General
UNIT 15:2D Shapes and their Properties
Key Unit Competency
A learner should be able to use geometric properties to classify shapes.
Attitudes and values
Appreciate the use of properties to distinguish shapes and recognise that
special quadrilaterals are a subset of all quadrilaterals.
15.1 2D Shapes
2D shapes/figures are two dimensional shapes or figures. These shapes
have only two dimensions, i.e., length and width. They do not have thickness.
Examples of 2D shapes are triangle, square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram,kite, trapezium, pentagon, etc.
15.2 Triangle
A triangle is a closed three sided figure. It has three angles and three sides.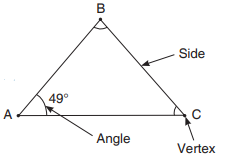
Vertex
A vertex is a point where any two sides meet. The plural of vertex is vertices.So, a triangle has 3 sides, 3 vertices and 3 angles.
Types of triangles
Triangles can be classified according to their sides or angles.Triangles in terms of sides
• A scalene triangle is a triangle in which all sides are unequal.
• An isosceles triangle is a triangle in which two sides are equal.• An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all sides are equal.
Activity 15.1
Complete this activity in groups of 5 learners• You are provided with the following paper/card objects:
• Identify the triangles by putting them separately from the other paper
objects.
• How many sides does a triangle have?
• How many angles does a triangle have?• How many vertices does a triangle have?
• Obtuse angled triangle is a triangle in which one angle is obtuse, i.e., more
than 90°.
• Acute angled triangle is a triangle in which all the angles are acute, i.e.,
less than 90˚.• Right angled triangle is a triangle in which one angle is a right angle (90°).
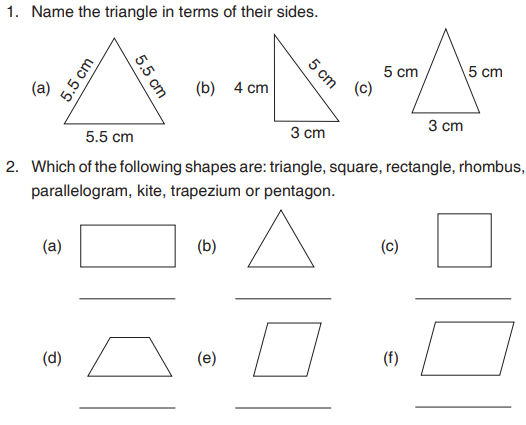
Example 15.2Write the names of the triangles in terms of their angles.
Solution
(a) Right angled triangle (b) Obtuse angled triangle(c) Acute angled triangle
15.3 Quadrilaterals
A closed plane figure bounded by line-segment is called a polygon. The line
segments are called its sides and the points of intersection of consecutive sides
are called vertices. Line segments joining non-consecutive vertices are calleddiagonals.
Activity 15.2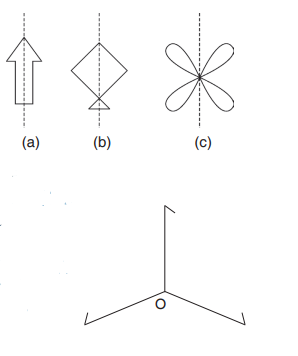 (a) Look at the following plane figures:
(a) Look at the following plane figures:
From the above figures we observe
that if these figures are folded along
a specific line (dotted line). Each
figure on the left hand of the dotted
line fits exactly on the figure on the
right hand side of dotted line.
Therefore, if a figure is divided into
two coincident parts (mirror images) by a line, then
the figure is called symmetrical about that line and
the line is called the line of symmetry.
(b) Look at the following figure:
The figure shown above does not have any lines
of symmetry or point of symmetry. Yet itseems balanced and has regularity of shape.
Let this figure be rotated through one complete turn (clockwise or anticlockwise)
about a point O. These are three occasions when it looks the same as it did
in its starting positions these are when it has been rotated through 120°,
240° and 360°. We say that this figure has a rotational symmetry of order 3.Definition: A quadrilateral is a 4 sided, closed and 2 dimensional figure.
Activity 15.3
Identify the 2D shapes given below by writing their names on each shape:
Activity 15.4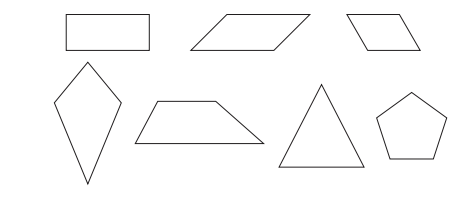
(a) Move around your classroom, library and the whole school compound.
Identify atleast 10 objects which have two dimensional (2D) shapes.
(b) With reasons, explain to your classmates whether the object is asquare, rectangle, rhombus, trapezium, triangle, etc.
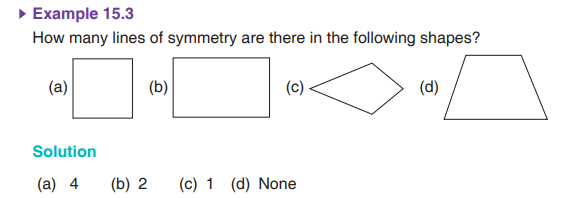
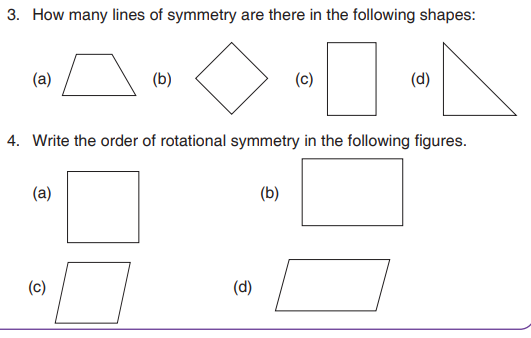
Assessment Exercise