1.2. Components of SET syllabus
Activity 1. 2
- Read the preprimary and SET primary syllabi and identify its components
- Write units found in SET syllabus of each grade.
- Identify the components of syllabus unit structure and establish the relevance of every component.
Summary Notes
The SET syllabus comprises many components which guide the understanding of users for its effective implementation.
The lower or upper primary SET syllabus has the following main components:
1. Preliminary pages
- Foreword
- Acknowledgement
- Introduction
- Pedagogical Approach
- Assessment Approach
- Resources
Each component of the preliminarily pages plays an important role at every step
of the teaching and learning process.
- Introduction of the syllabus provides all information related to: Background to curriculum review, Rationale of teaching and learning SET, Competences (generic and broad subject competences).
- Pedagogical approach part provides all information related to: the role of the learner, the role of the teacher and special needs education and inclusive approach while the teaching and learning of SET. In this part, various teaching strategies and approaches such as direct instruction, discovery learning, investigation, guided discovery or other methods are incorporated. Also, in this pedagogical part, a list of generic and broad subject competences are presented so that a SET teacher can consider them while preparing and delivering lessons.
- Assessment approach part provides information needed to formative assessment and summative assessments, record keeping, Item writing in summative assessment and reporting to parents.
- Resources are the part of the syllabus which provides a non-exhaustive list of materials needed for implementation of SET syllabus.
2. SET syllabus units for lower and upper primary
Syllabus units are composed by the following: Presentation of the structure of the syllabus units, units for each grade in lower primary (primary one , two, three) ; units for each grade of upper primary (Primary four , five , six), Key competences at the end of primary one, two, three, four, five and six.
At every grade, the syllabus is structured in topic areas, sub-topic areas where applicable and then further broken down into units and unit content. This breakdown promotes the uniformity, effectiveness and efficiency of teaching and learning SET.
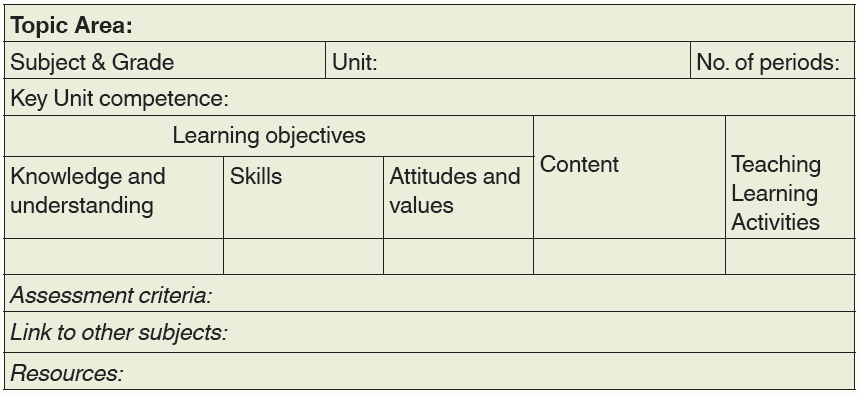
The Units have the following elements:
- Each Unit is aligned with the number of periods
- Each Unit has a key unit competence whose achievement is pursued by all teaching and learning activities undertaken by both the teacher and the learners.
- Each Key Unit Competency is broken into three types of Learning Objectives as follows:
- Learning Objectives relating to Knowledge and Understanding also known as Lower Order Thinking Skills.
- Learning Objectives related to acquisition of skills also known as Higher Order Thinking skills.
- Learning Objectives related to acquisition of Attitudes and Values also known as Higher Order Thinking Skills.
- Each Unit has content that indicates the scope of coverage of what is to be taught and learnt in line with the stated Learning Objectives.
- Each Unit suggests a non-exhaustive list of learning activities that are expected to engage learners in an interactive learning process as much as possible (learner-centered and participatory approach).
The table below is the structure of each syllabus unit
3. References and appendices
Units for SET syllabus for each grade
| Primary One (9 units) | |
|---|---|
| 1. Materials and Tools used at home and at school | 6. Plants |
| 2. Toys, various materials and teaching and learning aids |
7. Waste and Hygiene |
| 3. Basic ICT tools | 8. The Human Body |
| 4. Water | 9. Natural and artificial materials |
| 5. Animals | |
| Primary Two (8 units) | |
| 1. Tools and materials used at home and at school | 5. Soil |
| 2. Toys, various materials and teaching and learning aids |
6. Plants |
| 3. Computer my Friend | 7. Light and heat |
| 4. Air and wind | 8. Human Sensory organs |
| Primary Three (10 units) | |
| 1. Toys, basic materials and teaching aids | 6. Animals |
| 2. Use of telephone | 7. Muscles and Bones |
| 3. Computer my Friend | 8. Types of Energy |
| 4. Drinking Water | 9. Electricity |
| 5. Soil | 10. Magnet |
| Primary Four (14 units) | |
| 1. Agricultural tools | 8. Soil |
| 2. Objects production | 9. Animals |
| 3. Computer my friend | 10. Animals management |
| 4. Writing skills | 11. Plants |
| 5. Graphics and multimedia | 12. Human sensory organs |
| 6. Programming for children | 13. Human skeleton |
| 7. Air, wind and sound | 14. Muscles |
| Primary Five (16 units) | |
| 1. Carpentry tools | 9. Soil |
| 2. Masonry tool | 10. Animals |
| 3. Objects production | 11. Plants and environment |
| 4. Computer my friend | 12. Digestive system |
| 5. Writing skills | 13. Reproductive system |
| 6. Computer research | 14. Light |
| 7. Programming for children | 15. Electricity |
| 8. Water | 16. Materials |
| Primary Six (16 units) | |
| 1. Mechanics and blacksmith tools | 9. Plant reproduction |
| 2. Simple machines | 10. Sustainable waste management |
| 3. Objects production | 11. Circulatory system |
| 4. Writing skills | 12. Respiratory system |
| 5. Computer research | 13. Reproductive system |
| 6. Programming for children | 14. Energy management |
| 7. Air pollution | 15. Magnetism |
| 8. Animals | 16. States of matter |
Application Activity 1. 2
- Identify the similarities across grades syllabi of SET.
- Find out the vertical and horizontal progression in the SET syllabi.
End unit assessment
- There are many misconceptions about sciences in the society. As future teacher of SET, what do you predict as a solution to overcome those misconceptions?
- What are benefits of integrating ICT in teaching and learning SET at primary school?
- Explain the essence of teaching Science and Elementary Technology in primary and provide five examples showing scientific competences useful in everyday life.
