UNIT 2:UNIVERSE AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Key unit competency: The student-teacher should be able to distinguish between the components of the universe and the solar system.
Introductory Activity
One day, students from a certain school moved outside in the evening and all of sudden saw a running star that disappeared. The moon was fading, being covered by dark clouds. They wondered whether there are moons elsewhere and went back to bed. In the morning, the sunrise with golden rays replaced the dark and starry night.
a) Identify the heavenly bodies mentioned in the passage.
b) Using your experience and the passage above, identify other components of the universe not mentioned in (a) above.
2.1. The universe and solar systemLearning activity 2.1
Study the photograph provided below and use it to answer the questions that follow:
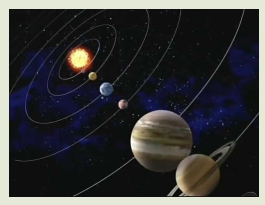
1. Explain what the above photograph represents.
2. Using the above photograph, explain the meaning of universe.
3. Describe the solar system.
2.1.1. Definition of the universe and Components of the universe
i) Definition of the universe
The universe refers to all the space and everything in it. It contains everything that exists, from the smallest particles to the largest structures known. The exact size of the universe is not known. Astronomers estimate that it contains about 100 bill
ii) The components of the universe
The Universe contains many components, which vary considerably in size, distance from each other and shape.
A galaxy is a large scale aggregate of stars, plus some gas, dust, and possibly solar systems, which are held together by gravity on galaxies. Astronomers are experts who study bodies in the sky or outer space. A galaxy is a system of stars, together with gas and dust. These are held together by forces of gravity. Each of the galaxies has an average of 100 billion stars. The origin of the universe is explained through the Big Bang Theory, which happened about 13 billion years ago.
Types of Galaxies
Astronomers classify galaxies into three major categories. Spiral galaxies look like flat disks with bulges in their centres and beautiful spiral arms. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The second type is called Elliptical galaxies which are redder, more rounded, and often longer in one direction than in the other, like a football. Finally, Galaxies that appear neither disk-like nor rounded are classified as irregular galaxies.
A star is a ball of hot gas held together by its own gravity. Gravity also causes stars to undergo nuclear fusion within their interior. The energy release causes the star to shine.
A solar system is an arrangement of planets and other small bodies around a central star or stars. The planets are kept in place by gravity.
A planet is a spherical body which circles a star in a regular orbit.
A comet is a kilometre-scale mass of frozen gas and rock which orbits the Sun. Comets are leftovers from the formation of the Solar System.
An asteroid is a mass of rock and minor amounts of frozen gas. Like comets, asteroids are leftovers from forming the pl2.1.2. Solar system
The term solar system is defined as the arrangement of the sun and planets that revolve around it (Sun). The solar system is therefore made up of the following: the sun, planets including the earth, the moon and other heavenly bodies such as asteroids, comets, meteorites, meteors, etc.
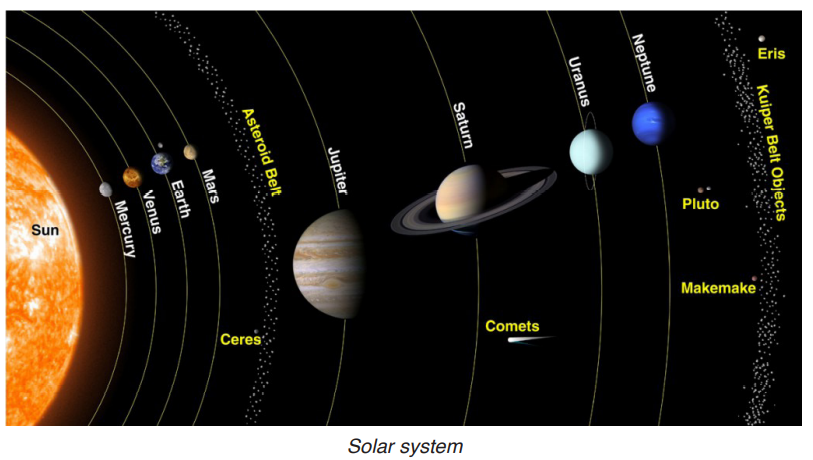
i) The sun
The sun as earlier studied, is one of the billions of stars that make up the Milky Way galaxy. It is one of the smallest stars in our universe. However, it is 109 times bigger than Planet earth. It forms the center of the solar system. Its gravitational
force keeps planets in their orbital position. All the 8 planets revolve around it.
1) Characteristics of the Sun
The sun as any other heavenly body, has characteristics that distinguish it from the rest of other components of the solar system. These are explained here under:
• It makes or emits its own light/heat.
• It has the diameter of 139,200 km.
• Its temperature ranges from 4000-9000 degrees Celsius.
• Its mass stands at 1.98892 x 1030 kilograms.
• It has a density of 1.4 grams per cubic centimetres.
• The sun is made up of hydrogen and helium.
• Its radius is estimated to be at 695,500 kilometres.
• It takes 25 days to turn once on its axis
2) The influence of the sun on the Earth
• It holds the earth in its orbital position.
• It contributes greatly in the balancing of the tidal bulge caused by the moon’s gravitational pull and the inertia.
• The sun is the source of the energy that is used by the earth and all that is therein.
• It engines the hydrological cycle.
• It supports life on earth through many ways such as creation of suitable and favourable temperatures.
• The sun influences the general climate at hand due to solar radiation received.
• It contributes to the formation of tides that support in one way or the other to ecosystem and man’s activities.
ii) Characteristics of different planets and their positions
The term planet means a large, round object in space that moves around a sun. Planets are grouped into categories as shown below:
Group of planets of the solar system


Pluto is known as a dwarf planet. It never developed fully. It is very important to know that Pluto was removed from the list of planets in 2006, because of the following reasons:
• Its size is too small to be classified as a planet.
• It has no uniform revolution around the sun.
• Its revolution is not circular but spherical in nature.
• Its movement is too slow when compared with the rest of the planets of our solar system.
List of planets and their major characteristics






Application activity 2.1
1. Imagine you represent your school in Geography competition; explain what you would tell others about the difference between inner and outer planets.
2. “The earth is the only planet that supports life” Explain.
2.2. Earth
Learning activity 2.2
Read the following passage and answer the questions provided.
Every day the sun rises in the east and sets in the west. This process led many people in the past to think that the sun is moving, and the earth is fixed. The sun moves around the earth. But with the advancement of science, this has been proved that the sun itself is moving and the earth has also been moving. Later it has been revealed that the sun does not move around the earth, rather the earth moves around the sun.
With the help of your knowledge and skills acquired in previous studies answer the following questions?
1. How many movements does the earth make?
2. Describe effects caused by the rotation and revolution movements.
i) Peculiar elements of the earth
The peculiar elements of the earth are the features or characteristics that belong to the only earth planet making it unique.
The peculiar elements of the earth are outer parts of the earth. They include the following:
1. Hydrosphere or water bodies
2. Lithosphere or Land and rocks
3. Atmosphere or Gases
4. Biosphere or flora and fauna
• Hydrosphere: This stands for all the waters found on the earth surface.It covers a big part of the earth’s surface.It includes: Lakes, Seas,Oceans,Wetlands , Rivers,Wells,Streams,Clouds.
• Biosphere: This is known as ecosphere. It is a part of the earth that includes the totality of life on the earth (Animals,Plants and Man).
• Lithosphere: This is the solid part of the external area of the earth.It is made up of the crust and a small percentage of the upper mantle (Land ,Rocks, Soils and Minerals).
• Atmosphere: It describes the zone occupied by air or gases that surround the earth.This zone is composed of gases such as:
Nitrogen,Oxygen, Argon ,Water vapour, Carbon dioxide, Helium, Methane.
i) Earth’s movements
1. Rotation of the Earth
Rotation of the Earth is defined as the movement of the Earth spinning on its own axis. This movement of the Earth on its own axis is in an anticlockwise direction during 24 hours. The earth takes 24 hours to complete 360˚. At the equator the earth rotates at a speed of 1676 km and zero km at the poles per hour.
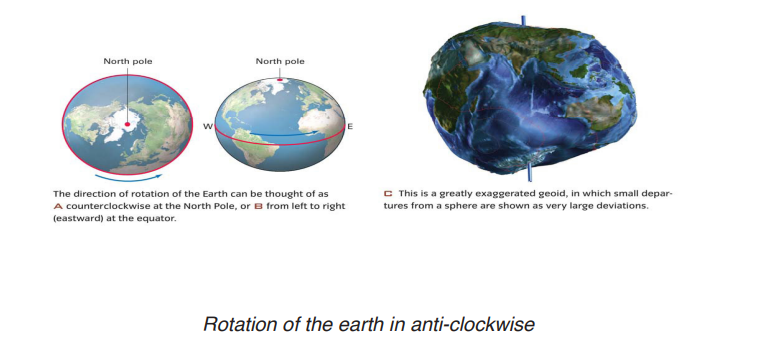
The effects of rotation of the earth
As the Earth turns around its axis, it affects some processes on the earth’s surface and other associated celestial phenomenon. Some effects of the earth’s rotation are:
• Rotation causes day and night
Earth’s rotation on its axis causes day and night. The one half of the Earth that faces the sun has day time, while the opposite half facing away from the Sun has night time.
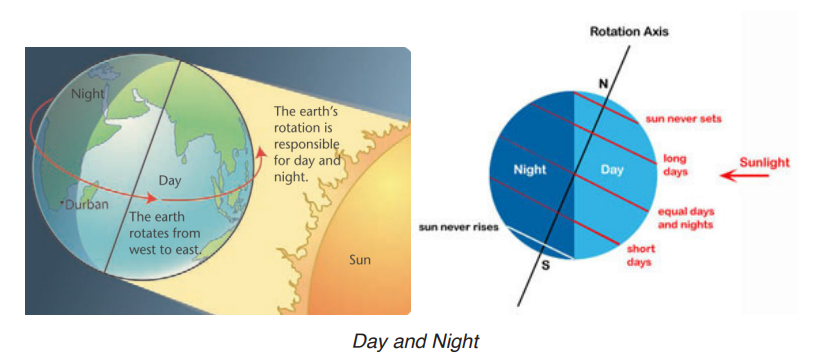
• Rising and falling of ocean water (tides): Rotation of the earth with the gravitation force pull of the sun and the moon, act on the ocean water to produce tides which may be high or low tides.
• Deflection of wind and ocean current (Coriolis Effect): Rotation causes winds to be deflected to the right in the Northern hemisphere or to the left in southern hemisphere whenever they cross the Equator.
This deflection is called the Coriolis Effect.
• Time difference between longitudes: One round of the Earth is completed after turning 360o
.Thus, for 1 hour, the Earth takes: 360o: 24 = 15o.

• Temperature difference: Due to the spherical shape, the parts of the Earth located in the tropical areas between 23.5˚North and south of the equator get direct sunlight all the year while regions located north and south of the mentioned altitude get less rays during the year
2. Revolution of the Earth
The revolution of the earth is the movement of the earth around the sun. Earth revolves around the Sun along an oval-shaped path called an orbit. The area of the oval-shaped path is called Plane of the ecliptic, in which the axis of the Earth is tilted at an angle of 23o27’. Earth takes 365 days and 6 hours or one year to complete one revolution, at a speed of 106,260 km/h around the Sun (30 kilometres per second).
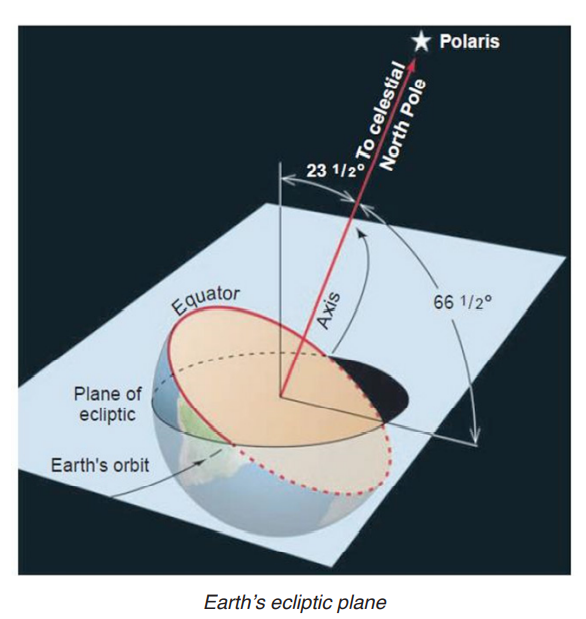
The Leap year is the year with 366 days which came after four years where February has 29 days instead of 28 days due to adding of the 6 hours of rotation of each year to make one year after 4 ordinary years.
The consequences of the revolution
• Determination of seasonal variation: The whole year has been divided into four divisions. Each of such division is known as a season. There are four seasons namely: summer, autumn, winter, and spring.
Before explaining the four seasons, it is important to explain first the two concepts of solstice and equinox:
• Solstice is either of two times of the year at which the sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky at midday, marked by the longest and shortest days over the tropics. Solstice occurs on 21st June and 22ndDecember.
• Equinox occurs two times in the year (around 21st March and 23rdSeptember) when the sun is above the Equator, day and night have equal length. There are spring and autumn equinoxes.
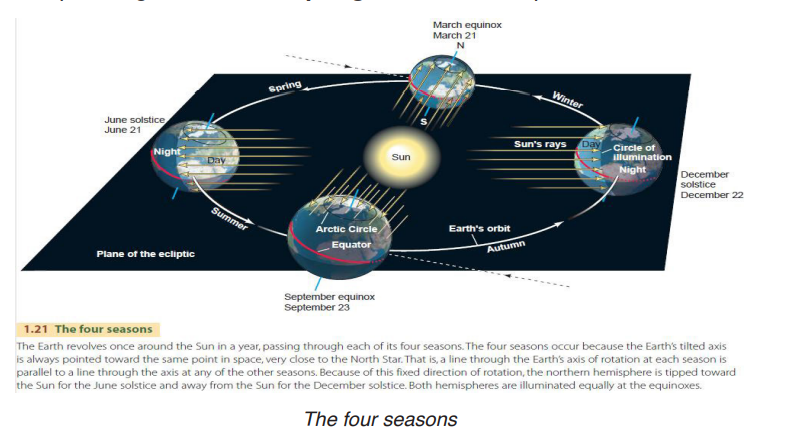
• The four seasons
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, falling after spring and before autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longer, and the nights are shorter, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after solstice. When it is summer in the northern hemisphere, it is winter in the southern hemisphere, and vice-versa.
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate zones. It occurs after autumn and before spring in each year. Winter is caused by the axis of the Earth in that hemisphere being oriented away from the Sun. when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. In many regions, winter is associated with snow and freezing temperatures. The days on which this occurs have the shortest day and the longest night with a day length increasing as the season processes after the solstice.
Spring is one of the four conventional temperate seasons, following winter and preceding summer. Days become longer, and weather gets warmer in the temperate zone because the Earth tilts towards the Sun. In many part of the World plants grows and flowers bloom.
Autumn is one of these seasons of the year between summer and winter during which temperatures gradually decrease and most vegetative growth decrease. It’s the season when the days get shorter and colder, and everything turns brown and drop.
• Varying length of day and night at different times of the year: The revolution causes variations in the length of the day and night over different latitudes. When the sun is in the southern hemisphere i.e. overhead the tropic of Capricorn, the latitudes in the northern hemisphere receive less hours of sunlight (daytime) but more hours of night time; while the southern hemisphere receives more hours of heating hence more hours of daytime.
During the summer solstice, day time is longer than night time at latitude beyond equator the hours of daytime increase from tropic towards poles (from 12hrs to 24hrs at the Arctic Circle and beyond). During the winter solstice, night time is longer than day time at latitude beyond equator.
Norway is known as the land of the midnight sun because the sun does not go below the horizon or comes above it on 21st June
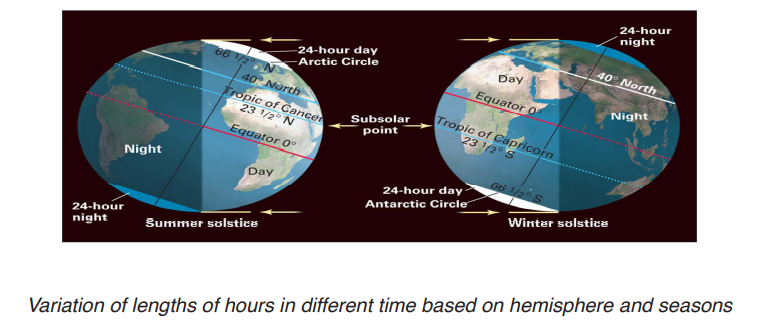
• Climatic zone: Climate zones are divisions of the Earth’s climates into general climate zones according to average temperatures and rainfall. The three major climate zones on the Earth are the Polar, Temperate, and Tropical zones. Temperatures in these three climate zones are determined mainly by the location, or latitude. The reason why the equatorial zone is hotter than the poles is that sun’s rays fall vertically at the equator and obliquely at the poles.
Example, the stations around the equator such as Kisangani, Masaka, Libreville, and Manaus experience hot temperatures while areas such as Alaska, Greenland and Siberia near the poles experience cold temperature.
Application activity 2.2
1. Explain why it is very important to conserve the peculiar elements of planet earth.
2. Rusizi is 28 E and the time is 6:00 am. What is the time in a place which is located at 60˚W?
3. Explain why some parts of the earth’s surface are getting hotter while others get cool and cold.
Skills lab
With reference to the relief features where you live, prepare an appropriate economic activity you can do.
End unit assessment
1. Study the photograph shown below.

a) Identify the heavenly bodies shown in the photograph.
b) Mention and describe the heavenly bodies found in the universe that are not shown in the photograph.
3. Examine the importance of the atmosphere.
4. Explain the impact of rotation movement on human activities.
