UNIT 12 TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATION IN THE WORLD
UNIT 12: TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATION IN
THE WORLD
KEY UNIT COMPETENCE:
By the end of this unit, I should be able to analyse the impact of transport and
communication projects on the sustainable development of different countries in
the world.
Introductory activity:
Read the passage below and answer the following questions.
In eastern province of Rwanda there is a high production of banana. Mr. Gatabazi imported a
lorry to help the people to carry their harvests to the market instead of using
their heads. Gatabazi extended his businesses and became a businessman in
the city of Kigali. He started to import his products from China. Sometimes he
goes there to purchase goods or calls his partners using his mobile phone,
then orders his goods, and pays using his BK Visa card, and finally gets his
goods without moving from Rwanda to China.
What types of transport mentioned are above?1. Explain the economic importance of the transport that Gatabazi12.1. Transport
introduced in that area.
2. Describe the types of transport that he uses to import goods from China.
3. What form of communication that he uses to get his products?4. Mention other types of communication he can use to order for his goods.
12.1.1. Meaning and types of transportLearning activity12.1
1. Observe the above photographs and identify the types of transport
shown.
2. Which type of transport is common in your area and why?
The term transport refers to the movement of passengers and goods from one
place to another. All means of transport need places where journeys start and end.These are called terminals.
Terminals for land transport are called Bus station or Train station. Those for air
transport are Airports while terminals for water transport are called ports. There are
two types of ports such as in-land ports and sea Ports. A port needs a productive
hinterland, that is an area from which the ports receives goods and passengers and
where they are delivered (areas surrounding a port).
A. Types of transport
There are three main types of transport as described below with their advantages
and disadvantages:
• Land transport
• Water transport
• Air transport
i. Land transport
Land transport is the type of transport that takes place on land. It can be
subdivided into: Human portage, Animal transport, Road transport, Railway
transport and Pipeline transport.
a. Human portage / porterage:
This is when people carry their load on their heads, on their backs or in their hands.
It is the most used transport by most people in various parts of the world. It is
predominant in developing countries because of limited capital and infrastructure
to use modern facilities and inaccessibility of an area. For example, lack of roads toreach remote areas.
Advantages
• It helps in inaccessible areas.
• It is cheap compared to other forms of transport.
Disadvantages:
• It is very slow compared to other forms of transport.
• It requires a lot of human energy and is time consuming.
b. Animal transport:
This form of transport is commonly used in areas where it is not easy to develop
other means of transport especially in arid (desert) areas. Animals used include:Camels, cows, Horses, Donkeys etc.
Advantages
• It is used in wild areas where other means are not possible.
• It is quicker than the human portage.• It is suitable in areas where human labour is limited
Disadvantages
• It is slow compared to road transport.
• Some animals cannot move in hilly areas.
• Some animals cannot withstand certain climatic conditions.
c. Road transport:
This involves the movement of goods and passengers mainly by vehicles, bicyclesand motorcycles.
Advantages
• Roads can be constructed in areas which are accessible to other forms of transport.
• Because of being flexible goods can be sold on route or can be delivered any
time.
• It is cheaper and faster for short distances.
• In some cases, it does not require large capital, except road construction.
• It is easier for people to own and purchase vehicles, bicycles and motor cycles
than airplanes, motors boats and ships.
• It provides door to door services.
Disadvantages• Heavy loaded Lorries are too slow.
• Weather conditions affect road transport especially during the rainy season.
• There are expensive to construct and maintain especially in towns.
• Roads are affected by congestion and traffic jams in heavily populated urban
areas.
• Unsuitable for heavy and bulky goods compared to water transport
• Vehicles at times run empty because of not having a scheduled timetable.
d. Railway transport
This involves the carrying of passengers and goods by train or tram along designatedroutes.

Advantages• It is cheaper for transporting bulky goods.Disadvantages
• It is less affected by weather conditions.
• It uses known routes and known timetable.
• It carries more load and a big number of people.
• It is safe since the chance of accidents or breakdowns are minimal.
• The use of railway lines does not allow trains to reach remote areas.• It is very expensive for short distances.e. Pipeline transport
• It is not suitable for carrying perishable commodities.
• It is time consuming/ slow.
• It is costly in terms of maintenance. Currently trams are being replaced by
buses in modern cities.This involves the movement of liquids and gases through a pipe from one point toanother.

Advantages:• It is cheap and easy to maintain.Disadvantages:
• It is relatively fast.
• It can be used to transport large quantities of liquids at a single time.
• It is not affected by weather conditions.
• It does not pollute the environment.
• It is free from traffic congestions.
• It is convenient in transporting highly inflammable commodities such as petroleum.• It cannot be used to transport other commodities, apart from gas and liquidf. Water transport
only.
• It may be damaged leading to heavy losses.
• It does not provide door to door services.
• It is expensive to construct.
This is the movement of goods and passengers on water by use of ships, ferries,canoes and boats. It involves both in-land and marine water ways.
Advantages of water transport.
• It does not require any route construction.• It is the cheapest for bulky goods.g. Air transport
• Bulky commodities can be transported over a long distance.
• It experiences less traffic congestion compared to road transport.
• It is suitable for carrying fragile goods because there is no shaking.
• Disadvantages of water transport.
• Construction of sea port is too expensive to be afforded by most countries.
• It is used by areas with navigable water bodies i.e. limited in use by landlocked
countries.
• It can be affected by sea pirates.
• It is very slow in movement compared to air and road transport.
• Obstacles on rivers such as rapids, waterfalls, floating vegetation, sand bars,
aquatic animals, make them un navigable hence affecting movement of water
going vessels.
• Canals are affected by seasonal changes.• Storms and winds sometimes interfere the ship schedule.
This is the form of transport that uses flying objects in the air such as airplanes,drones and balloons.
Advantages of air transport
• It is the fastest and most comfortable method of transport.
• It is suitable for transporting perishable commodities.
• It is suitable for carrying urgently needed goods.
• It can go to any place with an airport.
• It is secure, not subjected to robbers.
• It is less affected by relief features.
• It does not need any route construction compared to road and railway
transport.
• Its time saving sine it follows a specific time schedule.
Disadvantages of air transport
• It causes air and noise pollution.
• It has limited storage space.
• Usually weather conditions such as fog interfere with its schedule.
• It is very expensive in terms of movement costs.
• Long time is taken in air traffic control at airfields. e.g. checking and booking
• It requires large capital in airport construction and aircraft purchase.
• It requires highly skilled man power to operate.
• It is a target for terrorist attacks.
Application activity 12.1:
1. Explain why land transport is the most used type of transport in Rwanda
compared to air and water transport.2. Describe the challenges associated with road transport.
12.1.2. Factors influencing the development of transport and
importance of transport
Learning activity 12.2
1. Rwandair is improving its business worldwide. Explain the importance of
that improvement?
2. Make research and analyze the physical and human factors that influence
the development of transport in your district.
a. Factors influencing the development of transport
The factors affecting transport are physical, political and socio- economic. They are
discussed below:
• Relief: Steep slopes make the construction of roads and railway lines expensive.
On the other hand, valleys have swamps, that contain water logged soils that
are too soft to allow heavy objects like trailers, Lorries and trains to move on
them.
• Climate: Too much rainfall results into floods and landslides, hindering
transport on the ground. On the other hand, accumulation of fog and clouds
reduce visibility hence affecting transport.
• Vegetation: Thick vegetation cover makes construction of road and rail networks
difficult because it requires uprooting big trunks of trees. Furthermore, thick
vegetation modifies climate through evapo-transpiration hence affecting air
transport.
• Capital: The construction of roads, railway lines and airports is expensive. At the
same time, a lot of money is required to buy ships, trucks as well as airplanes.
• Political instabilities: Wars lead to massive destruction of transport means and
infrastructure such as roads, wagons, airports and ports, making transport
extremely difficult.
• International restrictions based on international boundaries: These affect
transport in that they restrict amount of freight. The same applies to road
transport.
• Economic factor: The structure and nature of transport costs are examined,
together with service quality and methods of pricing and charging.
• Government policy:These include political motives for transport facilities; g
overnment involvement in capital, monopoly, competition, safety, working
conditions and coordination between modes, transport as an employer and socialconsequences of transport developments.
A. Importance of transport to the development of countries
Efficient transport is an important factor for economic development on both global
and national scales. It can be a boost or a barrier to economic growth. Transports can
contribute to economic development in the following ways:
• Transport promotes trade and industrialization through the transportation of
necessary raw materials to factory for production of goods and finished goods
to consumers
• Transport systems offer employment opportunities to many people.
• Transport promotes urban development as many urban centers have
developed where transport network converges.
• Promotion of international relations since transport brings leaders together
face-to-face talks.
• Promotion of tourist industry, tourists move by use of means of transport.
• Stimulation of the development of other sectors such as, agriculture, fishing
and mining.
• Transport increases revenue through taxes to the government and income tolocal transporters.
Application activity 12.2:
Visit the nearest taxi park and note what you observe in terms of economicimpact of the transport.
12.1.3. Problems/challenges affecting transport and strategies of
improving transport.
Learning activity 12.3.
Analyse the photograph below taken in Nyabugogo andexplain the phenomena that occurred in relation to the problems affecting transport.
a. Problems/challenges affecting transport
There are major problems affecting transport activities as mentioned below:• Inadequate capital: Transport requires enough capital investment. That is why
it becomes difficult for developing countries that have weak economies to
construct and maintain transport facilities such as roads, airports, ports, and
railway lines.
• Natural barriers: Hostile environment such as deserts, forests, rugged and
mountainous terrain hinders the establishment of transport facilities.
• Political instability: Some countries have undergone periods of political
instability. With long periods of fighting in these countries, transport facilities
were targeted for destruction while new lines were not established.
• Climate like heavy rainfall and floods make roads muddy and slippery. BadApplication activity 12.3:• Mass wasting like landslides and mudflows affect roads in mountain areas andclimate disturb air transport also.
make roads impassable for some times.
• Low technology causes over dependence on imported expertise and
technology which are expensive. This is associated with lack of skilled man
power to construct infrastructure.
• Presence of water falls and rapids along river courses and their tributaries
make water transport difficult.
b. Ways of improving transport
• Ensuring political stability and avoid wars that destroy transport facilities.
• Containerization of the ports and harbors for effective handling of goods and
reduce delays.
• Government policies. Governments have to develop and implement
international transport projects like building international highways or railways
as the project understudy between Rwanda and Tanzania. Such policies boost
transport development.
• Bridges are constructed across rivers to connect different areas across rivers
and streams.
• Draining swamps for road construction.
• Improve engineering technology and use of national resources and materials
to construct transport infrastructures. There is also need to train skilled
manpower.
• To develop air transport for both domestic and international connections in big
countries like it is the case in USA, in areas with large impenetrable rainforests
like Equatorial forests in DRC or Amazonian forest in South America and largewater bodies (oceans).
1. Using examples, explain the challenges affecting transport in Rwanda.12.1.4. Case studies
2. Suggest different ways Rwanda as a landlocked country can use to
improve its international transport.Hui con ta estrari bunimum fautomperfinte popore tus, ses, culegerum se firtius inatui cum nihilic
Learning activity 12.4:
Make research, and find where the following are located on the world map:
Tanzam railway, Trans African Highway, Trans- Siberian railway, Rotterdam
Europort and St. Lawrence sea way.
a. Tanzam railway / Tazara railway
Tanzam railway also called Uhuru railway runs from Kapiri-Mposhi in Zambia,northwards to Dar es Salaam on the Indian Ocean in Tanzania. It was opened in 1975.
i. Major aims of Tanzam Railway • To promote Tanzanian and Zambian exports and imports.ii. Benefits of the Tanzam Railway
• To promote Tanzanian and Zambian exports and imports.ii. Benefits of the Tanzam Railway
• To solve Zambia’s problem of being landlocked,
• To create accessibility to the sea for export of copper.
• To open up the southern highlands of Tanzania which were productive butremote.
• Tanzam Railway provides landlocked Zambia with reliable access to the sea
and therefore made the flow of trade easier.
• It promotes economic development in remote parts of Tanzania which were
not accessible.
• It leads to political and economic development of Tanzania and Zambia.
• Industrial growth has been achieved since both raw materials and finished
goods can be easily transported by using railway. Tanzam railway encouraged
the development of mineral exploitation in Tanzania and Zambia e.g. coal and
Zambian copper.
• It provides employment opportunities for the local people like drivers,
technicians, casual laborers and earns income to improve their standard of
living.
• It has contributed to the economic growth of the port of Dar-es-Salaam while
increasing government revenue.
• It contributes to the development of tourism especially to Tanzanian through
port charges.
• It influences the development of other transport systems like feeder roads.
• Railway reduces transport costs incurred by Zambia compared to using the
ports of other countries for its trade such as Lobito in Angola.
iii. Shortcomings of Tanzam Railway
• The serious delays on the route because of the long distance covered.
• High cost of maintaining the railway lines due to frequent breakdown. Railway
need to be regularly rehabilitated and upgraded.
• It is affected by the weather conditions (heavy rain). Kilombero valley section
is always exposed to flooding.
• Zambia faces the problems of high taxes in the payment of port charges at
Dar-Es-Salaam.
• There is poor management of railway lines due to corruption and
embezzlement. Private sectors can better manage the railway.
• There is a use of old line structure with shortage and inappropriate locomo-
tives and wagons. There is a need to develop systematic programs to replaceold locomotives and wagons as well as communication systems.
b. Trans- African Highway (T.A.H)
This is a highway that starts from Cape Town to Cairo linking the Northern and
Southern regions of Africa. It passes through Bulawayo, Harare, Lusaka, Dar-es
Salaam, Nairobi, Addis Ababa and Khartoum to reach Cairo. It has deviations to serve
other regions adjoining the highway. It also runs from Mombasa through Uganda,
DRC and Cameroon to Lagos in Nigeria. The main purpose to build Trans-AfricanHighway was to promote trade between all corners of Africa.
i. Advantages of the Trans-African Highway:
The Trans-African Highway has too much benefited the African States in / by which
it passes in the following ways:• It has enhanced cooperation among the countries through which it passes.c. Trans- Siberian railway in Russia
• The highway spearheaded the formation of economic and political unions
such as East African Community (EAC) and Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
• It has increased trade prospects between member States and has also
stimulated trade on the continent by facilitating easy movement of people
and goods.
• It has enabled the development of the remote parts of African countries.
• It encourages tourism in those countries where it passes and the distribution
of human settlement patterns (linear and nucleated types).
• It is important in the transportation of agricultural raw materials.
ii. Problems facing Trans-African Highway
The following are the major problems facing trans-African highway:
• Political instability or wars) in some African countries in which the high way
pass has limited transportation of goods along this highway, this has affected
its effective use.
• Frequent civil conflict affects its performance in various parts of the continents
where the high way is passing.
• Some countries charge high tariffs at the border posts which is increasing the
cost of transport.
• The volume of trade along the highway has further reduced due to delays
caused by numerous border bureaucracies of screening and vetting of goods
and passengers across borders.
• Insecurity and loss of goods on transit caused by banditry and smuggling
along these highways have made the highways unsafe. This has further
reduced their usage.
The Trans-Siberian Railway is a network of railways connecting European Russia from
Moscow with the Russian Far East and the East Sea / Sea of Japan. It is the longest
railway in the world with a line length of 9,259 km. There are branch lines to Chinathrough Mongolia and Manchuria. It was started in 1891 and completed in 1916..
i. The importance of the Trans-Siberian Railway: • The Trans-Siberian Railway gave a positive boost to Siberian agricultural crops.ii. Challenges of Trans- Siberian railway:
• The Trans-Siberian Railway gave a positive boost to Siberian agricultural crops.ii. Challenges of Trans- Siberian railway:
Wheat, rice, potatoes and sugar beet are grown. This facilitates substantial
exports to central Russia and Europe.
• It influenced the territories it connected directly, as well as those connected to
it by river transport.
• It attracts many foreign tourists in Russia, Siberia through creating accessibility
to tourist attractions like Ural Mountains, Lake Baikal, and Moscow metro
tunnel.
• The Trans-Siberian Railway encourages rural settlement in the inhabited areas
of Siberia
• Development of towns. Trans-Siberian railway runs through important towns
like Omsk, Novosibirsk, Irkutsk and Ulan-Ude, etc. These towns developed
accommodation, commerce, health and education services.
• Improvement of industrial development through transportation of raw
materials such as copper, phosphates, coal, iron, etc.
• Development of trade between the Eastern Europe and Asian countries like
Japan, China and Siberian.• Political and economic unity between the East and West Russia was achieved.
• Its construction led to clearance of forests as well as destruction of Urald. Rotterdam (Europort in the Netherlands)
Mountains
• It led to over exploitation of resources such as iron and steel from Karaganda
field and oil from the west Siberian oil fields
• Loss of lives through accidents like derailing of the trains and sometimes
collision.
• It led to urbanization in former natural environment areas with its relatedproblems such as congestions, slums development, and pollution.
Rotterdam is a port located at the mouths of rivers Rhine and the Meuse on the
North Sea. The name is derived from a stream known as Rotte. Today, the major
development is concentrated on Euro Port on the seaward end of new waterway and
not at Rotterdam. It is one the busiest port in the world. Rotterdam port serves a largerich hinterland of Belgium, France, Netherlands, Luxembourg and Switzerland.
i. The factors which influenced the growth of Rotterdam
Inland water transport:
Rotterdam has a well-developed in-land water linkage to the interior of Western
Europe.
These navigable rivers link the port to its hinterland: Elbe, Rhone and Danube.
• Strategic location:
The port of Rotterdam is centrally located where sea routes converge such as the
sea route to the North America, Africa and various parts of Europe and even Asia.
It is an important waterway for Ruhr industrial region.
• Suitable climate:
Rotterdam experiences a cool temperate climate. Like the other ports in the world,
Rotterdam enjoys conductive weather conditions free from mist throughout the
year.
• Establishment of industries:
Rotterdam is located in a region of heavy industrialization. The major industries
are oil refineries, food processing, ship building, petrochemicals, iron and steel
industries. The importation and exportation of both raw materials and finished
products through the port have led to its expansion making it the busiest port
in the world.
• Large and rich hinterland:
Rotterdam has a wide and rich hinterland which traverses the neighboring rich
countries such as Belgium, Switzerland, Luxembourg, Germany, France, and
Austria. The hinterland is rich in grains, mineral ores, iron and steel products.
The port therefore handles a large volume of import and export goods which
influenced its growth.
• There is a high level of technology:
The high level of technology is used in the construction of canals and its
maintenance, pipelines, railway lines that link the port to its hinterland.
• The availability of sufficient capital:
This has facilitated the expansion of port activities over the years. Big projects
for the development of the port were implemented such as the expansion of
industrial storage facilities, construction of pipelines, canals, railways and high
ways, etc.
• Proximity of Rotterdam to the North Sea:
North Sea is one of the busiest international routes in the world. This proximity
increases the amount of Cargo handled by the port, thereby fastening its growth
and development.
• Low tidal range:
The difference between the low tide and high tide at Rotterdam is very small. This
allows large ships to use this port. Many ships are able to load and off-load their
Cargo because of this unique characteristic.
• Favorable government policies:
The government of Netherland supported the establishment, growth and
development of Rotterdam port. It provided the capital for establishment of port
structures, established the authority which was given responsibilities of running
the port activities.
• Skilled man power:
Being in an area that is developed with modern universities the port benefited
from a large supply of skilled man power required in the port establishment.
ii. Problems facing Rotterdam Euro port:
• Problem of congestion because of many water going vessels.
• Pollution of the environment as a result of industrialization, urbanization,
vehicles which releases fumes to the atmosphere.
• Siltation of the river Rhine is a problem that faces the port.
• There is limited land for further expansion of the port.
• Overcrowding at the port due to many people.
• Big Population at the port made housing very expensive.
• High levels of unemployment because of high demand for jobs and this
sometimes results into the problems of crimes
• The problem of flooding because Rotterdam is located on the north part of
Netherlands which is a low-lying area.
• The problem of poor visibility resulting from fog and smoke at the port. This
leads to accidents and sometimes delays delivery of cargos.
• The problem of accidents by ships which often leads to the loss of Cargo and
sometimes lives.
• There is also problem of prostitution brought about by attraction from a large
population.
iii. Steps being taken to solve the problem:
• The construction of storm surge barrier automatically operated the control
storm surges and minimizes flooding at the port. Dykes have also been
constructed for this purpose.
• There is an increased use of radar system to avoid collision of vessels during
foggy weather conditions.
• The port authority occasionally dredges the river Rhine and Maas thereby
ensuring that they are free from silt and can be safe to ships.
• The industrial wastes are treated before they are released to the environment.
This minimizes the case of pollution. The noise is also carefully monitored and
regulated to avoid noise pollution.
• There is containerization to ensure safety of cargo, fast handling and dispatch
of cargo.
• The port authority has also reclaimed land from the North Sea marshlands and
the rivers to create more space for the port.
• There is a strict control of crimes through deployment of security personnel to
monitor and discourage criminal acts at the port.
e. St. Lawrence sea way (USA-CANADA)
St. Lawrence seaway stretches from Port Duluth on Lake Superior to port St.
Lawrence on the Atlantic Ocean. It covers a distance of 3,800 Km. It is the longest
inland waterway in the world with the largest volume of traffic. It serves Canada
and the USA. It allows passage of ocean going vessels. Before the sea way was
constructed, large ships could only sail on the great lakes up to St. Lawrence town as
far as Montreal. The construction of St. Lawrence seaway was a joint project venture
between the governments of Canada and USA. The construction works began in
1954 and ended in 1959.
The main aim was to create deep water for navigation between Lake Ontario and
Montreal. This would allow ocean going vessels to sail from the mouth of the St.
Lawrence River onto the western shores of Lake Superior.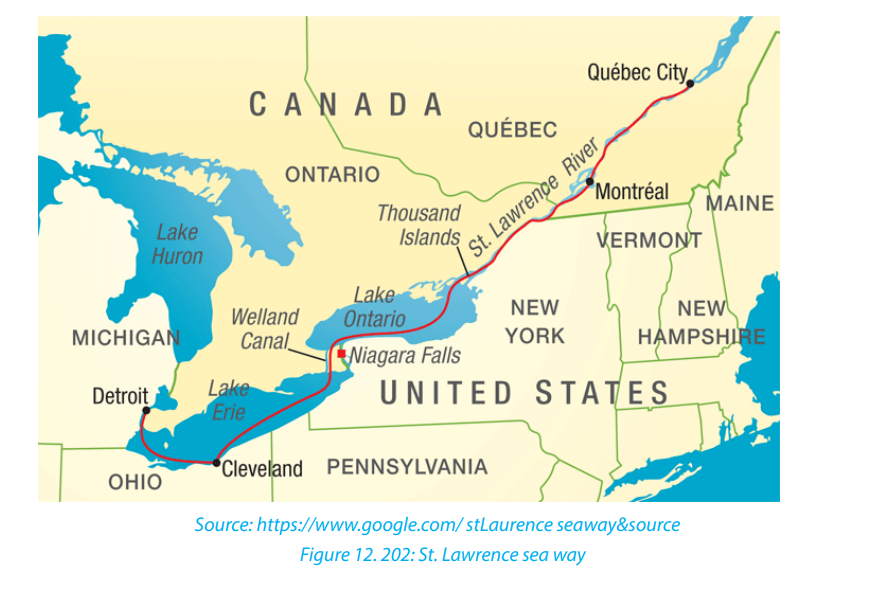
i. Economic benefits of St. Lawrence seaway for the USA and Canada• Cheap transport: The seaway has offered a cheap means of transport from
the interior of North America to the Atlantic Ocean. The ocean liner finds it
direct, quick and short to access the interior as opposed to the previous route
through New York. This has enhanced the movement of people and goods.
• Creation of employment: Through transportation of raw material and finished
products along the seaway, there has been an increased volume of traffic. This
has created job opportunities.
• Generation of hydroelectric power: The construction of dams along the seaway
like Saunders and Beauharnous on Niagara Falls has led to the generation
of abundant power. The power is cheap and reliable. It is used for both domestic and industrial use.
• Growth of Towns: St. Lawrence Sea Way has encouraged urbanisation along its
shores. This is because the ports along it have attracted settlement. Examples
of such towns are Quebec, Duluth and Hamilton.
• Increased volume of trade: St Lawrence Seaway has led to the increase of the
volume of trade between the USA, Canada and the rest of the world. This has
been due to the ease of transporting of goods such as iron ore, copper, wheatii. Problems of St Lawrence sea wayDevelopment of tourism: The seaway with the spectacular Niagara Falls is aand manufactured goods.
great tourist attraction. This has earned foreign exchange to the two countries.
• Development of industries: The seaway has contributed to the development
of industries in the USA and Canada. The power generated from the dams is
directly used in the industries. Likewise, water from the dams is used in cooling
industrial plants.• Congestion, unemployment, high crime rate due to the growth of urban centers.
• High cost of maintaining the seaway like dredging to solve the problem of
silting.
• Decline in fishing activities due to destruction of wetlands and fish habitant as
a result of dredging and blasting as well as pollution of water.
• Many rocks which are used to adjust the level of water to improve navigation.
These result into delays in movement.
• Increase of pollution due to oil and chemical spills as a result ofenormous increase of cargo size as well as industrialization.Application activity 12.4:1. Explain the problems that were encountered during the construction of12.2. Communication
Tran- siberian and Tanzam Railways.
2. Analyse the factors for the growth of Rotterdam port in Europe
3. Briefly describe how Trans African Highway and St Lawrence seaway have
contributed to development in their respective countries and continents.
Communication is a medium of sending and receiving information through various
means. It is a very vital aspect of the society. Without communication, spatial
interaction between people and communities would not be possible. People
communicate to get needed things such as information, money, advice or just
emotional support.
12.2.1. Meaning and types of communication
Learning activity 12. 5:
Observe the following images and explain how these devices are used forcommunication purposes
a. Types or forms of communication
There are different links, instruments and devices used in the transmission of
information from one point to another. Early modes of communication included
sending runners with verbal messages, fire and smoke signals, and later drums and
horn blowing. The invention of writing led to improved communication as letters
could be delivered to various destinations.
Those methods of communication were found to be slow and inaccurate in some
instances and limited in terms of the distances they could cover. The rise in electrical
technology led to a new concept in communication known as telecommunication,
which is communication over long distances.
The current modes of communication include telegraph, telephone, fax, e-mail,
courier, handwritten, television, radio, social networking.
The following are the main types of telecommunication:
i. Telegraph: Telegraph enabled messages to be transmitted by cables as
a series of electrical impulses. The signals were in the form of the Morse
code, which could be easily interpreted. Most places were thus linked by
telegraphic cables. Undersea cables were also laid below the oceans.
ii. Telephones: This is where cables connected to a local exchange are
used to transmit voice messages over long distances. The sound waves
are changed into an electric current which is then transmitted to the
receiver phone, where it is then interpreted by being re-transformed into
sound waves that can be interpreted by human ear. Due to technological
improvement, the cable fixed phones are being replaced by smart mobilephones which perform various communication tasks.
iii. Radio: is a way to send electromagnetic signals over a long distance, to
deliver information from one place to another. It also usually stands as a
machine which sends out and receives messages using air waves to a largemass of people
iv. Television: is a piece of electrical equipment which shows pictures
through the air or along cables
v. Internet: Internet means “interconnected networks”. It is a large system
of connected computers around the world that allows people to share
information and communicate with each other. It is a system that links
devices worldwide.
Application activity 12.5:
Explain the most forms of communication used in Rwanda and why.
12.2.2. Importance of communication, problems affecting
communication and their solutions
Learning activity 12.6
Many business people in the city of Kigali no longer need to travel to
purchase their goods in the foreign countries. They use different types of
communication to order for the goods and get them in few days in Kigali.
1. What do you think can be the consequences of such form of
communication?
2. Explain the importance of communication.
a. Importance of communication
The following are the main positive effects of communication:• Communication system facilitates economic development by sendingd. Interrelationship between Transportation, Communication and Economic
information to various locations of the world. Communication system
connects industries and business communities to take right decisions at the
right time by providing them with information and news related with business
and financial matter. For example, it is possible to know about the price of the
commodity prevailing at any part of the world quickly. This promotes domestic
and international trade.
• Communication is the basis of organisational functioning: good communication
is an essential tool in achieving productivity and maintaining strong
working relationships at all levels of an organisation. It is only when necessary
communications are made to subordinates and operators; about their jobs
that action is possible due to communication.
• Communication sector has led to the creation of employment opportunities
to a variety of categories of people such as journalists, media managers and
users
• Investors in the sector of communication such as radio, television and social
media (e.g. Facebook, WhatsApp, YouTube, etc. get more revenue and many of
them belong now in the world’s richest class.
• Communication facilitates easy dissemination of information to remote areas.
• Communication helps in building good public relations: good public relations
comprise relations of the enterprise with outside agencies, particularly
consumers and the public at large.
b. Problems affecting communication
The following are the problems affecting communication:
• Inadequate capital: Many developing countries experience a problem of weak
economies and few industries. They thus have insufficient funds needed to
construct and maintain communication facilities.
• High taxes:there are high taxes attached to the importation of communication
equipment as well as high operation charges.
• Inadequate technical know-how: This has hindered the growth of
telecommunication since most countries have to rely on expatriates whose
payments are very high.
• Natural barriers: desert, forest, rugged and mountainous terrains have hindered
the establishment of communication facilities like telephone boosters.
• Competition: there is competition between the local companies involved in
the sector and free online communication systems.
• Lack of skills: there is general lack of knowledge and skills to use
telecommunication devices such as computers, radios, newspaper, etc.
c. Possible solutions to the problems affecting communication
Drawing from the problems facing communication discussed above, it is evident
that most of them can be overcome by way of reversing them.
• Political stability: there should be dialogue between countries and the use of
peace talks should be emphasized.
• Investing in communication and where capital is not available, looking for
ways of getting it through loans or aid.
• Countries should invest more on training their people so as to equip them
with knowledge to hand the ever-changing technology. It is cheaper to train
home-grown personnel than to hire expatriates.
• To increase the knowledge in technology: Use the recent technology
radio, telephones, television, and internet to improve the standards of
communication.
• Communication is the link between knowledge and information. Therefore,
there is need to provide knowledge of the people to be able to communicateproperly.
Development
1. Both transportation and communication play some major roles in the
economic uplift of a country as they promote internal and external trade.
2. Transportation and communication systems help to promote the use of
natural resources, mobility of skilled labour-force, diversification of markets,
provision of fuel, increase in agricultural and industrial production.
3. Efficient transport and communication systems help to establish
relationships among people in different parts of the world, these have
also strengthened the feeling of unity among people in different cultural
backgrounds.
4. Transport and communication systems help to create job opportunity
for people living in the rural areas by connecting labourers and creating
employment for them in the industries, however these have also solved the
needs of industries and reduce unemployment.
5. The development of transport system also leads to development of
industries because transport system utilizes the product of industries and
both complement each other in different ways.
6. Efficient means of transport and communication have indeed shortened
time, distance, and cost that would have been used to move and to deliver
goods and information from one person to another.
7. Transportation and communication help to increase the size of the market
of your products by helping you to transport your products across different
countries which will help you to increase your sales in those countries that
is, by penetrating new markets.
8. Through the effective transport and communication systems one will know
how to strategies in terms of war and also curtail crisis from taking place at
any point in time.
9. Government can swiftly evacuate or inform her people against any
occurrence of natural disaster, outbreak of diseases and other social
problems through the means of transportation and communication system.
10. The production and distribution units (farms, factories, central places) that
are under primitive or high-cost transport conditions, had to be scattered
to serve distant markets, have tended to become spatially concentrated
in areas of greatest advantage. Market areas therefore have become even
more extensive as transportation has improved. Similarly, supply areas
have expanded. For instance, agricultural production has become more
profitable and so wider areas of production are opened up from the central
markets.
11. Transportation revolution has therefore significantly improved accessibility
of places and therefore bringing more developments and growth. This is
because transportation is the main vein through which developmentalfacilities and services are channelled. The level of transport development of
many areas therefore positively correlated to the level of economic growth
and development.
12. Transportation plays a major role in the economy, which increases theproduction efficiency and links to the logistic systems.
Application activity 12.6
1. Explain factors hindering effective communication in your area.
2. What is being done by Rwandan government to improve communication?
End unit assessment
1. Examine the relationship between communication and transport.
2. Explain the role of the government in ensuring effective
communication in Rwanda.
3. Referring to MTN, TIGO and AIRTEL explain the importance of
telecommunication companies in the development of the country.
4. Explain the factors that have contributed to the development of
transport in developed countries than developing countries.
5. Analyze the level of transport and the improvement of technology in
communication in Rwanda and describe how this process can support thesustainable development of the country
