General
UNIT 8:Mass Measurements
Key unit competence
By the end of this unit, a learner should be able to convert between units of
mass and apply them in solving mathematical problems related to daily life
situations.
Attitudes and values
Appreciate the importance of mass measurement in daily life, show respect
for one another, and appreciate difference in opinion while working with other
people and show fairness while measuring mass.
8.1 Estimating Mass
In this section, you will study to estimate the mass of an object by observing itonly.
Activity 8.1• You will be provided with a stone of
mass 500 g (0.5 kg) and another stone
of mass 1 kg. Other alternative masses
may be provided.
• Feel the mass of 500 g by holding the
stone in your hand.
• Feel the mass of 1 kg by holding the stone in your hand.
• You should repeat the experiment a number of times because this will help
you estimate masses of different objects.
• With the help of your teacher, measure the mass of a pen, small stone, asmall exercise book, your shoes and a bottle top.
Activity 8.2
• With the help of your teacher, measure and record your mass in your
exercise book.
• Compare your mass with the masses of your classmates.
• Record the least and the highest mass in the class.
• Use your imagination to estimate the mass of the teacher.
• Ask the teacher to tell the whole class his/her mass after all pupils have
given their estimates.
A butcher at a butchery in Kigali City sells meat. He is 2 m tall, very fat and
he puts on the biggest shoe size on market. What does he weigh?Think!!!
Exercise 8.1
Estimate the mass of the following objects:
(a) mass of a bottle of soda. (b) mass of a pawpaw fruit.
(c) mass of a goat. (d) mass of a bull.
(e) mass of a small car. (f) mass of a lorry.
(g) mass of a knife.mass of a mango leaf.
(i) mass of a 10 year old pupil. (j) mass of 10 sheets of paper.
8.2 Measuring of Mass
Activity 8.3
Which unit would you use to measure the mass of the following? A kilogram
or a gram?
(a) a tomato (b) an egg (c) a radio
(d) a baby (e) an exercise book (f) a school boy(g) a chair
an elephant (i) a mathematical set
Mass is the quantity of matter contained
in a substance. The more the matter, the
greater the mass. A house brick and a
piece of cotton of the same size have
different masses. A house brick has
more mass because it has more
quantity of matter than the cotton.
The standard unit for measuring and expressing mass is kilogram. The
kilogram is represented by ‘kg’.
However, mass can also be expressed in ton, denoted by ‘t’ where,
1 ton = 1 000 kg.
Instruments for measuring mass
The following instruments can be used to measure mass:Top pan balance, beam balance, triple beam balance, electronic balance, etc.
Exercise 8.2
Which units would you use to measure the following objects:
(a) mass of a pencil. (b) mass of a ball.
(c) mass of a cycle. (d) mass of a TV.
8.3 Conversion between units of Mass
Metric prefixes are very useful in converting units of quantities. The main metricprefixes dealt with at this level are the kilo, hecto, deca, deci, centi and milli.
From the above table we can see that;
• One kilogram = 1kg = 1000g.
• One hectogram = 1hg = 100g
• One decagram = 1 dag = 10g
• One decigram = 1 dg = 0.1g ( a tenth of a gram)
• One centigram = 1cg = 0.01g = (hundredth part of a gram)
• One milligram = 1mg = 0.001g = (a thousandth of a gram)
Note:
The tonne is equal to one thousand kilograms.1 tonne (1t) = 1 000kg
1q = 100kg.
Read the following units of mass aloud:
(a) 20 t (b) 250 kg
(c) 400 hg (d) 680 dag
(e) 500 g (f) 230 dg
(g) 100 cg570 mg
(i) 45 cg
Example 8.1
Convert the following units of mass:
(a) 2 kg to g. (b) 2 kg to hg.
(c) 10 kg to g. (d) 3 dag to g.(e) 40 g to mg. (f) 50 dg to cg.
SolutionConversion table
(a) 2kg = 2 000g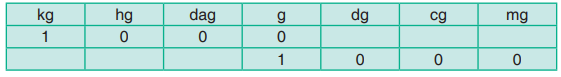
(b) 2kg = 20hg
(c) 10kg = 10 000 000mg
(d) 3 dag = 30g
(e) 40g = 40 000mg
(f) 50dg = 500cg
Example 8.2
Convert the following units of mass:
(a) 2 000 g to kg.
(b) 30 000 g to kg.
(c) 15 000 cg to g.(d) 200 dag to hg.
Solution
(a) 2000g = 2kg
(b) 30 000g = 30kg
(c) 15 000cg = 150g(d) 200dag = 20hg
Exercise 8.3
1. Convert the following into grams.
(a) 24 kg (b) 8 kg (c) 15 kg (d) 12 kg (e) 1.5 kg
(f) 321 kg (g) 2.8 kg
2. Express the following in kilograms.
(a) 15 000 g (b) 2 400 g (c) 7 000 g (d) 500 g
(e) 912 g (f) 1 500 g
8.4 Addition and Subtraction of Masses
Example 8.3
(a) Add: 4kg + 3hg = ........kg
(b) Subtract: 29dg – 2.4cg = ........cg(c) Subtract: 10t – 9 600kg = ........kg
Solution
(a) 4kg + 3hg = 4kg + 0.3kg = 4.3kg
(b) 29dg – 2.4cg = 290cg – 2.4cg = 287.6cg
(c) 10t – 9 600kg = 10 000kg – 9 600kg = 400kg
Exercise 8.4
(a) Add: 3.25 kg and 1.75 kg and express the answer in grams.
(b) Subtract: 5.25 kg from 25.65 kg and write answer in grams.
8.5 Application of Mass
In this section, we discuss the problems involving mass in real life situations.
Example 8.4
A school bought shields and cups for winners and runners-ups. There were
2 shields for the overall champions. If the weight of the smaller shield is
2 kg 120 g and bigger shield is 2 kg 865 g, then what is the difference in
their masses.
Solution
The weight of the bigger shield = 2 kg 865 g = 2 865 g
The weight of the smaller shield = 2 kg 120 g = 2 120 g
\ Difference in weight = 2 865 g – 2 120 g = 745 g
Assessment Exercise
1. Convert the following into grams.
(a) 285 kg (b) 19 kg (c) 2.5 kg (d) 196 kg.
2. Convert the following into kilograms.
(a) 2126 g (b) 9065 g (c) 850 g
3. There are 20 tins of biscuits in a shop. Each tin weighs 2 kg 500 g.
What is the weight of all the tins in kg?
4. A car weighs 3 tons. Express this mass in kg
5. An omnibus (taxi) is licensed to carry passengers with total mass
not exceeding 1 140 kg. If 20 people each of mass 60 kg board the
omnibus, find whether the omnibus is overloaded.
6. A truck carries 200 bags of cement. The total weight of all the bags in
the truck is 10 tons. What is the mass of only 1 bag of cement?
7. Each book in a certain bookshop has a mass of 20 dg. How many of
these books do I need to have 1 ton of books?
8. Yesterday, I bought 4 kg of mangoes and ate 2 000 g. How many
grams of mangoes are left?
9. The mass of 1 chocolate bar is 100 g. What is the mass of 30 chocolate
bars in kg?
10. The mass of 1 toy car is 600 g. What is the total mass of 60 toy cars?
11. Ms Annet packed 24 kg of sugar equally into 8 bags. How many grams
of sugar did she pack in each bag?
12. Peter has a mass of 82 kg. John is 5 kg heavier than Peter. What is the
mass of John?
13. John weighs 80 kg, Peter weighs 70 kg and Eric weighs 90 kg. Howmuch do the three people weigh altogether?
Internet ResourceFor more online support visit www.kidsnumbers.com
