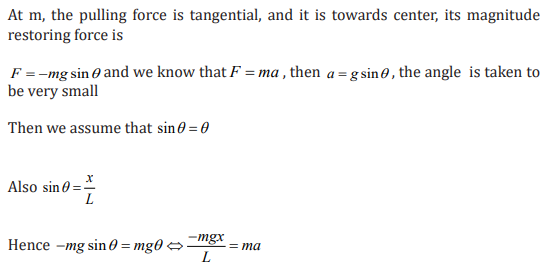UNIT 3:SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
a) Based on your observation,describe the motion of pupils in
i). Child’s swing
ii). Merry-Go-Round.
b) How is the kinds of motion described in a) above differ from linear
motion?
c) By using the situation above, state and explain all the energy changes
before and after undergoing motion.
d) How is the study of such kinds of motion in physics significant in reallife situations?
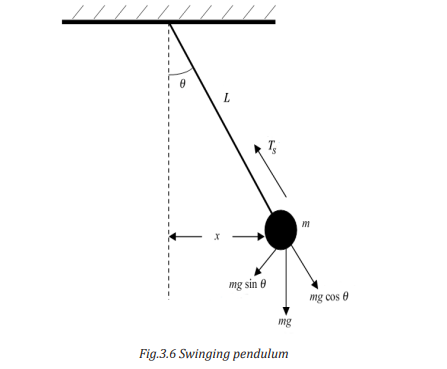
a) Examine the type of motion undergone by the bob in the pendulum.
b) Can you guess a point where the bob moves fast. Explain to support
your decision.
c) Discuss some of the factors that can make the bob to move faster or
slower while in the swing.
d) Would the bob continue oscillating indefinitely if displaced? If yesexplain why? If not, explain why not?
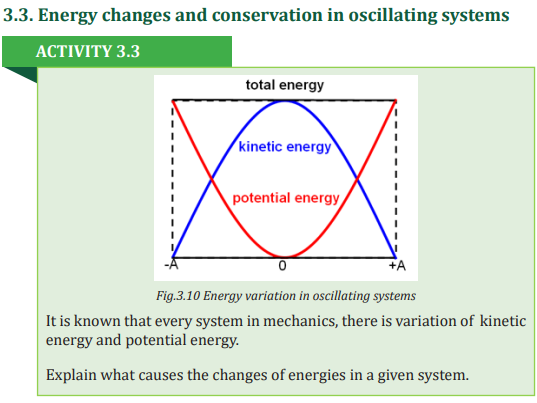
In simple harmonic motion a body moves periodically such that its acceleration
is directed towards a fixed point and directly proportional to the displacement
of the body from the fixed point, we say that a body has executed simple
harmonic motion.
Simple Harmonic motion can be defined as a special type of periodic motion in
which acceleration is directed towards a fixed point and directly proportional
to the displacement of the body from that fixed point.
CHARACTERISTICS OF SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
i) It is classified under periodic motion. Periodic motion is the motion of
the body which continuously retraces its paths in equal intervals of time.
ii) Its acceleration is directly proportional to the displacement from a fixedpoint
iii) Its acceleration is always directed towards a fixed point
iv) Mechanical energy is always conserved
Note: The motions, which all repeat in a regular cycle, are examples of periodic
motion. Whenever the object is pulled away from its equilibrium position, the
net force on the system becomes nonzero and pulls the object back towardequilibrium.



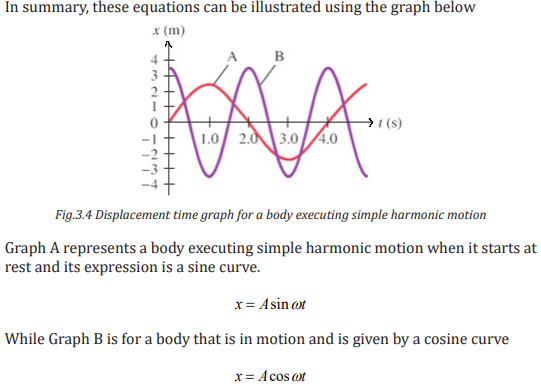

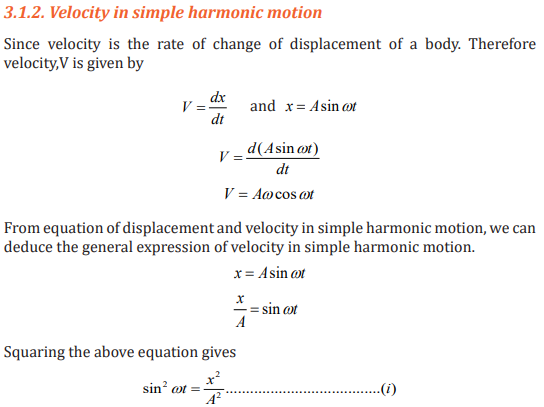

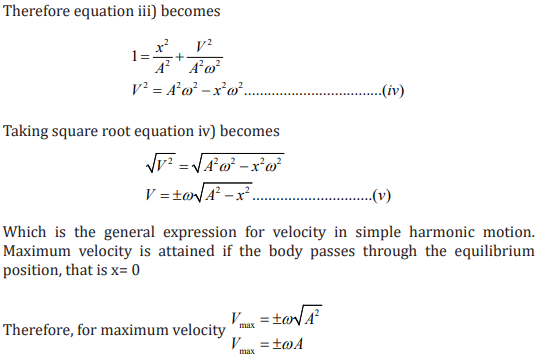
Example 3.2




One day you went to a picnic on a certain hotel .In the compound, there
is a swinging chair that is suspended on a string. When you sit down
on the chair, it oscillates vertically. After the oscillations have stopped,
you stand up slowly, and the chair rises up a small distance. Your friend
also sits in the chair, and you find that the rate at which the chair is
oscillating is different.
a) Basing on the scenario above,can you predict the kind of oscillator
shown above? What other examples of oscillators do you know?
b) Explain any two factors you think affects the number of oscillations
made by the swinging seat.
c) Imagine, the springs are replaced by an elastic rope. Do you think the
seat can swing the same way as when there were springs? Explain
your reasoning.
d) When your friend sat on the same seat, it oscillated with different
oscillations. Explain what you think caused the difference?
The following are some of examples of harmonic oscillators that will be
discussed in this unit.
a) Simple Pendulum,
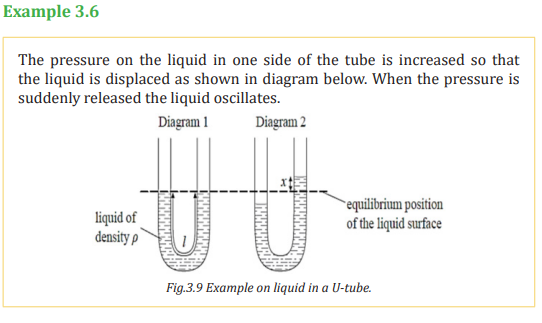
b) Mass on a helical spring (Helical Spring mass system)/ Stretched Springc) Water in a U-tube
3.2.1. Simple Pendulum
A pendulum consists of a small mass m attached to the end of wire/thread of
length l and the other end is attached to the fixed-point p.
If we displace the mass slightly and release it, we have the oscillation. The arc of
a circle of center P and radius l whose o is the equilibrium point.