UNIT 2:THE SOURCE OF INCOME AND EXPENDITURE INFORMATION
Key unit competence: Identify source of income and expenditure information
Introductory activity
IKIREZI PLC has started a poultry project two years ago with the aim of solving the problem of chicken meat in Rubavu town. When starting this business, it invested in his/her own money and other types of assets to buy everything needed in the business. Throughout business operations, IKIREZI PLC purchased different materials including drinkers, mangers and motor vehicle. IKIREZI PLC also paid a rent of one year immediately.
At the beginning, IKIREZI PLC bought 700 chicks at 1000 Frw each, and those chicks had to be vaccinated each seven days during their first 21 days. IKIREZI PLC company also purchased chicken foods and vitamins to make them grow faster. Even if IKIREZI PLC made more efforts to make their business successful during full year, IKIREZI PLC forgot to record the money spent and money generated from sales. This resulted into IKIREZI PLC ’s losses and disputes between IKIREZI company its suppliers and customers.
At the beginning of the second year, IKIREZI took new measures to avoid the loss. Hence IKIREZI company decided to hire a professional accountant who will help managers to record all the accounting information’s about purchasing and selling activities. At the end of the second year, IKIREZI PLC got profit and now IKIREZI PLC is predetermining to issue the shares on stock market.
1. What is the scenario above talking about?
2. What do you think is the main purpose of doing a business activity?
3. How do we call all those activities which involve IKIREZI PLC in the purchasing of materials and equipment?
4. What are the challenges that IKIREZI PLC faced in the 1st year of their business activity?
5. Diagnose the possible solutions to the above challenge faced by IKIREZI PLC?
6. Suggest the appropriate responsibilities of hired accountant in IKIREZI PLC?
7. Develop and show where do you think this accountant will find the data or accounting information to record.
2.1 Definition of concepts
Activity 2.1
Mr RUGERO is a person with A0 Bachelor Degree in Finance from Kigali Independent University (ULK-Kigali Campus). At the end of his studies, he started merchandizing activities with low capital. Suddenly, he got a financial support (Capital) from his nephew who lives in Canada. From the financial support, he started the business activity given the fact that he has learnt how to operate a business at the university. And after five year in the business, he received the RRA Award of the year as the good taxpayer. This Award is from not only good recording system of all income and expenditure transactions in their respective and efficient accounting system but also the declaration and payment of taxes on time. His business is still growing up and Mr RUGERO is planning to expand his business into import export sector on international markets.
1. Specify the name of money generated in business.
2. What is the name of money spent from the business to be returned after year?
2.1.1 Income
Income is the inflow of cash or its equivalents from sale of a good, a service or an asset.
Example :
• From work (wage or salary),
• From capital (interest or profit),
• From land (rent).
Income is defined in different ways depending on the context—for example, for purposes of taxation, financial accounting, or economic analysis. For individuals and businesses, income generally means the value or amount that they receive for their labour and products.
2.1.2 Expenditure
Expenditure is funds used by a business, organization, or corporation to acquire a new asset, improve existing ones, or reduce a liability. In other words, it is the use of a resource in the operation of a business.
Briefly, Expenditure means the use of cash or cash equivalents to purchase assets, pay down debt, or fund operation.
Main features of Income and Expenditure Account are:
• Income and Expenditure Account is a nominal account. Therefore, the rule of nominal account (debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains) is followed.
• The opening and closing balances of cash in hand and cash at bank are not recorded in it. It has no opening balance,
• While preparing it, only items of revenue nature are recorded and all items of capital nature are ignored. For example, the profit earned or loss suffered on the sale of an asset will be recorded in it but the amount received from the sale of an asset will not be recorded in it the
• Income and Expenditure Account is prepared at the end of an accounting period,
• Income and Expenditure Account contains revenue items only.
Application activity 2.1
1. Which of the following statement is not true regarding the expenditure meaning?
a) It is the use of fund by a business
b) It is the use of resources
c) It is the fund of operation
d) Use of cash equivalent
e) No one of the above
2. Which one of the following is not considered as income:
a) Salary from work done
b) Pocket money
c) Profit from sales
d) Assets improvement
e) No one of the above
3. All of the following are features of income and expenditure account except:
a) Income and Expenditure Account is prepared at the end of an accounting period
b) Income and Expenditure Account contains revenue items only.
c) Income and Expenditure Account is prepared on an nature basis
d) Income and Expenditure Account is a nominal account
e) No one of the above
4. Differentiate income from expenditure.
5. Explain the rule used when preparing nominal account
6. Explain how the income can increase in economic benefit during an accounting period.
2.2 Types of income
Activity 2.2
Analyse the picture above then answer the following questions :
1. What is about the image ?
2. Is it possible that those people may gain the same icome? if Yes or Not explain.
3. How do we call the income received by those people.
4. Classify the following incomes according to their main types : salary, wage, profit, rental income.
There are three types of income:
• Earned income (active income)
• Portfolio income
• Passive income
a. Earned income
Earned income (active income) is the money earned from working. It is compensation of human efforts.
Example: Salary; wages; bonuses; contract work
The different tasks are:
a. Working a job
b. Consulting
c. Any other activity that pays based on time/effort spent.
While earned income is the most common mechanism for making money, it is obvious downside is that once you stop working, you stop making money.
Additionally, because the amount of money that is made through earned income is directly proportional to the time and effort you spend working. It is difficult for someone to make more earned income without either learning a new (or more valuable) skill or working longer hours. Additionally, earned income is taxed at a higher rate than any other type of income.
One huge benefit of earned income over the other income types is that you generally don’t need any start-up capital in order to make earned income, which explains why most people rely on earned income from the start of their working file. In fact, earned income is a great way to start your investing career, as it allows you to save up cash that will help you generate the other two types of income.
b. Portfolio/ Investment income
This is the income that is generated by selling investments that were made earlier. In simpler words, this represents an increase in the value of the investment or capital gain as it is known in common terms. For instance, if a person buys shares and sells at a higher price or if they buy a house and sell it for a profit, the difference is called a capital gain.
This income has no relation to the number of hours worked. Also, this income is not received periodically. It keeps on accruing over a period and is paid out when the investor decides to liquidate it. Also, this type of income is more tax efficient as compared to earned income. This is true only if the investments have been held for a long period of time. Most countries in the world separate long term capital gains from short term capital gains and tax them at a lesser rate.
Example: Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, interest, etc.; money from buying/ selling real estate or other assets, such as automobiles.
Some activities that generate portfolio income include:
a) Trading (buying/selling) Paper and Assets Paper refer to things like stocks, bonds, mutual funds, T-bills, currencies or other types of futures/derivatives.
b) Buying and Selling Real Estate (specifically the profit from the sale)
c) Buying and Selling of any other Antique Asset or cars for example. Or other types of collectibles that have an appreciating value
Portfolio income certainly has some advantages over earned income. Once you have the knowledge and experience to generate portfolio income on a consistent basis, you can continually reap the benefits (compound your return) by reinvesting after each sale.
c. Passive Income
Passive income is another important source of income. It shares the characteristics of earned income and investment income. Just like earned income, it is paid for every period. However, the quantum of income does not depend upon the number of hours invested. Rather, it depends upon the capital invested. This is where passive income is like investment income.
Typical examples of passive income are rent, interest, and dividends, which are paid by shares and debentures. The taxes on this type of income are also less as compared to the earned income. Some incomes like dividends are totally tax-free in the hands of the investor. For other incomes like rent, there are tools such as depreciation, which can be used to lower the income and, therefore, the tax payable.
Some activities that generate passive income include:
• Rental Income or rent Income from Real Estate
• Business Income (assuming it’s not earned based on amount of time/ effort suent that would be Earned Income)
• Creating and Selling Intellectual Property, Books, Patents, Internet Content, etc
• Affiliate or Multi-Level Marketing
Application activity 2.2
1. List three (3) activities that can generate portfolio income
2. What is the main benefit of earned income over the other income types? At least one.
3. Explain the reason why Some peoples refer to portfolio income as “capital gains”.
4. By using typical examples, explain the passive income.
5. Discuss, interpret and present how is it possible for someone to make more earned income without either learning a new (or more valuable) skill or working longer hours? (answer by YES or NO)
2.3 Types of expenditure
Activity 2.3
Analyze the above picture then answer the following questions:
1. What about the image?
2. Explain the relationship presented on the above picture.
3. Which kind of transactions on which people are spending money?
4. How can one differentiate these expenses according to the ways in which these people spent money?
There three classes of expenditure
a. Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditure is an amount incurred for acquiring the long term assets such as land, building, equipments which are continually used for the purpose of earning revenue. These are not meant for sale. These costs are recorded in accounts namely Plant, Property, Equipment. Benefits from such expenditure are spread over several accounting years.
Example: Interest on capital paid, Expenditure on purchase or installation of an asset, brokerage and commission paid.
b. Revenue Expenditure
Revenue expenditure is the expenditure incurred in one accounting year and the benefits from which is also enjoyed in the same period only. This expenditure does not increase the earning capacity of the business but maintains the existing earning capacity of the business. It included all the expenses which are incurred during day to day running of business. The benefits of this expenditure are for short period and are not forwarded to the next year. This expenditure is on recurring nature.
Example: Purchase of raw material, selling and distribution expenses, Salaries, wages etc.
c. Deferred Revenue
Expenditure Deferred revenue expenditure is a revenue expenditure which is incurred in the present accounting period but its results or impacts on profitability are incurred in the following or the future accounting periods. This expenditure might be written off in the same financial year or over a period of a few years
Example: Development expenditure, Advertisement expenditure etc.
Application activity 2.3
1. Explain the types of expenditure
2. With typical examples differentiate capital expenditure from deferred revenue expenditure.
3. In which accounts capital expenditure must be recorded?
4. Classify the following expenditures according to their types:
• Purchase the sugar for a bread manufacturing company
• Payment of salary
• Give gifts to potential customers
• Offer end year rebate
• Purchase company shelves
2.4 Sources of income and expenditure information
Activity 2.4

Analyze the picture then provide answers to the following questions:
1. What is on the picture?
2. What do you think is recorded on these documents?
3. Why the person on the picture is recording the information on these documents while they are already recorded on these documents?
4. How do we call those documents that serve as the source of accounting information?
A source document is a document which contains information to be recorded in the books of account. They are properly written source of accounting information relating to various transactions like buying and selling of goods, return of goods bought or sold, settling of debts, etc. These documents must always be present to support whatever records or transactions have been made. They are hence called supporting documents.
The source documents may be income or expenditure source of accounting information.
Source document that serve as sources income information
• Sales order
• Bank statement
• Goods received note
• Credit note
a. Sales order
A sales order is a document generated by the seller specifying the details about the product or services ordered by the customer. Along with the product and service details, sales order consists of price, quantity, terms and condition etc.
* Components/elements of sales order document
A sales order usually carries information such as customer’s name, shipping address, transaction date, products ordered, description, units of measure, quantities, price, taxes, etc. The key details of the sales order are listed below.
• Name and contact information of the company (seller)
• Name and contact information of the customer
• Customer billing information
• Customer shipping information
• Information about product or service
• Price before taxes
• Tax, delivery and shipping charges
• Total price after taxes
• Terms and conditions
• Signature
• Any other relevant information as needed

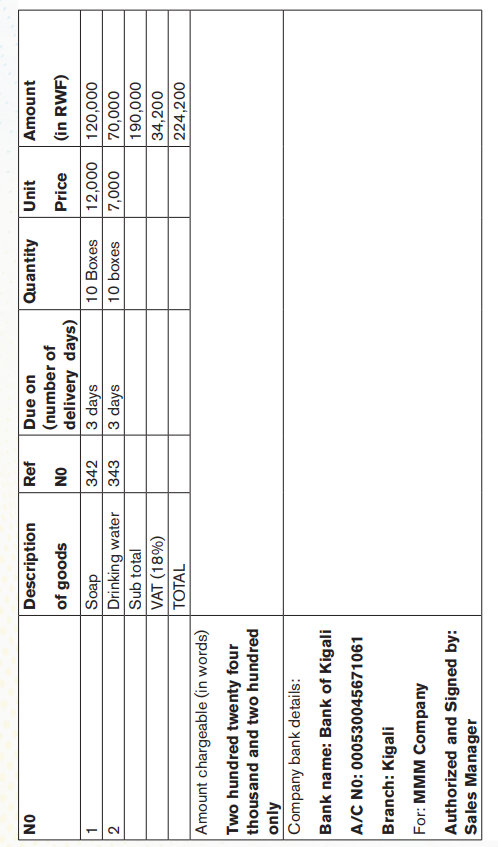
b. Bank statement
The bank statement is a statement issued periodically ( monthly or quarterly) by a banker to his/her customer informing him/her of the statement on his/her financial situation of affairs at the bank account. It is a customer’s account in his/ her banker’s books.
A good bank statement generally shows the name of the account holder along with sensitive information such as a bank account number and branch number or name. It also contains a summary table that shows the time period, opening balance, deposits, withdrawals, and closing balance.
Here’s what’s generally on a bank statement:
• Account number
• Home address
• Statement period
• Bank’s customer service number
• Beginning and closing balance for the time period
For each item, you’ll also see a transaction date and the payer or payee name. Each statement covers a certain period, such as a financial quarter or one month, but it might not begin on the first day of the month. For instance, your statement might run from September 6 to October 5.
If you find any inaccuracies on your statement, you should report them to your financial institution. Typically, disputes are done in writing, so be sure to provide any supporting documentation you have.
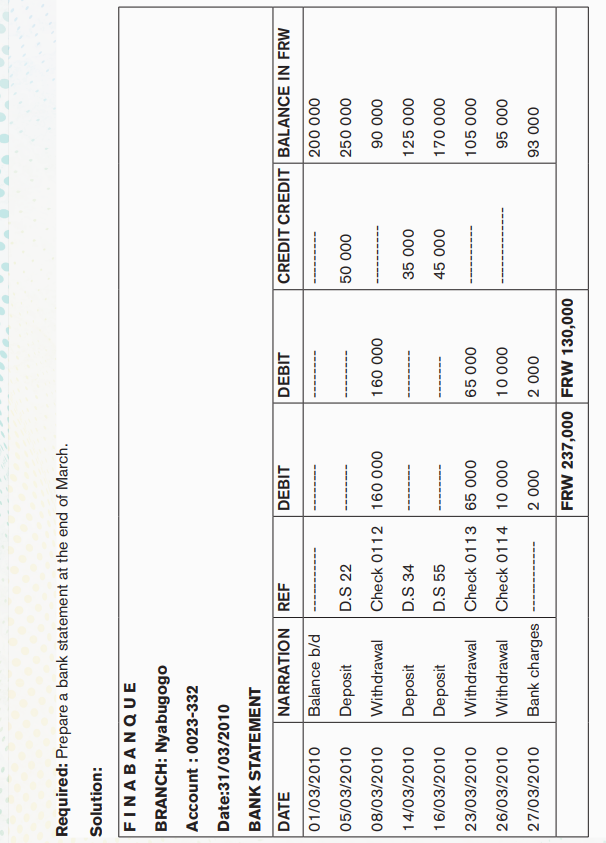
Example
The following information concerns ALL’s account held in FINABANQUE during the month of March and whose the balance at the beginning of that month were 200 000Rwf.
05/03/2010 deposit of money (deposit slip No 22) 50 000Rwf
08/03/2010 withdrawal (Check 0112). 160 000Rwf
14/03/2010 deposit of money (deposit slip No 34) 35 000Rwf
16/03/2010 deposit of money (deposit slip No 55) 45 000Rwf
23/03/2010 withdrawal (Check 0113) 65 000Rwf
26/03/2010 withdrawal (Check 0114) 10 000Rw
27/03/2010 bank charges 2 000Rwf
c. Goods received note (GRN)
The GRN is a document issued by a receiver (buyer) to seller indicating the goods received. The following are its characteristics:
• The date of receiving;
• The name and the address of supplier
• The delivery order number
• The description of goods purchase
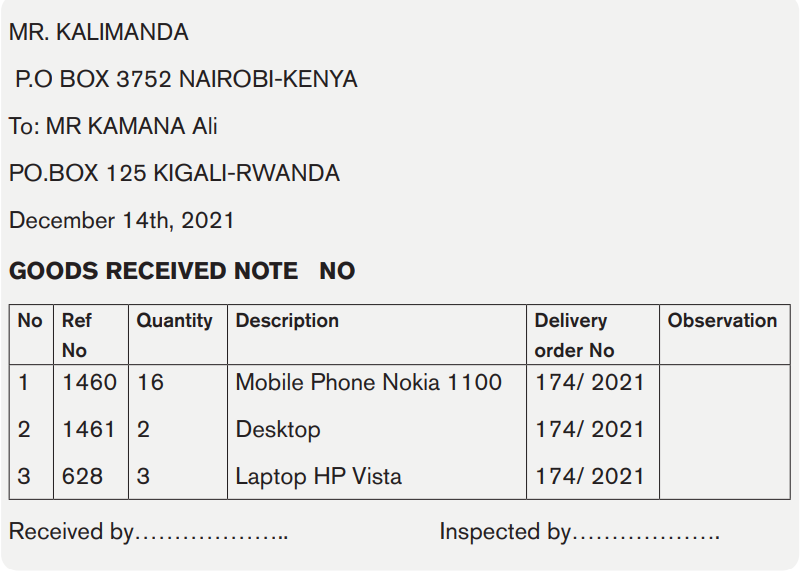
Example
Mr KALIMANDA received the following goods from his supplier, Mr KAMANA Ali from KIGALI:
- 16 Items mobile phone No 1100, Nokia Ref 1460
- 2 Desktop, Ref No 1461
- 3 Laptop HP Vista, Ref No 628
Date of delivery: December 14th, 2021
Number of delivery Order: 174 / 2021
Required: Prepare the goods received note.
Solution:
d. Debit note
A debit note, or a debit memo, is a document issued by a seller to a buyer to notify them of current debt obligations. You’ll commonly come across these notes in business-to-business transactions — for example, one business may supply another with goods or services before an official invoice is sent. The debit note ‘makes note’ of the transaction for documentation purposes.
Debit notes are also used in business-to-customer transactions, such as when a customer returns goods to a business received on credit. In this case, the buyer issues the debit note to the seller.
This note is issued by a seller in goal:
• To rectify a favorable mistake to buyer which it has been clearly fixed only after the sending of an invoice.
• To request additional payment as interests due a delay period made by the buyer in the payment of this invoice.
• To charge the customer who fails to return the packaging cases or containers not charged for in an invoice.
- Incoming debit notes are received from creditors; Outgoing debit notes are sent to debtors. Return outwards day books is written up from incoming credit note.
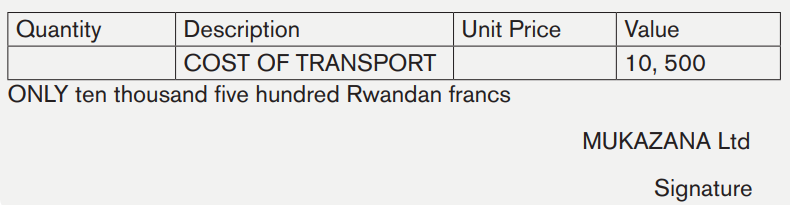
Example
MUKAZANA Ltd sent debit note concerning the transport cost to Mr MURENZI Samson. This amount (10, 500Rwf) was not charged to the customer (MURENZI) at the moment of issuing of the invoice.
Required: Prepare the debit note
Answer:
MUKAZANA Ltd
P.O BOX :……….
DATE:…………
DEBIT NOTE No ………………
TO:
Mr MURENZI Samson
Source documents that serve as source of expenditure information
• Purchase order
• Invoice
• Receipt
• Goods delivery note
• Quotation
• Payroll
• Credit note
• Purchase requisition
a. Purchase order (PO)
A purchase order is a commercial source document that is issued by a business’ purchasing department when placing an order with its vendors or suppliers. The document indicates the details on the items that are to be purchased, such as the types of goods, quantity, and price. In simple terms, it is the contract drafted by the buyer when purchasing goods from the seller.
Its characteristics are:
• The name and address of the company purchasing the goods or services,
• The name and address of the seller
• The date,
• Purchase order number,
• The description and quantity of the goods or services required,
• Unit Price
• Total amount of goods ordered
• Payment information
• Delivery mode
• Delivery term
Example
On February 1st 2019, KANDAMO MANUFACTURING LTD (P.O BOX 54781 KIGALI) orders to KANYANDEKWE (P.O BOX: 23000 KIGALI) the following items:
* 200 items of carbon paper ref no 6 at FRW 2,600
* 2 000 items of envelopes ref. no 7 for FRW 8, 000
* 10 000 items of Onion sheet (papers pelures) no 10 for FRW 1, 400
Time of delivery: 8 days; Method of payment: in cash
Required: Prepare purchase order
Answer:
KANDAMO MANUFACTURING LTD
P.O BOX 54781 KIGALI
PURCHASE ORDER No: 435
TO: KANYANDEKWE COMPANY
P.O BOX 23000 KIGALI
Date February 1st 2019
Please supply the following goods:
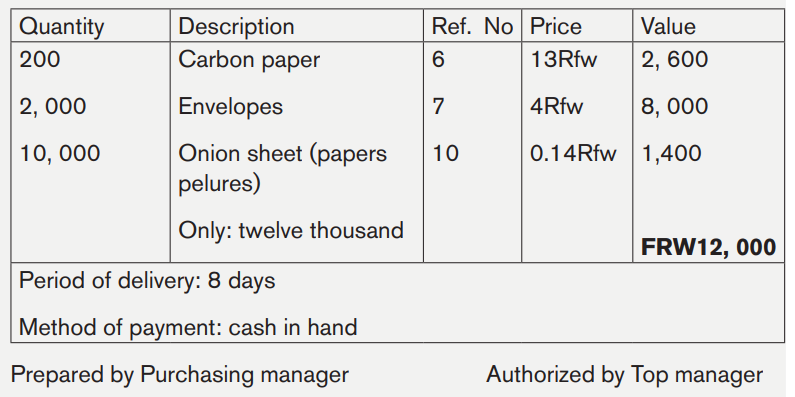
b. Invoice
This is a document which is issued by the seller to the buyer when goods have been sold on credit. An invoice or bill is a commercial document issued by a seller to the buyer, indicating the products, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services the seller has provided the buyer. Invoices generally outline payment terms, unit costs, shipping, handling, and any other terms outlined during the transaction.
Types of invoices may include a paper receipt, a bill of sale, debit note, sales invoice, or online electronic record.
Characteristics of invoice
To the heading:
The heading of the invoice contains:
• The word "invoice"
• A unique reference number (in case of correspondence about the invoice)
• Date of the invoice
• Name and contact details of the seller
• Name and contact details of the buyer
• Date that the product was sent or delivered
• Purchase order number (or similar tracking numbers requested by the buyer to be mentioned on the invoice)
The body:
• Description of the product(s)
• Unit price(s) of the product(s) (if relevant)
• Various reductions
• Total amount charged (optionally with breakdown of taxes, relevant)
• Payment terms (including method of payment, date of payment, and details about charges late payment)
Types of invoice
a. Pro-forma invoice
It is a document that states a commitment from the seller to provide specified goods to the buyer at specific prices. It is often used to declare value for customs. It is not a true invoice, because the seller does not record a pro-forma invoice as an account receivable and the buyer does not record a pro forma invoice as an account payable.
b. Commercial invoice
A custom declaration form used in international trade that describes the parties involved in shipping transaction, the goods being transported, and the value of the goods. It is the primary document used by customs, and must meet specific customs requirements, such as the harmonized system number and the country of manufacture. It is used to calculate tariff.
c. Sales invoice or outgoing invoice
It is an invoice from the point of seller. The sales day book is written from outgoing invoice.
d. Purchase invoice or incoming invoice
It is an invoice from the point of buyer. The purchases day book is written from incoming invoice.
Example
On November 28th 2021, KAPAKO RWANDA Company (Phone + 250 518646; P.O BOX 5053 Kigali; E-mail: kapako123@ yahoo.com), send to the MMM Company (Phone (+250) 0788302211; P.O BOX 160 Kigali), the invoice no 131/06 for furniture of:
* 100 items of Motorola E816 phones (product ID: P1003; unit price: Frw 32 000) and
* 120 items Nokia 3220 phones (product ID: P1000; unit price: Frw 43 000) VAT rate 18%
Required: Prepare invoice
Solution
KAPAKO RWANDA COMPANY
B.P 5053 KIGALI –RWANDA Date: November 28th 2021
PHONE + (250) 518646
E-mail:kapako123@yahoo.com
BILL TO: MMM Company INVOICENO131/06
P.O BOX: 160 KIGALI-RWANDA
PHONE: (+250) 0788302211
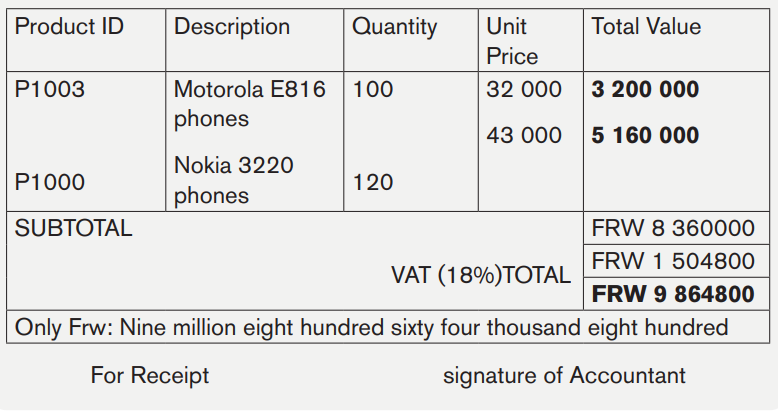
c. Receipt
The receipt is a written acknowledgement that something such as money or goods has been given to the person who issues the acknowledgement.
It is a written proof showing that the payment or deposit of goods or money has been done. This document contains:
• The name and address of the depositor
• The word in latter “Receipt”
• The number of the document
• The nature (description) deposited (if it is money, you must specify the sum in figures (digit) and Letters)
• The name and signature of the receiver
• The date and reason of payment or deposit.
Example
Miss KEZA Cecile (P.O BOX 200 BUTARE) pays to IRIS Enterprise, (shop specialized in selling of flowers and gift items, P.O BOX 322 KIGALI), the sum of 5, 000 Rwf in cash on 20 April 2021 for settlement of his invoice No 50 of April 10th, 2021.
Required: Prepare receipt No100.
Solution:
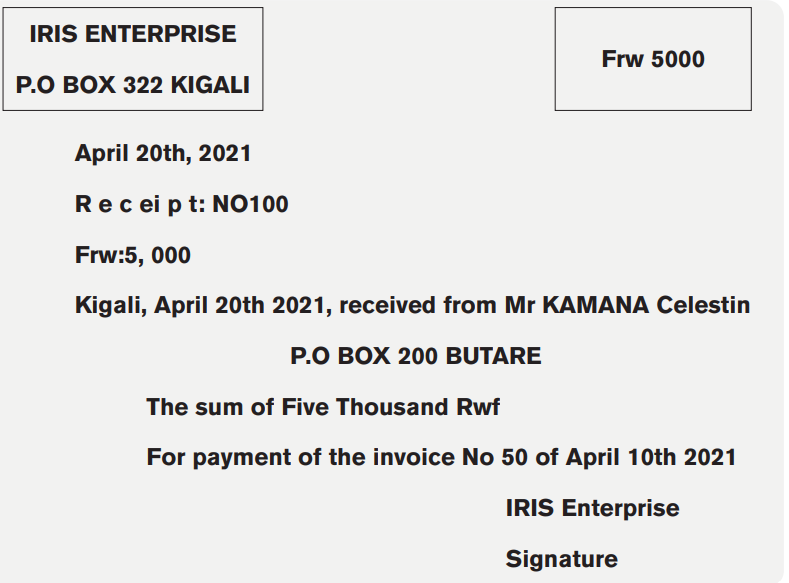
d. Goods delivery note
The delivery note is a document issued by a seller and sent to a buyer at the moment of the delivery of goods, when the invoice will be sent subsequently. It serves to verify if the goods delivered are conform with the order. It gives the details of the transactions such as:
• The date of delivery
• The name of the buyer
• The nature and quantity of delivered goods
• The name of the ship
Example
On October 19th 2019, BAMBA Ltd had ordered to BESTWAY MANUFACTURING LTD the following goods:
* 12 tyres Michelin xzx – size: 165 – 13
* 12 inner tubes, size 13D – 9
After receiving this purchased order, BESTWAY MANUFACTURING LTD, supplier makes the arrangement to deliver those goods.
Required: Prepare the delivery note on October 20th, 2019
Solution:
BESTWAY MANUFACTURING LTD
P.O BOX 54781 KIGALI
GOODS DELIVERY NOTE No:……..
TO: BAMBA Ltd
P.O BOX ………

e. Quotation (Proforma invoice)
Quotation is an offer to supply goods according to the terms and conditions stated. Quotations are received from different suppliers in response to letter of inquiry. A quotation is an offer to supply goods according to the terms and conditions stated.
These terms and conditions include for what period the prices stated are valid, rates of discount offered, mode of delivery, terms of payments etc.
Example
On 31st January 2020, the procurement department of Ms Ihogoza requested for a quotation from the sales manager of KARANGA Plastic Ltd (P.O BOX: 1020
about 20 plates and 15 cups as she is preparing to get married. KARANGA Plastic Ltd has presented the following information:
20 Plats Frw 1000 each
15 Cups Frw 200 each
All discount of plates and cups equal to 2%, and the VAT is equal to 18% Prepare a Quotation NO 024/1020 from from KARANGA Plastic Ltd to Ms Ihogoza.
Solution
FROM: KARANGA Plastic Ltd
P. O. BOX 1020
KIGALI
QUATATION NO024/1020
TO: Ms Ihogoza
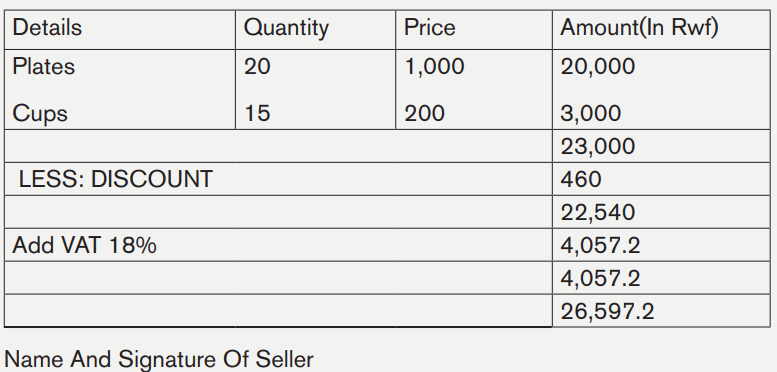
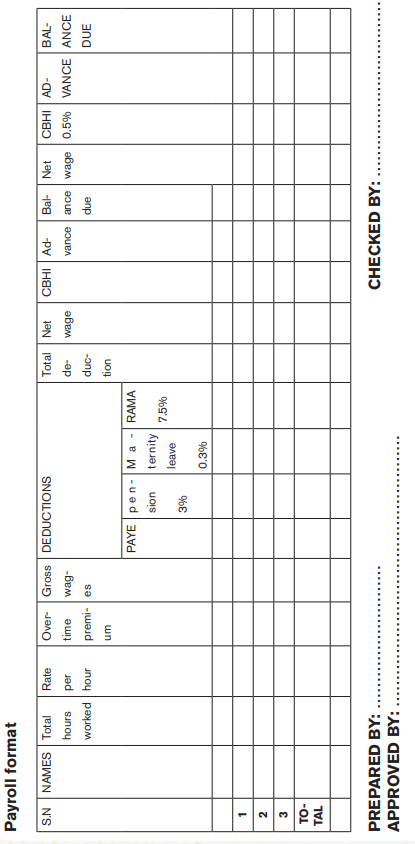
f. Payroll
The term ‘payroll’ means a list of employees within a company and how much they are to be paid. A payroll is the process of paying a company’s employees, which includes tracking hours worked, calculating employees’ pay, and distributing payments via direct deposit to employee bank account or by cheque.
The payroll process can include tracking hours worked for employees, calculating pay, and distributing payments via direct deposit or check. However, companies may also perform accounting, record-keeping, and set aside funds for medical insurance, Social Security, and employment taxes.
Main elements to consider while preparing payroll
a. Employee details
Before you’re able to run payroll, you’ll need to access to your employees’ details such as their name, address, national insurance number and salary.
b. Time or hour used on workplace by Employee
If you pay your employees on an hourly rate, you’ll need to have a system in place to monitor the hours they work, so you can ensure they are paid the correct amount. For employees that are on a salary, you may choose to monitor when they’re working to ensure they are adhering to their contracted hours.
c. Salaries, wages and net gross pay
You need to keep a record of whether your employees are on a salary or an hourly wage, as this will determine how you calculate their pay.
• A salary is a pay packet that an employee receives on a monthly basis. These payments are based on a yearly amount that is divided into 12 individual payments. But depending on the nature of your business, you may choose to pay your employees a wage instead of a salary.
• A wage is an amount based on hours worked rather than a yearly fixed amount. You’ll set an hourly wage and multiply this by the number of hours worked to calculate their total pay in a particular period. On your employees’ payslips you’ll need to indicate their gross and net pay.
• Gross pay is an employee’s total pay within that period.
• Net pay is the amount they receive after tax and any other deductions.
d. Tax and deductions
By law, every employee has to pay tax and national insurance from their total gross pay. The tax rate can vary depending on the total amount an employee has earned and their circumstances. Regardless, it is the employer’s responsibility to ensure the correct amount is deducted in payroll and paid to Rwanda revenue authority (RRA) each month. It’s important, you complete this on time each month or you could be charged a penalty.
g. Credit note
A credit note is a document issued by a seller to a buyer to notify that credit is being applied to their account. You might notice these referred to as credit memos, too. As a seller, you may issue a credit note when there’s a need to cancel all or part of an invoice for a variety of reasons, including:
• Changes to an order after an invoice is issued
• Goods returned or services rejected
• Goods were damaged during shipping
• Pricing mistakes on the original invoice
No actual money is exchanged with a credit note; rather, it’s used to offset a previous invoice that’s already been paid.
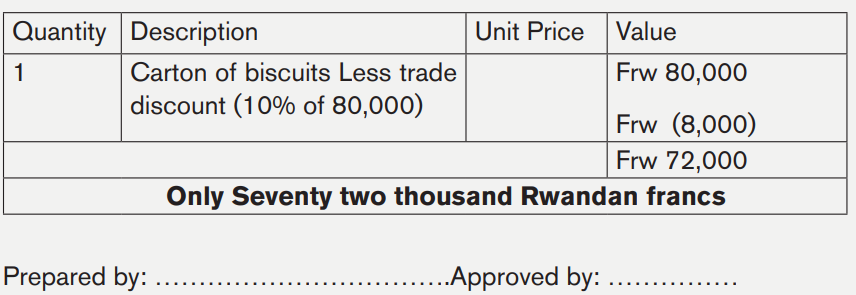
Example
On 24 March 2020, BABU Company (Tel: 0788288444), located in RWANDA bought 10 000 cartons of biscuits on credit from MMM manufacturing Ltd (E-mail: mmm@yahoo.fr; 0722233311) for 800 000Rwf and a trade discount of 10% was given.
The following day, BABU Company returns 1 carton of biscuit to MMM manufacturing Ltd. that had been damaged.
Required: Prepare credit note No795
Answer:
M.M.M MANUFACTURING Ltd.
E-MAIL : mmm@yahoo.fr
Tel: 0722233311
DATE: 25./.03../2010.
CREDIT NOTE No 795
TO :
BABU Company
Tel: 0788288444
h. Purchase requisition
The purchasing department is responsible for buying goods which are required by any business enterprise. For this purpose, written requests are sent by all departments for goods required by them to the purchasing department. These written requests are called purchase requisitions.
These purchase requisitions contain the description of goods required, quantity required and when required. These requisitions must be signed by an authorized person of the department that need these goods.
If the material involved is held in stock by the stores department then the purchase requisition would be prepared and signed by the head of stores department. If some specific items are required by the production department then the purchase requisition would be signed by the works manager.
Format
BESTWAY MANUFACTURING LTD
PURCHASE REQUISITION NO ..... DATE: ………….
DEPARTMENT/ SECTION: …………
Please arrange to purchase the following items: ……

Application activity 2.4
1. Complete the following table :
2. The EPRA, P.O BOX 115 Kigali sells on March 15th 2020, 400 baskets of eggplant to LUMAPLANT, P.O BOX 112 BUTARE, seller of flowers and vegetable, P.O BOX 542 BUTARE. Gross weight of each basket is 15kg, Tare 0.5kg per basket, price per kg is frw 500; trade discount 2%; packing cost FRW10 per basket. Transport paid by seller but chargeable to customer FRW2000. Debt payable before April 20th.
Required: Prepare the invoice
3. On 20th March, 2021, the student IRAKOZE David has paid the school fees of Frws50,000 for the second term to the accountant of RRR school, P.O BOX 234 KIGALI, phone number +250788233456, e-mail : rrr@gmail.com.
Required : Prepare the Receipt NO 046
Skills Lab Activity 2
Visit the school bursar and interview him/her about the different accounting documents used on daily basis. From the information discovered, respond to the following questions:
a) What different sources of income and expenditure information documents have you discovered?
b) What are their roles?
c) From those identified above, what documents do you think would be most useful for your business club?
End unit assessment 2 1.
1.All of the following are not income except:
a) Gift from a friend
b) Pocket money
c) Petty cash
d) Resources
e) B and C are correct answers
f) No one of the above
2. Choose the correct answer Earned income is:
a) Income from family
b) Income from all activity done
c) Money earned from working
d) Business income
e) B and C are correct answers
f) All of the above
3. Portfolio income involves the following except:
a) Money from all selling activities
b) Mutual funds
c) Money from buying real estate
d) A and C are correct answers
e) Money from stock selling
f) No one of the above
4. All of the following are expenses except:
a) Funds used by a business
b) Use of cash equivalents
c) Acquire new assets
d) Purchase assets,
e) Pay down debt,
f) Fund operation.
g) No one of the above
5. One of the following is not a type of expenditure:
a) Deferred revenue
b) Expenditure Company
c) Expenditure Revenue expenditure
d) Business expenditure
e) B and C are correct answers
f) C and D are correct answers
6. Match the document in column A with its meaning in column B, by putting the alphabet of the meaning against the number of the document then put the answer in the provided space.