General
UNIT 11:Money and Its Financial Applications
Key unit competence
A learner should be able to understand what money is and know its applications
in our daily life.
Attitudes and values
Appreciate the importance of money in daily life situations and show concern
and the need for honesty in spending money.
11.1 What is money?
Money is a piece of paper or metal which is legally accepted to be used for
buying goods and services within a country.
A service is something you cannot hold in your hand e.g. education, internet,
advice.
National Bank of Rwanda makes money for use in Rwanda.
Characteristics of money:
• It cannot be easily damaged.
• It is very scarce. That means it is hard to get money.
• It is easy to carry.
• It is hard to forge.
• It should be easily divisible into smaller denominations.
• It is accepted by everyone.
Uses of money:
• It is used for buying goods like books, cars, food, mobile phones.
• It is used for buying services like education (school fees), medical
treatment, airtime, insurance, etc.
• It is used to keep wealth.• It is used to pay debts.
11.2 Rwandan Currency
The money used in our country (Rwanda) is known as Rwandan francs. It is
usually denoted by ‘’. FRWIn Rwanda, we use both notes (paper money) and coins (metallic money).
Rwandan Currency Coins:
Activity 11.1
In this class activity, you are provided with 6 different Rwandan coins.
a) Identify the 1, 5, 10, 20, 50 and 100 Frw coins.b) Discuss with your friends what item can be bought by each coin denomination.
Rwandan Currency Notes:
Activity 11.2
In this class activity you are provided with four Rwandan currency notes.
a) Identify the following notes: 500 Frw, 1 000 Frw, 2 000 Frw and 5 000 Frw.
b) Discuss with your friends what item each currency note can buy in Rwanda.
c) Is there any other currency note whose picture is not shown above?
Example 11.1
My mother gave me money to buy a new school uniform. It was 5 150 Frw
in an envelope. In the envelope, there was only one note and two coins.
Identify the note and the coins my mother gave me.
Solution
Total money = 5 150 Frw.
Since there was only one note, it must have been the 5 000 Frw note. There
is no coin for 150 Frw, so the two coins are 100 Frw and 50 Frw.
Example 11.2
Paul bought sweets from a shopkeeper. He paid the shopkeeper
550 Frw using only coins of 50 Frw each. How many coins did he gave tothe shopkeeper?
Exercise 11.1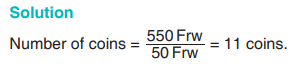
1. What do we call the national currency used in Rwanda?
2. Which Rwanda note has the highest value?
3. A mother gave three notes of 1 000 Frw and five coins of 50 Frw to her
son to buy school uniform. What was the total amount of money given
by the mother?
4. Three men shared 15 000 Frw equally. How much money did eachman get?
Sample Currency Notes from Other Countries
11.3 Planning According to Needs and Wants
A need is something you cannot live without. A need is something you must
have for you to survive. Examples of needs are food, shelter, clothing and
medical care.
A want is something you would like to have but you can live without it. It is not
absolutely necessary but it would be a good thing to have. Examples of wants
are music, TV, computer, car, toys, mobile phone, radio, electricity.
Scarcity and Budgeting
Those in towns and cities buy most of their needs and wants including food,
clothes, etc. Those in villages may get food from their gardens and also live in
their own houses for free. However, everyone needs money to buy salt, sugar,
medicine, airtime, soda, bicycle, clothes etc. One of the biggest problems that
we all have is scarcity of money. We don’t always have money for everything
that we need or want.
Therefore, every time we have money, we need to plan carefully for the moneyso that we buy only the most important things. This planning is called budgeting.
Activity 11.3a) Identify the basic needs from the below list
b) Plan your budget according to your priorities. How will you spend 5 000 Frw?
11.4 Buying and Selling
A person who buys goods or services and sells to others is called a trader or
businessman or businesswoman.
Selling is the act of giving out goods to someone in order to get money.
Buying is the act of giving money to someone in order to get goods that youneed.
Cost Price and Selling Price
A shop keeper goes to a factory and buys 1 crate of soda at 4 500 Frw. If he
sells the crate to a customer at 6 500 Frw, then the cost price is 4 500 Frw
and the selling price is 6 500 Frw.
11.5 Profit and Loss
• If the selling price is more than the cost price, then the shopkeeper makes
a profit. This means he gets extra money and he becomes richer.
• If the selling price is less than the cost price, then the shopkeeper suffers
a loss. This means he loses some money and he becomes poorer.
Example 11.3
Manzi was given 3 000 Frw by his father as pocket money for school
use. He bought a pen at 200 Frw, a book at 500 and geometry set at
900 Frw. How much money is left with him?
Solution
Cost of a pen = 200 Frw
Cost of a book = 500 Frw
Cost of a geometry set = 900 Frw
Total amount of money spent by Manzi = (200 + 500 + 900) Frw
= 1 600 Frw
Pocket money given to Manzi by his father = 3 000 Frw
Money left with Manzi = (3 000 – 1 600) Frw= 1 400 Frw
Example 11.4
A trader went to the market and bought a goat at 20 000 Frw, a sheep at
15 500 Frw and a cock at 5 000 Frw. How much money did he spend in the
market?
Solution
Price of a goat = 20 000 Frw
Price of a sheep = 15 500 Frw
Price of a cock = 5 000 Frw
Total amount of money spent by the trader = (20 000 + 15 500 + 5 000) Frw= 40 500 Frw
Example 11.5
Christa bought a tray of eggs at 2 000 Frw and sold it to Sandra at
2 200c Frw. Sandra sold it to James at 3 000 Frw and James also sold it to
Alex at 2 500 Frw.
a) What profit did Sandra get?b) What loss did James bear?
Solution
a) Sandra: Cost price = 2 200 Frw
Selling price = 3 000 Frw
Sandra’s profit = Selling price – Cost price
= (3 000 – 2 200) Frw
= 800 Frw
b) James: Cost price = 3 000 Frw
Selling price = 2 500 Frw
James’ loss = Cost price – Selling price
= (3 000 – 2 500) Frw
= 500 Frw
Activity 11.4
(a) You will do this activity in pairs, suppose a shopkeeper purchases goods
at 2 500 Frw and sells the goods at 3 000 Frw. What extra money does
the shopkeeper get? Discuss with your teacher.
(b) Shina went to the market and bought a dress at 5 000 Frw. The dress
was too big and so she decided to sell it at 6 000 Frw. Did she gain fromthe sale of her dress? Discuss with your friend.
Assessment Exercise
1. If the cost of one pen is 500 Frw, then what will be the cost of 4 pens?
2. Keza has 450 Frw. She buys an eraser at 250 Frw and a sweet at
125 Frw. How much does she remain with?
3. One metre of cloth costs 2 600 Frw. Maria went with one 5 000 Frw
and one 2 000 Frw note. She bought two metres of cloth. How much
balance was she given?
4. A plot of land was sold at 30 000 Kenyan shillings. This resulted in a
profit of 4 500 Kenyan shillings. What was the cost price of the land?
5. The bus fare from Kigali to Kampala is 12 000 Frw. How much does
one spend from Kigali to Kampala and back to Kigali?
6. The price of a litre of petrol is 1 200 Frw. A car fuel tank has a storage
capacity of 100 litres. How much does it cost to fill up the tank?
7. MTN charges 60 Frw per minute on calls to Kenya. How long do I
speak to a friend in Kenya if I have 1 200 Frw airtime in my phone?
8. A Samsung TV costs $ 340. How much will be charged for 2 similar
TV sets?
9. The price of a mobile phone is marked as 79 500 Frw. The trader sells
it to me and makes a loss of 3 500 Frw. How much do I pay for the
phone?
10. A refrigerator costs 80 500 Frw. Kamanda wants to buy the refrigerator
and he has 76 900 Frw. How much more money does he need to buy
the refrigerator?
11. A group of students are on a school trip to Gisenyi to tour the Methane
Gas Plant on Lake Kivu. The fare for each student is 6 250 Frw. There
are 40 students in the bus. How much does the conductor of the buscollect from the students?
Internet Resource
For more online support visit :http://www.math-play.com/fractions
