UNIT 5: MARKET RESEARCH
Key unit competence: To be able to conduct market research for
business start-up and growth
Introductory Activity
Kagoyire‘s Case Study
Kagoyire is a year one student of TTC in Rwanda. Having enough
competencies in some year one units among others, initiation to
entrepreneurship, career opportunities, setting entrepreneurial goals
and role of standards in Business she decided to start a small orange
juice processing factory and her main market was the restaurants
located in Agaciro village. Two years later, she found that the level of
sales was extremely declining and started wondering why? Thereafter,
she decided to gather all relevant information regarding the likely causes of such a decline.
Questions
Referring to the above text, answer the following questions:
• What didn’t Kagoyire do before starting her business and how
would she have done it?
• What is the meaning of market research?
• Why do you think it is important to carry out market research?5.1 Meaning of Market, Marketing and Market research
Activity 5.1
1. After analyzing the above pictures what comes to your mind?
2. What do you understand by the key terms which are reflected onthese two above pictures?
A market: This is defined as an arrangement through which the buyers/
customers/clients and sellers/business owner/entrepreneur come into
contact to negotiate an exchange of goods or services for money.
Marketing: This is the action of promoting and selling products including
market research and advertising.
• Market Research: This is the process of collecting and analyzing
information or data related to the demand of goods and services in a
particular market. Market research gathers information about products,
customers, distributors/ suppliers and competitors.
Application activity 5.1
Fill in the following gaps
1. …………………………is an arrangement by which a buyer and
seller come into contact and exchange
2. The act of collecting and analyzing information or data related
to demand of goods and other services in a particular market is
…………………
3. The activity of ………………………...products/services including
market research and advertising is marketing.
5.2 Components of marketing / marketing mix elements
(5Ps)
Activity 5.2
Suppose you are about starting a business; what elements would you put
into consideration for making your products/services more marketable?
5.2.1. Product:
A product is something either good or service that is offered to the market to
be sold in order to get profit. It can be goods (tables, rice, potatoes, beans,
cars, books, pens, clothes, etc) or services (transportation services, music,
medical care, communication, banking, etc.)
5.2.2. Price:
This refers to the amount of money paid by customer for a product. The price
has greater impact on the consumer demand for a product. If price is too low,
then consumers may lose confidence in the quality of the product. If the price
is too high the consumers will not be able to afford the product.
Objectives of price
• To target a market
• To maximize short term profits
• To maximize long term profits
• To stimulate the growth of the business
• To target the return on investment
• To maintain price leadership
Factors influencing / affecting pricing decision
• Government influence: Government may set prices mainly for
essential goods.
• Level of competition: When you have many competitors, you should
set the prices in line with those of your competitors
• Demographic factors: Decision to set prices depends on the number
of buyers, their location, economic strengths and consumption rate
• Costs incurred: If the production cost is high, the price will also be
high and vice-versa
Methods of price determination in the market
• Haggling (Bargaining): Negotiation between buyer and seller where
a buyer increases the price and the seller reduces.
• Auctioning (Bidding): The seller (Auctioneer) offers goods for sale and
requests for bids from buyers. The highest bidder takes the commodity.
• Fixing by treaties (Agreements): Buyers and sellers come into
agreement to fix the price of a commodity.
• Government determination (Legislation): This is when then
government fixes the price of a certain product.
• Interaction of forces of demand and supply: This is where the price
of the product is determined by the forces of demand and supply. If the
quantity demanded is higher than quantity supplied, price will rise and
vice-versa.
• Resale price maintenance: Manufacturers fix the price of a commodity
at which sellers/ retailers have to sell to the final consumer. The price is
usually written on the commodity. Eg: Newspapers, airtime,
5.2.3. Place:
The place /location should be attractive and nearest to the customer (that
place should be known). It involves the channels of distribution that are used.
The distribution process/ Supply Chain includes: Manufacturers, wholesalers,
Service providers, Retailers, marketing specialists and customers.
Types of marketing intermediaries/ Middlemen:
• Middlemen / Middlepersons: Refers to an independent business
concern that operates as a line between producers and consumers or
industry and consumers.
• Agents: These are wholesalers / retailers who do not own the goods
they sell. They sell on behalf of the owners.
• Wholesalers: They engage in bulk buying, storing and physically
handling the goods and sales of goods to retailers.
• Merchant middlemen: These engage in buying goods from the
wholesalers and selling them to final consumers.
• Brokers: These arrange deals between buyers and sellers.
5.2.4. Promotion:
This is a set of ways of attracting customers to buy products either for the first time or to buy more of them.
Forms of Promotion
• Advertising: This is the process of informing the public about the
existence of a product through the use of media such as newspapers,
radios, TV, Journals
• After sales services: These may include repairing and maintaining the
product at low cost, providing transport, guaranteeing the spare parts
for the product, inspecting the product on regular intervals, Providing
warranty, …
• Sales promotion: This refers to various techniques used to attract
customers and increase sales such as giving discounts, free gifts, selfservices,
fantastic music, delivering a product to customers’ home,
showing the knowledge of product to consumers and answer their
questions, etc…
• Public relations: The way of promoting good image of a business and
its products through various activities like: sponsoring matches, charity
donations
• Personal selling: This involves a direct face to face communication
between sellers and potential buyers. To make it effective, the sales
person should:
• Gain the attention to buyers
• Arouse interest of the customer for the product
• Influence and convince the customer to act (to buy)
5.2.5. Positioning
Positioning refers to the place that a brand occupies in the minds of the
customers and how it is distinguished from the product of the competitors.
Positioning is one of the most powerful marketing concepts. Product
positioning is the process marketers use to determine how to best
communicate their products’ attributes to their target customers based on
customer needs, competitive pressures, available communication channels
and carefully crafted key messages.
Application activity 5.2
Kamariza is a craft-woman who specializes in making sandals is
operating in one of the busiest trading center of Northern Province. She
sells her products at affordable prices and she is highly appreciated by
her customers. In fact she occupies the first place on the market. Looking
at how her business is expanding; she now plans to make an advert on
media so as to increase sales and revenue.
From the above scenario, do you think Kamariza has used all the
elements of marketing in her business Yes? No? Justify your answer?
5.3. Importance of marketing in a business
Activity 5.3
1. .” Umukobwa wabuze umuranga yaheze iwabo” What does this
Kinyarwanda proverb mean in a business context?
2. Do you think that “Umuranga “is very important in business?
Justify your position
3. Identify the major ways of attracting customers to buy products
of a business.
Importance of marketing in a business
• Marketing is an effective way of engaging customers hence,
increase the number of customers.
It’s important for your business to engage its customers. Marketing is a
tool to keep the conversation going. Engaging customers is different from
pushing your offers. Engaging involves furnishing your customers with
relevant information about your products and your business as well. Tell your
customers what they don’t know. Let it be interesting and worth their time.
Social media is one of the best platforms where you can engage your
customers. Some organizations use short videos while others use publicity
and other means. By engaging your customers, marketing gives them a
sense of belonging.
• Marketing helps to build and maintain the company’s reputation
hence, facilitates advertising
Growth and life span of your business is positively correlated to your
business’s reputation. Hence, it’s fair to say your reputation determines your
brand equity. A majority of marketing activities are geared towards building
the brand equity and loyalty of the company.
Your business’s reputation is built when it effectively meets the expectations
of its customers. Such a business is considered a responsible member of
the community. The customers become proud to be associated with your
products.
• Marketing helps to build a relationship between a business and
its customers
Businesses need to build a relationship of trust and understanding with their
customers. How does marketing establish this relationship?
Marketing research segments should be based on demographics, and
consumer behavior. Segmentation helps the business to meet the needs
of its customers hence gaining their trust. The product team ensures that
the business delivers what’s promised at the right time. This makes the
customers brand loyal.
Loyal customers will have the confidence to buy more products from you.
The trust and understanding between the business and its customers make
your commercial activities more fruitful.
• Marketing is a communication channel used to inform customers
hence, location of an enterprise
Marketing informs your customers about the products or services you’re
offering them.
Through marketing, the customers get to know about the value of the
products, their usage and additional information that might be helpful to the
customers. It creates brand awareness and makes the business stand out.
There’s stiff competition in the market and you need to be a constant voice to convince the customers. Inform your customers of discounts and other competitive tricks you intend to use.
• Marketing aids in providing insights about your business
Every marketer understands the need for targeting the right audience.
However, you must have the right content to share with such an audience.
Your marketing strategies can help you establish what business messaging
will convince the target audience.
At this point, you have to test different messages and see what works.
Once you have tested different sets of messaging on the target audience,
you will find a viable baseline for your marketing efforts.
It acts as a metric and provides the insight needed to make you avoid
guesswork.
• Marketing helps your business to maintain relevance
Every marketer understands the need for disrupting a potential consumer’s
opinion about other products. But don’t make a mistake of taking this chance
for granted.
Most businesses assume that they will always remain the client’s favorite
brand because up to now the client has never complained. This is the wrong
mindset. You need to find ways to remain at the top of the client’s mind.
Every relationship needs to be maintained. Marketing helps your business to
maintain a good relationship with customers by making you remain relevant.
Don’t focus on gaining new customers before addressing/solving the need
to retain the present ones.
• Marketing creates revenue options
During the start-up phase, you are mostly cash-strapped. This limits your
options. As your marketing strategies generate more customers and revenue
opportunities, you’ll begin having options.
Having options will give you the courage you need to penetrate new markets.
Without marketing, you will be forced to continue working with clients who
you have outgrown and are paying you peanuts.
• Marketing helps the management team to make informed decisions
Every business is confronted with problems such as to what, when, for whom
and how much to produce.
A complex and tedious process determine your business’s survival. As a
result, businesses heavily rely on marketing mechanisms to make these
decisions.
Why should you rely on marketing mechanisms? These mechanisms serve
as a reliable link between your business and society. They cultivate people’s
mind, educate the public and convince them to buy.
Application activity 5.3
1. From the above list of importance of marketing, identify the most
important in business that your business club can adopt to boost
its sales?
5.4. Market research/Survey
Activity 5.4
1. What do you understand by the term market research?
2. Enumerate any two stages one would consider while conducting
market research
Market research/Surveys
Market survey refers to the process of collecting/ gathering and analyzing
market related data (i.e. information related to buyers/customers, competitors,
suppliers/businesses and products.)
5.4.1. Steps to follow when carrying out market survey
1. Finding the topic of the research study. This is the title of all the
research work that has to be done in the field. E.g. an evaluation
of the influence of income levels of consumers to the growth of a
business.
2. Defining the research problem. This enables the entrepreneur
to find out how to deal with prevailing situation which consequently
enables him/her to achieve his/her target.
3. Setting of objectives. Specifically show what the research wants
to achieve at the end of the study. They should always be brief and
SMART (systematic/specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time
bound).
4. Selection of the basic data collection methods. (Observation,
interview, questionnaire, field experiments, focus group etc.)
5. Determine the scope. The researcher determines the limitations of
his/her study. That is to say, areas to be covered and what to be
included or excluded. (Sample/ population).
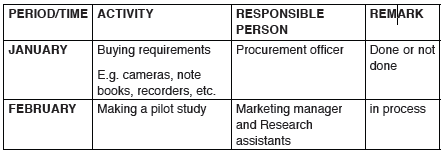
6. Designing a clear schedule for conducting the research or
coming up with a clear plan of the whole research process. Consider
the example below;
An example of a research schedule of activities on a topic of study
―Customer perception towards a new brand of product from a given
company
7. Collecting data: The researcher collects data on a number of things
such as price, product, promotion, target market etc. This is normally
done in the real field study.
8. Analyzing data: This is done during and after the real field study. It
enables the researcher to know how the market will be especially in
terms of demand.
9. Presenting data: After data analysis, the researcher presents
his findings to the relevant authorities for action. The researcher
should ensure that he presents empirical data and not estimates or
hypothetical figures to those who are supposed to take the action.
5.4.2. An example of action plan for making research
Depend on the time and nature of the topic of research study, the action plancan be short or long. Here is an action plan for six months.
5.4.3. Elements of market survey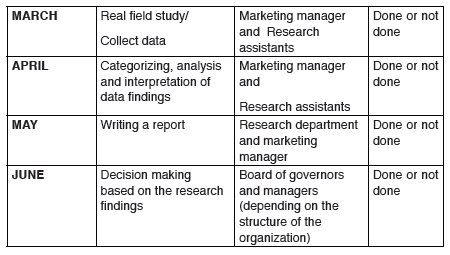
a. Customer survey
This is the process of finding out customer’s attitudes (their needs,
preferences, purchasing power) towards your product in the market or what
you plan to put in the market. For the survey to be successful, one must
know the types of customers.
Types of Customers
• Loyal customers: These are customers who buy from the business
regularly. They are few but they bring more money to the business
• Impulsive customers: These buy whatever items that are attracting to
them. No specific item in their mind, they just buy by impulse.
• Potential customers: These are people who are able to buy but not
yet ready to buy business products.
• They can be turned into customers in the near future.
• Real / Actual customers: These are customers who have already
done some transactions with the business.
• Discount customers: These are customers who buy low cost products
that have been discounted, they buy only when businesses discount
their prices.
• Cash, cheque or credit customers: These are customers who buy
depending on modes of payment.
Importance of customers to a business “A customer is the backbone
of the business”
• A customer is a source of income to the business
• They advise the entrepreneur by giving constructive feedback
• They provide capital to the business when they pay in advance
• Customers are the reason for the existence of the business, they
consume business products.
• Customers spread business reputation
• They provide important information on companies’ rivals
• Customers are sources of business profits
• Customers influence business innovations
• Customers recommend the business to other customers
• Customers advertise the business.
Importance of treating customers well
• It increases the sales of the business
• It improves business reputation
• It encourages prompt payment
• It is a source of business growth and success.
• It is a source of innovations and creativity
• It helps the business to improve on its operations
• It is a good way to maintain customers and attract potential customers
• Etc.
Customer data collection
You can collect the information on customers by using various methods
including:
• Mobile technology
• Internet
• Customers’ real time behavior (observing their actual behaviors)
• Questionnaires
• Social media like face book, WhatsApp, ...
• Interviews
• Experiments
• Suggestion boxes (feedback boxes)
• Personal tastes and preferences
• Being your own customer
Good ways of treating customers
• Giving them discounts (reduction on the prices)
• Giving gifts to customers
• Giving them credits
• Organizing parties for customers
• Being honest and kind to customers
• Delivering goods on time
• Offering after sales services like transport facilities to those who buy in
bulk
• Accepting goods returned in case they are defected or damaged
• Using appropriate weights and measures
• Selling them fresh goods i.e goods which are not expired
• Etc
b. Product survey / analysis
Product analysis / product evaluation refers to forming questions about a
product, its quality and forming some answers. Before launching a new
product, marketing professionals first test it with a selected audience. A new
product survey provides a way for marketers to understand when to start,
modify existing ideas, how and who to market. Product analysis can also be
carried out by comparing similar products with each other using the same
criteria.
The purpose of Product Analysis
• To help customers determine whether the product is worth buying
• To improve the version of a product
• To provide a prototype (something developed/ improved before a final
product is manufactured)
• To determine product price
Criteria to use while conducting product analysis
• Ergonomics: This refers to the study of working conditions. So, the
question would be like: will this product make consumers uncomfortable?
• Cost: How much will it cost to produce this product and for how much
will it be sold
• Aesthetics: How does a product look like?
• Construction method: What are the joining techniques used for that
product?
• Client’s requirements: is this product made in line with customers’
needs?
• Colors and texture: The color and texture and effectiveness of a
product should be assessed.
• Health and safety: Does the product fulfill health and safety standards?
• Materials: Are materials suitable for that product? Are they quality
materials?
• Environmental impact: Is the product environmentally friendly?
Are materials from suitable sources? Can the materials be recycled/
reused?
c. Supply survey
A supplier is any person or a company that provides goods or services to
another usually in exchange for payment.
Supply survey refers to the process of analyzing, finding out and establishing
the best potential suppliers of a given product.
Types of suppliers
• Manufacturers: These are businesses that turn raw materials into
finished goods. They supply their outputs to the wholesalers.
• Wholesalers: These business people buy large quantities and resell to
other traders especially to large scale retailers.
• Agents: These are suppliers who stock and supply products on behalf
of other business people especially manufacturers or wholesalers.
• Retailers: These are small scale suppliers who sell goods in smaller
quantities to final consumers.
The supply chain/ chain of distribution
The supply chain refers to the channels through which goods are distributed
from producers to the final consumer. It involves the relationship in terms of
people, organization, products and activities involved in moving products up
to final user.
Examples of a supply chain: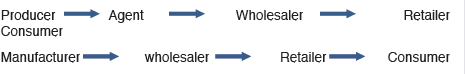
N.B: The length of a supply chain may be short or long; it depends on the
following factors:
Factors that influence the chain of distribution
a. Nature of goods: Expensive goods like cars tend to be sold directly
to the consumers
b. Scale of production: Some producers produce in great quantities
and have no ability to sell directly to the consumers.
c. Nature of market: For local goods, it may be possible to sell directly
to consumers but imported goods normally pass through middlemen.
d. Government policy: Government may set up a marketing board
such that producers sell through such bodies.
Ways of finding out potential suppliers
A potential supplier refers to that who is likely to provide you goods and
services at a later date/give you credit. To find this, a variety of ways is
proposed here:
• Recommendation from friends
• Exhibitions
• Media
• Trade associations
Factors to consider when choosing the best supplier
• The quality of goods and services supplied
• Consistency and reliability of the supplier
• Good communication
• Terms and conditions of payment
• Lead time and distance: The shorter the lead time and nearer supplier,
the better the supplier
• Taxes and regulatory procedures: A better supplier is the one with
goods of low taxes or non-taxable goods because taxes increase the
costs of the product.
• Financial capacity of the supplier: The supplier with higher financial
capacity supply enough and sufficient quantities whenever required.
• Price: The lower the price the better the supplier.
• After sale services
• Reputation of the supplier or legal status of the suppler
• Methods of delivery.
When the above factors are favorable, then the better the supplier.
d. Competitor survey/ competitor analysis
A competitor is any business firm that provides similar goods and services
like ours and whom we are sharing the same customers.
Competitor analysis refers to the process of assessing the strengths and
weaknesses of both current and potential competitors.
You cannot analyse competitors unless you know them; here are some types
of competitors:
• Potential competitors are those companies that are not yet in the
same market place as the one who intend to be in or who are already
in.
• Current competitors are those who are already in existence and
already producing similar goods and services.
• Direct competitor: This is the one who produces or sell identical/
similar products as your own business.
• Indirect competitor: This is a business that produces products and
services that are close substitutes. These competitors target the same
customer with a product that provides an alternative level of satisfaction.
Importance of competitor analysis
• It enables an entrepreneur identify market gaps
• It helps in knowing the competitors’ position
• It helps to know competitors’ strengths and weaknesses
• It helps to identify market opportunities
• It is a good way to develop new technologies
• It is a key element in business plan
• It helps in pricing goods and services
• It helps to predict competitor’s behaviors
• It is a good tool to adaptation of good strategies from competitors.Sources of competitor’s information for analysis:
Application activity 5.4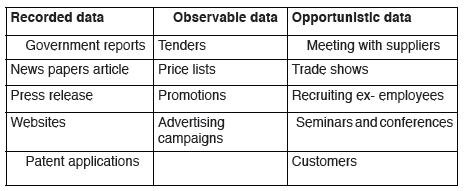
1. It is said that a customer is a king, explain this statement.
2. Explain the importance of competitors in business
5.5 Tools/techniques used in market survey and importance
of market survey
Activity 5.5
1. Jonathan is about starting a juice factory processing but is
worried about information on customers’ ability to buy, products
that customers want most, location of his business etc
Required: advise Jonathan on which technique/techniques he
would use to get the needed information?
2. Is market survey/research important? Justify your position
5.5.1 Tools/techniques used in market survey
a. Interviews
Interview as a source of research data refers to systematic talking and
listening to people. The person asking questions is the interviewer while the
person answering is called the interviewee or respondent. Interviews may be
face to face or over a telephone.
b. Observation
Observation may be defined as a systematic viewing of a specific phenomenon
in its proper setting for the specific purpose of gathering data for a particular
study. Observation as a method include both ―seeing and ―hearing. It is
accompanied by perceiving as well. Using observation of customers, the
researcher can observe peak days, time, age and sex of buyers, etc.
For example, if you want to find out which age group buys most from Huye
market, observation method would be simple and straight forward to find
out. The researcher positions him/herself in a strategic position near the
market main entrance gate, counts and records the most age group of all the
buyers entering the market. At the end of the research period, this data can
be analyzed to get the information required, that is which age group (male or
female) shops most from Huye market.
c. Focus groups
A focus group is a small, but demographically diverse group of people and
whose reactions are studied especially in market research or political analysis
in guided or open discussions about a new product or something else to
determine the reactions that can be expected from a larger population. It is
a form of qualitative research consisting of interviews in which a group of
people are asked about their perceptions, opinions, beliefs, and attitudes
towards a product, service, concept, advertisement, idea, or packaging.
Questions are asked in an interactive group setting where participants are
free to talk with other group members. During this process, the researcher
either takes notes or records the vital points he or she is getting from the
group. Researchers should select members of the focus group carefully for
effective and authoritative responses.
d. The Questionnaire
Questionnaire is a pre-determined set of questions used to get information
from a client. These questions are presented in a written form and taken
or given to the respondent. Questionnaires can be fact or opinion based.
Respondents are expected to return the filled questionnaire to the researcher
for analysis. The questionnaires should be well planned and carefully
formulated if it is to generate the right data.
Questionnaire questions
Questionnaire questions can either be open ended or closed ended questions.
Open-ended questions: Open-ended questions are questions that
allow someone to give a free-form answer. These questions are asked
to encourage a meaningful and full answer using the respondent‘s own
knowledge. Examples;
a. What do you think about the new product?
b. How is your relationship with your loyal customers?
Closed ended questions: These questions require the respondent to
respond by choosing from a limited range of responses pre-determined by
the researcher.
Examples:
1. What is your gender?
a. Female
b. Male
2. How are you likely to transact with our business this month?
a. Very likely
b. Likely
c. Unlikely
There are several basic principles to remember when developing such questions.
• The question should match the research objectives. You must
know why you want to conduct the survey in order to be able to ask the
right questions.
• Understand the participants. It is important to remember that it is
your respondents (and not you the researcher) who will be answering
the questions. Compose questions that they understand and not those
that you understand because it is them (the respondents) answering
and not you the researcher.
• Use familiar and natural language. Use the language level that is
understandable by your respondents. Consider their level of education
and age. Also consider your religious, social, political and culturalbackground in phrasing the questions.
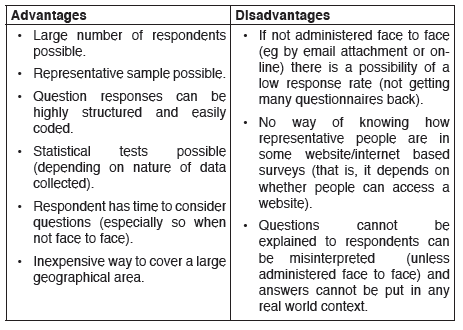
Advantages and disadvantages of questionnaires
5.5.2 Importance of market survey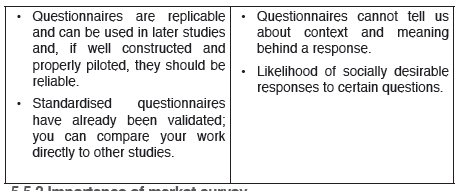
• Maximize sales and profits; whenever the collected information testifies
that customers are well handled and maintained, business increases
its sales and profits
• Retain customers; when customers’ needs are addressed accordingly,
customers remain in the business
• Identifying suitable suppliers hence, determining level of demand:
when suppliers sources are certain (shown by market research) it is
easy for the business to determine its productivity and level of demand
• Properly locate the business: when a market research has been
conducted well, the information like customers, income levels and
source of raw materials are available hence a business is located
nearest these opportunities.
Application activity 5.5
Imagine a situation when you have finished your secondary school
studies and one of your family members learns that you studied
entrepreneurship and so accepts to grant you the capital to start your
own business. But before he/she gives you that money he/she asks you
to first carry out market research for the feasible business.
He/she then asks you to first carry out the following market research
tasks after which you prepare report and present it to him/her for you to
obtain the promised capital.
1. What products (goods or services) that people in your community
would like to have but are currently not being provided?
2. Choose one product that you would be interested in dealing with.
3. Who from your community can give you information about the
product you identified?
4. Decide the population sample (the number of people identified in
no. 3 above) to ask
5. Formulate questions that you will use to collect the data that you
require about the product that you chose in no. 2 above)
6. Make a plan of how you will collect the data and how you will
analyse it.
Skills lab 5
Given the questions below, carry out a survey in your community and
thereafter make a report according to the findings from the research. Show
how you will use the 5Ps of marketing differently after analyzing feedback
from the community so as to ensure success of the business club.
Interview questions:
1. What do you like most about the products that you normally buy and
why? If you have a business club at the school, ask them what they
find interesting about the club product
2. What changes would you propose to the above product (ones they
normally buy?)
3. How do other products similar to the above product differ from others?
4. As aspiring entrepreneurs, advise us on how we can best extend our
products to bigger markets outside our community?
5. Name other products we could make from locally available resources
that can be most competitive.
End unit 5 assessment
1. Choose the best answer for the following statements
i. Having no research questions or poorly formulated research
questions will lead you to poor research findings because:
a. You will only consider epistemological queries
b. Marks are allocated for having a research question and without
them my project will be penalized.
c. You will not know what data analysis method used.
d. Your research is likely to be unfocused and you are likely to be
unsure of what data to collect.
ii. What is data collection?
a. Collecting the research question and objectives together
b. Gathering the information (data) which will help you address
your research question
c. Reviewing the literature
d. Outlining how you will gather the information for your research
question.
2. Explain how research can help the marketing department of abusiness in achieving its target.
