UNIT 4: CODING DATA METHODS
Key unit competence: To identify different methods of coding data
Introductory activity
KAMALI is Accountant of BRUNO PLC located in Kayonza District. He has many responsibilities including preparation of payroll, availing the sufficient petty cash, registering new assets. He needs to know different kinds of asset based on its specification. It requires to mark the physical inventory items and fixed assets. To name those assets helps the management to know each type and category of materials being used in business. In naming of physical asset KAMALI needs to think a head how much each item is different from other. The purpose of coding is to avoid the ambiguity in materials use, their misuse and maintaining good services delivery. To mark assets, the accountant is required to use different methods for differentiating those assets and to be sure that all assets are marked.
After analyzing above statement discuss the coding system in organization.
4.1 Definition of coding
Activity 4.1
While naming different category of assets from BRUNO PLC, KAMALI needs to encrypt each item of asset appeared in business. a) What would KAMALI like to do from above statement?
b) What are the assets KAMALI needs to encrypt from the statement above?
Coding
It is the process of assigning an encryption to something for classification or identification.
Or
It is management method which uses symbols or numbers in order to represent specification or categories of item, so that it is easy to recognize, track and monitor them.
4.2 Object to be coded
Object to be coded in management system can link to different types of data inventory, inventory image, file, code of transportation boxes that will identify the category of item using alpha-numeric characters.
a. Current asset (inventory)
In storage installations, item coding enables efficient inventory organization, which reflects positively on all operations carried out in the warehouse. Therefore, each product should be identified upon receipt. The item coding process consists of explicitly identifying the goods with a code or sign.
b. Fixed asset (material and tools)
Fixed asset to be coded is tangible assets that are assets with a physical form and that holding value.
Example: Property, Plant &Equipment (PP&E) include:
• Vehicle in truck . Filing cabinet
• Bookcases . Laptop
• Photocopy machine . Chair
• Printer machine . Desk
• Office furniture
Note: Coding depends on internal business organization procedures.
An example of a coding structure for BRUNO Ltd:
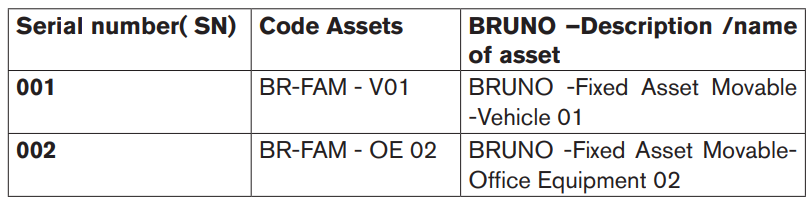
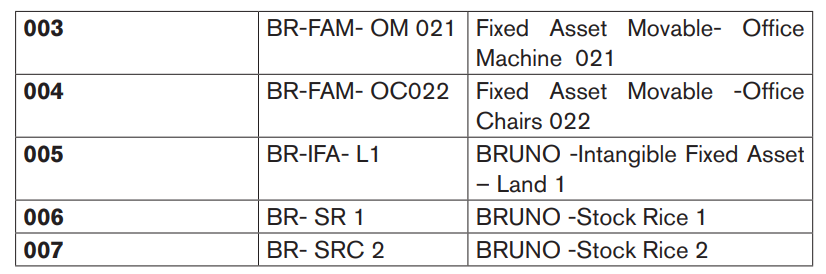
Application activity 4.1
Visit or invite any worker(s) from your school or community, accountant, local leader. Ask him/her how to code school materials and observe component of code, as a student of coding some asset, come up with items of asset and inventory to be coded in business solve the question of similar physical asset in company.
Identify correctly items to be coded in fixed assets and current asset?
4.3 Methods of coding
Activity 4.3
Thamar is a business woman specialized in merchandizing business of telephones and operating at Musanze District. In registering of new telephones, her accountant needs to code those telephones before being sold and stored. In this case he/she can use different methods for differentiating those telephones and to be sure that all telephones bought are coded and there is theft telephones and missing.
1. Suggest certain techniques to be used in coding.
2. From the above scenario, why is it necessary to code the telephones?
There are many coding systems in practice and each business will choose one that suits its transactions and operations. Probably the two most common methods are numeric coding and alpha-numeric coding.
Purely alphabetic systems may also be used, but these tend to be rather confusing to use.
a. Alphabetical
An alphabetic coding system uses just letters to code.
Examples: Income accounts AAA1-DZZ
Expenses accounts EAA-JZZ
Assets accounts KAA- PZZ
Liabilities accounts QAA-VZZ
Capital accounts WAA-ZZZ
Once the coding system has been set up, when entries are made in, for instance, the cashbooks are referenced to the general ledger then the reference would include the account code for that ledger account.
b. Mnemonic coding system
Under this method, different alphabets from material names are used to help the memory. It is very simple.
Examples: PU for Purchase, SA for Sales, RE for Rent c. Numerical coding A numerical coding system is where the code is entirely numerical.
Examples: The general ledger codes:
Income accounts: 0001-0199
Expenses accounts: 0200-0499
Assets accounts: 0500- 0699
Liabilities accounts: 0500-0699
Capital accounts: 0900-1000
There do not all to be used but the coding system must be flexible enough to allow for new accounts to be opened up.
d. The decimal method
Under this method, whole and decimal numbers are used for the identification of different materials.
Examples:
2.- Administration overheads
2.1- Salary of staff
2.11-Rent, rates& taxes
2.12-Account and audit
2.2-Stationery
2.21 – Printing
2.22- Insurance
e. Alpha-numeric
An alpha-numeric coding system uses a mixture of letters and numbers to code.
Examples:
Income accounts: A001-200
Expenses accounts: B001-200
Assets accounts: C001- 200
Liabilities accounts: D001-200
Capital accounts: E001-200
f. Colour codification
As the name indicates, under this method, colour codes are used to differentiate elements. This method can be applied to codify metal, cables, small component parts, drums of oil, and various other items if the colours are not too complicate. This method affords as reads means of identification on sight.
Example: In the case of metal:
Green for Iron
Blue for Steel
Red for Copper
Black for Aluminium
White for zinc
This method is simple but lacks flexibility. That is to say, when the number of store item increases, it is not possible to expand number of colour.
A coding system does not have to be structured entirely on any one of the above systems. It can mix the various features according to the items which need to be coded.
Characteristics of Good coding system
• Items each have a unique code
• Codes are uniform in structure and length.
4.4 Importance of coding materials in business
- Avoidance of length description
Codification helps in avoiding the use of length names and description for store item, thus saving time and energy.
- Accurate identification of stores
Codification assists in the accurate and convenient identification of store items. Easy identification of store items saves time and cost involved in store handling.
- Convenience in issue of materials Codification of store items on scientific lines helps in eliminating the possibility of errors in issue of materials. It also increases the efficiency of store-keeping staff.
- Maintenance of secrecy
Every manufacturing concern, owing to necessity, attempts to keep its production activities and processes a secret. Codification of store items helps in maintaining secrecy in production activities.
- Simplification of stores accounting
Codification of store items helps in maintaining accurate records since scientific codification enables systematic.
- Prevention of duplication
Codification prevents the duplication of items. As all similar items in the store are grouped together. When an item is coded once, it is not assigned an alternative name.
- Convenient in preparing Materials forms
Codification of store items makes the preparation of various forms and documents relating to stores easy and convenient (e.g., Bill of Materials, Purchase of Requisitions, and Material Requisition).
- Other advantages
Codification helps in the standardization of store items and in the reduction in their variety. It also helps in reducing storage cost and increasing efficiency
4.5 Principles of coding
Activity 4.5
KAMALI is Accountant of BRUNO PLC located in Kayonza District. He has many responsibilities including preparation of payroll, availing the sufficient petty cash, registering new assets. He needs to know different kinds of asset based on its specification. It requires to mark the physical inventory items and fixed assets. To name those assets helps the management to know each type and category of materials being used in business. to name physical assets, KAMALI needs to think a head on how much each item is different from other. The purpose of coding is to avoid the ambiguity in material use, their misuse and maintaining good services delivery. To mark assets, the accountant is required to use different methods for differentiating those assets and to be sure that all assets are marked.
What will KAMALI use as guidelines in coding the materials?
a. Exclusive
It means each item should have only one code and this code should not be used for any other item.
b. Certainty
Code numbers used for different types of material should be certain and there should be no possibility of confusion.
c. Elasticity
It means the code number should be arranged in such a way that it must be possible to include new items if need arises.
d. Brevity
Code should be as brief as possible.
e. Memorization
It should be easy and possible to remember and understand the code numbers.
f. Uniformity
Codes should be of equal length and of the same structure.
Application activity 4.5
Briefly explain principle of coding?
Skills Lab Activity 4
1. By visiting the store of food at school with the storekeeper, student codes different products in the store, and responds to the following questions: a) What is the role of coding? b) What are the methods used in coding?
2. By visiting the store of food at school, student codes different product in the store. The teacher clarifies the methods, and importance of coding.
End unit assessment 4
Answer the following questions:
1. Define the term code as used in the field of logistics.
2. Correctly identify 10 objects to be coded in company.
3. Correctly identify five materials on which we can use color codification.
