UNIT2:MODERN FAMILY PLANNING
Learning activity 2.4.2
2.1 Key unit competence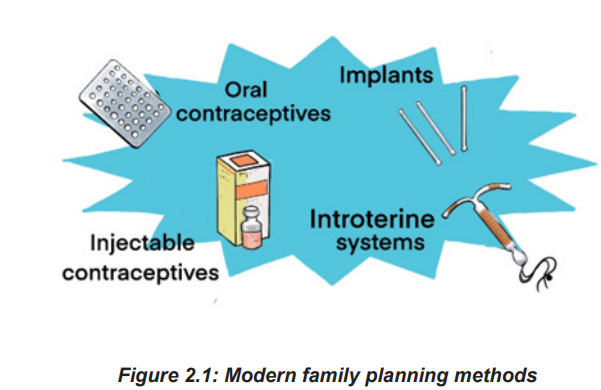
Provide modern family planning services
Introductory activity 2
i) What do you know about the above images?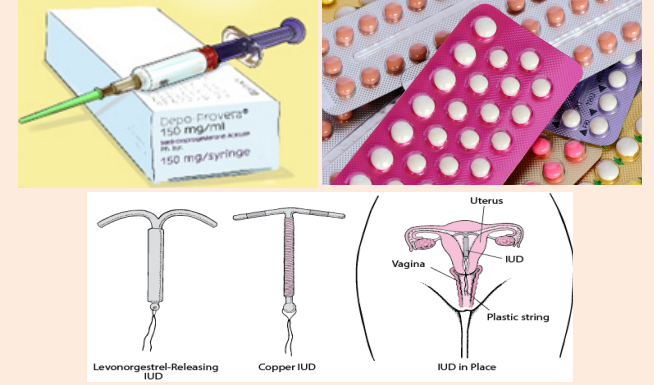
ii) What would you consider if a woman and/or a couple seeks your assistancein choosing any of the above family planning methods?
Introduction to modern family planning methods
Individuals and couples have to be informed about different options of available birth
control methods so that they make an informed choice on which one to use to plan
for pregnancy. Individuals’ and couples’ preferences can be influenced by a number
of factors such as beliefs, medical eligibility criteria, demographic factors, parity,
ease of use, duration of use, frequency of sexual intercourse, reliability, and the
side effects. In the previous unit, different methods of natural family planning were
discussed. In order to optimise the individuals’ and couples’ choice of contraception
suitable to them, Unit two proceeds with the discussion of different methods of
modern family planning namely oral contraceptives (pills), injectables, Implants andIUDs.
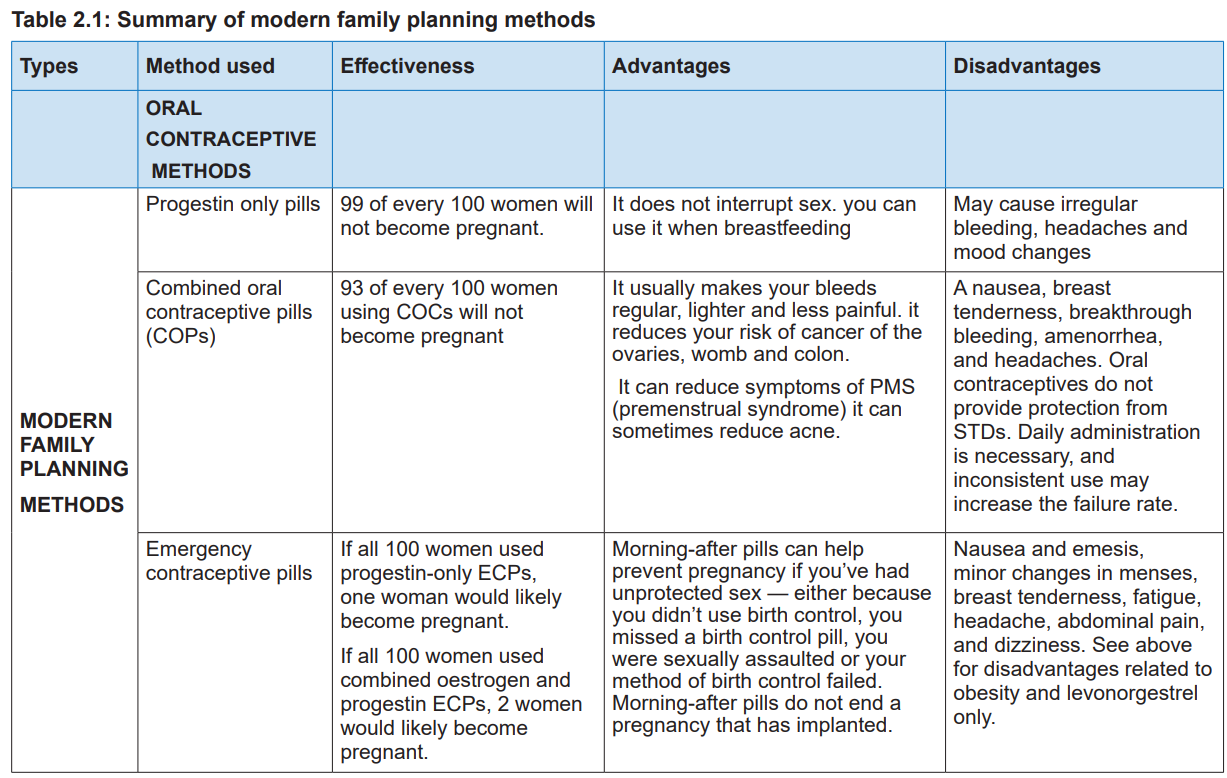
2.1. Oral contraceptive methods
2.1.1 Introduction to oral contraceptive
Learning activity 2.1.1
Students watch the video about birth control pills found on this link: https://www.
youtube.com/watch?v=Gu11uty__OY
i) Mention the oral contraception methods of family planning methods you
know.
ii) Choose one of the methods you have mentioned above and explain its
mode of action.iii) Briefly explain what progestin only pills are and who is eligible to use them?
Oral contraceptive methods are pills that a woman can use to prevent pregnancy.
These pills contain hormones that are similar to those of the woman’s reproductive
hormones which act by changing the woman’s body hormone balance and this
prevents the ovaries from releasing an egg each month (ovulation). The pill also
thickens the mucus in the neck of the womb and makes difficult for sperm to penetrate
the womb to reach the ovum. Oral contraceptive methods include progestin only
pills, combined oral contraceptive pills (oestrogen and progestin combined pills),and emergency contraceptive pills.
Self-assessment 2.1.1
i. How does oral contraceptive methods work?
ii. List oral contraceptive methods.
2.1.2 Progestin only pills
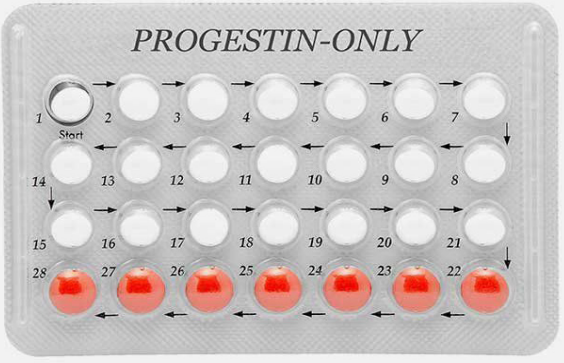
Figure 2.3: Progestin-only pills
Learning activity 2.1.2
Using internet and library (Read chapter two of the ‘Family Planning: A Global
Handbook for Providers, edition 2018’); answer the following questions.
i) Explain how the progestin-only pills work?
ii) Which clients can you advise not to take progestin-only pills as acontraceptive method?
Introduction
The progestin only pills contain a low dose of a progestin similar to the natural
hormone progesterone in a woman’s body. These pills do not contain oestrogen
hormones. The pills come in packs of 28 pills and women take one every day. One
pill is taken daily at approximately the same time (hour) without breaks between
packs. In order for these pills to ensure efficacy of progestin-only pills, the woman
has to avoid leaving an interval of 24 hours between pills.
The woman needs to be advised that once she initiates the use of these pills, she
is not protected from pregnancy prevention in the first seven days. For this reason,
the health provider needs to recommend her using an alternative method of birth
control along with progestin-only pills during the first week. If a woman misses a
tablet, she has to take the missed tablet as soon as she remembers and further
progress taking the next tablet at the usual time (taking two tables in one day). If
the woman misses two tablets in a row in the first or second week, she should take
two tablets the day she remembers and two tablets the next day, then she resumes
one tablet per day.
i) Indication
• A woman can start using the progestin only pills (POPs) any time she
knows that she is not pregnant.
• A woman can use progestin-only pills if she is breastfeeding.
• Women with or without children are eligible to use progestin-only pills.
• Progestin-only pills can also be the method of choice for even adolescent
girls who may need to use contraception to prevent unwanted pregnancies.
ii) Contraindication
• Progestin-only pills can be contraindicated in the following cases:
• Women with pre-existing breast cancer, cervical cancer, endometrial
cancer, ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, and vaginal cancer,
• Women with uncontrolled hypertension
• Women who smoke
• Women with pre-existing anaemia or who had anaemia in the past,
• Women who have varicose veins,
• Women living with HIV, whether or not on antiretroviral therapy.
iii)Mode of action
Progestin-only pills act by inhibiting follicular development and preventing ovulation.
Progesterone negative feedback signals the hypothalamus to decrease the pulse
frequency of gonadotropin releasing hormone, which in turn decrease the secretion
of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and the secretion of Luteinizing Hormone (LH).When the follicle is not developing, the oestradiol levels increase. When there is no
development of the follicle and no LH work, the ovulation is prevented. The pill also
thickens cervical mucus (this blocks sperm from meeting an egg). As the woman
keeps taking progestin-only pills regularly as prescribed, they cause menstrual
cycle change and this prevents the release of eggs from the ovaries (ovulation).
iv)Advantages of using progestin-only pills
Some advantages of using the progestin only pills include the following:
• The pill is more effective for lactating mothers and can be 99% effective if
used correctly and consistently by breastfeeding mothers.
• Do not interfere with breastfeeding and they are safe for breastfeeding
women and their babies because they do not affect milk production.
• The user can stop using progestin-only pills at any time without any help
of the provider.
• Do not interfere with sexual intercourse;
• Progestin-only pills use is controlled by the woman;
• Progestin-only pills cannot cause women infertile;
• Progestin-only pills do not cause diarrhoea in breastfeeding babies
v) Side effects
Some women taking progestin-only pills may develop some side effects such as
breast tenderness and breast enlargement, mood changes, headache and migraine,nausea and vomiting.
Self-assessment 2.1.2
i. How does progestin-only pills work?
ii. What are the advantages of using progestin only pills?iii. What do you know about indication of progestin only pills?
2.1.3 Combined oral contraceptive pills (COPs)
Learning activity 2.1.3
Using internet and books (“Introduction to Maternity and Paediatric Nursing”,
Page 111-112 about combined oral contraceptive pills), answer the following
questions:
i) What do you know about combined oral contraceptive pills?
ii) A woman who has forgotten to take 2 combined oral pills in the second
week of her last menstrual period comes to your health post for help. Whatwould you advise her to do?
Introduction to Combined oral contraceptive pills
Combined oral contraceptive pills contain both estrogen and progesterone
hormones. Those hormones are similar to the natural hormones produced by a
woman’s body. These pills come in packs of 21 or 28 pills. A user takes one pill
every day at the same hour. For greatest effectiveness a woman must take pills
daily, start each new pack of pills on time, and take any missed pill as soon as
possible.
Like the progestin-only pills, when a woman starts taking combined oral pills, she
may likely become pregnant in the first seven days if she does unprotected sexual
intercourses. To minimize the risk of pregnancy, an alternative method of birth
control is recommended along with combined oral pills for women who do sexual
intercourses frequently. When a woman misses a tablet, she has to take the missed
table as soon as she remembers and she has to take the next tablet at the usual
time (taking two tablets in one day). If woman misses two tablets in a row in the
first or second week, she has to take two tablets the day she remembers and two
tablets the next day, then after continues with her usual dose of one tablet per day.
i) Indication
The following are indications of using combined oral contraceptives pills:
• Have or have not had children
• Are married or are not married
• Are of any age, including adolescents and women over 40-year-old
• After childbirth and during breastfeeding after 6 months
ii) Contraindication
The contraindications to COPs are indicated in the following situations:
• Women with breast cancer,
• Women with a history of deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism,
active liver disease, use of rifampicin, familial hyperlipidaemia, previous
arterial thrombosis, epilepsy, diabetes, and sickle cell disease,
• Women who are pregnant,
• Smoking,
• Women with advanced age (over 35 years),
• Women with hypertensive disorders,
• Women who are currently breastfeeding before 6 months,
• Women with irregular spontaneous menstrual cycle.iii)Mode of action
The combined oral contraceptive pill works by stopping the ovaries from releasing
an egg each month (ovulation). It also thickens the mucus from the cervix which
makes it difficult for sperm to move through it and reach a matured egg. It also
makes the lining of the uterus (womb) thinner; it is less likely to accept a fertilized
egg.
iv)Advantages of combined oral pills
The following are the advantages of combined oral contraceptive:
• Women have control over their use and they can be stopped at any time
without a provider’s help.
• Do not interfere with sex and this method is easy to use. Reduce also the risk
of having anaemia.
• Combined oral pills may protect against pelvic inflammatory disease,
• Combined oral pills may protect against endometrial cancer and can also
reduce symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
• Combined oral pills can reduce the risk of cancer of the ovaries, womb and
colon for women.
• Combined oral pills can be used in the post-abortion and postpartum period
by woman who desire a fast return to fertility.
Side Effects
Combined oral pills can lead to changes in bleeding patterns (lighter bleeding
and fewer days of bleeding, irregular bleeding, infrequent bleeding or no monthly
bleeding among some women. In other cases, women taking combined oral pills
may develop headaches, dizziness, nausea, breast tenderness, weight change,
and mood changes.
In rare cases, women taking combined oral pills may develop these side
effects:
• Severe headache
• Bad pains in the chest
• Leg swelling
• Breathing difficulty
• Sudden problems with sight or speech• Numbness in an arm or leg.
Self-assessment 2.1.3
i. How does combined oral contraceptive pills works?ii. What are the advantages of using combined oral contraceptive pills?
2.1.4 Emergency contraceptive pills
Learning activity 2.1.4
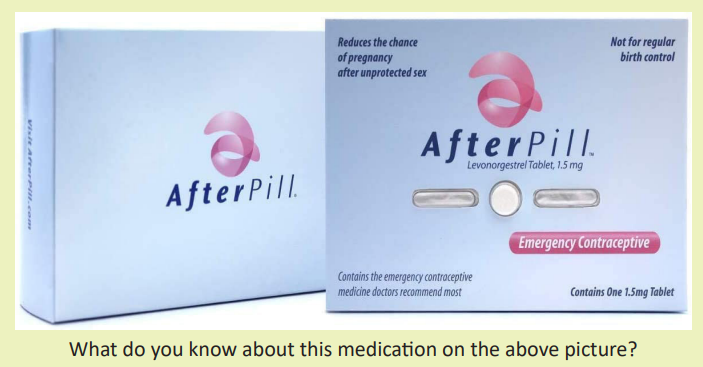
Introduction to emergency contraceptive pill
Emergency Contraceptive Pills (ECPs) also called “morning after” pills or “postcoital
contraceptives” prevent the release of an egg from the ovary or can act by delaying
its release by 5 to 7 days. If ovulation has occurred and the egg is fertilised, the
Emergency Contraceptive Pills cannot prevent implantation or disrupt an already
established pregnancy.
i) Indication
The following are indications of emergency contraceptives pills:
1. It is recommended for women who experience sexual assault
2. When current contraceptive method has failed (for example when the
condom breaks).
3. Unprotected sexual intercourse
4. Missed or late doses of hormonal contraceptivesii) Contraindication
Emergency Contraceptive Pills are not advised for use among women with the
following cases:
• A history of thrombosis,
• Current severe liver disease,
• Focal migraine at the time of presentation
• Breastfeeding women.
iii)Mode of action
The emergency contraceptive pill works by preventing or delaying ovulation. It also
inhibits an egg from being released from the ovary when taken before ovulation .it
thickens the cervical mucus making it not to allow the sperm to meet the egg.
iv)Advantages of emergency contraceptive pills
Emergency contraceptive pills (ECPs) help a woman to avoid pregnancy after she
has had sex without contraception.
Emergency contraceptive pills also prevents pregnancy when taken up to 5 days
after unprotected vaginal sex.
v) Side Effects
The use of emergency contraceptive pills may be associated with the following side
effects:
• Changes in bleeding patterns (Slight irregular bleeding for 1–2 days after
taking emergency contraceptive pills,
• Monthly bleeding that starts earlier or later than expected especially in the
first several days after taking the pills
• Nausea,
• vomiting,
• Fatigue,
• Abdominal pain,
• Headache,
• Dizziness,• Breast tenderness.
Self-assessment 2.1.4
i. How does emergency contraceptive pills work?
ii. What are the indications and contraindications of emergency contraceptivepills?
Reading activity
Read about injectable family planning methods found on this link: https://www.open.
edu/openlearncreate/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=141&printable=1#maincontent.You are going to present the information you read before the start of the next lesson.
Learning activity 2.2
i) Explain what you know about progestin-only injectables?
ii) List the progestin-only injectables you know and how they work.
iii) How long can a woman use progestin-only injectable method of family
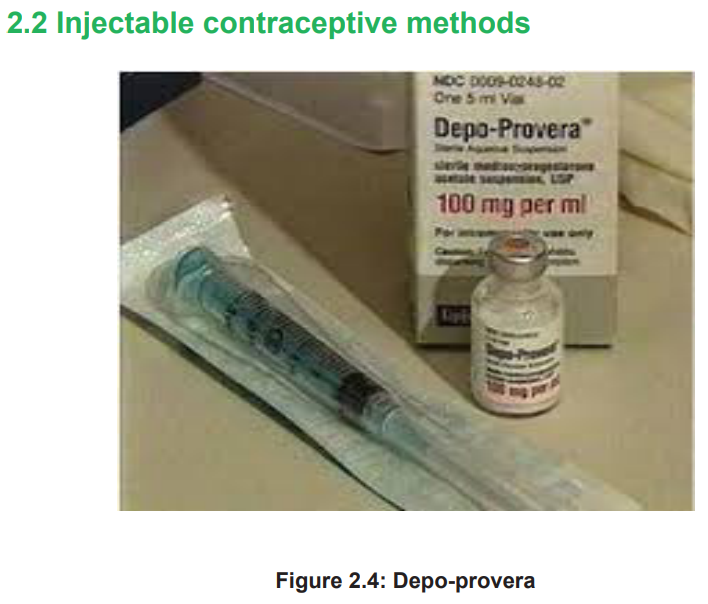
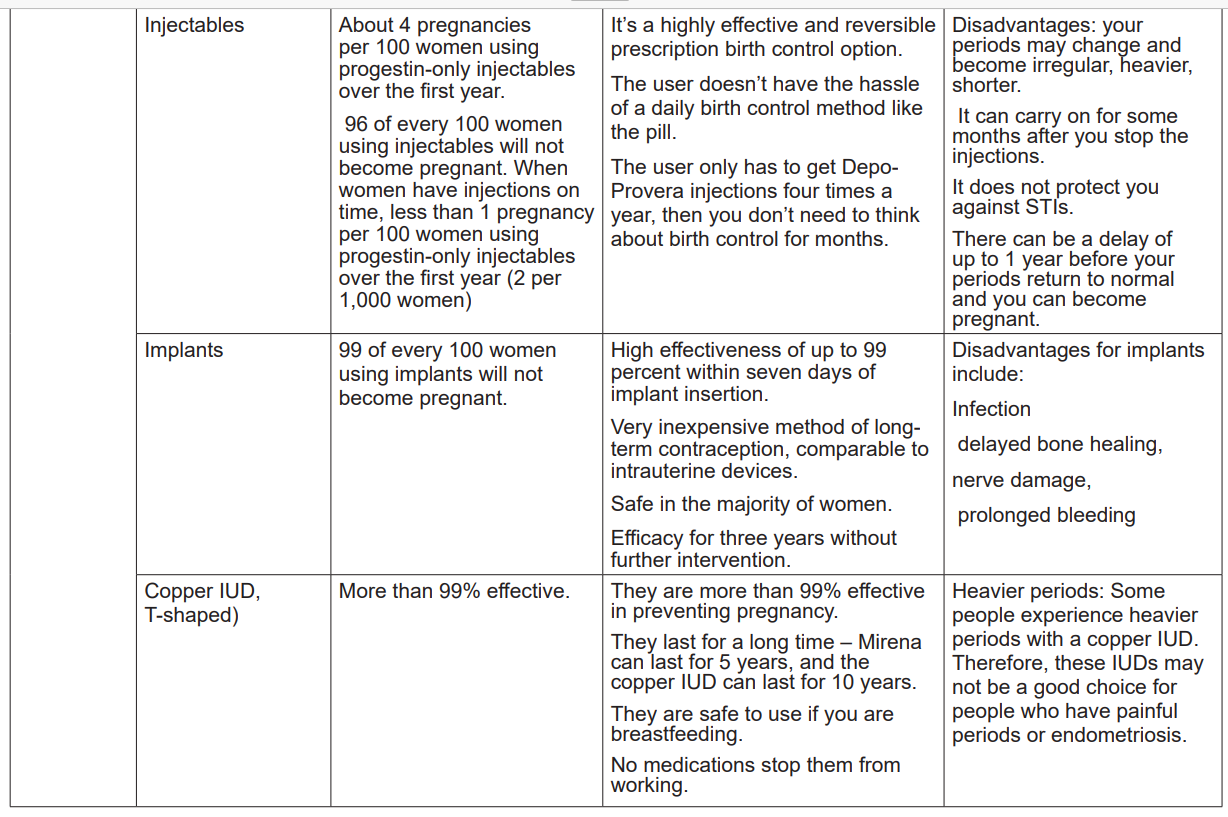
planning?Introduction to injectable contraceptive methods
Injectable contraceptive methods constitute of the intramuscular injection
administration into the muscle of the arm or buttock. This injection provides to the
body sufficient levels of hormones to provide contraception for one to three months.
Injectable contraceptive methods consist of progesterone-only preparations. Themost used progestin-only injectables are Depo-Provera and Noristerat. A woman
can have the progesterone-only injection at any time during her menstrual cycle as
long as she is not pregnant. Depo-Provera is given every three months whereas
Noristerat is given every two months.
i) Indication
Nearly all women fulfilling the following conditions can take Depo-Provera:
• No pregnancy
• No history of breast cancer in the family
• Absence of diabetes
• Absence of high blood cholesterol.
ii) Contraindication
• Depo-Provera should not be the method of choice if a woman has the
following conditions:
• Breast cancer or family history of breast cancer
• Diabetes or with history of diabetes in family
• Excessive high cholesterol levels in the blood
• Depression
• High blood pressure.
iii)Mode of action
This injection once administered to the woman, it slowly releases hormone
progesterone into the bloodstream which prevents ovulation from taking place each
month. It also thickens the cervical mucus, which makes difficult for sperm to sail
through the cervix. Depo-Provera further thins the lining of the womb to prevent a
fertilised egg from implanting to the uterus.
iv)Advantages
Depo-Provera has a number of advantages including the following:
• Does not require daily action
• Does not affect breastfeeding
• Does not interfere with sex
• Protects the woman’s privacy
• May protect against the risk of cancer of the lining of the uterus
• Protects against the uterine fibroids
• May help against symptomatic pelvic inflammatory disease
• Protects against iron-deficiency anaemia• Reduces symptoms of endometriosis.
v) Side-effects
Depo-Provera may cause side effects among women using it including the
following:
• Changes in the woman’s monthly bleeding from irregular to no monthly
bleeding;
• Weight gain
• Headaches
• Dizziness
• Abdominal bloating and discomfort• Mood changes
Self-assessment 2.2
i) If a woman does not have monthly bleeding while using progestin-only
injectables, what advice can be given to this client?ii) What are the side effects of progestin-only injectables?
2.3 Implants
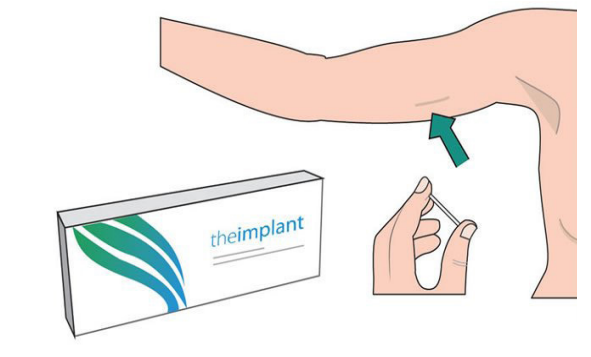
Figure 2.5: Implanon
Learning activity 2.3
Students watch a YouTube video about implants (https://www.youtube.com/
watch?v=XXRLSndJ-x4) and answer these questions:
i) Explain to the clients what an implant is and how it works?
ii) In your own understanding would you please briefly mention the advantagesof implants as modern family planning?
Introduction to implants
Implants are modern family planning that has progestin hormone. Implants
are plastic rods that are small, flexible about as size of match stick. The health
professional inserts the rod using local anaesthesia just under the skin on the
inside of the upper arm. Insertion takes place approximately one minute. Removal
requires a small incision and takes about three minutes. They are two types of
Implants in modern family planning which are currently known but one is shortterm acting
(Implanon) and another is long-term acting (Jadelle). They are both
hormonal methods of modern family planning. The implant should be removed
after 3 or 5 years depending on the type.
i) Indication
These are some of the indications of implants in modern family planning:
• Women with normal menstrual bleeding cycle.
• Women with no breast cancer and with no history of breast cancer in their
family.
• Women with no history of allergic reactions to implants.
• Women with no high blood pressure.
• Women with no liver disease or tumour.
ii) Contraindication
• These are some of contraindications of implants in modern family planning:
• Women with excessive weight.
• Women with heavy menstrual bleeding.
• Women with breast cancer or history of breast cancer in the family.
• Women with liver diseases e.g., liver tumour.
• Allergy to implants.
• Mood swings and depression.
iii)Mode of action
The implants work by releasing slowly amount of progestin hormone which
suppresses ovulation and it thickens the cervical mucus which stops sperms
from penetrating through to reach the mature egg to be fertilised. It also prevents
pregnancy to take place by thinning the endometrium which makes the implantation
not to take place.
iv)Advantages
Provide long-term pregnancy protection. Very effective for up to 5 years, depending
on the type of implant. Immediately reversible.v) Side effects
The side effects of implants include the following:
• It increases weight gain
• Irregular bleeding pattern
• They can cause vaginitis, breast pain, acne, headaches and pharyngitis.
• The implant does not provide protection against sexually transmittedinfections.
Self-assessment 2.3
i) Give explanations on how implants work to prevent pregnancy?
ii) Explain the indications and contra indications about implants?
iii) If a client comes to you seeking advice on the implants, outline the keypoints you will consider as beneficial to her.
Reading activity for the next lesson
Read the book titled ‘Introduction to Maternity and Paediatric Nursing’, page 82-83about IUDs
2.4 Intra uterine devices (IUDs)
2.4.1 Non-hormonal intra uterine device (Copper IUD, T-shaped)
Learning activity 2.4.1
i) What do you know about intra uterine devices?
ii) What important message have you noticed that can help the populationregarding the usage of IUDs?
Introduction
Intra-uterine device, also known as intrauterine contraceptive device or coil,
is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into the uterus to
prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one form of long-acting reversible birth control. Theseintrauterine devices are in two types, hormonal and non-hormonal.
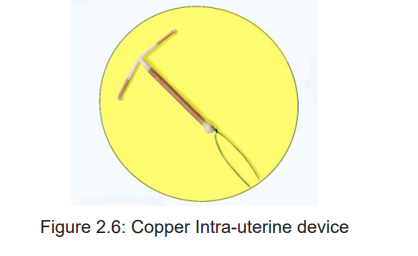
Introduction to copper Intrauterine Device
The Copper IUD is the most used as non-hormonal Intrauterine Device for women
who need long term pregnancy protection (normally between 5 to 12 years). The
copper IUD is a small, flexible plastic frame with copper sleeves or wire around it.
This device is inserted into the woman’s uterus through her vagina and cervix. Its
strings hand through the cervix into the vagina.
i) Indication
Copper IUDs can be used by women fulfilling the following conditions:
• Have or have not had children,
• Are married or are not married,
• Are of any age, including adolescents and women over 40 years old,
• Have just had an abortion or miscarriage,
• Are breastfeeding
ii) Contraindication
• Copper IUD can be contraindicated in the following conditions:
• History of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID),
• When pregnancy is suspected,
• History of ectopic pregnancy,
• Having uterine abnormalities or benign tumour in the uterus,
• Gynaecologic bleeding disorders,
• Having suspected cancer of the genital tract
• Known current cervical, endometrial, or ovarian cancer; gestational
trophoblastic disease; pelvic tuberculosis
• Women who are diagnosed with sexually transmitted infections, they
should not have an IUD inserted.
iii)Mode of action
Copper IUDs do not contain hormones. They work by using the properties of copper
to affect sperm motility and egg survival. The copper IUD causes a chemical change
that damages sperm and egg before they can meet to fertilise.
Other actions of Copper IUD include inhibiting the sperm ability to swim through
the uterine cavity and further inhibit the transport of the ovum. When the uterus is
exposed to a foreign body, a sterile inflammatory reaction occurs, which is toxic to
sperm and ovum and this impairs implantation.
iv)Advantages
Copper IUD has several advantages including:
• It is a long-term method used for 6 to 12 years.
• It is safe to use this method if the woman is breastfeeding.
• Prevents pregnancy very effectively.
• Has no further costs after the IUD is inserted.
v) Side effects
During the first days after insertion of copper IUD some women may have periodic
cramping that usually settles after a few days. Some users can report other side
effects like breast tenderness, headache, mood changes, and the period can be
changed. Spotting or frequent bleeding may manifest a side effect in the first three
to six months. For women who already have low iron blood stores before insertion,
the copper IUD can contribute to anaemia. In rare cases, the copper IUD can lead
to Pelvic inflammatory diseases especially if the woman has sexually transmittedinfections at the time of insertion.
Self-assessment 2.4.1
i) What are the advantages to the population using copper intra uterine
devices?
ii) Would you please mention the indications and contraindication of usingcopper intra uterine device?
2.4.2Hormonal Intrauterine device
Learning activity 2.4.2
Read the book titled ‘Introduction to Maternity and Paediatric Nursing’,
page 82-83 about IUDs.
i) What do you understand by hormonal intra uterine device?
i) Briefly explain the advantages of hormonal intrauterine devices (Mirena)?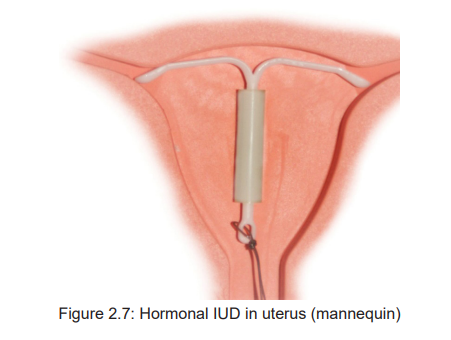
Introduction to hormonal intra uterine device (Mirena)
Intra uterine device (Mirena) is a hormonal intrauterine device (IUD) that can
provide long-term birth control (contraception). The device is a T-shaped plastic
frame that’s inserted into the uterus.
i) Indication
Mirena Can be inserted any time if the woman is certain that she is not pregnant.
However, she will need to a backup method for the first seven days after insertion.
Is indicated to women with heavy menstrual bleeding.
ii) Contraindication
Mirena can be contraindicated for a woman with the following medical conditions:
• Breast cancer,
• Liver disease,
• Uterine or cervical cancer,
• Uterine abnormalities (fibroids),
• Pelvic infection or current pelvic inflammatory disease.
• Blood clots.
iii)Mode of action
This type of IUD contains hormones which slowly releases a progesterone hormone
resembling that produced by the ovaries. This IUD works primarily by suppressing
the growth of the lining of the uterus to disrupt ovulation. It stays in the woman’s
uterus up for five years of use. It thickens mucus in the cervix to stop sperm from
reaching or fertilizing an egg.
iv)Advantages
Mirena helps protect against the risk of pregnancy, and iron deficiency anaemia. It
can also help protect against pelvic inflammatory disease and can reduce menstrual
cramps and symptoms of endometriosis. Mirena does not delay fertility return if
a woman stops using it. Mirena can be used up to five years and it is safe for
breastfeeding women.
v) Side effects
During the first days after insertion of Mirena, some users have periodic cramping
that may usually settle after a few days. Some users may report other side effects
including:
• Headaches,
• Mood changes
• Breast tenderness or pain
• Nausea• Dizziness
• Ovarian cysts
Self-assessment 2.4.2
i) According to your opinion, who is eligible to use hormonal intra uterine
device (Mirena)?
ii) Can you mention some of the side effects of hormonal IUD (Mirena) thatyou know?

End unit assessment
1. What do you understand by the term ‘modern family planning?’
2. Discuss the major difference between progestin-only and combined oral
contraceptive pills?
3. Briefly discuss some of the factors you may consider to advise a couple on
which modern family planning they can use in the next two years.
4. What do you know about indication of oral contraceptive method the
methods you have listed above?
5. Mention the advantages and side effects for someone who use emergency
contraceptive pills?
6. What is the mechanism of action of copper intra uterine device and its side
effects?
7. What can advise the woman who would like to use monthly injectable
contraceptive as her preferred family planning method?
8. Discuss how you can help families to have knowledge on implants as
modern family planning methods.
9. What is the difference between modern family planning and natural familyplanning methods?
