UNIT 11 INDUSTRIALIZATION IN THE WORLD
UNIT 11: INDUSTRIALIZATION IN THE WORLD11.1.1. Definition of industry
Key unit competence:
By the end of this unit, I should be able to evaluate the success of sustainable
development projects in the industry in different parts of the world.
Introductory activity:
Mr. Gatete is a farmer, he grows crops like coffee, cotton, bananas and
fruits and rears cows and goats. He sells both crops and animal products to
Amahoro Cooperative Society which transforms these products into Juice,
Packed milk, Cheese, Clothes etc.1. According to you, in which category of industry does Mr. Gatete belongto?2. Explain the factors on which Amahoro Cooperative Society base onto establish the factory which transforms Gatete’s products and theproblems that may be associated with the factory.3. Make research on internet and find out five examples of moreindustrialized countries in the world and describe the factors for their11.1. Definition, classification of industries, factors influencing locationindustrial development.
of industries and major industrial regions of the world
Learning activity 11.1
Use experience from your local environment and answer the following
questions:
1. Identify the categories of industries observed.
2. Describe the factors that influenced their location.
An industry is an establishment that involves production of goods and offering of
services. It also refers to the processing of raw materials into finished goods.
Industrialization refers to the concentration or to the development of industries inan area, country or region.
11.1.2. Classification of industries
There are three categories of industries which are closely interrelated.
• Primary / Extractive industries
These are industries which produce raw materials. They are concerned with the
extraction of natural resources. They involve agriculture, forestry, mining and fishing.
• Secondary / Manufacturing industries
These are industries that transform raw materials into finished products suitable for
consumption. They include food, beverages, chemical products, etc.
They are subdivided into two categories:
- Heavy industries: Such as engineering, metal goods, chemical, ship building
industries, etc.
- Light industries: Such as food processing, plastics, textiles, electrical equipment,
cosmetics and toilet articles etc.
• The tertiary / Service industries
These are industries involved in the provision of services. The tertiary industries do
not produce goods but provide backup services to the industrial sector. The services
provided include transport and communication, trade and commerce, financialinsurance, printing and publishing, education, health, banking, etc.
11.1.3. Factors influencing the location of industries and industrial
development
There are several factors, including physical, economic, political; historical that
influence the location of an industry. A brief description of these factors is shown
below:• Efficient labor: An adequate or skilled labor force is essential in the initiation
and continuance of an industry. It gives the company a maximum output with
lowest possible costs.
• Power and energy: Any industrial establishment must be located in the areas
with enough fuel or other sources of energy.
• Land: The location of any industry requires extensive land for set up and future
extension.
• Government policy: Government’s policy of encouraging industries is also
an important factor. This can be done through tax reduction, giving land
and energy to investors to establish industries in the areas. This is done foreconomic and political reasons e.g. job creation and regional balance.
.Raw materials: Raw materials in their different forms are important in the
location of industries. Therefore, the availability, the value, size, quantity,
quality, weight and proximity of the raw materials are essential requirements
for industrial location.
• Transport and communication: Modern industries require constant supplies
of raw materials, often in great bulk from various sources. Finished goods have
to be distributed to many places also. Thus the availability of a good network
of transport facilities is another important factor in the location of industries.
• Market: There is a very strong justification for industries to be located near
the markets which consume their finished products. Some types of industries
are more likely to be located near markets than others; e.g. perishable goods,
fragile goods, bulky goods etc.
• Capital: No industry can be developed unless it has financial support. The
finance may be provided by private investors, large companies, or by the
government. Capital is required in every phase of industrial development.
Money is required for the purchase of the land , construction of factories,
purchase of machines, acquisition of the required raw materials, transportation
of both raw materials and finished goods and for the payment of wages,
marketing, advertisement, etc.
• Water supply: Certain industries, especially iron and steel, aluminum smelting,
thermal power generation, pulping of timber, synthetic fibre manufacture and
chemicals, consume enormous quantities of water either in processing the
raw materials or for cooling purposes.
• Industrial inertia: This is when an industry remains in its original location even
if the initial advantage that led to its location is no longer available. This is due
to three main factors:
The presence of a good transportation network of roads, railways,
canals and so on. An industry moving to a new site might face
transportation difficulties.
Influence of skilled labor and experienced workers built up in that
area.
The cost of building and equipping a factory is extremely high.Industrial establishments do not readily undertake a complete move
with the new building and tooling-up costs that this entails.• Sites: Some industrial plants have to be sited on leveled ground instead of hilly
regions. Others require vast acreage of land and the cheapness of the available
land is a primary consideration.
• Climate: Climatic factors sometimes have to be taken into account especially
in countries with extremes of climate. Costs of heating, air conditioning
factories or offices may be prohibitive. Hot climate may create problems of
storage. Climatic factors such as severe winters or annual floods may affecttransportation adversely.
• Political stability: encourages long term investment necessary for industrial11.1.4. Major world industrial regions
development. This is why countries with little political instability like Western
Europe are advanced in industrial development than developing countries ofAfrica and Asia.
There are major industrial areas in both developed and developing countries. Japan,
USA, and Russia are the example of industrialized countries in developed countries,
Egypt, South Africa, China and South Korea in developing countries.
Application activity 11.1:1. Describe the categories of industries common in Rwanda.11.2. Importance of industries and problems affecting industrial
2. Visit the industries located in your area and describe the factors that led to
their location..
development
Learning activity 11.2
According to you, why is it important for a country to have industries?
11.2.1. Importance of industries
Industries have the following advantages:• Industries provide self-sufficiency in essential goods rather than the need for
imports and dependency on foreign aid. In other words, it causes import
substitution and export promotion, which encourages development.
• Self-sufficiency gives greater political and economic strength. It makes a
country more independent of foreign political or economic domination.
• It creates employment. It employs both skilled and unskilled labor.
• Industrialization earns the country foreign exchange. If the products are
manufactured for export, the value of the commodities is increased and so the
revenue obtained from their sale also increases.
• Industrialization raises living standards of the population as they contribute toincrease their income.
• It contributes to the diversification of the economy and reduces reliance on11.2.2. Problems affecting industrial development
agricultural products which may fluctuate in prices.
• Industrial growth is cumulative and can stimulate growth in other sectors of
the economy.
• It provides infrastructure particularly electricity, transport and communication.
• Industries also improve social amenities like schools and hospitals.
• It contributes to the development of research and technology and the regular
training of skilled man power.
There are several problems that affect many industries. Below are the main and
common ones:• Inaccessibility to the distant world markets which results into low demand forApplication activity11.2:
the manufactured goods especially in landlocked countries.
• Lack of real capital investment. Many countries have a problem of inadequate
funds to set up industries.
• Shortage of unskilled, semi-skilled and skilled labor. Inadequate managerial
and entrepreneurship skills have also affected industrial growth.
• Lack of adequate supporting infrastructure. This is critical for the development
of industrial activity.
• Developed countries face the twin challenges of reduced demand and
increased unemployment levels in older industries as well as finding new
market for their industrial output.
• Competition for markets has led to blocks of countries grouping to reduce
trade barriers and to increase integration of supply and demand. Such trade
agreements allow individual countries to take advantage of agglomeration
economies and cheap labor among themselves. However, for countries outside
the trading block, they act as barriers to trade and tariffs.
• The infrastructural facilities in the developing countries are not at the level
necessary to produce and support industrialization.
• The shortage of valuable minerals in some countries, such as iron ore which
form a basis for the establishment of industries. These countries have to import
raw materials at high costs.
• In developing countries, poverty lead to a low demand for industrial goodsresulting into a limited market, thus affecting the process of industrialization.
Explain why the industries in developed countries are highly developed than
the ones in developing countries.
11.3. Problems resulting from industrial development and ways to
mitigate them
Learning activity 11.3
Why is it not advisable to live near industrial areas?
Industrial development has both positive and negative effects on a given country.• Pollution of the environment: In the areas of heavy industrial concentration,
land, air and water are contaminated by industrial wastes.
• Wildlife Extinction: Industrial pollution affects habitats of wildlife and destroys
its species; it is hard to recover them in the environment. For instance, major
industrial accidents like oil spills, fires, leak of radioactive materials cause great
damages.
• Global Warming: With the rise in industrial pollution, global warming has been
increasing at a steady pace. Smoke and greenhouse gases are being released
by industries into the air and this contributes to global warming. Melting of
glaciers, existence of floods, tsunamis, hurricanes are some of the effects of
global warming.
• The accidents caused by the machines used in industries: The machines used
in industries for various purposes may cause the accidents from the misuses
by the employees or from other external causes; e.g. Lightening, tsunami,
electricity, collapses of mining tunnels, etc.
• Leaching of resources from the environment: Industries do require large
amount of raw materials to process into finished products. This requires
extraction of minerals from beneath the earth. The extracted minerals can
cause the environment destruction in different ways.
Ways to mitigate the problems caused by industries
- Isolation of industries from settlements and sources of water to reduce the
effects of pollution.
- Reducing of greenhouse effects through neutralizing industrial fumes before
they are disposed into either air or water.- Efforts should be made to control pollution. These can take the form ofApplication activity 11.3:
industries treating their wastes before disposing them as well as recycling
some of those waste products and the use of biodegradable materials.
- Promotion of training skilled manpower and use of appropriate technology to
reduce accidents in industries.
- Creation of special areas/ zones where industrial wastes are channeled or
poured.
Examine the ways of reducing problems caused by industries in developing
countries.
11.4. Case studies on major industrial regions in the world
Learning activity 11.4
Make research and identify the major world industrial regions.
11.4.1. Developed countries
a. Industrialization in USA
i. Factors for the high level of industrialization in USA
USA is the world’s leading industrial nation. About four-fifth of the industrial
output of North America is contributed by the United States alone. The factors,
which helped in the industrial development of USA, are:• A wide range of raw materials such as agricultural raw materials and mineralii. Industrial regions of USA
raw materials.
• The population of USA was made up of immigrant from many advanced
European countries especially from U.K, France, Germany, Holland and others.
These immigrants brought with them the experience skills and technical
knowhow of their mother countries. This encouraged rapid industrial
development.
• USA is located on the opposite side of Atlantic from Europe. This has stimulated
trade and growing world markets. It has also led to industrial expansion.
• USA has extended water transport from St. Lawrence Seaway to the heart of
Geography Senior Six Student Book 309the continent via the Great Lakes. This has stimulated industrial developmentby providing cheap means of transport for raw materials and finished goods.• USA has a high level of technology. This has been maintained by adequateeducational and training facilities and a technological system. This systemattracts skilled scientists and technologists. This brain gain helps to give theUSA a lead in scientific modern industries such as electronics computers andso on.• USA has abundant petroleum, natural gas, local and hydro-electric power. Theavailability of various sources of power in economic quantities has stimulatedthe development of large manufacturing industries.• Availability of capital generated from international trade (from exports)encouraged industrialization.• The government of USA also encourages rapid industrialization. It encouragesexport promotion.• There is internal competition among the industries and this has stimulatedindustrial development.• Availability of extensive land for industrial development.
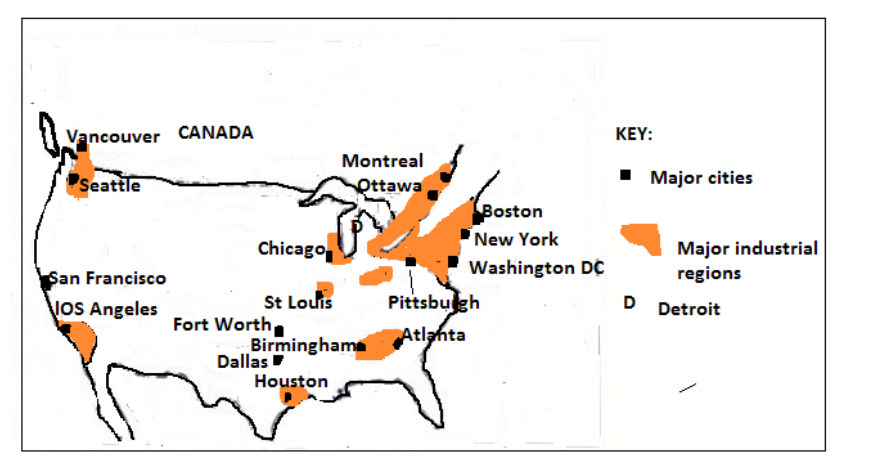
There are six industrial regions in USA:1. Southern New England: It is centered in Boston with two types of industries;Major industrial regions of USA
shipbuilding and textile,
2. Mid-Atlantic States: This region includes cities of New York, Philadelphia and
Baltimore. The industries here include iron and steel, engineering, printing,
electrical goods, foot wear and consumer goods.
3. Pittsburgh – Lake Erie region:this is the core of heavy industries, engineering,
glass, pottery, chemicals, synthetic, rubber, tyre making, generating
hydroelectric power from Niagara Falls, flour milling etc.
4. Detroit industrial region: this is the greatest automobile manufacturing
region of the USA. Other industries include electrical wires, glass, batteries,
paints, alloyed steel etc…
5. South Appalachian region: It is centered in Birmingham. Industries include
steel making, Hydro Electric Power generation, cotton textiles, metal works,
machinery manufacture etc.
6. Eastern Texas: It has major cities like Dallas, Fort Worth and Houston. Thisregion is the major USA source of oil and gas.
 b. Industrial development in Japani. Factors for high level of industrialization in JapanJapan is the most highly industrialized country of Asia and ranks among the mainindustrial nations of the world. Despite its shortage of industrial raw materials,Japan has been able to develop her industries because of the following reasons:• Development of hydro – electric power resources to provide enough power tosupport rapid industrial development because of little quantity of coal.• Efficient use of its limited raw materials such as copper, manganese, iron ore,sulphur and timber.• The coastline and many large ports facilitate the importation of large quantitiesof raw materials from all over the world. This is because of the geographicallocation of Japan.• The population that provides a large supply of labor and the development ofindustries since it has small land for agriculture.• The government that encourages industrial development. It has formulateda technically based education system. This has improved the country’stechnological development• A high and expanding market potential. It is located near Asian countrieswhich are mainly agricultural dependent. These provide market for Japanesegoods• Aid from USA: after the Second World War, Japanese industrial establishmentswere destroyed. It got financial assistance from rich countries specifically theUSA. These loans were used to replace and rebuild the ruined industries• Advanced technology: Japan adapted latest techniques from Westernindustries and have been able to improve upon them• Improved transport network: water transport, modern ports were build, roadsand railways were improved.ii. The Major industrial regions of JapanJapan is the most industrialized country in Asia and ranks among the industrialnations of the world. There are four main industrial zones in Japan:• The Keihin Region: This is the most industrial region in Japan located onthe Kwanto plain to the East of HONSHU. It is formed by the conurbationof three important towns; Tokyo, Kawasaki, and Yokohama. This regionhas 20 % of the Japan’s population and account for 33 % of the country’soutput. The major industries found in this region are Chemicals, machinery,textiles, food processing, furniture. Each town in the region specializesin a particular item. Tokyo is noted for electrical engineering (especiallyTelevision sets, refrigerators, washing machines and computers.)Yokohama has precision engineering, shipbuilding, oil refining, petrochemicalproducts and port industries. Kawasaki is renowned for marine engineering,cement works and glassworks. The manufacture of iron and steel products iscentered on Chiba.• The Hanshin Region: this stretches across a great industrial conurbation ofthree major cities formed by Osaka, Kobe and Kyoto. It accounts for about 20% of Japan’s industrial output. It is important for the manufacture of textile,iron, and steel products, handcrafts, and shipbuilding. Osaka is the greatesttextile industry. Plastics, footwear and textiles machines are also made. Kobeconcentrates on shipbuilding, oil refining, and petrochemical industries. Kyotois important for the manufacture of crafts, toys, and oriental (Asiatic) ware.• The Ise Bay Region: this is the third industrial region dominated by NAGOYAindustrial Region on the Nobi Plain with a wide range of manufacturingindustries including textile mills that process local silk, imported cotton ,wood and also synthetic fibres ; engineering industries including all kindsof machinery , automobiles ,locomotives and aircraft . The nearby towns ofTajimi and Seto are noted for musical instruments such as guitars, violins andpianos are mass-produced at Hamamatsu.• The Kitakyushu Region: in the northern Kyushu area, the Chikugo coalfieldand good accessibility gave rise to a conurbation, called Kitakyushu. This one,embraces several towns, including Yawata, Kokura and Moji. The industrial areaextends southwards to Fukuoka and Nagasaki. It makes steel, ships, machineparts, chemicals and textiles.Apart from the above four major industrial regions, there are several scatteredindustrial towns. Iron and steel are made at Muroran, oil refining is important atAkita and Niigata, engineering at Hiroshima, shipbuilding at Kure, and textiles atOkoyama, Hakodate and Sapporo in Hokkaido are also industrially developed.Major industrial regions of Japan
b. Industrial development in Japani. Factors for high level of industrialization in JapanJapan is the most highly industrialized country of Asia and ranks among the mainindustrial nations of the world. Despite its shortage of industrial raw materials,Japan has been able to develop her industries because of the following reasons:• Development of hydro – electric power resources to provide enough power tosupport rapid industrial development because of little quantity of coal.• Efficient use of its limited raw materials such as copper, manganese, iron ore,sulphur and timber.• The coastline and many large ports facilitate the importation of large quantitiesof raw materials from all over the world. This is because of the geographicallocation of Japan.• The population that provides a large supply of labor and the development ofindustries since it has small land for agriculture.• The government that encourages industrial development. It has formulateda technically based education system. This has improved the country’stechnological development• A high and expanding market potential. It is located near Asian countrieswhich are mainly agricultural dependent. These provide market for Japanesegoods• Aid from USA: after the Second World War, Japanese industrial establishmentswere destroyed. It got financial assistance from rich countries specifically theUSA. These loans were used to replace and rebuild the ruined industries• Advanced technology: Japan adapted latest techniques from Westernindustries and have been able to improve upon them• Improved transport network: water transport, modern ports were build, roadsand railways were improved.ii. The Major industrial regions of JapanJapan is the most industrialized country in Asia and ranks among the industrialnations of the world. There are four main industrial zones in Japan:• The Keihin Region: This is the most industrial region in Japan located onthe Kwanto plain to the East of HONSHU. It is formed by the conurbationof three important towns; Tokyo, Kawasaki, and Yokohama. This regionhas 20 % of the Japan’s population and account for 33 % of the country’soutput. The major industries found in this region are Chemicals, machinery,textiles, food processing, furniture. Each town in the region specializesin a particular item. Tokyo is noted for electrical engineering (especiallyTelevision sets, refrigerators, washing machines and computers.)Yokohama has precision engineering, shipbuilding, oil refining, petrochemicalproducts and port industries. Kawasaki is renowned for marine engineering,cement works and glassworks. The manufacture of iron and steel products iscentered on Chiba.• The Hanshin Region: this stretches across a great industrial conurbation ofthree major cities formed by Osaka, Kobe and Kyoto. It accounts for about 20% of Japan’s industrial output. It is important for the manufacture of textile,iron, and steel products, handcrafts, and shipbuilding. Osaka is the greatesttextile industry. Plastics, footwear and textiles machines are also made. Kobeconcentrates on shipbuilding, oil refining, and petrochemical industries. Kyotois important for the manufacture of crafts, toys, and oriental (Asiatic) ware.• The Ise Bay Region: this is the third industrial region dominated by NAGOYAindustrial Region on the Nobi Plain with a wide range of manufacturingindustries including textile mills that process local silk, imported cotton ,wood and also synthetic fibres ; engineering industries including all kindsof machinery , automobiles ,locomotives and aircraft . The nearby towns ofTajimi and Seto are noted for musical instruments such as guitars, violins andpianos are mass-produced at Hamamatsu.• The Kitakyushu Region: in the northern Kyushu area, the Chikugo coalfieldand good accessibility gave rise to a conurbation, called Kitakyushu. This one,embraces several towns, including Yawata, Kokura and Moji. The industrial areaextends southwards to Fukuoka and Nagasaki. It makes steel, ships, machineparts, chemicals and textiles.Apart from the above four major industrial regions, there are several scatteredindustrial towns. Iron and steel are made at Muroran, oil refining is important atAkita and Niigata, engineering at Hiroshima, shipbuilding at Kure, and textiles atOkoyama, Hakodate and Sapporo in Hokkaido are also industrially developed.Major industrial regions of Japan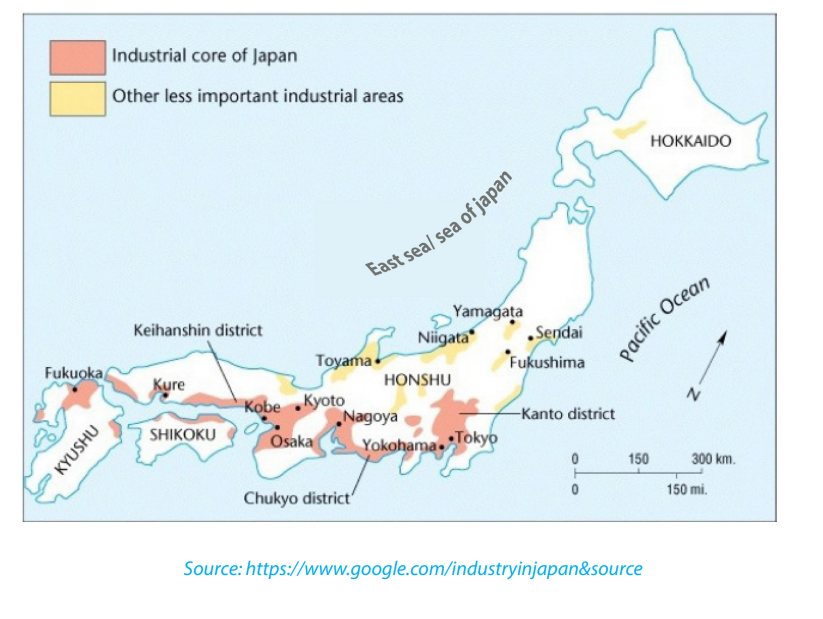 c. Industrialization in Russia11.4.2. Developing countries
c. Industrialization in Russia11.4.2. Developing countries
i. Factors for high level of industrialization in Russia• Presence of a variety of minerals such as Iron, copper, gold, diamond, coal etc.• Improved transport network of railways, aircrafts and developed road network.• Existence of agricultural raw materials such as cotton for textiles, milk fordairies, hides and skins for leather and footwear industries.• Availability of capital from financial institutions to promote industrialii. Industrial regions of RUSSIA
development.
• Improved research to develop cheap and highly efficient methods of
production. This has led to technology and industrial development.
• Government policy of promoting self-sufficiency in most of the manufactured
goods consumed in the country.
• Attraction of foreign investors from Europe, Japan and USA has greatly
contributed to industrial development.
• Presence of a large population which provide a large domestic market and
cheap labor force.
• Skilled labor in form of electrical, mechanical, chemical engineers, laboratory
assistance.
The Russian industries are concentrated in the four major areas:1. The Moscow – Gorki region: this region has diverse industries including
heavy engineering, steel industries, railways, equipment, automobiles,
aircraft and food processing.
2. The Ukraine industrial region: This region has developed during the period
of USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics) the main industries are iron
and steel, making machinery, chemicals, etc.
3. The Urals industrial region: engineering (heavy) and metallurgical industries
dominate all other activities,
4. The Kuzbas region: This area has large thermal plants, extensive coal
deposits, engineering, hydro-electric power plants, metallurgical plants,
chemicals including petrochemicals.Major industrial regions of Russia
a. Industrial development in ChinaIndustrial development in China began after the beginning of Communist rule in
1949, and now China is an art industrial power of Asia and of the world. There has
been a complete transformation of the industrial system during the last 60 years.
Under the new system and policy, China is developing its industrial system in a
planned manner. Rapid development has made China a leading producer of iron
and steel, textiles, and cheap consumer goods such as toys, household goods and
light metal goods.
i. Factors for industrial development in China
• Large quantities of natural resources: They constitute the raw materialsfor industries such as coal, copper, zinc, lead, and manganese. This has given rise to
industries dealing in copper processing, steel products, electrical equipment
etc.
• Deposits of coal and petroleum: They act as a source of energy for the industries.Coal is the single most important energy source.
• Large population: With over 1.3 billion people,China has large domestic market for its industrial goods.Chinese manufactured goods have a ready market
even in other countries like USA, Japan, UK, and the European union.
Geography Senior Six Student Book 315
• Location of China: On the Asian main land and the most populated continentprovides the market for manufactured goods, the promotion oftrade and procurement of raw materials.• Government policies: Communist system has great influence onthe development of industries where each commune was encouragedto have its own industries.• Education: Chinese system provides the basic skills on practical knowledgerequired in industries and workshops.• Cheap labor force: With a large population, China has a big labor force which ischeap, skilled and unskilled. China has a largest labor force in the whole world.• Transport and communication systems: Aircraft is developed to communicatewith the entire world and railway transport is improved for acquisition of rawmaterials and distribution of manufactured goods. Also the country has navigableinland water ways but has been improved by construction of canals.ii. Industrial regions of China• Manchurian Industrial Region: This is the most important industrial area of
China with centers at Anshan (steel industry), Penki (steel industry), Fushun
(coal, lubricating oil, and chemicals), Mukden or Shenyang (machinery and
tools) and Dairen (mills and shipyards). All of them are nearby coal and iron ore
deposits. Anshan, Fushun and Shenyang form a triangle, within which there
are numerous large plants.
• Tientsin and Beijing Region: This is a second industrial area located at the
northern end of the North China Plain, near the Kailan coal reserves, with
Tientsin, Peking or Beijing and Tangshan as its main centers. The presence of
coal-fields in Shansi and Hopei has contributed to the rise of the metallurgical
and engineering industries here.
• Lower Yangtze Industrial Region: This is China’s oldest industrial region.It existed since the middle of 19th century. Shanghai is the main industrial town
and port of this industrial region. The main goods produced are cotton, silk,
textile, food, leather, radio, television sets, utensils, leather, etc. There are also
shipyards, oil refineries, flour mills, steel plants, metal works and a great variety
of light industrial products.
• The Middle Yangtze Industrial Region: It is located on the middle Yangtze plain
around the former tree towns of Hankow-Hanyang-Wuhan. There iron and
steel works there that are based on Peninsiang coal and Tayeh iron ore.Shipbuilding, metallurgical and heavy industries, railway equipment andchemicals are important items of production.• Sichuan (Szechwan) Industrial Region: Sichuan (Szechwan) province above
the Chang Jian (Yangtze Kiang) gorge has many important industries around
Chongqing (Chungking) and Chengdu (Chengtu).The rich deposits of coal,
iron, Ferro-alloys and abundant agricultural raw materials have all encouraged
industrial development. Iron and steel, textiles, paper and pulp, machinery,
cement, and chemicals are made here.
• Si Kiang Delta Region: The port of Canton is the main industrial centre at the
mouth of the Xi Jiang (Si Kiang). Canton lacks local raw materials and once
was known largely for commerce. Modern industries are centered on silk production;there are silk mills, jute and cotton goods are manufactured, rubberIn China, many cities are considered to be the industrial cities. Some towns such as
is processed, and there are food-canning and match factories. Iron works andmachine factories occupy sites near the docks.
Anning, Kiuchuan (iron and steel); Yumen and Hangzhou or Hangchow (oil refining);
Lanzhou or Lanchow (chemicals, textiles, mining equipment) and Kunming(chemicals, machinery, textiles) have industrial development.
b. Industrial development in South Korea
i. Factors for industrial growth in south Korea• Highly skilled labor force: The education system provides basic skills required
in industries and workshops. There is highly trained labor force in managerial
and marketing which help the country to compete with other countries.
• High technology: In industries, microelectronics and computers which keep in
touch with scientific advancement.
• Government support: Policies aiming at export-oriented industries, rather
than to supply the local market.
• Agricultural development: The country is self-sufficient in rice growing with
large schemes of irrigated land this has made the rural economy more efficient.
• Many business people: Companies or businessmen from Europe, USA, Japan
who had the capital and skills to build industries have been attracted by low
wage rates in South Korea.
• Infrastructural development: Well developed transport and communication
network which makes the exportation of goods very easy.
• Research: This is highly emphasized especially in electronic industry, so as to
improve all the existing products and develop new products to meet the market demands.
ii. Major industrial regions of South Korea
• The major industrial regions of South Korea are: Seoul, Yeosu, Chongju,
Gwangju, Masan (Changwon), Ulsan, Pohang, Taejon, Busan, Yongdimpo.
• The major industries found in these regions are Iron and steel, petrochemicals,
ship building, agricultural equipment, machinery, electronics, textiles and
light industries.Major industrial regions of South Korea
c. Industrial development in Egypt
In the 1920’s, the Egyptian economy was characterized an agricultural economy.
Three quarters of the Egyptian exports was raw cotton. As a result, industrial output
was mainly cotton spinning and weaving, followed by preserved food, cigarettes,soap and handicrafts
i. Factors for industrial development in Egypt• Availability of raw materials: Egypt has agricultural raw materials to feed theii. Major industrial regions of Egypt
industries like cotton for textile and sugar for agro-based industries.
• Availability of minerals: Egypt has various mineral resources such as oil, Iron,
Zinc, Copper, Lead, phosphate that lead to the development of industries.
• Availability of power and energy: Egypt has the cheapest source of fuel (HEP)
due to Aswan High Dam which allowed the connection of most Egyptian
villages to use electricity.
• Internal market: Egypt as one of the most densely populated countries in
Africa, its population is the ready market for manufactured goods.
• Availability of water: Despite that Egypt is a desert country; it has high strategies
to use available water from the Nile River. Water is used as a raw material in food
processing, construction, cooling machines and other industrial activities.
• Improved transport: Water, canals, roads, and railway, provide the cheapest
water transport cost of raw materials and finished goods.
• Relief: The gentle relief of Egypt enables the construction of industries and
transport routes which facilitate the development of industries.
• Government policy: The government is currently adopting an industrial policy
that entails large-scale privatization of state owned enterprises as well as the
gradual removal of subsidies and price controls in the remaining public sectorcompanies.
1. Cairo:It is the industrial centre of Egypt with textile industries, food processing, motor2. Alexandria:
vehicle assembling and chemical industries. There are also Iron and steel industries
located at Hulwan near Cairo city.It is the main industrial centre in Egypt as well as the country’s largest sea port. It3. Helwan industrial area:
has agricultural, textile and chemical industries etc.It is found on the bank of river Nile with several industries mainly the agriculturalMajor industrial regions of Egyptindustries, sugar, gases and steel industries.

d. Industrial development in South Africa
South Africa is the most industrialized country in Africa. Today South Africa exports
a large amount from manufacturing sector. Two thirds of South Africa’s national
outputs are derived from manufacturing industries.
i. Factors for industrial development in South Africa• Large quantity of mineral resources: South Africa is endowed with a wide
range of mineral resources which constitute raw materials for industries. The
exploitation of minerals has stimulated industrial development.
• Presence of energy: The most important of this is coal. There are also numerous
rivers, which produce hydro-electric power. Such rivers include orange, the
Transvaal River and others.
• Climate: Ranging from the temperate climate, Mediterranean, desert and
tropical climate. The variety of climate contributes to a wide range of
agricultural products, which form the raw materials for many industries.
• Forest resources: contribute to the development of sawmills, furniture making
and manufacture of paper industries.
• Fish resources: South Africa has one of the most developed fishing industries
on the Africa continent. This has given rise to fish canning, freezing, fishmeal
and fertilizers industries.• Labour: Abundant labor supply
• Market: Large market for its finished manufactured products.ii. Major industrial regions of South Africa
• Capital: Enough capital to invest in Industries.
• Transport and communication: Good transport and communication networks.
• Government policy: Encouragement from the government.
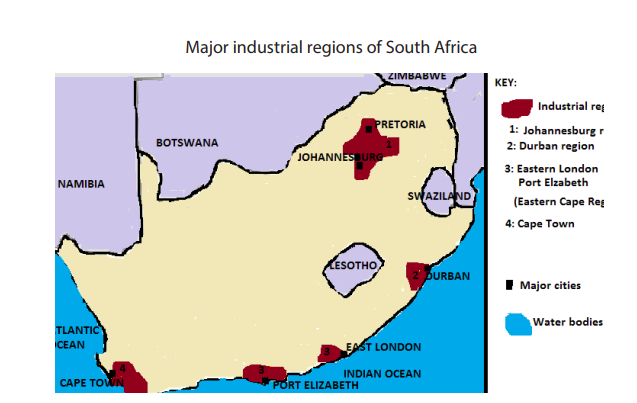
• Land: Availability of land for industrial location and extension.1. Johannesburg: The main industries found here are textile industries, chemical
industries, paper and printing, engineering, electrical equipment, saw milling
etc.
2. Springs: The major industries in this town include manufacturing of mining
machinery, electric goods, printing machinery, sheet glass, paper and food
canning industries.
3. Durban: Industries in this region include ship repairing, oil refining, soap
manufacture, textile, light engineering etc.
4. Cape Town: It has food processing, textile, chemical, paper and printing etc.
5. Pretoria: industrial establishment include glass, cement, metal working,
manufacturing railway wagons etc.
6. Eastern Cape Industrial Zone: Is formed by East London and Port Elizabeth. It is the
important port for international trade. It produces building material, soft drinks,furniture, clothes, local agricultural products etc.
Application activity 11.4
1. Compare the factors that have led to the development of industries in
Japan with those of South Africa
2. Analyse the economic importance of industrialization in these countries:
a. USA
b. Egyptc. Russia
End unit assessment
Make a field trip in any industrialized area around your area and answer the
following questions:1. Discuss the physical and human factors influencing location of industries
in an area.
2. Describe how industrialization contributes to sustainable development.
3. Analyse the ways of improving the level of industrialization in developingcountries.
