UNIT 6: BUSINESS GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
Key Unit Competence: To be able to analyze the factors that lead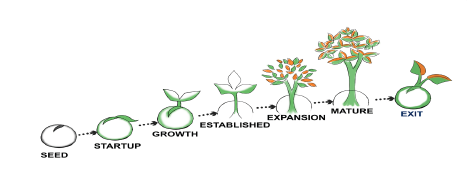
to business growth and development.
Introductory Activity
Hirwa’s Case Study
Hirwa lives in one of the Southern province districts where he started a
small boutique in his village with capital as little as 100,000Frw but with
a big number of customers. In his absence he is assisted by his wife and
sometimes his children during school holidays. Hirwa works so hard to
provide good customer care to his customers. After four years, he has
many customers and his capital has doubled.
Hirwa’s capital continues to grow and his profit has increased
tremendously. He has opened two more shops selling various items in
different Districts within the country employing five skilled workers and
has got enough market for his products. Hirwa is also planning to start a
wholesale shop in Kigali but he is uncertain if he will succeed.
Questions
Referring to the above case study, answer the following questions:
a. Is Hirwa’s business growing, or declining?
b. Differentiate between a growing business from a declining business
c. Describe different strategies Hirwa used to grow his business
d. What factors have favored the growth of his business?
e. As a student of entrepreneurship, what advice would you give to
Hirwa in order to continue expanding his business?
6.1. Meaning of business growth and business development
Activity 6.1
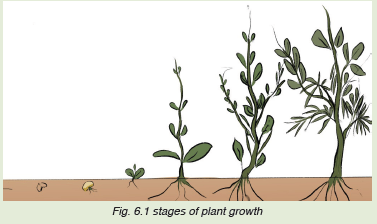
Questions
1. Analyze the picture below and comment in relation to different
stages of plant growth.
a. Assume you plan to start a business after school, do you think it
is possible to grow as it is illustrated in this picture? Justify your
answer.b. Referring to the picture below, is this plant growing or developing?
The meaning of business growth and business development
Business growth refers to the process by which business enterprises
increase their production, profitability and size. It is the expansion of the
business enterprise. Business growth can also be defined as a stage where
the business reaches the point of expansion and seeks additional options to
generate more profit.
Business development is an ever-evolving concept that can be approached
from different perspectives. As its basic level, business development is
defined as a growing business that is more competitive, expanding products
or services, and /or focusing on specific markets.
It can also be defined as a qualitative and quantitative increase in the level
of output, profits, sales, and other variables of any business.
In other words, business development is the practice of a growing business
beyond its current state.
There are three main components that business experts generally agree form
the base of business development: markets, customers and relationships.
In order to expand a business beyond its current state, it is important to
focus on one or more of these areas. The type of business and the direction
of growth determines where the focus is placed.
There is a relationship between business growth and business development
since all involve growth in terms of revenues, business expansion, increasing
market and profitability.A roadmap to Business Development
This figure above shows the process from the business start-up to business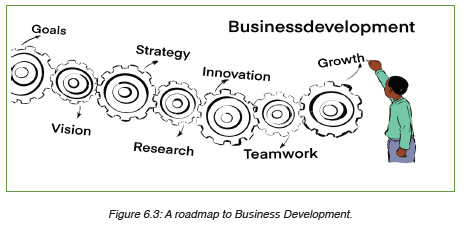
development i.e starting business with goals (know what you want ), Vision
(know where you are going), Strategy (techniques to be used to get there),
Research (know who is/are your customers, what they want, knowing
your suppliers, competitors,…), Innovation (improving things/doing things
differently from others) and team work (working together with others either
employees, suppliers, contractors, community, other businesses and
government) all of this process leads to business development (multisectoral),
business development impacts not only on growth but also on the
increase in business new branches, many employees, market expansion,
new technology, more business infrastructures etc. Business development
is achieved in long term compared to business growth which only impacts
on the production level.
Application activity 6.1
As a student of entrepreneurship and with vast knowledge obtained from
O’level, advise a friend on the indicators of a growing business and a
declining business.
6.2. Indicators of business growth
Activity 6.2
Mukamana started a business of selling women shoes in town. She
started the business with little money. After one month she would sell
an average of five shoes per day. Five months later, the number of
customers had increased to an extent that she could sell an average of
twenty shoes per day. She used the business profits and a small loan
from the bank to increase the stock and after a short time the shelves
were full of shoes. One year later, Mukamana had thought of expanding
her business by opening another shop in Kigali city.
Strategically, Mukamana used advertisement on different radios and
televisions to inform people about her new branch in Kigali and prices
of the shoes, as a result, there was an increase in customers and
sales respectively. She is now a successful business woman who sells
shoes in large quantities and has a license to export shoes to African
countries. This, coupled with other factors mentioned above enabled
her to accumulate a lot of profit.
Questions:
a. Referring to Mukamana’s business, what are the indicators of
her business growth?
b. Suggest other indicators not mentioned above responsible for
business growth.
Indicators of business growth
There are many indicators of business growth. They include the following:
• Increased capital: If capital of a business is increasing, then it is an
indicator that the business is growing.
• Increase in assets: Another indicator of business growth is the
increase in assets like buildings, vehicles, bank deposits, etc. The total
value of business assets can be revealed by the balance sheet of the
business for a particular period of time.
• Increase in business profit: When the business profits are growing,
then it is an indicator of business growth.
• Opening more branches: Opening more branches is an indicator that
the business is covering more areas and is serving more customers.
This is an indicator of business growth.
• Increased market share: When the market share of the enterprise is
growing, the enterprise is growing because it is serving more customers.
• Increased sales revenue: Increased sales revenue for a business is
an indicator of the business growth as it reflects an increase in the
number of customers and stock.
• Increased number of employees: When the business grows, it
normally increases the number of departments and employees. For
example, a restaurant that started with four workers and expands into
a hotel, it will need to recruit more employees than previously.
• Use of advanced/improved technology: Most businesses start
with simple technology but as the business expands, they use moreadvanced technology.
Increased stock of goods: When the enterprise grows, it produces and
sells more products. For example, in a shop there are more and wider varietyof goods and services.
Better salaries and wages paid to workers: When a business is growing,
it is able to give better wages and salaries to its workers due to increased
profits.
Application activity 6.2
Case study: Peter the maize farmer
Peter is a farmer of maize in eastern province. He started growing maize
on a small piece of land using traditional techniques like hand hoes and
did not use fertilizers to increase production. He employed two men on
his small farm. One day Peter got the chance of being selected by the
Ministry of Agriculture in the two days training that had the following
theme “Doing agriculture oriented to the market”.
When Peter went back home, he tried to improve on the methods he
used to grow maize production and decided to take a small loan from
Umurenge Sacco with the purpose of buying another land to grow
maize and acquiring enough capital to buy fertilizers that he mixed with
manure.
Since that time, the production increased considerably. In the season
that followed, he increased the number of workers from 2 to 50 workers.
After one year, he thought of using irrigation system in order to cope
with climate changes.
He also used tractors in farming instead of man power. Now he harvests
more maize and sells it to maize processing industries in Kigali and in
other provinces across Rwanda.
Questions
1. From the above Case study, what are the indicators of his
business growth?
2. What strategies can you use to grow if you have a small
business?
6.3. Business growth strategies
For a business enterprise to survive and expand, it needs to have specific
growth strategies. There are two separate types of business growth strategies
which are internal and external. Therefore, integration of both internal and
external growth strategies is crucial to the overall development of a business
and continuous increase of revenues.
These growth strategies are implemented using various resources such as
financial, human and material resources.
Activity 6.3
Basing on your knowledge of entrepreneurship subject and other
knowledge related to business, answer the following questions:
a. What do you understand by a growth strategy?
b. Describe any 5 internal growth strategies which you think
entrepreneurs in your community should use to grow their
businesses.
c. Propose any external growth strategies used by business people
in your community.
d. What is/are the importance of using the above growth strategies
in business?
6.3.1. Internal business growth strategies
Internal business growth strategy refers to the expansion of a business
enterprise using internal resources and capabilities. This means that all
business growth is established without using external resources or external
parties. It refers also to the growth within the organization by using its own
internal resources to increase their size, scale of operations, resources
(financial and non-financial) and market penetration.
The internal growth strategies which can be used by companies include the following:
• Improving customer care: This involves offering good customer care
to the customers as a way of attracting others and retain old ones.
• Delivering quality products and services: This strategy involves
providing quality products and services. This helps the company to
grow.
• Offering discounts to customers: A discount is a deduction on the
price. As a growth strategy, discounts attract customers and increase
sales revenue.
• Carry out sales promotion: This growth strategy involves all activities
done to inform and attract customers to buy more of the business
products. For example, giving discounts, advertising on Radio,
Television, Newspapers, etc.
• Human resources development: A business may seek to grow by
improving the quality and efficiency of its workers through trainings
and workshops. Better quality workers increase the productivity and
efficiency of a business leading to higher profits.
• Creating new distribution channels and locations: This involves
opening new branches and making products available in new outlets.
This increases sales and generates extra profits for the business.
• Bundling products: This involves selling a bundle of products as one
kit. For example, Mobile phone and SIM Card, Toothpaste and Tooth
brush bread and butter, etc. Even services can be bundled where two
separate services are packaged into one product and sold together.
For example, for computer software. Software is often sold in “suites”
bundle that contains multiple applications. If you buy Microsoft office,
you pay a single price and get Word, Excel, Power point, Publisher and
Access, etc.
Another example for service bundle is where some colleges and
universities may say that if you pay for a diploma or a degree course,
you will receive free computer training. This means that the degree/
diploma has been bundled with the computer training. Bundling helps
the company to sell two products at the same time, attract more
customers and earn more revenue.
• Market penetration and development. This involves selling more of
the company’s products or services to the existing as well as to the new
markets. This strategy is about reaching new customer segments by
targeting new both internal and external markets.
6.3.2. External business growth strategies
External growth strategies refer to the expansion of a business enterprise
by using external resources. These growth strategies focus on increasing
output using resources and capabilities that are not internally developed by
the company itself. The external business growth strategies include the following:
1. Merging with other firms or Mergers
Merging of firms refers to the combination of one or more corporations, or
other business entities into a single business entity; the joining of two or
more companies to achieve greater efficiencies of scale and productivity.
In most cases, this is done by the companies producing and selling related
goods or services as a way of reducing competition among themselves,
increasing profits, etc.
Types of mergers
The following are the types of mergers:
a. Horizontal merging (integration): Horizontal merging occurs when
two or more firms which are in the same industry of production join/
merge into one e.g. two hair dressing salons join together to form
one bigger hair dressing salon.
b. Vertical merging: This is merging of two or more firms which are at
different stages of production in the same industry. In this merging, a
business merges with another that is at the next or previous stage of
production process e.g. coffee farm combining with a coffee factory.
c. Conglomerate merging: This is merging of two or more firms which
produce unrelated products which do not compete with each other
e.g. if a book shop merges with a restaurant. Another example, if a
shoe manufacturing firm merges with a restaurant. The idea behind
this merger is to get a bigger market e.g. shoe clients going to the
restaurant and vice versa.
d. Concentric/ congeneric Mergers: Concentric mergers take place
between firms that serve the same customers in a particular industry,
but they don‘t offer the same products and services. Their products
may be complements, products which go together, but technically
not the same products. For example, if a company that produces
DVDs merges with a company that produces DVD players, this
would be termed as concentric merger since DVD players and DVDs
are complement products, which are usually purchased together.
These are usually undertaken to facilitate consumers, since it would
be easier to sell these products together. Also, this would help the
company diversify, hence higher profits. Selling one of the products
will also encourage the sale of the other, hence more revenues for
the company if it manages to increase the sales of one of its products
2. Franchising
Franchising: A franchise is an arrangement where one party gives another
the right to use its trademark or trade name to produce and market a good
or service e.g. telecommunication companies like Mtn, soft drinks industry
like Coca-Cola etc.
A franchiser (or a franchisor) is the owner of the name, logo and business
model who sells it for use by third parties.
A franchisee is the person or company who buys another company’s name,
logo and business model for use in his/her own business.
Companies can use franchising as a business growth strategy in two
ways:
a. By buying a franchise from well-known and reputable companies.
This helps it to sell more in the markets it would have found harder
to penetrate.
b. By selling the franchise. By selling its name and logo, to be used
by other companies, a business can spread further than it could have
done alone.
The following are the advantages of franchising
• It helps to reduce stiff competition.
• It helps to increase sales and profits.
• Banks can easily lend you money to buy a franchise that has a very
good reputation.
• The business is based on a proven idea and so chances of business
success are higher.
• It helps to attract customers who are already familiar with the name
and logo.
• The franchisee can get ideas from other business people who operate
similar franchises.
• The owner of the franchise normally provides support, trainings and
advice to the franchisee.
• A franchise gives you exclusive rights to sell the product or service in
your region.
• It is easier for a franchisee to perform better than a start-up business
whose name is not known and which has no reputation.
The following are the disadvantages of franchising:
• The costs of a franchise may be high.
• Profits are shared with the franchiser whose name, logo and business
model you are using.
• The franchise includes strict guidelines and restrictions on how to run
the business.
• In case you want to leave the business, it may be difficult to sell the
franchise to someone else because the buyer must be approved by the
franchisor first.
• If the franchisor runs out of the business or the reputation declines, it
affects the entire business.
• The process of buying a franchise involves a long legal process which
is costly.
3. Joint-ventures
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties,
generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and
shared governance.
Companies typically pursue joint ventures for a number of reasons: to access
a new market, particularly emerging markets; to gain scale efficiencies
by combining assets and operations; to share risk for major investments
or projects; or to access skills and capabilities. Companies that form joint
ventures share the profits and losses while simultaneously pooling their
resources to complete the specific objective.
Application activity 6.3
1. With examples in your community/village, describe at least
2 people or entrepreneurs whose businesses have grown up.
Imagine if you had to start up such a business what strategies
would you use?
2. Referring to business activities of entrepreneurs in Rwanda,
what do you think are the benefits from establishing clear growth
strategies?
3. What do you think would happen to business enterprises, if their
owners do not apply growth strategies?
4. Assume you have a small business with a small capital and
there are more competitors where your business is located. Do
you think it will be possible to compete successfully with your
competitors? What will you do to continue operating and out
compete your business rivals?
6.4. Factors that lead to business growth
Activity 6.4
Answer the following questions:
1. Give any three examples of entrepreneurs in your community/
village who have achieved businesses growth.
2. Think about any two main things that lead their businesses to
grow.
Factors that lead to business growth and development
Business growth can be achieved either by boosting the top line or revenue
of the business with greater product sales or service income, or by increasing
the bottom line or profitability of the operation by minimizing costs. There are
many factors that determine business growth these include,
• Availability of market: The market plays a big role in determining the
success of a business. A big and reliable market helps a business to
grow. More buyers will mean more sales and more revenue for the
business.
• Enough capital: The amount of capital available to a business
determines its growth.
• Competent business management: The quality and ability of the
business management team determines the growth of a business. If
the management is competent and hardworking, then the business will
grow faster.
• Proper location of the business: A suitable location may determine
the growth of a business. A business will grow if it is located near the
customers. In addition, a business may succeed if it is located in a
secured place without robbers.
• Level of competition: Competition may force a business to be more
efficient and as a result it grows.
• Technology used by the business: Technology as a method of
production determines the quantity and quality of output. It is a factor
that determines the growth of a business.
• Favorable government policies: Government policy may directly
affect business growth. Favorable government policy like low taxes,
tax holidays, subsidies, etc. determine the growth of a business.
• Political stability and security: The political environment affect
business growth; a peaceful political environment enables a business
to grow
• Quality of workers: The quality of workers in terms of skills, trainings,
experience and commitment is a factor of business growth.
• Proper business planning: Business planning is also a factor which
determines the growth of a business. Planning enables the business to
set targets to be achieved and properly control its resources and time.
• Favorable economic environment: The economic environment
refers to all the economic factors that affect commercial and consumer
behavior. ... “The term economic environment refers to all the
external economic factors that influence buying habits of consumers
and businesses and therefore affect the performance of a business.
• Presence of business support services like banks, insurance
companies, telecommunication companies, etc. This also determines
the business growth.
• Good entrepreneurial characteristics (traits) like self-confidence,
risk taking, perseverance, creativity and innovation, etc. This also
determines the growth of a business.
Application activity 6.4
1. Basing on your location (District) take one grown business and
discuss the factors that lead to its growth.
2. Explain briefly the following statement in relation to business
growth? ‘’Rome was not built in a single day’’
Skills lab 6
1. Analyse information the business growth strategies below and show
how you will each one to serve customers better and achieve the
business club’s growth and development goals.
• Bundling
• Promotion and discount
• Developing new product
• Franchising
• New distribution channels,
End unit 6 assessment
Fill in the following gaps:
1. Assume your business is attaining the following:
a. Increase in production, profitability and size.
Is known as ………………………………………….
b. A prolonged period of little or no growth for companies.
Is known as ………………………………………...
2. Assume that you have a mini-supermarket selling fresh milk,
juices, bread and cakes in one center of Kigali city;
a. How would you know that your business is growing?
b. What are the factors which you think can favor the growth of
your business?
c. How would you know that your business is declining?d. What can you do to minimize such a decline?
