UNIT 6: ECONOMIC INTEGRATION
Unit Competency:
Explain the importance of economic integration to the development of theireconomy
Introductory activity
Many countries consider regional economic integration as one of the
crucial elements of achieving their developmental goals. Rwanda as anation, has joined a number of economic groupings.
According to you:
1. What do you understand by economic integration?
2. Which economic groupings do Rwanda belong to?
3. What do you think is the aim of Rwanda joining different economicgroupings?
6.1: Meaning and objectives of economic integration
Activity 6.1.
(a) Write the following in full
(i) EAC
(ii) COMESA
(iii) SADC
(iv) ECOWAS
(v) OPEC
(b. Explain the major objectives behind economic integrations in developingcountries.
6.1.1. Meaning of economic integration.
Economic integration is a commercial policy where countries come togetherfor the sake of economic benefits by eliminating trade barriers among themselves.
It can also be defined as the coming together of countries in a given region
so as to promote trade and enjoy economic benefits by working collectively.
It is aimed at increasing the share of member countries in international trade
as a means of achieving political harmony amongst themselves and also toconsolidate their influence in international or global politics.
Examples of economic integration include
1. East African Community-EAC,
2. Common Market of East and Southern Africa-COMESA,
3. Oil and Petroleum Exporting Countries- OPEC,
4. Southern Africa Development Community (SADC),
5. Economic Community for West African States-ECOWAS,
6. European Union-EU,
7. African Union- AU,
8. African Caribbean Pacific Countries (ACPC)
9. Economic Community of the Great Lakes Countries (CPGL) and manyothers.
6.1.2: Objectives of economic integration
Coming together of countries in a given region so as to promote trade andenjoy economic benefits involves number of objectives;
1. To enlarge and diversify market for locally produced commodities in theregion.
2. To reduce or eliminate trade barriers among themselves e.g. use of
one currency or allowing local currencies among member states orencouraging barter trade.
3. To avoid duplication of commodities by encouraging specialization ineach country.
4. To increase the utilization of domestic resources which cannot beexploited by a single country.
5. To enhance free flow of ideas, skills and technology in the region.
6. To reduce the cost of production by adopting large scale enterpriseswhich makes them enjoy economies of scale.
7. To increase the bargaining power of member states in the internationalmarket.
8. To improve the terms of trade of member states.
9. To boost industrialization and production of commodities to out competemanufactured imports and reduce dependence among member states.
10. To promote political harmony and security in the region.
11. To expand employment opportunities for member states.
12. To decrease the exploitative powers of developed countries by reducingor stopping imports from developed countries that are always expensive.
6.2: Conditions necessary for successful economicintegration.
Activity 6.2.
Explain the necessary conditions for successful economic integration indeveloping countries.
1. Geographical proximity i.e. countries coming together into an integration
should be geographically close to one another or should share commonboarders in order to effect preferential treatment to each other.
2. Common and same ideology i.e. they should have common historical
background and ideology so as to harmonize their social economicpolicies e.g. socialism capitalism and mixed economies.
3. They should be at the same level of development so as to ensure fair
flow of resources otherwise resources would flow from less developedcountries to developed countries.
4. There should be strong political will or similar political organization amongcooperative countries i.e. commitment by leaders and their population.
5. Countries should be preferably of equal size because there is a likelihoodof them having unequal quantities of resources.
6. The economies of countries should be in position of producing differentproducts so that exchange is promoted.
7. There should be production of diversity of commodities thus specializationand exchange to be encouraged.
8. Citizens in the cooperative countries should have enough income so asto promote adequate market for commodities.
9. There should be political stability among cooperative countries so as toensure smooth operation of the regional activities.
10. There should be a well-developed infrastructure like roads in all
cooperative countries so as to make transportation of goods and serviceswithin the region simple and cheaper.
11. Countries should be complementary to one another so as to exchangetheir commodities.
12. There should be a common language in the region so as to makecommunication easy to all people within the region.
6.3: Process/ stages/ levels of economic integration.
Activity 6.3
For countries to fully integrate; they must pass through different levels of
economic integration. Most economists regard an economic integration
as “not a single day process” it requires a lot of effects, and a number ofstages are involved.
Why do you think economic integration is regarded as “not a single dayprocess” by most economists?
Economic integration is not a single day process, it’s a long time journey from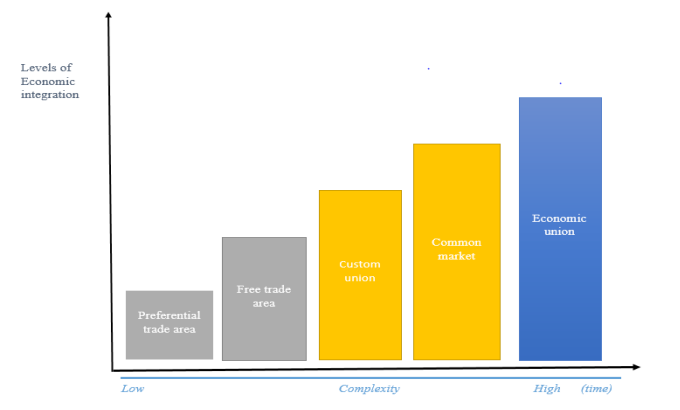
the day it was started (at low level) going through a lot of complexity up to the
point it takes the highest level. Therefore, it’s a gradual process that takes
different stages which don’t have a clear demarcation, but depends on how
committed and willing the integrated economies are to reach up their expectedgoals. These include among others the following;
1. Preferential Trade Area (PTA): This is the initial level in the development
of economic integration where countries start their cooperation. In here
member countries give preferential treatment to each other. There are low
tariffs charged on selected commodities from member states while high tariffs
are charged on commodities from non-member states. This is often the first
small step towards the creation of a trading bloc. Agreements may be madebetween two countries (bi-lateral), or several countries (multi-lateral).
2. Free Trade Area (FTA): Here member countries agree to abolish or
eliminate tariffs or trade barriers among themselves but each country retainsseparate tariff structure on commodities from non-member states.
3. Custom union (CU): This is where member countries eliminate all
tariffs or trade barriers amongst themselves and in addition countries adopt a
common tariff structure on commodities that are from non-member countriesbut there is no free flow of factors of production among member countries.
4. Common market (CM): In here, member countries eliminate trade
barriers amongst themselves; charge a common tariff on commodities from
non-member countries and allow free mobility of factors of production within
the region e.g. capital and labor. This is done to boost production, increase
employment and increase reward for factors of production and improve
economic welfare in the region.Economic community/ union (EC/ EU);
This is where there is eliminating of all tariffs among member states, adoption
of a uniform tariff structure on commodities from non-member countries; free
mobility of factors of production within the region; adoption of harmonious
economic policy where countries in the same region have the same economic
strategy, use the same policies and policy tools, joint ownership of enterprises
and use of the same currency is adapted thus have the monetary unions,
harmonization of the social services like education, health etc. increase thelevel of political identity and formation of political federation.
6.4: Advantages and disadvantages of economicintegration
Activity 6.4
Make research and discuss the view that Rwanda’s joiningof the EAC has brought more benefits than costs.
6.4.1. Advantages of economic integration.
As a country joins different economic groupings, it is very much expectant to
achieve its goals as had been the reason for its joining. These benefits includeamong others the following:
1. Trade creation effect. This is where the creation/formation of the economic
cooperation results into a shift from consumption of expensive products
from non-member countries to consumption of cheap products in membercountries.
2. Expansion and extension of large markets; most economic integration
provides sufficient wide export markets since member countries have to
import within the region which therefore boosts production and promoterapid economic growth.
3. Skill development and technological transfer i.e. due to free mobility of
factors of production, it facilitates skill development and technologicaltransfer within cooperative countries.
4. It increases the bargaining power of member countries in the internationalmarket, therefore this increases their benefits from the international trade.
5. It increases the competition which leads to high productivity in terms ofquantity and quality.
6. It facilitates specialization based on comparative cost advantage i.e. countries
avoid competition in the production but instead specialize on the basis of
comparative advantage which boosts production hence more volume ofexports.
7. Sharing of common services like research, education health transport and
communication becomes very easy which in turn increases efficiency sincethey are jointly operated thus reduction of duplication of services
8. It promotes industrialization among member states by establishingmanufacturing industries.
9. Common currency is used and state adopts a common currency and it isstrong and always stable which stabilizes prices in the region.
10. There is creation and expansion of employment opportunities and reduction
of unemployment among member states due to the flow of factors ofproduction freely amongst themselves.
11. It enhances political harmony and stability in the region i.e. common politicalproblems can be solved through consultation and sharing of ideas
12. It helps in redistribution of income in the region i.e. economic integration
fosters a more equitable distribution of resources when factors of production
are allowed to flow freely between or among countries thus equalizing returnsto each factor.
13. It reduces balance of payment deficit because economic integration leadsto reduction of foreign exchange expenditure and increased export earnings.
14. It increases consumers’ choice i.e. since a variety of goods are produced
with in the region, countries get commodities at low prices and low coststhus maximizing profits.
15. It reduces administrative costs involved in import-export restrictions.
16. It promotes self-reliance among the cooperative countries i.e. it reduceseconomic dependence of LDCs on MDCs
17. It is a vent for surplus; the resources formerly unutilized can be exploitedbecause of a wider market created by the integration.
6.4.2: Disadvantages of economic integration
Much as a country expects benefits from joining different economic groupings,
it should as well expect the adverse effects out of it which may include thefollowing;
1. Trade diversion i.e. this is where trade is diverted from low cost producers
outside the integrated region to high cost producers with in the region. In
addition, countries might continue using low quality products from within
the region when they could have secured high quality goods from outsideregion.
2. Loss of revenue which could have been got from tariffs due to free flow
of goods and services and factors of production within the region andcommon tariff structure on non-member states.
3. It may lead to loss and movement of resources and goods from lessdeveloped countries to more developed countries.
4. Most LDCs produce similar products and find it hard to trade amongthemselves leading to surplus.
5. When many industries are constituted in one country due to pull factors,it causes uneven distribution of industrial benefits.
6. Cooperative countries are forced to forego some of their national interestswhich reduce self-reliance and sovereignty.
7. It may lead to production of low quality products because of restriction ofsimilar commodities from non-member countries.
8. It may lead to over exploitation and quick exhaustion of resources in orderto supply a large market created in the region.
9. Large scale ventures may experience diseconomies of scale. It leads toloss of political sovereignty in case of a political integrated federation.
10. When there is political instability in one country, it may affect the wholeintegrated region because all countries depend on each other.
11. Other countries may retaliate and also impose restrictions on importsand thus may lead to formation of rival trade blocks.
12. It may lead to unemployment i.e. firms will be relocated to more cost
effective location within the block thus it may lead to unemployment toother countries from where the firms move.
Application activity 6.1
One of the advantages of economic integration is trade creation and oneof its disadvantages is trade diversion.
(a). Basing on the above statement distinguish between trade creationand trade diversion.
(b). Discuss the effects of trade creation and trade diversion on theeconomy.
6.5: Obstacles/ impediments to successful economicintegration in LDCs.
Activity 6.5
Explain the factors that hinder successful operations of economic integrations.
(i) Political instabilities in some developing countries. This hinder
economic integration because most countries fear absorb the problems ofother countries after integrating. Even after
(ii)Integration, some countries may fail to work with others effectively in the
region because of political problems in their countries hence hinderingeffectiveness of the regional integration.
(iii) Inadequate political commitments among member countries.
Where some member states are not committed to the activities of the
integration. Sometimes do not send to meetings those officials who have the
appropriate expertise on the issues to be discussed, and other times regionalmeetings are not attended to regularly.
(iv) Differences in political ideologies, itis very hard for the integration to
be successful if member states have different ideologies. Most integrations
in developing countries have failed simply because of differences in politicalideologies
(v)Differences in levels of development. It is very hard for countries to
integrate successfully when some countries are more developed than others.
Many economic integrations in Africa have failed after realizing that some
countries within the region benefit much more from the grouping than othersbecause of not being at the same developmental levels.
(vi) External obstacles by developed countries. These developed
countries always fight against the economic integration of developing countries.
Many economic integration in developing countries have been sabotaged by
developed countries who always look at integration in such countries as a bigobstacles towards their political and economic benefits.
(vii) Unfavorable exchange rate system. Some countries have currencies
which have more value than other countries. When the value of currencies in
the integration have different values this means that the exchange rate may bein favour of some countries and disfavour of others hence hindering integration.
(viii) Differences in cultures. It is always very hard for countries to
integrate successfully when people totally have different cultures. Sometimes
differences in cultures has been given as an excuse for the failure of some
economic integration in developing countries. Culture means a lot towards
people’s cooperation, so when it is totally different it means there are some
stages of cooperation which countries may not be able to reach at hencebeing an obstacle.
(ix) Production of similar products. It is totally hard for the integrated
countries to reach higher stages of the economic integration simply because
of producing similar products which makes it hard for countries to benefit fromeach other as it is always intended for thus being a big obstacle.
(x)Need for self-reliance. Some countries may refuse to integrate with
others because of their need for self-reliance. Regional integration requires a
country to sacrifice some of her national interest for the sake of the region like
self-reliance in order to effectively cooperate with other countries which somecountries fail to meet hence being an obstacle.
(xi) Difference in fiscal and monetary policies. It is very hard for countries
to integrate if their monetary and fiscal policies are totally different. Many
countries within the integration have failed effectively to cooperate with others
simply because of differences in their tax structures and of which sometimesnot favouring some member countries.
(xii)Differences in geographical boundaries, it is also very hard for
countries to integrate successfully if they are not near each other becausethis makes transportation of goods so costly and very hard.
Application activity 6.2
“Many economic integrations in developing countries have been successful
and others have failed to achieve their objectives”. Discuss your viewsabout the above statement.
6.6: Case study of economic integration.
Activity 6.6
Make research on East African Community (EAC) case study providedbelow and share with the whole class the following.
1. The countries that make up EAC
2. What are the objectives behind EAC formation?
3. Explain the achievements and challenges of EAC
4. Why did Rwanda join the EAC?
5. What has Rwanda benefited from EAC?
Africa: Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda, with
its Headquarters in Arusha. The organization was founded originally in 1967,
collapsed in 1977, and revived on 7 July 2000 following its ratification by the
Original 3 Partner States – Kenya, Uganda and Tanzania. And later in July 2009
Rwanda and Burundi Joined East African community and in April 2016 SouthSudan has also joined east African countries.
6.6.2. Aims and Objectives
The EAC aims at widening and deepening co-operation among the Partner
States in, among others, political, economic and social fields for their mutual
benefit and the following are some of the specific objectives of East Africancommunity;
The specific objectives of the EAC Integration are:
1. The attainment of sustainable growth and development of the Partner States
by the promotion of a more balanced and harmonious development of thePartner States
2. The strengthening and consolidation of co-operation in agreed fields that
would lead to equitable economic development within the Partner States
and which would in turn, raise the standard of living and improve the qualityof life of their populations.
3. The promotion of sustainable utilization of the natural resources of the Partner
States and the taking of measures that would effectively protect the naturalenvironment of the Partner States
4. The strengthening and consolidation of the long standing political, economic,
social, cultural and traditional ties and associations between the peoples of
the Partner States so as to promote a people-centered mutual developmentof these ties and associations;
5. The mainstreaming of gender in all its endeavors and the enhancement of
the role of women in cultural, social, political, economic and technologicaldevelopment;
6. The promotion of peace, security, stability within, and good neighborlinessamong the Partner States.
7. The enhancement and strengthening of partnerships with the private sector
and civil society in order to achieve sustainable socioeconomic and politicaldevelopment.
6.6.2. Achievements of the East African Community.
1. The most important achievement was the establishment of the EAC
Custom Union. The Custom Union Protocol was signed in March
2004 and came into effect on January 1, 2005. Under Customs Union
arrangements, goods produced within the EAC move across the border
of partner states without taxation provided they qualify under rules oforigin.
2. It has increased both inter and intra-regional trade, increased competition
that has increased consumer’s choice, reduction of costs, and attractionof foreign direct investments.
3. It has witnessed an increase in intra-EAC Foreign Direct Investments aswell as Foreign Direct Investments from outside.
4. There is mutual recognition of standards marks across the region wherethe bureaus of standards have developed an EAC catalogue of standards.
5. It has led to establishment of One Stop Boarder Posts that have already
been articulated within the auspices of the community law. This hasfacilitated trade within the community.
6. Has implemented Internal Tariff Elimination; this has facilitated smoothtrade among the states.
7. As part of the joint effort to promote East Africa as a single tourist
destination, partner states have participated in major international travel
markets forums including the World Travel Market in London November
2005 and the International Tourism Bourse in Berlin in March 2006 which
has helped in promoting East Africa as a single tourist destination and
has resulted in attracting more tourists and increasing the contribution ofthe tourism industry to the East African economy.
8. Promotion of foreign policy co-ordination through collaboration in
diplomatic and consular activities; collaboration in economic and social
activities; liaison and exchange of information; and collaboration inadministration and capacity building
9. The partner states have adopted an action program that has focused
on increased employment and poverty reduction in the EAC. In this
regard, the EAC projects and programs are assessed as to how they
contribute towards poverty eradication in the region. Furthermore, the
East African Community established an annual Ministerial Forum to focuson employment creation and poverty reduction.
10. Launched Lake Victoria Commission i.e. East African partner states have
taken a number of steps to preserve the lake through the implementation
of the Lake Victoria Environmental Management Program. This has
ensured sustainable use of Lake Victoria as vital for the sustainability ofLake Victoria.
11. Improvement of East African Infrastructure through the East African Road
Network Project where a Tripartite Agreement on Road Transport has
been ratified by partner states. The main objectives of the agreement
are to facilitate interstate road transport through reduced documentation
for crews and vehicles at border crossing, harmonized requirements for
operation licensing and customs and immigration regulations, among
others. In order to fast-track decisions on transport and communications,
the EAC established the Sectoral Council on Transport, Communicationsand Meteorology.
12. Harmonization of Monetary and Fiscal Policies i.e. Steps toward the
harmonization of monetary and fiscal policies have included convertibility
of the partner states’ currencies, harmonization of banking rules and
regulations, harmonization of Finance Ministries’ pre- and post-budget
consultations, regular sharing of information on budgets, and reading
of budget statements on the same day. In capital markets, there have
been changes in the policies and trading practices and regulations in the
three stock exchanges. The committee for The Establishment of Capital
Markets Development that oversees development of the capital markets
in the East African Community aims to develop East African CommunityCapital Markets including managing cross-listing of stocks.
13. Strengthened an East African Identity i.e. there have been developments
designed to foster the feeling of integration among the people of the
EAC and to facilitate an East African identity. These have included the
introduction of the East African Community flag, the launching of an EastAfrican anthem and the East African passport.
6.6.3. Challenges of the East African Community
Despite the progress made throughout the years, some challenges remain
noteworthy when it comes to establishment of some policies in the communityand this has hampered the progress of the community;
1. Some citizens of some member states lack awareness of the regional
integration process and cannot articulate the benefits that can be drawn fromthe EAC integration process. e.g. in Tanzania
2. Differences in social political ideologies amongst member states e.g. in
Tanzania the social political system that was in place for over 3 decades
after independence, makes people both in public and private sectors not veryentrepreneurial as they tend to rely on the government
3. One of the reasons for the collapse of the previous East African Community
in 1977 was the perception of disproportionate sharing of economic benefits
accruing from regional markets and lack of a formula for dealing with the
problem. It is still a challenge to the community to address problems arisingfrom the implementation of the treaty.
4. Improving the performance of major ports such as Mombasa and Dar-es
Salaam, and the East Africa Road Network and East Africa Railway Network
are key challenges facing the East African Community. Improving supplyconditions will enhance EAC capacity to withstand the forces of globalization
5. The EAC report on Fast Tracking (2004:81) reports that the fear of loss of
sovereignty is an issue in the minds of some members of the political elite of
East Africa. The fear is that as a Federation, the nation states would cease to
have any meaningful powers; that they would be relegated to mere provinces
within the Federation. This fear cannot be ignored and a mechanism is neededto eliminate such fears. This is a political challenge for East Africans.
6. Participation by citizens is at the core of the new East African Community.
The treaty advocates the need for people-driven and people-centered
development. East African people should play an active role in determining
the progress of the new community. The Community will therefore have to live
up to the expectations of the peoples of East Africa through implementing
the treaty’s provisions for the creation of an enabling environment for the
private sector and civil society participation, the strengthening of the private
sector; and enhancement of co-operation among business organizations andprofessional bodies.
Application activity 6.3
Examine the benefits of East African community towards the growth anddevelopment of your economy.
End unit assesment
1. a) What are the features of economic union
b) Analyze the objectives behind economic integration by nations
c) Examine the factors that may encourage formation of economic unionin eastern Africa.
2. a) Why did the former East African Community fail in 1977?
b) What good things can the current EAC learn from the former EAC?
In what ways may economic integration solve problems ofunderdevelopment?
