UNIT 14 LESSON PLANNING FOR LEARNERS WITH SEN IN AN INCLUSIVE CLASS
INTRODUCTORY ACTIVITY
Uwimbabazi has been a primary teacher since 2007. In the school year
2010, her school decided to be an inclusive school and therefore has to teach
in her class, two learners with intellectual disabilities and one learner with
Visual Impairment. She has been trained by REB on how to teach learners
with different types of disabilities and she has no problems in planning an
inclusive lesson. Every time Uwimbabazi is going to prepare a lesson, she
asks her self these questions: What are the abilities and characteristics of my
learners?What I am going to teach, how I am going to teach it, what should
learners be able to know or do by the end of the lesson, and how will I know
if they know it or can do it?
Uwimbabazi is a good teacher who is a role model to many teachers. She
takes care of all her learners needs and all participate actively. She takes
time to prepare an inclusive lesson to make sure all her students are actively
participating. No wonder, this year she has been rewarded by REB as an
innovative teacher and best performer in all the country. It is true: Hard
work always pays off.
1. What makes Uwimbabazi an innovator and best performer teacher in
the country?
2. There are important questions every teacher should ask him or herselfbefore he /she deliver a lesson, what are those questions?
14.1. Definition and importance of a lesson plan
ACTIVITY 14.1
1. How would you explain the term” Lesson Plan”?
2. Do you think, it is necessary to have a lesson plan before you
teach? Why?
Good lesson planning is essential to the process of teaching and learning. A
lesson plan is a teacher’s detailed description of the course of instruction or
‘learning trajectory’ for a lesson.
A daily lesson plan is developed by a teacher to guide class learning. Details will
vary depending on the preference of the teacher, subject being covered, and the
needs of the learners. A lesson plan is a detailed description of the individual
lessons that a teacher plans to teach on a given day. A lesson plan is developed
by a teacher to guide instruction throughout the day. It is a method of planning
and preparation.
Lesson plans are the teachers equivalent of a blueprint for a construction project.
Unlike construction, where there is an architect, construction manager, and a
myriad of construction workers involved, there is often only one teacher. They
design lessons with a purpose and then use them to carry out the instruction to
construct skilled, knowledgeable students. Lesson plans guide the daily, weekly,
monthly, and yearly instruction within a classroom.
Dynamic lesson planning is time-consuming, but effective teachers will tell you
that it lays the foundation for student success. Teachers who fail to put in the
proper time to plan accordingly short change themselves and their students.
The time invested in lesson planning is well worth any investment as students
are more engaged, classroom management is improved, and student learning
naturally increases.
The following are the importance of lesson planning:
• Lesson- Planning gives the teacher greater assurance and greater
freedom in teaching. The teacher who has planned his lesson wisely,
enters the class-room without anxiety, ready to embark with confidence
upon a job he understands and prepared to deliver.
• It provides for adequate lesson summaries, ensures a definite
assignment for class, and availability of materials for lesson when
needed.
• Since lesson planning establishes proper connections between different
lessons or units of study, it provides and encourages continuity in the
teaching process.
• It enables the teacher to know the most desirable type of teaching
procedures and to prepare tests of progress and checks for judging the
outcomes of instruction.
• Lesson-planning prevents waste because it helps the teacher to besystematic and orderly. It saves him form haphazard teaching.
SELF-ASSESSMENT 14.1
1. Explain what is a lesson plan?
2. Discuss the importance of lesson planning in teaching and
learning process?
14.2. Key elements in lesson planning
ACTIVITY 14.2
1. What do you think should be included in the lesson plan?
2. With an example, explain the difference between learning
objectives and instructional objectives
Planning a lesson is an important responsibility for a teacher and critical for
enhancing the students’ learning and teacher’s confidence. The competencebased
lesson plan has 27 different parts that teachers are expected to complete.
a. Check your scheme of work
Before the start of every academic year, teachers accomplish the scheme of
work based on the subject syllabus, the school calendar and time allocated
to the subject per week. For lesson plan preparation, consider the following
questions:
• What lesson have you planned to teach in a given period, such as a
term, a month and a week?
• What key competence do you hope to develop by the end of unit?
b. Identify the generic competences and cross cutting issues
From the scheme of work, the teacher identified the key unit competence by
looking at the subject syllabus. Each lesson must also incorporate generic
competences and cross cutting issues.
c. Set instructional objectives for the lesson
An instructional objective should have at least 5 components. The following
steps can guide you to write the statement:
1. Determine who you’re talking about
2. Note the behaviour/action/competence you’re looking for - evidence
of student action (choose from the list of verbs in the tips and aim for
higher levels of comprehension).
3. Include the content you want the student to learn
4. Reflect on the conditions, or how the student will accomplish the task
5. Have a standard of performance - criteria for acceptable performance
Examples of instructional objectives
1. Using an extract on agricultural products from an article in The New
Times, and transcribed in Braille for learners with Visual difficulties,
the learners will be able to read one paragraph on the importance of
avocado fluently 150 words in 5 minutes, 10 minutes for learners with
speech difficulties and 15 minutes for those with cognitive difficulties.
• Who: Learners (diverse learners)
• Behaviour: Will be able to read
• Content: one paragraph on the importance of avocado
• Condition: Using an extract on agricultural products from an article in
The New Times
• Performance standard: Fluently in fixed time
2. Given a gap-filling exercise on elements of a good map, learners will be
able to indicate and explain correctly the 5 elements of a good map in
5 minutes and in 15 minutes with more explanation for learner with
cognitive challenges. The teacher will read for the two learners with
visual difficulties and allow them to answer verbally.
• Who: Learner including those with intellectual disabilities and Visual
Impairment.
• Behaviour: Will be able to indicate and explain
• Content: Element of good map
• Condition: Using gap-filling exercise on elements of a good map
• Performance of standard: Correctly in fixed time
d. Identify the types and number of learners with SEN
In the section titled ‘Type of Special Education Needs and number of learners in
each category’, insert the type of SEN that you have identified in your class, and
the number of learners with SEN in the class. In addition, note how learners
with SEN will be integrated or accommodated in the game or activity so that
they are also able to participate and learn.
e. Identify organizational issues
This part of the lesson plan conforms to creating positive learning environments,
specifically related to physical safety and inclusion. In the section titled “Plan
for this Class (location: in / outside)”, you can write down where you will hold
the lesson.
f. Decide on the teaching and learning activities
In this part the teacher summarizes the learning and teaching process
including main techniques and resources required. Afterwards, the teacher
details activities to be carried out by the teacher and learners. In the column
of teacher’s activities, the teacher describes the activity using action verb in
infinitive form. The questions and instructions provided by the teacher are also
written in this column. In column of learner’s activities, the teacher describes
the learners expected activities, findings and answers. However, for some
activities or answers which cannot fit in that column, the teacher will indicate
them in appendix. The teacher will specify if the activities will be carried out
individually, in small groups, or by the whole class.
In the column of the generic competences and cross cutting issues to be
addressed, the teacher writes down generic competences to be developed
through learners’ activities and how they will be developed. The cross-cutting
issues to be addressed depend on the lesson content and activities. In the
column of steps and timing in the lesson plan format, there are three mainsteps; introduction, development of the lesson and conclusion.
SELF-ASSESSMENT 14.2
1. Explain briefly the key elements of lesson planning?
2. What is an instructional objective? Develop an inclusive
instructional objective?
14.3. A sample of an inclusive education lesson plan
ACTIVITY 14.3
1. What do you understand by inclusive lesson plan?
2. What are the main parts of a lesson plan?
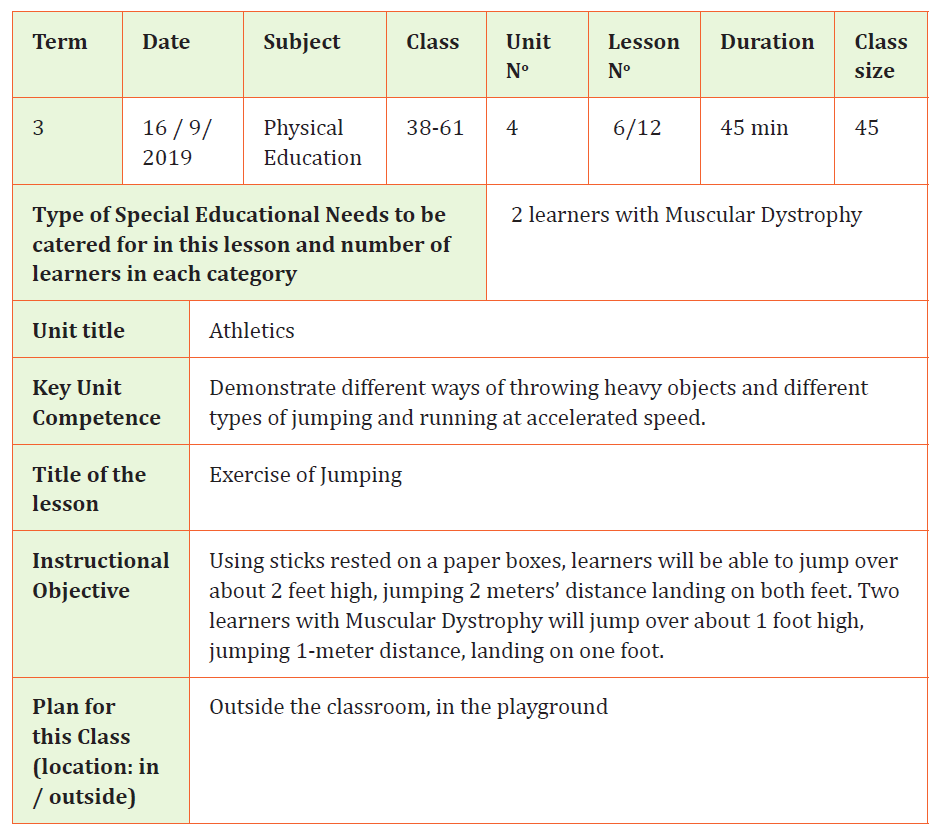
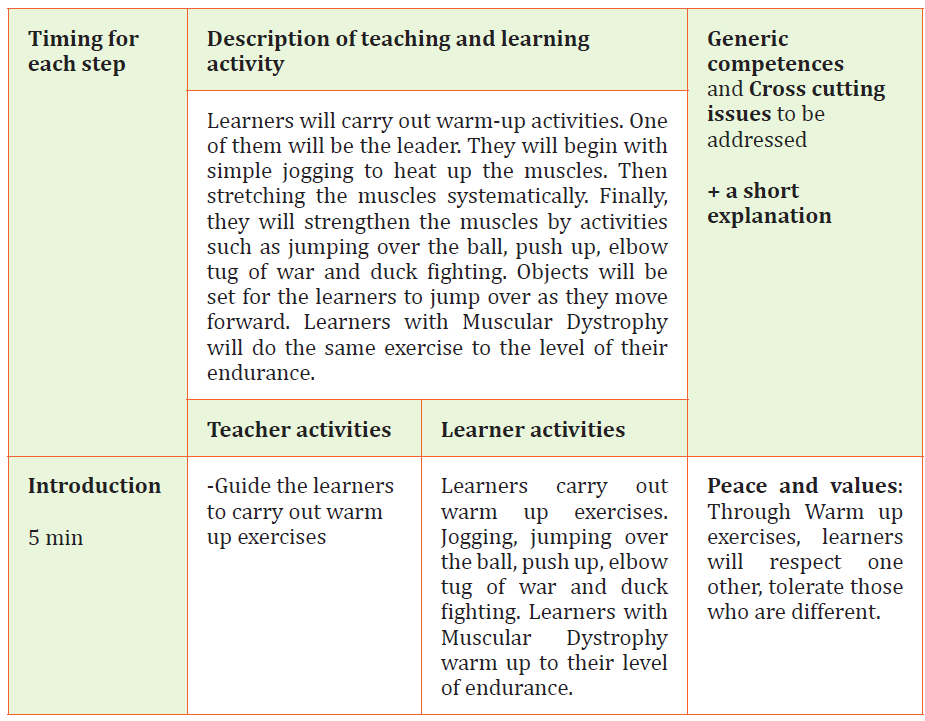
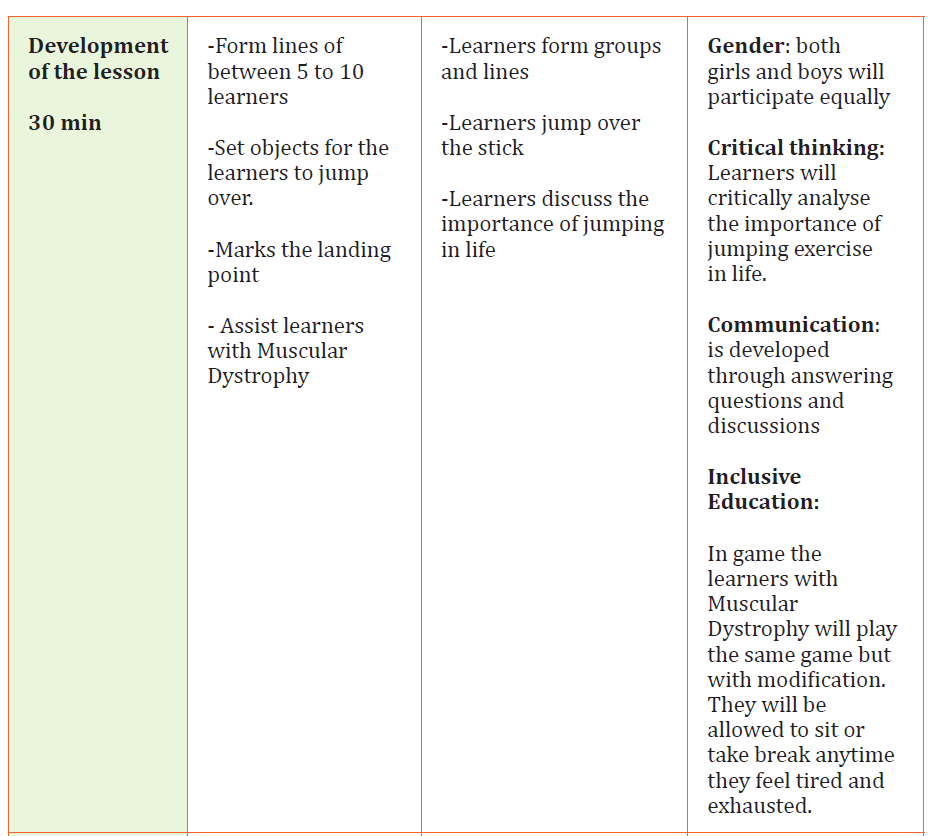
Physical Education Sample Lesson PlanSchool Name: GS Mayange A Teacher’s name Mutware Leopord

SELF-ASSESSMENT 14.3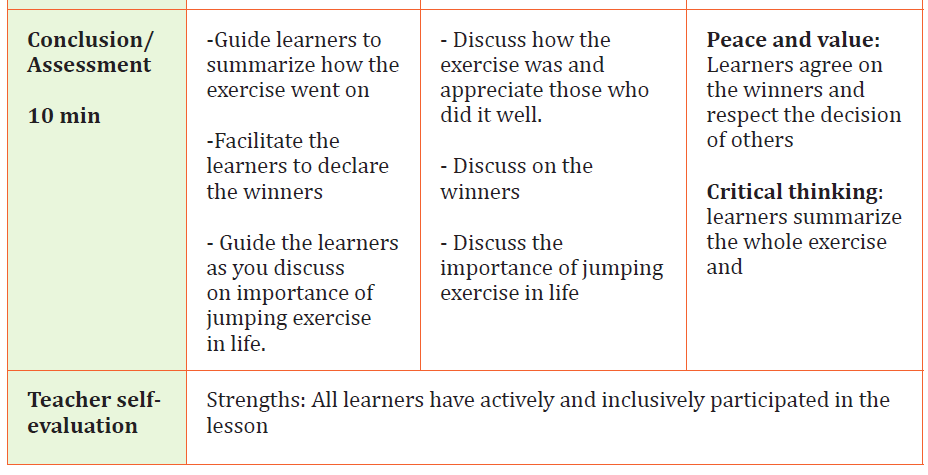
1. Briefly explain the element of inclusive lesson plan?
2. Analyse the instructional objective set above and show the
component of inclusive instructional objective?
SKILLS LAB
1. After you have graduated from TTC Rubengere, you have
been deployed to teach mathematics at EP Kayenzi. You are in
primary four and you have to teach a lesson on: “Reading and
writing numbers in words and figures”. In your class, you have
two learners with Dyscalculia and one learner with Visual
Impairment. Prepare an inclusive lesson plan and deliver it.
END OF UNIT ASSESSMENT
1. With an example, explain the components of an instructional
objective?
2. What do you think, teachers should have a lesson plan?
3. In your own words, explain what lesson plan mean?4. What are the main elements of an inclusive lesson plan?
REFERENCES
Braille Authority of North America (1994). English Braille American Edition.
American Printing: House of Printing.
Braille Authority of the United Kingdom (2004). A Restatement of Standard
English Braille Compiled and Authorized. Royal National Institute of the Blind
Bakewell Road, Orton.
Gargiulo, R.M. (2009). Special Education in contemporary society: An introduction
of exceptionality. SAGE, Los Angeles, London.
Hallahan, DP &Kaufffman, J.M(2007). Human exceptionality. School community
and family. New York: Allyn and Bacon
Howse, J., Kathy, R., and Leona, H. (2013). Unified English Braille: Australian
Training Manual. Australia: Round Table on Information Access for People with
Print Disabilities Inc.
Howse, J. (2006). Unified English Braille Primer. Australia. The NSW Department
of Education and Training Publisher.
Mwaura, M., and Mweu, J. (2009). Braille I (Basic English Braille). Kenya Institute
of Special Education.
Ndurumo, M. (2001). Exceptional learners: Developmental consequences and
intervention. Nairobi: National learners in needs network.
Rwanda Education Board ( 2018), All Children can learn together, Toolkit for
Awareness raising on Inclusive Education in Rwanda. Kigali, Rwanda.
Rwanda Education Board (2018). Training manual on Special Needs and
Inclusive Education.Kigali, Rwanda.
Rwanda National Union of the Deaf (2009). Rwandan Sign Language. First
Edition, Kigali.
HWO (2019)Learner
