UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO RELIGIOUS SCRIPTURES
Key Unit Competence: Describe the structure of the sacred books and
highlight their importance in spiritual growth
and worship.
Introductory Activity
Latifah, John and Christian are students in a one of teacher training
colleges in Rwanda. They often attend the school library to read different
books in order to supplement their information and knowledge. Latifah
and Christian are used to read scientific, literary and the Holy Scriptures.
John also does the same but he never read the Holy scriptures. He always
blames his classmates about wasting of time in reading the Holy sciptures.
By the end of term Latifah and Christian receive their school reports with
good marks but John gets failure in behaviour.
1. Do you think Latifah and Christian performed well in discipline and
John failed?
2. How do Holy Scriptures influence the behaviour of Latifafh and
Christian?
3. Why are some writings called Holy Scriptures?
4. The Holy Scriptures are said to be Word of God,do you think God
took materials and wrote it Himself? Explain.
5. What do you think is based on to structure or to group the biblical
books?
6. What is the importance of Holy Scriptures at home, at school and
in life in general
1.1. Holy Scriptures concepts
1.1. Learning activities:
1. Basing on your personal experience and using various resources,
research on the meaning of Holy Scriptures and give some
examples.
2. What do you think was the process of their writing?
3. Discuss their importance to individual, school community and
society in general. introduce their friends when together they meet
new people.
Religious texts or Holy Scriptures are those sacred and central to the teachings
of almost every given religion. They are significant as these almost every
given religion. They are significant as these texts convey spiritual truth,
establish a connection with the divine, foster communal identity, and provide
the promotion of mystical experiences and spiritual practices.
1.1.1. Bible
Etymologically the word Bible comes from plural Greek “ta biblia” that means
books or a collection of books, a library. Its singular “to biblion” gives name
Bible. The Bible is then a collection of books of Word of God consists of the
Old and New Testament. Bible is therefore a compilation of books considered
as one book.
1.1.2. Testament
The term Testament came from Latin “testamentum” meaning Alliance or
covenant: it is defined as treaty for mutual advantages: the following are
examples of the covenant found in the Bible:
• Abraham formed an alliance with Canaanite princes (Genesis 14:13)
• Abraham formed alliance with Abimelech (Genesis 21:22-23)
• The patriarchs concluded a covenant of alliance by blood of some
sacrificial animal except birds (Genesis 15:10)
• The Sinaitic Covenant or Mosaic Covenant refers to the Biblical
Testament between God and His chosen people, Israelites (Exodus
19-20): the sign of that Testament became the Decalogue or Ten
Commandments of God.
• Jesus Christ concluded the New and eternal Alliance and with the pillars
of the Church (Matthew 26:26; Luke 22:14-19): the sign of that Alliance
has been the Holy Meal, Holy Sacrifice known also as the Eucharist.Main parts of the Bible
The Old Testament
The Old Testament or Old Covenant is formed of all books about the
relationship between God and His chosen people, Israel. It is about preparation
of Human Salvation: creation of all, the fall of man, the call of Abraham, and
liberation of Abraham’s descendants from Egyptian slavery, conclusion of
the Alliance at Sinai Mount, giving the Promised Land etc. Christians give
the name Old Testament to differentiate it from the new one established by
Jesus Christ. The Old Testament into the Catholic Bible consists of 46 bookswhile the Old Testament for Protestant Bible consists of 39 books.
The New Testament
The New Testament is about 27 books that talks about the fulfilment of human
salvation through Death and Resurrection of Jesus Christ. The books of theNew Testament are mainly written in Greek language.

Divine revelation means that God made Himself known to man. The Bible
as Word of God, His creation and the incarnation of Verb constitute the
three main means by which God revealed Himself. By incarnation God
made Himself a man; God took flesh like us except sin. In Jesus Christ the
revelation reached its accomplishment and by His Death the Salvation was
fulfilled (John 19:30). Jesus Christ is the True word of God. By Him God is
revealed and accessible as it is declared into the Bible “I am the way, thetruth and the Life (John 14:6)
1.1.4. Inspiration of the Bible
The Bible is an inspired book because it is formed of the books that were
written under inspiration of the Holy Spirit so, it has God its Author. As the
Holy Scriptures testify, the authors were free to use their own faculties but
God acted in them “All Scripture is God breathed and is useful for teaching,
reproving, correcting and training in righteousness, so that the man of God
may be thoroughly equipped for every good work (2 Timothy 3:16-17). If
the Bible has God as its author, it cannot contain the errors. This is calledinerrancy of the Bible.
1.1.5. Authorship of the Bible
The authorship of the bible refers to its origin and its writing then to whom
the Bible is belonging. The Bible is a proper word of God written by sacred
authors called by God. They wrote history between God and people and
divine mean of education: story of creation and fall of man (Genesis 1-3);
laws and norms of life (Exodus 20-23); divine callings; men’s reactions like
praises, thanksgivings, interrogations; preparation and accomplishment ofhuman Salvation.
Into the Bible God speaks to man. He renewed and communicated His plan
of salvation when He firstly called Abraham. He concluded promises with
him (Genesis 12:1-5; 15:1-21). To save all humanity God then chose Israel
and both sides expressed their relationship in term of Alliance (Exodus 24:1-8).
1.1.6. Canonicity of the Bible
The concept canonicity comes from Hebrew word “Ganeh” and a Greek word
Kanon meaning, rod or reed that was used to measure, rule or standards
of measurement. Canon refers to the list of the books included in the Bible
officially accepted as inspired by God. Hence, canonicity is a legal Church
confirmation of a list of books as inspired books. The Church recognizes
that the books that were inspired are satisfactory and approved to be the
guide of Religious teaching. Origen (185-253) an early Christian scholar of
Alexandria and a theologian used the term Canon to denote the rule of faith,standards which are used to measure or to evaluate.
The Old Testament knew two main canons:
The first Canon: it is called Hebrew Canon, Protocanonical (prime) or
Jamnia canon (area in South Tel-Aviv. It was confirmed by Doctor of Laws
in 70 AC after destruction of Jerusalem. These books were translated in
Greek in Alexandria with additional books in Greek as original texts. These
translated books make the canon of Alexandria or Septuagint because 70
scientific translators separately finished translating them at the same time.
This translation was made for Jews in Diaspora who used Greek in that time.
This Old Testament of Hebrew canon considered 39 books while the GreekCanon contains 46 books as inspired.
• Jesus bore witness to the Old Testament: Jesus bore witness to these
three divisions of the Old Testament. “These are my words which I
spoke to you while I was still with you, that all things which are written
about Me in the Law of Moses and the Prophets and the Psalms must
be fulfilled” (Luke 24:44). Jesus mentions Psalms because it was thefirst and largest book of the writings.
• Jesus testified to the extent of the Old Testament canon. When arguing
with the religious leaders Jesus said, “Upon you may fall the guilt of
all the righteous blood shed on earth, from the blood of righteous Abel
to the blood of Zechariah, the son of Berechiah, whom you murdered
between the temple and the altar” (Matthew 23:35). Abel was the first
to be murdered and Zechariah was the last to be martyred in the Old
Testament order. Abel was slain by his brother Cain and Zechariah was
stoned in the house of God while prophesying. Genesis was the first inchronological order and Chronicles the last.
• Jesus testified to the sacredness of Old Testament. He said, “Do not
think that I came to abolish the Law or the Prophets; I did not come to
abolish but to fulfil. For truly I say to you, until heaven and earth pass
away, not the smallest letter or stroke shall pass from the Law until all
is accomplished” (Matthew 5:17-18). Speaking to the disciples after
His Resurrection He began “With Moses and with all the prophets, He
explained to them the things concerning Himself in all the Scriptures.
He said to them, ‘These are my words which I spoke to you while I was
still with you, that all things which are written about Me in the Law of
Moses and the Prophets and the Psalms must be fulfilled.’ Then Heopened their minds to understand the Scriptures” (Luke 24:27, 44-45).
Deuterocanonical (2nd canon) or Apocrypha books
The Deuterocanonical books of the Bible are books considered by
the Roman Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodoxy to be canonical parts of
the Christian Old Testamwent but are not present in the Hebrew Bible. The
word deuterocanonical comes from the Greek meaning ‹belonging to the
second canon›. These books are the following: Tobit, Judith, 1st Maccabees,2nd Maccabees, Sirach (Ecclesiasticus) and Baruch.
Note: These books make difference and bring about 2 versions of the Bibles:
a. Bible with 66 Books: These are mostly protestant Bibles who follow
only the Hebrew Canon. They recognize 39 books of Old Testament
and 27 books of the New Testament. They consider the 7 books as
Apocrypha books or non-inspired books hence do not include themin their list book books in the Bible.
b. Bible with 73 books: This is followed by Catholics and Orthodox.
They followed the Greek Canon. They considered the 7 books asdeuterocanonical books and consider them as inspired by God.
Both catholic and some Protestant Churches established the common Bible
known as Ecumenical Translation of the Bible (ETB) containing both Proto-canonical and Deuterocanonical.

a) Meaning and redaction
The literally meaning of the Quran is “the recitation”. It refers then to the Word
of God to be recited. It is the sacred book for Muslim believed as a revelation
from God (Allah). Muslims believe that the Quran was orally revealed to
Muhammad through the archangel Gabriel (Jibril) from 610AC up to 632
the year of his death. These words were Allah’s words of wisdom, truth,
and commandments to His creation. The Quran (which means recitation)
was revealed in the Arabic dialect used by the Quraish tribe of Mecca of
that time. This dialect became the formal Arabic of the Islamic nations due
to the distribution of Quranic scriptures throughout the Islamic empire. In
the Arabic, the Quran is poetic in style with rhymes, meter, and shifts in linelengths.
The Quran deals mainly with what and how Allah wants mankind to believe
and do in Man’s moral struggle. Its primary theme is that of completesubmission to the will of Allah. Other teachings of Quran include;
• there is only one sovereign God (3:191; 5:73; 112:1-4).
• there will be an end of the world and judgment day (:30; 35:33-37).
• those who do not submit themselves to Allah will go to hell (2:24; 3:12).
• that those whose good deeds exceed their bad will obtain paradise
(3:135; 7:8-9; 21:47).
• social and ethical behavior for Islamic society.
The Quran was not written by Muhammad by his disciples. The main
message of the Quran is the Oneness of God, God is unique: Allah. The
Quran is a book with content without mystery. The Islamic theology restricts
only what intelligent can grasp: God is one, Omnipotent, bounty etc. the
Quran talks about Jesus not as Son of God but as Prophet and about Maryas mother of Jesus.
• Short History of Qur’an Writing
In the year 610 (believed to be the 26th of Ramadan), while in a cave on Mt.
Hirah, which is now called Mount Jabal Nur, Muhammad said that the angel
Gabriel appeared to him and commanded him to recite (96:1-19). From
that point on, Muhammad claimed to have received revelations up to the
time of his death (23 years later in 632). In these encounters with the angel
Gabriel, sometimes Muhammad would see the angel, other times he would
only hear him, and at others, he only heard the sound of a bell through whichthe words of the angel came.
Since Muhammad could not read or write, his companions wrote down what
he said. These recitations were copied onto a variety of materials: papyrus,
flat stones, palm leaves, shoulder blades and ribs of animals, pieces of
leather and wooden boards. Additionally, these sayings were also being
memorized by Mohammad’s followers. In fact, to this day, great emphasis is
placed upon memorizing the entire Qur’an, and there are many thousandsof Muslims who have committed it to memory.
Apparently, there was no attempt made to collect all of the sayings given by
Muhammad during his lifetime. After all, Mohammad was continuing to give
‘recitations’ on a somewhat regular basis. But, after he died in 632, AbuBakr,
Muhammad’s father in law, became the caliph (religious leader of the
Muslims); and there was a small effort to collect the fragments of Qur’anic
sayings into a commonplace. But, it wasn’t until the fourth leader of Islam,
Caliph Uthman, that the whole Qur’an was finally assembled, approved, anddisseminated throughout the Muslim world.
The Quran also contains many biblical figures (Abraham, David, Moses, and Jesus)
as well as non-biblical figures. However, some of the accounts of biblical charactersare different from the Bible.
b) Structure/subdivisions of the Quran
• General structure
The Quran is divided into 114 Chapters called “Sῡrah” and Suwar in pluralwhich are subdivided into Verses “ᾱyah” in prular “ᾱyᾱt”.
The Quran is also divided into 30 equal sections, called juz’ or ajizain plural.
The divisions of the juz do not fall evenly along chapter lines. These divisions
allow a speed reading of the Quran over a month’s period and reading afairly equal quantity each day.
• Subdivision into Quarters
The Quran can be divided into 4 quarters based on the themes. Each quarterbegins with the words “Alhamdulillah” (All praises are for Allah):
• The first quarter: This part mainly discusses the concept of Allah beingthe Sole and Only Creator of everything
• The second quarter: The central theme of this part is that Allah is the
Only One Who is responsible for caring and nurturing everything aftercreating it.
• The third quarter: This part revolves around the discussion that Allah
has complete power to control and administer the affairs of the universe
as He pleases. It emphasises that He is the Supreme Sovereign andnone can be partner to Him.
• The fourth quarter: This part mainly discusses the fact that Allah shall
be the Master and Supreme Judge on the Day of Judgment and nointercessor can overrule His decree.
While all these themes have been discussed in great detail in the
respective parts of the Quran, they are all summarized in Surah Fatiha.
“Alhamdulillah” makes mention of the first part. It includes Allah’s name,
which tells us that He is the Creator of everything. This is so because themention of Allah’s name compels one to acknowledge this fact.
• Subdivison according to Juz’ (also known as Para or Siparah)
The Quran can be divided into 30 parts, of almost each length, each part iscalled Juz’. That means each Juz’ is 1/30ths of the Quran.
1.1.8 Torah
The word Torah literally means “instruction”, meaning some sort of guidance
in life. Though Torah is a part of the Bible, it was used by Jews as guidance
to live and offering sacrifice. But when Jews say “Torah,” they’re most likely
speaking of the Five Books of Moses, the foundation of all Jewish instruction
and guidance. We also call it the Chumash, from the Hebrew chamesh,
which means five. Often, when people talk about “a Torah,” they are referring
to a parchment scroll version of the Five Books of Moses that is kept in theark of the synagogue and taken out to be read during service.
The Torah also commands the elders to «keep the Children of Israel away
from impurity. Some authors also consider Tenah and Talmud as HolyScriptures of Jewish Religion.
The following is the summary of Holy Scriptures of some major Religions inthe world:
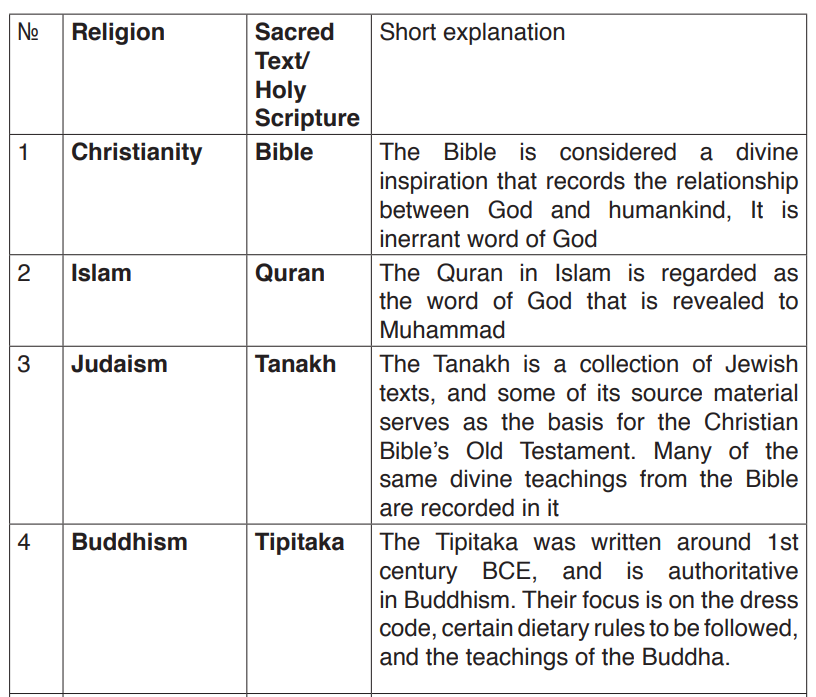


1.1. Application activity:
1. What are sacred books scriptures for Christianity and Islam.
2. Explain these terms: Testament, authorship and Canonicity.
3. Explain to your colleague what apocrypha books are.
4. Using various resources the difference and the similarity betweenQur’an and the Bible .
5. What should be your attitudes about to the Holy Scriptures? andtheir role in every day life.
1.2. Relationship between the New and Old Testament
1.2. Learning activitiy :
From this biblical text “Do not think that I have come to abolish the Law or
the Prophets; I have not come to abolish them but to fulfill them” (Matthew5:17). Discuss the links between the two Testaments of the Bible.
On the day of His Resurrection Jesus Himself reminded His disciples the
accomplishment of the Old Testament into the new one: He said to them
“These are my words that I spoke to you while I was still with you, that
everything written about me in the Law of Moses and in the prophets and
Psalms must be fulfilled”. Then He opened their mind to understand the
Scriptures. And He said to them, “Thus it is written that the Messiah would
suffer and rise from the dead on the third day” (Luke 24:44-46)
The Church becomes New Israel. The sign of the Old Alliance is the Ten
Commandments of God given at Sinai Mount Ex 20:1-17 while the sign of
the New Alliance becomes the holy Sacrifice: offering body and blood ofJesus Christ.
Jesus summarizes the commandments in love, and we are no longer
slaves of laws (Romans 6-8). Christ became the concluding mean of God’s
revelation (John1:18). In Jesus God proved his deepest love (John3:16). The
New Testament develops the process within human salvation reached its
fulfilment: conception of Saviour, birth, growth, teachings, miracles, suffering
death and resurrection. So the Old Testament became a preparation thatwas accomplished into the New Testament.
1.2. Application activity:
1. Find out, Explain the sign of Alliance between God and His people.
2. Explain the invention of the sign of the New Alliance betweenChrist and his Church.
3. Prove the link between the Old and New Testament
4. How did God proved His deepest love for humanity?
5. Is the Old Testament important christians. Justify.
1.3. Structure of the Bible
1.3. Learning activitiy:
With your previous readings, information, what you heard from the previous
lessons and the holy assembly you attendded, research on two biblical
books for each group below: Historical books; Pentateuch; Propheticbooks; Gospel; Letters; Poetic and Wisdom books.
1.3.1. Formation and structure of the Old Testament
a) Formation
Before they were written, some contents of the Old Testament were orally
transmitted: they are from Genesis to the books of Samuel where we findhistory of the Patriarchs, Moses, Judges, Kings, Elisha and Elijah.
In 11th-10th centuries, two schools of scribes wrote Pentateuch. Those
schools are Yahwistic Tradition in Juda and Elohistic tradition in Israel.
After the deportation to Babylon (-587-538) the scribes present the book ofJonah, Job, Ecclesiasticus (Sirach) to increase hope of people.
In 2nd century BC the persecution against Jews gave birth to spiritualresistance: book of Daniel and Judith
The Hebrew Bible (Only Old Testament) consists of 3 main parts:
• Torah: 5 books of Law of Moses that occupies the first place in Jewishlife
• Nevi’im that means Prophets: book of Joshua, Judges, Samuel andKings
• Ketuvim that means other writings: Daniel, Ezra, Nehemiah, Chronicles
b) Structure of the Old Testament
The structure of the Old Testament varies according to the centuries. All
editions present first the five books of law called “Pentateuch”.
In the 13th century after Christ, the Catholics structured the Bible into threecollections:
• Historical books with two sub-collections: Pentateuch (Genesis, Exodus,
Leviticus, Number and Deuteronomy). Others (Joshua, Judges, Ruth,
Samuel, Kings, Chronicles, Ezra, Nehemiah, Tobit, Judith, Esther, andMaccabees.
• Didactic books: Job, Psalms, Proverbs, Qohelet (Ecclesiastes), Songof Songs, Wisdom and Sirach (Ecclesiasticus).
• Prophetic books with two sub collections: Major Prophets (Isaiah,
Jeremiah, Ezekiel and Daniel) and Minor prophets (Hosea, Joel, Amos,
Obadiah, Jonah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah, Haggai,Zechariah, and Malachi.
Currently, the Bible consists of four collections with 73 books for CatholicBible and 66 books for Protestant Bible:
Torah or Pentateuch: Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers Deuteronomy.
Historical books: Joshua, judges, Ruth, 1st Samuel, 2nd Samuel, 1st
Kings, 2nd Kings, 1stChronicles, 2nd Chronicles, Ezra, Nehemiah, Tobit,
Judith, Esther, 1st Maccabees, 2nd Maccabees. Thefollowing books are not
found into Old Testament for protestant Bible: Tobit, Judith, 1st Maccabees,2nd Maccabees.
Poetic and wisdom books: Job, psalms, proverb, Ecclesiastes, song of
Songs, Wisdom, Sirach. The books of Wisdom and Sirach are not found intoOld Testament for Protestant Church.
Prophetic books: 3 Major Prophets (Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel)
15 books as minor Prophets (Lamentations of Jeremiah, Baruch, Daniel,
Hosea, Joel, Amos, Obadiah, Jonas, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah,
Haggai, Zechariah, Malachi. The book of Prophet Baruchi does not appearinto Old Testament for Protestant church.
Seven books are not accepted by Protestants because for them their origin
is hidden and their message is not clear: this is the origin of their name
“Apocrypha books”. These are: Tobit, Judith, 1st Maccabees, 2nd Maccabees,
Wisdom, Sirach and Baruch. But the Ecumenical Bible (common Bible forProtestants Orthodox and Roman Catholics) contains all 73 books.
1.3.2. Structure of the New Testament
The books of the New Testament are structured in four collections below:
a. Gospel: Good News formed by 4 books that account the fulfilment
of Salvation: they are Gospel according to Matthew, Mark, Luke and
John. The contents of three first gospels (Matthew, Mark and Luke)look almost the same reason why they are called Synoptic Gospel.
b. Acts of Apostles: 1 book written by Luke to testify the birth of theChurch (Pentecost) and the expansion of Good news.
c. Epistles or letters: 21 letters or epistles:
• 13 letters of Paul including:

• Oldest letters: the 1st and the 2nd to Thessalonians written in 50 AC
• Big letters: the 1st and the 2nd to Corinthians, letter to Galatians, toPhilippians and to Romans written between 56-60AC
• Letters of captivity: letter to Colossians, to Ephesians and to Philemonwritten between 61-63 AC
• Pastoral letters: the 1st and the 2nd letter to Timothy, letter to Tituswritten in70 AD
• 1 letter to Hebrews probably written by Paul’s disciple.
• 7 Universal letters including: 2 letters of Peter, 3 letters of John, 1letter of Jude and 1 letter of James.
The main message of letters has been to create unity of believers, call to leave
idols, encouragement to faith, peaceful life and respect between leaders andbelievers call to sharing, to work, to be aware of wrong teachings, etc.
d. Apocalypse: 1 book written by John Apostle. It is also called “book
of Revelation” aiming at strengthening Faith and hope of Christians
exposed to kings and emperors’ harassment.1.3. Application activity:
1. Talk about the collections of books into the Old Testament and the
New Testament.
2. Specify the Author for each book: Apocalypse, Acts of Apostles.
3. Identify 7 books found in Catholic Bible that are not found inProtestant Bible.
4. What lessons you get from the book of Job and Daniel.
1.4. Importance of Holy Scriptures in the lives of thebeliever
1.4. Learning activitiy :
Read the passage below and respond to the question that follows it:
Every book is bought by its importance. For example the books of Biology
help learners to get enough information about body functions. The books
of history recount the past. The books of Geography describe the earth.
The Bible and the Quran are the most read books in the world. If you
agree with the passage above how do you see one another important at
your school, at home or to the society in general?
We are social and religious being formed by visible body and invisible
soul. The Holy Scriptures then affect many of human fields:
Social and didactic importance of Holy Scriptures
• They highlight the guidelines for social relationship: solidarity, kindness
and sharing (Luke10:25-37), empathy (Romans 2:15, Matthew 7:12),
peaceful life (Isaiah 32:17; 57:21; Matthew 5:9), tolerance and anger
control (Ephsians4:26-27), fellowship (Mark12:31), social justice(Prophet Amos) etc.
• They are books for teachers and students
• They are used by witnesses to affirm that they tell the truth (justice)
• They are used by leaders to take oaths of offices for commitment
• They orient political leaders (Romans 23:1; Exodus 9:16)
• They comfort soul in the society (Proverbs 3:5-6; Matthew 5:4)
• They make inner-peace into people (Philippians 4:70
• They are sources of moralities and values: observe commandments of God,
discipline, obedience, hardworking, courage, forgiveness, unity, control
of language, etc. (Jeremiah 30:11; Deuteronomy8:5;1Corinthians11:32;
Proverbs 6:23; Luke11:28; 2Thessalonicians 3;8-10; Galatians 3:26,Exodus 14:13, Matthew 5:7, Romans 3:4)
Spiritual importance of Holy Scriptures
As the holy Scriptures were written under the guidance of God’s Spirit theymainly contain the spiritual and religious content:
• They are essential for spiritual growth: prayer in order to win devil
(Psalms141:5), call for repentance (Joel 2:12-27), it highlights the fruits
of the Spirit (Galatians 5:22-23), New heart and new spirit (Ezekiel36:26)
• They comfort soul of sick people (John33:16) and height hope foreternal life
• They call people to be role model (Matthew 5:13)
• They are used in religious ceremonies
1.4. Application activity:
Discuss the importance of the Holy Scriptures to individual, a family,Church and to the society in general.
1.5. End unit assessment
1. Refering to the Bible, make the following concepts clear :testament, revelation and canonicity.
2. Relate the main parts of the Bible.
3. Describe the sacred book for Muslims and its message.
4. Explain the apocrypha books.
5. Classify the Paulinic letters and highlight their general importance
6. How are the Holy Scriptures important to lives of people in general?
