Unit 7:7Stock Control
Unit 7:7Stock Control
Key unit competence
To be able to properly handle stock for the business
Introduction
A business can run smoothly only when enough inventory is kept on hand.
All operational processes, including production, warehousing, sales, etc., are
impacted by inventory. There should be a balance between opening and closing
inventories to prevent any negative effects on other business operations. As
a result, inventory is very important to operations management.
This unit is designed to equip you with knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values
that will enable you to manage stock effectively and make an inventory,
to comply with the standards, policies and procedures followed in the
procurement of goods, services and works in supply chain management.
Throughout this unit, you will learn how to use basic documents needed
in stock management, how to conduct perpetual and periodic inventory,procurement procedures, as well as evaluation methods on supplied stock.
Introductory Activity
Analyze the paragraphs below and answer the questions that follow.
Stock control, otherwise known as inventory control, is used to show how
much stock you have at any one time, and how you keep track of it.
It applies to every item you use to produce a product or service, from raw
materials to finished goods. It covers stock at every stage of the production
process, from purchase and delivery to using and re-ordering the stock.
Efficient stock control allows you to have the right amount of stock in
the right place at the right time. It ensures that capital is not tied up
unnecessarily, and protects production if problems arise with the supply
chain.
Questions
a) What is meant by stock, stock control/management and inventory?
b) What are the necessary documents for stock management in a
business?
c) Why is stock control important in a business?d) Describe the different methods of stock valuation
7.1. Concepts and necessary documents for stock management
Learning Activity 7.1
Read the story below and answer questions that follow.
Kamanzi is a prosperous trader in Nyarugenge district and owns a very
big business. He is considered an exceptional trader by many customers
mainly because during scarcity of scholastic materials like reams of papers
and exercise books, he is the only trader every parent refers to as he
helps them find the needed materials for their children. Kamanzi is also
exemplary in terms of stock management. This is attributed to the fact that
he has employees who are well trained and manages his stock properly.
Questions
a) Mention the documents that can be used for proper stock management
in Kamana’s business.
b) Under which circumstances can his employees record information?
7.1.1. Meaning of stock and inventory management
Stock
Goods obtained for resale or manufactured for sale that are yet unsold on
any particular date are known as stock.
It also means the value of the goods that you have on hand to sell to your
customers. If you sell services rather than goods, you will not have any stock.
Stock can be classified as:
◾ Opening Stock: Value of stock at the beginning of an accounting
period.◾ Closing Stock: Value of stock at the end of an accounting period.
Inventory
Inventory refers to a company’s goods and products that are ready to sell, as
well as the raw materials that are used to produce them. Inventory can be
categorized in three different ways, including raw materials, work-in-progress,
and finished goods. This term is better fit in the manufacturing businesses.
Therefore, a stock reflects the finished goods available for sale while an
inventory includes both finished goods and components that create a finished
product.
Stock management
Stock management is the practice of ordering, storing, tracking, and controlling
inventory.
It is also the process of managing the goods your business plans to sell. Or is
the process of buying and storing these goods while keeping order, shipping,
handling, and storage expenses under control.
7.1.2. Necessary documents for stock management
The following are the necessary documents in stock management process:
a) Material/ purchase requisition note
A materials requisition form is used to draw/ get materials from the stores,
and it specifies the quantity and quality of materials required, along with the
job number or work order for which it is needed.
Also known as a requisition slip or materials requisition note, a materials
requisition form is a document that authorizes and records the issue of
materials for use.An example of a purchase requisition template
b) Materials receipt note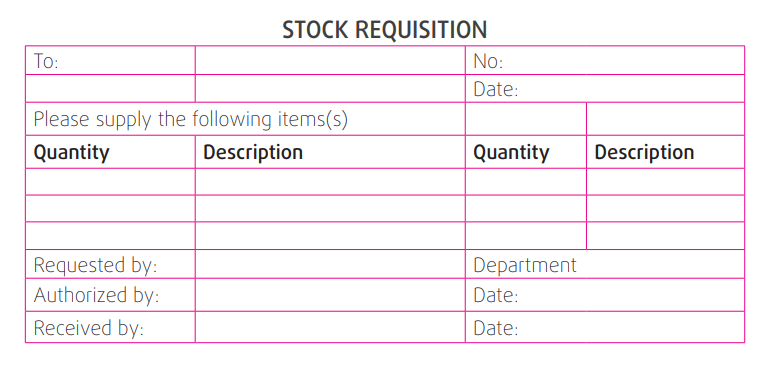
This is a document that keeps records of the materials received in the stores
at specific dates.An example of a materials receipt note.
c) Return-outward note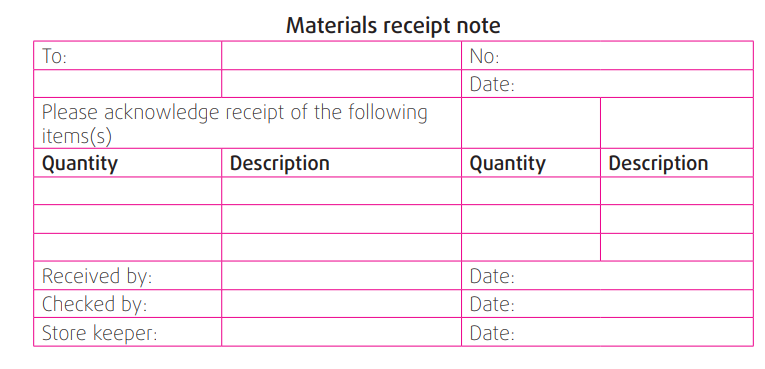
This records the materials obtained for a specific job but not fully consumed or
they are drawn in excess of requirements, and therefore need to be returned
to the stores.An example of a materials return outward note template.
d) Materials return inward note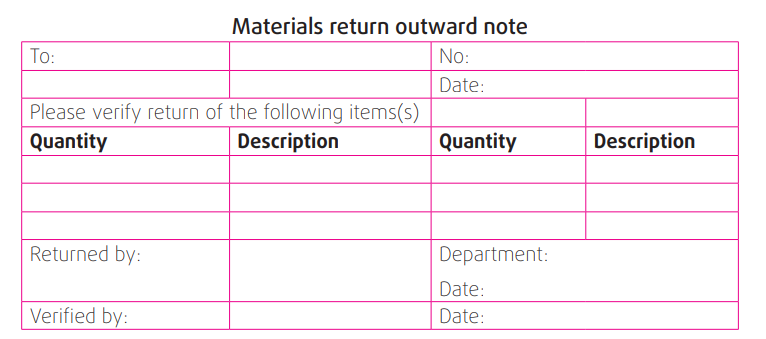
This is prepared by the store keeper to record the materials that were given
out for a specific job and were not fully consumed or they were drawn in
excess of requirements, and have been returned to the storesAn example of a materials return inward note template.
e) Stock sheet inventory
The stock sheet is a document that records regular movement of goods in the
store. The storekeeper indicates the goods received or issued.
The storekeeper determines the balance after the movement of purchases
and sales of goods. Each exit and entry of goods into stock must be justifiedwith a relevant document such as receipt note and purchase requisition note.
Application Activity 7.1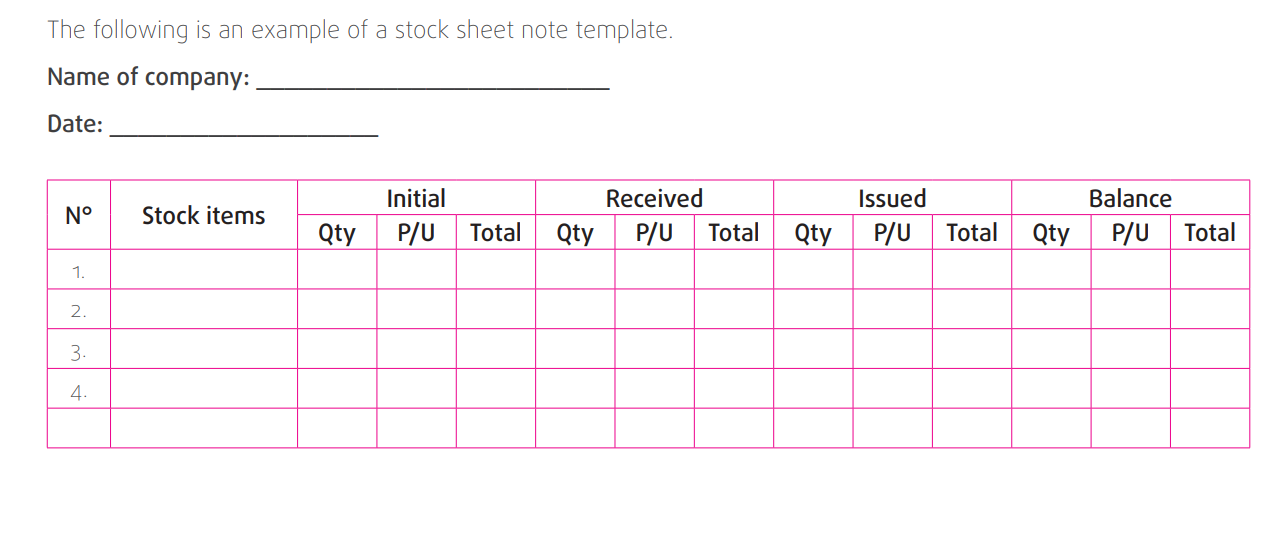
Nyiraneza is a stock manager for SABANA LTD, a distributor of BRALIRWA
products. On March 12th, 2018, SABANA LTD had the following items inthe stock:
In the morning of March 12th, 2018, Nyiraneza made a Purchase order for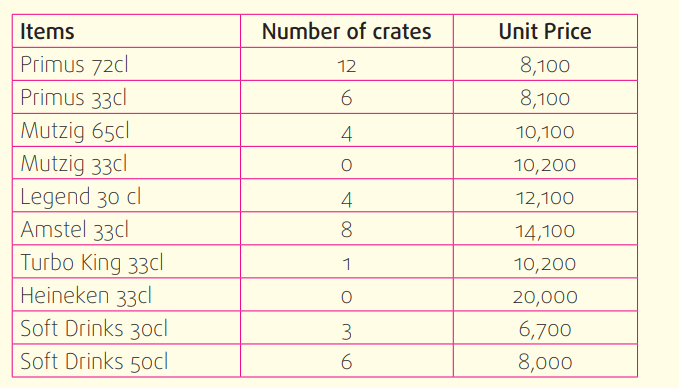
the following items:
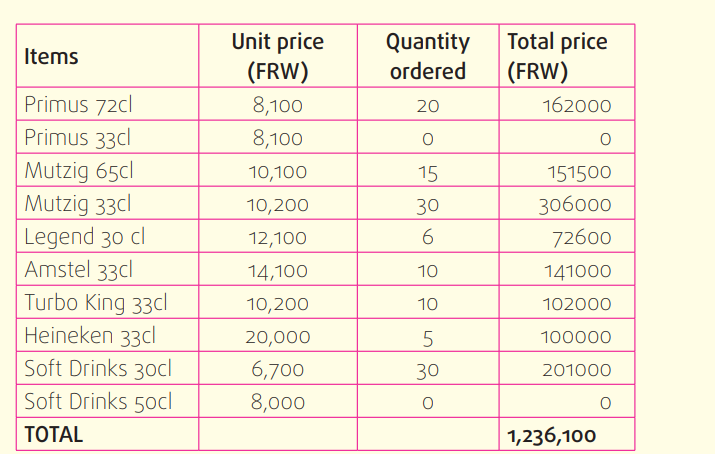
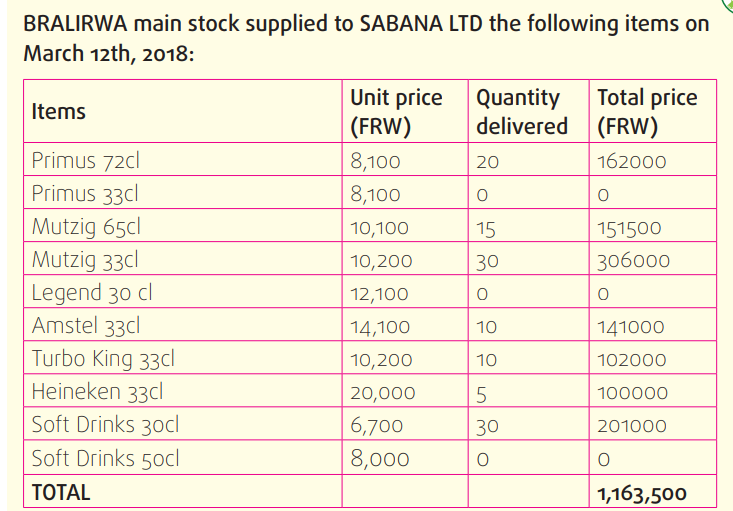
a) Complete the receipt note and stock sheet for SABANA LTD on March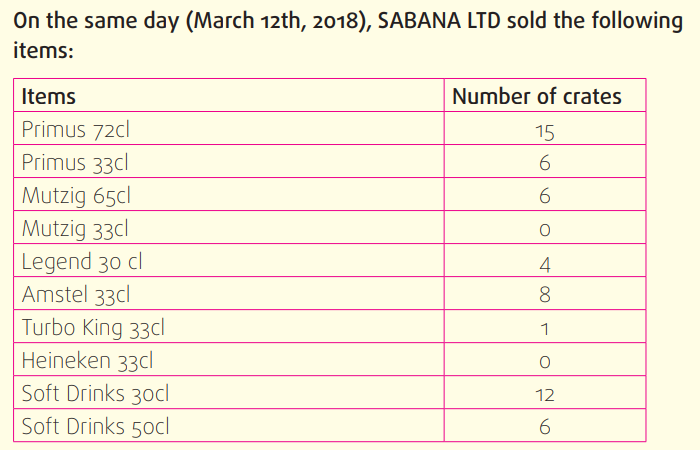
12th, 2018.
b) Develop a purchase requisition (10 crates for each identified item)
for SABANA LTD on March 13th, 2018, following the principle that theminimum stock level is 6 crates for each item.
7.2. Inventory management systems
Learning Activity 7.2
Read answer the following questions
1. Differentiate between perpetual and periodic inventories
2. Referring to your school, briefly explain how perpetual and
periodic inventories are carried out by the accounting department.
7.2.1. Meaning of inventory systems
One of the most challenging aspects of running a business is learning how to
effectively manage your inventory so you have what your customers need
and want without having too much excess, which can be a waste of money.
Whether it is deciding what and how much to order, when to order, keeping
an accurate count of your products, or knowing how to handle excess and
shortages, knowing how to control inventory properly will help ensure your
business’s success.
Inventory management systems therefore, refers to the accounting methods
that businesses use to track the number of products they have in their stores.They are two methods of tracking inventory and these include:
7.2.2. Types of inventory management systems
a) Periodic inventory is one that involves a physical count at various periods
of time. The periodic inventory system uses an occasional physical countto measure the level of inventory and the cost of goods sold.
Advantages of Periodic Inventory System
◾ Since no permanent employee is required for physical counting of
merchandise inventory under this system it is less expensive.
◾ It is applicable for all business organizations large or small dealing
with specific or a variety of goods.
◾ Since stock taking is done at the end of a period under this system
the normal activities of the business are not hampered.
◾ Since the stock-taking of merchandise is done on a particular date
the quantity of stock of merchandise is reliable.
Disadvantages of Periodic Inventory System
◾ On the very day of the physical counting of merchandise stock,
normal activities of business remain almost suspended.
◾ The act of counting merchandise stock is to be completed hurriedly
due to a shortage of time.
◾ Under this system the chance of fraud and forgery lies, because here
continuous control over merchandise is absent.
◾ Under this system on expiry of the particular period, the reasons for
differences between merchandise at hand and merchandise shown
in the books of accounts cannot be sorted out easily.
◾ Under this system, the stock control device is very weak. Their
employees get a chance to adopt corruption.
b) Perpetual inventory is computerized, using point-of-sale and enterprise
asset management systems. The perpetual system keeps track of
inventory balances continuously, with updates made automatically
whenever a product is received or sold.
Perpetual inventory can save the business money in these ways:
◾ There is no need to close facilities regularly to perform physical
inventories,
◾ Data from scanned barcodes help you forecast stock,
◾ You can account for all transactions, providing complete accountability
of your products.
Even though perpetual inventory is superior, it is not perfect. While there
is a constant, automatic product tracking system, there are still ways to
lose positive inventory control.
The disadvantages of using perpetual inventory include:
◾ You must still perform an annual inventory to synchronize your data,
◾ You must input every transaction, which requires more consistent
record-keeping and monitoring,
◾ Perpetual inventory systems have higher setup costs than other
methods since they require software and training.
Differences Between Perpetual and Periodic Inventory Systems:Perpetual Inventory Systems Periodic Inventory Systems
Track sales immediately Track sales on recurring basis
Use point-of-sale systems Utilize recurring physical counts
Better for large businesses Better for small companies
Smaller margin for error Larger margin for error
Cost of goods sold updated
constantly periodically
Cost of goods sold updated
Require less effort Require physical countsStart-up cost potentially high Less expensive to start up
Application Activity 7.2
Analyze the scenario below and answer questions that follow
Nishimwe and Rugwiza are employees of TURAHEZA COMPANY LTD which
has hardware stores in Huye and Kigali towns. Nishimwe is the manager
of the Huye branch, while Rugwiza is the manager of the Kigali branch. In
their daily work, Nishimwe records and controls the physical movements
of stock. Every time she sells or purchases an item, she puts the report in
the template that she has developed using excel software. For Rugwiza,
the stock manager of the Kigali branch, the inventory control is done at the
end of the month and the monthly stock value is determined.
Questions
1. Determine whether the system used by these employees is
perpetual or periodic and explain why.2. Identify advantages of each system.
7.3. Inventory valuation methods on supplied stock
Learning Activity 7.3
Read the scenario below and answer questions that follow:
AMBARUBERWE Limited bought a range of beachwear in the summer, with
each item costing 15,000 FRW and retailing for 30, 000 FRW. Most of the
goods were sold but, during the rainy season, ten items remained unsold.
These were put at a discount of 18,000 FRW each. On 31 December, at the
end of the store’s financial year, five items remained unsold.
a) At what price will they be valued at the end of year stock valuation?
b) Twelve months later, three items still remained unsold and have been
reduced further to 10,000 FRW each. At what price will they now be
valued at the end of year stock valuation?
The cost of unsold inventory is determined at the end of each accounting
period. Inventory is valued usually at cost or at the market value, whichever is
lower. Stocks are never valued at selling prices when selling prices are above
cost prices. The reason for this is that selling prices include profit, and to value
stock in this way would recognize the profit in the financial statements before
it has been realized.
The three common stock valuation methods Are First-In, First-Out (FIFO);Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) and Weighted Average Cost (WAC).
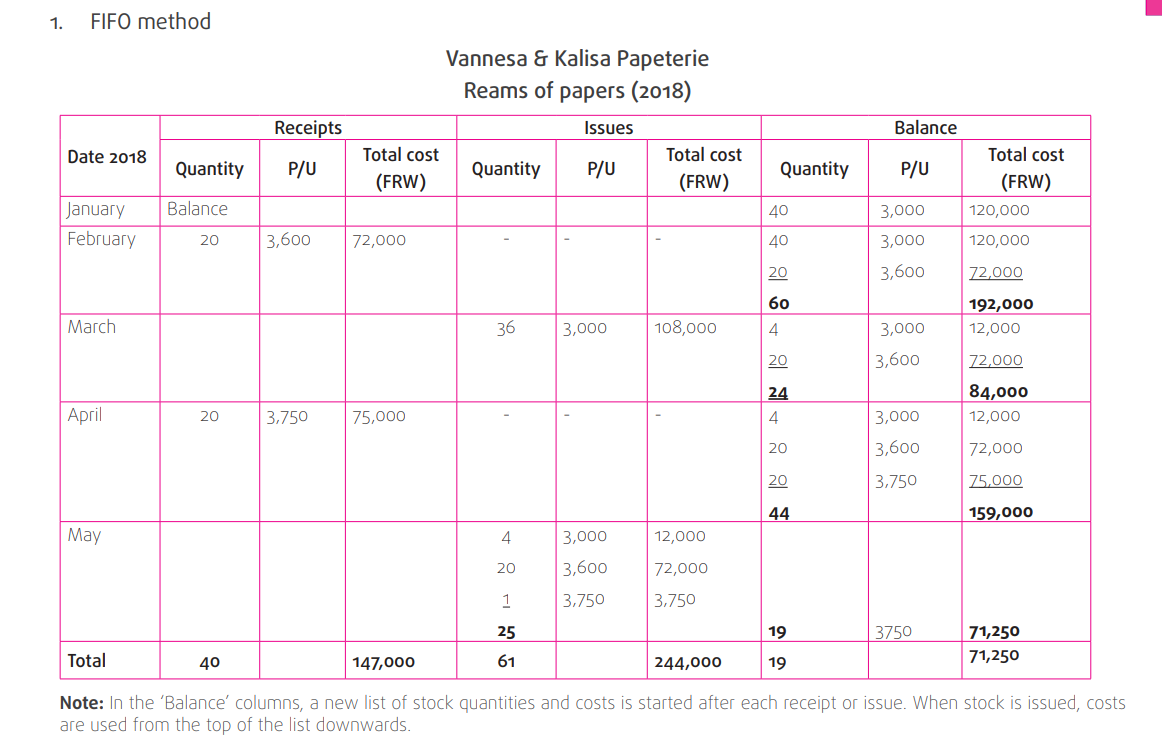
7.3.1. FIFO
FIFO is the acronym for First-In, First-Out. FIFO is a valuation method in which
assets produced or acquired first are sold, used, or disposed of first.Under FIFO, the oldest cost of an item in inventory will be removed first
when one of those items is sold. This oldest cost will then be reported on the
income statement as part of the cost of goods sold. Example: If a company
using FIFO method has four units purchased at different costs and in the
following sequence: 6,000 FRW; 6,400 FRW, 6500 FRW and 6,600 FRW, thecompany will report its cost of goods sold as 6,000 (the first cost)
7.3.2. LIFO
LIFO is the acronym for Last-In, First-Out. It is a valuation method in which
the last asset acquired (the newest), is the first asset sold.
Under LIFO the latest or more recent costs of products purchased (or produced)
are the first costs expensed as the cost of goods sold. This means that the
costs of the oldest products will be reported as inventory.
For example
Let us illustrate LIFO with a company that has three units of the same product
in inventory. The units were purchased at different costs and in the following
sequence: 6,000 FRW, 6,400, FRW and 6,600 FRW. Under LIFO the company
will report its cost of goods sold as 6,600 (the latest cost).
Note that the last cost of 6,600 FRW is the first cosT out of inventory-the LIFO
assumption.
LIFO has become popular because of inflation and the fact that the incometax rules can permit companies to use LIFO.
7.3.3. Weighted Average Cost method (WAC)
In Weighted Average Cost method (WAC or AVCO), the weighted average
cost of items is calculated, using the formula:
Weighted Average Cost =Total cost of goods in stock
Number of items in stock
The weighted average cost is then used to value goods sold. A new weighted
average cost must be calculated each time that further stocks are bought
during the year.
Recording stock values
To be able to accurately calculate the price at which stocks of materials are
issued and to ascertain a valuation of stock, a store’s ledger record or stock
card is used. Note that stock records are usually kept at cost price, not theselling price.
Example of stock card
Vannesa & Kalisa Papeterie sell office materials. One of the items stocked is
reams of papers. To show how the stock card would appear under FIFO, LIFO
and AVCO, the following data is used:
January 2018: Opening stock of 40 reams of papers at a cost of 3,000 FRW
each
February 2018: Bought 20 reams of papers at a cost of 3,600 FRW each
March 2018: Sold 36 reams of papers
April 2018: Bought 20 reams of papers at a cost of 3,750 FRW eachMay 2018: Sold 25 reams of papers.
3. Stock card using WAC (weighted average cost per unit)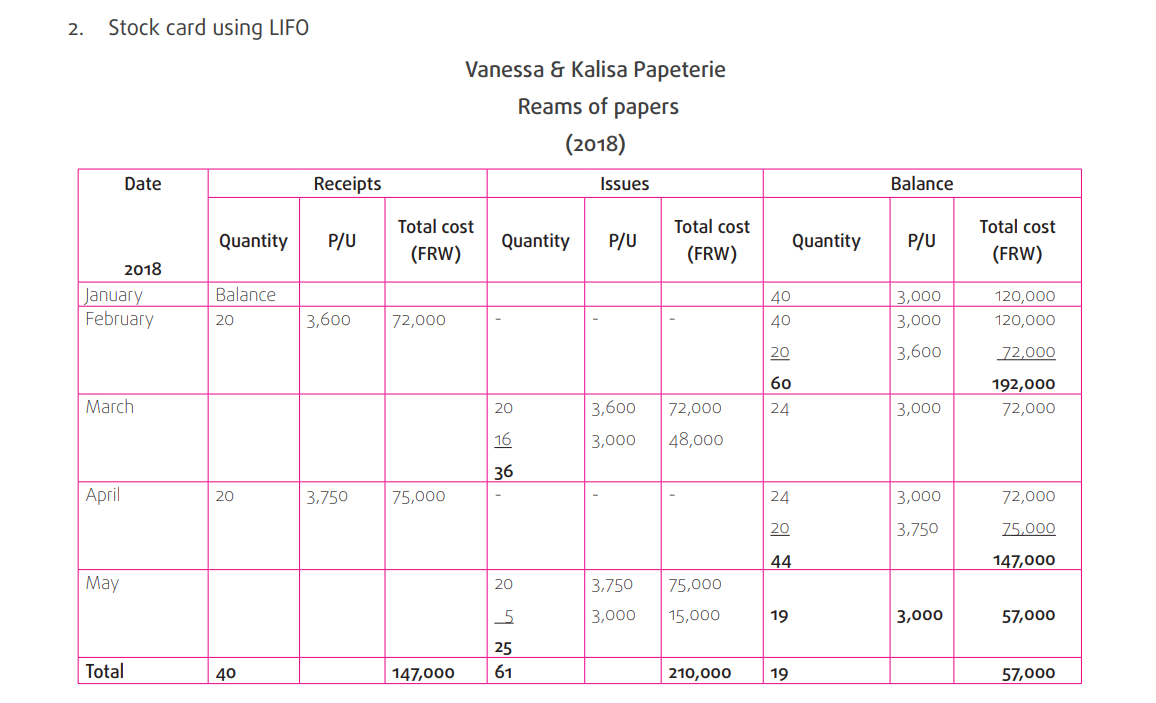
In this method, each quantity issued is valued at the weighted average cost per unit, and so is the balance instock. The complete list of different costs does not have to be re-written each time.
WAC method
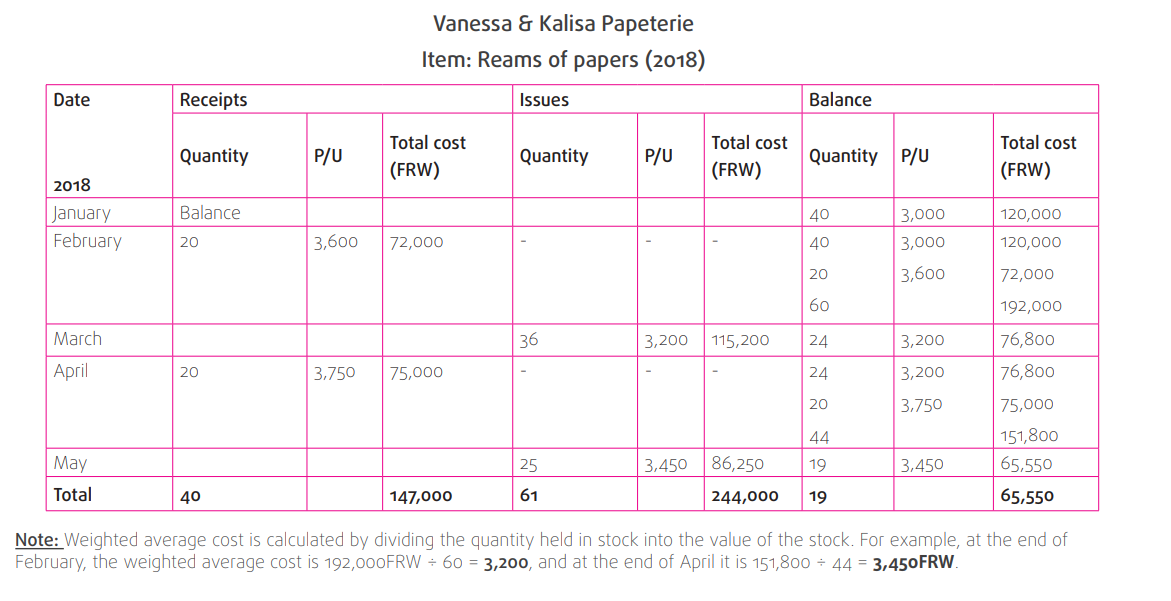 The closing stock valuations at the end of May 2018 under the three methods show total cost prices of:
The closing stock valuations at the end of May 2018 under the three methods show total cost prices of:
◾ FIFO: 71,250 FRW
◾ LIFO: 57,000 FRW
◾ WAC: 65,550 FRW
Application Activity 7.3Analyze the following information from the books of GASABO Bakery Limited
GASABO Bakery Limited Makes cakes which are sold to supermarket chains. The company uses the first in, first out(FIFO) method for valuing its stocks. Complete the following stock card for wheat flour for December 2017:
Skills Lab Activity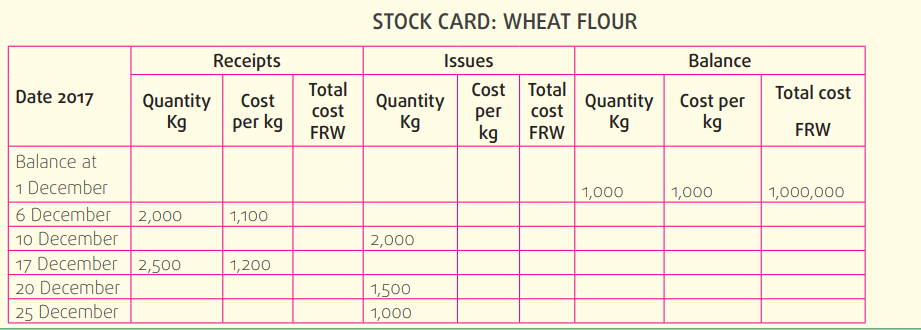
Interview a resourceful person such as a school bursar, accountant or an
entrepreneur about the procurement process using the following questions:
1. Why does the business/ school manager control a business
inventory/stock?
2. What documents does the school/business use in stock
management?
3. Which inventory system does the business/school use?
End of Unit Assessment
I. Project Activity
Each student creates 3 stock management documents for the business
they tend to start back home.
II. Other Assessment Questions
1. Suppose you are selected to be the Head of Finance Unit in a
newly established public school. Prepare a purchase requisition
for your office materials.
2. The following information is extracted in the books of a stock
manager:
• 200 bags of 50 kg of cement are bought in January 2016 at a
cost of 10, 000 FRW each
• 100 bags are sold in February
• 80 bags are bought in March at a cost of 9,500 FRW each
• 100 bags are sold in April
• 150 bags are bought in May at a cost of 9,800 FRW each.
From this information, prepare stock cards for cement using:
a) FIFO
b) LIFOc) WAC
