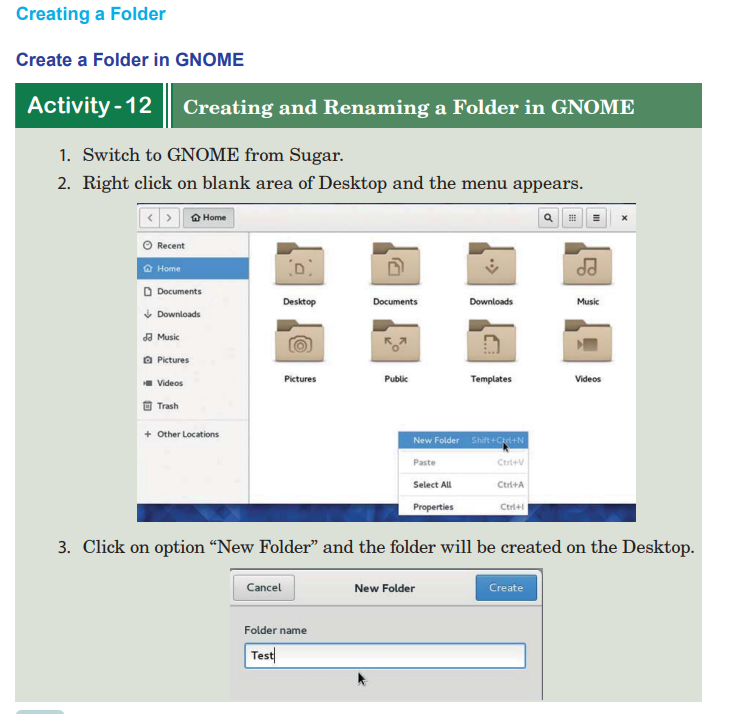
General
UNIT 3: Computer my friend
Computer is a basic need in every field.
Life becomes easier with the introduction of different Information and Communication Technology (ICT) tools.


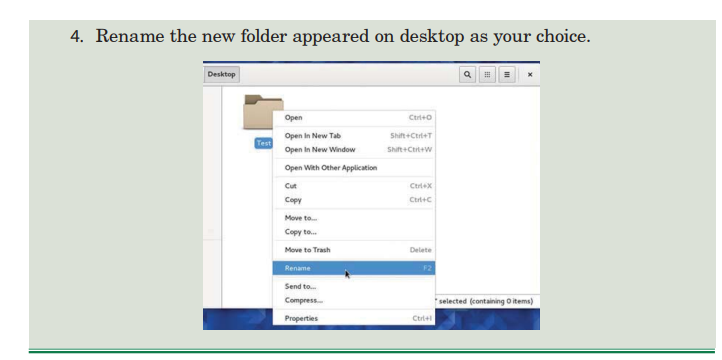
Computers, mobile phones, calculators, radios, scanner and fax machines are common ICT tools.
These tools help us to use information and share it digitally.

Computer is a machine. It accepts data and processes it.
Finally it produces output results. It is used to do difficult calculations.


A computer plays various roles in our daily life.
1. It can be used for personal computing.
2. It can be used for educational references.
3. It can be used in the field of health and medicine.
4. It can be used for scientific research.
5. It can be used for communication and entertainment.

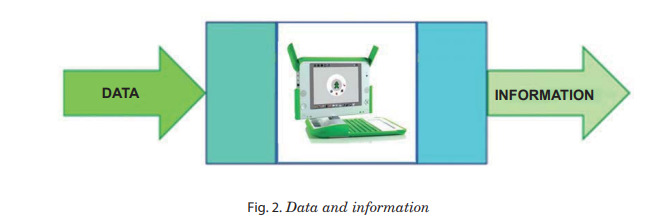
Data: Whatever you type from the keyboard is GDWD.
It may be numbers, alphabets and symbols.
Information: Computer processes data.
The processed data is called information. In a computer,
we can get information through output devices, for example, monitor and printer.


is the process of sending or receiving information.
We can communicate by speaking, writing, through art and music, and books.
With a mobile phone, we can communicate to any part of the world.
We can make calls, send and receive text messages.


1. Type a text message from a mobile phone keypad.
2. Send this message to one of your friends and a family member.
Role of Communication
Communication plays an important role in our day-to-day life.
1. It is a source of information.
2. We know what is happening around the world.
3. Without communication we cannot convey our thoughts and feelings.
d) Technology
Technology is the collection of techniques, skills, methods and processes used to complete a work.
Communication technology helps us to send and receive information.
With the help of communication technology, messages can be sent within a moment around the world.
Examples of technology used for communication are Internet, emails, fax, phones, chat groups and
social networking sites.

Internet : It is a large group of computers connected to each other.
It is used to send information quickly.
It is widely used at hospitals, railway stations, airports, schools and offices.
Website: It is a collection of web pages.
A website gives information about any subject.
Each website has its own web address.
It can be reached through an Internet connection by typing domain name in the address bar.
The first opening page of a website is called home page.

World Wide Web (WWW): It is a collection of millions of electronic pages.
These pages are interlinked just like a spider’s web.
These pages display a variety of information.
(e) Activity
Sugar is a collection of Activities.
Activities are Applications that involve active engagement from the learner.
They automatically save results to a journal, where reflections are recorded.
Activities can be shared between learners.
(f) Projects
A project is a planned set of interrelated tasks.
It should be completed over a fixed period within certain cost and other limitations.
On websites, we get necessary information regarding a project.
Online projects can be done with the help of related websites.


Sugar interface is both a desktop and a collection of activities.
Activities automatically save results to a Journal, where reflections are recorded.
You can write documents, share books and pictures or make music together with ease.
Power-on XO laptop or any computer with sugar installed, you should see the Sugar Home View.

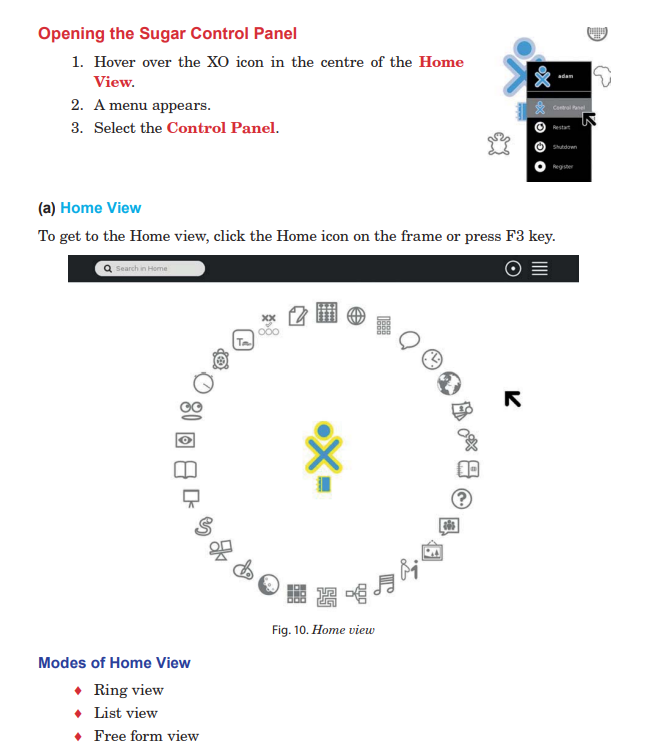
 All the icons are not arranged in a ring or a list, you can arrange
icons in a way that makes sense to you.
All the icons are not arranged in a ring or a list, you can arrange
icons in a way that makes sense to you.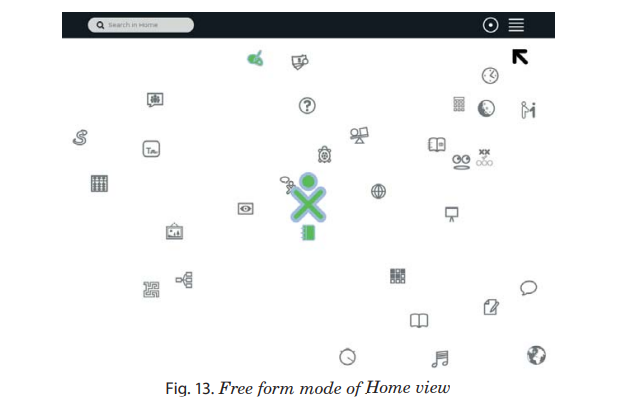

This view helps to see your friends or classmates’ activities, and you can join them in order to collaborate.

The XO menu appears when you point on the XO icon.
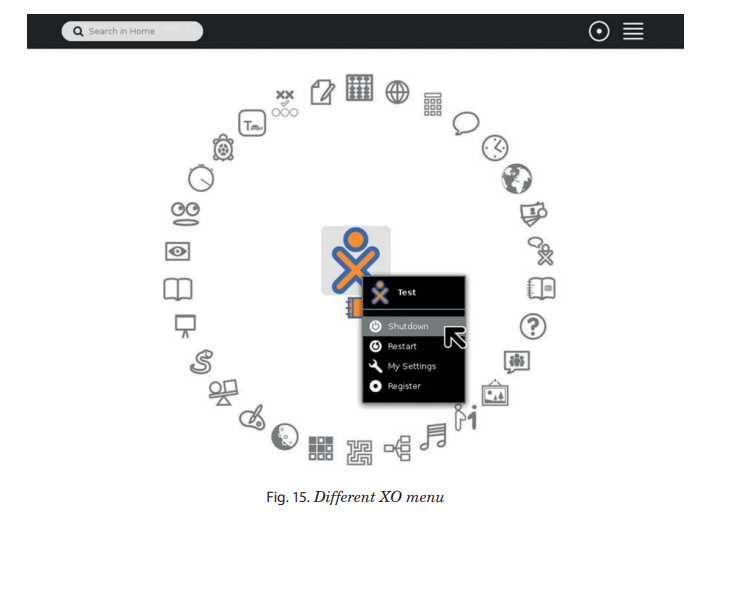

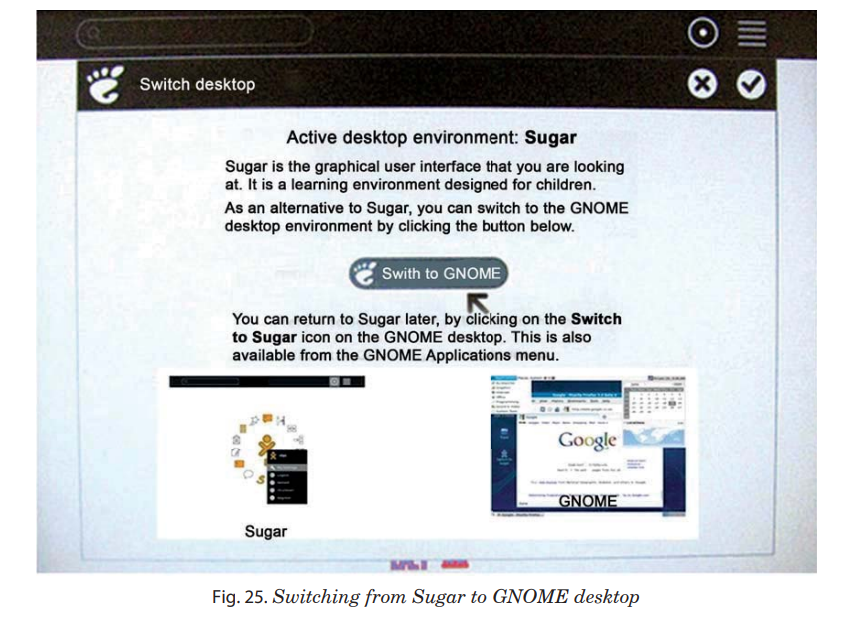
The XO laptop allows switching from sugar interface to GNOME interface.

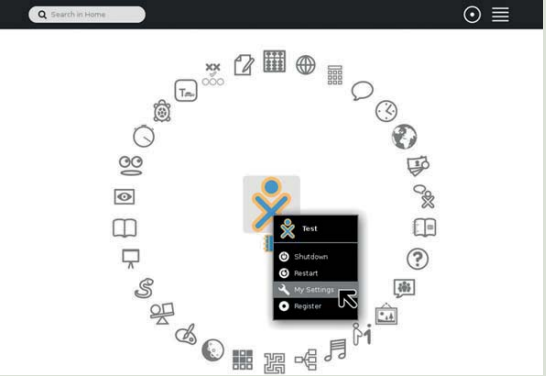
To switch to GNOME interface from Sugar Interface:
1. Hover over XO icon in the middle of ring of activities.

2. Choose the option “My Settings ".
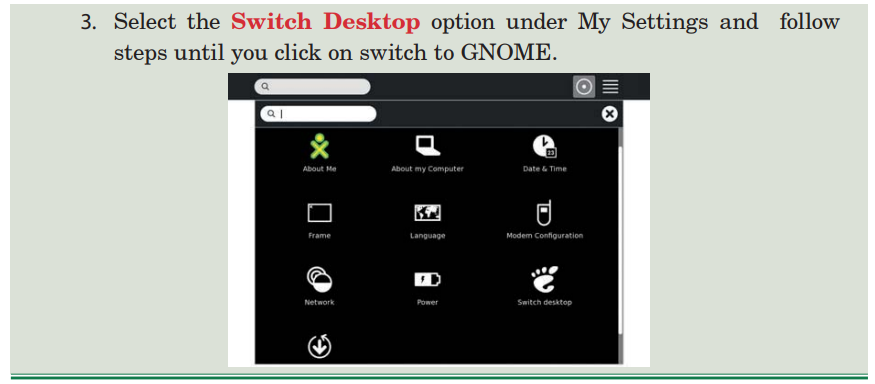
GNOME is a graphical user interface.

Figure 16 shows some major components of the GNOME desktop.
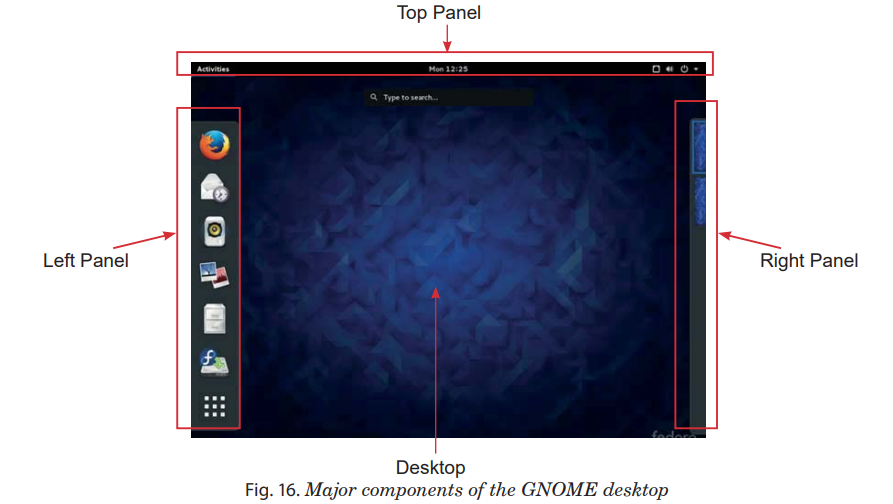

The desktop lies behind all other components on your screen.
You can place files and folders on the desktop that you want to have easy access to.
The desktop also has several special objects on it:
The computer icon gives you access to Compact Discs,
removable media such as pen drive, and also the entire files system.
All of your personal files are kept in your Home folder, labelled username's Home.
You can also open this folder from the places menu.
The Trash is a special folder where you can place files and folders you no longer need.

The bars across the top and bottom of the desktop are called top panel .
By default the top panel appears as follows:

The Application menu provides access to the applications installed in the system. The places menu provides a list of locations. On selection these are opened in file browser windows. The system menu provides options for:
configuring the system, and
desktop environment such as desktop theme and screen resolution. In the above picture of the desktop the icons next to the system menu provide quick access to common applications and tools.
The right hand side of the panel includes the current time, a volume control and a network status indicator.
The left desktop panel contains three items appearing as follows:

The area containing squares controls the currently displayed virtual workplace.
The GNOME desktop allows multiple workspaces to be active at any one time.
We can move from one application to another by clicking on one of the squares in the bottom toolbar.

A window is a rectangular area of the screen. It has a border all around and a title bar at the top. Each window displays an application. It allows you to have more than one application visible, and work on more than one task at a time.
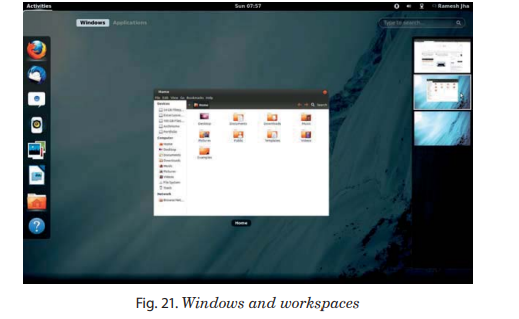
Buttons on title bar allow you to minimize, maximize, and close the windows. You can control a window’s position of the screen, as well as its size. You can control those windows which overlap other windows, so the one you want to work with is completely visible.

To work with an application, you need to give the focus to its window. Only one window can have focus at a time. The window that has focus will appear on top of other windows, so nothing covers any part of it.

Workspaces allow you to manage which windows are on your screen. Every workspace contains the same desktop, the same panels, and the same menus. By default, four workspaces are available. You can switch between them with the Workspace Switcher applet at the right of the bottom edge panel. This shows a representation of your workspaces, by default a row of four rectangles.
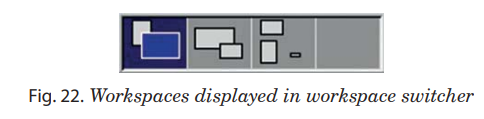

To switch between workspaces, follow these steps:
 1. Open the Launcher and click the workspace switcher button near the
bottom.
1. Open the Launcher and click the workspace switcher button near the
bottom.2. Double-click on any window or workspace to switch to it, or press the workspace switcher button again to return to your previous workspace.

1. Press
 to move to a workspace which is to the right of the
current workspace.
to move to a workspace which is to the right of the
current workspace. 2. Press
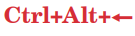 to move to a workspace which is to the left of the current
workspace.
to move to a workspace which is to the left of the current
workspace. 3. Press
 to move to a workspace which is below the current
workspace.
to move to a workspace which is below the current
workspace. 4. Press
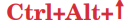 to move to a workspace which is above the current
workspace.
to move to a workspace which is above the current
workspace.
An application is a type of computer program that allows you to perform a particular task.
You might use applications:
to create text documents such as letters or reports;
to work with spreadsheets;
to listen to your favourite music;
to navigate the Internet;
to create, edit, or view images and videos.
For each of these tasks, you would use a different application.
To launch an application, open the Applications menu
and choose the application you want from the submenus.
The applications that are part of GNOME include the following:
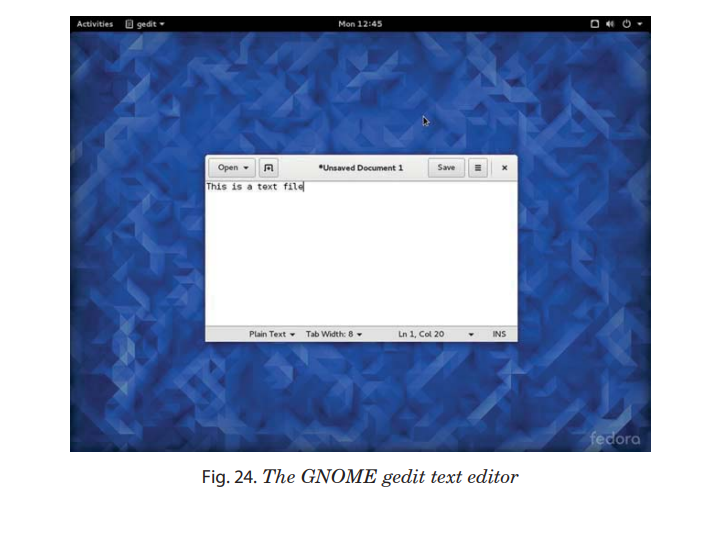
GEDIT is an application of GNOME that can be used to create,
edit, format and save a document .
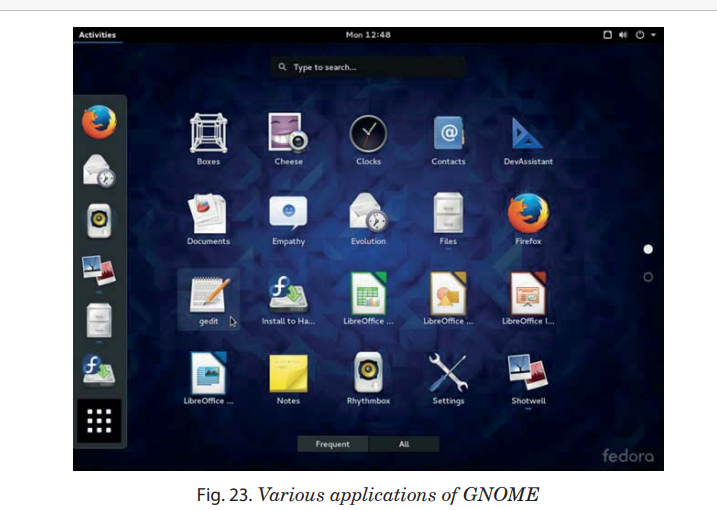
There are other applications in GNOME like, Dictionary, Image viewer and calculator.

Switching back to Sugar from GNOME can be done by clicking on icon “Switch to Sugar’’ of GNOME desktop.

The Sugar Journal records everything you do using Sugar interface. You can use a Journal as a place:
to revisit old work,
to resume incomplete work,
to organize completed work, and
to reflect upon your progress as the learner.

To show the Journal, click the - Journal icon on the Frame.
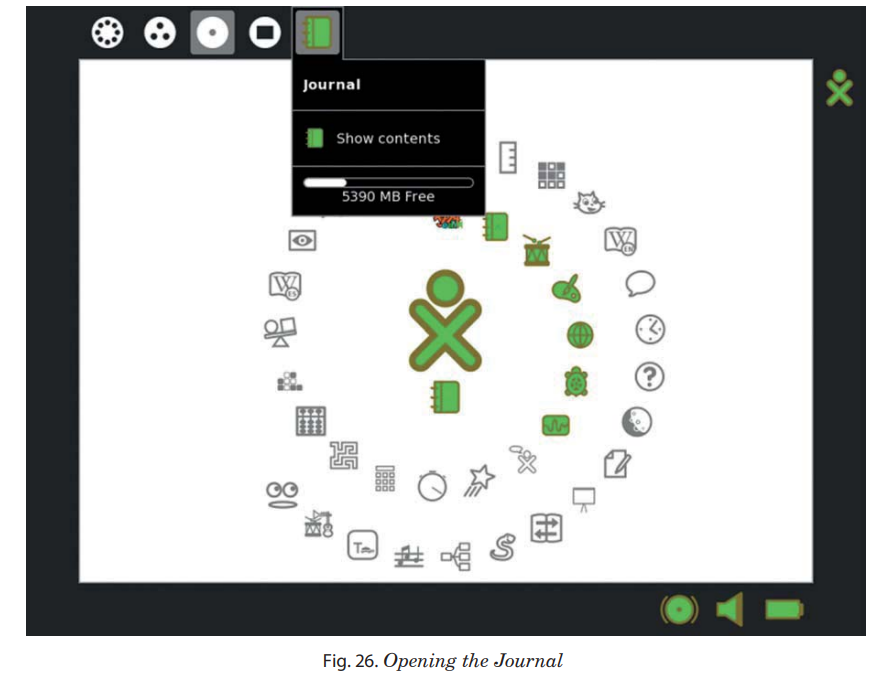
On an XO laptop, you can press the magnifying glass key
in the top row of the keyboard to immediately open the Journal and search .
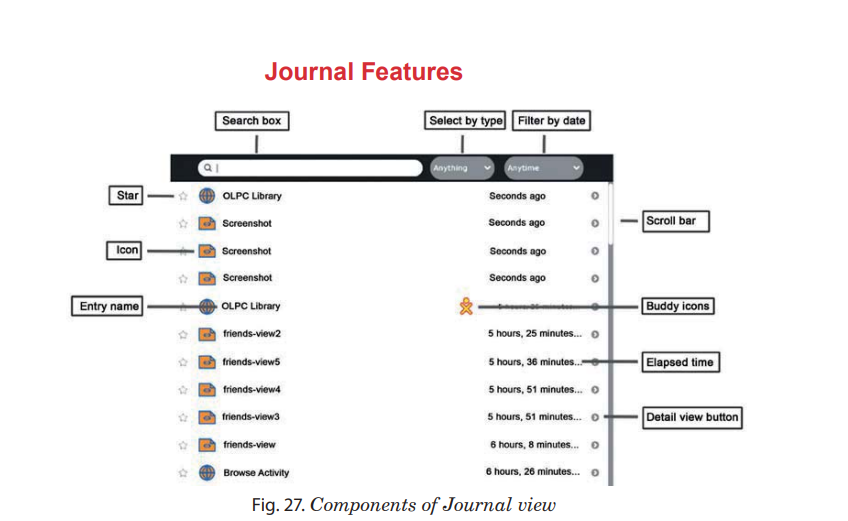
The Journal view contains a menu and a list of journal entries:
1. Star: You can mark important entries to help them stand out
in the list by clicking the star icon for that entry.
When you click the star icon, the star is colored in.
2. Icon : Each Journal entry has an icon.
The color of the icon shows who created the entry.
For example, if you copy a photo from a friend, the photo’s icon has your friend’s colors.
You can launch the Activity for the entry by clicking the icon.
A hover menu may reveal additional options. In particular,
“Erase” deletes that entry from your Journal.

3.
 Each entry has a name. You can edit the name by clicking it.
Each entry has a name. You can edit the name by clicking it. 4.
 If other participants join you in this Activity, icons in their colors
will appear here.
If other participants join you in this Activity, icons in their colors
will appear here.5.
 The Journal displays the time since the most recent change the entry .
The Journal displays the time since the most recent change the entry .6.
 Click this button to see detailed information about the
entry. See “Journal detail view”, on next page.
Click this button to see detailed information about the
entry. See “Journal detail view”, on next page. 7.
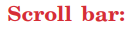 When there are more entries in the Journal than can fit on the
screen, you can use the scroll bar to scroll through them.
When there are more entries in the Journal than can fit on the
screen, you can use the scroll bar to scroll through them. 8.
 Type words in the box to search for entries that match those words.
Entries are displayed when they contain all of the typed words. Comparison will
be against all of:
Type words in the box to search for entries that match those words.
Entries are displayed when they contain all of the typed words. Comparison will
be against all of: the entry name field
the description field (see “Journal detail view”)
the tag field (see “Journal detail view”)
9.
 Choose an entry type to display only entries of that
type. Types include the Activity that created an entry, or the object type, such as,
picture, sound, text, and so on.
Choose an entry type to display only entries of that
type. Types include the Activity that created an entry, or the object type, such as,
picture, sound, text, and so on. 10.
 you can limit the Journal View to entries made
within the past day, week, or month.
you can limit the Journal View to entries made
within the past day, week, or month. You can search and retrieve a saved document in journal by using features such
as search box ,by selecting items, using options like Anything ,Anytime and Sort
View. You can also search by entering the item name in the search box.
You can search and retrieve a saved document in journal by using features such
as search box ,by selecting items, using options like Anything ,Anytime and Sort
View. You can also search by entering the item name in the search box.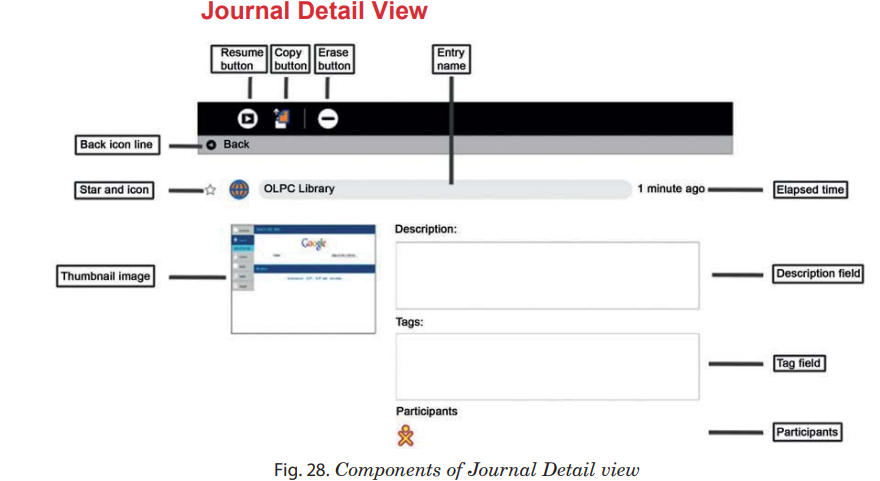
The Detail view appears when you click the
 button for an entry. This
view lets you examine and annotate the entry. The detail view has the following
components.
button for an entry. This
view lets you examine and annotate the entry. The detail view has the following
components. 1.
 You can click anywhere in this line to return to the main
Journal View.
You can click anywhere in this line to return to the main
Journal View.2.
 These items duplicate their functions on the main Journal
view—a star represents a special, never-deleted Journal entry and the icon
color indicates who created it originally.
These items duplicate their functions on the main Journal
view—a star represents a special, never-deleted Journal entry and the icon
color indicates who created it originally.3.
 Each entry has a thumbnail image that is created
automatically. The image shows the Activity screen when the last change
to the Journal entry was saved.
Each entry has a thumbnail image that is created
automatically. The image shows the Activity screen when the last change
to the Journal entry was saved. 4.
 You can change the name of the entry by clicking it and
typing in a new name.
You can change the name of the entry by clicking it and
typing in a new name.5.
 Displays the time since the most recent change to the entry.
Displays the time since the most recent change to the entry.6.
 You can type a description of the entry in this field.
Use a description to remind you of what you did.
You can type a description of the entry in this field.
Use a description to remind you of what you did. 7.
 You can enter search tags. Use keywords to describe a journal
entry so that you can find it later using the Search box in the main Journal
view.
You can enter search tags. Use keywords to describe a journal
entry so that you can find it later using the Search box in the main Journal
view. 8.
 Displays the XO icons of each person who participated in a
shared Activity.
Displays the XO icons of each person who participated in a
shared Activity. 9.
 You can click the Resume button to resume an Activity.
A hover menu may show additional options. For example, you can resume
working with an image using either the Browser or the Paint Activity.
You can click the Resume button to resume an Activity.
A hover menu may show additional options. For example, you can resume
working with an image using either the Browser or the Paint Activity. 10.
 You can copy a Journal entry to the clipboard (or to one of
the removable storage devices shown on the bottom edge of the Journal screen) by clicking the Copy button.
You can copy a Journal entry to the clipboard (or to one of
the removable storage devices shown on the bottom edge of the Journal screen) by clicking the Copy button.11.
 You can erase an entry by clicking the Eraser button.
You can erase an entry by clicking the Eraser button.
1. Plug a flash dish into the XO laptop.
2. Push on magnifying glass key to open Journal.
3. Write on the notebook two icons found on the button of Journal.
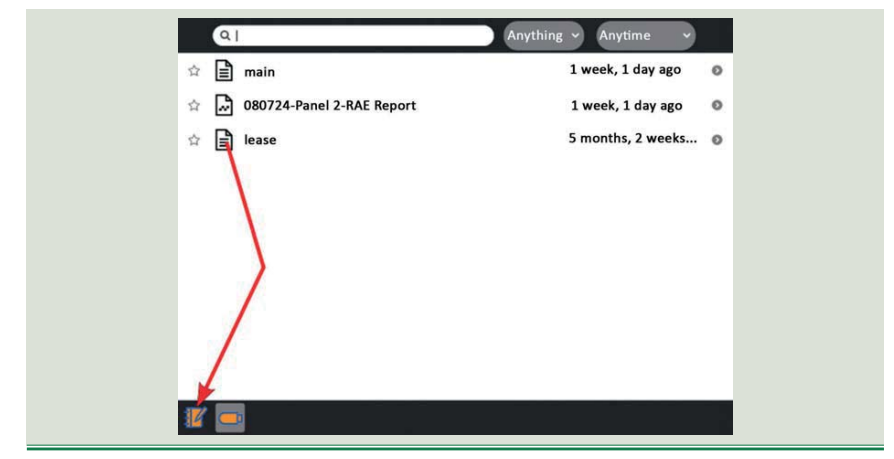
4. Open the Universal Serial Bus (USB) device by clicking on the icon representing flash disk on the bottom of the Journal. 5. Click on Journal icon besides the USB device icon to see the activities saved in Journal.
The Journal also supports external storage media such as USB device or Secure Digital (SD) card.


1. Plug USB device into XO laptop.
2. Open Journal.
3. Point on the entry you want to move and hold the touchpad key.
4. Drag down to the USB device icon.

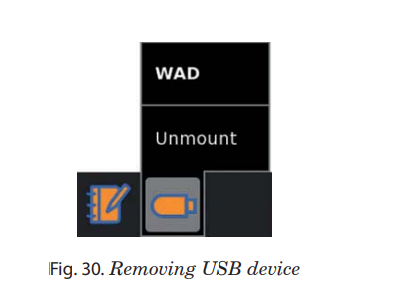
Hover over the icon of USB device and on the appeared menu, click Unmount or Remove option.

Find your friend’s XO Friend in the
 view. In your friend’s
pop-up palette menu select
view. In your friend’s
pop-up palette menu select  .
Use the search text box in the
.
Use the search text box in the  view tool bar to find a known XO friend name.
view tool bar to find a known XO friend name.

Computer: Computer is an electronic device that accepts data, processes, organizes and produces results.
Data: Whatever you have typed from the keyboard is the data.
GNOME Interface : A graphical user interface which has many applications designed to help you in your daily work.
Information : The processed data.
Internet : A large group of computers connected to each other.
Journal : An automated diary of everything you do within Sugar.
Website : A collection of web pages related to each other by a certain topic.

Communication is the process of sending or receiving information. We can communicate by speaking, writing, through art and music and books.
Technology is the collection of techniques, skills, methods and processes used to complete a work. Communication technology helps us to send and receive information.
Project is a planned set of interrelated tasks. It should be completed over a fixed period within certain cost and other limitations.
Computer hardware refers to physical parts that can be touched. For example, system unit, monitor, printer, keyboard and mouse.
Software is a set of instructions for a computer to perform specific operations that cannot be touched. For example, Windows Media Player and Word Processing.

Do these review exercises in your exercise book.
1. Fill in the blanks with the correct options :
1. …................ tools help us use information and share it digitally.
(a) ICT (b) UPS
(c) DATA (d) Website
2. .................... is a collection of web pages.
(a) Data (b) Website
(c) Digital (d) Analogue
3. The ................. lies behind all other components on your screen.
(a) mouse (b) keyboard
(c) desktop (d) none of these
4. The ............ is a special folder where you can place files and folders you no longer need.
(a) window (b) home
(c) Icon (d) trash
5. ............... is a type of computer program that allows you to perform a particular task.
(a) Application (b) Text Editor
(c) Calculator (d) Character map
II. State whether the following statements are true or false :
1. Computer hardware refers to physical parts that can be touched.
2. Gedit Text Editor can read, create, or modify any kind of simple text without any formatting.
3. Buttons on status bar allow you to minimize, maximize, and close the windows.
4. Sugar is a graphic user interface.
5. The Sugar Journal records everything we do using Sugar Interface.
III. Match the following :
Column A Column B
1. Project (a) processed data
2. Communication (b) an electronic device
3. Information (c) collection of electronic pages
4. www (d) exchanging information
5. Computer (e) a planned set of interrelated tasks
IV. Answer the following questions briefly :
1. What are the roles of a computer?
2. Differentiate between data and information.
3. Explain the features of website.
4. List some uses of the following:
(a) Scroll bar (b) Gedit Text Editor (c) GNOME interface
(d) System menu (e) Workspaces
5. Write the steps to switch on and switch off a computer.
6. What is the Journal Activity ?
Clues:
Across
2. A device or program that enables a user to communicate with a computer.
6. This is the processed data.
7. It is a large group of computers connected to each other.
Down
1. The collection of techniques, skills, methods and processes used to complete a work.
3. This is a set of instructions for a computer to perform specific operations.
4. Something on which operations are performed by a computer.
5. An electronic device that accepts data, processes, organizes and produces results.

Students in group practice switching from Sugar to Gnome interface and vice versa.

Send a document to your classmates through sugar interface. Discuss it with each other.
