Topic area Human and economic
Geography
Sub-topic area Economic activities
Key unit competence
By the end of this unit, you should be able
to explain the impact of industrialisation on
sustainable development in Rwanda.
Unit objectives
By the end of this unit, you should be able to:
• Recall the definition of industry.
• Name the types of industry in Rwanda.
Industry in Rwanda UNIT
16
• State the factors affecting location of
industries in Rwanda.
• Identify the importance of industries in
Rwanda.
• Identify the problems affecting industrial
development in Rwanda.
• Outline the environment and health
issues associated with industrialisation.
Definition of industry and industrialisation
Activity 16.1
Work in pairs.
Study the flow chart below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
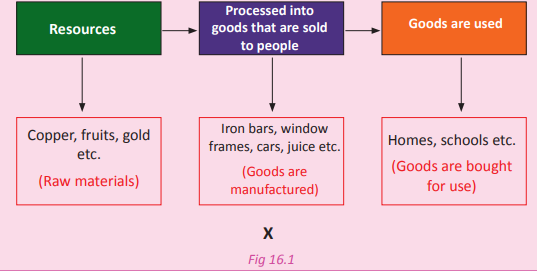
1. Name the process that the flow chart
represents.
2. Describe the process represented by
the flow chart.
3. What is represented by X and why is
it important?
4. Name at least two areas in Rwanda
where the processes shown in the
flow chart are carried out.
5. Discuss your answers in a class
presentation.
Industry is defined as an establishment
set up to process and transform complex,
simple and ordinary raw materials to
either semi-finished or finished materials.
Industrialisation refers to the process
concerned with the mechanical or
chemical transformation of inorganic and
organic substances into new products. It is
the process that transforms raw materials
into new products.
Industrialisation in Rwanda takes place
in a very low scale when compared
to other countries such as Kenya and
Uganda. The government of Rwanda is
working hard to turn the economy from
being predominantly agrarian to a more
industrialised one.
However, the challenges of limited natural
resources such as minerals and the fact
that the country is landlocked slow down
the industrialisation process. Most of the
industries in Rwanda are agro-based with
a few manufacturing industries found in
urban centres especially Kigali.
Activity 16.2Use the Internet and other geographical
journals;
1. Explain the concept of industrialisation
in relation to Rwanda.
2. Write down your findings and discuss
them in a class presentation.
Types of industries and
industrial products in Rwanda
Activity 16.3
1. Study the table below and fill in the
missing information.
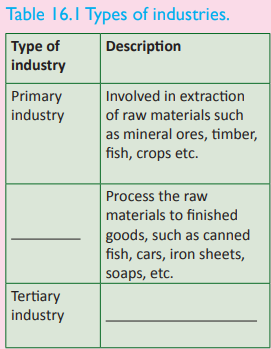
2. Giving examples, identify the different
types of industries that are found in
Rwanda.
3. Discuss your answers in a class
presentation.
There are three types of industries and
their products that are discussed below.
(a) Primary industries
These industries are involved in the
extraction of raw materials directly from
the Earth’s crust, forests and seas. Examples of such industries include forestry, mining,
fishing and agriculture.
They extract products such as trees, fish,
iron ore and maize among others.
(b) Secondary industries
These are industries that process raw
materials into semi-finished and finished
goods. Examples of these industries
include the
heavy and light manufacturing
industries. They are industries such as food
processing and construction industries.
The products of these industries include
canned foods, cement, clothes and shoes.
(c) Tertiary industries
These are also called service industries.
Their main purpose is to provide services
that support other industries. Examples
of tertiary industries in Rwanda include
transport agencies, teaching and medical
services, recreation and entertainment,
tourism and finance.
The products of these industries are
transport services, education services,
medical services, insurance and financial
services among others.
(d) Quaternary industries
The quaternary industries provide
knowledge based services. They include
services such as information technology,
information generation and sharing,
media, research and development, as
well as knowledge-based services like
consultation, education, financial planning,
blogging and designing.
The products of these industries include
ICT services, research and development
findings, media services among others.
Activity 16.4 Work in pairs.
1. Giving examples, name the types of
industries that are located in an urban
centre that is near your school.
2. Discuss the importance of the industries
to the economy of the region and the
country.
3. Write down your findings and present
them in a class discussion.
Factors affecting the location
of industries in Rwanda
Activity 16.5
Work in groups.
Study the photograph showing the Inyange
industry in Masaka and use it to answer the
questions that follow.

1. Identify the type of industry shown in
the photograph.
2. Find out the factors that influenced its
location.
3. Relate the factors identified to the
location of other industries in the
country.
4. Write down your findings and discuss
them in a class presentation.
Industries in Rwanda are located in different
places. There are factors that affect their
locations. They include the following.
(a) Availability of raw materials In determining the location of an industry,
closeness to sources of raw materials is of
vital importance. This reduces the cost of
production and increases the profit margins
of the company.
(b) Transport and communication facilities
Industries are usually located near transport
and communication facilities in order to
easily transport raw materials and finished
goods to and from the industries.
(c) Availability of power and other
energy sources
Most industries in Rwanda are located near
sources of energy and power, such as areas
in Kigali city.
(d) Proximity to markets Most industries in Rwanda are located in
areas where there is already market for
their products.
(e) Government policies
The Rwandan government has demarcated
areas for industries through the Rwanda
Development Board.
(f) Availability of labour
Industries that are labour intensive in
Rwanda are located in areas where there
is assurance of a steady supply of labour.
This is possible in areas that are densely
populated such as Kigali, Musanze and
Masaka areas.
(g) Availability of land
This has a great influence in the location of
industries in Rwanda. Industries that require
large pieces of land have to be established
in areas where there is available land.
 Availability of water
Availability of water
Industries that need to use a lot of water are
usually located near water sources. Water
is a raw material for some industries, acts
as a cooling agent in some industries and is
sometimes used to transport raw materials
and finished products to the market centres.
(i) Investors preferences Industries may be located in specific areas
due to the investor’s personal preferences.
(j) Proximity to aids to trade
Industries in Rwanda are located near areas
where aids of trade such as banking and
insurance services are available
(k) Industrial inertia Investors would want to establish new
industries in areas where other industries
were located. This is due to the advantages
of already established infrastructure and
other public utilities that can be of help to
the industry.
(l) Climate
There are some industries in Rwanda that
are located in given areas due to favourable
climatic conditions. Examples of these
industries are agro-based industries such as
tea processing factories that are located in
areas where climate is favourable for the
growth of tea.
(m) Relief
Most of the industries in Rwanda are located
in lowland areas where the landscape
favours easy construction of industrial
infrastructure.
Factors influencing industrial
development in Rwanda
Activity 16.6
Study the photograph below that shows the
interior of one of the sections of the Inyange
Industry in Kigali-Masaka. Use it to answer
the questions that follow.

1. State at least two products produced
by Inyange group of industries.
2. Identify and explain the factors that
affect the development of the industry.
3. Find out other factors and relate them
to the development of industries in the
country.
4. Are the factors that you have mentioned
in (3) above valid for the development
of industries in the country?
5. Write a report of your findings and
discuss them in a class presentation.
The development of industries in Rwanda
is influenced by a number of factors. Some
of them are discussed below.
(a) Availability of raw materials
In areas where there is a constant supply of
the required raw materials, industries grow
and develop. For example, the presence of
limestone at Bugarama has contributed to
the success of CIMERWA.
(b) The presence of a steady market Industries produce goods and services
for commercial purposes. This means
that the prosperity of industries depends
on the availability of a ready market. For
example the Inyange group of industries
has developed and grown due to the high
demand for its products both locally and
internationally.
(c) Presence of transport infrastructure
The Rwandan industries heavily depend on
the available means of transport in order
to transport both inputs and outputs. This
explains why industries are located near
roads and water bodies such as Lake Kivu.
(d) Technology
Technological advances help an industry to
grow. This is because it is technology that
makes the conversion of raw materials into
quality finished products possible. Industries
in Rwanda are gradually mechanising
their operations. This calls for improved
technology for higher outputs.
 (e) Availability of power and energy
resource
(e) Availability of power and energy
resources
Industries depend on power and energy
to run machines that are used in the
production of goods. Those that have access
to a steady and constant supply of power
develop faster since the production process
is also quick.
(f) Influence of industrial inertia This assists the newly established industries
to grow and develop. They benefit from
already existing infrastructure such as
roads, warehouses, banking institutions and
sometimes the industrial establishments.
(g) Steady supply of labour Industries develop when there is a steady
supply of labour. In urban areas like
Musanze, Kigali and Rwamagana, there is
a steady supply of labour due to the high
population.
 Government policies
Government policies
The government of Rwanda has designed
various policies that aim at enabling the
industrial sector to develop and grow. The
registration of industries can be done online
and be processed within 24 hours. Investors
are also given tax holidays when they start
operations for specific periods of time.
(i) Political stability Industries in Rwanda have developed
because of the stable investment
environment that is available for them to
operate in.
(j) Water resources
The supply of water is of great importance
to industries. This is because water is a raw material to some of the industries, it is a
cooler and most importantly, it is used for
sanitation.
(k) Availability of capital For industries to grow and develop, there
must be adequate financial resources.
This is needed for meeting the financial
requirements such as paying the human
resource, buying machinery, purchasing
of raw materials and paying for marketing
services. Credit facilities are available for
entrepreneurs and other investors.
(l) Availability of land When industries expand, they need more
land space to expand their premises
and other industrial infrastructure. Land
has been made available to industries in
Rwanda through the implementation of
land reform programs in the country.
Task 16.1 1. Define
(a) Industry
(b) Industrialisation
2. Discuss the types of industries in
Rwanda.
3. Explain the factors that affect the
development of industries in Rwanda.
The importance of industries
in Rwanda
Case study
Read the extract below and answer the
questions that follow.
Nyirangarama, Rwanda (CNN)— A maverick
entrepreneur and self-made millionaire,
Sina Gerard is probably Rwanda’s most
famous businessman. Having established a
business empire from the bottom up, he’s now training local farmers to help make
Rwanda an agricultural exporter.
“My aim is to make sure that the Rwandan
people build themselves and get out of
poverty,” he says. “My aim is to make sure
Rwandan farmers, because they are rated
at 90%, feel proud to be farmers. I’m sure
I’ll achieve it because so far I have achieved
a lot.”
There’s no disputing Gerard’s achievements.
Twenty-five years ago he had just one
employee, who helped him sell the bread
he baked at his parents’ farm. Now, Gerard
says he employs hundreds of workers and
buys produce from thousands of farmers.
Source: CNN’s Marketplace Africa.
(a) Identify and explain the importance of
industries that are mentioned in the
extract.
(b) Giving examples, highlight the
importance of industries to the socio
economic development of Rwanda.
(c) Write down your findings and present
them in a class discussion.
Industrialisation is among the most
significant sectors that faster modernisation.
This is due to the following reasons.
(a) Employment opportunities Industries create varied employment
opportunities to the people thereby reducing
the problem of unemployment and underemployment in the country.
(b) Provision of products needed by
the society
The agro-based industries in Rwanda
such as the Inyange and Urwibutso agroindustries provide products that satisfy the
needs and wants of the people.
(c) Source of foreign exchange The government of Rwanda is able to
earn foreign exchange from the export of
products from the industrial sector. This
assists the government to stabilise its
balance of trade.
(d) Improved standards of living
The industries enable the population of
Rwanda to improve their standards of living.
They provide processed food stuffs and
other materials for use in the day to day life
of the Rwandan people.
(e) Diversification of the Rwandan
economy
Industrial development in Rwanda has
provided an alternative source of revenue
to the economy of the country. This has
helped to reduce overdependence on
primary products whose prices fluctuate
from time to time.
(f) Growth of infrastructure
Rapid industrial growth has resulted in
the expansion of infrastructural facilities.
The development of modern industries in
Rwanda has stimulated the growth of the
banking, insurance, commerce, air and
road transport services to industrialise the
economy.
(g) Research and development
Creativity and innovation defines Rwanda’s
industrial sector. Constant research ensures
that the sector is up to speed with advances
in technology that are needed for further
growth and development. This is aimed at
producing quality goods and services.
 Source of markets for other materials
Source of markets for other materials Industries have contributed to the expansion
of the markets for agricultural crops,
minerals and forest products. They have
contributed to the expansion of the markets
for capital goods like plants & machinery.
(i) Facilitation of the utilisation of
resources
Industrialisation contributes to better
utilisation of natural resources like minerals,
forests and fisheries, which are available in
the country.
(j) Promotion of friendly international
relations
Rwanda has had a better relationship with
other countries that import her natural
resources such as China (9.1%), Thailand
(8.6%), Germany (7.3%), USA (4.5%) and
Belgium (4.1%). This has additional benefits
such as foreign exchange and bilateral trade.
Problems affecting industrial
development in Rwanda
Activity 16.7
Work in pairs.
Study the photograph shown and use it to
answer the questions that follow.
1. Describe what is happening in the
photograph shown.
2. Find out how the disaster shown affects
the growth of the industry.
3. Find out other problems affecting
industrial growth and development in
the Rwanda.

Some of the problems affecting industrial
development in Rwanda include the
following.
(a) There is a shortage of skilled labour.
This results in reduced production and
poor utilisation of resources.
(b) There is limited market for products
from industries because of the low
income of most Rwandans.
(c) The technical development in Rwanda
is still low. This affects the quality of
industrial products.
(d) There is inadequate supply of raw
materials especially those needed
in metal work industries. These raw
materials have to be imported making
them expensive beyond the reach of
many Rwandan citizens.
(e) Rwanda is a landlocked country.
This poses a great challenge to
industrialisation since it has to depend
on the delivery of raw materials from
other countries.
(f) Rwanda faces stiff competition in
the international market from other
industrial countries like Kenya and
Uganda in the region.
(g) There is limited investment in
the industrial sector as a result of
insufficient capital required to put up
and operate industries.

The education system of Rwanda
has been theoretical only equipping
learners with knowledge without the
skills required in the job market. This
has resulted in a shortage of technical
industrial skills.
(i) There are limited raw materials to be
used in the manufacturing of different
products.
(j) Fire outbreaks have claimed some of
the industries in Kigali. This leads to
huge losses .
(k) Industries cause pollution that affects
the environment and the lives of the
workers.
Solutions to problems faced
by industries in Rwanda
Activity 16.8
Work in pairs.
1. Suggest possible solutions to the
problems that affect industrial
development in Rwanda.
2. Write them down and present them in
a class discussion.
There are several solutions to address the
problems affecting industries in Rwanda.
They include the following.
(a) I m p ro v i n g t h e t ra n s p o r t a n d
communication network in the country
through construction of new roads and
rehabilitation of the existing ones.
(b) Encouraging more investors, both
foreign and local to invest more capital,
and managerial skills in the sector. This
will ensure smooth running of industrial
activities.
(c) Training of more human resources
in different industrial jobs such as
communication and marketing. This
will help to deal with the problem of
shortage of labour.
(d) Cooperating with major development
partners such as the World Bank and the
African Development Bank to provide
credit facilities so as to address the
problem of inadequate capital.
(e) Widening both the local and international
markets through joining economic blocs
such as the East African Community
(EAC) and Common Market for Eastern
and Southern Africa (COMESA).
(f) Improving technology in order to
produce high quality goods which can
attract high demand in both the local
and foreign markets.
(g) Importation of raw materials which are
not found in Rwanda in order to sustain
production.

The government should design policies
that encourage the establishment of
local industries and protect them from
external competition.
Environmental and health
issues associated with
industrialisation and ways to
mitigate them
Environmental and health issues
associated with industrialisation in
Rwanda
Activity 16.9
Work in pairs.
Use the Internet and other geographical
documents.
1. Find out the impact of industrialisation
on the environment and on human life.
2. Suggest ways in which the effects can be
addressed and their negative impacts
lessened.
3. Write down your findings and present
them in a class discussion.
Industrialisation has had several impacts
on the environment and on human health.
Some of the impacts are discussed below.
(a) Industries emit poisonous gases and
smoke that pollute the atmosphere.
This affects the environment, creating
micro climates and endangering the
lives of people and animals.
(b) The establishment of industrial
infrastructure requires vast amounts of
land. This means that the preparation of
sites requires the removal of vegetation
in readiness for construction. The
destruction of vegetation destroys
the ecosystem exposing the land to
erosion.

(c) Industries that deal with forests,
mining and processing, destroy the
environment because they use up the
scarce natural resources available
(d) Industries emit a lot of heat that
is produced during the production
processes of certain products. This
heat affects the temperatures of the
surrounding air leading to global
warming.
(e) The industrial waste products are
sometimes improperly disposed. This
makes it hard to find clean water for
domestic consumption especially in
areas that are near the industries. The
effluents also destroy aquatic life.

(f) The raw materials used in industries
are sometimes from the environment
in areas such as forests, water bodies
and land. The exploitation of these
materials has had negative effects on
the environment.
(g) There are diseases that have come
up as a result of the establishment of
industries.

Industrialisation in Rwanda has
caused rural urban migration. Many
people leave the rural areas to go to
urban centres to work in industries
that are found in the urban areas.
(i) There are accidents that occur in
industries which have caused the loss
of many lives.
(j) Some industries produce goods that
are harmful to the lives of people.
The mitigation of the environmental
and health issues associated with
industrialisation in Rwanda
There are various mitigation measures that
the government has put in place to address
the environmental and health issues that
are related to industrialisation. They include
the following.
(a) The government has designed various
policies that aim at protecting the
environment and people against the
negative effects of industries.
(b) The government has put in place the
Environmental Impact Assessment
(EIA) requirement before the
establishment of any industry.
(c) The government has set up new
industrial areas such as the Free Trade
Zone at Ndera, the Masaka region
and the new huge industrial region in
Gashora in Bugesera district.

(d) There are standards that have been
put in place that the industrialists
have to follow. These are safety
standards to ensure that the working
conditions do not endanger the lives
of the workers and the communities
around.
(e) There is emphasis put on chemical
neutralisation of the industrial wastes
that could cause serious problems.
This aims at reducing the toxicity of
the industrial wastes.
(f) Rwanda has demarcated areas to
be disposal sites. These sites are
located far away from homes and
are relatively protected as secure
hazardous waste disposal sites.
Activity 16.10
Your teacher will organise for you to go on
a field visit to one of the industries in the
country.
Observe and find out the following;
1. Factors that determined the location of
the industry.
2. The importance of the industry to the
local environment and to the country.
3. The effect of the industry on the
environment and on human health.
4. Suggest ways to mitigate the impacts
highlighted in (3) above.
5. Write a report on your findings that you
will present in a class discussion.
Task 16.2
1. Give five reasons why industries are
important in Rwanda.
2. (a) Discuss five problems that affect
industrial development in Rwanda.
(b) Provide the solutions to the
problems listed in (a) above.
3. Explain three environmental issues
associated with industrialisation in
Rwanda.
Case studies
Tea and coffee factories
(a) Mulindi tea factory
This is one of the oldest tea processing
factories in Rwanda. It is located in Gicumbi
District. It was established in 1962 with
a production capacity of 3200 tonnes of
tea leaves at the time. Its long historic and
successful existence has made it the biggest
tea processing factory in the country. It was
first owned by the government but was later
privatised. Currently, the factory produces
over 15 million tonnes of green leaves
output per year.
Mulindi tea factory was greatly affected
by the liberation war. During the period
between 1995-1996, there was intensive
rehabilitation of the factory and the tea
plantations which had grown into tea
forests. The tea leaves are mostly from
privately owned plantations and villagers
who grow tea. The factory does not have
its own tea plantations.
The main green leaf producer is under the
COOPTHE cooperative, The villagers’ tea
on the other hand is also grouped into
one cooperative called COOTHEVM. The
COOPTHE production is about 35 % with
the total area under tea plantation being
585 hectares. The villagers’ tea plantations
contribute 55% to the total green leaf
production covering 1150 hectares of the
tea plantation.
The Mulindi tea processing industrial
block covers 174.4045 hectares. The tea
plantations put together cover a total area
of 1909.4045 hectares. The tea plantations
associated with Mulindi tea processing
factory are divided into 10 agricultural
sectors.
The tea plantations are located in the
lowland areas that are situated in the
reclaimed swamps found in the vicinity.
The plantations that are found in the
valleys account for 90% of the tea produced
while other tea plantations and small scale
growers along the gently sloping areas make
up 10 %.
 (b) Rwandan Farmers Coffee Company
(RFCC)
(b) Rwandan Farmers Coffee Company
(RFCC)
This company was established in 2014
and commenced operations officially in
2015. It is located in the Gikondo area of
Rwanda. The factory is jointly owned by
RFCC and other shareholders who include
Clinton Hunter development initiative –
Development bank of Rwanda, the Hunter
Foundation and The National Agricultural
Export Board.
The factory produces 3 tonnes of coffee
daily. The brand name for its products is
‘Gorilla’s coffee’. The factory exports much
of its products although a small percentage is locally and regionally bought. It has a
steady market in the UK, the USA and other
European countries. The company works
with the local coffee growers.It assists them
to produce high quality coffee beans.
 (c) Inyange industry
(c) Inyange industry
The Inyange industry is a leading food
processing industry in Rwanda. The industry
produces a wide range of high quality
products. The industry was set up in
1997. After two years, it began producing
pasteurised milk and yoghurt for the local
market. The industry was very successful
that it was able to invest its economic
returns back into the business. It expanded
further and in the year 2001, it opened
another branch that began the production
of bottled mineral water. The industry
operated in Kigali.
The high demand for Inyange products
made the company grow and expand. It
opened a new site at Masaka. This enabled
the company to increase its production,
necessitating the need to expand both the
domestic and international market. The
establishment of the East African Community (EAC) and the scrapping away of custom
duty made it easy for the industry to capture
the foreign market. The neighbouring
countries such as Uganda, DRC and Burundi
all provide a ready market for products
from the Inyange industries. The Inyange
group of industries has modernised their
operations by upgrading their equipment
and equipping their staff with relevant skills
so as to meet the international standards.
The products produced include; fruit juices,
quality mineral drinking water as well as
milk and milk products. Ensuring quality
is one of the key points of concern in the
Inyange industries.
 (d) Bugarama cement factory
(d) Bugarama cement factory This is one of the most prosperous cement
making industries in Rwanda. It is the
cement producer in the country. However
its production capacity is not able to meet
the country’s cement needs. Most of the cement products are imported from Uganda
and Kenya. The Bugarama cement factory is
locally known as CIMERWA. It is situated in
Bugarama in Rusizi District in the Western
Province of Rwanda. The industry is one of
the oldest industries found in the country
having been in existence for 31 years. It was
located in Bugarama due to the availability
of large deposits of limestone and water
from the hot springs that are required in
the process of cement making.
Its cement is utilised locally and also
exported to the DRC and Burundi.
CIMERWA has assisted the communities
that live close to it through corporate social
responsibility programmes.
 (e) Bralirwa
(e) Bralirwa Bralirwa is one of the most well developed
brewery companies in Rwanda. It was
first established in 1957. It is located in
Rubavu, approximately 117 km by road to
the west of Kigali, Rwanda’s capital city.
The administrative headquarters of the
company are located in Kigali. In Rwanda,
it is the largest producer of a wide variety
of beer and soft drinks.
It was established after its sister brewery
companies in the DRC and Burundi to meet
the demand that was beginning to crop up
in the Rwandan side. It was located near
Lake Kivu in the current Rubavu district.
The influencing factor for its location is
the presence of large deposits of methane
gas as an alternative source of fuel. The
presence of different forms of transport
such as air, road and water transport and
the availability of labour due to the strategic
position in the highly populated area also
influenced its location.
Bralirwa started with production of Primus
as the only beer up to 1957. In 1987 it
started brewing another brand of beer
called Mützig. Two years later, it introduced
Guinness under license.
In 1971, the Heineken Group, a Dutch
brewing conglomerate, obtained 70%
majority shares in Bralirwa. After the
acquisition, Bralirwa greatly improved its
brewing processes. It also, partners with the
Coca-Cola company to produce soft drinks.
Did you know? • The agricultural sector continues to
be the biggest employer and the most
important contributor to the economy .
• The industrial sector is small,
contributing 16% of GDP in 2012. In
2013, the industrial growth rate was 6%.
• Rwanda’s manufacturing sector is
dominated by the production of import
substitutes for internal consumption.
The larger enterprises produce beer, soft
drinks, cigarettes, hoes, wheelbarrows,
soap, mattresses, plastic pipe, roofing
materials, and bottled water.
• Other products manufactured include
agricultural products, small-scale beverages, soap, furniture, shoes,
cement, plastic goods, textiles and
cigarettes.
• There are abundant natural gas reserves
in Lake Kivu, which Rwanda shares with
the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
End of unit revision task
1. With specific examples, account for the
development and growth of medium scale
industries in Rwanda.
2. To what extent has the presence of a
steady supply of labour contributed to
the location of the Bralirwa industry in
Rwanda?
3. With reference to Kigali;
(a) Examine the factors that have
influenced the location of industries.
(b) State and explain the factors that
have led to the development and
growth of industries in the area.
4. Account for the distribution of industries
in Rwanda.
5. (a) Distinguish between industry and
industrialisation.
(b) Examine the implications of
industrialisation to the socioeconomic development of Rwanda.
6. Pollution is the only environmental
concern associated with industries in
Rwanda. Discuss.
7. Analyse the problems affecting
industrialisation in Rwanda.
8. Analyse the problems resulting from
industrialisation in Rwanda.
Availability of water
Government policies
Source of markets for other materials
The education system of Rwanda has been theoretical only equipping learners with knowledge without the skills required in the job market. This has resulted in a shortage of technical industrial skills.
The government should design policies that encourage the establishment of local industries and protect them from external competition.
Industrialisation in Rwanda has caused rural urban migration. Many people leave the rural areas to go to urban centres to work in industries that are found in the urban areas.
