UNIT 8: FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
Key unit competence: To be able to classify different forms of businesses

Mukamana is one of the ladies involved in handicraft activities in her area. She makes baskets, mats, hats, necklaces and other related products. Of recent they had to register as individuals so as to obtain a trading license but Mukamana and the other ladies face challenges when buying raw materials for making their products. Marketing their finished products is also difficult as they work individually. Sometimes they travel to Kigali in search for customers to buy their products and when they are away, they have to close their workplaces and open them for work when they return from Kigali.
Questions.
1. What benefits would Mukamana and the other ladies enjoy if they decided to do their handicraft work together?
2. Identify the advantages they also enjoy working individually
3. Using your knowledge of entrepreneurship, identify the classification of enterprises to which they belong.
4. Explain the reasons why Mukamana and other ladies decided to register their business.
5. Which advice would you give to Mukamana in order to benefit more from their activities
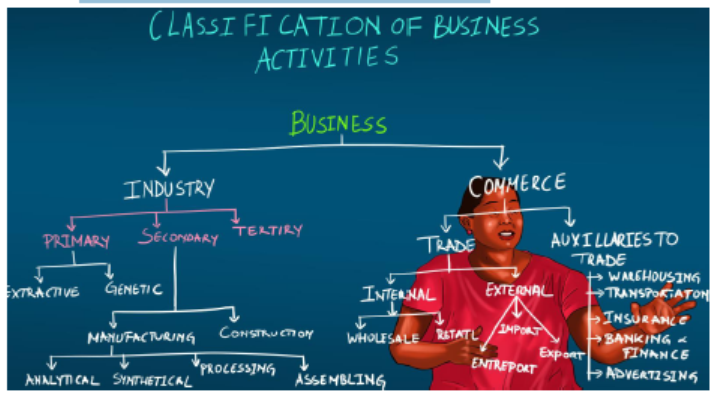
8.1. Meaning of business organisation and classifications of business organisations
Visit your Library or use the internet to research on the categories of enterprises according to life span and fill in the table below:
Business is any economic activity done by any person or a group of persons with the purpose of making profits. It involves the exchange of goods or services for money. The main purpose of carrying out business is to make profits.
A business organisation is a group of people who form a business together in order to achieve a particular aim usually making profits.
Business organisations can be classified according to sector of activities, size, legal status and lifespan.
Business organizations are numerous and vary widely in the nature and types of goods or services provided. Their classification can therefore take many forms. The major bases upon which enterprises can be classified are by:
•Sector or activities
•Size
•Legal status and
•Life span
Classification of Business organizations according to legal status/ according to ownership
The following are the classifications of business organizations
1. According to legal status.
-Sole proprietorship
-Partnership
-Joint stock company
-Cooperative
-State owned enterprises (SEO) parastatalsSole proprietorship/ sole trade business

Sole proprietorship is a business started and owned by one person. The sole proprietor makes a decision alone, takes all the business profit and in case of losses he/she suffers them alone. E.g.: Restaurant, Internet cafes, boutiques, etc.
Joint stock companies
A joint stock company is at times called a limited liability company or simply a company.
This is a type of business formed and owned by a group of people called shareholders who have a separate legal identity. It is an artificial person created by law with capital divided into transferable shares.Co-operatives
A co-operative enterprise or a society is a form of business made by a group of people who join efforts in the production or distribution of goods and services with the purpose of sharing profits among themselves. A cooperative is an organization owned by the people who work in it and share the profit or with the purpose of benefiting its members.

Give examples of enterprises from your community and Rwanda at large by filling in the table below.
8.2 Business registration procedures according to form in Rwanda
1. Suppose you intend to start a small business in your vacation out of your pocket money savings that you have accumulated over time suggest the major steps that you are to follow before starting.
You can register your business Online or at the office of the Registrar General which is a department within the RDB located in Kigali, the capital city of Rwanda. The registration process has been covered after each business form.
8.2.1. Business Registration Process
For Sole Proprietorship business, an entrepreneur can start the business with few legal procedures. There are no formal procedures such as registration and document, an entrepreneur only pays a trading license and starts the business. But if he/she needs to register the business in the commercial registry, he/she is required to submit an application letter indicating.
▪Personal names, place and date of birth, domicile and residence, nationality, sex.
▪Name of the spouse in case he/she is married, and their matrimonial regime
▪Consent of the spouse if their regime is based on joint ownership.
▪Name of the business and its trademark if applicable.
▪Commercial activities to be carried out.
▪Headquarters of the business enterprise.
Partnership business may register with the registrar of companies. In this case, they will be required to submit partnership deed agreement (containing information discussed earlier in this unit). In the absence of an agreement between partners, the partnership cannot be registered.
Joint Stock Company/ Limited Liability Company, or a Cooperative, the following steps are normally followed:
▪The promoters prepare a memorandum of association which outlines the activities the firm is to be engaged in, its objectives and its general organization.
▪Preparing the Articles of association of the company that lays down the rules and regulations which will govern the internal organization of the company.
▪A minimum initial share capital for companies is required. For Limited Liability Company it is 500,000Rwf, for Public limited company it is 100,000,000Rwf.
▪The registration can be processed by the promoters themselves or through a lawyer.
▪An application form is filled and deposited with the records assistant in the registrar’s office.
A search will be conducted to confirm that firm uses similar names as those chosen by the promoters of the company.
The application forms are then passed on to the registrar of companies for endorsement and approval.
If all the required documents are in order; the registrar of companies will issue a Certificate of Incorporation. This document allows the owners to commence the business. If it is a public
company, it is required to get a Certificate of Trading in order to commence operations. It puts the company into existence and the company becomes a separate legal entity.
8.2.2. Registering a Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) in Rwanda
1. Local Non-Governmental Organization
A local NGO is required to get an approval from the district where it plans to undertake its activities, provide its constitution as well as register with Ministry of Local Government (MINALOC).
2. International Non-Governmental Organization
An INGO is registered by department of Immigration and Emigration. The applicant makes an application letter addressed to Director General of Immigration and Emigration and attaches.
-A detailed action plan.
-A memo indicating the source of funding of INGO
-Its annual budget
-Evidence of collaboration of the district where it operates
-Recommendation letter from the line Ministry (ies)
-Articles of INGO
-A memo linking relationship between its program with Community Development Plan (CDP)
-A correctly filled inventory form
-Summary of business Registration process in Rwanda
-To register a local enterprise or a foreign subsidiary, RDB provides a quick and efficient registration service allowing you to have your business incorporated within 24hours. The process ends simultaneously by obtaining the certificate of incorporation (business registration), Tax Identification Number (tax registration) and the Social Security Registration for Employee Pension Submission.Take a look on the table below to see how you can start, add or cease business activities in Rwanda.
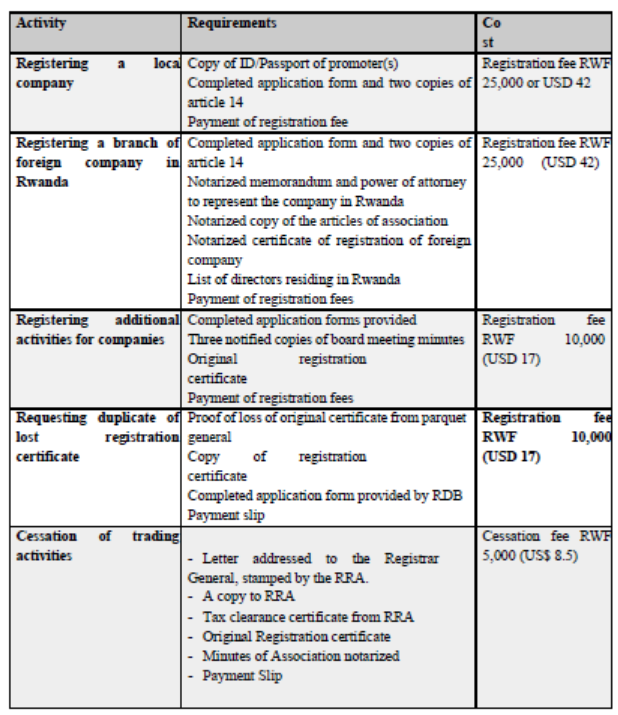

1. Discuss the various procedures followed in registering a domestic company following Rwandan setting today.

Hope is a chairperson of the student business club in her school. In the last 3 weeks, she noticed team members were not showing up for meetings. She found out that there has been a fight about money, team members were accusing one girl of stealing cash. Create a strategy Hope can use to help the team achieve their goals.
Case study: Different forms of business organization/ enterprises
Read the case study below and answer the questions that follow:
Jean Paul Nyimana is a friend you have known for many years. He is a computer expert. He has been working for a large computer supplies company in Kigali for many years. The company supplies and services computers. Most people and organizations are experiencing technical problems with their computers, take them to the company where Jean Paul is assigned to service the computers. He is now well known by many people for his skills in handling technical problems relating to computer breakdowns.
He informs you that he has been thinking of starting a business enterprise dealing with servicing and maintenance of computers. He has saved money for this purpose, but the amount is not quite sufficient for the type of business he would like to start. However, the money is sufficient to start a small size business.
He also tells you that he has two uncles who are very rich. Both have a lot of money and have expressed their willingness to invest in the business enterprise with him.
Nyimana would like to get your advice on various options of the type of enterprise to invest in.
(a) Advise him on the forms of enterprises he can choose citing examples.
(b) Analyze the advantages of each form of enterprise.(c) Analyze the disadvantages of each for of enterprise.
