Topic outline
INTRODUCTION
This textbook is part of school curriculum reform in Rwanda in particular how the curriculum is taught. It is hoped that this change will make what you learn in school more useful both at school and when you leave school.
In the past, the main reason for schooling was to obtain knowledge – that is facts and ideas about each subject. But nowadays the main reason due to changes that are happening in the environment and the job market is becoming more competitive therefore you should be able to use the knowledge you will obtain to develop competencies. These competencies include ability to think for yourself, ability to communicate with others and to explain what you have learnt, as well as being creative in developing your own ideas, not just following those of the Teacher and the textbook. In this textbook, different approaches are used to help you to develop competences and make this textbook user friendly. Among these approaches are the following:
Activity-based learning
These activities present you with instructions to follow that will help you to learn some and discover others for yourself. You already have knowledge and many ideas based on the experiences you have had and your life within community. Some of the activities, therefore, require you to use the knowledge and ideas you already have.
In using this book, therefore, it is essential that you do all the activities and follow all the instructions. You will not learn very well unless you complete these activities provided. They are the most important part of the Textbook.
In some ways this makes learning more of a challenge. It is usually challenging to think for yourself than to copy what the Teacher tells you. But if you take up this challenge you will become a better person and become more productive and successful in your life.
Group work
You can also learn a lot from other people in your class. If you have a problem, it can often be solved by sharing it with others. Many of the activities in the book, therefore, involve discussion. Your teacher will help to form and organize these groups in a conducive learning environment facing each other. You cannot discuss properly unless you are facing each other.
Research
One of the objectives of the new curriculum is to help you discover for yourself. Some activities, therefore, require you to do research using Textbooks in the library, the internet if your school has access, or any other source such as newspapers and magazines etc. This means that you will develop skills of learning for yourself that can help you both when still in school and after school. Your teacher will help in case your school does not have a fully equipped library or internet.
Skills lab
Entrepreneurship subject is more practical than theoretical that is why it requires time for skills lab which is a regular time on the normal timetable when students are required to complete learning activities working in manageable groups.
During skills lab activity students are given an opportunity to talk more and get more involved in the lesson than teachers. Students receive constructive feedback on work done (Teacher gives quality feedback on student presentations).
The Skills Lab prepares students to complete portfolio assignments on their own after classes. So, classroom activity should connect directly to the portfolio assignment and the teacher during the skills lab makes sure that he links the unit with the student’s business club and back home projects.
Icons
To guide you, each activity in the book is marked by a symbol or icon to show you what kind of activity it is. The icons are as follows:

This icon reminds you to link your previous knowledge with the topic you are going to learn. As a student feel free to express what you already know about the topic. What is most important is not giving the right answer but the contribution you are making towards what you are going to learn.

Some activities require you to complete them in your exercise book or any other book. It is time for you to show if you have understood the lesson by answering the questions provided.


This icon requires you to write down the responses to activities including experiments, case studies and other activities which assess the attainment of the competences. Teachers are expected to observe the changes in you as student.
UNIT 1: INITIATION TO ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Key unit competence: To be able to analyze entrepreneurial stages for the success of a business.

Introductory activity
After completing S.3 national exams, Umuhoza thought of starting a small project that will help her get money for school fees at advanced level, using the knowledge of entrepreneurship she learnt in the three years and her great appetite for mandazi. she asked herself what project she could start! she talked to a nearby small business owner who inspired her to start a small bakery project because it required limited capital, Umuhoza was happy and liked the idea, her mother also taught her how to make bread, she decided to start that small project with personal savings accumulated from pocket money while at school. Before starting this project, she first researched about the most marketable bakery product and found out that cakes and chapattis are marketable than bread. she also discovered that the whole village had one supplier of these items and in many shops, such items were lacking. Because she had little money, she prepared a budget focusing on sources of revenue and projected expenditure. Amidst all these challenges, Umuhoza was able to start and operate her bakery project within the trading centre. she named her business Hoza Bakery Supplies. she is now able to borrow loans from the village co-operative bank, pay tuition (school fees), support her family, and offer jobs to her friends using the profits generated. she has a plan of extending her project to Kigali by opening a branch.
Questions.
a)
What skills do you think Umuhoza acquired from O’level entrepreneurship that motivated her to start her bakery project?
b)
What inspired Umuhoza to start her own business?
c)
What did it take Umuhoza to start a bakery project?
d)
Is Umuhoza an entrepreneur? If yes, explain?
e)
How will the above project solve community problems?From the above passage, we can conclude that being an entrepreneur takes an extra effort and all
the activities undertaken by entrepreneurs such as Umuhoza to start production is called ‘entrepreneurship’.
1.1. Meaning of entrepreneurship, an entrepreneur, Intrapreneur and manager
Activity 1.1
Using your knowledge of entrepreneurship obtained in O’level and research made from internet or libraries distinguish between the following terms, entrepreneur, entrepreneurship, Intrapreneur and manager.1.1.1. Meaning of an entrepreneur
The word entrepreneur is derived from a French word “Entreprendre” meaning to undertake. It is used to mean a person who takes the risk of starting a new organization or introducing a new idea, product or service to the society.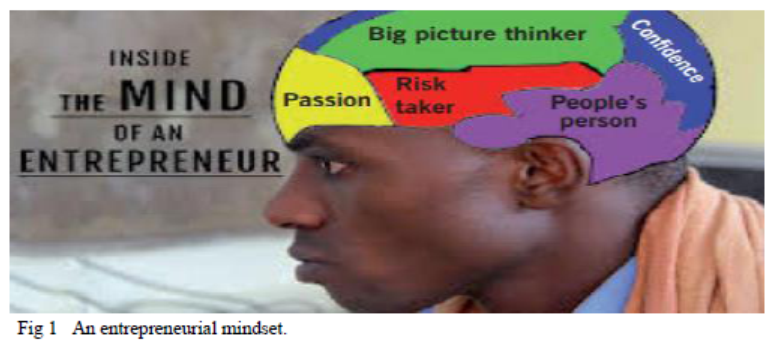
According to J.B. Say, “An entrepreneur is an economic agent who unites all means of production; land, labor and capital which are used to produce goods and services.
By selling commodities in a goods market, he/she pays rent to land, wages/salary to labor and interest to capital and remains with a profit.
According to Richard Schumpeter, “An entrepreneur is an individual who introduces something new in the economy; a method of production not yet tested by experience in the branch of manufacturing, a product which is new in the market from a new or old source of raw materials using new or existing methods of production.”
The entire definitions highlight: bearing of risks, combining factors of production, innovation and introduction of new methods and products, and bringing about economic change as a function of entrepreneur.Therefore. An entrepreneur is a person who has the ability to see and evaluate business opportunities, gathers necessary resources and uses them to initiate and manage the identified business; takes risks in the business with the aim of making profits.

NB: Any person who assumes risks of any business and owns that business enterprise with an aim of making profits is an entrepreneur irrespective of the size and mode of operation of the business.
1.1.2. Meaning of entrepreneurship

Different scholars have defined entrepreneurship as below:
Arthur H. Cole in his book, Business Enterprise in its social setting; defines entrepreneurship as “the purposeful activity of an individual or a group of associated individuals undertaking to initiate, maintain and increase profits by production or distribution of economic goods and services”.
Higgins in his book, The Economic Development defines entrepreneurship as “the function of foreseeing investment and production opportunities, organising an enterprise to undertake new production process, rising capital, hiring labour, arranging the supply of raw materials, finding sites, introducing new techniques, discovering new resources or raw materials, and selecting top managers for the day-to-day operations of the enterprise.
Grey Watson: defines entrepreneurship as “the process through which individuals identify opportunities, allocate resource and create value”.
From the above definitions, it can be observed that entrepreneurship.
- Involves the ability of a person to identify business opportunities.
- It involves mental attitude of risk taking, resource organisation and exploitation.
- It involves one or more individuals.
- It involves creativity, being innovative, initiative
Therefore, entrepreneurship is the process of identifying business opportunities from a locality, organising necessary resources, and using them to start an enterprise to produce goods and services, market them while covering risks with the aim of making profits.
Entrepreneurship is also a way of thinking and acting that focuses on identifying opportunities, apply action with analysis, and is driven by a passionate individual or team.1.1.3. Intrapreneur

An Intrapreneur is a person within a large corporation/enterprise who takes direct responsibility for turning an idea into a profitable finished product or service through assertive risk taking and innovation. Great ideas and products can result from letting your employees think, experiment, and try using new technology and production techniques. This is different in each company but what is important is to embrace the idea of engaging employees, and to choose a system for applying that vision in a way that fits your company culture.
Intrapreneurs are usually employees within a company who are assigned a special idea or project and are instructed to develop the project like an entrepreneur would.
Example: If an employee working in Airtel Company Rwanda suggests and introduces the use of Airtel cash for its customers to access funds on their bank accounts i.e. can withdraw and deposit money using Airtel cash then such an employee is an Intrapreneur and has to be paid for such
inventions by Airtel Company in Rwanda.
1.1.4. Meaning of Manager
A manager is a person who organizes resources, allocates tasks, oversees and controls business operations so as to achieve the organizational goals, mission and vision.
1.1.4. Entrepreneur vs Manager
The term entrepreneur is often used synonymously with Manager, yet these are conceptually different. It is true that an entrepreneur is a manager of his own enterprise but not all managers are entrepreneurs.Difference between an entrepreneur and a manager
Kharim is a graduate who recently graduated from UR college of science and technology with a degree in Computer Programming. He has developed an application that he believes will make him earn a living. He performed very well and was called by prominent telecommunication company for a job, he accepted and worked for one month and after he thought to leave that Company so as to start his own project of designing new software. He wants to challenge himself and work the way he wants without answering to a boss. He is using a small inheritance to fund the start-up alongside contributions from his grandparents. As an entrepreneur, Kharim is not only starting a business, but is risking his personal wealth to establish it.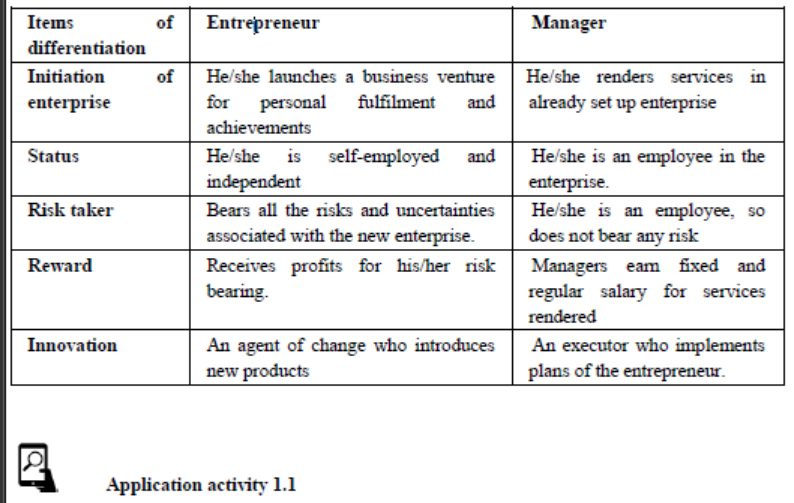
Kharim is also trying to convince some friends from school to form an entrepreneurial team with him. Kharim has a friend who majored in Web designing and another in marketing. He is hoping they may come along with him and bring their skills. He is building the right team so that they can co-operate and achieve more together than they would individually.
Kharim hopes that his entrepreneurial gamble will pay off as well as the gambles of other well-known entrepreneurs.
Questions:
1. What lessons can be learnt from Kharim’s experience?
2. Briefly explain the relationship between an entrepreneur and entrepreneurship.1.2. Qualities/characteristics of an entrepreneur
i) Do you have a role model that inspires you to join business? YES/NO?
ii) State and describe characteristics your role model possesses.
Qualities or characteristics of a successful Entrepreneur
▪Hard working: This involves using extra effort to do whatever one is doing. It involves working extra or additional hours, days and nights. A hard-working person commits more time, more energy and more resources to achieve the desired objective. Commitment and hardworking are essential to success in business.
▪Creative and Innovative: Creativity involves using ideas to come up with new products. For a person to be successful in life, S/he must be creative by doing new things or doing old things differently. Being innovative helps a person find new business ideas, improve existing business activities, and find solutions to difficult problems. All these help an entrepreneur to become successful.
The relationship between Creativity and Innovation is like the relationship between recycling and upcycling. One brings new idea, new product while others improve what is existing.
▪Risk taking: Entrepreneurs are risk takers. They risk starting a business. This is not to mean that they are reckless people. Good entrepreneurs assess the risks related to their business before they take them. They do not take every risk; they only take moderate risks that they will be able to manage.
▪Decision making skills: A successful entrepreneur makes intelligent, right and informed decisions on various issues, follows the decisions made, and accepts their results.
▪Persistence and Perseverance: Starting and growing a business requires a lot of determination and a “never-give-up” attitude. It is said that winners never quit and quitters never win. Entrepreneurs never give up, irrespective of all problems and setbacks met in the business. They put in as much efforts as possible to ensure business success.
▪Opportunity seeking: A good entrepreneur is able to spot opportunities even where other people are not able to see any. Ability to see opportunities also helps the entrepreneur to take advantage of other opportunities like identifying the best employees, taking advantage of cheap loans from commercial banks, raw materials, etc… he/she sees society’s challenges or problems as basis for business creation or expansion.
▪Seek information: good entrepreneurs are always on the lookout for information related to their businesses to make good decisions. Good decisions are based on right and updated information. For example, for a manufacturing business, the entrepreneur seeks information about suppliers of new machinery, new industries entering competition, potential customers, new government policies, etc. All this information is helpful in making informed and profitable decisions.
▪Self-confidence: An entrepreneur should have a strong belief in his/her abilities. He/she should be confident that he/she will achieve what s/he sets himself to achieve. If a person is not confident of himself/herself, he/she cannot be a good entrepreneur.
▪Financial Discipline: A good entrepreneur has excellent money management skills. He/she does not spend business money on unplanned activities or things.
▪Goal setting and planning: good entrepreneurs set goals and strive for achieving them. The goals set should be SMART that is to say specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time frame/ bound.
▪Commitment: An entrepreneur will succeed in business if he/she is committed to the business and to fulfilling obligations; for example, he/she should spend a lot of time in the business and make sure that customers are served properly, they are given very good services and when he/she makes a promise, he/she has to fulfill it.
▪Persuasive and good at networking: Persuasiveness is the ability to convince others and change their thinking. Networking involves meeting other people involved in the same kind of work, to share information and support each other. A good entrepreneur will always get time to meet and share ideas with people who matter to the business such as suppliers, competitors who can give him/her good advice, etc. A good entrepreneur will not be an ‘island’ but will always be networking.
▪Controlling/monitoring: An entrepreneur ensures that results match with plans. Monitoring business activities helps him/her to know whether the business is succeeding or failing. By doing this he/she decides on what to do if the business is not achieving desired results.

1. a) Discuss the various qualities an entrepreneur should possess.
b) Choose two best entrepreneurs in the world today that act as your role models: one male and one female.
(i) …………………………………………………………..
(ii) …………………………………………………………2. Explain briefly how the above entrepreneurs have demonstrated the following characteristics basing on your knowledge about them.
1.3. Stages of entrepreneurship process.
Looking at fully developed businesses with tangible products in your home area.
e.g., Inyange industries. What stages do you think the above business went through to get to where it is today?The stages of entrepreneurship development

At this stage an entrepreneur generates ideas, recognizes opportunities, determines the feasibility
of ideas, markets, and ventures and other prior information.


Here an entrepreneur starts and operates business and utilizes resources to achieve its goals and objectives.
Harvesting:

Here an entrepreneur decides on the venture’s future (growth, development, or demise).
Gap-filling questions
1.…………...an entrepreneur decides on the venture’s future (growth, development or demise).
2.…………… here an entrepreneur plans the business, identifies needed resources through developing a business plan.
3.……… an entrepreneur starts and operates business and utilizes resources to achieve its goals and objectives.
4.………. acquires needed resources for the venture startup including financial, material, and human and technology.
Draw a new product design that uses recycled materials and solves customer’s need. Explain what problem it solves and what innovation it possesses.
1) Joanna is a senior 4 student and wants to start a small business project in her holidays. Imagine a situation where she comes to you for advice. How would you advise her to apply the five stages of the entrepreneurship process to start a successful business?
2) Come up with a business opportunity by analysing a need in your community, your own skills or passion and available resources.UNIT 2: CAREER OPPORTUNITIES
Key unit competence: To be able to make rational career choices and related decisions

1. Identify the type of careers shown in each photograph above.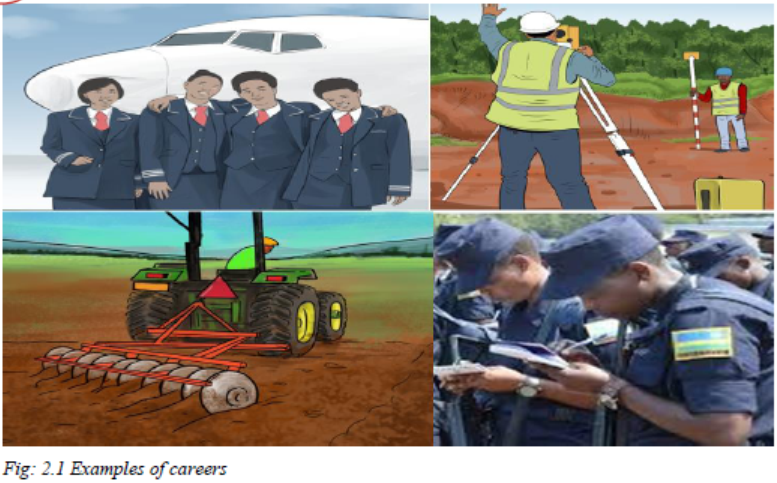
2. Identify the subjects one needs to study so as to pursue each of the above careers.
2.1. Meaning of Career concept, choosing work to do and fields of career opportunities
Activity 2.1
a. What do you understand by the term career?
b. Observe the images below and indicate the jobs related to each career opportunities
2.1.1. Meaning of career A career is an occupation undertaken for a significant period of a person's life and with opportunities for progress. It can also mean a job or profession that one does for a long period of life for survival which enables him or her to achieve set goals.
It can also be defined as a profession for which one has been trained for as an undertaking or as a permanent calling. It is what one wants to become in the future.
2.1.2. Choosing work to do and fields of career opportunities
Work can be understood as undertaking we get involved in pursuit for our long-life goals. Therefore, it is important to note that, work pre-trained and done for a long time can be referred to as career.
The choice of a career is very important for every person. It requires serious consideration, planning and analysis. Planning your career involves self-evaluation on the following questions, who am I?, what are my interests?, what work environment?, what will I be doing and what are the job trends?. A person can get into many careers.
In each industry or sector of the economy, there are many careers to choose from. Some careers require a lot of physical effort (muscle based) while others require a lot of mental effort (knowledge based). Some other careers require many years of training while others can be joined without formal training.
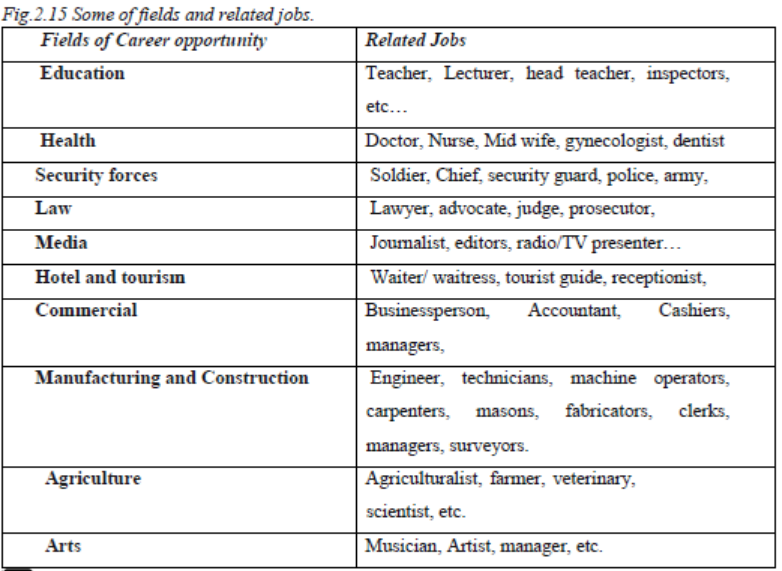
The following are some of the fields of career opportunities and careers that one can pursue:
There are very many careers in the world. The main fields include:
-Education field for example, head teachers, teachers, school administrators, bursars, and university lecturers.
-Medical field for example, doctors, nurses, surgeons, pharmacists, gynecologists, dermatologists, physicians and so on.

-Agricultural field for example; livestock farmers, dairy farmers, crop growers, etc.

Engineering field for example, biomedical engineers, electrical engineers, civil engineers, telecommunication engineers, mechanical engineers, land surveyors and so on.

-Political field for example, presidents, vice presidents, mayors, ministers, members of parliament (senators), community leaders and so on.

- Commercial and manufacturing field for example, wholesalers, retailers, vehicle manufacturing, textile production, bakeries and confectioneries.

-Transport field for example, freighters, cargo couriers, pilots, air hostesses, drivers, captains and so on.

-Legal field for example, lawyers, judges, juries and attorney generals.

-Finance field for example, bankers, accountants, auditors, money changers, finance consultants and so on.

Security field for example, police, military and army, secret service/intelligence, etc.

-Media field: This involves people working as news readers, news anchors, and television and radio presenters, journalists and so on.

-Hotel and tourism field for example, waitresses, waiters, chefs, tourist guides, and so on.

You have acquired very essential and accurate information about what a career is, as well as numerous fields of career opportunities.
Questions:
(a) Reflect on different fields of career opportunities available around your school community
(b)What would you consider while choosing work to do?
2.2. Sources of career information
1 Identify places and people in your home area that can be an inspiration to your career.
2 Use your internet, search on www.gostudy.net to choose a career field by filling in the questionnaire provided.
There are many sources of career information from which an individual may choose from and these sources may include the following:
▪Parents, friends, and relatives: Families and friends can be extremely helpful in providing career information. While they may not always have the information needed, they may know other knowledgeable people and be able to put you in touch with them. These contacts can lead to an “information interview” which usually means talking to someone who can provide information about a career. This person should have the experience to describe how he or she trained for the job, received promotions, and the likes or dislikes of the job. Not only can the person advise what to do but he or she can also advise what not to do.
▪Professional societies, trade groups, and labor unions: These groups have information on careers with which they are associated or which they actively represent. This information may cover training requirements, earnings, and listings of local employers. These groups may train members or potential members themselves or may be able to put you in contact with organizations or individuals who have been in that career for a long time.
▪Personal skills, talent, and passion: The first place to start from when looking for business ideas or opportunities is to look within you. Most people miss this greatest source of career information because of ignorance, laziness, and self-doubt’s. If you are talented or having a proven track record in a specific field, then it is time to analyze that skill or talent. You can discover what you are good at, what career to take by asking yourself the questions such as; what skills or talents do you possess? what are your hobbies? what are you passionate about? do you possess a skill that people are willing to pay for?
Note: It is because of personal skills, talent, and passion that some people popular have the careers they chose.
▪Mass media: This is a wonderful source of information, ideas, and opportunities. Magazines, TV stations, Cable networks, radios, newspapers, and internet sites are all examples of mass media. A careful look at the commercial advertisements in newspapers or magazines, you will discover information on careers, as well as the skills and education level required to join the desired career.
-Guidance and career counsellors:
-Counsellors can help you make choices about which careers might suit you best.
-Counsellors can help you determine what occupations suit your skills by testing your aptitude for various types of work and determining your strengths and interests.
-Counsellors can help you evaluate your options and search for a job in your field or help you select a new field altogether.
-They can also help you determine which educational or training institutions best fit your goals and find ways to finance them. Some counsellors offer other services such as interview coaching, resume building, and help in filling out various forms.
-Counsellors in secondary schools and post-secondary institutions may arrange guest speakers of different career fields, field trips, or job fairs to equip you with detailed information about careers.
▪Libraries: These can be an invaluable source of information since most areas have libraries, they can be a convenient place to look for career information. Also, for those who do not otherwise have access to the Internet or e-mail, many libraries provide this access. Libraries may have information on careers locally and internationally, potential contacts within occupations or industries. Libraries frequently have subscriptions to various trade magazines that can provide information on occupations and industries. These sources often have references to organizations which can provide additional information about training and employment opportunities.
▪Tertiary institutions such as colleges, universities frequently have career centers with libraries of information on different careers, listings of related jobs, and alumni contacts in various professions. Career centers frequently employ career counsellors who generally provide their services only to their learners and alumni. Career centers can help you choose a career, build your resume, find internships and co-operations which can lead to full-time positions, and tailor your course selection or program to make you a more attractive job applicant.
▪Exhibitions, expos, and trade shows: Another means to get career information is to attend exhibitions and trade fairs. These are usually advertised on the radio or in newspapers. By visiting such events regularly, you will not only find out new products and services, but you will as well meet sales representatives, wholesalers, distributors, manufacturers, and franchisers. These are always excellent sources of career information.
▪Listening to customer complaints: Complaints and frustrations on the part of customers have led to prospective career opportunities. Whenever consumers complain badly or bitterly concerning a product or service then, you have the potential for a career opportunity. This will prompt you to acquire more skills as a career opportunity and also to provide better and competitive services or goods.
▪Surveys: You can carry out a survey online or offline. One can visit different people of different career fields and find out the advantages and disadvantages of each career field. This helps you to compare and make an informed decision on which career to undertake.
Note: The above sources aren’t independent but rather complement each other towards choosing an appropriate career. Therefore, in choosing career for example teaching one can use Ministry of education and internet while others can refer to guidance and career counselors.
Application activity 2.2
Assume that you are invited to address your community members after a community service in your home locality. Take this advantage to advise young people in the audience on how to utilize sources of career information available to them to select appropriate careers. What will be entailed in your speech?
2.3. Career guidance and sources of career guidance
a) How can you define the term “career guidance”?
b) Reflecting on your choice of combinations, give reasons why you chose that combination and who helped/influenced you to make your choice
c) Why is career guidance important?
d) Make a list of sources where career guidance can be obtained
2.3.1. Meaning of career guidance
Career guidance is the act of assisting students and adults to successfully choose the right career for themselves, manage and develop it.
2.3.2. Sources of career guidance
Having the right and accurate information is important in the choice of a career. The choice should be based on accurate information. Career guidance can be obtained from various sources:
i. Teachers: Teachers provide best source of career guidance to learners because they spend most of their time with learners hence, they understand their strengths, weaknesses, talents and skills.
ii. Parents: Some families have bias either against or in favor of certain careers and consequently encourage or discourage their family members to either take them up or leave them. Some people, therefore, choose to undertake certain careers because all their family members are taking the same career and are successful.
iii. Career guidance counsellors: These are professionals trained to help people assess their strengths and weaknesses, evaluate their goals and values and determine what they want in a career.
iv. Government officials. Government officials may act as models that can guide us when approached and some have testimonies that can help young people find strength amongst themselves
v. Heroes and mentors. For example, political and humanitarian heroes e.g., Nelson Mandela’s biography is a touching story and an inspiration to many young politicians.
vi. Role models e.g., musicians, athletes are persons looked up to by others as an example to be imitated
vii. Friends and relatives offer advice and support that help to shape and develop career
Application activity 2.3
BAMURANGE, a S3 student at G.S Ntarabana wishes to enroll in associate nursing program. She has been asking her teacher about the program, and the teacher managed to provide her with some information about the program to the best of his knowledge. He also told her about other possible careers.
As a student enrolled in the program,
1. In not more than 4 sentences, guide her on how to join associate nursing program,
2. Evaluate the sources of career guidance which should help Bamurange to make a rational career choice.
3. Advise Bamurange’s teacher on key principles that he should bear in mind while guiding his student.
1.Design a flyer that promotes the Student Business Club to new senior 4 students. The flyer should be attractive and present at least 3 arguments why students should start business projects while they are in school.
1.Read the sentences in the table below and indicate true or false.
a. A journalist belongs to the education field.
b. A DJ belongs to the media field.
c. Teachers belong to the medical field.
d. Police officers belong to the political field.
e. Pilots belong to the airfield.
f. A barrister and chef belong to the same field.
g. Accountants and bankers belong to the finance field.
h. Lawyers and teachers belong to the same field
2. Formulate 5 interview questions you can ask an entrepreneur in your community to find out the advantages and disadvantages of running a business.
3.Give examples of careers one can take in each field by filling in the table below
UNIT 3: BUSINESS IDEAS AND OPPORTUNITIES
Key Unit Competence: To be able to generate viable business ideas and opportunities.
Introductory activity:Analyze the photo below and answer the following questions
Questions
1.From the picture above analyze different sources of business ideas.
2.Generate different business ideas from the above environment.
3.Not all business ideas are business opportunities. Is this statement true or false? Give reasons to justify your response.3.1 Business, business idea and a business opportunity
The government of Rwanda is encouraging youth to be job creators but not job seekers.”
a) What viable business opportunities can you think of in order to foster development of your community and country at large?
b) Explain why customers will be compelled to buy your products.
Meaning of a business idea
Business refers to any economic activity that involves the production, selling of goods and services, covering risks with the aim of getting profits.
An idea is called an opportunity if there is evidence that the entrepreneur’s idea can be turned into reality.
A business idea simply refers to any thought that the entrepreneur may come up with as a result of scanning the environment with the possibility of developing it into a business opportunity. It requires
the entrepreneur to exercise creativity and innovativeness in order to come up with the necessary business ideas for the environment. Examples of business ideas in Rwanda include Real estate, clothing and textiles, food processing, E-Commerce, internet and computer services, food delivery services, photography and videography, horticulture business.
Meaning of a business opportunity.
A business opportunity can be defined as an identified situation or chance that can be turned into a real and profitable business.
An opportunity is a favorable set of circumstances that creates a need for a new product, service, or business. Such opportunities are determined by customer requirements and lead to the provision of a product or service which creates or adds value for its buyers or end-users.
A business opportunity is said to be viable, when it has the ability to grow and expand.
Examples of business opportunity and their business idea
-Lack of sufficient safe water in your community is a business opportunity. Provision of JIBU can be a business idea.
-High demand for charcoal as source of energy in your community is business opportunity. For that opportunity, many business ideas can be generated like Provision cooking Gas, making charcoal in wastes, planting trees, buying big vehicle to transport charcoal from far forest…
-A business idea may not necessarily be a business opportunity; one needs to filter and sift through these ideas to realize whether they are real opportunities.
Case study: A reality T.V. Show
Rwiyemeza is a nurse by profession and a prominent entrepreneur too dealing in growing and processing of Mushrooms in Kicukiro district. One day she was invited to give an interview on Rwanda Broadcasting Agency (RBA) about her business to the whole nation by Mr. Makuru.
Read through the excerpts from the interview
Makuru: why did you decide to get into mushroom growing and processing? How did you start?
Rwiyemeza: It was during my school time when I joined a school business club. I got the idea when our club mentor told us that we can start a back home business, we used to call it a ‘BHB’. I introduced the idea to my parents and I was lucky that they supported me. It was not a very easy task with everyone telling me different things about growing mushrooms. Many people that I talked to focused on the challenges but about three people told me that I can overcome the challenges if I plan in advance. I therefore decided to take on the business of Mushroom growing and processing.
Makuru: What was the biggest challenge and how did you overcome it while starting your Mushroom business?
Rwiyemeza: There were so many challenges such as unsure market, competition, pests, weather vagaries but deciding on turning my business idea into a profitable business was most challenging. I had to make a lot of research from existing entrepreneurs, Sector officers, and financial institutions. I also had to do personal evaluation. I found that I could market my product very widely to beat the market problem and ensure much cleanliness and timely watering to avoid pests.
Makuru: What are the benefits of your business to the community?
Rwiyemeza: Apart from earning me and my family a living, my business employs three ladies and 2 gentlemen who earn a monthly salary. Important to note also, is that I have inspired a lot of other young entrepreneurs especially women to start their own businesses.
Makuru: What advice would you give to the young people who may want to start businesses?
Rwiyemeza: My advice would be that all around us are opportunities of business ideas but one has to be careful because NOT all business ideas can be turned into profitable businesses. Before I finally decided to start mushroom growing and processing, I had tried a number of businesses which failed because they were not viable. So, I again advise the young people to take time and research about the business ideas before investing money because “Not all business ideas are business opportunities”.
Questions
Referring to the case study (A reality T.V. Show) above, answer the following questions.
a) What do you understand by a business and what is Rwiyemeza’s business?
b) Mention any sources of business ideas for Rwiyemeza’s business activity.
c) Rwiyemeza says it was not easy for her to start up the business activity. Explain what you understand by a business opportunity and identify some challenges Rwiyemeza faced.
d) Why do you think it is very important to do a research and personal evaluation before deciding to start a business activity?
e) Think of two viable business ideas in line with your career as an associate nurse that you can invest in. give reasons to justify your opinion.
3.2. Reasons for generating business ideas
1) Why do you think that it is important to generate smart business ideas?
2) In your own words, explain why the following Enterprises: Urwibutso, Inyange, Mara phone, Volkswagen were started?
The simplest purpose of business is to solve a customer's problem or meet the customers’ needs. By providing the goods and services that meet the customer’s needs, the business owner may realize profits (and at times may incur losses). Businesses exist to impact on people's lives. This happens by businesses providing people with goods and services they desire to meet their needs. While the people buying the business’ products (goods and services) are meeting their needs, the business owners expect to realize profits. Businesses serve as conductors of economic activity and development.
Business may be done by private individuals, government, companies, co-operatives, or non-governmental organizations (popularly known as NGOs).
There are many reasons why entrepreneurs would need to generate business ideas.
-You need an idea: a good idea is essential for a successful business venture – both when starting a business and to stay competitive afterwards
-To respond to market needs: markets are made up essentially of customers who have needs and wants waiting to be satisfied.
-Changing fashions and requirements: provide opportunities for entrepreneurs to respond to demand with new ideas, products, and services
-To stay ahead of the competition: Remember, if you do not come up with new ideas, products and services, a competitor will. So, the challenge is to be different or better than others
-To exploit technology – do things better: Technology has become a major competitive tool in today’s markets and for one to be better with changing technology, generation of business ideas is crucial.
-Because of product life cycle: All products have a finite life. The firm’s prosperity and growth depends on its ability to introduce new products and to manage their growth
-To spread risk and allow for failure: It is necessary for firms to try to spread their risk and allow for failures that may occur from time to time by constantly generating new ideas.
a) Identify two main problems in your community and suggest the business opportunities you would come up with to solve them.
b) Case study.
Read the case study and answer the questions that follow.
We hear you. Hear us too.
Kigali Global Shapers (KGS) hub, a group that works with young Rwandan entrepreneurs, presents ‘Twumve-Twumve’ entrepreneurship evenings. Loosely translated, the event means ‘We hear you. Hear us too.’ The events aim is to find solutions for problems faced by Rwandan businesspeople, such as the high failure rate of start-up businesses.
What are the likely causes of failure of start-up businesses?
3.3 Sources of Business Ideas.
Referring to your community and beyond, explain at least 5 business ideas that you can generate from the different sources in the figure above.
“When the going gets tough, the tough get going, so goes an old saying.”
Most people think of doing business as the last option and yet it is a major source of income and reduces the dependence syndrome.
The following are some of the sources of business ideas:
-Looking within you and examining skills, talent, and passion: The very first place to start looking for business ideas and opportunities is to look within yourself. Self-examination is an important thing that can help in reaching to different decisions. It is important to examine your own skills, talent or passion that can fit into the business. Therefore, such businesses, which corresponds according to your skills is the most appropriate and are expected to be successful in future.
-Inventing a new product or service: Another great source of business opportunity is inventing a new product or service. Different people are creative with a mindset of thinking out of the box and solving problems with the best appropriate solution. One needs to think like great entrepreneurs such as Such as SINA Gerald of urwibutso enterprise, Zulphat Mukarubega proprietor of Rwanda Tourism University College, etc. However, for winning ideas you need to be specific on your target market and analyze the problem.
-Adding value to an existing product: Rather than inventing a product, one can also add a value to existing product. These kinds of innovations can be proved as a great source of business opportunities. Since most of the inventions have already taken place, so it is prevailing as innovation.
-Franchising: By looking on the demographics and the need for a particular service or product, one can also start a franchising business. It can be really profitable since much of business modeling is not required because a person uses the rights of another retailer
-Mass Media: Mass media has become comprehensive from past few years. Magazines, TV, Newspapers etc. are a great source of ideas and opportunities. Different businesses are on sale and different commercial advertisements are available to choose.
-Attending Exhibitions: Trade shows and Expos help to develop a strong business network.
-Industrial Survey: Another important source for a business can be industrial surveys. Since, the main point of a business is to fulfill the needs of a customer. Therefore, surveying and analyzing the underlying need of a customer can help in reaching a rational decision that addresses the customer’s problem and result in a profitable business.
-Listening to customer complaints: Complaints are a part of customers’ relationship that led into the development of new or improved products and services. Whenever customers report badly it means, that the customer satisfaction is not being achieved and there is some issues with the product. This can help in generating new business ideas for addressing problems of customers.
Describe the sources and qualities of a viable business idea that can be turned into a Back-Home Business.
3.4. Steps of generating business ideas
a) What would you do to take on the best business opportunity?
b) Would you advise a friend on how to assess business ideas and opportunities? If yes, how? If no, what would you do?
1. Start thinking/get your brain at work
The first thing to do when you get a business idea is determine whether it’s a good idea. Not every idea that seems good at first is practical. And some business ideas have no market. You will need to do some research to evaluate your business idea. Here is a checklist of questions to use as a guide:
-Is there a need for this product or service? Some of the most popular products and services meet a need that people currently have. The product or service may improve upon or complement an existing product or service, or your idea may be a completely approach to meeting a need.
-Is there a desire for this product or service? Admittedly, some of the most popular products are desire-based rather than need-based. That means that someone is purchasing the product because they want to. A few needs-based reasons for a purchase include to increase status or to follow a trend.
-Who is currently meeting the need for this product or service? Answering this question gives you a start on evaluating your competition. You need to know not only who your competitors are, but also how many are they? Don’t forget to consider indirect competition.
-Who will buy this product or service? Find out who your typical customer is likely to be. This may involve conducting surveys, testing the waters, finding a focus group, and more. The better your understanding your potential customer, the more likely you are to create a successful business.
-How big is that market? You may have a great business idea. It may even be brilliant. But, if the market for your idea is very small, your business might not be viable–that is unless people are willing to pay a premium for your product or service. This brings us to the next question.
-How much are people willing to pay for your product or service? Your intake from your product or service needs to cover your costs and should include a healthy profit. Remember, that even a small niche market can be profitable if potential customers are willing to pay you enough money.
How hard will it be to implement the idea? Let’s face it, some ideas are easier to implement than others. When answering this question, take into consideration the amount of time it will take you to launch your business as well as whether or not you will need to hire someone to help.
-After doing your research, you should be able to tell whether you want to continue and develop your business idea.
2. Buy a notebook
Now that you know how to stimulate your brain and get started with the creative thinking process, you need to keep count on your ideas and make sure that you can document them to study and examine them further. Every business you can think of started with a small idea somewhere, from a small observation, a frustrating situation, or while taking a shower. You never know when the inspiration comes, so always keep a notebook close to you to write these ideas down whenever they come.
3. Follow your passion
Once you start your business, you will spend most of your day for several years doing that business. So, make sure you choose a business that you feel passionate and excited about. If you don’t like the business, you are, chances are, you might not succeed in that business, probably not because you don’t have what it takes, but mostly because you might lose interest too easily in the face of the challenges that will come your way.
4. Keep your eyes open
New business opportunities get born from new situations every day. Keep an eye on what is happening around you, make it a habit to read the newspaper and identify new opportunities. You may read that people are complaining from poor health services in your area, or the lack of schools in your neighborhood. Talk to your neighbors and the people you know, what is frustrating them? What would they want to change in your neighborhood? Is your neighbor complaining that he/she needs to drive long distances to get to the nearest dry cleaner? Or is your other neighbor complaining about the lack of groceries in close proximities to where you live? Are you coworkers frustrated that there are no restaurants close to your work building?
5. Capitalize on your strengths
Most people are good at something. Look at your experiences and career, what is it that you can do well? Have you been working in project management for 15 years and know the ins and outs of the business, this is often the best place to start. Instead of focusing on the things you cannot do well, focus on the things you are good at. What can you do better than others? How are the others doing it? And how can you do it differently?
6. Explore new things
As mentioned earlier, change is one of the biggest stimulators to the brain. Even if you don’t want to open your own coffee shop, next time you are in one, look at how things are done and think of new ways to improve it. Often this thinking might lead you to new ways to improve on your business ideas in your chosen field.
7. Check your bank account
Starting and running your business requires money. Depending on your situation, you need to think of businesses that suit your budget. Everyone’s finances are limited, so make sure whatever business idea you come up with is doable. If you have a small amount of money, then look into business ideas that are not cash hungry, maybe start small and then grow with the business.
8. Know what you want in life
Aside from your business goals, think about the reasons you want to start the business in the first place. What is it that you are looking for? What are your goals in life? Are you starting a business to be able to spend more time with your family? To make more money? To be respected among your peers?
Whatever your goals are, make sure that your business idea complements these goals and helps you achieve them. If your goal is to find more time to spend with your family and do other things, then starting a business that requires you to work 16 hours a day or travel constantly might not be the best idea.
9. Choose a business that suits your personality
Are you a morning person or a night creature? Each person has his/her own peak hours of the day. You will find very few successful bakers or newspaper owners that don’t like to wake up in the morning. If you are not a morning person, avoid businesses that will need you to work in the early hours of the morning. If you are a night person, then maybe running a night club or a restaurant that stays open till late hours is more suitable for you. Conversely, if you sleep early, running a business that requires you to stay late might not be suitable for you.
Are you an indoor or outdoor person? Do you like working in an office for long hours or can’t stand the office and feel that you need on the move all the time? If you like the office quiet environment, then pick a business that can be done from an office. If you like to be on the move, pick a business that requires you to go to different places and meet new people.
Are you brainy or handy person? People do things differently, some people like to do things that involve thinking and working their brains, other people like to do things that involve craftsmanship and handy work.
Are you shy or outgoing person? If you are a shy person, then becoming a public speaker might not be the best idea for you. If you are an outgoing person and like to meet new people all the time, having an internet-based business might deprive you from that joy.
I think you get the idea, think of your personal traits and attributes, and pick a business idea that suits your personality.
10. Read about other people that started their own business
A large part of becoming successful involves looking at other successful people and learning how they achieved their success. Reading autobiographies about prominent and successful business figures and learning how they started their journey will give you great insight on how they did things and what exactly they did to become successful.
Most successful entrepreneurs started from scratch. Many of them failed in several businesses and had to listen to people that told them they will never be successful. But they stood up and tried again
and again until they succeeded. It is not whether you fail that makes you the man you are, it is how you stand up after the fall.
Study their characters, what do successful entrepreneurs have in common? How did they achieve their vision? What challenges did they have to overcome? Look for similarities between their stories and your situation right now. You will find that it is a great source of inspiration and motivation. If others just like you, did it, then you can do it too.
3.5 Factors to consider when generating and evaluating viable business ideas and opportunities
Discuss factors to consider when generating and evaluating viable business ideas and opportunities both in your community and elsewhere.
It is very important to examine and evaluate your business opportunity and determine your potential for success before you spend time and money developing a business plan.
Entrepreneurs need to determine whether the business opportunity they have identified is viable or not. When evaluating the viability of the business opportunity, the following factors need to be taken into consideration:
1. Market Business evaluation process goes through analyzing the market. If there isn’t a big enough market for your product or service, you should rethink whether this business opportunity makes sense.
· Who will be your target consumer?
· Is there a need for your business idea?
· Can you fill a market need?
For instance, you might think of a great business idea to produce a carbonated beverage flavored with roots, berries, and other natural flavors.
However, in your evaluation you might find that this type of product is already saturated in the market. The idea is good and a market exists, but if the market is flooded with competitors, it would not likely be profitable.
2. Business plan
The bottom line of any business is to make money. Without positive cash flow, you won’t succeed. Business owners with the best of intentions often fail because the financial potential isn’t big enough.
· Will there be sufficient financial reward?
· Do you see a potentially growing market for the product?
· Do you have others who believe in your business ideas?
· Are there other businesses that are similar (which is a validation that this potential business opportunity could be worth pursuing)?
You as an entrepreneur have a lot of thinking to do. Come up with great business ideas. Be creative and get enthusiastic about your ideas. However, always take the time to perform sound business opportunity evaluation.
3. Technology and other resource requirements
The business should be evaluated in terms of whether there is an appropriate technology that can be used in production. Factors to be looked into include.
-Appropriateness of the technology. The cost of the technology. The possibility of the business suffering in case the technology becomes outdated/obsolete. Availability of raw materials and other resources.
-The raw materials and resources required should be within the reach and affordable to the
entrepreneur.
- Infrastructure: Easy access to infrastructure such as roads, water, electricity, telephone, and postal services among others enables business enterprises easily make orders for goods and deliver them, hence reducing operating expenses. With low operating expenses, profits can be maximized.
-Government policy: An entrepreneur should consider the requirements of the government before starting a business e.g., the government may require certain businesses to be in certain areas only.
-Amount of capital required: The capital required to run and maintain the business should be considered i.e., the source of capital.
-Security: Availability of security should be considered.
4. Impact of the business operations on the environment.
Some businesses operations on the environments lead to environmental degradation and should be in appropriate environment. Are the political, economic, geographical, legal, and regulatory contexts favorable? Will the business do any damage to the physical environment? The above questions are typical of the type of issues that need to be addressed. Responses to these questions will determine the attractiveness of any business opportunity.
5. Competition and competitive advantage:
Competition is regarded as a threat to business of similar kinds operating in a similar location. Although competition is a threat, it is healthy in the sense that it goes along the way in controlling the price of goods offered. It is crucial for entrepreneurs to consider opportunities where competition is not high as this will enable them to get reasonable market.
6. Length of the window of opportunity:For example, one may inform you of an upcoming workshop for educators in your area, you realize that there is an opportunity for you to supply water, food and airtime among others, but for you to determine whether you should invest in this, you need to know how many people are coming, the length of the workshop, such that you know how much stock is needed, you also base on that to determine whether you will get back your money or not.

Analyze the photo below and answer the questions that follow.
Questions
1)What kind of activity is represented in the photo?
2)What are the effects of such business ideas to the community?
3)As an entrepreneur, suggest any two business ideas you may generate in response to the effects of the activity above.
4)Picking one idea, give the factors you will base on while choosing that idea.
5)What advice would you give to potential entrepreneurs while generating business ideas in relation to the photo above?
Skills Lab 3:
Choose 2 business ideas and conduct a viability test to find out which one is better in terms of; 1. Potential for growth, 2. Infrastructure, 3. Market for the goods/services (real demand), 4. Profitability, 5. competitive advantage, 6. Financial viability. Make posters indicating how each of the above factors favors or limits their business ideas with clear examples.
Recommend the most viable business ideas the Business club should start/continue running basing on the results of the viability tests and suggest action steps for the implementation.
End of unit 3. Assessment:
Read the following scenario,
Mr. and Mrs. Kaberu visited their friend Kambanda who lives in Kigali. They were surprised to see how Kambanda’s business of Coca-Cola wholesaling was booming. They didn’t even ask him how and why he chose to do that business. When they went back home in Nyagatare, they sold all their cows and opened up a wholesale depot of Coca-Cola products, just like their friend’s. Months went by and they had to pay rent, pay the attendant, pay utility bills, but there were no customers. Even the crates and bottles got covered in dust and cobwebs because they were kept for long. The landlord chased them out of the house because they couldn’t pay rent any more. Out of frustration, Mr. Kaberu had to sell all his stock at half price because he had nowhere else to keep them. On hearing this, his wife Mrs. Kaberu cried the whole day and night to the extent that she collapsed and was taken to the hospital at the mercy of the neighbours because her and her husband couldn’t afford the medical bills.
Questions
1a) Explain whether the business idea was good or bad.
b) Write a letter to Mr. and Mrs. Kaberu advising them on the importance of assessing a business idea or opportunity in case they have another one.2) There are many business opportunities that we can get from our communities, why should we always assess a business opportunity before investing our resources and time? To answer this, discuss in your groups and raise at least 5 business opportunities that you can think of. Assess each one of them and choose the best two viable ones which you will present to the class.
UNIT 4: SETTING ENTREPRENUERIAL GOALS

Key Unit competence: To be able to set achievable entrepreneurial goals Introductory activity
Introductory activity
Imagine that you are dreaming of standing at the top of Mount Karisimbi, Rwanda’s highest
mountain. Do you think that this dream could become a reality one day? How should you go about
achieving this dream?
4.1. Meaning of an entrepreneurial goal
1. What is a goal?
2. Think of an example of a goal.
Goals are defined as the lifelong aims, which an individual or entity endeavors to achieve/pursue.
A goal, in business, describes what a company expects or hopes to accomplish over a specific period.
People commonly use the term “entrepreneurial goal” with the same meaning. On a personal level, agoal is an idea of a desirable or future result that people envision, plan, and commit to achieving.
Reaching a short-term goal can be like harvest, it is a good step on the way. To be able to achieve our goals we need people and resources around us. That is why our personal development depends on our goals. For us to achieve our goals, we imagine ourselves as a fully-grown tree with fruits, thorns, roots, stem, and many branches where.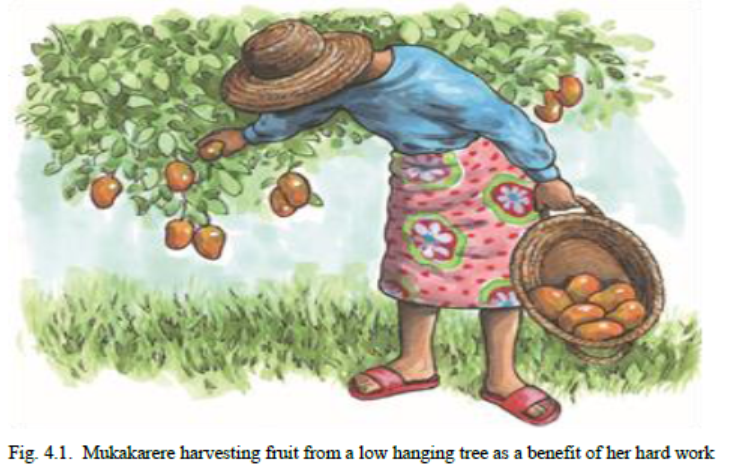
▪Roots mean values and skills
▪The stem means areas in our lives that give us strength e.g., churches, families, friends etc.
▪Branches mean our main interests and goals (what we always want to do or accomplish)
▪Leaves mean resources that will be needed to reach our goals i.e., people, information, etc.
▪Thorns mean obstacles or challenges we always meet toward achievement of our set targets
▪Fruits mean the benefits an individual achieves in relation to the set goal e.g., earning a salary after becoming a doctor.
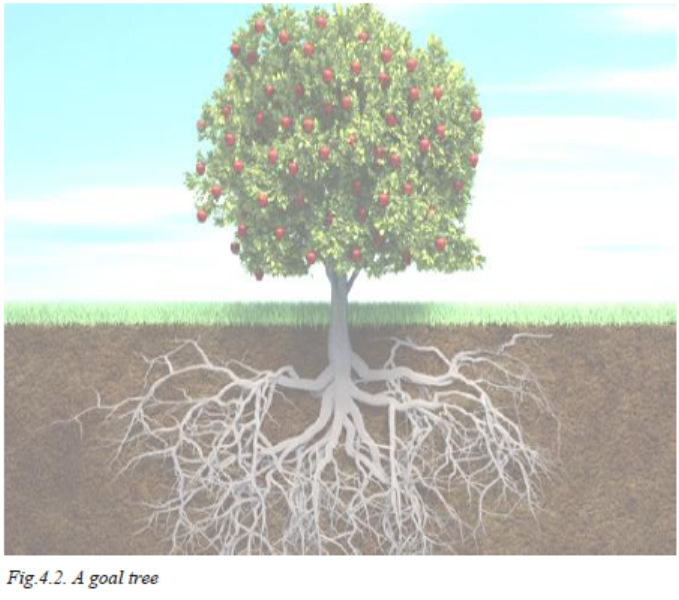
1. Study the picture below and answer the questions that follow.
Explain the following parts of a tree in relation to your personal development goals. What do the following represent?
1)Roots……………………………………………………………………………………………...…..
2) The stem (tree trunk) ……………………………………………………………………………..
3) Branches…………………………………………………………………………………….….……
4)Leaves…………………………………………………………………………………………...……
5) Fruits…………………………………………………….………………………………………...…
6)Thorns ………………………………………………………………………………………
….……
4.2. Characteristics of a goal

Using your knowledge acquired in O’level, explain the meaning of a SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic and Timeframe) goal.
Sometimes a goal seems like it is just a dream. You may wish to do something one day that never seems to happen but it takes courage, patience, and hard work to get where we desire to be. SMART is an acronym that stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable or Attainable, Realistic, and Timely. Therefore, a SMART goal incorporates all of these criteria to help focus your efforts and increase the chances of achieving your goal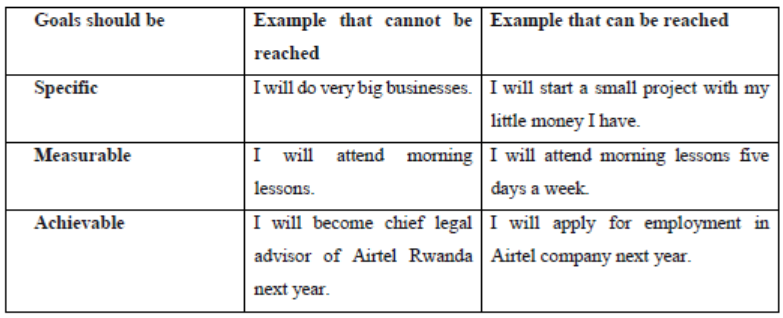

SMART is a useful tool for setting goals that you can reach. When we set a SMART goal, we can direct our actions into achieving the goal.
Therefore, a good goal should be characterized by Specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, time bound aspects.
UMULISA, a head teacher at UBUMWE secondary school is preparing to address and welcome new students joining associate nursing program at her school. The theme was “how to set a SMART academic goal”
Question
In not more than 100 words, explain what would be entailed in her speech as the meaning of a SMART goal.
4.3. Strategies of setting entrepreneurial goals
As a student of entrepreneurship:
a. Set at least one entrepreneurial goal?
b. Identify unexpected life events that might come your way and prevent you from accomplishing your goal?
c. What can you do to overcome/avoid such events and minimize their impact?
The first step to success is knowing where you want to go. The second step is having a plan to get there. Your goals are your roadmap, follow them and you will be on your way to success. Some strategies of setting entrepreneurial goals are discussed below:
1. Identify your goal
First, within the cloud area, you should write down the goal that you would like to achieve. It is better to use keywords only and be as specific as possible.
2.Identify current reality
Write down a list of keywords that define your current reality by basically outlining where you are right now in your life. here, you list your current life circumstances. Include everything that is good, bad and ugly.
3. Identify desired reality
Write down a list of keywords that define your desired reality by essentially defining the type of life that you would like to live on the date you specified. Be as brief as possible at this stage and avoid going into too much detail.
4.Identify obstacles
Within the gap between current and desired identified realities, write down all the obstacles that are standing between your current reality and your desired reality. Again, write down only keywords without going into too much detail.
5. Identify key resources
Outline at least five key resources at your disposal that you could use to help you overcome the obstacles standing between you and your desired reality.
6. Bridge the gap
Now that you are clear about where you are, where you want to be, the obstacles standing in your way, and the resources you have at your disposal, it is time to build a bridge that will take you towards your desired reality.Note: Setting goals is more than deciding what you want to do. It involves figuring out what you need to do, to get where you want to go, and how long it will take you to get there.
The steps listed below are posed in question form while setting entrepreneurial goals.
In order to set smart goals, the following steps should be observed:
1. Where do l want to be in the next period of time e.g., 4 months, 6 months, one year etc.? Consider the example of a goal, I want to start a big business project after my secondary studies i.e., after two years. This shows exactly what the person wants to be in next two years.
2. What must I know to get there? for example to start my business, I will need to discover which type of business to get involved in, I have to know how many are doing it, how they do it, for whom they produce (market), prepare my Weaknesses, Strength, Opportunities available and Threats (SWOT analysis) and where to do the business from.
3.What steps must I take in order to know and be able to do these things?
For example, I have to prepare a business plan i.e., production, marketing, organisation, financial, action plans etc. Obtain a trading license and a business registration among others.
4. What abilities and experience do I already have that are going to help me take these steps?
Refer to the qualities of an entrepreneur. Do you possess any?
5. What obstacles might be on my way and how can l deal with them?
You have to list the challenges that you may meet on the away to achieving your goal. This is because you don’t expect everything to go on smoothly. A lot of challenges can be met. Refer to the above goal in the question, suggest possible challenges that can be met.
Many of your responses may be:
▪ Inadequate funding (capital)
▪ Small market size, may be because of strong competition
▪ Strategic business location.
6. What should I do first, second and so on?
In setting goals, one has to specify short term goals first then the long-term goals, a person can suggest short term goals stating when it should be achieved, and resources needed to achieve them.
a. Write a SMART goal for a business project you want to start after school.
b. Examine the major steps that you would put into consideration in order to achieve the above goal.
4.4. Steps of creating an action plan for entrepreneurial goals
Based on entrepreneurial goal set previously, make a plan in order to achieve that goal in the period set.Use template below
An action plan is a useful tool that can help you to reach your goal. A plan helps you determine: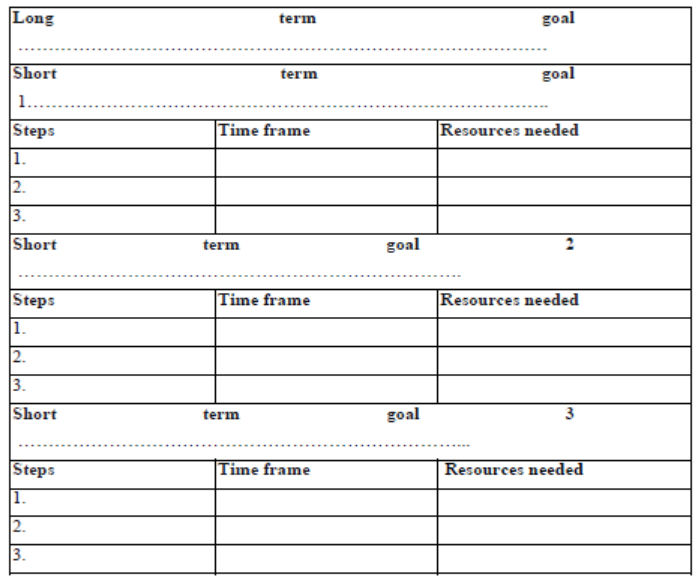
- What needs to be done?
- When the tasks must be done?
- Who will do the tasks?
Step 1:
Create a list of the tasks that need to be done. Start each task with a verb (doing word) because a task is something that you can do.
Step 2:
Break down the tasks into short-term and long-term actions. To identify short-term actions, ask yourself ‘What can I do right now that will bring me closer to my goal?’
Step 3:
Write a to-do list of actions and include guidelines (describe how to do each task).Step 4: Create a timeline for your actions and include milestones.
A timeline is a tool that shows the progress of a task, time a project will take and how each task fits into the overall project. The most common type of timeline is the bar chart or Gannt chart. The chart shows the activities that need to be done. The chart also shows the start and finish date of each activity. It shows how the activities relate to each other. For example, if you build a house, you cannot fit the roof before you build the walls.
How to create a timeline
Step 1 Draw a graph where the X-axis (horizontal line) represents the time period for your project. You can use days, weeks, or months as the time units. The Y-axis (vertical line) represents activities or tasks. The activities can be practical such as designing, constructing, or installing. They can also include periods where there are no tasks, such as holidays or waiting for approval for your plans. Waiting time also influences how long it will take you to complete the project.
Step 2 Add tasks to your graph. If the first task (A) will take two weeks, then fill in a bar across two weeks on the X-axis. The next task (B) will take one week and can only start when task A is complete.
Step 3 Identify start and end points for your project. Write the date when you can start the project. When you have added all the tasks, you can also see the date when your project will be complete.
Resources
To reach your goals you also need resources. Those resources can be money, materials, people, etc. The resources must also be included in an action plan.
Importance of setting goals
▪ It helps in allocating scarce resources▪ Setting goals is important in decision making
▪It’s a tool for planning
▪It helps a person to stay focused on achieving the set targets
▪It’s motivating to the entrepreneur
▪It helps to allocate tasks to employees and setting employment targets
▪It helps to avoid wastage of resources
Achieving SMART goals
An action plan is a tool that you can use to break up a large goal into smaller actions. The action plan uses the four Ws (What, When, Who and whenever) to reach the goal.
A timeline is a tool that shows the chronological progress of a task. It has a start date, end date, all the activities that must be completed and how activities relate to one another. To reach a goal, you need to allocate the correct resources.
Your class has been appointed as festival coordinators for the annual Umuganura celebrations. The event occurs on the first day of August. This year, you have been asked to plan a festival with decorated trucks and musical processions.
You are given the following list of responsibilities:
▪ Create a route for the procession through your community.
▪ Ask the cell council for permission if you need to close roads.
▪ Arrange a theme for your truck to celebrate the harvest and the importance of agriculture for Rwanda.
▪ Arrange bands and musicians and other forms of entertainment.
▪ Allocate spaces for stalls that offer food and drinks.
▪ Advertise the event to attract as many visitors as possible.
To plan the festival, you need to:
▪ Draw up an action plan where you identify the tasks and resources needed.
▪Develop a timeline that shows start and end points.
Answer the following questions:
1. a) What are the obstacles that you need to overcome for better planning of the festival?
b) Which skills do you need to run the festival?
c) Which opportunities does this festival give your community?
2. a) Write a smart goal for a business project you want to start after completing your studies in associate nurse program.
b) Describe the major steps that you would put into consideration in order to achieve the above goal
1. Draw a goal tree for one of your personal career goals.
2. Jeremy wants to improve his results in mathematics. He set the following goal: I want to increase my grade from 80% to 90%. Compare his goal to the SMART framework.
a) Which of the SMART elements did Jeremy incorporate in his goal?
b) Which SMART elements are missing?
End of unit 4 assessment
Read the case study and answer the questions that follow.
The future is bright for Haguminshuti’s chicken empire. Haguminshuti discovered farming opportunities in 2003, while working on a project in Kanombe. Here he developed poultry farming projects for people living with HIV. The work gave him an idea to start a business in agriculture. However, it would take him many years to make his dream a reality. After learning about poultry farming in the United States, Haguminshuti returned to Rwanda. His first application for a bank loan was rejected. He did not have collateral security (property or other wealth) for the loan. Haguminshuti also faced other difficulties such as an irregular supply of chicken. He also had problems with the quality of the chicken. However, he did not give up on his dream. He continued applying for funds and eventually the Rwanda Development Bank agreed to fund the project. There were many conditions for the loan. He had to invest all his savings to get the project running. Today, he runs a successful poultry farm in Bugesera district in the Eastern Province. The farm contains four chicken houses that each house accommodates 25 000 chicken. His customers include supermarkets such as Nakumatt and Simba. Haguminshuti is an ambitious businessman and he has further plans (goals) for his chicken empire. He is currently looking for investors who can assist him with his plans to increase production. He estimates that he can increase meat production to 70 000 kilograms in nine months. Then he will spend the next six months increasing production at the chicken hatchery from 60 000 to 300,000 chicks per week.
i. What was Haguminshuti’s goal in 2003?
ii. Describe some of the obstacles that he had to overcome to reach his goal.
iii. The poultry farming is still growing. Use SMART goal concept to list his growth goals.
iv. Create a timeline to assist Haguminshuti with planning.UNIT 5: MARKET RESEARCH

KEY UNIT COMPETENCE: To be able to conduct market research for business start-up and growth.
Kagoyire is a senior 4 student of Associate nursing in Rwanda. she is equipped with some competencies of starting a business, having learnt entrepreneurship in O-level. she decided to start a small orange juice processing factory and her main market was the restaurants located in Agaciro village. Two years later, she found that the level of sales was extremely declining and started wondering why? Thereafter, she decided to gather all relevant information regarding the likely causes of such a decline.
Questions
Referring to the above text, answer the following questions:
1. What did Kagoyire not do before starting her business and how would she have done it?
2. Why do you think it is important to carry out market research?5.1 Meaning of Market, Marketing and Market research

1. After analyzing the above pictures what comes to your mind?
2. What do you understand by the key terms which are reflected above?
A market: This is defined as an arrangement through which the buyers/customers/clients and sellers/business owner/entrepreneur come into contact to negotiate an exchange of goods or services for money.
Marketing: This is the action of promoting and selling products including market research and advertising.
Market Research: This is the process of collecting and analyzing information or data related to the demand of goods and services in a particular market. Market research gathers information about products, customers, distributors/ suppliers and competitors.
5.2. Elements of market research/Surveys
Enumerate any two elements one would consider while conducting market research.
a) Customer survey
This is the process of finding out customer’s attitudes (their needs, preferences, purchasing power) towards your product in the market or what you plan to put in the market. For the survey to be successful, one must know the types of customers.
Types of Customers
•Loyal customers: These are customers who buy from the business regularly. They are few but they bring more money to the business
•Impulsive customers: These buy whatever items that are attracting to them. No specific item in their mind, they just buy by impulse.
•Potential customers: These are people who are able to buy but not yet ready to buy business products. They can be turned into customers in the near future.
•Real / Actual customers: These are customers who have already done some transactions with the business.
•Discount customers: These are customers who buy low-cost products that have been discounted, they buy only when businesses discount their prices.
•Cash, cheque or credit customers: These are customers who buy depending on modes of payment.
•Wandering customers: These are customers who have no specific need in mind but go to the shop to get a sense of experience.
This refers to forming questions about a product, its quality and forming some answers. Before launching a new product, marketing professionals first test it with a selected audience. A new product survey provides a way for marketers to understand when to start, modify existing ideas, how and who to market. Product analysis can also be carried out by comparing similar products with each other using the same criteria.
The purpose of Product Analysis
•To help customers determine whether the product is worth buying.
•To improve the version of a product.
•To provide a prototype (something developed/ improved before a final product is manufactured)
•To determine product price.
b. Supply survey
A supplier is any person or a company that provides goods or services to another usually in exchange for payment. or
Supply survey refers to the process of analyzing, finding out and establishing the best potential suppliers of a given product.
Types of suppliers
▪Manufacturers: These are businesses that turn raw materials into finished goods. They supply their outputs to the wholesalers.
- Wholesalers:
These businesses buy large quantities and resell to other traders especially to large scale retailers.
▪Agents: These are suppliers who stock and supply products on behalf of other businesspeople especially manufacturers or wholesalers.
▪Retailers: These are small scale suppliers who sell goods in smaller quantities to final consumers.
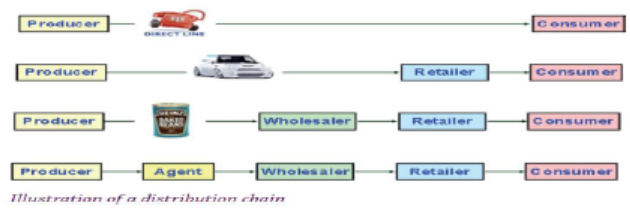
c. Competitor survey/ competitor analysis
A competitor is any business firm that provides similar goods and services like ours and whom we are sharing the same customers.
Or refers to the process of assessing the strengths and weaknesses of both current and potential competitors.
You cannot analyze competitors unless you know them; here are some types of competitors:
▪Potential competitors are those companies that are not yet in the same marketplace as the one who intend to be in or who are already in.
▪Current competitors are those who are already in existence and already producing similar goods and services.
▪Direct competitor: This is the one who produces or sell identical/ similar products as your own business.
▪Indirect competitor: This is a business that produces products and services that are close substitutes. These competitors target the same customer with a product that provides an alternative level of satisfaction.
Importance of competitor analysis
▪It enables an entrepreneur identify market gaps
▪It helps in knowing the competitors’ position
▪It helps to know competitors’ strengths and weaknesses
▪It helps to identify market opportunities
▪It is a good way to develop new technologies
▪It is a key element in business plan
▪It helps in pricing goods and services
▪It helps to predict competitor’s behaviors
▪It is a good tool to adaptation of good strategies from competitors.
1. It is said that a customer is a king, explain this statement.
2. Explain the importance of competitors in business
5.3. Steps to follow when carrying out market survey
Discuss steps to follow when carrying out market research
1.Finding the topic of the research study. This is the title of all the research work that has to be done in the field. E.g., an evaluation of the influence of income levels of consumers to the growth of a business.
2. Defining the research problem. This enables the entrepreneur to find out how to deal with prevailing situation which consequently enables him/her to achieve his/her target.
3. Setting objectives. Specifically show what the research wants to achieve at the end of the study. They should always be brief and SMART (systematic/specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time bound).
4. Selection of the basic data collection methods. (Observation, interview, questionnaire, field experiments, focus group etc.)
5. Determine the scope. The researcher determines the limitations of his/her study. That is to say, areas to be covered and what to be included or excluded. (sample/ population).
6. Designing a clear schedule for conducting the research or coming up with a clear plan of the whole research process. Consider the example below.
An example of a research schedule of activities on a topic of study ―Customer perception towards a new brand of product from a given company
7. Collecting data: The researcher collects data on a number of things such as price, product, promotion, target market etc. This is normally done in the real field study.
8. Analyzing data: This is done during and after the real field study. It enables the researcher to know how the market will be especially in terms of demand.
9. Presenting findings: After data analysis, the researcher presents his findings to the relevant authorities for action. The researcher should ensure that he presents empirical data and not estimates or hypothetical figures to those who are supposed to take the action.
Imagine a situation when you have finished your secondary school studies and one of your family members learns that you studied entrepreneurship and so accepts to grant you the capital to start your own business. But before he/she gives you that money he/she asks you to first carry out market research for the feasible business.
He/she then asks you to first carry out the following market research tasks after which you prepare report and present it to him for you to obtain the promised capital.
1. What products (goods or services) that people in your community would like to have but are currently not being provided?
2. Choose one product that you would be interested in dealing with.
3. Who from your community can give you information about the product you identified?
4. Decide the population sample (the number of people identified in no. 3 above) to ask
5. Formulate questions that you will use to collect the data that you require about the product that you chose in no. 2 above)
6. Plan of how you will collect the data and how you will analyze it.
5.4. Components of marketing / marketing mix elements (4Ps)
Activity 4.
Suppose you are to start a business; think about the elements you will take into consideration for making your products/services more marketable.Marketing mix refers to the term used to describe all activities which go into marketing a product. It is composed of: Product, Place, price, Promotion
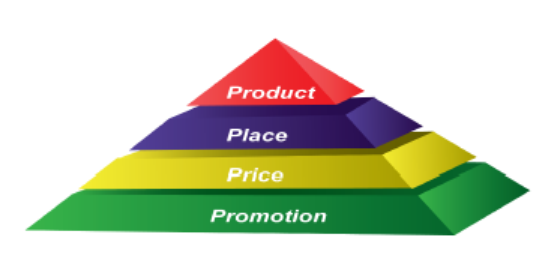
5.4.1. Product:
A product is something either good or service that is offered to the market to be sold in order to get profit. It can be goods (tables, rice, potatoes, beans, cars, books, pens, clothes, etc) or services (transportation services, music, medical care, communication, banking, etc ...)
5.4.2. Price:
This refers to the amount of money paid by customer for a product. The price has greater impact on the consumer demand for a product. If price is too low, then consumers may lose confidence in the quality of the product. If the price is too high the consumers will not be able to afford the product.
5.4.3. Place:
The place /location should be attractive and nearest to the customer (that place should be known). It involves the channels of distribution that are used.
The distribution process/ Supply Chain includes Manufacturers, wholesalers, Service providers, Retailers, marketing specialists and customers.
5.4.4. Promotion:
This is a set of ways of attracting customers to buy products either for the first time or to buy more of them. Forms of promotion include Advertising, aftersales service, sales promotion, personal selling etc.
Design a marketing mix for your business club products.
list down examples of items that you always use at home. Where do you get these items? How do you get them? Can you tell the class about the most interesting products that you always enjoy buying? How much do you pay for them? How do you know where to find them?
Skills Lab 5
Given the questions below, carry out a survey in your community and thereafter make a report according to the findings from the research.
Interview questions:
1) What do you like most about the products that you normally buy and why? If you have a business club at the school, ask them what they find interesting about the club product
2) What changes would you propose to the above product (ones they normally buy?)
3) How do other products similar to the above product differ from others?
4) As aspiring entrepreneurs, advise us on how we can best extend our products to bigger markets outside our community?
5)Name other products we could make from locally available resources that can be most competitive.
1. Choose the best answer for the following statements
i. Having no research questions or poorly formulated research questions will lead you to poor research findings because:
a) You will only consider epistemological queries
b) Marks are allocated for having a research question and without them my project will be penalized.
c) You will not know what data analysis method used.
d) Your research is likely to be unfocused and you are likely to be unsure of what data to collect.
ii) What is data collection?
a) Collecting the research question and objectives together
b) Gathering the information (data) which will help you address your research question
c) Reviewing the literature
d) Outlining how you will gather the information for your research question.
2) Explain how research can help the marketing department of a business in achieving its target.UNIT 6:BUSINESS GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT

Key Unit Competency: To be able to analyze the factors that lead to business growth and development.
Hirwa lives in one of the Southern province districts where he started a small boutique in his village with capital as little as 100,000Frws but with a big number of customers. In his absence he is assisted by his wife and sometimes his children during school holidays. Hirwa works so hard to provide good customer care to his customers. After four years, he has many customers and his capital has doubled.
Hirwa's capital continues to grow and his profit has increased tremendously. He has opened two more shops selling various items in different Districts within the country employing five skilled workers and has got enough market for his products. Hirwa is also planning to start a wholesale shop in Kigali but he is uncertain if he will succeed.
Questions
Referring to the above case study, answer the following questions:
a) Differentiate between a growing business from a declining business
b) Describe different strategies Hirwa used to grow his business
c) What factors have favored the growth of his business?
d) As a student of entrepreneurship, what advice would you give to Hirwa to continue expanding his business?
6.1. Meaning of business growth and business development
Questions
1. Analyze the picture below and comment in relation to different stages of plant growth.
a) Assume you plan to start a business after school, do you think it is possible to grow as it is illustrated in this picture? Justify your answer.
b) Referring to the picture below, is this plant growing or developing?
Business growth refers to the process by which business enterprises increase their production, profitability and size. It is the expansion of the business enterprise. Business growth can also be defined as a stage where the business reaches the point of expansion and seeks additional options to generate more profit.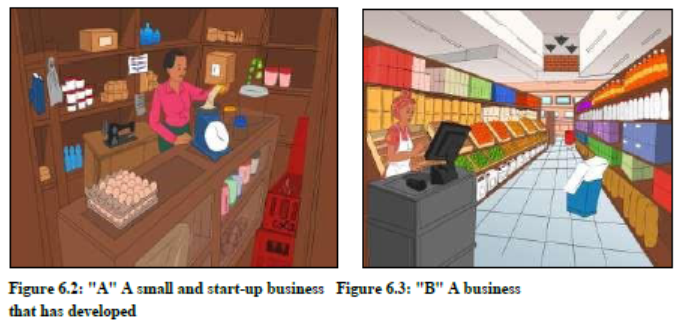
Business development is an ever-evolving concept that can be approached from different perspectives. As its basic level, business development is defined as a growing business that is more competitive, expanding products or services, and /or focusing on specific markets.
It can also be defined as a qualitative and quantitative increase in the level of output, profits, sales, and other variables of any business.
There are three main components that business experts generally agree form the base of business development: markets, customers, and relationships. To expand a business beyond its current state, it is important to focus on one or more of these areas. The type of business and the direction of growth determines where the focus is placed.
There is a relationship between business growth and business development since all involve growth in terms of revenues, business expansion, increasing market and profitability.A roadmap to Business Development
Figure 6.3: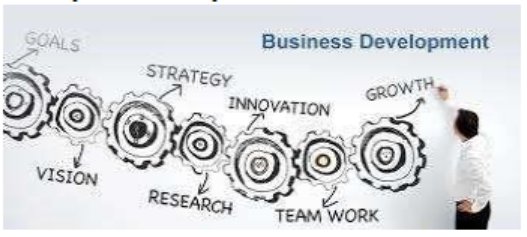
This figure above shows the process from the business start-up to business development i.e starting business with goals (know what you want ), Vision (know where you are going), Strategy (techniques to be used to get there), Research (know who is/are your customers, what they want, knowing your suppliers, competitors,…), Innovation (improving things/doing things differently from others) and team work (working together with others either employees, suppliers, contractors, community, other businesses and government) all of this process leads to business development (multi-sectoral), business development impacts not only on growth but also on the increase in new branches, many employees, market expansion, new technology, more business infrastructures etc. Business development is achieved in long term compared to business growth which only impacts on the production level.
As a student of entrepreneurship and with vast knowledge obtained from O’level, advise a friend on the indicators of a growing business and a declining business.6.2. Indicators of business growth

Mukamana started a business of selling women shoes in town with little capital. After one month she would sell an average of five shoes per day. Five months later, the number of customers had increased to an extent that she could sell an average of twenty shoes per day. She used the business profits and a small loan from the bank to increase the stock and after a short time the shelves were full of shoes. One year later, Mukamana had thought of expanding her business by opening another shop in Kigali city.
Strategically, Mukamana used advertisement on different radios and televisions to inform people about her new branch in Kigali and prices of the shoes, as a result, there was an increase in customers and sales respectively. She is now a successful businesswoman who sells shoes in large quantities and has a license to export shoes to African countries. This, coupled with other factors mentioned above enabled her to accumulate a lot of profit.
Questions:
Referring to Mukamana’s business, what are the indicators of her business growth?
Suggest other indicators not mentioned above responsible for business growth.
There are many indicators of business growth. They include the following:
▪Increased capital: If capital of a business is increasing, then it is an indicator that the business is growing.
▪Increase in assets: Another indicator of business growth is the increase in assets like buildings, vehicles, bank deposits, etc. The total value of business assets can be revealed by the balance sheet of the business for a particular period of time.
▪Increase in business profit: When the business profits keep on increasing, then it is an indicator of business growth.
▪Opening more branches: This is also an indicator of business growth to serve more customers.
▪Increased market share: When the market share of the enterprise is growing, the enterprise is growing because it is serving more customers.
▪ Increased sales revenue: increase in the number of customers and stock reflects that the business is growing.
▪Increased number of employees: When the business grows, it normally increases the number of departments and employees. For example, a restaurant that started with four workers and expands into a hotel, it will need to recruit more employees than previously.
▪Use of advanced/improved technology: Most businesses start with simple technology but as the business expands, they use more advanced technology.
Figure 6.5: An entrepreneur in a company using a computer in recording
Increased stock of goods: When the enterprise grows, it produces and sells more products. For example, in a shop there are more and wider variety of goods and services.
Better salaries and wages paid to workers: When a business is growing, it is able to give better wages and salaries to its workers due to increased profits.

1) Case study: Peter the maize farmer
Peter is a farmer of maize in eastern province. He started growing maize on a small piece of land using traditional techniques like hand hoes and did not use fertilizers to increase production. He employed two men on his small farm. One day Peter got the chance of being selected by the Ministry of Agriculture in the two days training that had the following theme "Doing agriculture oriented to the market".
When Peter went back home, he tried to improve on the methods he used to grow maize production and decided to take a small loan from Umurenge Sacco with the purpose of buying another land to grow maize and acquiring enough capital to buy fertilizers that he mixed with manure.
Since that time, the production increased considerably. In the season that followed, he increased the number of workers from 2 to 50 workers. After one year, he thought of using irrigation system to cope with climate changes. He also used tractors in farming instead of manpower. Now he harvests
more maize and sells it to maize processing industries in Kigali and in other provinces across Rwanda.
Questions
a) From the above Case study, what are the indicators of his business growth?b) What strategies can you use to grow if you have a small business?
6.3. Business growth strategies
Basing on your knowledge of entrepreneurship subject, answer the following questions:
a) What do you understand by the term growth strategy?
b) Describe any 5 internal growth strategies which you think entrepreneurs in your community should use to grow their businesses.
c) Propose any external growth strategies used by entrepreneurs in your community.
d) Discuss the importance of using the above growth strategies in business?
For a business enterprise to survive and expand, it needs to have specific growth strategies. There are two separate types of business growth strategies which are internal and external. Therefore, integration of both internal and external growth strategies is crucial to the overall development of a business and continuous increase of revenues.
These growth strategies are implemented using various resources such as financial, human and material resources.
6.3.1. Internal business growth strategies
Internal business growth strategy refers to the expansion of a business enterprise using internal resources and capabilities. This means that all business growth is established without using external resources or external parties. It also refers to the growth within the organization by using its own internal resources to increase their size, scale of operations, resources (financial and non-financial) and market penetration.
The internal growth strategies which can be used by companies include the following:
▪Improving customer care: This involves offering good customer care to the customers as a way of attracting others and retain old ones.
▪Delivering quality products and services: This strategy involves providing quality products and services. This helps the company to grow.
▪Offering discounts to customers: A discount is a deduction on the price. As a growth strategy, discounts attract customers and increase sales revenue.
▪Carry out sales promotion: This growth strategy involves all activities done to inform and attract customers to buy more of the business products. For example, giving discounts, advertising on Radio, Television, Newspapers, etc.
▪Human resources development: A business may seek to grow by improving the quality and efficiency of its workers through trainings and workshops. Better quality workers increase the productivity and efficiency of a business leading to higher profits.
▪Creating new distribution channels and locations: This involves opening new branches and making products available in new outlets. This increases sales and generates extra profits for the business.
▪Bundling products: This involves selling a bundle of products as one kit. For example, Mobile phone and SIM Card, Toothpaste and Toothbrush bread and butter, etc. Even services can be bundled where two separate services are packaged into one product and sold together. For example, for computer software. Software is often sold in "suites" bundle that contains multiple applications. If you buy Microsoft office, you pay a single price and get Word, Excel, Power point, Publisher and Access, etc.
Another example for service bundle is where some colleges and universities may say that if you pay for a diploma or a degree course, you will receive free computer training. This means that the degree/diploma has been bundled with the computer training. Bundling helps the company to sell two products at the same time, attract more customers and earn more revenue.
▪Market penetration and development. This involves selling more of the company's products or services to the existing as well as to the new markets. This strategy is about reaching new customer segments by targeting new both internal and external markets.
6.3.2. External business growth strategies
External growth strategies refer to the expansion of a business enterprise by using external resources. These growth strategies focus on increasing output using resources and capabilities that are not internally developed by the company itself. The external business growth strategies include the following:
1. Merging with other firms or Mergers
Merging of firms refers to the combination of one or more corporations, or other business entities into a single business entity; the joining of two or more companies to achieve greater efficiencies of scale and productivity. In most cases, this is done by the companies producing and selling related goods or services as a way of reducing competition among themselves, increasing profits, etc. examples of companies that have merged include Soras and Saham insurance company, Airtel and Tigo companies.
Types of mergers
The following are the types of mergers:
a) Horizontal merging (integration): Horizontal merging occurs when two or more firms which are in the same industry of production join/merge into one e.g., two hair dressing salons join together to form one bigger hair dressing salon.
b) Vertical merging: This is merging of two or more firms which are at different stages of production in the same industry. In this merging, a business merges with another that is at the next or previous stage of production process e.g., coffee farm combining with a coffee factory.
c) Conglomerate merging: This is merging of two or more firms which produce unrelated products which do not compete with each other e.g., if a book shop merges with a restaurant. Another example if a shoe manufacturing firm merges with a restaurant. The idea behind this merger is to get a bigger market e.g., shoe clients going to the restaurant and vice versa.
d) Concentric/ congeneric Mergers: Concentric mergers take place between firms that serve the same customers in a particular industry, but they don‘t offers the same products and services. Their products may be complements, products which go together, but technically not the same products. For example, if a company that produces DVDs merges with a company that produces DVD players, this would be termed as concentric merger since DVD players and DVDs are complement products, which are usually purchased together. These are usually undertaken to facilitate consumers, since it would be easier to sell these products together. Also, this would help the company diversify, hence higher profits. Selling one of the products will also encourage the sale of the other, hence more revenues for the company if it manages to increase the sales of one of its products
2.Franchising
A franchise is an arrangement where one party gives another the right to use its trademark or trade name to produce and market a good or service e.g., telecommunication companies like Mtn, soft drinks industry like Coca-Cola etc. In Rwanda, Bwalirwa holds the coca cola franchise.
Companies can use franchising as a business growth strategy in two ways:
a) By buying a franchise from well-known and reputable companies. This helps it to sell more in the markets it would have found harder to penetrate.
b) By selling the franchise. By selling its name and logo, to be used by other companies, a business can spread further than it could have done alone.
The following are the advantages of franchising
▪It helps to reduce stiff competition.
▪It helps to increase sales and profits.
▪Banks can easily lend you money to buy a franchise that has a very good reputation.
▪The business is based on a proven idea and so chances of business success are higher.
▪It helps to attract customers who are already familiar with the name and logo.
▪The franchisee can get ideas from other entrepreneur who operate similar franchises.
▪The owner of the franchise normally provides support, trainings, and advice to the franchisee.
▪A franchise gives you exclusive rights to sell the product or service in your region.
▪It is easier for a franchisee to perform better than a start-up business whose name is not known and which has no reputation.
The following are the disadvantages of franchising:
▪The costs of a franchise may be high.
▪Profits are shared with the franchiser whose name, logo, and business model you are using.
▪The franchise includes strict guidelines and restrictions on how to run the business.
▪In case you want to leave the business, it may be difficult to sell the franchise to someone else because the buyer must be approved by the franchisor first.
▪If the franchisor runs out of the business or the reputation declines, it affects the entire business.
▪The process of buying a franchise involves a long legal process which is costly.
3. Joint-ventures
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and shared governance.
Companies typically pursue joint ventures for a number of reasons: to access a new market, particularly emerging markets; to gain scale efficiencies by combining assets and operations; to share risk for major investments or projects; or to access skills and capabilities. Companies that form joint ventures share the profits and losses while simultaneously pooling their resources to complete the specific objective.
1.With examples in your community/village, describe at least 2 people or entrepreneurs whose businesses have grown up. If you know or heard how they started, what strategies did they use to grow?
2.Referring to business activities of entrepreneurs in Rwanda, what do you think are the benefits from establishing clear growth strategies?
3.What do you think would happen to business enterprises, if their owners do not apply growth strategies?
4.Assume you have a small business with a small capital and there are more competitors where your business is located. Do you think it will be possible to compete successfully with your competitors? What will you do to continue operating and out compete your business rivals?
1) Given a form of business growth strategy as
▪Bundling
▪Promotion and discount
▪Developing new product
▪Franchising
▪New distribution channels,
2) Discuss the following questions and there after present your findings.
a) Where does the given growth strategy fall? (Internal or external growth strategy) explain your answer
b) Explain the activities that can be done to apply the above strategies in the business club activities or in the business you want to start back at home.
3) Basing on the school’s business club, identify areas that need growth, set realistic growth targets and discuss strategies of how the business club will grow and develop.
Fill in the following gaps:
1. Assume your business is attaining the following:
a) Increase in production, profitability, and size.
Is known as ………………………………………….
b) A prolonged period of little or no growth for companies.
Is known as ………………………………………...
2. Assume that you have a mini supermarket selling fresh milk, juices, bread and cakes in one center of Kigali city.
a) How would you know that your business is growing?
b) What are the factors which you think can favor the growth of your business?
c) How would you know that your business is declining?
d) What can you do to minimize such a decline?UNIT 7: TECHNOLOGY IN BUSINESSES

Key Unit Competence: To be aware of how new technologies can affect business activities.

Analyze the Photos below and answer the questions that follow.
Questions.
a) Looking at picture 1,2,3and 4, explain the advantages and disadvantages of using the above techniques in the production of goods and services.
b) Which production technique is suitable for your school business club? Give reasons to justify your answer?
7.1 Meaning of technology
1. a) You wish to start up a feasible business in your community. Which type of technology will you use in your business and why?
b) How would you define the term technology as used in business?
2. Distinguish intermediate technology from capital intensive and labor-intensive technologies.
Technology
refers to methods, systems, and devices which are the result of scientific knowledge being used for practical purposes. Technology is changing fast. Technology is human knowledge which involves tools, materials, and systems. Many businesses are using technology to stay competitive; they create new products and services using technology, and they also use technology to deliver those products and services to their customers on time and within budget. Technology in business allows organizations to improve both the performance and overall effectiveness of products, systems and services, which, in turn, enables businesses to expand quickly and efficiently. Another role of technology in business is to provide security to a business.
Examples of some tools, systems or devices used by technology in business.
· Desktop Computers and Laptops.
· Software and Productivity Tools.
· Networking of Computers and Printers.
Telephone and VoiceMail Systems.
In Rwanda there are different technologies used to improve the services such as
-Tap and Go: This is One of the biggest technologies that has changed the face of public transport. It’s a smart transport system that enables passengers to board public buses without using hard cash but rather smart cards.
- Zipline’s drone technology: this is a global race for commercial drone deliveries of small packages. In Rwanda it is used to transport blood to remote areas where access to roads is impassable.
- Irembo: The burden of walking long distances to seek some government services has consistently been removed. There are large numbers of people who do not have to necessarily travel to apply for a marriage certificate, land transfer, drivers’ related services, birth certificate, criminal record clearance certificate, and other services. These few examples show how technology in business comes to enable businesses to expand quickly and efficiently.
Types of technology.Intermediate technology is one that fits into the level of development of the host country. It is neither too simple nor advanced. For instance, the use of ox-ploughs, solar cookers etc.
Capital-intensive technology is the production method/ technique where more machines are used than labor. It is also called labor saving technology because we save more labor to use machines. Its common in industries, factories, mining etc.

Labor Intensive Technology is the production method /technique where more labor is used than machines. It is also called capital saving technology meaning we save capital and use more labor. It's commonly used in hotels, restaurants etc.

1. Justify why the government of Rwanda is encouraging businesses to use capital intensive technology.
2. Refer to your school and describe how technology has helped in the efficiency of the school for both students and the school itself.
7.2. Importance of technology in business.
Debate “The use of technology in business has done more good than harm”
Technology is an essential tool in the day today business operations; no matter the size of the business, technology has both tangible and intangible benefits.
These include the following:
1. The use of ICT through internet helps entrepreneurs to carry out market research. This helps it to grow and acquire more opportunities across the globe, hence widening the market. by use of E-commerce sites like eBay, Amazon, Jumia, etc.
2. Technology helps to increase productivity of the labor through collaborating with each other hence speeding up the work.
3. It helps to keep track of records with the use of the accounting software.
4. Technology can be used for security purposes thus reducing threats of losing financial data and vandalism to unknown persons. For example, by using passwords on computers.
5. Technology improves the efficiency of businesses. The use of mobile phones, printers and E-commence which eases the work in business.
6. ICT enables easy access to funds through the use of ATM cards, such as debit cards, credit cards, and electronic money transfer etc.
7. It also enables better decision making as entrepreneurs can get information at the right time.
8. Technology helps businesses grow with the use of artificial intelligence. This gives the business a competitive edge over other businesses.
9. Advanced technology helps to produce better quality products that may fetch a lot of money for the enterprise thus increasing customer satisfaction.
10. Technology helps to perform complicated tasks with ease and faster. For example, use of computerized accounting software like quick books, sage and pastel helps in accounting with ease.
11. ICT helps firms to monitor the buying habits of their customers and be able to stock the right products in the right quantities at the right time. Speed Governors help to keep track drivers from over speeding hence reducing the number of accidents.
12. Computers can perform a lot of work in the shortest time possible which would require a lot of time if done manually. Examples include preparation of control accounts, financial statements and preparing payrolls etc.
13. Technology also helps to cut down costs. For example, the costs incurred while transporting and delivery of goods can all be done using computers and the internet.
Carry out research and identify the various technologies that are being used in businesses be it in your school or other business enterprises. Suggest their importance in terms of communication, management, accounting and transport.
7.3 Technological tools used in business
Observe the pictures below and explain the importance or uses of each machine, equipment or technology as used in business.

Figure 7.4: Most common technologies used in business.
From the above pictures, you realize that businesses use various technological tools, depending on the type of business, and department. The table below shows the common tools used in business departments.
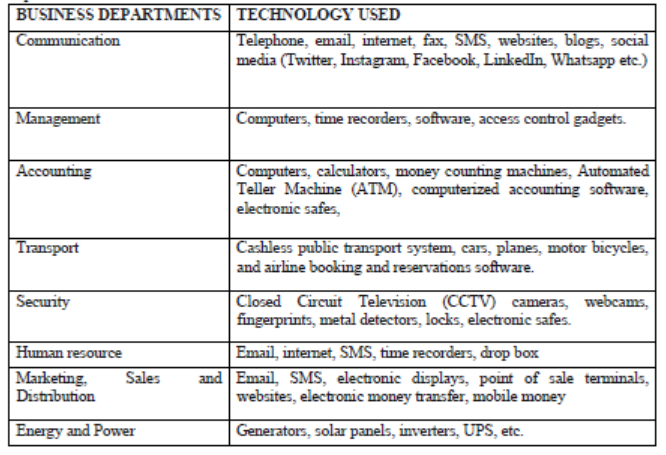
1) Describe how new technologies affect business activities either in groups or in pairs.
2) Depending on the purpose of the application activity, choose an appropriate method to assess learners’ findings, answers, or responses. Depending on the performance or results, you may decide to give remedial or extension activities.
Use available resources like the internet, textbooks, magazines, resource persons among others to research, choose the appropriate technology that would improve the performance (Quality, quantity and efficiency of work) of the projects your business club is running or plan to run at the college, in terms of.
a. Business registration
b. Production of Goods and services
c. Packaging and branding
d. Marketinge. Selling of the products and / services. And explain why you have chosen that particular type of technology and how you will acquire it.

1) Case study
Mugiraneza has a peanut butter making business. Last week she announced the purchase of new equipment and modern technology that would make a radical change in the production process. The investment would make some employees lose their jobs. Mugiraneza explained to them but there was no doubt, it was in the best interests of the company in general. Employees were not consulted because it would slow down the process and Mugiraneza felt that it was the best decision to make. In the long run, the modern technology and equipment should increase the businesses’ competitiveness and produce quality products and in large quantities. The working practices would obviously be changed, and employees would have to learn new skills of using them. The employees were promised to be trained, although it was not a guarantee to employ all of them if they fail to adapt successfully. After the announcement, the employees were so furious and considered taking industrial action. Hearing the rumors of a possibility to strike, Mugiraneza admitted that the issue was not handled very well but would not reconsider the decision.
Questions:
a) What factors may have made Mugiraneza decide to invest in modern technology?
b) Do you think the employees were right in taking industrial action? Give reasons for your arguments.
c) Analyze the factors that Mugiraneza might have taken into account before acquiring the modern technology.
d) Mugiraneza admitted that the issue was not well handled. In your opinion, how should she have handled it? 2. Peter produces flowers and sells them both in the local and international markets. He plans to use e-commerce in his business.
(i) Mention any 3 e-shops he can contact for advice.
(ii) How can peter find other e-shops to sell his products on the international market? iii) Explain the merits and demerits of using e-commerce in a business like that of Peter.
(iii)Write a letter to Peter advising him on how to use e-commerce for the success of his business. 3. Many people think that the key to better performance is good management rather than more technology. As an entrepreneurship student, critically assess this view.
UNIT 8: FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
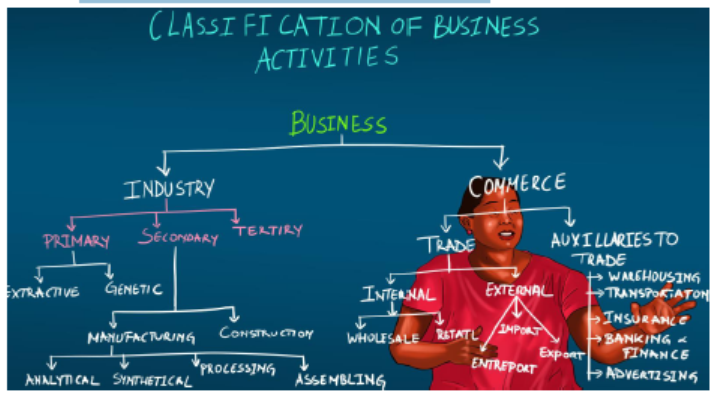
Key unit competence: To be able to classify different forms of businesses

Mukamana is one of the ladies involved in handicraft activities in her area. She makes baskets, mats, hats, necklaces and other related products. Of recent they had to register as individuals so as to obtain a trading license but Mukamana and the other ladies face challenges when buying raw materials for making their products. Marketing their finished products is also difficult as they work individually. Sometimes they travel to Kigali in search for customers to buy their products and when they are away, they have to close their workplaces and open them for work when they return from Kigali.
Questions.
1. What benefits would Mukamana and the other ladies enjoy if they decided to do their handicraft work together?
2. Identify the advantages they also enjoy working individually
3. Using your knowledge of entrepreneurship, identify the classification of enterprises to which they belong.
4. Explain the reasons why Mukamana and other ladies decided to register their business.
5. Which advice would you give to Mukamana in order to benefit more from their activities
8.1. Meaning of business organisation and classifications of business organisations
Visit your Library or use the internet to research on the categories of enterprises according to life span and fill in the table below:
Business is any economic activity done by any person or a group of persons with the purpose of making profits. It involves the exchange of goods or services for money. The main purpose of carrying out business is to make profits.
A business organisation is a group of people who form a business together in order to achieve a particular aim usually making profits.
Business organisations can be classified according to sector of activities, size, legal status and lifespan.
Business organizations are numerous and vary widely in the nature and types of goods or services provided. Their classification can therefore take many forms. The major bases upon which enterprises can be classified are by:
•Sector or activities
•Size
•Legal status and
•Life span
Classification of Business organizations according to legal status/ according to ownership
The following are the classifications of business organizations
1. According to legal status.
-Sole proprietorship
-Partnership
-Joint stock company
-Cooperative
-State owned enterprises (SEO) parastatalsSole proprietorship/ sole trade business

Sole proprietorship is a business started and owned by one person. The sole proprietor makes a decision alone, takes all the business profit and in case of losses he/she suffers them alone. E.g.: Restaurant, Internet cafes, boutiques, etc.
Joint stock companies
A joint stock company is at times called a limited liability company or simply a company.
This is a type of business formed and owned by a group of people called shareholders who have a separate legal identity. It is an artificial person created by law with capital divided into transferable shares.Co-operatives
A co-operative enterprise or a society is a form of business made by a group of people who join efforts in the production or distribution of goods and services with the purpose of sharing profits among themselves. A cooperative is an organization owned by the people who work in it and share the profit or with the purpose of benefiting its members.

Give examples of enterprises from your community and Rwanda at large by filling in the table below.
8.2 Business registration procedures according to form in Rwanda
1. Suppose you intend to start a small business in your vacation out of your pocket money savings that you have accumulated over time suggest the major steps that you are to follow before starting.
You can register your business Online or at the office of the Registrar General which is a department within the RDB located in Kigali, the capital city of Rwanda. The registration process has been covered after each business form.
8.2.1. Business Registration Process
For Sole Proprietorship business, an entrepreneur can start the business with few legal procedures. There are no formal procedures such as registration and document, an entrepreneur only pays a trading license and starts the business. But if he/she needs to register the business in the commercial registry, he/she is required to submit an application letter indicating.
▪Personal names, place and date of birth, domicile and residence, nationality, sex.
▪Name of the spouse in case he/she is married, and their matrimonial regime
▪Consent of the spouse if their regime is based on joint ownership.
▪Name of the business and its trademark if applicable.
▪Commercial activities to be carried out.
▪Headquarters of the business enterprise.
Partnership business may register with the registrar of companies. In this case, they will be required to submit partnership deed agreement (containing information discussed earlier in this unit). In the absence of an agreement between partners, the partnership cannot be registered.
Joint Stock Company/ Limited Liability Company, or a Cooperative, the following steps are normally followed:
▪The promoters prepare a memorandum of association which outlines the activities the firm is to be engaged in, its objectives and its general organization.
▪Preparing the Articles of association of the company that lays down the rules and regulations which will govern the internal organization of the company.
▪A minimum initial share capital for companies is required. For Limited Liability Company it is 500,000Rwf, for Public limited company it is 100,000,000Rwf.
▪The registration can be processed by the promoters themselves or through a lawyer.
▪An application form is filled and deposited with the records assistant in the registrar’s office.
A search will be conducted to confirm that firm uses similar names as those chosen by the promoters of the company.
The application forms are then passed on to the registrar of companies for endorsement and approval.
If all the required documents are in order; the registrar of companies will issue a Certificate of Incorporation. This document allows the owners to commence the business. If it is a public
company, it is required to get a Certificate of Trading in order to commence operations. It puts the company into existence and the company becomes a separate legal entity.
8.2.2. Registering a Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) in Rwanda
1. Local Non-Governmental Organization
A local NGO is required to get an approval from the district where it plans to undertake its activities, provide its constitution as well as register with Ministry of Local Government (MINALOC).
2. International Non-Governmental Organization
An INGO is registered by department of Immigration and Emigration. The applicant makes an application letter addressed to Director General of Immigration and Emigration and attaches.
-A detailed action plan.
-A memo indicating the source of funding of INGO
-Its annual budget
-Evidence of collaboration of the district where it operates
-Recommendation letter from the line Ministry (ies)
-Articles of INGO
-A memo linking relationship between its program with Community Development Plan (CDP)
-A correctly filled inventory form
-Summary of business Registration process in Rwanda
-To register a local enterprise or a foreign subsidiary, RDB provides a quick and efficient registration service allowing you to have your business incorporated within 24hours. The process ends simultaneously by obtaining the certificate of incorporation (business registration), Tax Identification Number (tax registration) and the Social Security Registration for Employee Pension Submission.Take a look on the table below to see how you can start, add or cease business activities in Rwanda.

1. Discuss the various procedures followed in registering a domestic company following Rwandan setting today.

Hope is a chairperson of the student business club in her school. In the last 3 weeks, she noticed team members were not showing up for meetings. She found out that there has been a fight about money, team members were accusing one girl of stealing cash. Create a strategy Hope can use to help the team achieve their goals.
Case study: Different forms of business organization/ enterprises
Read the case study below and answer the questions that follow:
Jean Paul Nyimana is a friend you have known for many years. He is a computer expert. He has been working for a large computer supplies company in Kigali for many years. The company supplies and services computers. Most people and organizations are experiencing technical problems with their computers, take them to the company where Jean Paul is assigned to service the computers. He is now well known by many people for his skills in handling technical problems relating to computer breakdowns.
He informs you that he has been thinking of starting a business enterprise dealing with servicing and maintenance of computers. He has saved money for this purpose, but the amount is not quite sufficient for the type of business he would like to start. However, the money is sufficient to start a small size business.
He also tells you that he has two uncles who are very rich. Both have a lot of money and have expressed their willingness to invest in the business enterprise with him.
Nyimana would like to get your advice on various options of the type of enterprise to invest in.
(a) Advise him on the forms of enterprises he can choose citing examples.
(b) Analyze the advantages of each form of enterprise.(c) Analyze the disadvantages of each for of enterprise.
UNIT 9: BUSINESS ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE
Key Unit competence: To be able to design business organization structure
Read the following paragraph and answer questions that follow:
Uwineza started a maize flour processing farm in her community. She is renting the place where her business is operating from. She buys her raw materials (maize grain) from a nearby town. She says she trusts her employees so they never write down anything about duties. She always has a meeting with her employees in the morning or uses a telephone call at a distance to assign tasks. Recently, after some advice from a friend, she discovered that she was so wrong in tasks assignments and immediately take a step forward to collect the errors previously done.
Questions:
a) What errors/mistakes did Uwineza do?
b) What are the likely consequences of Uwineza‘s actions mentioned above?
c)What advice would you give to Uwineza to avoid the consequences above and why?
9.1. Meaning of organization structure and department in an organization.
1. Read the following statements to identify an organization structure, give reasons to support your response
a) Claudette and Niragire playing football against Uwera and Mutesi
b) Uwimana is the deputy of one TTC, she outlined and documented the ways subjects’ teachers teach and assigned supervisory duties to different heads of departments
c) A group of fellow students with whom they are going to represent the school in a debate competition
d) A group of five girls reading science magazines in the library preparing for a science competition against another class
2. What is a department in your own point of view?
3. Give any two departments that you know.
9.1.1. Organizational structure
Organizational structure is a system that outlines how certain activities are directed in order to achieve the goals of an organization. These activities can include rules, roles and responsibilities. The organization structure also determines how information flows between levels within the company. Simply, an organizational structure is a system used to define a hierarchy within an organization. To achieve organizational goals, there must be a team and teamwork
▪ Team
A team is a group of individuals working together to reach a common goal. It can also be seen as a group of people with different skills and different tasks, who work together on a common project, service, or goal.
▪ Teamwork
Teamwork is the collaborative effort of a team to achieve a common goal or to complete a task in the most effective and efficient way. (From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia)An organizational chart is a graphical representation of a firm’s hierarchy of authority. An organizational structure is primarily represented by an organizational chart. It shows how different people and departments are linked together in the organization. People at the same rank in the business are at the same level on the organizational chart.
An example of organizational chart/Organogram
9.1.2. Departments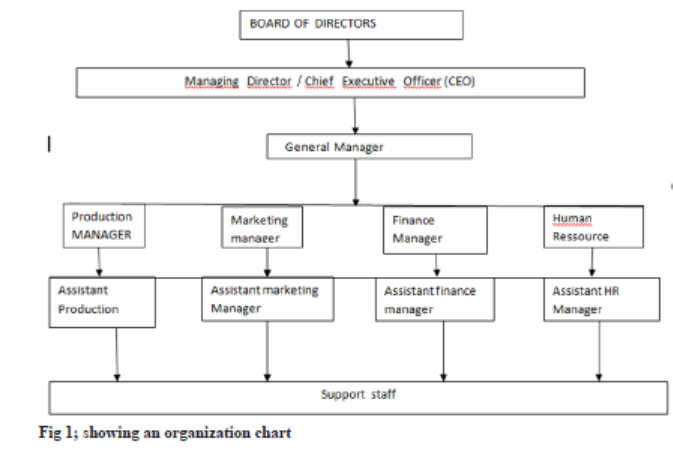
Department is also known as a section, Division or a single unit (special unit) within an organization that has specific functions which help the entire firm to achieve its goals.
Any organizational structure must be departmentalized i.e subdivided according to responsibilities.
Departmentalization can be done through 4 ways such as
a) By functions
b) By product
c) By geography
d) By type of customersSome of the departments that may be found in different organizations
1) Assume you are working in a business, which department do you wish to work from and why?
2) From the list of departments, you have gone through which one is very important to you and why?
3) From your community, identify some business organizations that operate from there, explain how they are organized and the way they operate in different positions.
9.2. Managerial functions
Mugisha attended a business meeting organized by Executive Secretary of the Sector together with the one in charge of business where business owners who attended were told to abide to the rules and regulations regarding the business. They were also told to properly plan and take into consideration other business managerial functions related to the effective and efficient production, hence, develop particularly our sector and our country in general.
From your point of view what do you think are other managerial functions discussed in that meeting?
9.2.1. Definition of concepts
a) Management is the process of getting things done by using other people and resources like capital, raw materials, and time.
b) Business management involves planning, organizing and coordination of the activities of an enterprise to achieve defined objectives. Without proper coordination and planning, a business cannot achieve its goals and objectives.
9.2.2. Managerial functions
These are special activities that are designed for a manager to perform in order to achieve the goals and objectives of an enterprise.
a) Planning: Refers to the process of setting goals and determining a course of action, defining who, when and how to achieve them.
b) Organizing: Refers to the coordination and supervision of factors of production particularly land, capital, and labor. It involves grouping activities and assigning tasks to people who would assume them. Organizing includes Identifying tasks, assigning them to responsible workers and Developing work plans. An organization chart is one of the tools managers use to organize the people in business.
c) Leading: This involves directing/ influencing or inspiring the workers towards achieving organizational goals.
d) Staffing: Refers to identification of the right people who will do the jobs as necessary to achieve organizational objectives. This is done through recruiting them through test, training, and paying them for the work done.
e) Controlling: This refers to the evaluation of achievements compared to the plans/standards and taking measures towards success of organizational goals/objectives.
f) Budgeting: This refers to making monetary estimations of the expected revenue and
expenses of the business over a given period of time, usually a year.
g) Coordination: This refers to bringing together different workers and departments of the business so that they work in harmony and strive to achieve the set goals.
h) Motivating: This involves inspiring and encouraging workers by appreciating the work well done, allowing them to participate in decision making, paying their salaries on time and giving them incentives, bonuses and benefits. This encourages the workers to work harder, increase the output/productivity and improve on its quality.
i) Commanding: This involves giving orders and instructions to staff members so that the targets and deadlines are met.
j) Communicating: This involves passing on information between people and departments. The manager passes on information regarding responsibilities, targets to achieve, suppliers, laws and regulations, …
Mugabo is an entrepreneur who always commands his employees with a harsh voice and assigns them tasks basing on nepotism. While recruiting employees Mugabo never set exams for selection but rather considered groupmates, neighbors, and his relatives.
From the passage above, with justification what managerial functions does Mugabo fail to obey/follow?
9.3. Personnel (Human Resource) Management
Analyze the following case study.
Mr. Busan’s factory is among the oldest brick making factories that has been operating in their area. It started operating in the first half of the 20th Century. It employs over 200 employees and owns production machines. Last year, the external auditor of the factory found out that the business was about to collapse. When the manager read the report, he was shocked about the eminent collapse of the business and could not figure out what to do to prevent the business collapse. He consulted many people for help, but he was not able to get a clear solution.
a) As an entrepreneurship student, what do you think could be the main cause of poor performance of that oldest brick making factory?
b) Suppose you are appointed as the manager of this factory, what can you do so that this business does not collapse?
9.3.1. Meaning of Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management is a process or a managerial activity that consists of four main activities, namely, acquisition, development, motivation, as well as maintenance of human resources.
It involves several functions concerned with the management of people at work. It includes manpower planning, employment, placement, induction, training, motivation and appraisal and compensation of employees.
9.3.2. Human Resource Management process
It involves determining the number and kinds of personnel required to fill various positions in the organization.
Recruitment:
Selection and placement of personnel,
This requires ensuring that the right people are recruited and placed to the right jobs through selection exam/test.
Induction: is the process where new employees are welcomed in the business /company and are prepared for their new duties.
Training and development of employees for their efficient performance and growth. Enabling employees to carry out their responsibilities effectively and make use of their potential.
Appraisal of performance of employees and taking corrective steps such as transfer from one job to another is evaluating the performance of employees and to identify the abilities of a person for further growth and development.
Motivating the workforce by providing financial incentives and avenues of promotion.
Remuneration of employees. The employees must be given sufficient (equivalent to work done) wages and fringe benefits to achieve higher standard of living and hence higher productivity.
Note: According to Edwin Filippo; Performance appraisal is the systematic, periodic and an impartial rating of an employee’s excellence in matters pertaining to his present job and his potential for a better job.
According to Cummings, the overall objective of performance appraisal is to improve the efficiency of an enterprise by attempting to mobilize the best possible efforts from individuals employed in it. Such appraisals achieve four objectives including the salary reviews, development and training of individuals, planning job rotation and assistance promotions.
Claudette is a human resource manager of Berwa enterprise, who is humble, always manages her employees in harmony and handle every personal issue accordingly. She normally performs her duties the way they are, whenever employees’ challenges happen Claudette addresses those issues with integrity and professional manner, she always faces the person to whom they are talking to, listen carefully and takes step forward to solve any complaint of that person. Claudette is the best employee of Berwa enterprise in 2018.
1) Basing on this ‘scenario what do you think is her duty/duties in Berwa enterprise?
2) Is her duty/duties important in Berwa enterprise? Give your point of view.
With reference to a business project owned by your school business club
a. Design an organization chart of the business club and give functions for each department
b. How do you think that project got the right persons to work within different departments?
1. Fill in the gap the following:
i.…………………………...is a process, which consists of four main activities, namely, acquisition, development, motivation, as well as maintenance of human resources.
ii.…………………………. Is one of the managerial functions consisting of:
a) preparation of task force.
b) allocation of work to individuals.
c) integration of the efforts of the task force; and
d) coordination of individual work with that of the department
2.Design an organizational chart of your school.UNIT 10: EMPLOYEE RECRUITMENT PROCESS

Key unit competence: To be able to design a strategy for recruiting workers in their businesses and prepare for job opportunities in the community.
1. Explain the meaning of employee recruitment and selection.
2. Explain any 3 factors considered while recruiting employees/workers.
3. Describe procedures/stages in recruitment process.
4. Identify required documents to apply for a job.10.1 Meaning of recruitment and selection process, and factors considered to recruit workers.
1. Using clear examples, explain the meaning of the following terms as used in entrepreneurship:
a. Recruitment
b. Selection process
2. Assume you are selected by a start-up business in your home locality and appointed as a human resource manager to help in recruiting new employees, explain factors you will consider while recruiting employees/workers.10.1.1 Meaning of recruitment and selection process
Recruitment: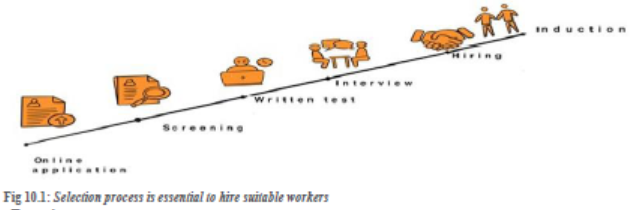
Refers to the overall process of attracting, shortlisting, selecting, and appointing suitable candidates for job (either permanent or temporary) within an organization.
According to Edwin Filippo: “Recruitment is the process of searching the candidates for employment and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization “. Recruitment is the activity that links the employers and the job seekers.
• The process begins when new recruits are sought and ends when the new employees are hired.
• The result is a pool of application forms from which new employees are selected.
Selection:
On the other hand, is a process whereby out of the many job applicants, the best is taken to fill the vacancy. Selection means reducing the application pool by using the screening tools such as test, assessment centers, background and reference checks. During selection of employees, the choice can be on the candidates both from within the organization or from outside.Every organization creates a selection process because organizations have their own requirements. Although the main steps remain the same, let us understand in brief how the selection process works:
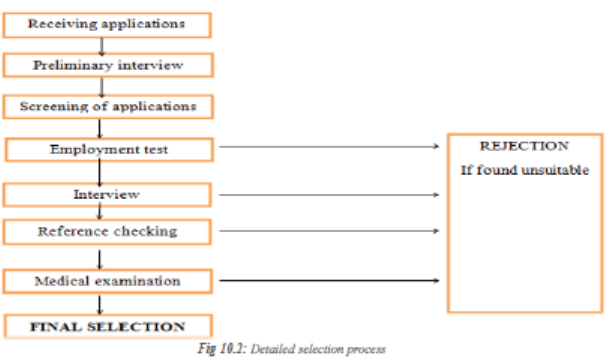
10.1.2 Factors considered when recruiting employees
a) Size of the firm: The size of the organization affects the recruitment process. If the organization is planning to increase its operations and expand its business, it will think of hiring more personnel which will handle its operations. Size of the firm also defines the recruitment scope and need. Small firm’s Human Resource department has to handle less manpower. As the organization grows wider, the recruitment complexities increase.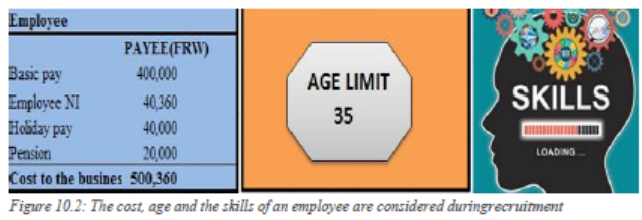
b) Human resource needs: Staffing is an ongoing process that begins with finding the right people through proper planning, recruiting, and selecting. But staffing does not end once employees are hired; management must keep and nurture its people via training, appraising, compensating, and implementing employment decisions that determine such things as promotions, transfers, and layoffs. When recruiting new workers, you think about the prospective human resource needs that may arise due to new hires.
c) Employment costs: These costs fall into several broad categories:
•Recruiting expenses: Finding technically qualified people who are effective in a rapidly growing start-up venture is not easy task. This is a one- time cost in the total employee cost calculation. Recruitment costs include advertising, fees for
online
recruiting services, etc.
• Basic salary: Basic salaries vary all over the place depending on the industry and a variety of other factors. Be sure to establish rational salary ranges given your growth plans. This means that in most cases there should not be great salary differentials between early hires and later employees.
•Employment taxes: In preparing a personnel budget, be sure to include all the employment related taxes such as professional income tax.
•Benefits: Basic salary and employment taxes are not enough. In most cases, an employer will need to provide some benefits such as life insurance, dependent care assistance, tuition reimbursement, accommodation, and any other possible allowance where applicable.d) Age of employees:
Age of the worker is a very important criterion to consider during the recruitment process. This is because some duties require workers with strong physical abilities while others require those with wisdom. To help your young and old employees find common ground, you need to treat them as individuals and not just as members of certain generational categories. Help them realize that they can learn from their differences. driving is suitable for young while research requires experienced people (old).
e) Employees’ skills: One of the easiest ways to select through candidates is by looking at their skillset. Can they do the job and can they do it efficiently? Skill can be easy to measure based on the facts in front of you (resume, cover letter and interview). It is true that some tend to fabricate or “stretch” their experience so a solid approach to confirm skills is to contact previous employers and verify if the skills communicated match up with what the previous employer(s) saw. Of course, if the candidate lacks experience they should communicate and express a desire to learn and pick up those skills.
f) Employee’s experience: Work experience might be one of the most important considerations you have for particular jobs at your facility. Experience in particular areas such as answering busy telephone lines or ha ndling accounts, for example, can be essential for specific staff roles. For other positions, work experience might not be necessary, but a strong work background is always a good thing as it exemplifies/illustrates a good work ethic.
ndling accounts, for example, can be essential for specific staff roles. For other positions, work experience might not be necessary, but a strong work background is always a good thing as it exemplifies/illustrates a good work ethic.
g) Nature of job: The nature of an employee’s work is best defined as the type of work that he/she does. This can refer to the basic daily tasks carried out as part of a job and can refer to other non-routine tasks that may be required. Added together, the characteristics of these tasks comprise the nature of an employee’s work. The nature of this work may be summed up in the employee’s title and taken into consideration during the recruitment process. For example, a human resources manager is someone who manages a human resources department and performs all of the tasks required of such a position.
h) Number of workers: When one is recruiting employees, he/she must consider both the number of workers needed and available qualified applicants. The number of workers a business recruits depends on different criteria most importantly the available vacant positions and its corresponding budget.
i) Health conditions: A lot of job applications have a section saying, «Do you have any existing or prior medical condition that may affect your ability to do the job»? Employees with good health conditions are liked by recruiters.
j) Language: The language is one of the effective communication drives. A candidate who can effectively communicate as many languages as possible is advantageous in the recruitment process.
Assume you are selected as one of the school business club leaders, and you have a very strong income generating project at your school. Advise your business club on factors to consider when recruiting employees.
10.2 Procedures/ stages of recruitment process of workers
Case study:
Umutoni, a human resource manager of sweet bread bakery was having the challenges of getting a suitable finance manager for the company. She was advised to prepare job analysis. Furthermore, she was advised to prepare a job description which outlines the responsibilities and duties to be carried out by the financial manager. Umutoni was also advised to prepare a job specification which outlines the requirements, qualifications, expertise, physical characteristics, for the financial manager. All these were to appear on the job advert. The task was so challenging, but she managed to come up with the documents, and a suitable financial manager was got after the selection and interviews.
a.Describe the following stages as involved in recruitment process:
i) Job analysis
ii) Job description
iii) Job specification
iv) Job advertisement
b. Why do you think it is important to prepare the above documents?
If an organization needs to hire right employees, the following stages should be put into consideration:
a. Conduct a job analysis: Job analysis involves establishing the nature of the job (tasks, activities, responsibilities, and accountabilities) which will also determine associated required talents and competencies defining behavioural attributes for best performance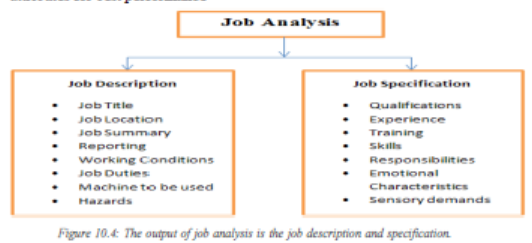
A personnel manager has to undertake job analysis to recruit the right person on the job.
b. Create a job description: Job description is a process of describing the job to be performed. This is also referred to as a written statement which outlines the duties and responsibilities involved in performing a job such as who does what, when where and why. The main contents are the job purpose and the job tasks and responsibilities. It informs employees exactly what is expected of them and provides a useful document to refer to when you are evaluating an employee’s performance. You can also use it to develop selection criteria, identify training needs, and manage performance.Example of a job description for a finance manager:
• Responsible for accountants, cashiers, and workers in the finance department. To take a supervisory role.
Main duties:
• Preparing pay rolls.
• Making financial reports for external auditors and other stake holders.
• Advise the general manager and the managing directors on financial issues.
• Supervise the subordinate staff.
• Advising staff when queries arise.
Occasional duties:
•Appointment of new staff.
•Training new staff in their duties.
•Training new staff on how to use new equipment. Disciplining staff as and when required.
• Dismissing staff if necessary.
c. Create a job specification: Job specification involves a definition of qualifications, experiences and competencies required by the jobholder and any other necessary information on the special demands made by the job such as physical conditions, unusual hours or travel away from home. Job specification sets out terms and conditions of employment such as pay, employee benefits, general health, mental health, intelligence, aptitude, memory, judgment, leadership skills, emotional ability, adaptability, flexibility, values and ethics, manners, and creativity, etc.
Qualifications
Essential: Bachelor’s degree in finance and accounting. Master’s degree in a related field will be an added advantage.
Experience:
Desirable minimum is 5years’ experience of working in the finance department.
Skills:
• Communicating effectively with others.
• Ability to manage people.
• Computer literate with computerized accounting software packages e.g. Sage or Quick books.
Others
• Physical fitness needs to be fit all day.
• Personal characteristics: Honest and responsible, friendly, helpful, organized, high integrity, etc.
d. Defining a job position: This section contains providing general information about the job position. The current or requested classification, working title, pay range, exemption status, department name and number, position number, percentage of effort, the job description summary, comparable positions, etc. This is all about what responsibilities you might have.
e. Attracting the applicants (Job advertisement): Job advertising is way organizations communicate to attract new employees to work with them. Recruitment advertisements typically have a uniform layout and contain the following elements:
• Brief description of the organization.
• The title of the job advertised the grade and the manager to whom the job holder will report.
• Duties and responsibilities of the job holder.
• Skills and competences of the job holder.
• Conditions of educational qualification and experience of that job position holder.
• The channel of communication used for submitting the application.
• The timeline during which applications will be submitted.
• The channel of communication for feedback.
• Signature and the stamp of the organization manager who is posting the advertisement. Some business organizations use recruitment advertising agencies to receive professional advice and also help them to recruit new workers. They offer a service which they are paid for in return.
Examples of recruitment agencies in Rwanda include:
- Tohoza.com
- Umurimo.com
- Jobs in Rwanda
NFT consult
- Ndangira.n
f. Selection: This is the process of getting human resources into organizations’ departments, sections, and jobs. Human Resource Managers are responsible for recruitment and selection which should be clear on the type of employees they are looking for. Lack of clarity may lead to poor selection criteria and may result in the wrong person being recruited for the job.
There are important steps in the process for effective competence-based selection.
• Development of competence models for selection.
• Determination of selection methods.
• Training of assessors.
• Assess job applicants.
• Validate the assessment methods.
• Development of a database for future use.
g. Hiring: After successfully completing all the previous stages, an appointment letter will be issued by the employer to the worker. A reference check is made about the candidate selected and then finally he/she is appointed by giving a formal appointment letter.
h. Integrating the new employee to the organization/Orientation: On-boarding helps to foster a positive first impression and increases the likelihood that employees will buy into the corporate culture and assimilate into the position. Properly executing the orientation process can greatly increase the new employee’s satisfaction and success, which bodes/ promises well for retention.
The following are essential five steps to effectively on-board new employees to your organization:
i. Prepare the office for the new arrival
The first day on the job should be organized and scheduled before the new workers come. Managers should build out a schedule in advance that includes learning the job in particular and company policy and process in general. Share this agenda with your new hire in advance. Also, send a copy to all team members involved with the on -boarding process.
i) Assign a mentor
One of the best facilitation strategies for on boarding is mentor relationship. Mentors provide guidance that goes beyond traditional training. Match up a seasoned employee with the new hire in the early stages of training. A mentoring relationship will prove invaluable to the new employee’s integration into the workplace.
ii) Make positive introductions a priority
Create good will toward the new hired by introducing them to the current team with a short explanation of the person’s expertise and qualifications. This type of introduction helps current employees become familiar and acceptance of the new person. Also, avoid statements that create competitive or insecure feelings.
iii) Request feedback from new employee
Consistent feedback from the new employee is valuable in knowing which facets of the on-boarding process work and which ones need to be improved. Periodically, ask for input on the training process, and measure its effectiveness.
iv) Provide a cohesive goal
From the beginning, every new employee or seasoned should understand the company goals along with his or her specific tasks. A common goal serves to create greater collaboration and harmony. Facilitation strategies for integrating new employees require planning and follow-up. The results bring a more engaged, dedicated employee and fewer workplace conflicts.
1. Design a job description for one of the following.
a. A school business club cashier
b. Shop assistant
2. Design a job specification for your chosen job.
3. How do a job description and job specification help to ensure the most suitable person for the job is recruited?
10.3 Required documents to apply for a job
1. TUYISHIMIRE is a senior six graduate. Having learnt about a job advert by INYANGE Industries (a famous manufacturing company in Rwanda), posted in the new times has approached you a fellow student for advice, advise her pointing out the requirements to apply for the job.
2. a) Identify the difference between a curriculum vitae and an application letter?
b) Identify the major parts that a good curriculum vitae should have.
To prove that you are eligible for work and to apply for a job, the following are some of the documents you will have to submit:
10.3.1 Application letter:
Writing an application letter will be the first correspondence you are going to have with your possible employer. The employer will definitely judge you on your application letter if you are worthwhile being interviewed. Always remember that any job competition
is very tough. Therefore, your application letter must stand out because employers usually deal with hundreds of job applications for a single position.
Start your letter by adding your contact information at the top. You want to make it as easy as possible for your prospective employer to contact you and know who you are. Before you begin your letter, make sure that you have the proper letter- head.
i) Name
ii) Address
iii) Phone number
iv) Email address
v) Personal website (if you have one)
• Include the company’s information: After you include your information, you need to include the title of the employer to whom you are applying for the job, the name of company and address. By including the contact information of the company to which you are applying, you are showing that you have taken the time to write a specific letter or application to this company and have done your research on the hiring manager for the position.
• Address your letter to the person whom you are writing: To begin your letter you want to be formal and start with a proper/correct address. Once again, a simple “Dear Manager, Director”, etc. This will depend on the information given from the advertisement.
• Salutations: These are greetings used in a letter, e.g. Dear Sir, Dear Madam.
• Subject line: This indicates the title, or the position being applied for.
• Body of the letter: This has three distinct parts:
- In the first paragraph, you have to mention the job you are applying for and where you saw the job listing.
- The next paragraph(s) are the most important part of your letter. Remember how you gathered all that information about what employers were seeking, and how you can meet their needs. This is where you will share those relevant details on your experience and accomplishments.
- The third and last part of the body of the letter will be your word of appreciation to the employer; and you can also offer follow-up information.
• Complimentary close: Complete your letter with a polite close, such as
«Faithfully» or «Sincerely, » followed by your signature and your name.
Notice: When you apply online through the-Recruitment, follow the structure/ format provided to you.
Sample hint of an application letter
Name Address
Telephone Number
Email Address
Month, Day, Year
Title of the authority receiving the application
Name of Organization
P. O. Box Address
Dear Mr. /Ms. /General Director
Subject line: Include the title /position you are applying for
Opening paragraph: State what position you are applying for and a brief introduction about yourself; how you learned of the organization or position, and basic information or qualifications about yourself.
2nd paragraph: Indicate why you are interested in the type of work; demonstrate that you know enough about the position to relate your background to the position. Mention specific qualifications which make you a good fit for the employer’s needs. This is an opportunity to explain in more detail’s relevant items in your CV/resume. Refer to the fact that your CV/resume is enclosed. Mention other enclosures if such are required to apply for a position.
3rd paragraph: Indicate briefly why you’re so passionate about the opportunity you’re applying for. State that you would be glad if you are granted a job. Thank the employer for her/his consideration in advance.
Sincerely,
(Your handwritten signature)
Your name typed
SAMPLE APPLICATION LETTER
Keza Silvie
Gasabo District
+250783075559 esilvie@gmail.com
September 14, 2020
General Director
Airtel company KG, 17 Ave, Kigali Dear Director General,
RE: Application for the position of Marketing Officer
As a long-term admirer of the impressive work being done by your company, I’m delighted to submit my application for the Marketing Officer position at Airtel company which was advertised in the new times papers on the 2nd of September 2020. I have followed many of your recent marketing campaigns with interest and believe that my sharp, witty approach to marketing content would be a good fit for your customer base.
I have spent the last six years learning entrepreneurship, a course in which I have gained a lot of skills and knowledge, those related to marketing also included. In this class, I’ve learned about different marketing strategies which I’m confident can be of good help to your company. For the practical part, during different activities of my clubs we create, develop, and print flyers and other marketing materials. My responsibilities include coordinating meetings and project deadlines as well as managing a production team of these flyers. I attend different clubs which means I’ve experience working with large groups of people which gives me valuable experience in teamwork and organization. I have enclosed my CV with more detailed information about my skills and education, please refer to it for more details.
I see marketing as an ever-evolving field with endless opportunities for innovation and creative new strategies for customer engagement. I believe my strong teamwork, communication, and collaboration skills would make me an excellent fit for a marketing Officer position at Airtel company. I would be more than happy to work with you and take the company to the next level. I look forward to discussing my ideas and strategies with you to explore how I might best fit your needs. Thank you for your consideration.
Yours Sincerely,
Keza Silvie
10.3.2 Curriculum Vitae (CV):
The letters CV stand for curriculum vitae which in Latin means “Course of life”. When used in a job seeking context, a CV is a brief history of your education, work experience and activities, skills, accomplishments, and any other information relevant to getting a job.
CV writing and format tips:
i) Include relevant information only: Your CV should not include all details about your life. Keep it simple, clear and neat.
ii) CV Length: While resumes are generally one page long, CV is longer. Most CV are at least two pages long, and often much longer.
iii) Font and Size: Do not use ornate/decorative fonts that are difficult to read; Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, or a similar font is best. Your font size should be between 10 and 12 points, although your name and the section headings can be a little larger and/or bolded.
iv) Format: However, in deciding to organize the sections of your CV, be sure to keep each section uniform. For example, if you put the name of one organization in italics, every organization name must be in italics. If you include a sentence or two about your accomplishments in a position, fellowship, etc., make a bullet list of each accomplishment. This will keep your CV organized and easy to read.
v) Be accurate: No spelling or grammatical errors. Be sure to edit your CV before sending it. Check spelling, grammar, tenses, names of companies and people, etc. Have a friend or career services counsellor check over your CV as well.
vi) Be consistent: Punctuation, highlighting, verb tense, spacing etc. should be verified.
vii) Spells out acronyms: The first time it appears, put the acronym in parentheses and then use the acronym after that.
B. Elements of Curriculum Vitae
Not all curriculum vitae s look the same. But there are general sections that must be included in almost all CVs. However, one may choose to include only some sections because others do not apply to his/her background or industry. Include what seems appropriate for your area of specialty. In your CV you can include:
a. Contact information: At the top of your CV, include your personal identification/name and contact information (address, phone number, email address, etc.).
Education background: This may include the school/institution attended, dates of study, and degree received.
b. Work Experience: List relevant work experience; this may include non-academic work that you feel is worth including. List the employer, position, and dates of employment. Include a brief list of your duties and/or accomplishments.
c. SKILLS
- Professional competencies relevant to the position for which you are applying.
- Computer skills.
- Language skills, etc.
d. References: In this part, include people who know you and who might be contacted in case they need any information about you. Lastly, end by certifying that the information is from the best of your knowledge.
Below is a sample of curriculum vitae (CV)
Curriculum Vitae
1. PERSONAL IDENTIFICATION
• Names: BUTERA Jane
• Date of Birth: 8/12/1995
• Gender: Female
• Nationality: Rwandan
• Marital status: Married
• Telephone: (+250) 738469764
• E-mail: butejane@yahoo.fr
• Contact address: P.o. Box 1010
Bugesera District
Eastern Province – Rwanda2. EDUCATION BACKGROUND
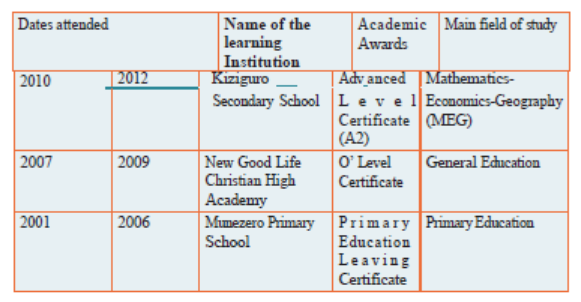
3. PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE

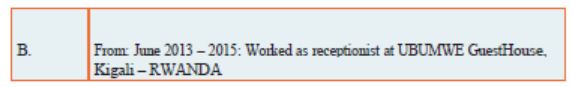
4. OTHER SKILLS ACQUIRED
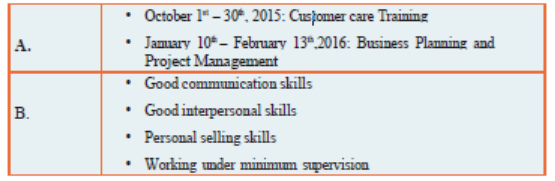
5. LANGUAGES
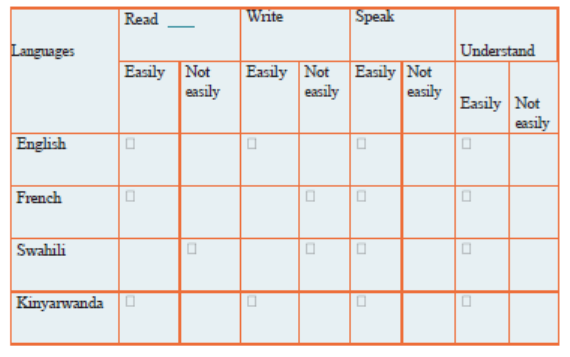
6. HOBBIES
7. REFEREES
1.) Mr. Kayar john
DG Airtel Rwanda
Tel;0785432111
2.) Mrs. Ineza Beatrice
Country director
Red cross
Tel;0788303030
3) Miss Buranga Egidie
Manager
Hilton hotel
Tel; 0783031242
I, BUTERA Janet do declare that the above information is true to the best of my knowledge.
BUTERA Jane, The manager,
BUTEJA Min Supermarket
10.3.3 Academic credentials/ relevant qualification papers
Credentials often refer to academic or educational qualifications, such as degrees or diplomas that you have completed or partially completed. Credentials can also refer to occupational qualifications, such as professional certificates or work experience.
These are examples of academic credentials:
• Secondary (high) school diploma
• College diploma
• Bachelor’s degree
• Master’s degree
• PhD or Doctorate degree
• Professional school degree (for example, for law, medicine, teaching)
A few organizations evaluate international academic credentials to compare them to credentials you can get in your country. You may need this for work or if you apply to a college, university, or institute.
Assume you want to apply for a post in any business company.
Design an application letter and a curriculum vitae.
Bright Business club wants to expand by introducing other viable projects. In efforts to ensure the club grows effectively, they will recruit a strong marketing manager from one of the members in the club. The key role of the marketing manager is to ensure the right projects are implemented in the club.
1. As students of entrepreneurship, create a relevant job specification and make an advert for the above position.
2. Discuss the importance of creating a job specification for a given position.
1. You have come across an advertisement on the internet about the need for Head of Security in a prominent shop. Write an application letter to apply for the above post.
2. Gikundiro is a senior six level student who wants to start a fruit processing business and she needs help from you to design an advert for various posts in her fruit processing business.UNIT 11: TEAM BUILDING IN A BUSINESS
Key Unit competence: To be able to demonstrate a good leadership strategy for leading teams in the business.
Introductory activity (Self-assessment)
11.1. Meaning of leadership and Leadership styles
Activity 11.1
1. Read the following paragraph and answer questions that follow.
Think about a time when you have been a leader. It can be a leader of anything, a group task at school, home or in your community, at a job, being a leader on a sports team...
a) How did you like playing that role?
b) What made it difficult or easy for you?
c) Based on your experience described above, what do you understand by leadership?
2. Referring to your community, or country, name any three (3) examples of leaders who you think are inspiring (famous people or people from your community).
3. Analyze the Leadership styles below and answer questions that follow:
• The “Authoritarian” Leader/ Autocratic style/Authoritarian
• The “Persuading” leader:
• The “Consulting” Leader:
• The “Joining” Leader:
• The transformative leader:
Required:
a) Explain the meaning of each leadership styles above
b) Think and give examples of people you know who tend to lead or have led in each of the leadership style explained above.
c) Describe when each leadership style would be appropriate to use
11.1.1 Meaning of leadership
Leadership is the art of motivating/ influencing a group of people to act towards achieving a common goal. This leadership definition captures the essentials of being able to inspire others and being prepared to do so. Effective leadership is based upon ideas (whether original or borrowed), but will not happen unless those ideas can be communicated to others in a way that engages them enough to act as the leader wants them to act. Put even simpler, a leader is the inspiration and director of the action. He or she is the person in the group that possesses the combination of personality and leadership skills that makes others want to follow his or her direction.11.1. 2 Leadership styles
As a leader, it is important to understand the different styles of leading. The style you choose will depend on the context in which you are working in, the people you are working with, their needs and expectations, whether or not you have a deadline, the task, etc. The following are the most typical leadership styles: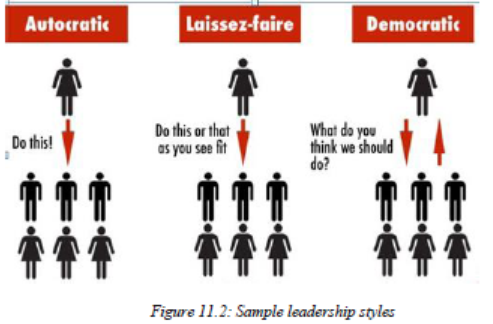
a) The “Autocratic/Task-oriented/Authoritarian/” style
• Identifies a problem, considers alternative solutions, chooses one of them, and then tells followers what they are to do.
• May or may not consider what the group will think or feel about the decision, but they clearly do not participate in the decision-making.
• Assigns roles.
• Relies primarily on his or her own judgment.
b) The “Persuading” style
• Like the “Authoritarian” leader, he/she makes the decisions without consulting the group. Instead of simply announcing the decision he or she attempts to persuade the group members to accept the decision.
• Describes how the decision fits everyone’s interests.
c) The “Consulting/ Democratic” style
• Gives the group a chance to influence the decision from the beginning.
• Presents the problem and relevant background information, and then asks the members for their ideas on how to solve the problem.
• May offer a possible solution for the group members’ reaction.
• Selects the solution the members regard as most promising.
d) The “Joining” style:
• Participates in the discussions as “just another” member agreeing in advance to carry out whatever decision the group makes.
• Encourages group decisions.
• Allows for individual recognition.
• Tends to guide, not rule.
e) The transformative style
• Leader identifies the needed change,
• Creates a vision to guide the change through inspiration, and
• Executes the change with the commitment of the members.
f) Laissez-faire leadership
• The leader makes the subordinates aware of the broad goals and objectives of the business
• The subordinates are left free to organize themselves and make their own decisions
• The leader totally trusts their employees/team to perform the job themselves
• The leader just concentrates on the intellectual/rational aspect of his work and does not focus on the management aspect of his work
• This leadership style works only when the employees are skilled, loyal, experienced and intellectual.
Application activity 11.1
1. Read the following extract from “Rwanda. A remarkable turnaround of a nation, 2014, page 9) and answer questions that follow:
To produce the desired outcomes, structural advantages have to interact the agency – social organization and leadership. Fortunately for GS RUGWIRO, at the heart of its success has been focused on good leadership to guide the institution through various reforms. The head teacher and his colleagues have exhibited extraordinary leadership values and skills aimed at navigating local difficulties and external pressures to steer the institution to success. Yet, its achievements are not singularly because of the intrinsic values of its internal organization, the institution – however, important these may be. Rather, they have largely been because of institution’s ability to build a broad-based collaborative relationship with other schools and social wellbeing of staff in the school to sustain the momentum for progressive change.
a) Do you describe GS RUGWIRO as a team? Give reasons to support your response
b) From the extract, why do you think GS RUGWIRO has a good leadership
c) Do you describe the head teacher of the above school as an effective leader? Support your response with four qualities from the extract
2. Analyze the scenarios below, and determine which leadership style is more appropriate for the scenario and give reasons to support your choice.
a) You are at the workplace and suddenly the building where the finished products are stored catches fire.
b) In the finance department, workers are complaining that the rules and regulations in their department are not favorable to all and therefore, need to be changed
c) In your department, as a leader you want to introduce computers because you believe they will improve on the efficiency of the workers but they feel computers are not necessary, as it is a wastage of the company’s money
d) Recently, there have been changes in government policies that automatically affect the performance of the business. You as the Managing Director are to lead senior management to come up with strategies to counter the effects of the new policies
e) At school, all the classrooms are dirty and need to be cleaned.
f) Implementing government programs such as “Umuganda”11.2 Team building
Activity 11.2
1. Explain the meaning of team building
2. Describe the characteristics of a good team
3. Using your own knowledge on team building, explain team building steps/techniques.
4. Think of a situation at work, school or home where there is a new/unfamiliar task for everyone to accomplish. People are required to get themselves organized to accomplish it. This particular task will need leaders to emerge and assume
responsibilities, manage people and the communication process for the success of the given activity.
5. Referring to your class group activities, explain the importance of teams in business.
11.2.1 Meaning
A team is a group of people working towards a common goal. Team Building involves the process of enabling the group of people to reach their goals. It consists of steps like clarification of team goals; identification of hindrances to goal achievements; facing the identified challenges and enabling the achievement of the goals.
Team building is the action or process of causing a group of people to work together effectively as a team, especially by means of activities and events designed to increase motivation and promote cooperation. This is a collective term for various types of activities used to enhance social relations and define roles within teams, often involving collaborative tasks.
The formal definition of team-building includes:
• Aligning around goals
• Building effective working relationships
• Reducing team members' role ambiguity• Finding solutions to team problems The effectiveness of team building differs substantially from one organization to another. The most effective efforts occur when team members are interdependent, knowledgeable and experienced and when organizational leadership actively establishes and supports the team.
Effective team building incorporates an awareness of team objectives. Teams must work to develop goals, roles and procedures. As a result, team building is usually associated with increasing task accomplishment, goal meeting, and achievement of results within teams.
Katzenbach and Smith (1993) list the following requirements for building effective teams:
(i) It should be small enough in the number of members.
(ii) Adequate levels of complementary skills.
(iii) Truly meaningful purpose
(iv) Specific goal or goals.
(v) Established clear approach to the team's work.
(vi) A sense of mutual accountability.
(vii) Defined appropriate leadership structure.11.2.2. Characteristics of a good team
• Clear goals: Clear goals are necessary so that all team members understand the purpose and vision of the team.
• Defined goals: Goals should be defined so as team members understand their job function for leaders to tap into the skills and talents of group members.
• Open and clear communication: Effective communication will keep a team informed and focused. It is important to focus on hearing message before forming our own conclusions.
• Effective decision making: Awareness of various decision-making methods can help a team member make efficient decisions. Team members should select a method that works best them.
• Balanced participation: Full involvement of team members is valued and sought. It is important that leaders define what type of participation they expect from members.
•Valued diversity: Diversity of thinking, idea generating, problem solving and experiences help to create an effective team.
•Cooperative relationship: Team members need to work together for the good of the team and understand that combining the skills of numerous people will produce something that could not be created alone.
20
• Participative leadership: A good team is characterized by shared leadership among team members at various times.
11.2.3. Steps for building productive and effective teams
Without team building skills, the manager risks limiting the productivity of his/her employees to what each member can do on their own, whereas if he/she fosters team building, he/she can unite teams around a common goal, which will raise productivity as a result.
The following are five steps to building a productive and effective team:
Step 1: Establish leadership.
If your employees trust your judgment, they will work effectively even when you are not around. Before you start team building, you need to develop the right kind of leadership skills. This doesn’t mean asserting authority, instead try to foster trust through honesty and transparency.
Step 2: Establish relationships with each of your employees.
A manager tries to learn more about each member of his/her team, their skillsets, how they are motivated and their likes and dislikes. This knowledge is invaluable to managers as it allows them to match each employee’s expertise and competencies to specific problems, which will help increase their productivity and job satisfaction.
Step 3: Build relationships between your employees.
As a team starts to cooperate more, examine the way they work together and take steps to improve communication, cooperation and trust amongst the team. If there are any conflicts, try to resolve them amicably. Listen to both sides of the argument and act as a mediator. One way to do this is to brainstorm solutions, which helps to empower your employees and may lead to new solutions to the problem.
Step 4: Foster teamwork.
Once relations with and between employees have been established, it is time to help them work together effectively. Encourage the team to share information, both amongst them and within the wider organization. Also, try to communicate more with the team. This goes beyond simply holding meetings, and includes things like being open to suggestions and concerns, asking about each team member’s work and offering assistance where necessary, and doing everything to communicate clearly and honestly with the team.
Step 5: Set ground rules for the team.
Finally, begin officially establishing the team through creating team values and goals, as well as evaluating team performance alongside individual performance. Be sure to include the team in this process so that they know what is required and agree with it.
Team building is one of the most important responsibilities a manager has. It isn’t something that can be achieved in a short time and then forgotten. It is an ongoing organic process that you will have to facilitate and guide.
11.2.4. Strategies for managing a team
Assume you are selected as the leader; describe some strategies you will use to have the people accomplish the task.
Leaders can employ different strategies while bringing people to work together and developing teamwork:
• Work with the team to develop a common goal
• Nurture sense of belonging; focus on what team members have in common
• Help team members work together to efficiently solve problems
• Encourage members to set aside personal goals and desires for the benefit of the team
• Treat team members fairly and equally.
• Structure the work of the team in a simple & logical fashion; distribute work fairly
• Manage team efficiently so that work proceeds in a timely manner
• Create an environment that supports and rewards openness, creativity, trust, mutual respect and a commitment to provide high quality services
• Value everyone’s contribution
• Encourage discussion
• Ensure all team members understand that their ideas & opinions are equally important and relevant
• Encourage people with different abilities & personalities to work together
• Value everyone’s contribution. Team members have different skills and experience and so each team member must be given an opportunity and feel that their contributions are valued
• Empower team members. Delegating authority and empowering the team to make decisions is more likely to pull together members together and work collaboratively to achieve business goals.
• Resolve conflict within the team. Constructive conflict among team members is a sign of a healthy team. However, unhelpful arguments and conflict should be tackled for the team to stay focused
• Celebrate team successes. When the team achieves a milestone or target, you should encourage team members to celebrate their success together act as an incentive to reach the next milestone or target.
11.2.5. Importance of teams in business
There are numerous advantages of teamwork in business. Some of the genuine advantages of are discussed below:
• Division of work and achieving set goals: Teamwork ensures that there is an equal and fair distribution of work within the organization. A fair work distribution ensures that every person or every working unit executes any task at hand, with the best possible efficiency. The division of work also ensures that the work is done on time and deadlines are not extended hence achievement of set goals.
• Reduction of risk: When the task at hand is executed with the maximum possible efficiency, there is a reduction in risk. The best advantage of teamwork in business is that the burden of failure is borne by all the members of the team and it does not fall on the shoulders of just one person.
• Subordination of personal interest to organizational interest: One of the biggest advantages of teamwork is that personal interest is subordinate to organizational interest. This ensures that all the team members put in the maximum possible efforts into their work, thereby ensuring a high quality and timely output.
• Eases work:

Sharing the workload eases burnout. Team members can provide emotional support to each other because they often understand the demands and stress of completing the work even better than managers. This also helps workers to share the tasks according to their ability differences.
• Easy management of workers: when workers are assigned tasks in groups, it is easy to delegate some of the managerial powers to team leader hence easy management of employees.
• Increases teamwork spirit: Most modern businesses are structured around teams. Even those with highly individualized jobs like graphic design and publishing need active cooperation among various members of the organization for a final product to emerge. It is critical then for every member of the organization to understand the concept of teamwork and to consider his or her job as part of a team effort.
Ways to encourage team spirit in the workplace:
1. Employ the right people
2. Eating lunch together
3. Organize social events
4. Workshops can also be useful
5. Sharing praise and feedback
6. Being inclusive
• Quick business growth: Teamwork can be the smartest strategy for growth as it influences performance results and organizational objectives. Teamwork makes people share the same goals and responsibilities for outcomes, namely the common objective of an organization. It also enhances effectiveness and productivity of a company which would gain an organization more profit (Beal, 2003), etc.
Application activity 11.2
1. Read the following activity and answer questions that follow.
You are the president of your school business club. The District Youth leader has advised you that for your club to win the upcoming competitions, the club should have an overall impact on the school and community. Club membership should comprise students from S1 to S6, but S4&5 members are not willing to accept students from other classes. They claim that the new members will simply enjoy current club achievements, and they will not bring much since most of the work has been done, and projects are already running; the club is not united as well. As the president:
a) What should you do to ensure the club is united?
b) What characteristics are required for the club to be successful?
2. As a student representative, you have been challenged to ensure that all students in your class participate in a community day. However, most students are saying it their only time to do private activities and thus have no time. As a leader, how would you apply the steps for building productive and effective teams to manage the above challenge?
3. Mutoni has been voted as a youth representative in one of the sectors in Ngoma district. In this sector, there are over 100 youths who have been asked by the executive to find a viable project they can start that can solve the problem of unemployment. This project will be financed by the sector. The biggest issue they have however is they don’t agree with each other on which project they would select. Assuming that you are Mutoni, as their representative, what team management strategies can you apply to solve the above given issue?
4. Using your college-based club example, analyze the advantages of the club working as a team.
Skills lab 11:
Read and analyse the scenarios below and answer the questions that follow:
Scenario 1
Mushimiyimana is the leader of an organization that provides computer services. She has realized that there is a problem with the way they advertise their business. Sitting at her desk, she lists some approaches they can take to improve their communications. She then tells the other employees what they need to do without asking for anyone else’s ideas.
Scenario 2
Abatoni is the manager of a catering service called Best Bakery. They have been asked to prepare cakes for an upcoming wedding of the daughter of a political leader. She decides that coconut cakes will be the best and calls the staff together to discuss the order. She informs them of the order and then launches into a speech about all the advantages of making coconut cake. Others express an interest in making vanilla cakes but in the end Abatoni convinces them coconut is best.
Scenario 3
Karamuzi is the owner of a successful auto mechanic workshop. A customer has brought a vehicle in that has multiple problems. He asks his team to assess the problems and get back to him with possible solutions. A few hours later they have a meeting to discuss what they have found and what they propose. They have a discussion, Karamuzi gives some advice and the team begins the repairs.
Scenario 4
Habimana runs a tailoring business in town. He has 5 employees. With an upcoming holiday, they have many orders to fulfill. Habimana gathers all the employees to get their opinions on how to best manage the process so they can meet the deadlines. In the end, they decide together to divide tasks amongst themselves. Habimana and two others were tasked with cutting and shaping the cloth while the other tailors would do the sewing. In the end they managed to keep all of their customers satisfied.
1) Describe the leadership styles applied in each of the scenarios above and give reasons to support your answers.
2) Role-play, justifying how this was the most appropriate style to apply.
3) In your school business club practices, imagine the situation where your club president has inappropriately dictated the club members to do something and come up with best advises on how better he / she could influence the team members to accomplish the tasks.
End of unit 11 assessment
1) Read and analyze the following scenarios and decide which leadership style is depicted:
a) Juliet is the leader of an organization that provides computer services. She has realized that there is a problem with the way they advertise their business. Sitting at her desk, she lists some approaches they can take to improve their communications. She then tells the other employees what they need to do without asking for anyone else’s ideas.
b) Jean de Dieu is the owner of a successful auto mechanic workshop. A customer has brought a vehicle in that has multiple problems. He asks his team to assess the problems and get back to him with possible solutions. A few hours later they have a meeting to discuss what they have found and what they propose. They have a discussion, Jean de Dieu gives some advice and the team begins to repair.
c) Peter runs a tailoring business in town. He has 5 employees. With an upcoming holiday, they have many orders to fulfill. Peter gathers all the employees to get their opinions on how to best manage the process so they can meet the deadlines. In the end, they decide together to divide tasks amongst themselves. Kwesi and two others were tasked with cutting and shaping the cloth while the other tailors would do the sewing. In the end they managed to keep all of their customers satisfied.d) Keza is one of the leading members of the community youth association in a rural area. Following the illness of several community members, she decided it was necessary for community members to have better access to potable water. During weekly youth association meetings, she shared her vision and got others interested in resolving the problem. Together they researched different possibilities such as working with local government offices to mobilize resources to install a borehole (pipe drilled down to access clean water). During their association meetings, Keza always recognized the effort individuals were making. Eventually the youth were able to mobilize the resources necessary to access clean water. The youth and the community members were all inspired by her commitment and hard work to make it happen.
2. Sheja is the manager of a catering service called Best Bakery. They have been asked to prepare cakes for an upcoming wedding of the daughter of a political leader. Advise Sheja on how she would motivate her employees to successfully complete the order in time and reveal which leadership style is suitable for this scenario.
UNIT 13: DRAFTING A VALID BUSINESS CONTRACT
Key Unit Competence: To be able to make a valid contract in business operations
Introductory activity
Sam met with a businessperson on a football match who requested him to be supplied with beans at a price of 500 Frws per kilogram. When Sam delivered 200kgs, he was not paid the full amount of money they had agreed upon.
Questions.
a) Has such a situation ever happened to you? When and what happened?
b) What mistake did Sam do?
c) Assume you were the one in such a situation, what would you do?
d) What advice would you give to Sam and the businessperson?
e) What lessons do you learn from the above situation?
12.1 Meaning and Forms of Business contracts
Activity 12.1
Bayigana operates a small medium enterprise in Huye and wants Ishimwe to supply his business with goods. Bayigana tells her to start right away and supply the goods they will discuss other issues later. She insists that she needs an agreement between the two
especially on issues of price, mode of payment, delivery period, quantity and quality, among others.
Questions;
a) How do you call an agreement Ishimwe insists should be between them?
b) Do you think she is right to have the agreement before starting the supply of goods? Give reasons to support your answer.
c) In which way/form may the agreement be made between the two? Support your answer
d) What do you understand by the term contract and business contract?12.1.1 Meaning of contract and Business contract
A contract is a legal binding between two or more parties and can be enforced by law.
Example in marriage the woman and man make a contract during civil marriage. The three parties are woman, man and witness will come to testify before the law represented by Executive secretary of sector.
Before starting a job, the employer and employee make a contract. In this case there two main parties and the law is now represented by official labor law because it is not possible to make a job contract which is against the labor law.
A business contract is a legal binding between two or more persons/ entities
to perform an agreed business transaction and can be enforced by law. The day today running of the business involves making contractual obligations with suppliers, buyers etc.
Example: A farmer can make a contract of supplying chicken to the hotel. In most cases this contract is written and two parties should sign to that document. This contract should
follow the official law like the right person who represents the hotel and the farmer should have maturity age. The two parties should sign with free consent. Once signed it becomes a document which binds the two parties.
12.1.2 Forms of business contracts
Oral contract is an agreement between two or more parties by use of words. They are non-written contracts. They rely on the good faith of the parties but can be difficult to prove. Once the contract is verbal, the wittiness is mandatory and provides evidence.
Written contract is a contract documented on paper, signed by the contracting parties and witnessed by a third person (the witness).

Read the following statements and answer questions that follow:
- Nkusi wants to lend his car to Niragire for 5,000Frw per day for five days.
- Niragire agrees with a handshake to borrow the car from Nkusi and pay the money in witness of Rukundo.
- Ntezimana promises to take his girlfriend Bagirishya for an outing to Lake Kivu.
- Niyokwizerwa promises to pay 10,000Frw to whoever finds her lost phone.
- Gato puts on paper his commitment to provide printing services to Umutoni on agreed terms.
- Mutesi promises to pay for her brother’s school fees and puts it in writing.
Questions:
Which of the above statements are?
a) Contracts.
b) Not contracts.
c) Business contracts.
12.2 Valid contract.
Activity 12.21) Analyze the figure below and answer the following questions.
Questions
a) Do you think the above sample is a contract? Give reasons to support your answer.
b) Name the elements of the written contract above.
c) Do you think the sample above is a valid contract? Support your response by mentioning the elements of a valid contract in the sample provided. (If any?)
2) Describe different parties to a valid contract.
3) Kamaliza’s 16-years old son, who looks a bit older, he signed a contract joining a health club. He has dues of 15000 Frws. is this contract valid?
12.2.1. Parties to a contract
are persons who can sign the contract. For a contract to be considered valid, it shold include three parties. These are Offeror/promisor who makes an offer, Offeree/promisee to whom an offer is made and Witness who sees an event happening.
For example, in the above template Mr. John Muhire Offeror/promisor agrees to sell his car to Umugwaneza Nadine Offeree/promise at 2 million.
Two parties to contract Offeror/promisor and Offeree/promisee must have “capacity”, legal ability to make valid contract. Assent of parties is a must. If either parties is deprived, use of his understanding or deemed by law not have attained then such an agreement shall not bind him. All parties should have Age majority, sound mind and qualified for contract by law.
The information of two parties in contract should be clear, complete and concise. In any case, the names are not enough, it should be better to include other information like number of identification card, the location where those documents are issued. Ensure that all information is well reflected on the contract. For example, in above contract there is a mistake in writing names. Umugwaneza Nadine who sells the car is not the same Mugwaneza Nadine who signs the contract. These slit mistakes can disqualify the contract.Witness is a person who sees an event happening. In a legal contract, a witness is someone who watches the document be signed by the person they are being a witness for and who verifies its authenticity by signing their own name on the document as well. However, if you have a legal document such as a mortgage or a Will the chances are that you will want a witness to attest to your signature. Generally, the person you choose to witness a document should have no financial or other interest in an agreement. A neutral third party is the best choice
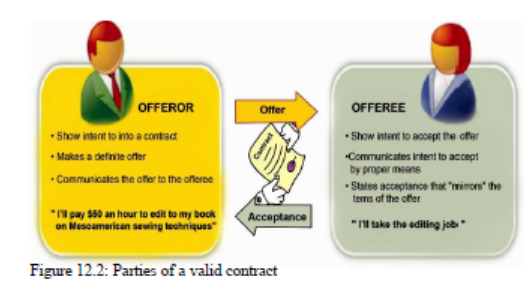
12.2.3. ELEMENTS OF A VALID CONTRACT.
For a contract to be valid and therefore enforceable by law, it must have the following elements:
Intention to be bound by the contract: the two parties should have intended that their agreement be legal. Domestic agreements between husband and wife are not taken as valid
Offer and acceptance: there must be an offer and the two parties must lawfully come to acceptance leading to a valid contract. Until an offer is accepted, it’s not a valid contract
Consideration/price: this is the price agreed upon by the parties to the contract and paid by one party for the benefit received or promise of the other parties
Capacity of the parties: the parties to the contract must have contractual capacity for the contract to be valid, i.e. should be sober, above 18years, not bankrupt, not insane, properly registered.
Free Consent: parties to the contract must agree freely without any of the parties being forced to accept or enter the contract
Legality/lawful object: the consideration/object of the contract must be legal and not contrary to the law and public policy.
Possibility of performance: if the contract is impossible in itself either physically or legally, then such contract is not valid and cannot be enforced by law
Certainty: the terms of the contract must be clear and understandable for a contract to be valid. If the terms are vague or ambiguous, where even the court may not be able to tell what the parties agreed, then it will be declared invalid.
Imagine if you make a contract without considering the elements of a valid contract. what will happen if the person/ business refuses to pay?
12.3 Designing a contract sample
Prepare a sample of a contract for your school business club with supplies.Employee Contract Template:
Employment Contract
This contract, dated on the ____ day of ______________ in the year 20____, is made between [company name] and [employee name] of [city, state]. This contract constitutes an employment agreement between these two parties and is governed by the laws of [state or district].
WHEREAS the employer desires to retain the services of the employee, and the employee desires to render such services, these terms and conditions are set forth.
IN CONSIDERATION of this mutual understanding, the parties agree to the following terms and conditions:
1. Employment
The employee agrees that he or she will faithfully and to the best of his/her ability to carry out the duties and responsibilities communicated to him/her by the employer. The employee shall comply with all company policies, rules and procedures at all times.
2.Position
As a [job title], it is the duty of the employee to perform all essential job functions and duties. From time to time, the employer may also add other duties within the reasonable scope of the employee’s work.
3.Compensation
As compensation for the services provided, the employee shall be paid a wage of ___________ [per hour/per annum] and will be subject to a[quarterly/annual] performance review. All payments shall be subject to mandatory employment deductions (State taxes, Social Security, Medicare).
4.Benefits
The employee has the right to participate in any benefits plans offered by the employer. The employer currently offers
5.Probationary Period
It is understood that the first [time frame] of employment constitutes a probationary period. During this time, the employee is not eligible for paid time off or other benefits. During this time, the employer also exercises the right to terminate employment at any time without advance notice.
6.Paid Time Off
Following the probationary period, the employee shall be eligible for the following paid time off: • [length of time for vacation] • [length of time for sick/personal days] • Bereavement leave may be granted if necessary.
The employer reserves the right to modify any paid time off policies.
7.Termination
It is the intention of both parties to form a long and mutually profitable relationship. However, this relationship may be terminated by either party at any time provided [length of time] written notice is delivered to the other party.
The employee agrees to return any employer property upon termination.
8. Non-Competition and Confidentiality
As an employee, you will have access to confidential information that is the property of the Employer. You are not permitted to disclose this information outside of the Company.
During your time of employment with the employer, you may not engage in any work for another Employer that is related to or in competition with the Company. You will fully disclose to your employer any other Employment relationships that you have and you will be permitted to seek other employment provided that (a.) it does not detract from your ability to fulfill your duties, and (b.) you are not assisting another organization in competing with the employer.
It is further acknowledged that upon termination of your employment, you will not solicit business from any of the employer’s clients for a period of at least [time frame].
9. Entirety
This contract represents the entire agreement between the two parties and supersedes any previous written or oral agreement. This agreement may be modified at any time, provided the written consent of both the employer and the employee.
10. Legal Authorization
The employee agrees that he or she is fully authorized to work in [country name] and can provide proof of this with legal documentation. This documentation will be obtained by the employer for legal records.
11. Severability
The parties agree that if any portion of this contract is found to be void or unenforceable, it shall be struck from the record and the remaining provisions will retain their full force and effect.
12. Jurisdiction
This contract shall be governed, interpreted, and construed in accordance with the laws of [state, province].
In witness and agreement whereof, the Employer has executed this contract with due process through the authorization of official company agents and with the consent of the employee, given here in writing.Employee Signature
Date
Company Official Signature
Source: www.betterteam.com/employee-contract-template
Sample of a sales contract
PRIVATE CAR SALES CONTRACT
The Car Details
Make: Toyota SOLD FOR:……… frws
Model……… Registration Number…….. Registration document completed by buyer/seller ..Yes/No . Mileage………. Registration document (V5) exchanged ....Yes/No .
Additional notes and comments agreed on this sale
SELLER'S DETAILS: Name…………….. Address……………… CERTIFICATE of PURCHASE: I am the undersigned buyer of the above car. I have purchased it from the seller named above for the amount of cash also mentioned above (SOLD FOR). This is the final price agreed. I have paid for this car in full and I am in receipt of this car and all the relevant documents to it. The Seller above also acknowledges being in full receipt of all the total amount but I do accept that full title to the car does not fully pass from the seller to purchaser until all cash is paid. Any cheques will need to be cleared before full title passes to myself. It is fully understood that this vehicle is sold as seen. I the buyer agree that I have tried, tested, and approved this car as suitable for my personal needs without any representations, warranties or conditions expressed or implied whatsoever.
Buyer's Name:…………………
Buyer's Address: …………
Buyer's Signature in agreement: …………
Seller's Signature in agreement: …………
Date: …………
Assume, your parents have houses to rent at home, help them design a rental contract that will be signed by the tenants.
Skills Lab 12
With reference to the knowledge of Business contracts, design contract templates to be used in the school business club when dealing with; a) suppliers. b) Customers, c.) Employees of the club, d.) Club members.
End of Unit 12 Assessment
1) Read the case study below and answer questions that follow.
Shine Business club
Shine business club wanted 3crates of soda which they wanted to sell to their school that was organizing a visiting day. Chantal an active member of the club having been close to Bizimungu an entrepreneur dealing in retail business convinced the club to deal with him. The club paid him and agreed he would deliver the sodas to the club after three days but unfortunately after the agreed time, he didn’t deliver the sodas as expected. When the club contacted him for the sodas, he denied having entered any dealing with them that if he did, he would be having at least a formal document to prove that. The club reported the matter to the school administration, but it couldn’t help them since it was not notified of that dealing.
a) What are some of the essential elements of a valid contract observed in the above case study?
b) Was there a valid contract in the above case study? Support your answer
c) What advice do you give to shine business club?
d) How would you approach the situation or the above problem if it was your business club?
2) Analyze the example below and answer questions that follow:
Nkusi and Mukarutesi are capable adults. Nkusi is in the need for a new car. it is on a budget, so he scans the classified advertsiments and finds Mukarutesi, who is selling an old Toyota Carina for 2,000,000Frw. Nkusi calls Mukarutesi and offers 1,800,000Frw. Mukarutesi accepts Nkusi’s offer and they decide to meet. At the meeting, Nkusi hands over 1,800,000Frw and Mukarutesi hands over the keys for the Toyota Carina.
Questions:
a) Is there a valid contract in the above example?
b) Referring to the elements of a valid contract, support your response.
c) Which form of business contract would you advise Nkusi to sign with Mukarutesi?
d) What do you think may lead to the contract in the example above to be terminated?
1) Read the following passage and answer questions that follow.
Ntwali started a business selling general merchandise in his community. He is renting the place where his business operates. Ntwali paid his property owner three months’ rent in advance but never asked for receipt. After two months, his property owner says he wants the rent for the two months. Ntwali is perplexed and tries to remind the property owner that he paid his rent for three months. The property owner denies and asks Ntwali for proof of the payment which he does not
have. Ntwali is stuck, does not know what to do while the property owner threatens to evict him if he does not pay his rent.
Questions:
a) What is the cause of the conflict in the example above?
b) Advise Ntwali on how he can resolve the conflict with the property owner
c) What are the disadvantages of the form of contract between Ntwali and the property owner?
d) Help Ntwali design a written contract that he can sign with his property owner to avoid such conflicts again.UNIT 13: TAXES IN BUSINESS
Key unit competence: To be able to analyze the role of tax towards economic development of a country and pay taxes.
Introductory Activity: A case study
Why Do You Have to Pay Taxes?
Every year around, before and after June 15, everybody especially business people will be discussing about tax changes in the national budget. This is because tax reforms and new taxes introduced are announced on that day. However, have you ever wondered why you and businesses need to pay taxes?
In Rwanda, there are arms of the government (ruling bodies) from the village, sector, district, provincial and national levels. These bodies comprise: Legislature (who make laws), Executives (who enforce laws) and Judiciary (exercise laws). The salaries that public servants receive to do their jobs come from taxes. Paying taxes is considered a civic duty, although doing so is also a requirement of the law.
Taxes take many forms, too. When you work at a job to make money, you pay income taxes. Depending on how much money you make, a certain percentage (part) of the money you make is withheld (kept out of your paycheck and sent to the government).
When you buy things at a store, you also usually pay sales tax, which is a percentage of the cost of the item charged by the store. If you own property, you also pay property taxes on the value of your property.
Paying your taxes is considered a civic duty, although doing so is also a requirement of the law. If you do not pay your taxes, the government agency that oversees taxes — the Rwanda Revenue
Authority or RRA - will require you to pay your taxes or else face penalties, such as fines or going to jail.
The money you pay in taxes goes to many places. In addition to paying the salaries of government workers, your tax also help to support common resources, such as police and firefighters.
Tax money helps to ensure the roads you travel on are safe and well-maintained. Taxes fund public libraries and parks. Taxes are also used to fund many types of government programs that help the poor and less fortunate, as well as many schools!
Each year as the “Tax Day” rolls in, adults of all ages and businesses must report their income to the RRA, using special tax forms. There are many, many laws that set forth complicated rules about how much tax is owed and what kinds of special expenses can be used (“written off") to lower the amount of taxes you need to pay.
For the average worker, tax money has been withheld from paychecks throughout the year. On “Tax Day," each worker reports his or her income and expenses to the RRA.
Employers also report to the RRA how much they paid each worker. The RRA compares all these numbers to make sure that each person pays the correct amount of taxes.
If you have not had enough tax money withheld from your checks throughout the year to cover the amount of tax you owe, you will have to send more money (“pay in") to the government. If, however, too much tax money was withheld from your paychecks, you will receive a check (get a “refund") from the government.
Adapted from https://wonderopolis.org/wonder/why-do-you-have-to-pay-taxes)
From the passage answer the following questions:
a) What are the major changes expected by people especially business people on June 15, every year?
b) What makes the businesspeople so anxious to know the changes mentioned above in a)?
c) Why do you think it is important for businesses to pay taxes to the government?
d) How do the following benefit from taxes?
i) Entrepreneur.
ii) Government.
iii) Society.
e) Identify and briefly explain at least two types of taxes paid in Rwanda?
f) What happens to businesses or people who do not pay taxes?
g) What is the difference between tax and taxation?13.1 Tax and business tax
Activity 13.1
1. Explain the meaning of the following terms used in taxation:
a) Tax b) Business tax
2. In your community, you have probably heard people and business people complaining about the taxes they pay or charged to different or similar items. Identify any 5 things you have heard normally people complain about.
3. If you were the one determining or imposing taxes to people and businesses, mention any five things you would put into consideration.
Meaning of taxation concepts
Tax is a fee without direct exchange requested to the members of the community by the State according to the law, to financially support the execution of the government tasks.
Business tax refers to compulsory and non-refundable payments made by the business to the government or local authority to raise revenue to the government or local authority.
Taxation is a system of raising money or revenue by the government from individuals/businesses and companies by law through taxes.
Taxation is a system/practice of government collecting money from its citizens to pay for public services.Characteristics or principles of a good taxation system
A good tax system should possess certain characteristics. These include the following.
1) Convenience: places, periods and seasons in which the tax dues are collected should be convenient to the taxpayer. For example, the convenient time to a trader is when s/he has made a profit. For a farmer, is when s/she has sold his/her produce
2) Simplicity: the type of tax and the method of assessment and collection must be understandable by both the taxpayer and tax collectors. Complicated taxes may lead to disputes, delays and high costs of collection in terms of time and resources.
3) Certainty: the taxpayer must know the nature, base and amount of tax without doubt. Unpredictable taxes discourage investment and reduce work effort. Simply the tax should not be arbitrary.
4) Economy: the cost of collection and administration of tax must be much lower than the tax collected
5) Elasticity: a tax should change directly with a change in the tax base. If the tax base increases, the tax charged on the tax base should also increase.
6) Productivity: the fiscal authorities should be able to predict and forecast accurately the revenue a particular tax would generate and at what rate it would flow in.
7) Equity: tax assessment should be in such a way that taxpayers bear a proportionately equal burden. I.e., people who earn more income should be taxed more than those who earn less income.
8) Diversity: this canon requires that there should be several taxes of different varieties so that every class of citizen may be called upon to pay something towards the national priorities
Application activity 13.1
1. Why is it important to have principles of taxation?
2. Referring to the principles(characteristics) of a good taxation system you know, briefly explain why each is important to the taxpayer and tax authority (RRA)
3. With examples, differentiate between Tax and Taxation
13.2. Importance of paying taxesA good taxation system can contribute a lot to the economic development of a country and its national exchequer
Sources: http://www.kigalicity.gov.rw Figure 13.2 Taxes help the government to build infrastructures
Activity 13.2
1. With examples from your community or Rwandan community at large, why do you think people and business enterprises need to pay taxes to the government?
2. As an entrepreneur to be or referring to activities of entrepreneurs in your community, how do you think businesses or entrepreneurs benefit from paying taxes?
3. In general, how does your society benefit from paying taxes? Give examples to support your views.Importance of paying taxes to an entrepreneur
• Paying taxes by the entrepreneur helps the business activity to continue, as it does not face penalties and associated costs from the RRA for non-payment.
• When an entrepreneur pays taxes, it improves his/her reputation or public image which may result in increased customers and better services from the government
• To avoid inconveniences of closure of the business and its associated costs: when entrepreneur fails to pay assessed taxes, his/her business is subject to penalty even closure to some cases.
• Business needs certain infrastructures to operate successfully such as roads to move raw materials, finished goods, workers; security for their enterprises, goods, among others, which are provided by the government.
• Paying taxes means contributing money to government agencies or departments such as Development Bank of Rwanda (BRD), Business Development Fund (BDF), which support entrepreneurs to operate business activities through soft loans and other financial support.
Importance of paying taxes to the government
• Source of government revenue: taxes are the main source of government revenue to finance its public expenditure. So taxes enable the government to pay it workers, construct roads, maintain security, provide health care, education among others
• Taxes benefit the Rwandan government to meet its objectives and goals such constructing affordable houses to the citizens which helps improve the standards of living
• Taxes help the government to finance its policies especially on poverty alleviation through programs such as “GIRINKA”, “VUP”, “UBUDEHE” among others
• Taxes enable the government to regulate the prices of goods and services in the country hence ensuring a low cost of living and maintaining the standards of living of the citizens
• Taxes enable the government to maintain a balance between the poor and rich. The government uses the taxes from business people to provide services needed by the poor, which otherwise the rich could not provide.
•Taxes enable the government to promote its policy industrialization through reducing products from other countries that would otherwise outcompete the home industries.
• Taxes enable the government to ensure that the citizens have enough products. This can be through taxes charged to reduce products moving out of the country or removing taxes on goods needed in the country. This helps maintain a high standard of living.
Importance of paying taxes to Society
• There are reduced rates of poverty among the community due to a significantly equal distribution of income through various activities and projects set by the government.
• Improved wellbeing among the vulnerable and elderly as they benefit from the different government programs financed through taxes.
• Reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy due to improved access to health facilities and services.
• Increase in the percentage of the population that completes secondary and TVET education, reducing the literacy levels, improving on the peoples’ skills through programs such as 12YBE.
• Increased community/social solidarity, general happiness, life satisfaction, and a significant more trust among the community members and for public institutions.
• Taxes are charged on some products to discourage their production and usage hence controlling over-exploitation of resources as well as protecting the environment which is vital for the existence of the society.
Application activity 13.2
1. By giving specific examples from your community, how does your society benefit from taxes?
2. What do you think would happen in the country if taxes were not paid?13.3. Calculation of taxes
Activity 13.3
1. Do you think it is important for an entrepreneur to know how to compute the amount of tax he/she is supposed to pay? Give reasons.
2. What do you think the term “Pay-As You-Earn (PAYE) tax means”? And how is it calculated?
There is a variety of taxes that a business has to pay such as corporate income tax, trading license tax, professional income tax or PAYE (Pay-As-You-Earn), rental income tax, fixed asset tax, Value Added Tax (VAT), Sumptuary tax, etc. but here, an emphasis is made on:
1. Pay- As- You Earn (PAYE) and
2. Value Added Tax (VAT
Pay-As -You-Earn (PAYE) tax or professional income tax The tax law requires that when an employer makes available employment income to an employee the employer must withhold, declare, and pay the PAYE tax to the Rwanda Revenue Authority within 15 days following the end of the month for which the tax was due.PAYE: is composed of Wages, salaries, leave pay, sick pay, medical allowances, pension payment etc. All kinds of allowances including any cost of living, subsistence, rent, and entertainment or travel allowances. Pay-As-You-Earn tax is computed as follows:
Example: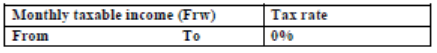
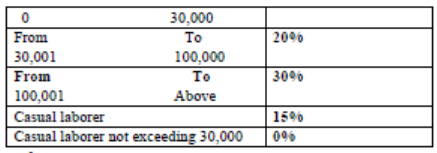
The following relate to monthly salaries of Kanyarwanda enterprise employees for 2018.
a) Rukundo earns 450,000Frw
b) Karinganire earns 89,000Frw
c) Keza earns 28500Fw
d) Buzima earns 12,5000Frw
Required:
Calculate the total PAYE for above employees that Kanyarwanda enterprise pays to RRA every month.
Solution:
a) Rukundo :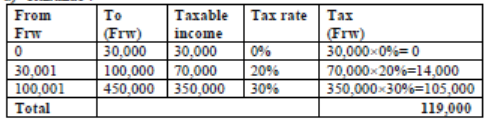
Total TAX for Rukundo = 14000+105000= 119,000Frw
b) Karinganire: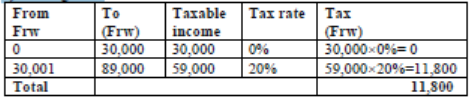
Total tax for Karinganire is 11,800Frw
c) Since Keza earns less than 30000Frw she does not pay PAYE. Her total tax =0 (28500*0)d) Buzima
Total tax for Buzima =14000+7500=21,500Frw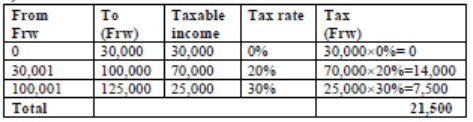
Total PAYE for Kanyarwanda enterprise every month = (119,000+11,800+21,500) Frw= 152,300Frw
Note:
Exemption for PAYE is that every person who earns income less than 30000 does not pay PAYE to RRA.
The “casual laborer” means an employee or worker who performs unskilled labor activities, who does not use machinery or equipment requiring special skills and engaged by an employer for an aggregate period not exceeding thirty (30) days during the tax period.Value Added Tax (VAT)
Source: exceldatapro.com: VAT varies according to the level of value added on a product
Value Added Tax was introduced in Rwanda in 2001. VAT is a tax on the added value achieved by a firm. This is the difference between the buying price (of raw materials) and the selling price of the product in whatever forms it is sold.
Value added = F.P – I.C where F.P is final product, IC is intermediate costs
Tax rate
The VAT rate is applied to duty-free goods. Several rates can be applied depending on the nature of products. The standard rate is usually 18%
Example 1:
UTEXRWA industry bought cotton from a local farmer worth 1200, 000Frw to use in production of blankets.170 blankets were manufactured and sold to a wholesaler at a cost of 4,000,000Frw who later supplied it to LEMIGO hotel at a value of 8,000,000Frw VAT included. Calculate the value of VAT paid on blankets.
Possible solution
Step 1 VAT paid by local farmer:
VAT =1,200,000Frw*18% = 216,000Frw
Step 2 VAT paid by wholesaler:
VAT = FP -IC where FP is final product and IC is intermediate cost
Value added =4,000,000Frw-1,200,000=2,800,000Frw
VAT paid by wholesaler =2,800, 000Frw*18%= 504,000Frw
Step 3 VAT paid by LEMIGO hotel:
VAT paid by LEMIGO hotel= 8,000, 000-4,000,000Frw= (4,000,000Frw*18%)=720,000Frw
Therefore, total VAT =216,000+504,000+720,000 =1440, 000Frw
Alternative:
VAT is calculated on sales.
VAT =sales *18%
Which is equal 8,000,000Frw*18%=1,440,000Frw
Example 2:
A students’ business club has sold goods to XY enterprise at 100,000 Frw VAT excluded.
Calculate:
a) VAT received
b) The price VAT included
Solution:
a) VAT received=𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 𝑉𝐴𝑇 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑙𝑢𝑑𝑒𝑑∗18100=100,000𝐹𝑟𝑤∗18100=18,000Frw
b) The price VAT included=100,000Frw+18,000Frw=118,000Frw
OR
The price VAT included=𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 𝑉𝐴𝑇 𝑒𝑥𝑐𝑙𝑢𝑑𝑒𝑑∗118100=100,000𝐹𝑟𝑤∗118100=118,000Frw
Example 3:
A students’ business club has bought goods from XY enterprise at 1,000,000 Frw VAT included.
Calculate:
c) VAT paid
d) The price VAT excluded
Solution:
a) VAT paid=𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 𝑉𝐴𝑇 𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑙𝑢𝑑𝑒𝑑∗18118=1,000,000𝐹𝑟𝑤∗18118=152,542.37Frw
b) The price VAT excluded=𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 𝑉𝐴𝑇 𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑙𝑢𝑑𝑒𝑑∗100118=1,000,000𝐹𝑟𝑤∗100118=847,457.63Frw
OR
The price VAT excluded= Price VAT included VAT paid
= 1,000,000Frw- 152,542.37Frw = 847,457.63Frw
Application activity13.3
1. A students’ business club (SBC) in one of the TTCs has the following regular employees. Their salaries are in accordance with their appointment as follows:

Calculate
a) The PAYE tax on each individual employee
b) The PAYE tax to be withheld and paid by the business club to RRA
2. Using the information available on the above EBM issued receipt, compute the following:
a) Price VAT excluded
b) VAT to prove the amount appearing on the receipt
Skills lab 13
Justify the following statements with concrete examples:
• “Taxes are more of a benefit than a cost to an entrepreneur”
• “Tax evasion is a shortcut to business growth”
2. A business club at one of the TTCs has 3 regular employees namely KALISA, KALIZA and BERWA with monthly salaries of 35,000Frw, 40,000Frw and 20,000Frw respectively. On top of that the business made sales of 300,000Frw VAT exclusive, and the input VAT is 34,000Frw.
a) Calculate the total amount of tax that the business club has to pay to RRA
b) Advise the above business on how the above taxes would be paid.
End of Unit 13 Assessment
1. It is said that “tax is the free money to central or local authorities from taxpayers” do you agree with this statement. Justify your answer
2. Describe any four characteristics of a good taxation system
3. How are taxes used by government to:
a) Support Entrepreneurs
b) Support the community
4.
a) …………. punishment is the jail for a period between six (6) months and two (2) years; even the Minister’s order determines an award given to any person who denounces a taxpayer who engages in that act.
b) …………. is the compulsory and non-refundable payment made by the business to the Government or Local Authority so as to raise their revenues.
c)…………. is the one that is exempted from VAT.
d) …………. one of the taxes vested to the local government (Districts).
e) The degree to which the taxpayers meet their tax obligations as set out in the appropriate legal and regulatory provisions is……………………….
f) The………………. means an employee or worker who performs unskilled labor activities, who does not use machinery or equipment requiring special skills and engaged by an employer for an aggregate period not exceeding thirty (30) days during a tax period.
Bibliography
1. Akazi Kanoze Youth Livelihood project, (2009), Work Readiness Trainers’ Manual
2. Educate! Exchange, (2017), Resources & Competency-based Entrepreneurship Subject S4 Skills Lab Lesson Plans
3. Kalungi Rogers, Ngobi Dennis, Mutegaya Herbert, Okoroi David, Entrepreneurship for Rwanda Secondary Schools, Learner’s Book
4. Mark Ssempija (2011), Entrepreneurship Education for Advance level and business institutions, Kampala. Uganda: Book shop Africa
5. Mark Amon Mugaru, Edward Erasmus Kayanja (2017), Ordinary Level Entrepreneurship. Kigali, Rwanda: MASTEP General Suppliers Ltd
6. Richard Barekye, Alele Kevin. (2016). Entrepreneurship for Rwandan school (senior 1 students’ book). Kigali, Rwanda: East African Educational Publishers Ltd
7. Rwanda Education Board, (2015), Advanced Level Entrepreneurship syllabus for Rwanda General Education
8. Rwanda Education Board (2018) Entrepreneurship Senior 5 - Content and activities: Experimental version, Kigali, Rwanda
9. T Manimbi and S Paarman , Entrepreneurship FOR RWANDA S1 Student’s Book
10. Microsoft. (2019). job-specification-sample-marketing-manager. Retrieved September 16, 2019, from www.thebalance.com: https://www.thebalance.com/job-specificationsample-marketing-manager-1918560
11. Schneider Electric. (2005). tac-best_practices_for_telecom_network_reliability.pdf. Retrieved March 26, 2018, from www.tac.com: https://www.schneiderelectric.co.uk/.../best_practices_for_telecom_network_reliabilit...
12. Mutamba, A. H. (2008). In entrepreneurship. kampala: mk publishers.
13. Schneider Electric. (2005). tac-best_practices_for_telecom_network_reliability.pdf. Retrieved September 10, 2019, from www.tac.com: https://www.schneiderelectric.co.uk/.../best_practices_for_telecom_network_reliabilit...
14. http://www.teammate360.eu/index.php/en/teammatehttps://www.thebalance.com/leadership-definition-2948275http://courses.washington.edu/ie337/team.pdf https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teamwork
15. http://smallbusiness.chron.com/5-sources-power-organizations-14467.html http://smallbusiness.chron.com/5-sources-power-organizations-14467.htmlhttps://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_00.htm http://s3.amazonaws.com/inee-
assets/resources/14_PEP_Facilitators_Manual_for_Community_Workshops_EN.p df
16. http://www.cheryltay.sg/5-steps-for-effective-problem-solving/
17. https://sites.google.com/a/studentmba.org/ms-desalvo-s-classroom-page/civicsand-government/unit-1a-nature-of-power-politics-and-governmenthttps://www.slideshare.net/danishmahusay/essentials-of-leadership-1
18. http://www.teammate360.eu/index.php/en/teammatehttps://www.thebalance.com/leadership-definition-2948275http://courses.washington.edu/ie337/team.pdfhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teamwork
19. http://smallbusiness.chron.com/5-sources-power-organizations-14467.htmlhttp://smallbusiness.chron.com/5-sources-power-organizations-14467.htmlSource:https://pt.slideshare.net/KritikaKeswani2/10-characteristics-of-successfulteam
