing the underlying
need of a customer can help in reaching a rational decision that addressesthe customer’s problem and result in a profitable business.
Listening to customer complaints: Complaints are a part of customers’
relationship that led into the development of new or improved products
and services. Whenever customers report badly, it means that the
customer satisfaction is not being achieved and there is some issues
with the product. This can help in generating new business ideas foraddressing problems of customers.
Application Activity 1.3
Describe the qualities of a good business idea in your home communitythat can be turned into a Back-Home Business.
1.4. Steps of generating business ideas
Activity 1.4
Referring to your community and beyond, explain at least 5 business
ideas that you can generate from the different sources.
a. What would you have to do in order to take on the best business
opportunity?
b. Would you advise a friend on how to assess business ideas andopportunities? If yes, how? If not, what would you do?
1. Start thinking/get your brain at work
The first thing to do when you get a business idea is determine whether it’s
a good idea. Not every idea that seems good at first is practical. And some
business ideas have no market.
You will need to do some research to evaluate your business idea. Here is a
checklist of questions to use as a guide:
-Is there a need for this product or service? Some of the most popular
products and services meet a need that people currently have. The
product or service may improve upon or complement an existing product
or service, or your idea may be a completely new approach to meeting a
need.
-Is there a desire for this product or service? Admittedly, some of the
most popular products are desire-based rather than need-based. That
means that someone is purchasing the product because they want to. A
few needs-based reasons for a purchase include to increase status or to
follow a trend.
-Who is currently meeting the need for this product or
service? Answering this question gives you a start on evaluating your
competition. You need to know not only who your competitors are, but
also how many are they? Don’t forget to consider indirect competition.
-Who will buy this product or service? Find out who your typical
customer is likely to be. This may involve conducting surveys, testing the
waters, finding a focus group, and more. The better your understanding
your potential customer, the more likely you are to create a successful
business.
-How big is that market? You may have a great business idea. It may even
be brilliant. But, if the market for your idea is very small, your business
might not be viable–that is unless people are willing to pay a premium for
your product or service. This brings us to the next question.
-How much are people willing to pay for your product or service? Your
intake from your product or service needs to cover your costs and should
include a healthy profit. Remember, that even a small niche market can
be profitable if potential customers are willing to pay you enough money.
-How hard will it be to implement the idea? Let’s face it, some ideas
are easier to implement than others. When answering this question, take
into consideration the amount of time it will take you to launch your
business as well as whether or not you will need to hire someone to help.
After doing your research, you should be able to tell whether you want tocontinue on ,and develop your business idea.
2. Buy a notebook (Think on paper)
Now that you know how to stimulate your brain and get started with the creative
thinking process, you need to keep count on your ideas and make sure that you
can document them to study and examine them further. Every business you
can think of started with a small idea somewhere, from a small observations,
a frustrating situation, or while taking a shower. You never know when the
inspiration comes, so keep a notebook close to you at all times to write theseideas down whenever they come.
3. Follow your passion
Once you start your business, you will spend most of your day for several
years doing that business. So make sure you choose a business that you feel
passionate and excited about. If you don’t like the business you are doing , you
might not succeed in that business, probably not because you don’t have what
it takes, but mostly because you might lose interest too easily in the face of thechallenges that will come your way.
4. Keep your eyes open
New business opportunities get born from new situations every day. Keep an
eye on what is happening around you, make it a habit to read the newspaper
and identify new opportunities. You may read that people are complaining from
poor health services in your area, or the lack of schools in your neighborhood.
Talk to your neighbors and the people you know, what is frustrating them?
What would they want to change in your neighborhood? Is your neighbor
complaining that he/she needs to drive long distances to get to the nearest dry
cleaner? Or is your other neighbor complaining about the lack of groceries in
close proximity to where you live? Are your coworkers frustrated that there areno restaurants close to your work building?
5. Capitalize on your strengths
Most people are good at something. Look at your experiences and career, what
is it that you can do well? Have you been working in project management for 15
years and know the ins and outs of the business, this is often the best place to
start. Instead of focusing on the things you cannot do well, focus on the things
you are good at. What can you do better than others? How are the others doingit? And how can you do it differently?
6. Explore new things
As mentioned earlier, change is one of the biggest stimulators to the brain. Even
if you don’t want to open your own coffee shop, next time you are in one, look
at how things are done and think of new ways to improve it. Often this thinking
might lead you to new ways to improve on your business ideas in your chosenfield.
7. Check your bank account
Starting and running your business requires money. Depending on your
situation, you need to think of businesses that suit your budget. Everyone’s
finances are limited, so make sure whatever business idea you come up with is
doable. If you have a small amount of money, then look into business ideas thatare not cash hungry, maybe start small and then grow with the business.
8. Know what you want in life
Aside from your business goals, think about the reasons why you want to start
a business in the first place. What is it that you are looking for? What are your
goals in life? Are you starting a business to be able to spend more time with
your family? To make more money? To be respected among your peers?
Whatever your goals are, make sure that your business idea complements these
goals and help you to achieve them. If your goal is to find more time to spend
with your family and do other things, then starting a business that requires youto work 16 hours a day or travel constantly might not be the best idea.
9. Choose a business that suits your personality.
Are you a morning person or a night creature? Each person has his/her own
peak hours of the day. You will find very few successful bakers or newspaper
owners that don’t like to wake up in the morning. If you are not a morning
person, avoid businesses that will need you to work in the early hours of
the morning. If you are a night person, then maybe running a nightclub or a
restaurant that stays open till late hours is more suitable for you. Conversely, if
you sleep early, running a business that requires you to stay late might not be
suitable for you.
Are you an indoor or outdoor person? Do you like working in an office for long
hours or can’t stand the office and feel that you need on the move all the time?
If you like the office quiet environment, then pick a business that can be done
from an office. If you like to be on the move, pick a business that requires you to
go to different places and meet new people.
Are you brainy or handy person? People do things differently, some people like
to do things that involve thinking and working their brains, other people like to
do things that involve craftsmanship and handy work.
Are you shy or outgoing person? If you are a shy person, then becoming a public
speaker might not be the best idea for you. If you are an outgoing person and
like to meet new people all the time, having an internet based business might
deprive you from that joy.
I think you get the idea, think of your personal traits and attributes and pick abusiness idea that suits your personality.
10. Read about other people that started their own business
A large part of becoming successful involves looking at other successful people
and learning how they achieved their success. Reading autobiographies about
prominent and successful business figures and learning how they started their
journey will give you great insight on how they did things and what exactly they
did to become successful.
You find that most of them started from nothing. Many of them failed in
several businesses and had to listen to people that told them they will never be
successful. But they stood up and tried again and again until they succeeded. It
is not whether you fail that makes you the man you are, it is how you stand up
after the fall.
Study their characters, what do successful entrepreneurs have in common?
How did they achieve their vision? What challenges did they have to overcome?
Look for similarities between their stories and your situation right now. You
will find that it is a great source of inspiration and motivation. If others just likeyou did it, then you can do it too.
1.5 Business opportunities
Activity 1.5
1) What do you understand by a viable business opportunity?
2) What business opportunities can you think of? Among those, whichones are viable for you and why?
1.5.1. Meaning of business opportunities
A business opportunity can be defined as an identified situation or chance
that can be turned into a real and profitable business.
An opportunity is a favorable set of circumstances that creates a need for a new
product, service, or business. Such opportunities are determined by customer
requirements and lead to the provision of a product or service which creates or
adds value for its buyers or end-users.
A business opportunity is any situation that can be turned into a possible andprofitable business activity.
1.5. 2. Characteristics of a good business opportunity
1. Demand
Demand is the first thing that one ought to take into account before planning
to start a business is to ask themselves where there is a significant demand for
the particular product or services they intend to launch i.e. is there a gap in the
market? If the answer is NO then that idea isn’t a viable business opportunity. It
would also be profitable to target a specific niche as this increases the chancesof you becoming a dominant player for that specific niche.
2. Return On Investment (ROI)
If the business opportunity you have in mind has the potential of bearing fruits
within a set period of time and which can cover the capital that was used in
addition to bearing profits there is a high chance that you have got a winner
but if it only requires more and more capital to be injected in with minimal
or no possibility of having any returns any time soon then you ought to treadcarefully.
3. Availability of resources
You should have all the resources needed to take advantage of that particular
business opportunity as well as a time frame for implementing it, lest someoneelse beats you to it.
4. Skill
You need to have the experience required to tap into that particular business
opportunity e.g. if you want to start a bakery but don’t know a thing about
baking ,then that is not a viable business opportunity. It is therefore important
that you have the required skill i.e. experience and expertise, for the businessyou would like to start.
5. Scalability
Can the business grow gradually within a given period of time and can it adapt
to the changing times i.e. is it flexible enough? If the answer is NO then that ideaisn’t a viable business opportunity.
6. Healthy Profit Margin
Does the business have a good profit margin that will ensure the business
remains profitable even as it meets the gap in the market? If the answer is NOand you’re not in it for charity then that idea isn’t a viable business opportunity.
7. Customer Retention
It’s said that customers are the lifeblood of any business but if you can’t retain
your customers then your business won’t last very long. You therefore need to
put in place mechanisms that will ensure you prolong your customers stay withyou i.e. that they will keep buying from you for as long as possible.
8. Low capital requirement
A good business opportunity should be cheap to finance. Access to capital is a
major obstacle to entrepreneurship implying that entrepreneurs should focus
on ideas that are cheap to finance. Entrepreneurs exploit financing methods
such as loans, venture capitalists and contributions from friends and family
among others. Capital suppliers are reluctant to finance new businesses withhuge capital requirements.
9. Aligns with your passion
A good business opportunity is one that aligns with the individual’s passion.
The founder’s motivation is a key determinant of the success of a start-up.
A passionate founder has an internal motivation towards building a bright
future for the business. If you are like this leader, you will create a clear vision
and mission statements and use them to motivate stakeholders towards theorganizational goals.
Application Activity 1.5
Suggest a project you need to start in your students business club andidentify the requirements you need to start your project.
1.6. Factors to consider when generating and evaluating
viable business ideas and opportunities
Activity 1.6
1) What do you understand by a viable business opportunity?
2) What business opportunities can you think of? Among those, which
ones are viable for you and why?
Discuss different ways in which you can use to learn about existing business
ideas and opportunities both in your community and elsewhere.
It is very important to examine and evaluate your business opportunity
and determine your potential for success before you spend time and money
developing a business plan.
Entrepreneurs need to determine whether the business opportunity they
have identified is viable or not. When evaluating the viability of the businessopportunity, the following factors need to be taken into consideration:
1. Market
Business evaluation process goes through analyzing the market. If there isn’t a
big enough market for your product or service, you should rethink whether this
business opportunity makes sense.
• Who will be your target consumer?
• Is there a need for your business idea?• Can you meet that market need?
For instance, you might think of a great business idea to produce a carbonated
beverage flavored with roots, berries, and other natural flavors.
However, in your evaluation you might find that this type of product is already
saturated in the market. The idea is good and a market exists, but if the marketis flooded with competitors it would not likely be profitable.
2. Business plan
The bottom line of any business is to make money. Without positive cash flow,
you won’t succeed. Business owners with the best of intentions often fail
because the financial potential isn’t big enough.
• Will there be sufficient financial reward?
• Do you see a potentially growing market for the product?
• Do you have others who believe in your business ideas?
• Are there other businesses that are similar (which is a validation that
this potential business opportunity could be worth pursuing)?
You as an entrepreneur have a lot of thinking to do. Come up with great business
ideas. Be creative and get enthusiastic about your ideas. However, always take
the time to plan for a sound business because the better the business plan, thehigher chances for your idea to succeed.
3. Technology and other requirements
The business should be evaluated in terms of whether there is an appropriate
technology that can be used in production. Factors to be looked into include;
Appropriateness of the technology, the cost of the technology, the possibility
of the business suffering in case the technology becomes outdated/obsolete,availability of raw materials and other resources.
4. Infrastructure
Easy access to infrastructure such as roads, water, electricity, telephone and
postal services among others enables business enterprises easily make orders
for goods and deliver them hence reducing operating expenses. With lowoperating expenses, profits can be maximized.
5. Government policy
An entrepreneur should consider the requirements of the government before
starting a business e.g. the government may require certain businesses to belocated in certain areas only.
6. Amount of capital required
The capital required to run and maintain the business should be considered i.ethe source of capital.
7. SecurityAvailability of security should be considered.
8. Impact of the business operations on the environment
Some business operations on the environment lead to environmental
degradation and should be located in appropriate environment.
Are the political, economic, geographical, legal, and regulatory contexts
favorable? Will the business do any damage to the physical environment?
The above questions are typical of the type of issues that need to be addressed.
Responses to these questions will determine the attractiveness of any businessopportunity.
9. Competition and competitive advantage
Competition is regarded as a threat to business of similar kinds operating in a
similar location. Although competition is a threat, it is healthy in the sense that
it goes along the way in controlling the price of goods offered. It is crucial for
entrepreneurs to consider opportunities where competition is not high as thiswill enable them to get reasonable market.
10. Length of the window of opportunity
For example, one may inform you of an upcoming workshop for educators in
your area, you realize that there is an opportunity for you to supply water,
food and airtime among others, but for you to determine whether you should
invest in this, you need to know how many people are coming, the length of the
workshop, such that you know how much stock is needed, you also base on thatto determine whether you will get back your money or not
Application Activity 1.6Analyze the photo below and answer the questions that follow;
1) What kind of activity is represented in the photo?
2) What are the effects of such business ideas to the community?
3) As an entrepreneur, suggest any two business ideas you may
generate in response to the effects of the activity above.
4) Picking one idea, give the factors you will base on while choosing
that idea.
5) What advice would you give to potential entrepreneurs whilegenerating business ideas in relation to the photo above?
Skills lab
Choose 2 businesses/ business ideas and conduct a viability test to
find out which one is better in terms of; 1. Potential for growth, 2.
Infrastructure, 3. Market for the goods/services (real demand),
4. Profitability, 5. Competition and competitive advantage, 6.
Financial viability. Make posters indicating how each of the above
factors favors or limits their business ideas with clear examples.
Recommend the most viable business ideas the Business club should
continue/ start running basing on the results of the viability tests andsuggest action steps for the implementation.
End of unit 1 Assessment
1. Read the following scenario:
Mr. and Mrs. Kaberu visited their friend Kambanda who lives in Kigali.
They were surprised to see how Kambanda’s business of Coca-Cola
wholesaling was booming. They didn’t even ask him how and why he
chose to do that business.
When they went back home in Nyagatare, they sold all their cows and
opened x because they were kept for long. The landlord chased them
out of the house because they couldn’t pay rent any more.
Out of frustration, Mr. Kaberu had to sell all his stock at half price because
he had nowhere else to keep them. On hearing this, his wife Mrs. Kaberu
cried the whole day and night to the extent that she collapsed and was
taken to the hospital at the mercy of the neighbours because her andher husband couldn’t afford the medical bills.
Questions
a) Explain whether the business idea was good or bad.
b) Write a letter to Mr. and Mrs. Kaberu advising them on the importance
of assessing a business idea or opportunity in case they have anotherone.
2. There are many business opportunities that we can get from our
communities, why should we always assess a business opportunity
before investing our resources and time? To answer this, discuss in
your groups and raise at least 5 business opportunities that you can
think of. Assess each one of them and choose the best two viableones which you will present to the class.
UNIT 2: DRAFTING A VALID BUSINESS CONTRACT
Key Unit Competence: To be able to make a valid contract in business
operations.
Introductory activity
Sam met with a businessperson on a football match who requested him to be
supplied with beans at a price of 500 Frws per kilogram. When Sam delivered
200kgs, he was not paid the full amount of money they had agreed upon.
a) Has such a situation ever happened to you? When and what happened?
b) What mistake did Sam do?
c) Assume you were the one in such a situation, what would you do?
d) What advice would you give to Sam and the businessperson?e) What lessons do you learn from the above situation?
2.1. Meaning and Forms of Business contracts
Activity 2.1
Bayigana operates a small medium enterprise in Huye and wants
Ishimwe to supply his business with goods. Bayigana tells her to start
right away and supply the goods they will discuss other issues later.
She insists that she needs an agreement between the two especially on
issues of price, mode of payment, delivery period, quantity and quality,
among others.
a) How do you call an agreement that Ishimwe insists to be between them?
b) Do you think she is right to have the agreement before starting the
supply of goods? Give reasons to support your answer.
c) In which way/form may the agreement be made between the two?
Support your answerd) What do you understand by the term contract and business contract?
2.1.1 Meaning of contract and Business contract
A contract is a legally binding agreement between two or more parties which
can be enforced by law.
Example in marriage the woman and man make a contract during civil marriage.
The three parties are woman, man and witness will come to testify before thelaw represented by Executive secretary of sector.
Before starting a job, the employer and employee make a contract. In this case
there are two main parties and the law is now represented by official labor law
because it is not possible to make a job contract which is against the labor law.
A business contract is a legal binding between two or more persons/ entities
to perform an agreed business transaction and can be enforced by law. The
day today running of the business involves making contractual obligations withsuppliers, buyers etc.
Example: A farmer can make a contract of supplying chicken to the hotel. In
most cases this contract is written and two parties should sign to that document.
This contract should follow the official law like the right person who represents
the hotel and the farmer should have maturity age. The two parties should sign
with free consent. Once signed it becomes a document which binds the twoparties.
2.1.2 Forms of business contracts
Oral contract is an agreement between two or more parties by use of words.
They are non-written contracts. They rely on the good faith of the parties but
can be difficult to prove. Once the contract is verbal, the wittiness is mandatoryand provides evidence.
Application Activity 2.1
Read the following statements and answer the questions that follow:
- Nkusi wants to lend his car to Niragire for 5,000Frw per day for
five days.
-Niragire agrees with a handshake to borrow the car from Nkusi
and pay the money in witness of Rukundo.
-Ntezimana promises to take his girlfriend Bagirishya for an outing
to Lake Kivu.
-Niyokwizerwa promises to pay 10,000Frw to whoever finds her lost phone.
-Gato puts on paper his commitment to provide printing services
to Umutoni on agreed terms.
-Mutesi promises to pay for her brother’s school fees and puts it inwriting.
Which of the above statements are?
a) Contracts.
b) Not contracts.c) Business contracts.
2.2 Valid contract2.2.1. Parties to a contract
Activity 2.2
1) Analyze the figure below and answer the following questions.
a) Do you think the above sample is a contract? Give reasons to
support your answer.
b) Name the key elements of the written contract above.
c) Do you think the sample above is a valid contract? Support your
response by mentioning the elements of a valid contract in the
sample provided. (If any?)
2) Describe different parties to a valid contract.
3) Kamaliza’s 16-years old son, who looks a bit older, he signed a
contract joining a health club. He has dues of 15000 Frws. Is thiscontract valid?
Parties of contract are persons who can sign the contract. For a contract to be
considered valid, it should include three parties. These are; Offeror/promisor
who makes an offer, Offeree/promisee to whom an offer is made and Witnesswho sees an event happening.
For example, in the above template Mr. John Muhire Offeror/promisor agreesto sell his car to Umugwaneza Nadine Offeree/promisee at 2 millions.
Two parties to contract Offeror/promisor and Offeree/promisee must have
“capacity”, legal ability to make valid contract. Assent of parties is a must. If
either party is deprived, use of his understanding or deemed by law not have
attained consent, then such an agreement shall not bind him. All parties shouldhave should be mature, sound mind and qualified for contract by law.
The information of two parties in contract should be clear, complete and
concise. In any case, the names are not enough, it should be better to include
other information like number of identification card, the location where those
documents are issued. Ensure that all information is well reflected on the
contract. For example in above contract there is a mistake in writing names.
Umugwaneza Nadine who sells the car is not the same Mugwaneza Nadine whosigns the contract. These slit mistakes can disqualify the contract.
Witness is a person who sees an event happening. In a legal contract, a witness
is someone who watches the document be signed by the person they are being
a witness for and who verifies its authenticity by signing their own name on the
document as well. However, if you have a legal document such as a mortgage or
a Will the chances are that you will want a witness to attest to your signature.
Generally, the person you choose to witness a document should have no financialor other interest in an agreement. A neutral third party is the best choice.
2.2.2. Elements of a valid contract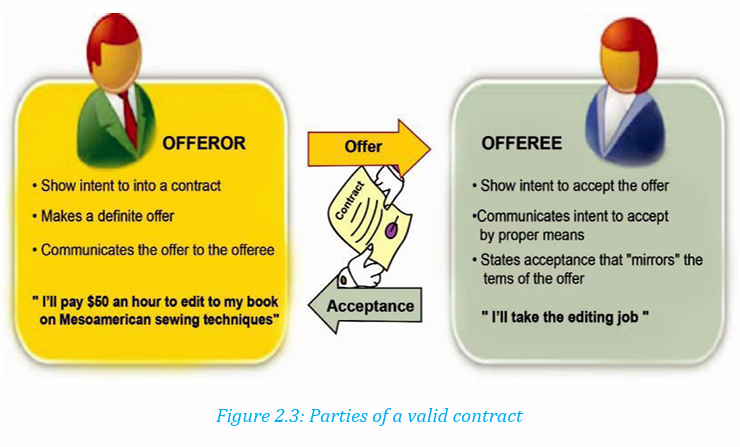
For a contract to be valid and therefore enforceable by law, it must have the
following elements:
Intention to be bound by the contract: the two parties should have intended
that their agreement be legal. Domestic agreements between husband and wife
are not taken as valid
Offer and acceptance: there must be an offer and the two parties must lawfully
come to acceptance leading to a valid contract. Until an offer is accepted, it’s not
a valid contract
Consideration/price: this is the price agreed upon by the parties to the
contract and paid by one party for the benefit received or promise of the other
parties.
Capacity of the parties: the parties to the contract must have contractual
capacity for the contract to be valid, i.e. should be sober, above 18years, not
bankrupt, not insane, properly registered.
Free Consent: parties to the contract must agree freely without any of the
parties being forced to accept or enter the contract.
Legality/lawful object: the object and the consideration of the contract must
be legal and not contrary to the law and public policy.
Possibility of performance: if the contract is impossible to be executed in
itself either physically or legally, then such contract is not valid and cannot be
enforced by law.
Certainty: the terms of the contract must be clear and understandable for a
contract to be valid. If the terms are vague or ambiguous, where even the courtmay not be able to tell what the parties agreed, then it will be declared invalid.
Application Activity 2.2
Imagine if you make a contract without considering the elements of avalid contract, what will happen if the person/ business refuses to pay?
2.3. Importance of business contracts
Activity 2.3
Why is it essential to prepare business contracts?
Referring to the activities in the previous lessons, do you think it is
important to have contracts in business operations? Give reasons tosupport your answer.
In business life, contracts are important because they outline expectations
for both parties, protect both parties if those expectations aren›t met and lock
in the price that will be paid for services. There are so many relationships that
affect the way the business operates such as customers or clients, employees,
suppliers, government, financiers. Contracts are then important in the followingways:
- Contracts reduce business risks by compelling business partners to
perform what they have agreed to as per contract.
- Business contracts specify terms and conditions of business
transactions including price, quantities, quality, date of delivery, etc.
which avoids misunderstandings.
-Contracts help entrepreneurs to get the goods on credit because
the suppliers are aware that the entrepreneur is bound by contract and
therefore will make effort to pay the agreed amount.
-Written contracts act as evidences. They are important because it is easy
to forget details you have agreed upon verbally and therefore provide apermanent record.
-Contracts may be used by entrepreneurs to convince bankers that the
entrepreneur has a business that will generate income so as to obtainloans.
Application Activity 2.3
Demonstrate the importance of business contracts to the schoolbusiness club.
2.4 Designing a contract sample
Activity 2.4Prepare a sample contract with suppliers for your school business club.
2.4.1 Sample of Employee contract
Employee Contract Template:
Employment Contract
This contract, dated on the ____ day of ______________ in the year 20____, is made
between [company name] and [employee name] of [city, state]. This contract
constitutes an employment agreement between these two parties and is
governed by the laws of [state or district].
WHEREAS the employer desires to retain the services of the employee, and the
employee desires to render such services, these terms and conditions are set forth.
IN CONSIDERATION of this mutual understanding, the parties agree to the
following terms and conditions:
Employment
The employee agrees that he or she will faithfully and to the best of his/her
ability to carry out the duties and responsibilities communicated to him/her by
the employer. The employee shall comply with all company policies, rules andprocedures at all times.
Position
As a [job title], it is the duty of the employee to perform all essential job functions
and duties. From time to time, the employer may also add other duties withinthe reasonable scope of the employee’s work.
Compensation
As compensation for the services provided, the employee shall be paid a wage of
___________ [per hour/per annum] and will be subject to a[quarterly/annual]
performance review. All payments shall be subject to mandatory employment
deductions (State taxes, Social Security, Medicare).
Benefits
The employee has the right to participate in any benefits plans offered by the
employer. The employer currently offers
benefits will only be possible after the probationary period has passed.
Probationary Period
It is understood that the first [time frame] of employment constitutes a
probationary period. During this time, the employee is not eligible for paid time
off or other benefits. During this time, the employer also exercises the right to
terminate employment at any time without advance notice.
Paid Time Off
Following the probationary period, the employee shall be eligible for the
following paid time off: • [length of time for vacation] • [length of time for sick/
personal days] • Bereavement leave may be granted if necessary.
The employer reserves the right to modify any paid time off policies.
Termination
It is the intention of both parties to form a long and mutually profitable
relationship. However, this relationship may be terminated by either party at
any time provided [length of time] written notice is delivered to the other party.
The employee agrees to return any employer property upon termination.
Non-Competition and Confidentiality
As an employee, you will have access to confidential information that is the
property of the employer. You are not permitted to disclose this informationoutside of the company.
During your time of employment with the employer, you may not engage in any
work for another employer that is related to or in competition with the company.
You will fully disclose to your employer any other employment relationshipsthat you have and you will be permitted to seek other employment provided
that (a.) it does not detract from your ability to fulfill your duties, and (b.) youare not assisting another organization in competing with the employer.
It is further acknowledged that upon termination of your employment, you will
not solicit business from any of the employer’s clients for a period of at least[time frame].
Entirety
This contract represents the entire agreement between the two parties and
replaces any previous written or oral agreement. This agreement may be
modified at any time, provided the written consent of both the employer andthe employee.
Legal Authorization
The employee agrees that he or she is fully authorized to work in [country name]
and can provide proof of this with legal documentation. This documentationwill be obtained by the employer for legal records.
Severability
The parties agree that if any portion of this contract is found to be void or
unenforceable, it shall be removed from the record and the remaining provisionswill retain their full force and effect.
Jurisdiction
This contract shall be governed, interpreted, and construed in accordance withthe laws of [State, province].
In witness and agreement whereof, the employer has executed this contract
with due process through the authorization of official company agents and withthe consent of the employee, given here in writing.
Employee Signature
Date
Company Official Signature
Source: www.betterteam.com/employee-contract-template
2.4.2. Sample of a sales contract
PRIVATE CAR SALES CONTRACT
The Car Details
Make: Toyota
SOLD FOR:……… frws
Model……… Registration Number…….. Registration document
completed by buyer/seller ..Yes/No . Mileage………. Registration document (V5)
exchanged ....Yes/No .
Additional notes and comments agreed on this sale
SELLER’S DETAILS: Name…………….. Address………………
CERTIFICATE of PURCHASE: I am the undersigned buyer of the above car.
I have purchased it from the seller named above for the amount of cash also
mentioned above (SOLD FOR). This is the final price agreed. I have paid for this
car in full and I am in receipt of this car and all the relevant documents to it. The
Seller above also acknowledges being in full receipt of all the total amount but I
do accept that full title to the car does not fully pass from the seller to purchaser
until all cash is paid. Any cheques will need to be cleared before full title passes
to myself. It is fully understood that this vehicle is sold as seen. I the buyer agree
that I have tried, tested and approved this car as suitable for my personal needs
without any representations, warranties or conditions expressed or implied
whatsoever.
Buyer’s Name:………………………
Buyer’s Address: …………
Buyer’s Signature in agreement: …………
Seller’s Signature in agreement: …………Date: …………
Application Activity 2.4
Assume, your parents have houses to rent at home, help them design arental contract that will be signed by the tenants.
2.5 Termination/discharge of business contracts
Activity 2.5
What do you think would lead you to terminate a contract with your
suppliers?
To terminate a contract means to end the contract. Contract may be terminated
under the following circumstances:
By performance: If the contract is performed and fulfilled as expected under
the terms and conditions of the contract and both parties are satisfied, then the
contract may be terminated.
By agreement: The parties to the contract may freely agree to end the contract
if both consent to end the contract.
By destruction of the subject matter: The contract may be put to an end
when the subject matter of the contract ceases to exist such as being destroyed,
stolen or died.
By operation of the law: The contract may be terminated by law if it is illegal,
if one party becomes bankrupt, insane or dies.
By frustration: A contract can be put to an end when a condition set in hinders
one of the parties from performing his/her contractual obligations.
For convenience: Where the contract allows a party to terminate the contract
at any time by providing notice to the other party for example employment
contract.
Due to a breach: Where one party has not complied with an essential contract
condition, the other party may decide to terminate the contract and seek
compensation for damages.
By lapse of time: If the offeror fails to perform and the offeree fails to take
action within this specified period, then the latter cannot seek remedy through
law. It discharges the contract due to the lapse of time. For example, Ngabo
takes a loan from Kamikazi and agrees to pay instalments every month for the
next three years. However, he does not pay even a single instalment. Kamikazi
calls him a few times but then gets busy and takes no action. Four years later,
she approaches the court to help her recover her money. However, the court
rejects her suit ,since she has crossed the time-limit of three years to recoverher debts.
Application Activity 2.5
1) Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow:
Musoni started a business selling general merchandise in his
community. He is renting the place where his business operates. He
buys his goods from a nearby town through a fellow businessperson.
He says he trusts his friend, so they never write down anything when
sending for goods but just gives him the money. He always sells
goods to his customers on credit but rarely make any record of such
transactions. Recently, after some advice from a friend, he contracted
a construction company to build for him a two-roomed building from
where he will shift his shop.
a) Mention some of the mistakes Musoni is doing in his business
activities?
b) What are the likely consequences of Musoni’s actions mentioned
above?
c) What advice would you give to Musoni to avoid the consequences
above and why?
d) What may cause Musoni to terminate the contract with the
construction company?
2)Kizito offered 10,000Frw for the return of his lost dog, but then he
refused to pay because he thought the person who brought the dog
back had stolen it.
Was there a valid contract in the scenario above?
Do you think Kizito is right? Give reasons to support your answer.
What advice would you give to the person who brought the dog back?
Skills lab 2
With reference to the knowledge of Business contracts, design contract
templates to be used in the school business club when dealing with; a)suppliers. b) Customers, c.) Employees of the club, d.) Club members.
End of unit 2 Assessment
1) Read the case study below and answer the questions that follow:
Shine Business club
Shine business club wanted 3crates of soda which they wanted to sell
to their school that was organizing a visiting day. Chantal an active
member of the club having been close to Bizimungu an entrepreneur
dealing in retail business convinced the club to deal with him. The
club paid him and agreed he would deliver the sodas to the club after
three days but unfortunately after the agreed time, he didn’t deliver
the sodas as expected. When the club contacted him for the sodas, he
denied to have entered into any dealing with them that if he did, he
would be having at least a formal document to prove that. The club
reported the matter to the school administration, but it couldn’t help
them since it was not notified of that dealing.
a) What are some of the essential elements of a valid contract
observed in the above case study?
b) Was there a valid contract in the above case study? Support your
answer
c) What advice do you give to shine business club?
d) How would you approach the situation or the above problem if it
was your business club?
2) Analyze the example below and answer the questions that follow:
Nkusi and Mukarutesi are capable adults. Nkusi is in the need for a
new car. it is on a budget, so he scans the classified advertisements
and finds Mukarutesi, who is selling an old Toyota Carina for
2,000,000Frw. Nkusi calls Mukarutesi and offers 1,800,000Frw.
Mukarutesi accepts Nkusi’s offer and they decide to meet. At the
meeting, Nkusi hands over 1,800,000Frw and Mukarutesi handsover the keys for the Toyota Carina.
a) Is there a valid contract in the above example?
b) Referring to the elements of a valid contract, support your
response;
c) Which form of business contract would you advise Nkusi to sign
with Mukarutesi?
d) What do you think may lead the contract in the example above tobe terminated?
3) Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow.
Ntwali started a business selling general merchandise in his community.
He is renting the place where his business operates. Ntwali paid his
property owner three months’ rent in advance but never asked for
receipt. After two months, his property owner says he wants the rent for
the two months. Ntwali is frustrated and tries to remind the property
owner that he paid his rent for three months. The property owner denies
and asks Ntwali for proof of the payment which he does not have. Ntwali
is stuck, does not know what to do while the property owner threatensto evict him if he does not pay his rent.
a) What is the cause of the conflict in the example above?
b) Advise Ntwali on how he can resolve the conflict with the property
owner
c) What are the disadvantages of the form of contract between Ntwali
and the property owner?
d) Help Ntwali design a written contract that he can sign with hisproperty owner to avoid such conflicts again.
UNIT 3: TAXES IN BUSINESS
Key unit competence: To be able to analyze the role of tax towards economic
development of the country and pay taxes.
Introductory activity: A case study
Why Do You Have to Pay Taxes
Every year around, before and after June 15, everybody especially business
people will be discussing about tax changes in the national budget. This is
because tax reforms and new taxes introduced are announced on that day.
However, have you ever wondered why you and businesses need to pay taxes?
In Rwanda, there are arms of the government (ruling bodies) from the
village, sector, district, provincial and national levels. These bodies comprise:
Legislature (who make laws), Executives (who enforce laws) and Judiciary
(who exercise laws). The salaries that public servants receive to do their jobs
come from taxes. Paying taxes is considered a civic duty, although doing so isalso a requirement of the law.
Taxes take many forms too. When you work at a job to make money, you pay
income taxes. Depending on how much money you earn, a certain percentage
(part) of the money you make is withheld (kept out of your paycheck andsent to the government).
When you buy things at a store, you also usually pay sales tax, which is a
percentage of the cost of the item charged by the store. If you own property,you also pay property taxes on the value of your property.
Paying your taxes is considered a civic duty, although doing so is also a
requirement of the law. If you do not pay your taxes, the government agency
that oversees taxes — the Rwanda Revenue Authority or RRA - will requireyou to pay your taxes or else face penalties, such as fines or going to jail.
The money you pay in taxes goes to many places. In addition to paying the
salaries of government workers, your tax also help to support commonresources, such as police and firefighters.
Tax money helps to ensure the roads you travel on are safe and well
maintained. Taxes fund public libraries and parks. Taxes are also used to fund
many types of government programs that help the poor and less fortunate,as well as many schools!
Each year as the “tax day” rolls in, adults of all ages and businesses must
report their income to the RRA, using special tax forms. There are many laws
that set forth complicated rules about how much tax is owed and what kinds
of special expenses can be used (“written off”) to lower the amount of taxesyou need to pay.
For the average worker, tax money has been withheld from paychecks
throughout the year. On “tax day,” each worker reports his or her income andexpenses to the RRA.
Employers also report to the RRA how much they paid each worker. The RRA
compares all these numbers to make sure that each person pays the correctamount of taxes.
If you have not had enough tax money withheld from your checks throughout
the year to cover the amount of tax you owe, you will have to send more
money (“pay in”) to the government. If, however, too much tax money was
withheld from your paychecks, you will receive a check (get a “refund”) fromthe government.
From the passage answer the following questions:
What are the major changes expected by people especially business people
on June 15, every year?
What makes the business people so anxious to know the changes mentionedabove in a)?
Why do you think it is important for businesses to pay taxes to the government?
How do the following benefit from taxes?
i) Entrepreneur.
ii) Government.
iii) Society.
a) Identify and briefly explain at least two types of taxes paid in Rwanda?
b) What happens to businesses or people who do not pay taxes?c) What is the difference between tax and taxation?
3.1. Tax and business tax
Activity 3.1
1. Explain the meaning of the following terms used in taxation:
a) Tax b) Business tax
2. In your community, you have probably heard people and business
people complaining about the taxes they pay or charged to different
or similar items. Identify any 5 things you have heard normally
people complain about.
3. If you were the one determining or imposing taxes to people andbusinesses, mention any five things you would put into consideration.
3.1.1. Meaning of taxation concepts
Tax is a fee without direct exchange requested to the members of the community
by the State according to the law, to financially support the execution of the
government tasks.
Business tax refers to compulsory and non-refundable payments made by
the business to the government or local authority to raise revenue to finance
public expenditures.
Taxation is a system of raising money or revenue by the government from
individuals/businesses and companies by law through taxes.
Taxation is a system/practice of government collecting money from its citizens
to pay for public services.
Tax avoidance is a situation where a business person does not pay tax because
s/he has avoided the product or activity on which the tax is imposed. It is the
taxpayer’s exploitation of loopholes in the tax system there by paying less tax
than what they are supposed to pay.
Example of Tax Avoidance:
• Taking legitimate tax deductions to maximize business expenses and
thus lower your business tax bill.
Tax evasion is the illegal practice of not paying taxes by either not reporting
income, reporting expenses not legally allowed, or by not paying taxes owed. In
businesses, tax evasion can occur in connection with income taxes, employment
taxes, sales, etc.
Examples of practices considered as tax evasion:
• It is considered tax evasion if you knowingly fail to report income.
• Under-reporting income (claiming less income than you actually received
from a specific source).
• Providing false information to the RRA about business income or expenses, etc.
3.1.2 Characteristics or principles of a good taxation system
A good taxation system can contribute a lot to the economic development of a
country and its national treasury. Equitable taxation system bears a significant
role in bringing harmony in the lifestyle of the population of the country. A good
tax system should consist of taxes which conform to the canons of taxation. Thecanons or principles of taxation are explained as follows:
1) Convenience: Places, periods and seasons in which the tax dues are
collected should be convenient to the taxpayer. For example, the convenient
time to a trader is when s/he has made a profit. For a farmer, is when s/she
has sold his/her products.
2) Simplicity: The type of tax and the method of assessment and collection
must be understandable by both the taxpayer and tax collectors.
Complicated taxes may lead to disputes, delays and high costs of collection
in terms of time and resources.
3) Certainty: The taxpayer must know the nature, base and amount of tax
without doubt. Unpredictable taxes discourage investment and reduce
work effort. Simply the tax should not be arbitrary.
4) Economy: The cost of collection and administration of tax must be much
lower than the tax collected
5) Elasticity: A tax should change directly with a change in the tax base. If the
tax base increases, the tax charged on the tax base should also increase.
6) Productivity: The fiscal authorities should be able to predict and forecast
accurately the revenue a particular tax would generate and at what rate it
would flow in.
7) Equity: Tax assessment should be in such a way that taxpayers bear a
proportionately equal burden. I.e. people who earn more income should
be taxed more than those who earn less income.
8) Diversity: This canon requires that there should be a number of taxes of
different varieties so that every class of citizen may be called upon to paysomething towards the national priorities
Application Activity 3.1
1. Why is it important to have principles of taxation?
2. Referring to the principles (characteristics) of a good taxation system
you know, briefly explain why each is important to the taxpayer and
tax authority (RRA).
3. With examples, differentiate
a) Tax and Taxation
b) Tax avoidance and Tax evasion
4. Do you think tax evasion is good? Give reasons to support your response
3.2. Importance of paying taxes
Sources: http://www.kigalicity.gov.rw
Figure 3.2 Taxes help the government to build infrastructures
Activity 3.2
1. With examples from your community or Rwandan community at
large, why do you think people and business enterprises need to pay
taxes to the government?
2. As an entrepreneur to be or referring to the activities of entrepreneurs
in your community, how do you think businesses or entrepreneurs
benefit from paying taxes?
3. In general, how does your society benefit from paying taxes? Give
examples to support your views.3.2.1. Importance of paying taxes to an entrepreneur
• Paying taxes by the entrepreneur helps the business activity to continue,
as it does not face penalties and associated costs from the RRA for non
payment.
• When an entrepreneur pays taxes, it improves his/her reputation or
public image which may result in increased customers and better services
from the government.
• To avoid inconveniences of closure of the business and its associated
costs: when entrepreneur fails to pay assessed taxes, his/her business is
subject to penalty even closure to some cases.
• Business needs certain infrastructures to operate successfully such as
roads to move raw materials, finished goods, workers; security for their
enterprises, among others, and all these are provided by the government
from taxes.
• Paying taxes means contributing money to government agencies or
departments such as Development Bank of Rwanda (BRD), Business
Development Fund (BDF), which support entrepreneurs to operatebusiness activities through soft loans and other financial support.
3.2.2. Importance of paying taxes to the government
• Source of government revenue: taxes are the main source of government
revenue to finance its public expenditure. So taxes enable the government
to pay its workers, construct roads, maintain security, provide health care,
education among others.
• Taxes benefit the Rwandan government to meet its objectives and goals
such constructing affordable houses to the citizens which helps improve
the standards of living
• Taxes help the government to finance its policies especially on poverty
alleviation through programs such as “GIRINKA”, “VUP”, “UBUDEHE”
among others.
• Taxes enable the government to regulate the prices of goods and services
in the country hence ensuring a low cost of living and maintaining the
standards of living of the citizens.
• Taxes enable the government to maintain a balance between the poor
and rich. The government uses the taxes from business people to provide
services needed by the poor, which otherwise the rich could not provide.
• Taxes enable the government to promote its policy industrialization
through reducing products from other countries that would otherwise
outcompete the home industries.
• Taxes enable the government to ensure that the citizens have enough
products. This can be through taxes charged to reduce products moving
out of the country or removing taxes on goods needed in the country. Thishelps maintain a high standard of living.
3.2.3. Importance of paying taxes to Society
• There are reduced rates of poverty among the community due to a
significantly equal distribution of income through various activities and
projects set by the government.
• Improved wellbeing among the vulnerable and elderly as they benefit
from the different government programs financed through taxes.
• Reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy due to
improved access to health facilities and services.
• Increase in the percentage of the population that completes secondary
and TVET education, reducing the literacy levels, improving on the
peoples’ skills through programs such as 12YBE.
• Increased community/social solidarity, general happiness, life satisfaction,
and a significant more trust among the community members and for
public institutions.
• Taxes are charged on some products to discourage their production
and usage hence controlling over-exploitation of resources as well asprotecting the environment which is vital for the existence of the society.
Application Activity 3.2
1. By giving specific examples from your community, how does your
society benefit from taxes?
2. What do you think would happen in the country if taxes were not paid?
3.3. Calculation of taxes
Activity 3.3
1. Do you think it is important for an entrepreneur to know how to
compute the amount of tax he/she is supposed to pay? Give reasons.
2. What do you think the term “Pay-As You-Earn (PAYE) tax means”?And how is it calculated?
There is a variety of taxes that a business has to pay such as corporate income
tax, trading license tax, professional income tax or PAYE (Pay-As-You-Earn),
rental income tax, fixed asset tax, Value Added Tax (VAT), Sumptuary tax, etc.
but here, an emphasis is made on:
1. Pay- As- You Earn (PAYE) and
2. Value Added Tax (VAT
3.3.1. Pay-As -You-Earn (PAYE) tax or professional income tax
The tax law requires that when an employer makes available employment
income to an employee the employer must withhold, declare, and pay the PAYE
tax to the Rwanda Revenue Authority within 15 days following the end of the
month for which the tax was due.
PAYE: is composed of Wages, salaries, leave pay, sick pay, medical allowances,
pension payment etc. Pay-As-You-Earn tax is computed as follows: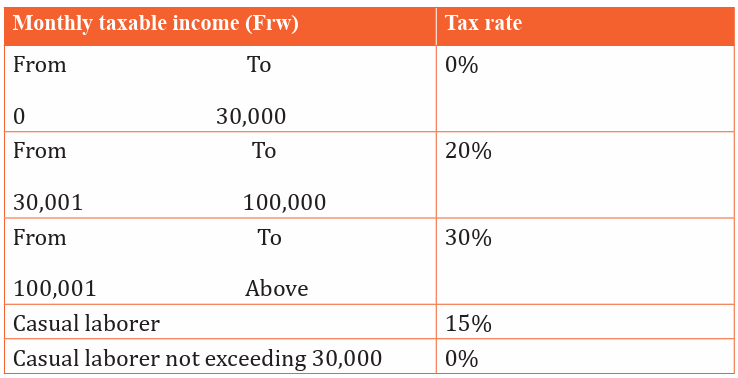
Example:
The following relate to monthly salaries of Kanyarwanda enterprise employeesfor year 2018.
a) Rukundo earns 450,000Frw
b) Karinganire earns 89,000Frw
c) Keza earns 28500Fwd) Buzima earns 12,5000Frw
Required:
Calculate the total PAYE for above employees that Kanyarwanda enterprisepays to RRA every month.
Solution:
a) Rukundo :
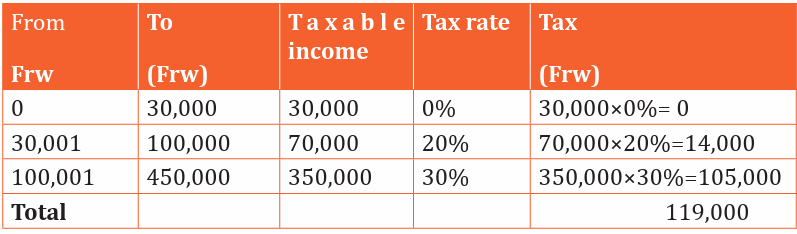
Total TAX for Rukundo = 14000+105000= 119,000Frw
b) Karinganire:
Total tax for Karinganire is 11,800Frw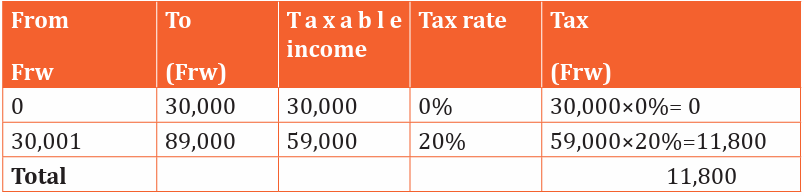
c) Since Keza earns less than 30000Frw she does not pay PAYE. Her total tax =0(28500*0)
d) Buzima:
Total tax for Buzima =14000+7500=21,500Frw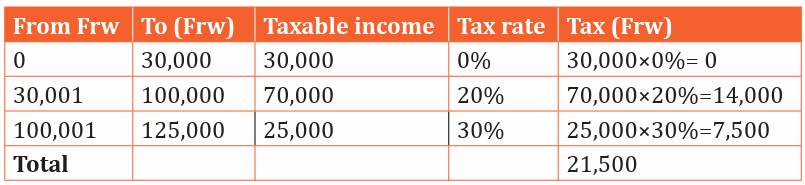
Total PAYE for Kanyarwanda enterprise every month
= (119,000+11,800+21,500)Frw= 152,300Frw
Note:
Exemption for PAYE is that every person who earns income less than 30000
does not pay PAYE to RRA.
The “casual laborer” means an employee or worker who performs unskilled
labour activities, who does not use machinery or equipment requiring special
skills, and engaged by an employer for an aggregate period not exceeding thirty(30) days during the tax period.
3.3.2. Value Added Tax (VAT)
Value Added Tax was introduced in Rwanda in 2001. VAT is a tax on the added
value achieved by a firm. This is the difference between the buying price (ofraw materials) and the selling price of the product in whatever forms it is sold.
Value added = F.P – I.C where F.P is final product, IC is intermediate costs
Tax rate
The VAT rate is applied to duty-free goods. Several rates can be applieddepending on the nature of products. The standard rate is usually 18%
Example 1:
UTEXRWA industry bought cotton from a local farmer worth 1200, 000Frw to
use in production of blankets;170 blankets were manufactured and sold to a
wholesaler at a cost of 4,000,000Frw who later supplied it to LEMIGO hotel
at a value of 8,000,000Frw VAT included. Calculate the value of VAT paid onblankets.
Possible solution
Step 1 VAT paid by local farmer:
VAT =1,200,000Frw*18% = 216,000Frw
Step 2 VAT paid by wholesaler:
VAT = FP -IC where FP is final product and IC is intermediate cost
Value added =4,000,000Frw-1,200,000=2,800,000Frw
VAT paid by wholesaler =2,800, 000Frw*18%= 504,000Frw
Step 3 VAT paid by LEMIGO hotel:
VAT paid by LEMIGO hotel= 8,000,000-4,000,000Frw=
(4,000,000Frw*18%)=720,000Frw
Therefore, total VAT =216,000+504,000+720,000 =1440, 000Frw
Alternative:
VAT is calculated on sales.
VAT =sales *18%
Which is equal 8,000,000Frw*18%=1,440,000Frw
Example 2:
A students’ business club has sold goods to XY enterprise at 100,000 Frw VAT
excluded.
Calculate:
a) VAT receivedb) The price VAT included
Solution:
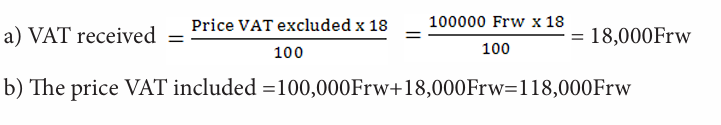
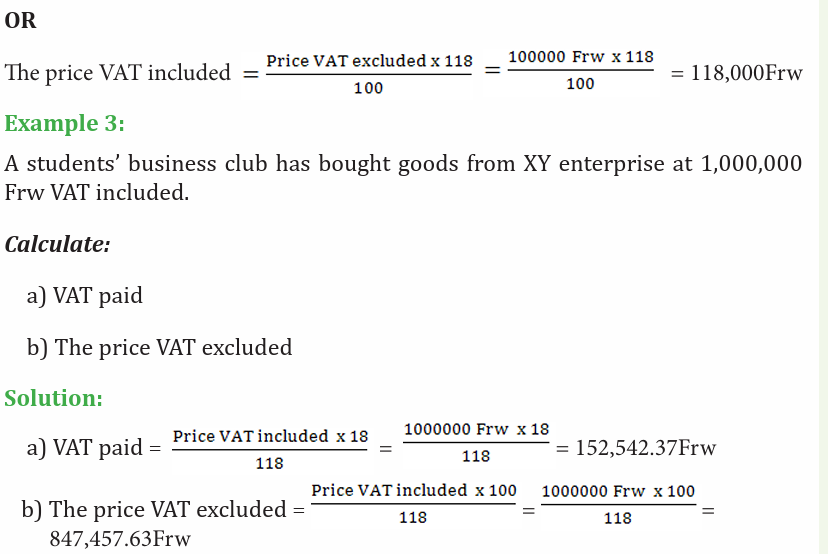
OR
The price VAT excluded= Price VAT included-VAT paid= 1,000,000Frw- 152,542.37Frw = 847,457.63Frw
Exemptions on Value Added Tax
The following goods and services shall be exempted from value added tax:
1. Services of supplying clean water and ensuring environment treatment
for nonprofit making purposes with the exception of sewage pump- out
services;
2. Goods and services for health-related purposes: (health and medical
services, equipment designed for persons with disabilities, goods and drugs
appearing on the list made by the Minister in charge of health and approved
by the Minister in charge of taxes.
3. Educational materials, services and equipment; books, newspapers and
journals
4. Transportation services by licensed persons:
5. Lending, lease and sale: (sale or lease of land, sale of a whole or part of a
building for residential use, renting or grant of the right to occupy a house
used as a place of residence of one person and his/her family) etc.
6. Financial and insurance services:
7. Precious metals: sale of gold in bullion form to the National Bank of Rwanda;
8. Any goods or services in connection with burial or cremation of a body
provided by an Order of the Minister in charge of finance;
9. Energy supply equipment appearing on the list made by the Minister in
charge of energy and approved by the Minister in charge of taxes;
10. Trade union subscriptions;
11. Leasing of exempted goods;
12. All agricultural and livestock products, except processed ones. However,
milk processed, excluding powder milk and milk derived products, is
exempted from this tax;
13.Agricultural inputs and other agricultural and livestock materials and
equipment appearing on the list made by the Minister in charge of agriculture
and livestock and approved by the Minister in charge of taxes.
14. Gaming activities taxable under the Law establishing tax on gaming
activities;
15. Personal effects of Rwandan diplomats returning from foreign postings,
Rwandan refugees and returnees entitled to tax relief under customs laws.
16. Goods and services meant for Special Economic Zones imported by a zone
user holding this legal status;
17. Mobile telephones and SIM cards;
18. Information, communication and technology equipment appearing on the
list made by the Minister in charge of information and communicationtechnology and approved by the Minister in charge of taxes.
Application Activity 3.3
1. A students’ business club (SBC) in one of the TTCs has the following
regular employees. Their salaries are in accordance with theirappointment as follows:
Calculate the PAYE tax on each individual employee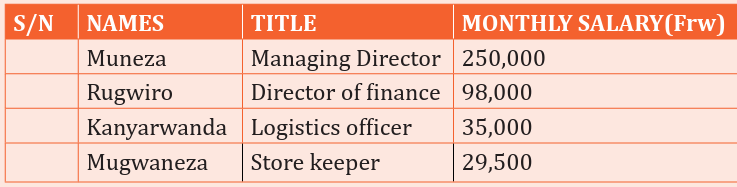
2. The PAYE tax to be withheld and paid by the business club to RRA2.
Using the information available on the below EBM issued receipt,
compute the following:
a) Price VAT excludedb) VAT to prove the amount appearing on the receipt.
3.4. Penalties of not paying tax
Activity 3.4
1. Identify instances through which a taxpayer may undergo various
penalties.
2. What do you think may happen to an entrepreneur if he/she does not
comply with the tax obligations?
The penalties of not paying tax include:
• Fines and interest: A taxpayer who fails to comply with the provisions
of law determining and establishing a tax shall be liable to a fine. The
fines will vary according to types of taxes.
Example of Penalties and Interest on not paying PAYE
A taxpayer who fails to pay tax within the due date is required to pay interest
on the amount of tax. Interest is calculated on a monthly basis at the inter-bank
offered rate of the National Bank of Rwanda plus 2 (two) percentage points. For
example, if the inter-bank rate is 9%, interest is imposed at 11% annually.
• Imprisonment: A tax fraud’s punishment in Rwanda, is the jail for a
period between six (6) months and two (2) years; even the Minister’s
order determines an award given to any person who denounces a
taxpayer who engages in that act. Failure to pay tax withheld: this
undertakes 100% penalty and 3months to 2years in jail.
• Closure of the business for 30 days;
• Cancellation or withdrawal of registration certificate;
• Banned from public tenders;• Exposure in the media
Application Activity 3.4
1. Discuss why RRA charges fines and penalties?
2. What do you think will happen if taxpayers don’t pay both taxesassessed and fines/penalties?
Skills lab 3
1. Justify the following statements with concrete examples:
• “Taxes are more of a benefit than a cost to an entrepreneur”• “ Tax evasion is a shortcut to business growth”
2. A business club at one of the TTCs has 3 regular employees namely
KALISA, KALIZA and BERWA with monthly salaries of 35,000Frw,
40,000Frw and 20,000Frw respectively. On top of that the business
made sales of 300,000Frw VAT exclusive, and the input VAT is
34,000Frw.
a) Calculate the total amount of tax that the business club has to pay
to RRAb) Advise the above business on how the above taxes would be paid.
End of unit 3 Assessment
1. It is said that “tax is the free money to central or local authorities from
taxpayers” do you agree with this statement. Justify your answer
2. Describe any four characteristics of a good taxation system.
3. How are taxes used by government to:
a) Support Entrepreneurs
b) Support the community
4. Fill in the missing gaps, with the most appropriate term:
a) …………. punishment is the jail for a period between six (6) months
and two (2) years; even the Minister’s order determines an award
given to any person who denounces a taxpayer who engages in that
act.
b) …………. is the compulsory and non-refundable payment made by
the business to the Government or Local Authority so as to raise
their revenues.
c) …………. is the one that is exempted from VAT.
d) …………. is one of the taxes vested to the local government (Districts).
e) The degree to which the taxpayers meet their tax obligations
as set out in the appropriate legal and regulatory provisions
is……………………….
f) The………………. means an employee or worker who performs
unskilled labour activities, who does not use machinery or
equipment requiring special skills, and engaged by an employer for
an aggregate period not exceeding thirty (30) days during the taxperiod.
UNIT 4: TECHNOLOGY IN BUSINESSES
Key Unit Competence: To be aware of how new technologies can affect
business activities.
Introductory activity
Analyze the Photos below and answer the questions that follow.

a) Looking at picture 1,2,3and 4, explain the advantages and disadvantages
of using the above techniques in the production of goods and services.
b) Which production technique is suitable for your school business club?Give reasons to justify your answer?
4.1. Types of technology in business
Activity 4.1
1.a) Suppose you wish to start up a feasible business in your community.
Which type of technology will you use in your business and why?
b) How would you define the term technology as used in business?
2. Distinguish intermediate technology from capital intensive and laborintensive technologies.
4.1.1. Meaning of technology
Technology refers to methods, systems, and devices which are the result of
scientific knowledge being used for practical purposes.
Technology can also be defined as a human knowledge which involves the use
of tools, materials, and systems to perform an activity.
Many businesses are using technology to stay competitive, they create new
products and services using technology, and they also use technology to deliverthose products and services to their customers on time and within budget.
Technology in business allows organizations to improve both the performance
and overall effectiveness of products, systems and services, which, in turn,
enables businesses to expand quickly and efficiently. Another role of technologyin business is to provide security to a business.
Examples of some tools, systems or devices used by technology in business.
• Desktop Computers and Laptops.
• Software and Productivity Tools.
• Networking of Computers and Printers.• Telephone and Voice Mail Systems.
In Rwanda there are different technologies used to improve the services such as
• Tap and Go: This is One of the biggest technologies that has changed
the face of public transport. It’s a smart transport system that enables
passengers to board public buses without using hard cash but rather
smart cards.
• Zipline’s drone technology: this is a global race for commercial drone
deliveries of small packages. In Rwanda it is used to transport blood to
remote areas where accesses to roads are impassable.
• Irembo services: The burden of walking long distances to seek some
government services has consistently been removed. There are large
numbers of people who do not have to necessarily travel to apply for
a marriage certificate, land transfer, drivers’ related services, birth
certificate, criminal record clearance certificate, and other services.
These few examples show how technology in business comes to enable
businesses to expand quickly and efficiently.
It is important to note that both technologies (Tap and Go & Irembo) aligned
with our country’s policy of promoting our economic growth through CASHLESStransactions.
4.1.2. Types of technology
1. Intermediate technology is one that fits into the level of development of
the host country. It is neither too simple nor advanced. For instance, theuse of ox-ploughs, solar cookers etc.
2. Capital-intensive technology is the production method/ technique where
more machines are used than labor. It is also called labor saving technology
because we save more labor to use machines. It is common in industries,factories, mining etc.
Advantages of Capital -Intensive Technology
• Commodities of high quality are produced, which compete favorably
both in the domestic and international market.
• There is mass production. With the use of machines more output is
produced which stimulates the rate of economic growth in a country.
• Exploitation of idle resources is encouraged since it is efficient which
increases the production of more goods and services.
• Promotes the development of skills. Using machines requires highly
skilled labor therefore encourages people to do research innovations
and inventions.
• Reduces labor unrest for instance demonstrations and strikes. This
increases production of more goods and services therefore it is easy to
control machines than labor.
• It saves time and increases labor productivity because a worker who
uses a machine will do his or her work in the shortest period and are less
exhausted than using manual labor to perform a given task.
• Promotes specialization this leads to production of excess (surplus) at
a low cost. The surplus is exported yielding foreign exchange earnings.
• High profits for the entrepreneur since it minimizes costs in the form
of wages bills and other fringe benefits.
• It promotes industrialization. When capital intensive technology
is adopted, many industries will come up and development of other
infrastructures such as roads, hence promoting the tertiary sector.
• It strengthens good relationships between countries where machines
are exported or imported, hence fostering trade.
Disadvantages of capital-intensive technology.
• It is very expensive to buy machines. Most developing countries
depend on foreign aid and loans to finance their budgets, so if they adopt
the use of machines, they will have too much debts.
• It leads to technological unemployment since more machines are
used than labor in the production process therefore most labor will be
unemployed, which is an economic problem.
• It widens the income inequality gap where a few skilled labor will be
engaged in the production process to run machines and the unskilled
will remain unemployed hence widening the gap.
• High costs as a result of maintenance, repairs when broken down and
depreciation. therefore, it is expensive because it requires a lot of foreign
exchange to import spare parts and other machines.
• It encourages rural- urban migration since most machines are used
in urban centres this leads to development of shanty towns or slums in
cities.
• It is not helpful in the eradication of poverty since there are very few
people employed in the production of goods and services.
• It is inappropriate technique in some activities that require human
judgement, such as picking flowers and tea, sorting printed papers. In
this instance machines may not be applicable at all stages of production.
etc.
3. Labor Intensive Technology is the production method /technique
where more labor is used than machines. It is also called capital saving
technology meaning we save capital and use more labor. It’s commonlyused in hotels, restaurants etc.
Advantages of labor-intensive Technology
• It generates more employment opportunities for nationals due to
investments in various sectors. This leads to an even distribution of
income in the country since they are many people involved.
• It reduces costs of production since in most countries labour is cheap
and abundant.
• It helps to reduce rural-urban migration (RUM) since it can easily
be established in the rural areas where labor is abundant. This leads to
rural transformation hence reduction in RUM, poverty is also reduced and
crime rate levels.
• It increases effective demand, many people are employed which
increases their chances of investing in an economy.
• Monopoly control, it minimizes monopoly tendencies in the industry
since the economic power cannot easily be concentrated in a few hands.
• Labor is more mobile than capital technology. It’s easy to move
workers from one town to another compared to moving machinery or
capital assets.
• It does not require a lot of skills and is suitable to work in industries
that require human judgement. For instance, picking flowers, picking tea
leaves.
• Labor can provide feedback and craftsmanship in the production
process, this provides ideas for continuous improvement hence workers
can also adapt to introduce innovative ideas in hand crafts.
• It encourages decentralization as it allows industries to be established
in various parts of the country. That is to say, the rural areas and small
towns.
• It minimizes the dependency on technology which might be complex
and very expensive, hence increasing self-reliance.
• It is flexible. Unlike machinery, it can be used to meet the changing levels
of consumer’s demands.
• It helps to increase the standard of living. When labor intensive
techniques are adopted, many people in families will get jobs and earn
income hence increasing their standards of living.
• It encourages infant industries, which act as training grounds for man
power and this helps in the acquisition of skills. These also play a vital
role in the economic development of a country.
• Personal touch, people can interact properly with customers and mostservices cannot be done with the use of machines for instance hairdressing.
Disadvantages of labor-intensive technology
• It is relatively expensive in the long-term when compared to
machinery, because it is associated with other labor benefits. For
example, housing, insurance, medical bills, trainings,... which increases
cost of production.
• Inferior quality products are produced, when labor intensive
techniques are adopted, many people produce products without carrying
research thus poor-quality products.
• Limited hours of work. Machines can work day and night hence produce
high quantity output. Economic Growth remains low in a country with the
use labor intensive techniques of production.
• It requires a lot of supervision which leads to under utilization of
resources and increased costs.
• Lack of uniformity in production, with the use of labor- intensive
techniques of production there are most likely to produce products that
are not uniform which makes them not competitive to the market.
• Specialization is not promoted in the production process which may
slow down the production process.
• Managerial complexity arises. It is not easy to manage people since
they have individual differences especially when a business grows this
may further lead to bureaucracy in decision making.
• It is difficult to get skilled manpower it is easy to get machines than
skilled labor in a given field and this hampers the production of goods andservices. Etc.
Application Activity 4.1
1. Justify why the government of Rwanda is encouraging businesses to
use capital intensive technology.
2. Refer to your school and describe how technology has helped in theefficiency of the school for both students and the school itself.
4.2. Characteristics/ features of appropriate technology
Activity 4.2
Referring to the types of technology you mentioned above, which type
of technology, is appropriate in;
a) Northern province
b) Eastern province
c) Southern provinced) Western province
Developing countries face challenges of how to utilize resources fully. The
dilemma is that labor is so abundant and capital is scarce, therefore they have
to choose which technology is appropriate. The following are some of the
characteristics of appropriate technology.
1. It should be simple to use without requiring special skills.
2. It should also be effective in order to increase productivity in the country for
economic growth to be attained.
3. It should also be readily available not complex to get.
4. It should be durable and meets the needs of the community.
5. It should also be cost effective and not very expensive.
6. It should be able to reduce income imbalances through employment potential.
7. It should produce for an identified market to prevent resources being wasted.
8. It should be able to produce efficiently the right quality and quantities of the
products needed by the consumers.
9. It should also minimize the use of imported inputs like labor, raw-materials
and some capital equipment.10. It should be flexible/ easy to use and require locally available resources.
Application Activity 4.2
1. Try to find an example of simple and more complicated technique ofproduction from each of the following areas of human activity.
2. If you were to start a business in any of the above human activity
areas, which technology will you likely choose? A simple technology
or a more complex technology?
3. What could be the reasons guiding your choice?
4. Now that you have identified possible businesses from these areas
of activities, which technology do you think will be more effective
in order to improve the productivity of the specific businesses or toimprove your qualities?
4.3. Importance of technology in business
Activity 4.3
Debate “The use of technology in business has done more good than
harm”
Technology is an essential tool in the day today business operations; no matter
the size of the business, technology has both tangible and intangible benefits.
These include the following:
1. The use of ICT through internet helps entrepreneurs to carry out market
research. This helps it to grow and acquire more opportunities across the
globe, hence widening the market by use of E-commerce sites like eBay,Amazon, Jumia, etc.
2. Technology helps to increase productivity of the labor through collaborating
with each other hence speeding up the work.
3. It helps to keep track of records for instance with the use of the accounting
software.
4. Technology can be used for security purposes thus reducing threats of losing
financial data and vandalism to unknown persons. For example, by using
passwords on computers.
5. Technology improves the efficiency of businesses. The use of mobile phones,
printers and E-commerce, eases the work in business.
6. ICT enables easy access to funds through the use of ATM cards, such as debit
cards, credit cards, and electronic money transfers etc.
7. It also enables better decision making as entrepreneurs can get information
at the right time.
8. Technology helps businesses grow with the use of artificial intelligence. This
gives the business a competitive edge over other businesses.
9. Advanced technology helps to produce better quality products that may fetch
a lot of money for the enterprise thus increasing customer satisfaction.
10. Technology helps to perform complicated tasks with ease and faster. For
example, use of computerized accounting software like quick books, sage
and pastel helps in doing accounting with ease.
11. ICT helps firms to monitor the buying habits of their customers and be able
to stock the right products in the right quantities at the right time. Speed
Governors help to keep track drivers from over speeding hence reducing the
number of accidents.
12. Computers can perform a lot of work in the shortest time possible which
would require a lot of time if done manually. Examples include preparation
of control accounts, financial statements and preparing payrolls etc.
13. Technology also helps to cut down costs. For example, the costs incurred
while transporting and delivery of goods can all be done using computersand the internet.
APPLICATION ACTIVITY 4.3
Carry out research and identify the various technologies that are being
used in businesses be it in your school or other business enterprises.
Suggest their importance in terms of communication, management,accounting and transport.
4.4. Technological tools used in business
Activity 4.4
Observe the pictures below and explain the importance or uses of eachmachine, equipment or technology as used in business.
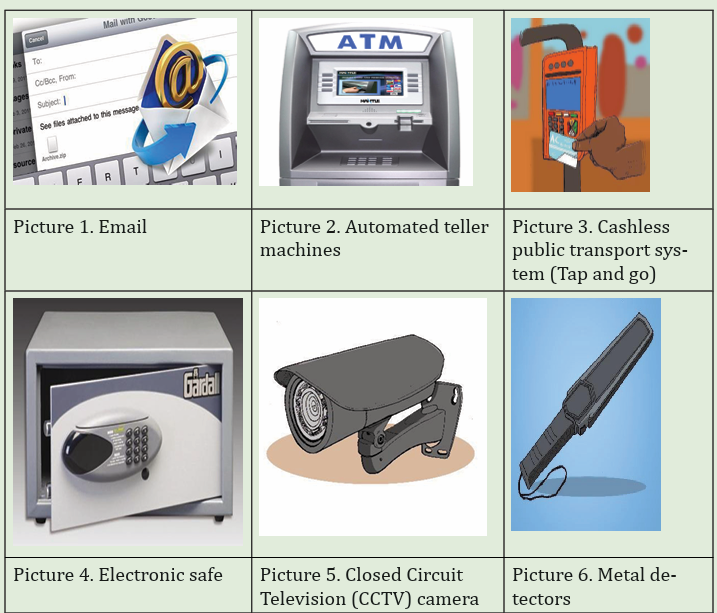
From the above pictures, you realize that businesses use various technological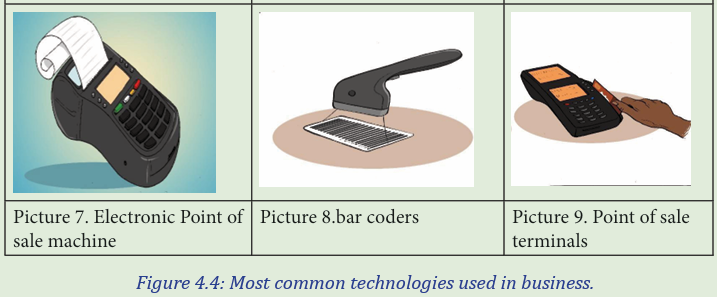
tools, depending on the type of business, and department. The table belowshows the common technology tools used in business departments.
Importance of the technological tools in figure 4.4 above as used in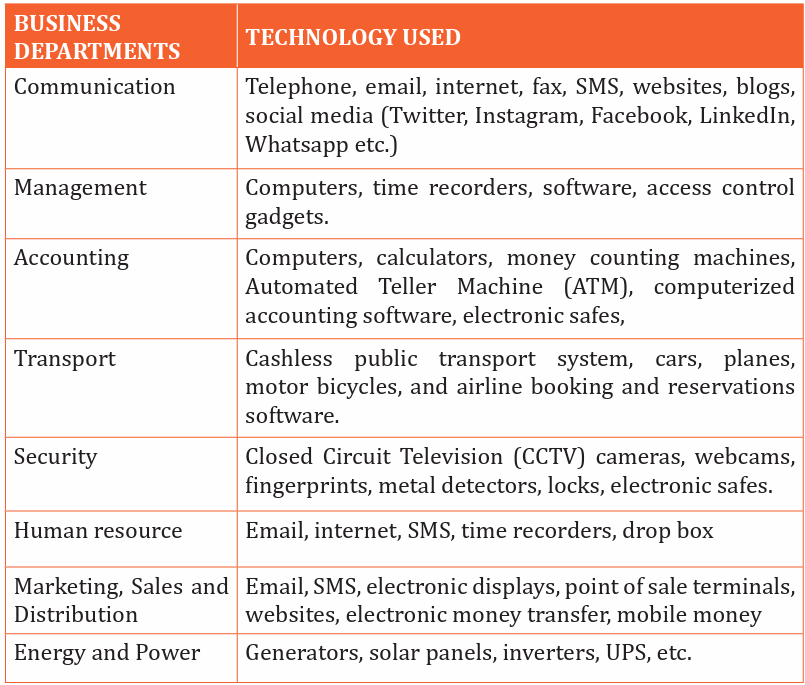
business
Electronic mail: It is one of the ways businesses can use to reach its clients.
Communication is fast and convenient because you can send messages and
they are received between the customers and the business.
Automated Teller Machines: These machines help customers to deposit,
withdraw at any time. This reduces the queues people would make to get their
money. They are also located in different places which eases access to cash
Cash less public systems: (Tap and go) These help businesses to increase
customer satisfaction. They are also secure and convenient which minimizesfraud cases.
Electronic safes: These machines are used to keep money. These are assets to
the business because they are secure.
Closed Circuit Television (CCTV): These are televisions that can be installed
in your business. They can help you monitor your business operations from
anywhere. They increase safety for the owner, employees and customers. If a
crime occurs, they can be used to provide evidence to catch the criminal.
Metal detectors: These are handheld detectors which are used to identify
metallic objects that may be considered dangerous. They also help provide
security.
Bar codes: They are used to track and store information of goods. This
increases the efficiency of the business instead of the storekeeper entering the
information manually.
Point of sale terminals: A POS solution provide a faster checkout process than
the cash registers. This helps people not to make long lines while paying for the
goods bought. Using this tool can increase efficiency and improves the image of
the business.
Application Activity 4.4
1) Describe how new technologies affect business activities.
2) Explain the challenges of using such technologies in local and small
scale businesses in Rwanda.
Skills lab 4
Use available resources like the internet, textbooks, magazines, resource
persons among others to research, choose the appropriate technology
that would improve the performance (Quality, quantity and efficiency
of work) of the projects your business club is running or plan to run at
the college on each of the following business aspect:
a. Business registration
b. Production of Goods and services
c. Packaging and branding
d. Marketing
e. Selling of the products and / services.
And explain why you have chosen that particular type of technology
and how you will acquire it.
End of unit 4 Assessment
1) Case study
Mugiraneza has a peanut butter making business. Last week she
announced the purchase of new equipment and modern technology that
would make a radical change in the production process. The investment
would make some employees lose their jobs. Mugiraneza explained to
them but there was no doubt, it was in the best interests of the company
in general.
Employees were not consulted because it would slow down the process
and Mugiraneza felt that it was the best decision to make.
In the long run, the modern technology and equipment should increase
the businesses’ competitiveness and produce quality products and in
large quantities. The working practices would obviously be changed, and
employees would have to learn new skills of using them. The employees
were promised to be trained, although it was not a guarantee to employ
all of them if they fail to adapt successfully.
After the announcement, the employees were so furious and considered
taking industrial action. Hearing the rumors of a possibility to strike,
Mugiraneza admitted that the issue was not handled very well but would
not reconsider the decision.
a) What factors may have made Mugiraneza decide to invest in modern
technology?
b) Do you think the employees were right in taking industrial action?
Give reasons for your arguments.
c) Analyze the factors that Mugiraneza might have taken into account
before acquiring the modern technology.
d) Mugiraneza admitted that the issue was not well handled. In your
opinion, how should she have handled it?
2. Peter produces flowers and sells them both in the local and
international markets. He plans to use e-commerce in his business.
(i) Mention any 3 e-shops he can contact for advice.
(ii) How can Peter find other e-shops to sell his products on the
international market?
iii) Explain the merits and demerits of using e-commerce in a
business like that of Peter.
(iii) Write a letter to Peter advising him on how to use e-commerce
for the success of his business.
3. Many people believe that the key to better performance is good
management rather than the use of more technology. As an
entrepreneurship student teacher, critically assess this view.
4. The Government of Rwanda is intensifying the campaign of starting
small and medium enterprises to boost made in Rwanda and to export
made in Rwanda products to the rest of the world. Entrepreneurs in
order to meet the international market standards and demand, they
prefer an investment in automatic and capital intensive technologies,
however this affects the numbers of labour force to be employed as
very few people with the right skills will be retained and many of the
rest with no skills to operate the machines are likely to lose jobs.
Required: With your expert knowledge on technology, advise the
entrepreneurs, government and employees on how technology cancreate a win - win situation for all?
UNIT 5:MONEY MANAGEMENT
Key Unit competence: To be able to manage money responsibly and to keep
financial records.
Introductory activity
Case study:
Elizabeth and Kabayiza are married with two children, aged three and five.
Kabayiza works full-time in manufacturing and Elizabeth works four days a
week as a nurse. When they got married, they were renting and maintained
two separate accounts as well as a joint account for bills. Now they own a
home and are paying off a mortgage and saving determinedly for the future
so that they can afford private education for their children by the time they
enter high school.
Referring to the story above and your knowledge about entrepreneurship
skills learnt and competences developed before, answer the questions below.
a. Why do Elizabeth and Kabayiza need money?
b. What are the best ways of the couple to save money?
c. Why do they need to save money?
d. Explain the moral lesson that you learn from the above case study
5.1. Meaning of money, savings and saving goals
Activity 5.1
Using the knowledge acquired in O’level, explain the meaning of the
following terms as used in entrepreneurship:
a) Money
b) Savingsc) Saving goal
A. Money
Money is anything that is generally accepted as a medium of exchange and
repayment of debts.
Money is one of the most important inventions of modern times. It has
undergone a long process of historical evolution.Stages in the evolution of money
1st Stage: Barter trade: Human beings passed through a stage when money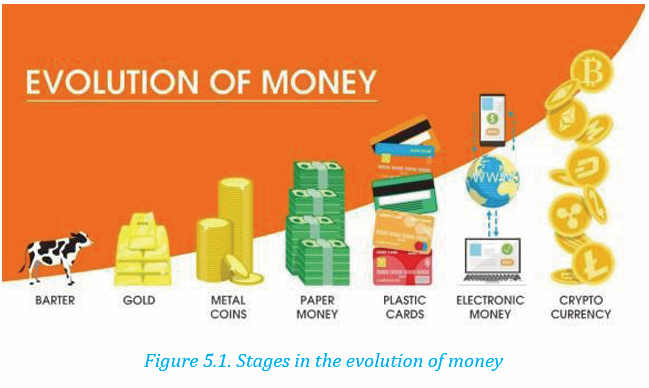
was not in use and goods and services were exchanged directly for goods
and services. Such exchange of goods or services for goods or services iscalled Barter Exchange.
2nd Stage: Commodity money: The inconveniences and drawbacks of
barter trade led to the gradual use of a medium of exchange. In the historical
study of money it is found that all sorts of commodities like seashells, pearls,
precious stones, tea, tobacco, cow, leather, cloth, salt, wine, etc. have beenused as a medium of exchange (i.e. money).
3rd Stage: Metallic money: Inadequacy of commodity money led to the
evolution of metallic money (gold and silver). The problem of uniformity ofweight and purity of precious metals led to private and public coinage.
4th Stage: Paper money: This process was finally taken over by the state
as one of its essential features and ultimately commodity money gave way
to paper money which means currency notes. Nowadays, the use of paper
money has almost become universal along with coins made of copper, bronzeor nickel, etc.
5th Stage Bank money: The process of evolution of some better medium
of exchange still continues. As the volume of transactions increased, even
paper money started becoming inconvenient because of the time involved in
its counting and space required for its safe keeping. This led to bank money
or credit money in the form of cheques, drafts, bills of exchange, credit cards, etc.B. Savings
Savings is the portion of income not spent on current expenditures. Because
a person does not know what will happen in the future, money should be
saved to pay for unexpected events or emergencies. An individual’s car may
breakdown, their dishwasher could begin to leak, or a medical emergency
could occur. Without savings, unexpected events can become large financial
burdens. Therefore, savings helps an individual, family or business becomefinancially secure.
C. Saving goals
Money can also be saved to purchase expensive items that are too costly
to buy with monthly income. Buying a new house, clothes, purchasing anautomobile, or paying for a vacation, etc. can all be accomplished by saving a
portion of income. We usually save for:
• Basic needs
• Household expenses
• Education
• Emergencies/safety
• Retirement/security
• Family wellbeing
• Esteem• Self-actualization
Application Activity 5.1
Using the knowledge and skills acquired in year 1, Unit 3: Settingentrepreneurial goals, set a SMART saving goal.
5.2. Need for money
Activity 5.2Observe the following figures and answer the questions that follow:
a. Describe at least five household expenses.
b. Discuss different sources of income (money).
In everyday life, human beings have different needs. Money is used in exchange
when selling and purchasing different products and services. Money is not only
needed to be used personally but also in business activities.
Money is most especially needed for the following reasons:
• Investment: Money is used to purchase goods that are not consumed
but are used in the future to create wealth. It is used for things that can
generate more money in the future.
• Personal needs: Money is used to make personal expenditure including,
but not limited to, the need for food, clothing, shelter, health care and
safety.
• Emergency: Some money is put set aside to specifically cover any
unexpected expenses that may come up. An emergency fund may cover
unexpected car repairs, medical bills or other emergency situations.
• Education: Money is used for the purpose of completing the education.
• Retirement: Retirement is the years that an individual is able to enjoy
after spending a majority of his/her life devoted to career. One should
put aside a portion of the income to help him or her after working age, etc.
Application Activity 5.2
1.As a student of entrepreneurship, come up with different ways of
getting money.2. Make the total cost of all household expenses in your family.
5.3. Obstacles to achieving saving goals
Activity 5.3
Assess your home community and describe any five obstacles for people
in that community to achieving saving goals.
Saving is a conscious and deliberate way of setting aside a portion of the
personal income for future use.
The following are some of the hindrances to achieving saving goals:
• Procrastination: Delaying savings or putting savings off for another time.
• Poor spending habits: It includes spending on unnecessary items;
Impulse buying; hedonistic lifestyle.
• Culture of dependency: Being over dependent on others.
• Lack of financial literacy: Spending on liabilities or items that
decrease in value over time; not knowing how your money will grow
or work for you.
• Not budgeting: A budget is the bedrock of your personal finances.
Without a budget, your money may be standing on shaky ground.
Why? A budget helps you see how much money you have coming inand going out. And, having a budget in place can help you save money.
Application Activity 5.3
Youth are a rapidly growing percentage of the Sub-Saharan African
population, and many are economically vulnerable. Financial inclusion
for youth, particularly the promotion of savings behavior is associated
with a number of positive social and economic outcomes and is an
international priority. However, the majority of youth in Sub-SaharanAfrica are not saving.
Question:
According to the extract above, discuss any ten reasons why majority ofyouth of sub-Saharan Africa do not save.
5.4. Where to save
Activity 5.4
In your community, you have probably heard people and business
people talking about where they save a portion of their earnings. Identify
where to save money according to what you have heard normally peopletalking about.
Banks provide savings account services
Some savers place their money in a jar, coffee can or a piggy bank which all is
not safe and not encouraged. . It is wise to store money in financial institutions
like banks depository institution. The following are examples of where to savemoney:
• Banks: Through opening up different savings account, one can save his/
her money. For instance, if you find a bank or credit union that offers a free
savings account, you can open up several savings accounts. Then every
time you get an income, you can put money into each of these accounts
for every specific thing that you are saving for. This way you can keep your
money safe from accidentally being spent, and it will be there when youneed it.
• Assets: Individuals can save money through investing in fixed assets.
A good example can be when someone invests his/her money in rental
houses (real estates). The stock market may be down, but your tenantswill still be paying some rent every month.
• Securities: Securities are generally classified as either equity securities
such as stocks and debt securities such as bonds and debentures. The sale
of securities to investors is one of the primary ways that publicly-traded
companies drive new capital for operations. People or businesses cansave their money through buying available securities at the market.
• Small savings groups: This is when someone joins a group comprised of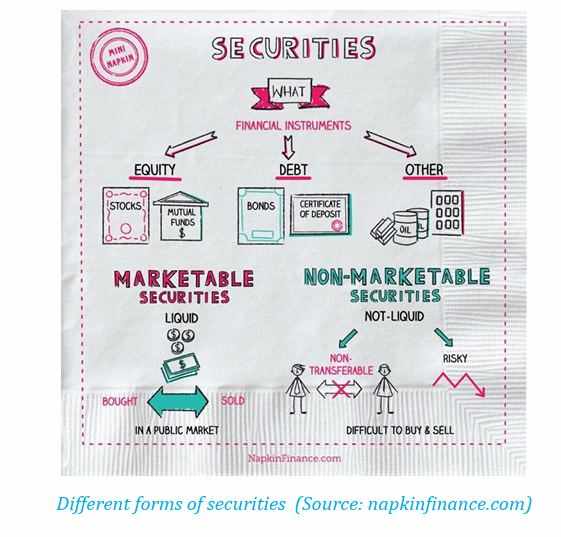
15-25 self-selected individuals who save together and take small loans
from those savings. Savings groups provide members the opportunity
to save frequently in small amounts, access to credit on flexible terms, etc.
• Starting a business: Saving can be through starting up a business thatmay generate incomes and profits in future time.
Application Activity 5.4
KABASHA won entrepreneurship competition. He received a cheque
of 5,000,000Rwf as a reward, but he doesn’t have a ready plan for that
money won.
Required:
Advise KABASHA to identify where to save his money to avoid needlessexpenditure.
5.5. Managing money
Activity 5.5
Extract (Money management-How to make your money go further)
The way you spend your money today will determine what you have
in six months from now, a year from now, five years from now, and in
your lifetime. You control your financial destiny. You are responsible for
the amount of money you earn and for the amount of money you spend.
Successful money managers control the way they spend their money.
They use money to accomplish the things that are important to them.
Good money managers manage their money rather than letting it dribbleaway from them.
Required:
1. Do you have control of the way you spend your money? If yes, how
do you do it?
2. Do you live within your income, or do you have to borrow money or
use savings to meet your regular monthly expenses? Yes/No. Explain
your answer.
Money management is the process of budgeting, saving, investing, spending or
otherwise overseeing the financial usage of an individual or group. The ability
to manage money has to be learned, developed, and practiced on a daily basis.There are eight steps to successful money management:
1. Get organized.
2. Decide what you want to do with your money.
3. Look at all available resources.
4. Decide how much money you are worth.
5. Find out how much money you make.
6. Find out how much money you spend.
7. Set up a plan for spending your money and stick to it.
8. Evaluate your spending plan
The following are essentials for good money management:
• Keeping financial records
• A simple cash book
• Financial forecast
• A simple cash flow plan
• Practicing money management habits E. g. re-use, recycle, repair andreduce.
KEEPING FINANCIAL RECORDS
Good financial recordkeeping enables business organizations to plan properly
and also check for misappropriations of resources. Everyone in business must
keep records. Keeping good records is very important to your business. A simple
cash book, financial forecast and a simple cash flow plan are very important formoney management.
• A simple cash book
The simple cash book (also known as single column cash book) is a cash book
that is used to record only cash transactions of a business. It is very identical to
a traditional cash account in which all cash receipts are recorded on left hand
(debit) side and all cash payments are recorded on right hand (credit) side in a
chronological order.
The single column cash book has only one money column on both debit and
credit sides titled as “amount” which is periodically totaled and balanced like a
T-account. As stated earlier, a single column cash book records only cash related
transactions. The entries relating to checks issued, checks received, purchases
discount, and sales discounts are not recorded in single column cash book.Format of Simple Cash Book:
The purpose of four columns used on both sides of a single column cash book
is briefly explained below:
• Date: The date column of the cash book is used to record the year,
month and actual date of each cash transaction. This column ensures the
chronological record of each business transaction involving receipt or
payment of cash.
• Details: The details column is used to record the account titles to be
debited or credited as a result of each cash transaction. This column is
sometimes titled as “particulars”.
• Ledger Folio: This column is used to write the page number of each
ledger account named in the description column of the cash book.
• Amount: The amount column of single column cash book is used to
record the money value of each cash transaction.
• Note: The debit side (receipt side) of a single column cash book is always
heavier than the credit side (payment side) because we cannot pay more
cash than what we receive during a period.
Example:
The Student business club at one of TTCs uses a single column cash book to
record all cash transactions. It engaged in the following cash transactions
during the month of September 2019.
• Sep.01: Cash in hand at the beginning of the month Rwf 4,654.
• Sep.02: Paid salaries to employees for the last month Rwf 3,000.
• Sep.05: Cash received from S & Co. for a previous credit sale Rwf 2,720.
• Sep.06: Merchandise purchased for cash Rwf 1,400.
• Sep.07: Merchandise sold for cash Rwf 4,700.
• Sep.10: Office furniture purchased for cash Rwf 3,080.
• Sep.12: Stationery purchased for cash Rwf 170.
• Sep.15: Merchandise sold for cash Rwf 9,000.
• Sep.17: Cash paid to A & Co. for a previous credit purchase Rwf 1,780.
• Sep.20: Merchandise purchased for cash Rwf 2,460.
• Sep.21: Merchandise sold for cash Rwf 4,680.
• Sep.24: Cash received from S & Co. for a previous credit sale Rwf 2,400.
• Sep.28: Cash paid for office rent Rwf 1,600.
• Sep.30: Merchandise sold for cash Rwf 7,200
Required: Record the above transactions in a single column cash book (simple
cash book) Solution:
The Student business club’s simple cash book for the month of September 2019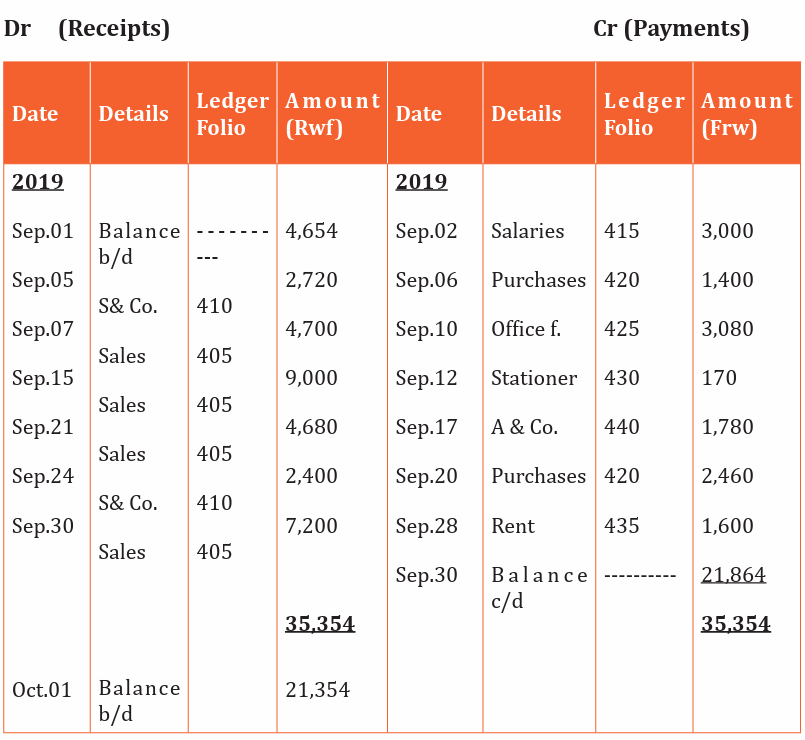
Financial forecast
‘Forecast’ means to form an opinion beforehand i.e. to make a prediction. Thus
financial forecasting means a systematic projection of the expected action of
finance through financial statements. It is a kind of plan which will be formulated
at a future date for a specified period.
The merits of the financial forecasting are noted below:
(i) It can be used as a control device in order to fix the standard of performances
and evaluating the results thereof
(ii) It helps to explain the requirement of funds for the firm together with the
funds of the suppliers.
(iii) It also helps to explain the proper requirements of cash and their
optimum utilization is possible and so surplus/excess cash, if any,
invested otherwise.
Elements of Financial Forecasting:
Financial forecasting involves preparation of proforma financial statements
and also the preparation of Cash Budget.
Therefore, it includes the preparation of:
A. Pro-forma Income Statement: Pro forma income statement is the statement
prepared by the business entity to prepare the projections of income
and expenses which they expect to have in the future by following certain
assumptions such as competition level in the market, size of the market,
growth rate
B. Pro-forma Balance Sheet: This summarizes the projected future status
of a company after a planned transaction, based on the current financial
statements.
C. Cash Budget: A cash budget is an estimation of the cash flows for a business
over a specific period of time. This budget is used to assess whether the
entity has sufficient cash to operate
A simple cash flow plan
Cash flows statement is a statement that provides valuable information about
a company’s gross payments and receipts and allows insights into its future
income needs. Cash flow statement is important because:
• Cash from operating activities can be compared to the company’s net
income to determine the quality of earnings. If cash from operating
activities is higher than net income, earnings are said to be of “high
quality.”
• This statement is useful to investors because, under the notion that
cash is king, it allows investors to get an overall sense of the company’s
cash inflows and outflows and obtain a general understanding of its
overall performance.
• If a company is funding losses from operations or financing investments
by raising money (debt or equity) it will quickly become clear on the
statement of cash flows
Why is it necessary for an entrepreneur to make a Cash flow statement?
• It helps to identify the source of cash inflows in the business and also
identify how cash was used
• It helps management in proper cash planning to avoid excess cash or
cash deficits in the business
• It reports the total amount of cash used during a given period in long
term investment activities such as purchase of fixed assets
• It shows the amount of cash received from various financing sources
such as long term loans and sale of shares
• It helps management to avoid liquidity problems by anticipating when
cash is expected to flow in and plan payments accordingly
• It helps investors to understand how a company’s operations arerunning, where its money is coming from and where it is spent.
FORMAT OF CASH FLOW STATEMENTCash flow statement for the year ended as at……/ …… /……...
At the end of that given period, the business will have a surplus if cash inflows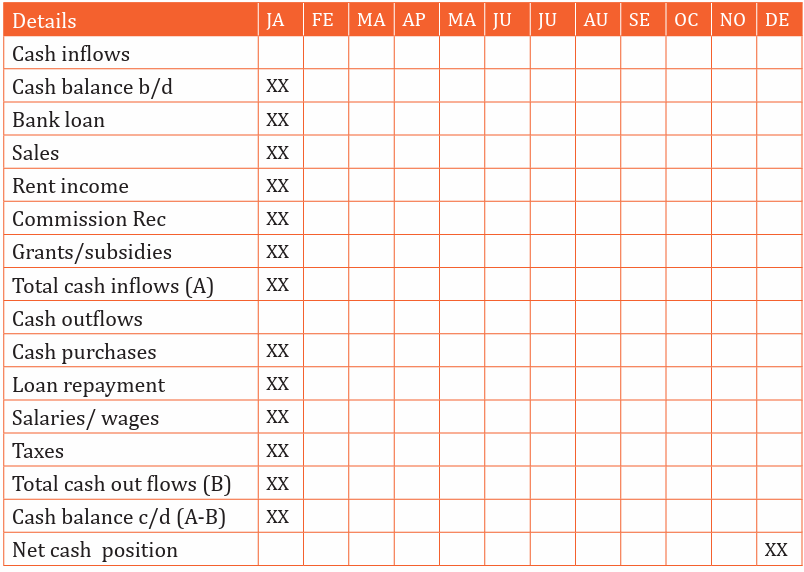
are more than the cash outflows or deficit if cash inflows are less than the cashoutflows.
Example: Prepare Didi’s cash flow for the month of January, February, March
and April 2006, given the following information below:
Cash balance b/d or b/f in January was 15000,000Rwf
Monthly rent income was 5000,000Rwf
Monthly credit sales to be paid in the next month were 4000,000 Rwf
Sold a business van in February 14,500,000 Rwf
Monthly commission received was 3000,000Rwf
Monthly cash sales 10,000,000 Rwf
Monthly cash purchases 12,000,000Rwf
Bought a truck in January 800,000 Rwf
Monthly salaries and wages 5000,000Rwf
Bought machinery worth 15,000,000Rwf, payment of 8,000,000 Rwf was
made in January and the balance was paid in two equal installments duringthe month of February and March.
Solution
DIDI’S CASH FLOW STATEMENT FOR JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH AND APRIL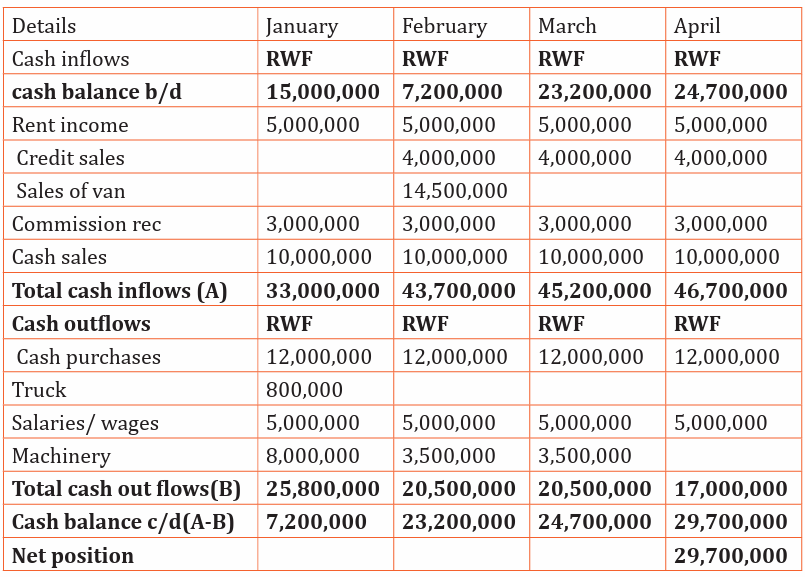
PRACTICING MONEY MANAGEMENT HABITS
With the cost of goods and materials rising, using resources efficiently and
reducing your business’ waste makes good financial sense. It’s also better for
the environment. The cost of sending waste to landfill is increasing, and so
are the restrictions on what you can send. You can face penalties if you do not
handle waste appropriately or have the right paperwork before it leaves your
premises.
You can save money and make your business more efficient by focusing on how
you reduce, reuse, recycle or recover and repair in your business, and how you
deal with the waste that remains.
1. Reducing waste
• Cutting the amount of waste your business has to handle is the most cost
effective and environmentally-friendly method of dealing with waste.
• There are a number of areas you could focus on:
-Procure carefully - buy only what you need, control stock and
streamline processes across departments. Buy equipment in bulk to
reduce packaging and consider the product›s durability and lifespan -
replacing equipment less often will reduce the waste you create.
-Look for easy wins - seemingly trivial changes can produce significant
savings, such as printing and photocopying double-sided, refilling
printer cartridges, switching off lights and electrical equipment, and
using rechargeable batteries.
-Review your processes - ensure that equipment and materials are
used efficiently and packaging is kept to a minimum.
-Product design - keep the amount of materials you use in products to
a minimum.
-Packaging design and use - make sure you use as little packaging as
possible to achieve an adequate level of protection for your products.
2. Reusing waste
You may be able to reuse materials and equipment in your own business or
another organization.
For example, consumers can refill a purchased bottle of water with water from
home to minimize the number of plastic bottles being discarded.
Reusing your own business waste can reduce your costs as you won’t need to buy
raw materials or pay to dispose of the waste. You may also be able to generate
income from materials and goods that are valuable to another organization.
3. Recycling waste
Recycling is the third-best waste management option for your business, after
reducing and reusing waste. Even so, recycling is important because it reduces
the amount of waste sent to landfill and reduces the need to use new raw
materials. Recyclables include glass, newspaper, aluminum, cardboard and a
surprising array of other materials.
4. Repair
The business can repair broken materials and equipment such as lampsinstead of buying new ones
Application Activity 5.5
1. Write up a single column cash book of UBUMWE Enterprise forthe month of April 2015, from the following?
Requirement: Prepare cash book at April 30, 2015: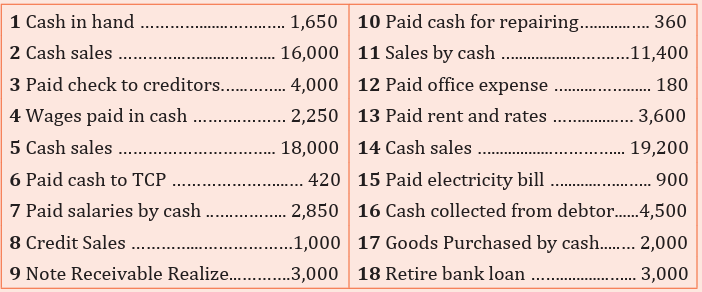
2. Given the information below on Central Trading Company Ltd for
the month of April, May & June
• On 1st April, 2005 Central Traders Company Ltd had a cash
balance of 10,000,000 Frw.
• It expected monthly cash sales of 5000,000 Frw.
• Credit sales were 3,500,000 Frw per month and the payments
• would be made in the following months.
• Monthly rent income from some of its properties was expected
to be 1,000,000 Frw
• Monthly cash purchases were 6,000,000 Frw.
• Monthly salaries and wages bills were projected at 800,000 Frw.
• A loan from Umwalimu Sacco was 10,000,000 Frw was received in May.
• Monthly interest payment of 100,000 Frw on the loan.
• Monthly raw material for 5000,000 Frw.
Required: Prepare central trading company’s cash flow statement for
the month of April, May, and June
Skills lab 5
Discuss and suggest strategies or how you will cut costs/expenses
using the 4Rs (reducing, recycling, repairing and reusing) in your
student business club. Prepare a new projected cash flow statement
after applying the suggested strategies.
End of unit 5 Assessment
1. Read the following dialogue and answer the questions that follows;
Peter: Does what you know now about money management affect
your future?
Peace: Of course what you know today affects tomorrow. You
couldn’t drive a car without a license, and that is why you need to
begin learning about how to spend your money wisely today.
Peter: How does your attitude towards money change as you age?
Peace: Five-Year-Old: Come On mom, can I have some money to buy
that ring?
Fourteen-year-old: Mom, I want 10,000Frw to buy designer label
top and those cool pants.
Eighteen-Year-old: Shoot, I know how i can get money for college.
I will ask mom.
Forty-Year-Old: I need to save for my retirement. No excessive
spending.
Questions
i. With examples explain how your money management affects your
future wellbeing.ii. Where do you think a person can save?
UNIT 6: FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
[
Key unit competence: To be able to choose suitable financial institutions for
business transactions.
Introductory activity
Today, people with full time jobs or part time jobs who use debit cards,
credit cards are most likely to have a close relationship with financial
institutions. Basing on the knowledge and the community you live in,
a) Identify any financial institutions known to you.
b) Do you think those financial institutions are important in managing localbusinesses? Support your answer.
6.1. Meaning of financial institutions
Activity 6.1
i) Read the case study and answer the questions that follow;
Keza started up a project of making paper bags at school having seen that
a lot of paper was trashed and littered around the school compound. She
sold these paper bags to the neighboring shops. She got a lot of money
and felt insecure to keep it in the dormitory, so she thought of opening
an account in the nearby bank. She also thought of saving the money in
the bank so that it accumulates interest and also in the long run acquire a
loan and expand her business by making flower vases, artefacts.
a) Do you think Keza took a wise decision? Why?
b) If it were you, what would you do to feel secure with the money
while at school and why?
c) How would you define financial institutions?ii) Differentiate banking from non-banking financial institutions.
Financial institutions are institutions that deal in providing financial services
to their clients. They offer both short- and long-term finance to entrepreneurs
for their business operations. Financial institutions include; Central bank,
commercial banks, microfinance institutions, merchant banks, development
banks, Savings and Credit Societies and insurance companies etc.
Financial institutions provide a variety of financial services to the public which
include deposits and withdraw services, loan services and financial advice toentrepreneurs among others.
Types of financial institutions
a) Banking financial institutions are financial institutions that are authorized
to receive deposits and create credit. These banking institutions include:
1. Central bank,
2. Commercial Banks
3. Other Banks:
• Development Banks
• Savings and Credit cooperatives (SACCOs)• Micro finance institutions and Microfinance banks. etc
b) Non- banking financial institutions these are institutions that accept
deposits but don’t create credit and offer other bank related services such as
investment and risk pooling.
Examples include:
-Insurance companies
-Building societies
-Pension funds-Capital markets
Application Activity 6.1
Imagine you are to start up a business in your community.
a) Which type of financial institution will you work with closely and why?
b) Why would you insure your business?
6.2. Factors for selecting suitable financial institutions to deal with
Activity 6.2
Analyse the factors that would be considered to choose a suitable
financial institution to work with.
There are several factors considered while selecting suitable financial
institutions which include the following:
i. Interest rate: In case of borrowing money from the banks. Entrepreneurs will
opt for banks with lower interest rate and when it comes to entrepreneurs
saving their money in banks, they will prefer a relatively higher interest rate.
ii. Proximity: Most people will prefer banks that can easily be accessed. This
means institutions that have many branches.
iii. Customer care: Financial institutions which provide good customer care
are normally liked than those without.
iv. Payback period: Refers to the time taken to recover the initial investment.
Financial institutions that give a long pay back period are normally considered
preferable than those that give short payback period.
v. Terms and Conditions of issued loans: Financial institutions that provide
soft loans are chosen faster than those that give hard loans. Soft loans are
loans with low interest rate or not at all.
Vi. Legal procedures: The financial institutions that have licenses to operate
and are recognized by the central bank are always preferred.
vii. Time of operation: It is better to deal with a well-established financial
institution than a newly established one. In other words, it is better to deal
with those that have been in operation for a longer period than new ones.
viii. Collateral Security required: Banks which don’t require a lot of collateralsecurity are always considered by most people.
Application Activity 6.2
Role play on the factors for choosing a suitable financial institution to
deal with.
Visit a nearby financial institution to identify services offered by thatinstitution
6.3. Services offered by financial institutions

Activity 6.3
Examine the services offered by:
a) Commercial banks
b) Central bank
c) Insurance companies
Various services offered by financial institutions:
Central Bank (National Bank) Eg: BNR- National Bank of Rwanda
• Issuing of currency: The National Bank is the only bank that is authorized
to issue and renew the old notes and coins of a given country.
• It is a banker to all other commercial banks.
• It stabilizes the country’s currency in circulation by using various
monetary policies.
• It acts as an advisor to the government on issues regarding the economic
situations like how to control inflation, etc
• It acts as a lender of last resort to commercial banks.
• It manages the government debts that is both internal and external
debts.
• It licenses, controls and supervises all the banking activities of
commercial nature.
• It’s a banker to international institutions working in the country e.g.
FAO, Red Cross, WHO, UNICEF etc.
Y2_Entrepreneuship_SB.indd 91 22/07/2020 04:44:43
Commercial Banks ( Eg: BK, Equity Bank, KCB, I&M Bank, etc)
• They accept customer’s deposits.
• They also advance short and long term-loans to the public in order to
generate interest as profit.
• They facilitate easy transfer of money nationally and internationally
and from one account to another.
• They facilitate international trade through offering or selling travelers
cheques.
• They provide foreign exchange services where one can easily exchange
one currency to other currencies.
• They provide overdrafts to clients that is, where one can withdraw
money which is in excess of his / her bank account balance. .
• Most commercial Banks provide financial training.
• They provide a variety of accounts to the public to be used when
depositing or withdrawing their money each with varying benefits
such as savings accounts, fixed deposit accounts, current accounts etc.
• They act as referees or trustees where one can trust them to safeguard
valuable items like land titles, car log books, Wills and other valuable
items.
• They act as agents of stock exchange. They buy/sell shares of different
limited companies on behalf of their clients.
• They provide foreign exchange to the customers operating foreign
exchange accounts e.g. dollar accounts.
• They also protect business properties.
Insurance companies (Non Banking Financial institutions)
An insurance company refers to a business that provides coverage, in the form
of compensation resulting from loss, damage, injury, treatment or hardship in
exchange for premium payments. The company calculates the risk of occurrence
then determines the cost to replace (pay for) the loss to determine the premium
amount. Eg: RADIANT, CORAR, SAHAM, UAP, BRITAM, etc
The following services are offered by insurance companies:
• Business Insurance,
• Professional Indemnity,
• Property Insurance. ...
• Motor Insurance,
• Home & Contents Insurance,
• Cyber Insurance, etc
Application Activity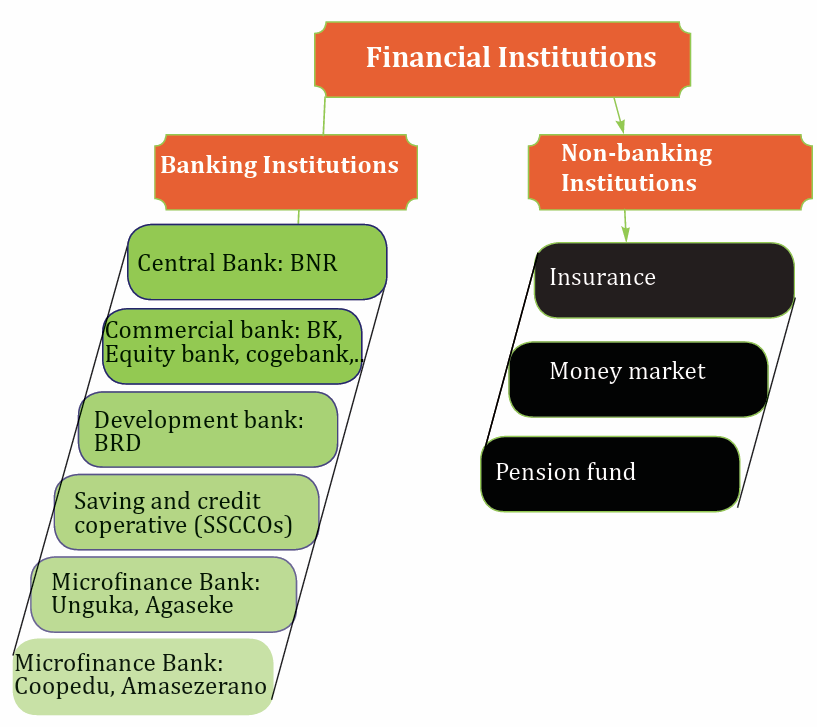
a) Carryout research on any two financial institutions that are near your
school and evaluate the services they offer.
b) Select an appropriate financial institution to deal with in your school
business club. Give reasons to justify.
6.4. Role of financial institutions in social economic development
Activity 6.4
Describe the role of financial institutions in social economic development
Financial institutions play an indispensable role in the overall development of
a country. They include the following;
a. Financial institutions play a key role in creating employment in an
economy. Many people are employed in different financial institutions thus
improving their wellbeing.
b. They help to control inflation in the country by use of the monetary policy
tools.
c. They provide loans to the public which are used to start-up businesses
hence improving their standards of living.
d. They offer a safe custody for the public finances thus reducing cases of
theft.
e. Financial markets help in boosting economic growth. They encourage
people to save by buying shares and bonds and then use it to invest in large
projects and industries.
f. Financial institutions do offer loans to businesses at substantial interest
rates. This helps businesses to increase their production and distribution
activities.
g. They promote foreign exchange markets through supporting entrepreneurs
in exporting and importing goods and services. Businesses can receive and
transfer funds in other currencies.
h. Economic growth depends on the growth of infrastructural facilities of the
country. These infrastructures require a lot of funds which are funded by
these financial institutions.
i. They also help to facilitate domestic and international trade.
j. They help to balance economic growth since all the different sectors in an
economy rely on financial institutions. The primary, secondary and tertiary
sector industries all need sufficient funds from these institutions.
k. They help to attract foreign capital through the capital market authority.
Foreign companies can buy shares, stocks in another country. Such as KCB,
IM bank, equity bank among others.
l. Financial systems of different countries can promote economic integration.
This is when common economic policies, such as common employment
laws, commercial laws are applied. For example, the East African
Community (EAC).
m. They also help in the development of new technology to be used. For
instance, computers and other new technologies to be used in recording
information.
In general, financial institutions play a key role in social economic development
of any economy and no economy can run successfully without a sound financialsystem.
Application Activity 6.3
Write an essay on the following statement: “Financial institutions arethe key engine to the development of the country”
Skills lab 6
a) As future entrepreneurs, discuss the financial needs you have in your
school business club.
b) Research on the internet and through resource persons in your
community for the terms and services offered by other financial
institutions as much as savings and credit cooperatives are concerned.
Then, compare with those discussed in this book and choose the one
that is more appropriate to your business club. Give clear reasons asto justify your choice.
End of unit 6 Assessment
1) As an entrepreneurship student, choose two suitable financial
institutions to work with in the school business club and give reasons
why you chose the above institutions?
2) Why is the government of Rwanda encouraging people to invest incapital markets?
UNIT 7: QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY COMPLIANCE IN BUSINESS
Key Unit competence: To be able to maintain effective quality compliance
system in business.
Introductory activity
Quality assurance and Compliance Case Study:
The government of Rwanda through Rwanda Standards Board is mandated
to provide National standards and conformity assessment guidelines
that entrepreneurs/traders ought to follow during production and selling
of their goods and services. These guidelines help entrepreneurs to be
cautious and careful with the quality and measurements of raw materials
used, goods produced and the technology used. If your business conforms
to the required quality management, assurance and compliance standards,
it reduces mistakes and inconsistencies that could make these goods unsafe.
If you manufacture a food product, your quality control processes should
monitor temperature and foreign bodies to decrease the likelihood that
you will make someone sick. Ensuring customer safety saves your businessmoney and averts damage to your reputation.
One of the ways that the business can strengthen its quality is by listening to
its customers and incorporating their feedback in the business processes and
production systems. Product quality issues that customers normally report
should be tracked and managed through a rigorous process of investigation
and resolution. These and more processes help the business to continually
enhance customer satisfaction. It’s also important that businesses aregenuine in their measurements of goods produced and sold.
Questions
Referring to the above case study, answer the following questions below;
a.What does the National Standards and conformity assessment
guidelines expect entrepreneurs to do ?
b. What are likely negative effects the business may face if customers are
not satisfied as a result of wrong measurements of the goods bought ?
c. What strategies would you propose to the entrepreneurs to implement
and ensure the safety of their customers?
d. Design a simple quality management system of the business idea youintend to start in your community.
7.1. Quality assurance and quality compliance
Activity 7.1
Explain the meaning of:
1. Quality assurance,
2. Quality compliance and3. Quality management
7.1.1. Meaning of quality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is any systematic process of determining whether a
product or service meets specified requirements. It is also referred to as the
maintenance of a desired level of quality in a product or service, especially by
means of attention to every stage of the production process or delivery.
A quality assurance system is meant to increase customer confidence and a
company’s credibility, while also improving work processes and efficiency, and
it enables a company to better compete with others.
Quality assurance is very important because it helps a company create
products and services that meet the needs, expectations and requirements of
customers. It yields high-quality product offerings that build trust and loyalty
with customers. The standards and procedures defined by a quality assurance
program help prevent product defects before they arise. Quality assuranceincludes two principles:
1. “Fit for purpose” (the product should be suitable for the intended
purpose); and
2. “Right first time” (mistakes should be eliminated).
It includes management of the quality of raw materials, assemblies, products
and components, services related to production, and management, productionand inspection processes
7.1.2 Meaning of quality compliance
Quality compliance means acting in accordance with systematic processes of
determining whether a product or service meets specified requirements at
every stage of the production process or delivery. Complying with the quality
requirements helps the business in different ways such as satisfying customers’
needs, increasing the level of sales due to a large number of customers attached
to the product or service, complying with the state’s quality requirementsamong others.
Application Activity 7.1
Using typical examples differentiate quality assurance from qualitycompliance.
7.2. Measurement standards
Activity 7.11. Study the illustrations below and answer the questions thereafter.
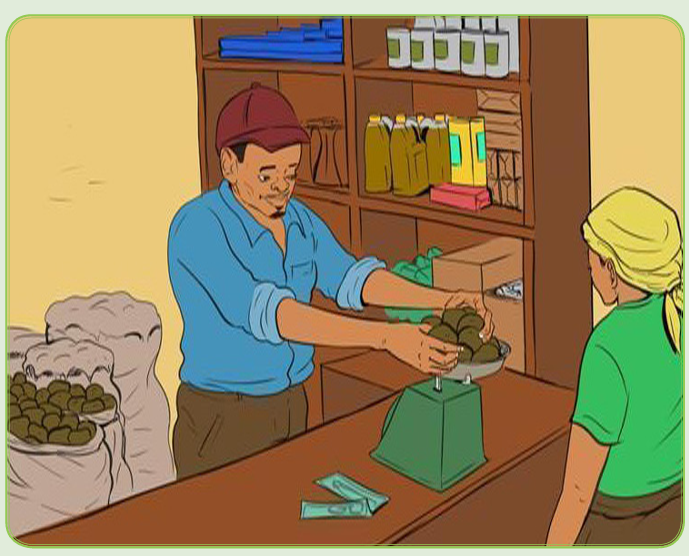
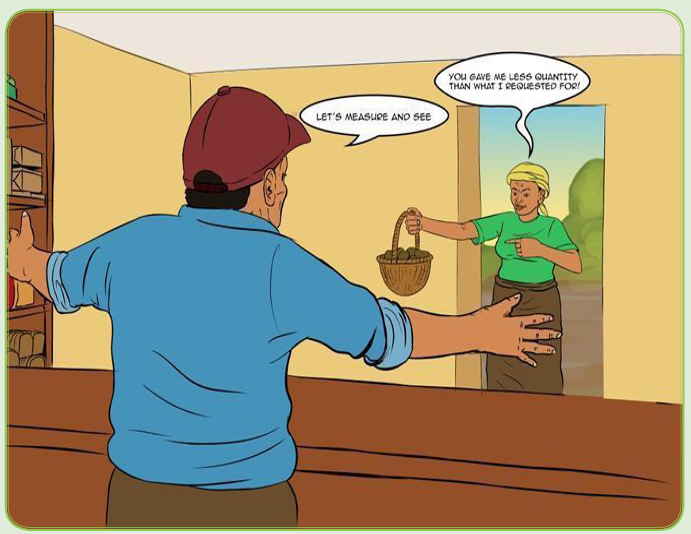


a) What do you observe in the above illustrations?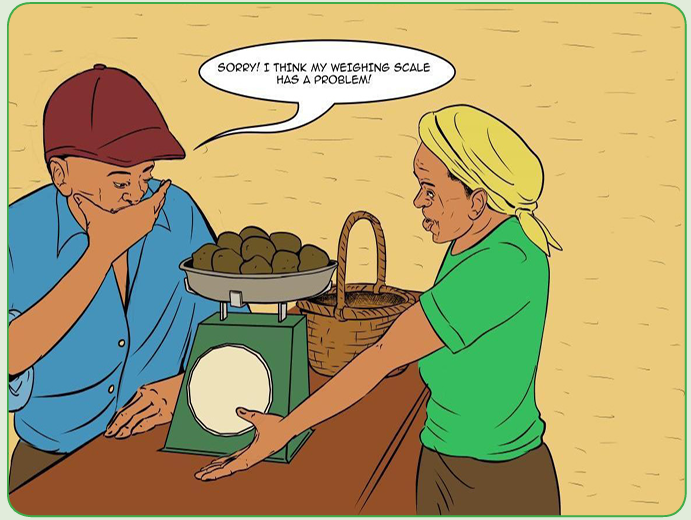
b) What lessons do you learn from the above illustrations?
c) Why should buyers of given products make sure that productsbought conform to the right measurements?
2. Based on your knowledge in Physics(O’level), explain the measurementstandards used in business activities
Measurements are often made using instruments such as measuring tapes,
weighing scale, rulers, clocks, etc. Measurement is a comparison process. It
involves comparison of the quantity to be measured with a chosen standard
or unit. In the past, for example, the length of an object was compared with
familiar lengths: strides, length of a man’s foot, arm and fingers. Ancient people
also used stones or seeds as their standards or units to measure weight. The
position of the sun and the moon were used to tell time and seasons, the
dimensions of the human body. Below are some of measurement standardsthat are used in business activities.
The base quantities according to the International System of Quantities(ISQ) are listed in the following table:
Other quantities are derived from the base quantities and some of them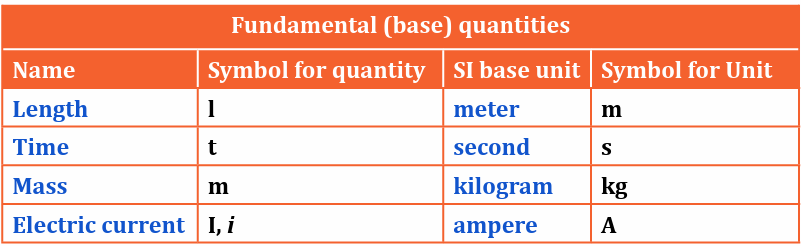
are listed in the table below.
Examples of measurements in business (measurement standard and
measurement materials)
Application Activity 7.2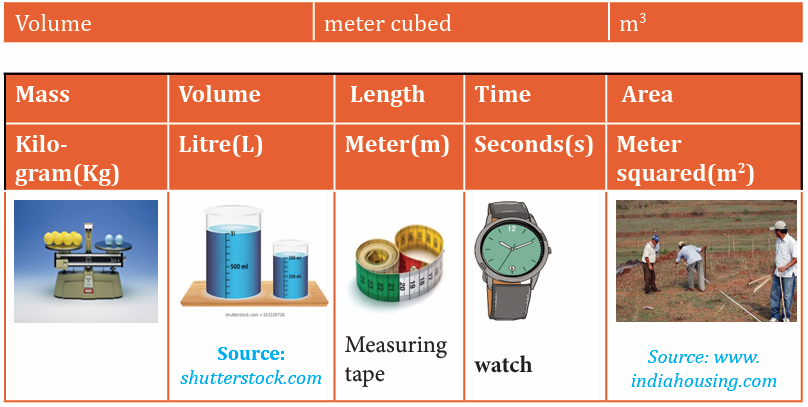
For the business you intend to start in your community, analyse differentmeasurement standards you would emphasize, and why?
7.3. Meaning and relationship between quality
management, assurance and quality compliance
Activity 7.3
Describe the relationship between quality management, quality
assurance and quality compliance
It is important for businesses to pay close attention to Quality Assurance (QA),
Quality Compliance (QC) and Quality Management (QM) since they form an
integral part of the business’ success. Customer satisfaction and maintenance
(customer retention) rely heavily on the applicability of the quality assurance,
compliance and management in production and management processes.
Looking at the above illustration, quality assurance and compliance must be
managed and controlled by the given quality control department of the business.
The illustration shows that if businesses have clear processes of managing
quality and abide to laws and guidelines set by regulatory body (RSB), then
there is quality management.
The relation between the three in terms of standards means that quality
management system is comprised of quality assurance and compliance activities
that ensure the establishment of a set of quality policies and objectives which
act as guidelines within an organization or business.
Quality Management system
A Quality Management System (QMS) is a formalized system that documents
processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies and
objectives.
For businesses to be able to promote quality standards, they need to develop
quality management system. This system becomes part and parcel of business
culture and it is monitored by the business’ quality control team. The following
is a quality management system that can be used by business to promote and
ensure the quality of their products or services:
i) Define and document necessary components of quality management
system. This would include key guidelines and elements of what the business
takes as quality. For example what kind of raw materials will have to be used.
ii) Define the quality policy. This includes the business’ mission that is what
customers want and value from the business. This should be given top
priority in the business.
iii) Quality objectives must be communicated to the team and well
understood, ISO requires that quality objectives are derived from quality
policy and measures.
iv) Define the product defect; that is what contributes to poor quality,
whenever such defects are seen they must be recorded and communicated
accordingly.
v) Develop the documents for the system. This could be a manual that
includes the necessary policies, procedures and forms.
vi) Define the quality process; this includes corrective and preventive action
process, management review and communication process. In short this
involves ways of solving given challenges to quality implementation.
vii) Determine the training needs; Entrepreneurs must identify the gaps
within the team so that the workers are trained and supported accordingly
to meet and comply with quality standards.
viii) Use the system. This is the stage when the system is implemented
accordingly.
ix) Measure and monitor performance. Measuring performance happens
after implementation and would vary greatly from organization to
organization depending on size, potential risk, and environmental impact.
x) Take action that improves performance. This is the last step that is
implemented and when solutions to the risks are identified as per the qualityprocess, they communicate them to the employees.
Application Activity 7.3
1. Interrelate quality management, quality assurance and quality
compliance
2. Think about businesses that exist in your community, how have theyfailed to observe quality expectations?
7.4. Levels of accreditation and accreditation bodiesActivity 7.4
1) What do you understand by the term accreditation?
2) Identify levels of accreditation and accreditation bodies.
Accreditation is one of the critical quality infrastructure elements that facilitate
trade. Accreditation of conformity assessment bodies provides the acceptance
of tests results, inspection reports and certificates that accompany products
and services traded across borders.There are three levels for accreditation which include the following;
National standards
The national standards body helps to develop consensus-based standards.
As such it considers the balanced views of all stakeholders (traders, industry,
consumer associations, regulators, academia, research institutions, Non
Government Organizations etc.) the standards developed at the national level
can also be used as inputs to develop international standards.
Examples of national standard bodies in Rwanda: Rwanda Standards Board,
Rwanda Environmental Management Authority, Ministry of Health, Rwanda
Development Board, Rwanda National Police, Ministry of Agriculture andAnimal Resources etc.
Regional standards
These are standards set in each region such as EAAB, East Africa Community
Standards (EACS) to enforce standard of goods and services in each region. They
promote trade and commerce in accordance with the progress and prosperityof a given region.
International standards
The international standards bodies develop standards at the international
level. They are composed of representatives from various national standards
bodies. They help to overcome technical barriers in international trade.
Examples of such bodies include, International Organization for Standards(ISO), International Electro-technical Commission (IEC)
Application Activity 7.4
1) Visit the Rwanda Standards Board website and research about
products made in Rwanda with S mark and ISO.
2) Research from internet to come up with different recognizedaccreditation bodies which ensure quality compliance.
7.5. Role of quality compliance in business
Activity 7.5
Why is it important to comply with quality requirements in business?
Compliance means meeting the regulatory requirements.
1) Quality compliance in business ensures that the product satisfy their
intended use.
2) It also reduces the risk of fines, penalties and closure of businesses. When
a business does not meet some compliance requirements it faces the law.
3) It leads to improved health and safety.
4) It leads to improved health and safety quality improvement.
5) Quality compliance maintains or increase market share for the
businesspeople.
6) There is fair competition among businesses hence increasing customerssatisfaction from the products.
Application Activity
1.Research on the Rwanda Standards Board website about the
requirements needed to get an ‘S’ mark for the products in the
school business club.
2. 2) use the link below and explain the importance of the program“Zamukana Ubuziranenge “http://ryaf.rw/?p=2333
Skills lab 7
For any product you produce in the school business club: Discuss and
write down the steps, measurements and procedures of making that
product to ensure standardization of practices in your business, align
with the acceptable RSB standards and make an action plan to acquire
RSB certification for services or products that your business clubproduce or offer. Then, share with the class.
End of unit 7 Assessment
1. James and Rosset intend to start a business of making Chapati and
mandazi, but they have a challenge ensuring consistency in quality
(maintaining the same test, size and thickness) . With your knowledge
on quality assurance and standardisation;
a) Advise James and Rosset on how they can set quality standards
in their business.
b) What measurement tools could they use to achieve the quality
standards?
2. Explain the importance of accreditation for certification services andtesting laboratories.
UNIT 8: FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Key Unit Competence: To be able to recognize the value of accounting in
managing the business.
Introductory activity
Financial Statements “The language of business decision making.”
James is a local entrepreneur in Huye town, he is so passionate and
committed to solve community problems in his home town and country, he
started a crafts business in Huye town, he moves to villages and collect crafts
from women groups and put them in his shop which is strategically placed
to target tourist heading to Nyungwe forest and Akanyaru Centre. He had
a book where he instructed his workers to be recording all sales for each
day, supplies and operating expenses. He believed that this is the best way to
keep track of all business transactions and a sure way to growth.
He wanted to expand the business and felt that 5 million Francs would be
enough. He was advised by his sister Uwera a student of entrepreneurship,
to approach investors and bankers and pitch his business and convince them
to provide funding to enable him to meet the business growth needs.
The investors only gave him 10 minutes to explain the profitability of his
business, the net financial position and the financial projection he needed
for the next 2 years, but this challenged him because the book he kept could
not easily provide this information in the given time, so he failed to convince
the investors and missed the funding.
James realized that he needed to have organized the financial information he
was keeping in a certain order that would enable him to make quick decisionsand make it more presentable and easy to explain to external stakeholders.
Questions:
1. What kind of documents James would have used to organize his
business’s financial information before presenting to investors?
2. What do you understand by financial statements?
3. What is the difference between financial statements and the books of
accounts? Give examples of each.
4. Why is financial information important to any business?
5. What is the purpose of financial statements in business?6. Distinguish between income statement and balance sheet
8.1. Meaning and importance of Financial Statements
Activity 8.1
Study the quote below and respond to the questions that follow.
1.What does the quote above mean to you as a student of
entrepreneurship?
2. Why does the author of the quote emphasize the reliability of the
financial statements?
3. What is the meaning of financial statements?
4. What financial statements should every entrepreneur use tocommunicate and manage businesses effectively? Why?
8.1.1. Meaning of Financial Statements
Financial statements are reports prepared by a company’s management to
present the financial performance and position of a business at a point in time.
Financial statements consist of four statements namely:
1. Income statement
2. Balance sheet
3. Statement of owner’s equity and
4. Cash flow statement
Generally, the most important financial statements are:
(i) The income statement / Financial performance statement or Trading, profit
and loss account.(ii) Balance sheet or the Financial position statement.
8.1.2. Importance of Financial Statements
Evaluation
It’s possible to assess future cash flows, and compare economic and financial
results year by year.
Internal Decision Making
The management can use all the information to guide and lead the company
through future performances.
Planning
Financial Report can be the basis to plan the activity, allocate resources, scheduleActivities etc.
External Decision MakingExternal users can evaluate the possibility to invest in the business or company
Application Activity 8.1
With clear examples, explain the reasons why the following people may
be interested in looking at the financial statements of any business?
-Employees
-Business Manager
-Entrepreneur
-Government-Investors
8.2 Income statement (Trading, Profit & Loss Account)
Activity 8.2
“An income statement is mostly important for well established companies
like Bralirwa, Rwandair, among others, a developing entrepreneur only
needs a book to record day to day transactions”
a. Do you agree with the above assertion? Explain your decision.b. What is an income statement?
Main elements of Income Statement
Income statement is a financial statement that reports a company’s financial
performance over a specific accounting period. Financial performance is
assessed by giving a summary of how the business incurs its revenues and
expenses through both operating and non-operating activities. The income
statement is made of two accounts:
• Trading account where the value of the gross profit is determined bydeducting the cost of goods sold from net sales i.e.
1) Trading account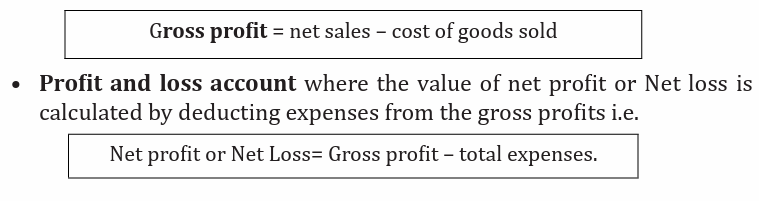
Trading account is an account which is prepared to determine the gross profit
or gross loss of the business concern. It shows the revenues from sales, the cost
of those sales or goods sold and the gross profit or loss from the specific period
ended. It is prepared after the preparation of the trial balance.
Items found in a trading account:
a) Sales: Refer to the value of goods which were bought for resale and have
been sold by the business. It is revenue earned from goods sold. They are
entered in the trading account for the purpose of calculating gross profit or loss.
b) Sales return: Roods that were previously sold but have been returned to the
business due to different reasons including but not limited to poor quality/defects, wrong pricing and delayed delivery.
c) Opening stock: Unsold goods in the business available at the beginning of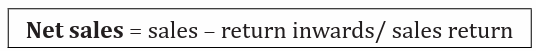
the new trading period.
d) Purchases: Goods bought by the business for resale.
e) Purchases return: Goods previously bought by the business for sale but
have been sent back to the suppliers. This value is treated in the tradingaccount and its subtracted from the purchases to get the net purchases i.e.
f) Carriage inwards: Refers to the cost of transporting the goods or bringing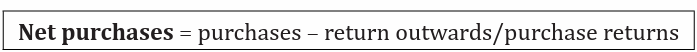
the goods up to the premises. It forms part of the goods bought hence addedto purchases in the trading account.
g) Closing stock: Goods not sold by the business at the end of a trading period.
It’s included in the trading account and it is subtracted from the goodsavailable for sale to get cost of sales. i.e:
h) Drawings of goods: Sometimes an entrepreneur may take physical items
out of the business for private use. This must be subtracted from the goods
available for sale in the trading account. It should be noted that “only
drawings in form of goods” must be treated in the trading account.
i) Gross profit: Excess of net sales over the cost of goods sold or cost of sales. It
also refers to the total profit obtained by an enterprise before paying off the
operating expenses. Thus
Gross profit = net sales – cost of salesj) Gross loss: This is excess of cost of sales over the net sales of the business.
Format of a trading account
There are basically two formats that are used to prepare a trading account. i.e
a) Horizontal
b) Vertical formatHorizontal format / T - Format
Note: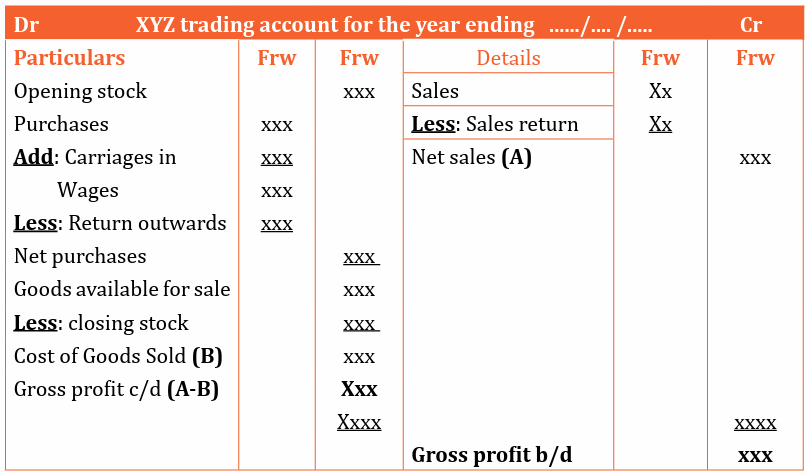
• Goods available for sale (GAS) = Opening stock + Net purchases
• Cost of Goods Sold (COS) = Goods Available for Sale – Closing stock.
• Gross profit = Net sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Vertical format of an Income statement
Income statement for the yearended. date



b) Notice use of brackets on the amounts mean deduction of the amount. The
other option would be to use the word ‘Less’ before the item concerned.
Profit and Loss account:
As seen in the above vertical format of an income statement, you will realize
that Profit and Loss account part represent the company’s NET PROFIT or
NET LOSS which is determine by deducting operating expenses (these includeselling and distribution expenses and administrative expenses) from the Gross income.
Application Activity 8.2
KUNDUMURIMO Enterprise showed the following balances as on 31stDecember 2012
Required: Prepared an income statement for KUNDUMURIMO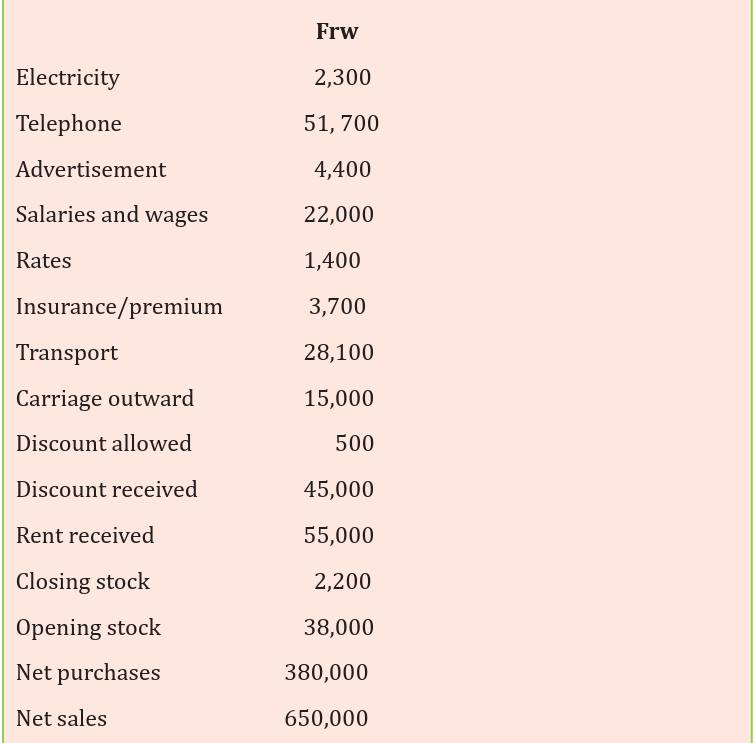
Enterprise for the period ended 31st December 2012.
8.3. Balance sheet
Activity 8.3
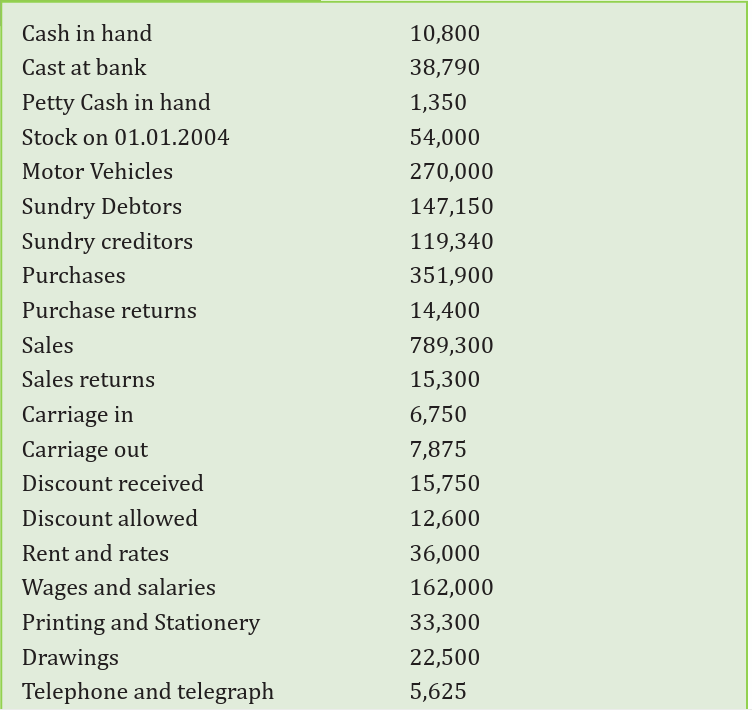
A balance sheet is a statement of assets and liabilities of a business organization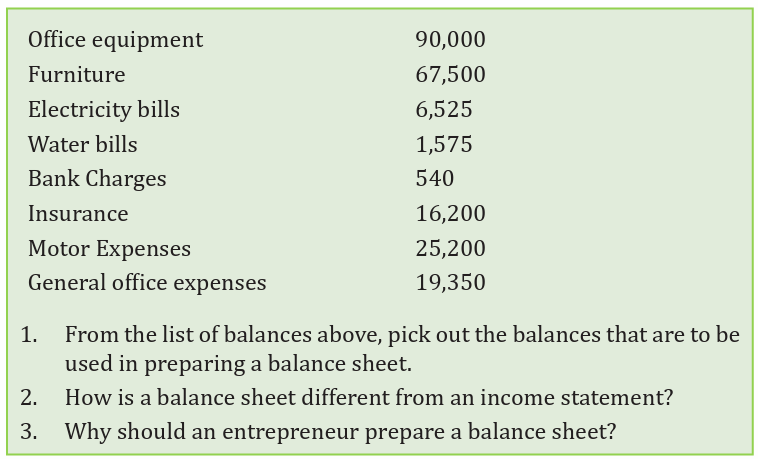
at a given period of time. It is a statement that shows what you own, what youowe, and what you are worth at the end of each accounting period.
A balance sheet is not an account therefore, not part of the double entry but
it is prepared based on the ACCOUNTING EQUATION, which states that: Assets
=capital + liabilities. That is why a balance sheet is also defined as “a statementin which the business accounting equation is expressed”
Parts of a balance sheet:
There are three major parts of a balance sheet;
• Assets
• Liabilities• Capital / Owner’s equity
Assets
These are possessions owned by the business and have got money value.
They are grouped into two;
• Fixed assets
• Current assets
a) Fixed assets: These are the possessions of the business which are of a
durable nature bought for use in the business for a long period of time
usually above one year. E.g. land, equipment, machinery, fixtures and fittings,motor vehicle etc.
b) Current assets: Possessions or properties of the business which lasts for
a short time and usually easily changed into cash. Current assets keep on
being converted from one form to another e.g. stock of goods, debtors, cash
at hand , prepaid expenses or expenses paid for in advance, outstandingincome etc.
Liabilities
These are debts or amount of money that the business owes the outsiders.
They are claims of outsiders on the business’ assets. They are also properties/
possessions that are used by the business and which must be paid back in the
future. There are 2 types of liabilities:
• Long term liabilities
• Short term liabilities
a) Long term liabilities: These are debts of the business that are expected to
be paid after a long time usually after one-year e.g. bank loans, debentures.
b) Short term liabilities/current liabilities: These are debts of the business
which are to be paid within a short time usually within a year. They are claims
by outsiders of the business that are repaid within one accounting year e.g.
trade creditors, bank overdraft, outstanding expenses, prepaid income etc.
Capital
These are the resources invested by the owner or the entrepreneur in the
business. Capital is also known as owner’s equity. To start any business a person
requires capital; which can be in the form of money or other physical resources.
The balance sheet can be reported in two different formats: Horizontal format
referred as account form and Vertical format referred to as report form.
• The Horizontal format consists of two columns displaying assets
on the left column of the report and liabilities and equity on the rightcolumn.
An example of the balance sheet in horizontal format:BALANCE SHEET AS AT ……/………/……….
• The Vertical format, on the other hand, has only one column. This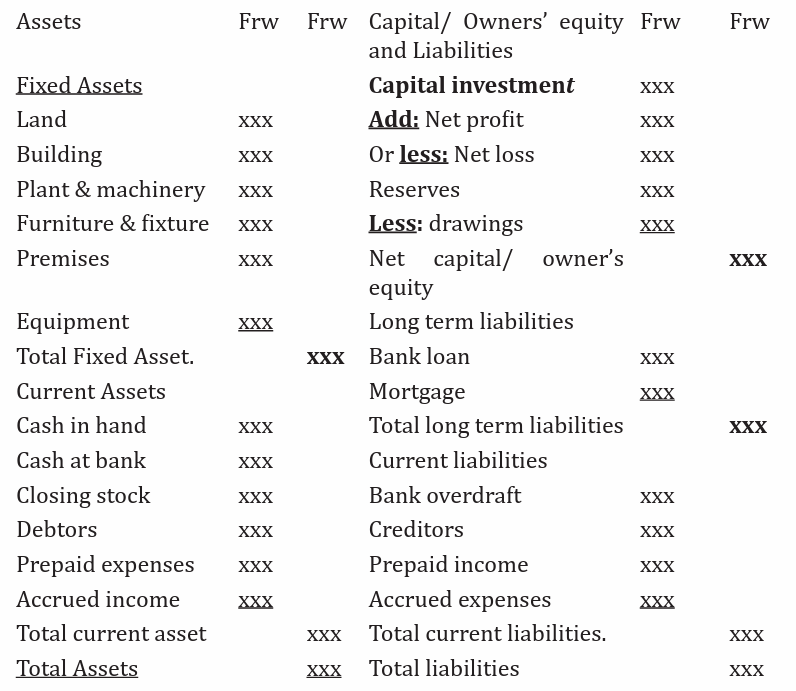
form is one of the most widely used today. Assets are always presentedfirst, followed by liabilities and equity.
An example of the balance sheet in Vertical format:
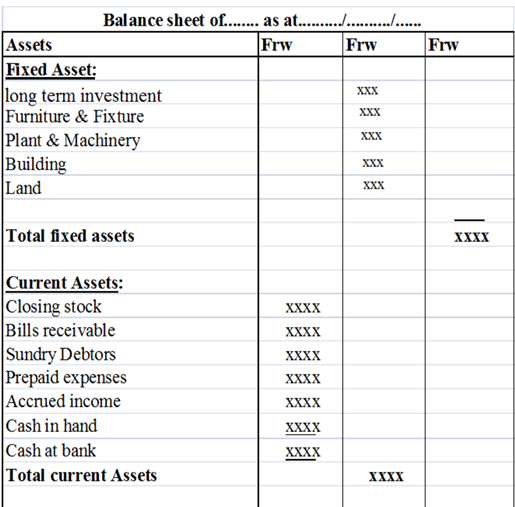
Also assets and liabilities can be arranged according to their realization and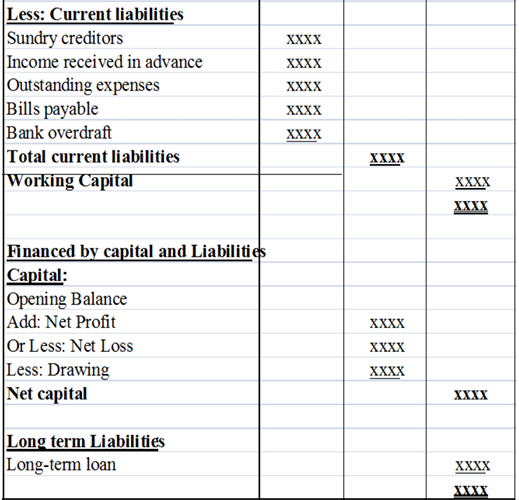
payment preference, which is called liquidity order basis or on the assumption
that these will be sold and paid only on the liquidation of business which is
called the permanence/fixity basis.
Application Activity 8.3
Analyse the accounting information below in the trial balance anddiscuss the questions that follow.
Required: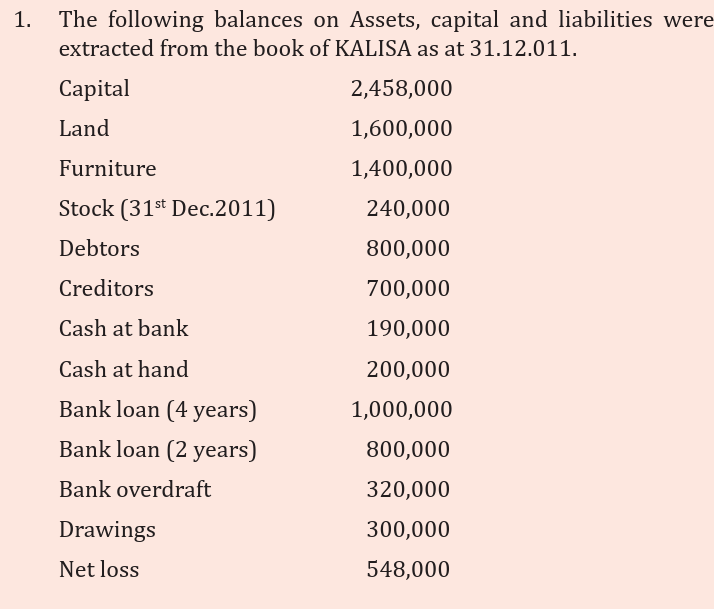
a) Prepare KALISA’s Balance sheet as at 31st Dec. 2011
b) What advice would you give KALISA to improve on his business’sfinancial position?
Skills lab 8
Use the current financial data you have so far in the business club and
prepare an income statement and a balance sheet (or projected income
statement & Balance sheet) for your business club. Analyse the Income
statement and Balance sheet, describe the net financial position of the
business club. Basing on the financial position, suggest action steps to
improve the financial life of your Business club.
End of unit 8 Assessment
1) The following information was obtained from the books of Kanezaand Kamali Ltd Company as at 31 March 2010.
You are required to: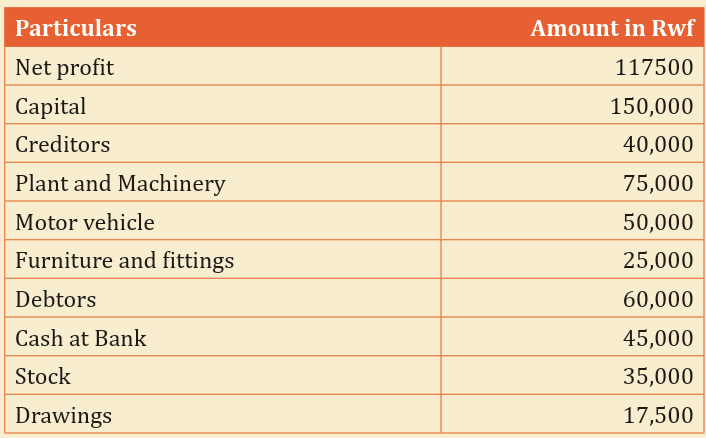
a) Prepare the business balance sheet as at 31 March 2010 in both
formats (Horizontal and vertical).
b) How do you describe the financial status of Kaneza and Kamali
Ltd Company given their balance sheet status?
2) The following was extracted from the books of Alexis traders Ltd asat 31st December 2011

Additional Information: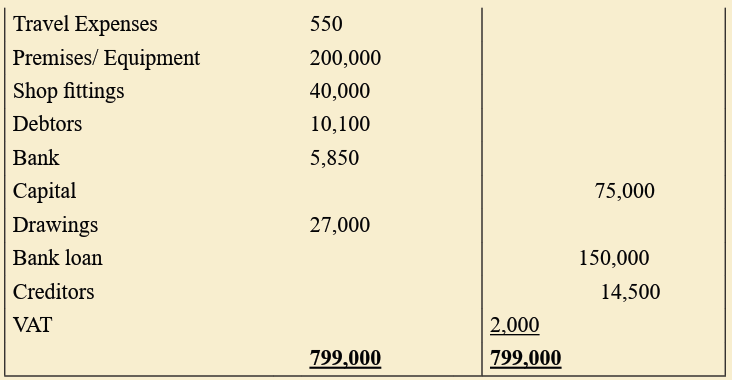
• Stock at 31st December 2011 was valued at 42,000Rwf.
Required:
Using a Vertical format, Prepare Alexis traders’ Ltd trading, profit and
Loss account for the year ended 31st December 2011.
What advice would you give to the business operators given the natureof the profit and loss account?
UNIT 9: RIGHTS AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF WORKERS AND EMPLOYERS

Key unit competence: To be able to demonstrate rights and responsibilities of
employees at workplace.
Introductory activity
OPTIMISMUS Ltd is a company based in KAJEVUBA village. When AKALIZA,
a head of production department claimed to correct some dangerous
aspects in the production system, MAHORO, the Managing Director refused
because it could take 2 weeks to fix the problem while it was a period of busy
production due to a big number of orders received from the company loyal
customers. When AKALIZA was called to report to the Managing Director’s
office to discuss about that issue, she rudely talked to MAHORO, Director of
the company accusing him of not caring about the lives of workers in her
department.
1. Describe the rights that have been violated in regard to employment
relationship.
2. Basing on the scenario above, identify responsibilities which have not
been fulfilled on both employer and employee sides.
9.1. Meaning of rights and responsibilities
Activity 9.1
In 2019, GIRAMAHORO Enterprise dealing in agricultural activities was
established and based in NTARABANA sector. For the smooth running
of the business, the owner took an initiative of using his employment
right to recruit five new workers (employees) to help in achieving the
business objectives. On one hand, some of the main responsibilities of
an employer is to clearly show the worker’s tasks, to train new workers
for better performance of the tasks, and pay the workers regularly for
the work done. Besides, the earlier stated responsibilities of employers
are to give rights to the five recruited workers. The later have
responsibilities of performing the tasks as instructed by the employer,
to report at work on time, etc.
Referring to the above case, answer the following questions:
1. In the case study above, the enterprise owner had the right to hire
workers. What do you understand by rights?
2. Basing on the workers’ responsibilities stated in the case study,
explain what you understand by responsibilities.
3. Explain the difference between rights and responsibilities.
Rights are moral or legal, social, entitlement to have or do something. That is,
rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people
or owed to people, according to some legal system, social convention, or
ethical theory. Examples: Right of peaceful assembly and association, Right to
participate in government and in free elections, Right to be considered innocent
until proven guilty, etc.
Responsibility is the state or fact of having a duty to deal with something or
of having control over someone. It is also referred to as a state or fact of being
responsible, answerable, and accountable for something within one’s power,
control, or management. E.g. an employer is responsible to supervise the
worker and make sure that the work is done in suitable conditions as far as
security, health and dignity of the worker are concerned
Workers’ rights or labour rights are a group of legal rights and claimed human
rights having to do with labour relations between workers and their employers,
usually obtained under labour and employment law. In general, these debates
are about negotiating workers’ pay, benefits, and safe working conditions.
Application Activity 9.1
Youth are a rapidly growing percentage of the Sub-Saharan African
population, and many are economically vulnerable. Financial inclusion
for youth, particularly the promotion of savings behavior is associated
with a number of positive social and economic outcomes and is an
international priority. However, the majority of youth in Sub-Saharan
Africa are not saving.
The following are the rights and responsibilities of workers. Based on your
understanding and skills, tick the following statements where appropriate;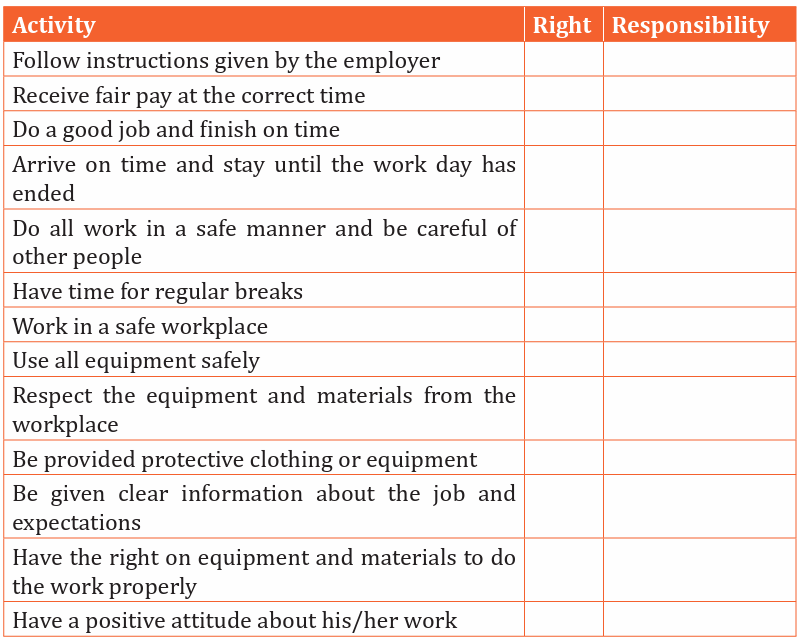
9.2. Examples of rights and responsibilities of workers
and employers
Activity 9.2
1. Read the following scenario and answer the questions thereafter.
KEZA is a newly-hired employee at a restaurant based in Kajevuba
village. KABERA, the human resource manager, pays a lot of attention
to her. At first, she feels flattered, but when he starts touching and
cuddling her she worried. She wants him to stop but is afraid that
if she says anything she might lose her job or strain the working
relationship.
Required:
a. How were KEZA’s rights violated?.
b. Discuss the obligation of an employer that was ignored by KABERA
the line manager to KEZA.
2. Read the following extract, and answer the questions that follow,
Labour law covers all rights and obligations within the
employer
employee relationship whether current employees, job applicants,
or former employees. Because of the complexity of employment
relationships and the wide variety of situations that can arise, labour
law involves legal issues as diverse as discrimination, wrongful
termination, wages and taxation, and workplace safety.
Many of these issues are governed by applicable state law. But, where
the employment relationship is based on a valid contract entered into
by the employer and the employee, state contract law alone may dictate
the rights and duties of the parties.
(a) Describe any 3 rights of workers in a business .
(b) Explain any 4 responsibilities of the workers in the business.
9.2.1. Rights and responsibilities of workers
Employers and employees have responsibilities to each other; they should
also expect their rights to be upheld. These rights and responsibilities relate
to areas such as Health and Safety, the provision of terms and conditions of
employment, equal opportunities and the right to be paid a minimum wage.
Employees have the right to:
1. Be given by the employer the agreed work conditions, at the time and place
as agreed;
2. To implement the work contract signed with the employer;
3. To be paid by the employer the agreed remuneration regularly and in due
time;
4. To be affiliated by the employer to the social security scheme;
5. Enjoy the rights that are provided for workers with dependents by the law;
6. To enter into a performance contract with the employer based on collective
negotiation within the establishment;
7. Work in a respectful, inclusive work environment free of discrimination;
8. A safe and healthful workplace;
9. Ask employer to correct dangerous conditions;
10. Receive training from employer;
11. To be given the needed means for the execution or completion of the work;
12. To benefit from all legal provisions related to the work.
The responsibilities of the worker
According to the article 48 of Labour law in Rwanda, the worker has the
following:
Principal responsibilities:
1. To personally carry out the duties of his/her position: The worker must
personally execute the contract of employment in the time, place and under
conditions agreed between the parties. He/she is not competent to request a
third party to do his/her job or to assist him/her without the consent of the
employer even when the remuneration of the third party will be paid by the
employee or gratuitous.
2. To respect the employer’s or his/her representative’s orders when given so
as to have the work done.
3. To abstain from all that might threaten his/her security or that of his/her
companions or third party, or jeopardize his/her dignity and the one of his/
her colleagues.
4. To respect workplace rules, regulations, policies and legislation prescribed
by the establishment, its branch or the place where he/she is to do his/her
work.
5. To keep in good conditions tools given to him/her and give them back to the
employer at the time the work is completed.
6. Treating clients, coworkers and the public with respect and dignity.
9.2.2. Rights and responsibilities of employers
The employer has the following principal rights:
• Hiring rights: The employers have the right to hire the workers in
accordance with proper procedures and to expect reasonable performance
from their employees.
• Firing an employee: Basing on some legal reasons and after official
warnings, the employer has the right to fire an employee. Some legitimate
reasons for firing a worker include:
- Poor performance/productivity problems
- Gross misconduct/unprofessionalism at work
- Stealing
- General layoffs, etc.
• To see his orders respected: An employee is required to respect
the orders of the employer or his/her representative when given in
furtherance of work, but the level of devotion required of an employee
should not exceed his obligations. In as much as the employee owes
the entirety of his professional activities to the enterprise, nonetheless,
outside his working hours, it is lawful for him to perform any activity of
a professional nature which is not harmful to the proper execution of his
obligations as per the terms of his contract of employment.
• To see his work well executed: The employer has the right to see the
work wholly done by the worker in the time, place and under conditions
agreed between the parties.
• To see all legal provisions in his favor being respected: The employee
is required to respect all obligations contained in the contract of
employment. If the employee is in breach of his/her contractual obligation,
he may be liable to indemnify the employer.
The employer has the following main responsibilities:
• To give to the workers the agreed work conditions;
• To ensure the responsibility of implementing the work contract signed on
his/her behalf;
• To supervise the worker and make sure that the work is done in suitable
conditions as far as security, health and dignity of the worker are
concerned;
• To pay the worker the agreed remuneration regularly and in due time;
• To avoid whatever may hamper the company’s functioning, its workers
and the environment;
• To affiliate workers to the social security scheme;
• To make those workers with dependents enjoy the rights that are provided
for by the law;
• To enter into a performance contract with the worker based on collective
negotiation within the establishment;
• Ensuring no discrimination in the workplace;
• Provide a workplace safe and free from hazards;
• Provide training to employees;
• Provide competent supervision, etc.
Application Activity 9.2
A. Circle the correct answer for each statement.
1. In Rwanda, an employer does not need to:
a. Provide regular breaks for employees
b. Maintain a safe workplace
c. Pay employees the agreed-upon wage on time
d. Pay for employee’s transportation to work
2. In Rwanda, an employee has the responsibility to:
a. Respect and follow the directions given by the employer
b. Avoid hazards at the workplace
c. Keep equipment in good working order
d. Show up on time
e. All of the above
B. State whether the following statements are True or False
1.Rights and responsibilities are the same for employers and
employees
2. The Rwandan labor law protects workers against harassment,
intimidation and violence.
3. Women should not report sexual harassment by their supervisors
because they will lose their job.
4. Rwandan labor law protects adults, not youth.
5. Think about a business, organization or any other institution in your
home locality employing workers. Answer the following questions:
a. Discuss the responsibilities of the employer ( business/
organization employing workers)
b. What rights do employers expect their employees to provide?
Skills lab 9
1. For the business you intend to start in your community;
i) How will you ensure that the rights of workers are observed?
ii) What will be the responsibilities of different workers that you
will employ?
iii) As the employer, what will be your responsibilities?
iv) How will you ensure that workers have performed their
responsibilities?
2. Draw 3 pictures showing human rights violation in your portfolio
notebooks.
End of unit 9 Assessment
KAZENEZA, an Adventist by religion was selected as the best candidate
to work as a teller at URWUNGUKO bank. Saturday is always a very busy
day of the week most especially to cashiers due to the fact that, on this
day, the bank experiences huge amounts of deposits and withdrawals
in almost equal proportions hence many customers. In the employment
contract, the bank highlighted Saturday as a special working day under
the terms and conditions of working days.
Questions:
1. What advice would you give to KAZENEZA taking into consideration
his religious beliefs and the bank’s terms and conditions of the
employment contract?
2. Assume that you are selected by RITCO Ltd; one of the biggest
and famous transport companies in Rwanda to train company
administrative and managing staff on the rights and responsibilities
of employer.
3. Discuss what will be contained in your training presentation as
the rights and responsibilities of employers to make sure that
employees’ rights and responsibilities are not violated by their
employers.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
A-Text books:
Agriculture, U. o.-C. (1989). Money Management-How to Make Your Money Go Further.
University of Kentury.
Akazi Kanoze Youth Livelihood project, (2009), Work Readiness Trainers’ Manual
Ashe-Edmunds, S. (2018, October 15). Importance of Compliance in Business.
Retrieved October 22, 2019, from https://smallbusiness.chron.com
Board, R. E. (2018). Taxes in business. In R. E. Board, Entrepreneurship S5 text book.
Kigali: Rwanda Education Board.
Board, R. E. (2018). Entrepreneurship S.5. Kigali: Rwanda Education Board.
Educate! Exchange, ( 2017), Resources & Competency-based Entrepreneurship
Subject S4 Skills Lab Lesson Plans
Gorgio. (2019, September 27). Rights of employees and employers. Retrieved October
18, 2019, from Businesscasestudies: https://businesscasestudies.co.uk
Jeshwanj, H. (n.d.). Financial Forecasting: Meaning, Elements and Applications.
Retrieved October 20, 2019, from Accounting notes: http://www.accountingnotes.
net
Kalungi Rogers, Ngobi Dennis, Mutegaya Herbert, Okoroi David, Entrepreneurship for
Rwanda Secondary Schools, Learner’s Book
Stebbing, L. (1993). Quality Assurance: The Route to Efficiency and
Competitiveness (3rd ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 300. ISBN 978-0-13-334559-9.
B- Online sources:
Li Zou, S. M.-T. (2015, April 28). Facilitators and Obstacles in Youth Saving: Perspectives
from Ghana and Kenya. Retrieved October 17, 2019, from Springer link: https://link.
springer.com/
Margaret Rouse, D. S. (2019, July). Quality Assurance (QA). Retrieved October 22,
2019, from https://searchsoftwarequality.techtarget.com
Seth, t. (n.d.). Characteristics of a Good Tax System. Retrieved October 21, 2019, from
http://www.economicsdiscussion.net
Labor, M. (2013). Employee Rights and Responsibilities. Retrieved October 18, 2019,
from safety Works: https://www.safetyworksmaine.gov
Limited, M. B. (n.d.). Money management case study. Retrieved October Thursday,
2019, from Macquarie Online Trading: https://www.macquarie.com
What Are The Characteristics Of a Good Tax System? (2016, September 11). Retrieved
October 21, 2019, from https://www.knowledgiate.com
www.smallbusinesschron.com /disadvantages of+ information technology
Entrepreneurship for Rwanda by Asimwe Herbert
www.betterteam.com/employee-contract-templateAdapted from https://wonderopolis.org/wonder/why-do-you-have-to-pay-taxes)
