General
UNIT 13:Filling in the Missing Numbers
Key unit competence
By the end of this unit, a learner should be able to solve missing number
problems involving addition and subtraction.
Attitudes and values
Appreciate the importance of inverse operations when solving missing number
problems and checking answers.
Arithmagon
An arithmagon is a polygon with numbers at its vertices and sum of these
numbers determine the numbers written on its edges.Example:
Here, the numbers 7, 9 and 12 are at the vertices of the Arithmagon and the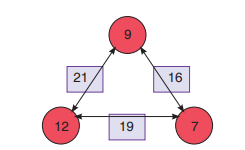
numbers 16, 21 and 19 are at the edges.
You can see that 12 + 9 = 21, 12 + 7 = 19 and 9 + 7 = 16.
So, add the numbers at the vertex to get the number on the edge. This rule
applies to this arithmagon only. Other arithmagons have different rules. Youcan study them carefully and discover the rules by yourself.
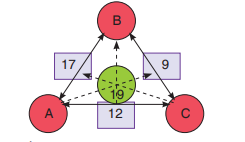
In the arithmagon shown above
Activity 13.1A = 19 – 9 = 10B = 19 – 12 = 7C = 19 – 17 = 2
You will complete this task in groups of 5
learners.(a) Find the value of b
(b) Find the value of c
Example 13.1Fill in the missing number.
Solution
In the arithmagon above, there are 4 numbers at the vertices namely 2, 7, 3and 12. You can see that 2 + 7 = 9, 7 + 3 = 10, 3 + 12 = 15 and 12 + 2 = 14.

Assessment Exercise
1. Study the arithmagons below and complete them by inserting appropriatenumbers:
2. Complete the Arithmagon below by inserting correct numbers
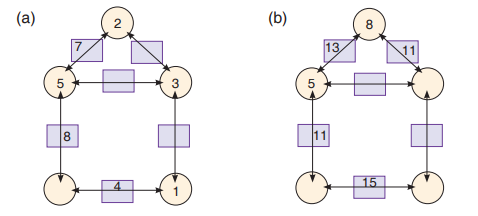
3. Fill in the missing numbers to make the arithmagon correct.
4. Complete the arithmagons below by filling in the right numbers in thecircles
5. If a number is multiplied by 6, the answer will be 24. What will be the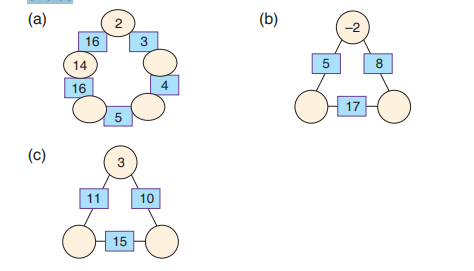
value of the number.6. If ‘X’ is added to 6. The number obtained is 19. What is the value of ‘X’.
Think!!!
If you were running a race and you run past the one in second position, whatposition would you be in now?
Internet Resource
For more online support visit:http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/math.htm
