Topic area
Human and Economic
Geography
Sub-topic area
Economic activities
Key unit competence
By the end of this unit, you should be able
to investigate the impact of mining on
sustainable development in Rwanda.
Unit objectives
By the end of this unit, you should be able
to:
• Identify major minerals in Rwanda.
• State methods used in mining in Rwanda.
• State factors affecting the exploitation of
minerals in Rwanda.
• Identify the importance of mining to the
economy of Rwanda.
• State the problems affecting mining.
Types and distribution of
major minerals in Rwanda
Activity 14.1
Work in pairs.
Study the photograph provided and use it
to answer the questions that follow.

1. Identify the activity that is taking place in
the photograph shown above.
2. Name other areas in Rwanda where the
activity identified takes place.
3. Name two examples of products that are
obtained from the activity shown.
4. Assess the impact of the activity on the
environment.
5. Write down your answers and present
them in a class discussion.
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals from the Earth. The minerals could be
in liquid, solid or gaseous state. Minerals occur in layers of rock, alluvial deposits and
weathered materials.
Rwanda is not naturally endowed with a variety of minerals. The few that exist occur in
small deposits and are not fully exploited.
For example, methane gas that is found under the bed of Lake Kivu has not been fully
exploited.
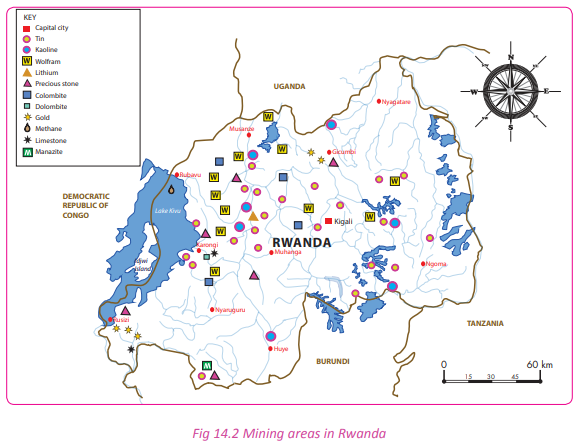 Activity 14.2
Activity 14.2 Work in pairs.
Use the Internet and maps of Rwanda.
1. Identify the major mining areas in Rwanda.
2. State the minerals that are mined in each of the areas that you have located.
3. Draw a sketch map of Rwanda and on it, indicate the various mining areas and the types
of minerals found in the areas.
4. Display your map on the class notice board.
5. Compile your findings and present your work in a class presentation.

 Activity 14.3
Activity 14.3
Do this in pairs.
1. Account for the uneven distribution of
minerals in Rwanda.
2. Show how the government compensates
for the unequal distribution of mineral
resources in the country.
3. Write a report and discuss it in a class
presentation.
Methods of mining in Rwanda
Activity 14.4
Use the Internet and a mineral map of
Rwanda.
1. Identify and discuss the mining methods
used in Rwanda.
2. Name the mining method used to
extract each of the minerals found in
Rwanda.
3. Write down your findings and present
them in a class presentation.
There are different methods of mining in
Rwanda. They include the following:
(a) Open-pit mining/open cast method
This is a mining method that is used when
a mineral ore occurs near the surface of
the Earth. The layers covering the mineral
bearing rocks are removed and the rock is
exposed. The mineral ore is then extracted
from the pit created, hence the name open
pit mining/open cast method.
This method is used in the mining of
wolfram, coltan, limestone rocks and
cassiterite.
 (b) Shaft or underground method
(b) Shaft or underground method
This method is used where minerals are found deep in the rock
strata.

It involves the construction of vertical
shafts
or horizontal tunnels called
adits to reach
layers containing minerals. This method
is used in the extraction of minerals such
as cassiterite and wolfram in the highland
areas that include Bugarama, Rutongo and
Musha.
(c) Alluvial mining method
This is the most common method used in
mining the alluvial deposits of Rwanda. It
involves mixing of alluvial deposits with
water. The mixture is then filtered until
all the unwanted material such as silt or
mud and other light particles are removed
leaving the minerals behind. This method
is used in Gicumbi, Rusizi and Nyamasheke
areas where gold is mined.
 (d) Drilling method
(d) Drilling method This is a mining method that is used to
extract the liquid and gaseous minerals. It
is used in Rubavu district in Lake Kivu where
methane gas is mined. The method involves
sinking pipes into the earth’s crust until the
gas is reached.
 Activity 14.5
Activity 14.5 Study the photographs provided below and
answer the questions that follow.

 Task 14.1
Task 14.1
1. Define mining.
2. State the major minerals mined in
Rwanda.
3. Identify the mining methods used in
Rwanda.
Factors affecting the
exploitation of minerals in
Rwanda
Activity 14.6
Use the Internet, Geography textbooks,
journals and other geographical documents.
1. Find out the factors that affect the
exploitation of minerals in Rwanda.
2. Write down the findings and present
them in a class discussion.
Some ofthe factors that affect the
exploitation of minerals in Rwanda include
the following:
(a) The size of mineral depositsRwanda has few mineral resources. The
few that are there occur in small deposits.
This has encouraged
artisanal mining. This
is because it is difficult for companies to
invest in the exploitation of small deposits
of minerals because it makes little or no
economic sense. However, in areas where
large mineral ores are found in large
deposits, commercial mining is practiced.
(b) Mineral quality or grade The quality or grade of the mineral ore to
be mined greatly influences mining. It is
economical to mine a mineral that is of a
high quality because the economic returns
expected will be high. On other hand, it is
difficult to exploit low grade minerals since
their demand and economic returns are
very low.
(c) Type of minerals
The type of mineral mined affects mining. If
the minerals mined are of a very high quality
such as gold or diamond, mineral investing
companies will invest in its exploitation. On
the other hand, minerals whose value is
not very high do not attract investors and
are thus not exploited or are exploited in a
small scale.
(d) Availability of capital
Mining requires expensive equipment that
are used to exploit the minerals. However,
being a developing country, Rwanda does not have enough capital to adequately fund
the mining industry. To meet this demand,
both foreign and private companies have
invested their money in the exploitation of
the minerals found in Rwanda.
(e) Availability of means of transport
and communication
There are mineral deposits in the highlands
of Rwanda that have remained unexploited
due to the absence of transport and
communication networks in the region.
It is easier to mine minerals in areas
that have well developed transport and
communication systems than in areas
without any or with poor infrastructure.
(f) Availability of adequate labour force
The presence of a steady supply of labour
favours the exploitation of minerals. This has
not always been easy in Rwanda especially
when skilled workers are required in the
mines. Rwanda depends on consultants and
expatriates to oversee the mining.
(g) The presence of reliable power
supply
Mining depends on a reliable power supply
since heavy drilling machines are used
especially in the creation of shafts and adits.
Power is also needed in the aeration system
for the underground mines in underground
mining. The power supply in Rwanda is not
robust and therfore not very dependable.
 Favourable government policies
Favourable government policies
The government has developed policies
that favour the exploitation of minerals.
Companies interested in mining are able
to register within a short time. They also
have a favourable working environment that encourages investment in the mining sector.
(i)The availability of technology
Technology influences mining in various
ways. The mining sector involves heavy use of
machinery. This is only possible with availability
of updated technology. The exploitation of
minerals that occur deep into the crust will
not be possible without technology. Rwanda
highly depends on foreign investors in the
mining sector. The technological advances in
the developed countries are high thus making
mining possible.
(j) Political climate The political stability in Rwanda has played
a great role in influencing the exploitation of
minerals. Foreign and local companies that
have invested in Rwanda’s mining sector
have done so because of the prevailing
peace and security. This allows them time
and space to engage in mining activities.
(k) Availability of markets The mining sector is a commercial sector.
Therefore mining activities will go on if
there is a demand and ready market for the
minerals mined. In Rwanda’s mining sector,
there is a high demand for coltan therefore,
its exploitation is viable.
Importance of mining to the
economy of Rwanda
Activity 14.7 Use the Internet, Geography textbooks,
journals and other geographical documents.
1. Find out the importance of mining to the
economic development of the country
2. Write down your findings and discuss
them in a class presentation.
The mining sector in Rwanda plays a
significant role in the economic development
of the country. It is important in the
following ways:
(a) The mining sector earns the country
foreign exchange through the export
of minerals.
(b) The sector provides employment to
the people who work in the mines thus
providing them with a source of income
that improves their standards of living.
(c) The sector provides revenue to the
government through taxation.
(d) Mining has led to the development of
other industries which use the minerals
as a raw material.
(e) Mining has led to the development
of infrastructure such as roads
in areas where mining takes place.
These infrastructure not only benefits
the mines but also the surrounding
communities.
(f) Mining has led to the development
of social facilities such as schools and
hospitals that are located near the
mining centres.
(g) Mining has improved the country’s
balance of trade.

Mining provides energy to the country
through the provision of natural gas
and peat coal.
(i) Mining has led to economic
diversification. It has reduced the
country’s overdependence on
agriculture.
(j) Mining has promoted Rwanda’s
relationship with other countries
through trade, the presence of
foreign investors and expatriates.
(k) Mining has led to the development
of urban centres. Examples of urban
centres that have developed as a result
of mining activities include Burera town
that grew due to coltan mining, Rulindo
town which grew due to wolfram
mining and Gicumbi which grew due
to gold mining.
Products from minerals in
Rwanda
Activity 14. 8
Work in pairs.
1. Observe and write down the products
of minerals that are found within your
school and home.
2. Display some of them to the class
specifying which minerals they are
made of.
Some of the mineral products that are used
in Rwanda include the following.
• Cement
• Jewellery
• Chemicals
• Metals
• Electrical
products
• Glass
• Ceramics
• Arts
• Batteries
• Fertiliser
• Medicine
• Light bulbs
filaments
• X-ray tubes
• Capacitors used
in electronic
devices
• Laptop
computers
• Cellular phones
• Jet engines
• Rockets
• Cutting tools
• Camera lenses
• Ink jet printers
• Hearing aids
• Pacemakers
Problems affecting mining in
Rwanda
Activity 14.9 Use the Internet, case study documents of
various mining areas and other geographical
documents.
1. Find out the problems that affect mining
in Rwanda.
2. Suggest possible solutions to the
problems that you have listed in (1)
above.
3. Draw conclusions, compile your findings
and write an essay on the problems
that affect mining in Rwanda and their
solutions.
4. Present your findings in a class discussion.
Some of the problems that affect mining
include the following.
(a) Lack of capital which hinders mineral
exploration and exploitation.
(b) Poor infrastructure that makes
some areas especially those in the
mountainous areas inaccessible.
(c) Some of the mineral deposits in Rwanda
exist in small quantities. This makes it
uneconomical to exploit them.
(d) Lack of skilled labour in the mining
sector. The country relies on foreign
experts who are expensive to hire.
(e) Insufficient power supply to the mining
areas especially those in the rural areas.
This hinders mineral exploitation in the
remote areas.
(f) Most mining activities are controlled
by foreign companies. As a result, a big
part of the revenue from the sector is
repatriated.
(g) Loss of lives in the mining areas. Some
mining sites collapse with the workers inside the mines. This leads to loss
of lives and discourages people from
working in the mines.

Stiff competition from other countries
for markets on the international scene.
(i) The sector faces competition from
other sectors of the economy where the
government puts more emphasis on.
Possible solutions to the
problems affecting mining in
Rwanda
The following are some of the solutions to
the challenges that affect mining.
(a) Introduction of improved and modern
methods of mining. This will increase
the mining output and the quality of
products.
(b) Hiring a skilled labour force and training
the local workers in order to empower
them.
(c) The government should give local
companies financial assistance and
offer foreign companies
tax holidays.
This will boost their financial abilities
and make the country an investment
destination of choice for foreign
investors.
(d) In areas where large mineral deposits
have been identified, the government
should construct roads, railways and
airports.
(e) Safety standards and the working
conditions of the employees should
be improved so as to guard against
accidents that lead to loss of lives.
(f) More industries that use minerals as
raw materials should be established in
order to increase the local demand for
mining output.
(g) The mineral ores should be processed
and value added to them so that they
can have a competitive advantage in
the market.

The government should encourage
mineral exploration so that more
mineral deposits can be discovered and
exploited.
Activity 14.10 Work in pairs.
1. Assess the impact of mining methods
used in Rwanda to the environment.
2. Suggest environmentally friendly
methods of mining that should be used
by mining companies in Rwanda.
3. Make a written report on mining and
the environment and share it in a class
presentation.
Activity 14.11
1. Assess the mining of Rwanda’s resources.
2. Do you think it is important for the
government to regulate and control
the mining of Rwanda’s resources?
3. Write a report of your findings that
you will present to your teacher for
assessment.
4. Share your report with your classmates
in a class presentation.
Did you know?
• Rwanda produces about 9% of the
world’s tantalum, used in electronics
manufacturing, and about 4% of global
tungsten.
• In October 2012, Rwanda’s Ministry of
Natural Resources suspended mining activities in the country’s western
province on the basis that they were
endangering the River Sebeya.
• Mining activities in Rwanda started in
the early 1930’s, developed by Belgian
foreign companies.
• Mining in Rwanda has continued to
gain significance as a source of export
revenues.
• Rwanda is the only country within
the East Africa region implementing
the traceability and tagging schemes
to guarantee transparent and ethical
trading of minerals.
End of unit revision task
1. Examine the challenges faced by the
mining sector in Rwanda.
2. To what extent is mining a significant
sector in the development of the economy
of Rwanda?
3. (a) Describe the mining methods used in
Rwanda.
(b) Assess the impact of mining on the
environment.
(c) Suggest ways of protecting the
environment from the damage
caused by mineral exploration and
exploitation.
4. (a) Name five products obtained from
minerals.
(b) Suggest possible solutions to the
problems facing the mining sector in
Rwanda.
5. Give the main types of minerals mined in
Rwanda and the places where they are
found.
Favourable government policies
Mining provides energy to the country through the provision of natural gas and peat coal.
Stiff competition from other countries for markets on the international scene.
The government should encourage mineral exploration so that more mineral deposits can be discovered and exploited.
