UNIT 9:POPULATION IN RWANDA
Key unit competence: The student-teacher should be able to examine demographic problems in Rwanda and suggest their solutions.
Introductory Activity
The study of population is necessary for proper national planning in relation to the provision of social services to the people. Rwanda is one of the most populated countries in Africa and there is fear that the rate at which population growth is increasing and presents great challenges to the development of the country. The proper strategies to solve the problems related to the rapid population growth should be taken.
1. Explain the terms related to population concepts.
2. Discuss the factors influencing population growth in Rwanda.
3. Explain the population problems related to the rapid population growth in Rwanda.
4. Describe the population policies that should be taken by Rwanda to control rapid population growth.
9.1. Population concepts
Learning activity 9. 1
Use the Internet and other Geographical sources of information and explain the following terms with reference to the population of Rwanda: Population, population density, birth rate, death rate, growth rate, fertili-ty rate, life expectancy.
9.1.1. Population concepts
Population is defined as the total number of the people living in an area or a region or country in a given period of time.
a) Birth rate
Birth rate refers to the number of new born babies per every 1000 people of the total population of a given place.
The birth rate is determined by the following formula.

Example
Suppose a given location has a total population of 21,346 inhabitants and the new born babies are 3240. The birth rate will be calculated as shown below.

c) Growth rate
Population growth rate refers to the natural change in the number of population. A population will either increase or decrease. Population growth rate is expressed as a percentage. It is the ratio of death rate and birth rate per 1000 people. The number of people living in an area can increase, decrease or remain stagnant for some time. The population growth rate of Rwanda is on the increase. Population growth rate is calculated using this formula:
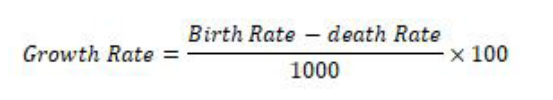
d) Fertility rate
Fertility rate refers to the average number of children born to a woman in her life time. It is calculated per every 100 women in a population. The fertility rate of Rwanda is 5.2. This is calculated using the formula given below.

e) Life expectancy
Life expectancy refers to the average period or number of years that a person expects to live. In Rwanda, life expectancy has increased due to improvement in standards of living and healthcare. In the year 2013, the life expectancy of Rwanda was at 63.99 years. Life expectancy is affected by factors such as socio-economic status, including employment, income, education and economic wellbeing, the quality of the health system and the ability of people to access it; health behaviors such as tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, poor nutrition and lack of exercise.
f) Population density
Population density is simply the number of people living in an area per square kilometer (sq km). If the population of Rwanda is 9,300,000 million people and the size (area) of Rwanda is 26,338 sqkm then, its population density is:

This means that for every one km2 there is 353 people occupying it. Because of this, Rwanda is said to be one of the most densely populated countries of Africa.
Application activity 9.1
Explain the relationship between population growth and population density
9.2. Population growth in Rwanda
Learning activity 9. 2
Read the following case study and answer the questions that follow:
In recent years there is a large inflow of refugees from neighboring countries entering Rwanda. Besides, this is happening when the infant mortality rate in Rwanda has declined tremendously. The life expectancy level in Rwanda has also risen.
1. Discuss the factors that influence the population growth in Rwanda.
2. Find out the consequences of rapid population growth to the local area and to the country.
Population growth is the increase in the number of individuals in a population while population Growth rate is the rate at which the number of individuals in a population increases in a given period of time. Rwanda has a high population growth which keeps increasing every year. As at 2014, the population growth rate of Rwanda was estimated to be at 2.63%.
9.2.1. Factors influencing population growth in Rwanda
The following are the factors that influence population growth in Rwanda:
• Religion: Some religious faiths teach their followers to procreate and have many children in the quest to fill the world. Other faiths favour polygamy. All these teachings lead to an increase in the population. On the other hand, other religious faiths teach against polygamy and allow family planning. These practices lead to a low population.
• Early marriages: In most developing countries like Rwanda, girls get married when they are still very young. The longer they stay in their marriages; the more number of children they are likely to have. This leads to an increase in population.
• High birth and fertility rates: This has contributed to an increase in population. In Rwanda, the fertility rate averagely stands at about 5 children per every female. This means that families are big translating to an increase in population.
• Polygamous marriages: Polygamous marriages lead to population growth. The more women that are in a marriage, the more number of children they are likely to get collectively.
• Improved health care: In Rwanda, improved health facilities, immunisation programs and the use of modern drugs have led to reduction in the diseases such as malaria and other epidemics which claimed many lives. As a result, there is an increase in birth and fertility rates and a decrease in infant mortality rate.
• Illiteracy: High levels of illiteracy have made many people unable to utilise family planning methods. Lack of this information encourages people to get many children leading to an increase in population.
• Migrations and refugees: Migration refers to the movement of people from one place to another.
• This movement leads to an increase in population in the area where the people move to and a decrease where they come from.
• Traditions and cultural beliefs: Most rural citizens uphold traditional values that encourage big families for labour and wealth. Most families therefore have many children in order to uphold the cultural values of their communities. This leads to an increase in population.
9.2.2. Consequences of rapid population growth in Rwanda
There are both positive and negative consequences of rapid population growth. Some of the consequences are discussed below.
Positive effects
• Source of labour: A high population offers cheap source of labour.
• Source of revenue: A high population means a high source of revenue to the government through tax levies.
• Creation of markets: The rapid population growth in an area or country leads to a high demand for goods and services.
• Exploitation of resources: An increase in population enables the use and full utilisation of resources.
• Urbanisation and industrialization: The movement of people from areas of high population to areas with low population contributes a lot to the development of towns, cities and industries.
Negative effects
• Food shortages: In areas with high populations, there is always a shortage of food supply due to the high demands.
• Shortage of land: Rapid population growth has resulted in scarcity of land due to pressure on land.
• Unemployment: A rapid population growth means there is a high number of job seekers with few employment opportunities.
• Migration: The rapid population growth has influenced many to move from one place to another in search of better survival opportunities and living conditions.
• Environmental degradation: Rapid population growth is a cause of environmental degradation. People encroach on the reserved areas, degrading the environment.
• Shortage of social facilities due to congestion: Rapid population growth has increased population pressure on the existing social facilities, like schools and hospitals.
• Insecurity and increased crime rate: Crime is increasingly becoming common in the highly populated areas of Rwanda. This is because of congestion and joblessness. The crime rate is higher in urban areas.
• High cost of living: Rapid population growth has led to an increase in the cost of living. Due to the increase in demand for various resources such as housing, food and transport, the cost of obtaining the resources is very high.
• Increased government expenditure: The government spends a lot of funds in addressing the effects of rapid population growth. For example, huge sums of money are used to establish more social facilities, resettle people and to improve on security.
• Development of slums: Rapid population growth has come along with the emergence of shanty towns also known as slums. Such areas harbor criminals, have poor hygiene and drainage systems and have substandard houses. Other social ills such as organized crime, prostitution and drug trafficking are rife in slum areas.
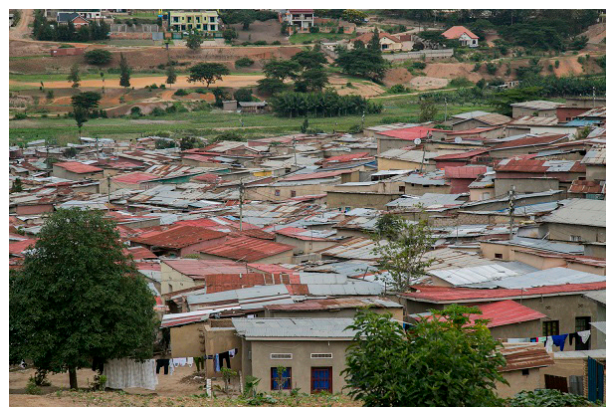

A slum in Kigali city
9.2.3. Solutions to rapid population growth
There are several ways that can be used to address the challenges resulting from rapid population growth. They include the following:
• Encouraging migration: The government should encourage people to migrate from high to low populated areas.
• Education on the importance of family planning: The population should be educated on the importance of family planning methods in order to have small families.
• Emphasis on education especially of the girl child: Educating the girl child to higher levels tends to delay the age at which the girls get married. This discourages early marriages which lead to high birth rates and big families.
• Economic empowerment: Economic empowerment of the masses especially of the women gives them the power to make wise decisions among them, the number of children they should have and have comfortable support.
• Government intervention: The government can intervene by providing incentives to the families that have few children. The incentives could be through things like sponsored education and health care. This will discourage people from having big families hence reducing the population growth.
Application activity 9.2
Observe the local environment near your home or school;
1. Identify the factors that contribute to the growth of population in the observed area.
2. As prospective teacher, suggest different ways to address the challenges of rapid population growth in your village.
Skills lab
Discuss the disadvantages of population growth to a country like Rwanda
End unit assessment
1. Assess the impact of life expectancy to the economy of Rwanda.
2. Explain any six factors that influence population distribution in Rwanda.
3. Discuss five factors that influence population growth in Rwanda.
4. Analyse five consequences of population increase in Rwanda.
