UNIT 9:AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT
Unit competency:
Analyze the contribution of development strategies on the economy.
Introductory activity

Using photos, A, B, C and D in figure1 above, discuss the following
questions.
1. What activities are taking place in the photos above?
2. What is the difference between the activities carried out in the last two
photos C and D?
3. What is agricultural development?
4. Give the advantages and disadvantages of agricultural development
9.1. Meaning
Activity 9.1
(a). What is meant by the term agriculture.
(b). Explain the advantages and disadvantages of agricultural practices in
your district.
Agriculture is the growing of crops and rearing of animals. There are both food
crops and cash crops involved together with a variety of animals. Agriculture is
basically the backbone of developing countries contributing wholesomely to
their economies and thus its development is paramount.
Agriculture development therefore is the process of promoting proper
conditions for farming so that the quantity and quality improve drastically. It can
also be looked at in the perspective of providing assistance to crop producers
with various agricultural resources for better output attainment.
9.1.1. Arguments in favor of agriculture.
1. Provides enough food necessary to feed the population in both rural and
urban areas.
2. Provides raw materials for agro based industries e.g sugar factories textile
factories etc. which increases the rate of industrialization.
3. Provides employment to the people which enables earn income and improve
their standard of living.
4. Increased output for export and reduced expenditures on imported agricultural
goods which in turn increases the country foreign exchange.
5. Source of medicine to the people of the country especially through the herbs.
6. Provides backward linkages to the industrial sector where it acts as market
for the industrial output such as the hoes, pangas etc.
7. Reduces rural urban migration because people are employed in the agriculture
sector which is normally carried out in rural areas.
8. Facilitates development of infrastructure like roads because of the need to
transport commodities from rural areas to the market.
9. Leads to fair distribution of income because of the employment provided to
the people through agricultural activities.
10. It is source of government revenue through taxing commercial agricultural
products which leads to the development.
11. It acts as training ground to many people, many people get skills from
managing agricultural activities and apply them in other sectors which also
lead to the development.
9.1.2 Disadvantages of agriculture.
1. Agriculture prices keep on fluctuating consistently due to the differences
between planned output and actual output together with poor climate
conditions all which affect the supply and affect the producers
2. Agriculture development may involve expansion of the firms among others
and this may affect the growing population in terms of settlements leading
to fragmentations
3. Products are perishable and difficult to store. This is a big problem that
affects developing countries and worse still they are bulk and may not be
transported easily to other parts of the country
4. Some crops have a long gestation period and thus the farmer may take long
to gain from them even if the prices increase at present, the farmer may not
increase supply thus losing out.
5. Agriculture mostly depends on nature. If the rains fail to come, the farmers
may fail to increase supply than what they may have anticipated and prices
may go up. The inconsistencies in climate worsen the problem of price
fluctuation of agricultural products.
6. Most of the developing countries produce the same types of agricultural
goods and thus products flood at the world market causing prices to fall
down.
7. Development of synthetic fibres which also have the same purpose with
agricultural raw materials these reduces the demand for agricultural
products.
8. High rates of conservatism among the many farmers who prefer quantity to
quality leading to poor quality and low revenue to them as earnings and to
the government as through taxation.
Application activity. 9.1
Examine the role of agricultural development towards a country’s
development.
9.2. Approaches to agriculture development
9.2.1Agriculture Mechanization
Activity 9.2
Basing on the photos A and B.

1. What type of activities are taking place photos A and B above?
2. Describe the method of production used in the two picture?
3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using the above
mentioned machines?
4. Give reasons why using such machines is not common in your home
areas.
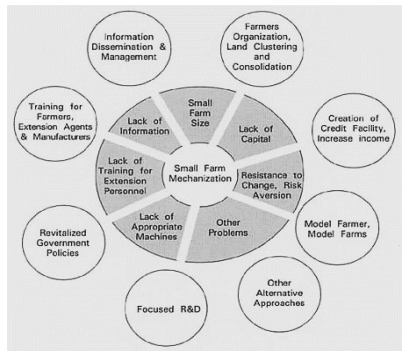
C (problems and solutions to agriculture mechanization)
9.2.1.1 Meaning of agriculture mechanization
Agriculture Mechanization is part of agriculture modernization that involves
the use of capital intensive techniques such as tractors, harvesters, irrigation
pumps, ploughs and milking machines among others in production process. It
is normally done to increase quality and quantity and also for time saving.
9.2.1.2. Arguments in favor of agriculture mechanization
1. Time saving especially during times of planting, ploughing among
others. The machines do the work very quickly and save time that would
have been used by the people
2. Encourages large scale production because machines use large
pieces of land and this increases output that would be exported to earn
the country foreign exchange.
3. Good quality output is produced because of constant use of machines
which can be tuned and adjusted to produce good quality.
4. Reduces the cost of production because the expenditure to buy
machines is not recurring but happens once compared to labour that has
recurring expenditures i.e wages.
5. Encourages specialization depending on the machines which the
farmers have and this increases the quality and quantity and time saving.
6. Easy management because the use of machines doesn’t need close
supervision than labour
7. Machines can act as collateral security when acquiring loans from
financial institutions
8. Irrigation is possible which reduces dependence on nature and it may
help increase output even when during dry periods.
9.2.1.3 Disadvantages of mechanization
1. Capital intensive techniques cause technological unemployment
where machines replace humans.
2. Rural urban migration may occur because mechanization requires
large pieces of land and therefore the local people may lack for settlement
3. Requires large sums of capital to use because the machines such as
tractors, sprinklers, harvesters, all have to be imported.
4. Machines destroy the ecology of the soil since they may not be
appropriate to the soil.
5. Requires gently or flat large pieces of land yet most parts of the country
are hilly with steep slopes thus being disadvantage.
6. Specialization as a result of mechanization may affect the country export
earning incase world market prices fall.
7. Over production. This is because of the work easily done by machines
during the process and this leads to surplus and resource wastage. This
happens where the market is small.
8. Over exploitation of resources due to the desire for the high profits
and excess production by the machines.
9.2.1.4 Limitations of mechanization
1. Requires high skills to operate the machines which are inadequate in the
developing countries due to limited trainings.
2. Existence of inadequate capital, most people in agricultural sector
cannot afford buying agricultural machines like tractors hence limiting the
strategy.
3. Requires large pieces of land which is scarce in LDCs where the land
is divided into small pieces called fragments due to high population growth
rates.
4. Existence of poor topography in some parts of country where the
land is surrounded by many hills. This limits the use of modern machines
like tractors in the agricultural sector.
5. High degree of conservatism in the agricultural sector especially in rural
areas. Here most farmers still have poor attitudes towards mechanization
where by most of them prefer traditional methods to modern ones hence
being a big limitation.
6. Requires a good and efficient agricultural planning which is not
possible in terms of costs and management in developing countries.
7. Underdeveloped infrastructure and technology limits the use of
machines since they require a well-developed road network.
8. Existence of small market for the agricultural output discourages most
farmers from using machines so as to increase output since it may lead to
surplus and a fall in prices.
9. Price fluctuation in agricultural sector also discourage many people from
investing a lot of their money in buying machines because they may fear to
make loses when prices reduce hence being a limitation.
10.Land fragmentation in the country where land is divided into small pieces
yet this strategy requires large pieces of land hence being a limitation.
11.Machines sometimes destroy the ecology of the soil sine they may
not be appropriate to the structure.
Application 9:2
Discuss the factors that hinder agriculture mechanization in most parts of
the country
9. 2.2 Commercialization of agriculture in Rwanda
Activity 9.3
Basing on the photos A, B and C and D the figure given below, discuss
the following questions.

1. What activities are being carried out in the figures A, B, C and D in the
figure show above?
2. What are the benefits and demerits of carrying out the activities below?
3. Give reasons why using such activities are not common in your home
area
9.2.2.1. Meaning of commercialization of agriculture
Commercialization of agriculture is the type of production that is intended
for sell with an aim of getting profits. It normally involves large scale production
with high technology most of the times. The quality tends to be better than
that of subsistence production. In Rwanda the major food crops grown for sell
include Irish potatoes, banana, and rice among others while the cash crops
include tea and coffee among others. Among the animals are cows for beef
and milk, goats and sheep among others. Commercial production involves the
following characteristics:
1. Production is for the market either domestic or international
2. Use of improved seeds and breeds of cattle for better quality
3. Use of modern tools like tractors, harvesters, and sprinklers among
others.
4. Skilled workers are employed compared to family labour used in
subsistence production
5. High levels of productivity due to the need to serve a wide market and
accumulate high profits
6. Land improvements through the use of fertilizers all in the need for
high productivity. High quality is produced since the major aim is profit
maximization.
9.2.2.2. Benefits of commercial agriculture
1. Develops skills of workers because of specialization and constant doing of
the same work.
2. Increases the gross domestic product of the country because of the need
for high profits and revenues.
3. Increases the incomes of the workers and the farmers at large. This is
because production is for sale. This increases the standard of living of the
workers.
4. Good quality products are produced since farmers produce purposely for
sale which improves on standards of living of the people and their way of
life.
5. Increases the exports of the country hence the increase in the foreign
exchange earnings.
6. Increases the supply of food because in most cases it is carried out on large
scales and this in turn reduces the price of food stuffs which increases
people’s standards of living.
7. Promotes industrialization because it involves production of raw materials
on large scales in the country.
8. Capital accumulation may increase because of increased output for sell that
will bring in revenues.
9. Sometimes it is done on a large scale so it utilizes the idle land that may be
unproductive
10. Employment creation. The desire for too much profits make the owners of
the farms to increase the number of workers hence creating employment.
9.2.2.3 Disadvantages of commercial agriculture.
1. Reduction in the food needed by the local people since production is
mainly for sell and not home consumption.
2. Capital intensive techniques cause unemployment in the villages since
mainly machines are used on the extensive land.
3. Requires large sums of capital to use because the machines such as
tractors, sprinklers, harvesters, all have to be imported.
4. Requires large pieces of land and this is a problem in countries where land
has rugged terrain with steep slopes in many parts of the country.
5. Specialization as a result of mechanization may affect the country incase
world market prices fall.
6. Over production. This is because of the work easily done by machines
during the process and this leads to surplus that may not be absorbed by
the available market.
7. Over exploitation of resources due to the desire for the high profits and
excess production by the machines
9.2.2.5 Limitations of commercial agriculture
(i) Poor land tenure systems. Some of the land is owned by absentee land
lords and hence it is inactive.
(ii) Narrow markets. The market is low due to poverty among the people and
the low quality that cannot yield much revenues.
(iii) Poor infrastructure. This limits the movement of goods from gardens to
market and also from areas of low prices to areas of high prices
(iv) Lack of skilled man power. Most people have low skills and worse still they
take long to adjust to the new techniques
(v) Conservatism of farmers. Some farmers are very conservative and are not
able to change to good quality output hence end up getting low revenue
(vi) Inadequate capital. This is still very low and many producers cannot access
the improved equipment necessary to improve the quality and quantity.
(vii) Competition from other countries that produce the same at the world
market. This leads to surplus and constant price fluctuation which affects
the foreign exchange and incomes of the commercial farmers.
Application activity 9.3
Discuss the reasons as why commercial agriculture is encouraged in
Rwanda.
9.3 Measures to improve agricultural productivity.
Activity 9.4

Basing on the photos given above; identify some of the measures taken by the
government of Rwanda to improve agricultural productivity in the country.
1. Encouraging security in the country. This encourages many people both
local and foreigners to invest in commercial agriculture which improves
on agricultural productivity in the country.
2. Establishment of credit schemes in the country which support farmers
with loans this can help to increase on farmers’ capital which encourages
them to produce on large scales.
3. Encouraging agricultural diversification where farmers are encouraged
to carry out different activities in agricultural sector this increases their
levels of income and output hence improving on agricultural productivity.
4. Establishing and developing agro based industries in the country. This
increases the market for agricultural products and encourages many
investors to invest in agricultural sector which in turn leads to increased
agricultural productivity.
5. Educating farmers about different modern methods of farming this can
help them on ways of improving their levels of output.
6. Developing infrastructures like roads which can easily help farmers to
transport their products from rural areas to urban areas where the market
is so big and this encourages many people to invest in the sector.
7. Establishing many agricultural research centers in which farmers can
research and discover modern methods which can be used in the sector
and also to provide improved seeds to them which in turn leads to
increased outputs.
8. Promoting agricultural cooperatives in the country which extend
agricultural services to farmers like storage services, improved seeds,
transport services which all lead to the development of agricultural sector.
9. Improving on land tenure system where people are not allowed to
divide their land into small plots this can help to encourage commercial
agriculture which in turn leads to increased production.
10. Encouraging farmers to use pesticides which can help in fighting against
pests and diseases, this in return can also help to increase on agricultural
outputs.
11. Encouraging agricultural commodity agreements where the farmers of
certain commodity come together and agree the price and the quality of
their commodity this helps to reduce on price fluctuations hence leading
to increased outputs.
Application activity 9.4
(a). Examine the major challenges faced by the agricultural sector in
developing economies.
(b). Discuss measures being taken by most developing economies to
solve such challenges.
Skills Lab
After having learnt about role of agriculture and commercial agriculture.
Identity the most demanded agricultural goods at your school and come
up with the proposal of agricultural project around the school that can
provide such goods to school so as to reduce expenses, and then share
your proposal with the school administration for further consideration.
End unit assesment
(viii) Explain the reasons why agriculture is referred to as the “back
bone” of many developing countries.
(ix) In Rwanda using machines in agriculture sector has not been very
common. Explain the reasons behind this scenario.
(x) Mutoni is among the few farmers in Byumba district who has been
producing beans, peas and ground nuts on large scale for commercial
purposes.
(a). Which special name is given to the nature of agriculture Mutoni
practices?
(b). Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Mutoni’s agricultural
practice.
(c) Explain the factors that hinders other people from joining the same
agricultural practice like that of Mutoni.
4. Explain the measures taken by the government of Rwanda to
improve agricultural productivity.
