UNIT1:NATURAL FAMILY PLANNING
Key unit competence
Provide natural family planning servicesIntroductory activity 1
a. What can you suggest for Family B to do in order to achieve sustainable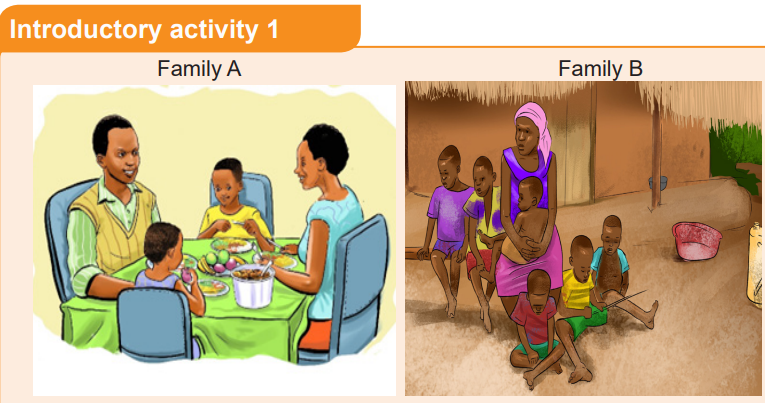
development and wellbeing?
b. Do you know the methods that can be used for family planning?
c. According to you, what are the methods that can be used easily withoutvisiting the health facilities?
1.1 Introduction to family planning
a) What do you understand by family planning and contraception?b) Why do you think family planning is important?
Learning activity 1.1
1.1.1 Concepts of family planning
Family planning refers to individual’s or couple’s’ conscious and informed decision
to decide when to become or not to become pregnant throughout the reproductiveyears.
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
Contraception is defined to the intentional use of artificial methods and/or other
techniques to prevent pregnancy as a result of doing sexual intercourse.
Natural family planning This refers to the methods of contraception which do not
use hormones and devices. Natural family planning includes abstinence, coitus
interruptus, lactation amenorrhea, and fertility awareness methods.
Modern family planning refers to all products and/ or medical procedures that
interfere with reproduction whenever there is coital activity. Some of the products
act by preventing ovulation from occurring and others may inhibit sperms fromfertilising the matured egg.
1.1.2 Benefits of family planning
Family planning can lead to sustainable development. It enables women and
couples to avoid unwanted pregnancies, attain the desired number of births,
and control the intervals between births. Family planning can contribute to
delaying pregnancy in young girls who may at increased risk of health problems
from early childbearing, and further reduces the rates of unsafe abortions and
HIV transmission. Family planning can benefit the education of girls and lead to
women’s empowerment within the community. In addition, family planning may
prevent pregnancies among older women who can be at increased risk of pregnancyrelated complications.
Self-assessment 1.1
i. With examples, explain the following terms:
a.Family planning
b.Contraception
ii. Discuss the role of family planning for women in their reproductive age?iii. What can be the role of family planning for young adolescents?
Homework 1.1
Go to the computer lab and read about principles of family planning.
1.2 Principles of family planning
Learning activity 1.2
In your own understanding, what are the principles of family planning that can beconsidered in providing quality services to the clients?
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
Introduction
Smaller families and increased child spacing contributes to reducing rates
of infant and child mortality. Family planning further improve the social and
economic conditions of women and their families, and improve maternal health.
Whilst providing family planning services, individuals’ and couples’ rights and
preferences have to be followed. This is achieved by following the principles of
families that are discussed in the next sections.
Autonomy
Providers should enable the women and individual couples to exercise free and
informed decision-making whilst choosing among a full range of safe, effective, and
possible family planning methods.
Accessibility
Family planning providers need to ensure that women and couples have the ability
to access accurate, clear and readily understood information about a variety of
family planning methods and how they are used. Health care facilities have to
ensure that contraceptive methods, trained providers, and contraceptive methods
are accessible to women and couples.
Acceptability
By acceptability, health care facilities, trained providers, and available family
planning options must be acceptable by women and couples. They must also meet
the medical standards, and individual preferences. Services provided and available
family planning methods must be sensitive to gender, life-cycle requirements,
dignity, and culture.
Equity and non-discrimination
Quality family planning services should be provided to women and couples free
from any form of discrimination such as age, gender, language, ethnicity, religion,
sexual orientation, income, and race. Women and couples must not be coerced
and/or violated when they seek family planning services from a healthcare provider.
Quality
Services and information provided to women and couples should be of good quality,
and should be based on the best available evidence. Quality encompasses a full
range of choices including quality contraceptive methods, accurate information,
and presence of technically competent providers, client-provider interactions thatrespect the clients’, confidentiality, and preferences
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
Availability
By availability, family planning enabling environment with the following is ensured:
a) Health care facilities,
b) trained providers;
c) Counselling information
d) contraceptive methods are available to ensure that individuals can exercise
full choice from a full range of contraceptive methods
e) Availability of follow-up and removal services for implants whenever necessary
and needed.
Empowerment
Women and individual couples are empowered as principal actors and agents to
decide on their family planning needs. They are also empowered to implement these
decisions through seeking information about family planning, seeking services, and
choosing a family planning method suitable for them.
Informed consent
When providing family planning services, the provider needs to always seek the
woman’s and/or the couple’s informed consent and offer her comprehensiveinformation about the services provided as shown below
Table 1.1: Informed consent applied to family planning services

Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
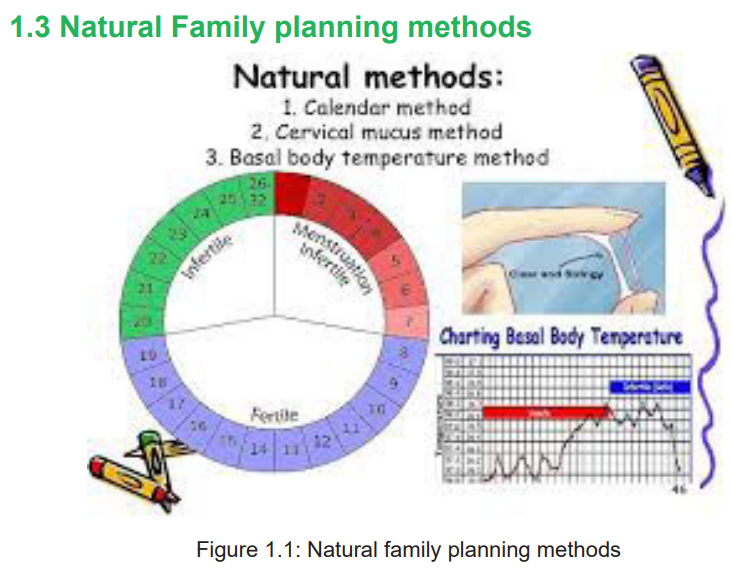
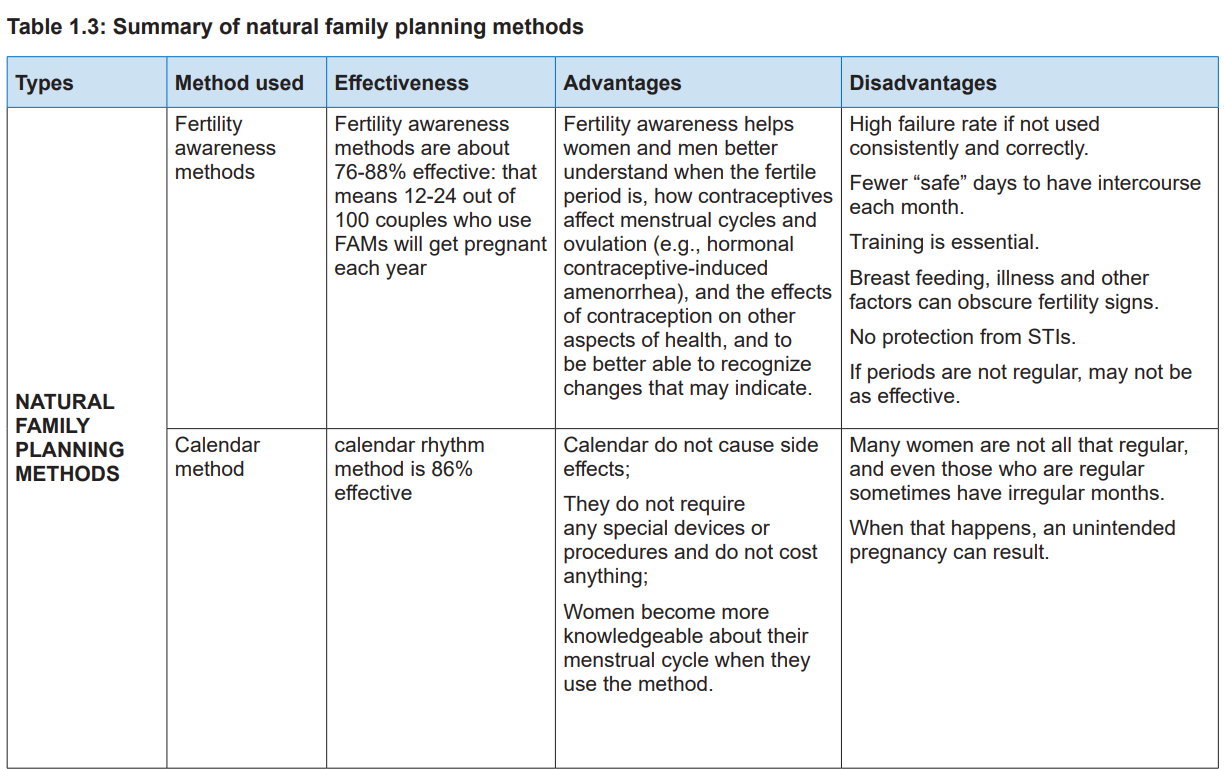
1.3.1 Fertility awareness and calendar methods
Learning activity 1.3.1
Students watch a YouTube video titled ‘How I Use Natural Family Planning To
Prevent Pregnancy’ about fertility awareness methods: https://www.youtube.
com/watch?v=lCsuefLt9eA&t=45s
1. What do you understand by fertility awareness as a family planning
method?
2. With examples, explain different methods of fertility awareness that canbe used to prevent unwanted pregnancy?
a. Fertility awareness method
Fertility awareness methods (FAM) also known as the rhythm method, encompass
all methods that are used based on the fertile and infertile phases of a woman’smenstrual cycle.
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
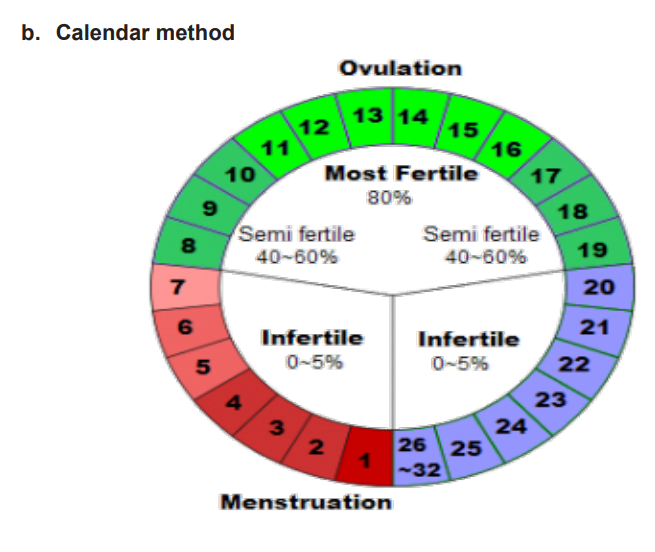
Figure 1.2: Fertile period
The fertile days are determined by correctly charting the span of the menstruation
cycle over a period of six months.
The calendar method has indications, contraindications and mode of action as
follows:
i) Indication
• To all women in reproductive age and with regular menstrual cycle.
• To all women who are capable of reading and able to chart properly.
• To all women who are capable of abstaining from sexual intercourse
during the fertile period.
• To all couples ready to use calendar method along with method with
barrier method during the fertile period to make it more effective.
ii) Contraindication
• Calendar method is not allowed to psychotic women.
• Calendar method is not allowed to non-cooperative couples.
• Calendar method cannot be used by a couple who is not ready to abstain
from sex during the woman’s fertile period.
• Calendar method is contraindicated to women who have irregularmenstrual cycle.
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
iii)Mode of action
Using a calendar, the woman monitors her menstrual cycle to track down her fertility
days starting from the first day of her menstrual period. The commencement of the
fertile period is determined by deducting or subtracting 18 days from the length of
the shortest cycles. The termination of the fertile days is determined by subtracting
11 days from the extent of the longest cycle (see figure 2 below).
Table 1.2: Formula used to calculate fertility days using the calendar method
A woman keeps track of the length of her menstrual cycles for at least 6 months.
Then she calculates her fertile window by subtracting 18 days from her shortest
cycle and 11 days from her longest cycle. For a woman whose shortest cycle is 24
days and longest cycle is 28 days, the calculation would be
as follows:
Shortest cycle
24
-18
=6
Longest cycle
28
-11
=17
Based on this calculation, the woman’s fertile window would be days from 6th
to 17th day of her menstrual cycle. During these days, the woman and her male
partner should abstain from sexual intercourse or else use a condom to avoidpregnancy in this period.
Self-assessment 1.3.1
i) How do you calculate the calendar family planning method?
ii) When is the woman most likely to become pregnant if she is using calendar
method?
iii) What precautions should be taken by the couple when they are usingcalendar method?
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
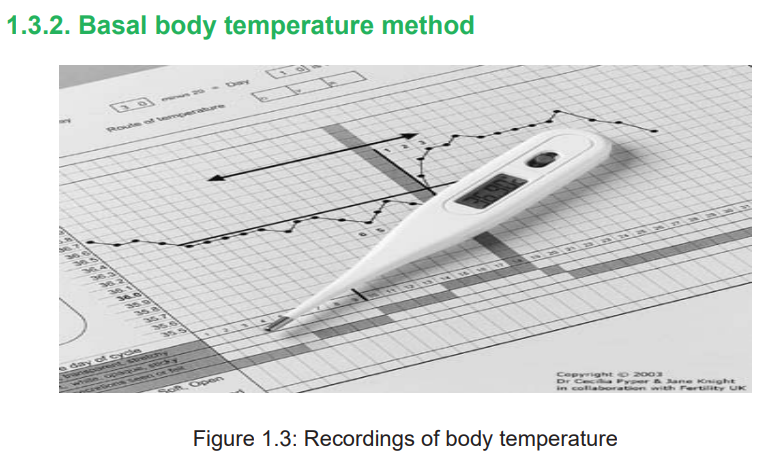
Learning activity 1.3.2
i) With the image above what do you understand by term ‘basal body
temperature’?ii) What factors do you think can affect basal body temperature?
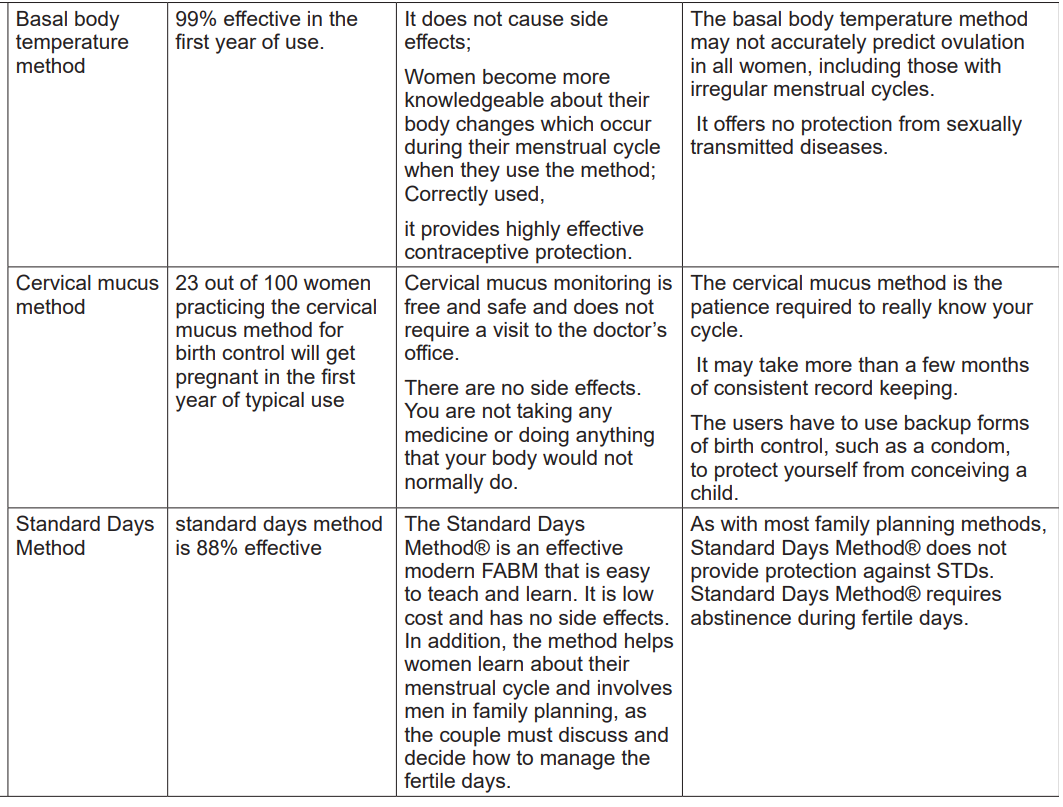
Introduction
The basal body temperature is the lowest normal temperature of a well person,
measured immediately after waking up and earlier after getting out of the bed. The
basal body temperature depends on the woman’s recognising the shift in her body
temperature around the time of ovulation. The BBT normally ranges from 36.2°C to
36.2°C during menses, and for about 5 to 7 days after. At about the time of ovulation,
a slight drop in temperature may occur, followed by a slight rise (approximately
0.4°C–0.4°C) after ovulation, in response to increasing progesterone levels. This
temperature elevation may last between 2 and 4 days before menstruation.
The basal body temperature drops to the lower levels recorded during the previous
cycle, unless pregnancy occurs.
i) Indication
• To all women who are capable of reading the thermometer measurements.
• To all women who are capable to know that their temperature has risen
from their normal temperature.• To all women with no infection.
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
ii) Contra-indication
• The women who cannot read measurements on the thermometer.
• To all women with infection. e.g. vaginitis, malaria etc.
• To all women who are not using warm blankets.
iii)Mode of action
This method works effectively if the woman has a temperature which does not
change. Hence, if a woman has a condition that may increase or lower hertemperature such as infection, fatigue, and anxiety, the method does not work.
Self-assessment 1.3.2
i) Describe how the woman’s basal body temperature changes across her
monthly cycle.
ii) When is the basal body temperature likely to rise and why?
iii) At what temperature can a couple using basal body temperature avoidunprotected sexual intercourse?
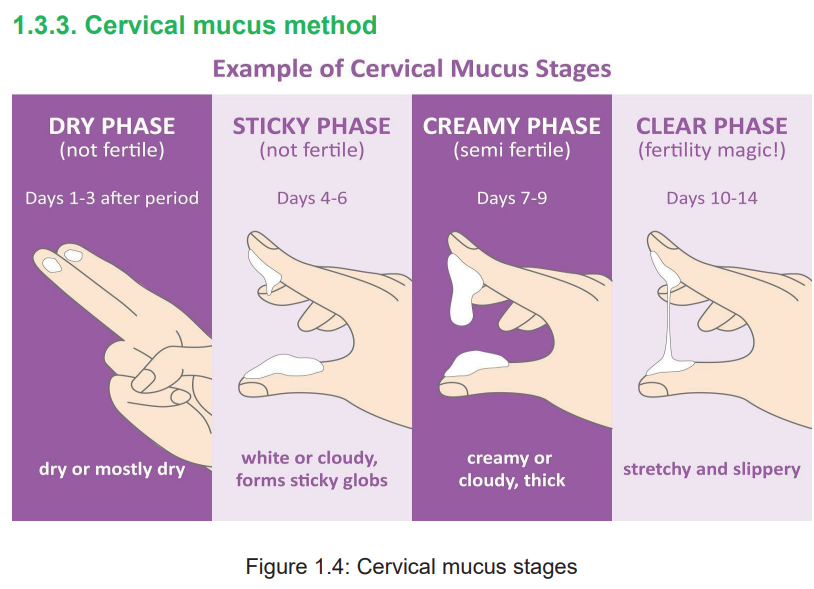
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
Learning activity 1.3.3
i) How does cervical mucus test can help the woman to predict the time of
her ovulation?Introduction
The cervical mucus method refers to the recognition and interpretation of changes
in the amount and consistency of cervical mucus through the menstrual cycle.
Before ovulation, cervical mucus is thick and does not stretch easily. During the
fertility days, the cervical mucus becomes more abundant and thinner with an
elastic quality. After ovulation, cervical mucus becomes thick or may disappear
completely. This quality inhibits sperm from entering in the cervix. The change of
cervical mucus occurs to facilitate the viability and motility of sperm and allowing
the sperm to survive in the female reproductive tract until ovulation.
i) Indicatio
• To women who are capable of abstaining from coitus during ovulation.
• To all couples who are capable of recognising the changes in appearance
of cervical mucus during the fertile period.
• To all couples who are capable of being cooperative during the ovulation
time.
ii) Contra-indication
• This method is contraindicated to all women who feel uncomfortable
touching their genitals.
• The method is not allowed to all women with vaginal infections, sexual
transmitted infections, and hormonal imbalances should also not use
cervical mucus method.
iii)Mode of action
When a woman is using cervical mucus method, she is supposed to check her
vaginal discharge every day for consistency and recognition of the change inappearance of her cervical mucus to determine her fertile period.
Self-assessment 1.3.3
i) Who should not use cervical mucus method in family planning?
ii) When should a woman be cautious while determining her fertile periodusing cervical mucus method?
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
1.3.4. Standard Days Method
Learning activity 1.3.4
Mrs. Lina have had a regular menstrual cycle of 30 days for six months. On 31st
July, she noticed that she had seen her menstrual bleeding. She is currently
using a cycle bead as a family planning method.
i) Which days will be safe for Mrs. Lina to do sexual intercourses with her
partner?ii) Which days will Mrs. Lina cannot do unprotected sexual intercourses?
Introduction
Standards Days Methods is another fertility awareness in which women and couple
use a cycle beads necklace to track their cycles (see the picture above). The cyclebeads have 32 beads, each representing a day in the woman’s menstrual cycle.
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
i) Indication
• To all women with regular menstrual cycle.
• To all women who have had 3 menstrual cycles after child birth, with the
last one recording 26 to 32 days.
ii) Contra-indication
• To avoid unprotected sexual intercourse from 8th day to 19th day of every
cycle.
• Uncooperative couples should not use SDM.iii)Mode of action
The woman moves a rubber ring onto one bead each day based on her monthly
cycle. The red bead marks the first day of her period. Brown beads correspond to
safe days; that days when she may not likely become pregnant if she does sexual
intercourse. From the brown beads, the woman moves the rubber ring onto the
white beads. These white beads represent the when she is likely to get pregnantand are labelled “unsafe” times to have unprotected vaginal intercourse.
Self-assessment 1.3.4
1. Mrs. Dana has given birth one month ago. As she is not breastfeeding
regularly, she has seen her menstrual bleeding on 15 June. She wants to
use the cycle beads as a method of family planning.
i) At what date would you advise to explore the use of Standard Days
Method?
ii) What would Mrs. Dana take into consideration before deciding to use acycle bead as a preferred family planning method?
Homework
Read the book ‘Family Planning: A Global Handbook for Providers’, Chapter 19;Lactational Amenorrhoea, Page 257
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
Learning activity 1.3.5
i) Explain how breastfeeding can delay ovulation after the birth of the baby?
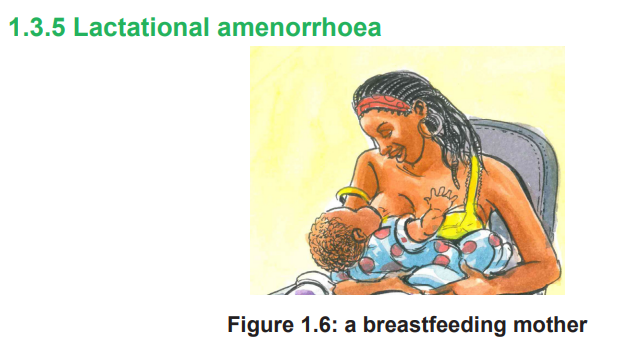
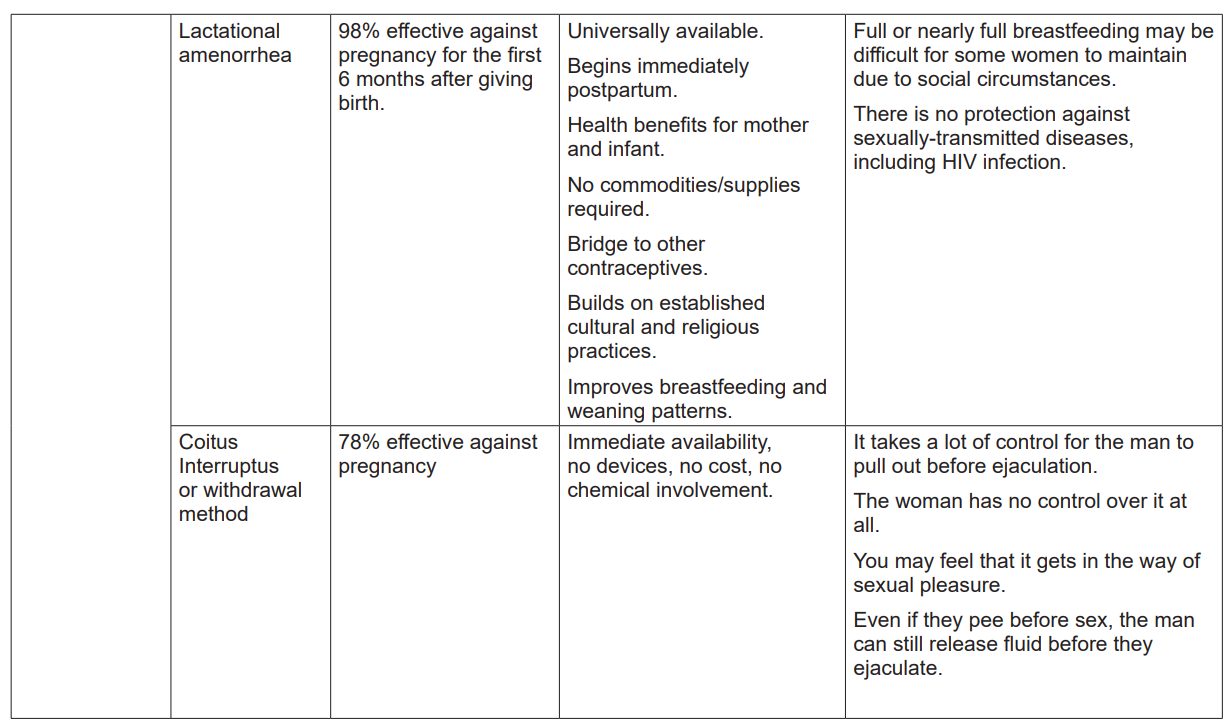
ii) Who can use Lactational amenorrhea and why?Introduction
Lactational Amenorrhea Method is a type of natural family planning which depends on
the woman’s breastfeeding regularly (every two to three hours) without interruption
in the first six months after delivery. When the woman breastfeeds consistently,
prolactin levels become elevated and suppress ovulation.
a. Indication
• This method can be operational within 6 months after delivery.
• If the mother has not had menstruation since the time of birth.
• When the mother is able to breastfeed her baby at least every 2 to 3 hours
regularly without stopping within six months.
b. Contra-indication
• Not to be practiced after 6 months post birth.
• Not to be used when the mother has had the return of menstrual period.
• Not to be used by mothers who are not available to breastfeed their babies
regularly.
c. Mode of action
For this method to be more effective, LAM requires constant breastfeeding. Breast
feeding stimulates prolactin hormone which is responsible for breast milk production.
This hormone further hinders gonadotropin hormone which is responsible for
ovulation to be produced. Thus, when the woman does sexual intercourse, she willnot likely become pregnant.
Self-assessment 1.3.5
i) If the couple is using Lactational amenorrhea, what do they have to care of
to prevent the woman from becoming pregnant?
ii) Discuss the factors that can influence the use Lactational AmenorrheaMethod.
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
1.3.6 Coitus Interruptus or withdrawal method
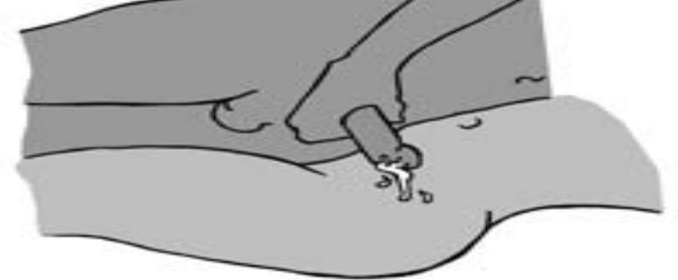
Figure1.7: Coitus interruptus
Learning activity 1.3.6
Read the book titled ‘Family planning: A global Handbook for Providers’ (2018
Edition), Chapter 18 and answer the following questions:
i) What happens when a couple practises withdrawal method?
ii) Whom can you likely recommend to practice coitus interruptus and why?
iii) In your own opinion would you recommend coitus interruptus as a firstchoice of family planning method?
Introduction
The male partner pulls his penis out of the vagina before ejaculation occurs to avoid
depositing sperm in or near the vagina. In so doing, he must keep his semen away
from the female partner’s external genitalia.
i) Indication
• All men in their reproductive age can use withdrawal method.
• It is indicated if there is no other family planning method available for
partners to use.
• This method requires much attention during the sexual act because at
times the man may reach climax and releases the pre-ejaculate fluid which
may contain sperm before withdrawing his penis to ejaculate outside the
vagina.• This method might be appropriate for couples who are highly motivated
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
and able to use it without failing.
• It can also be used by couples with religious or philosophical reasons for
not using other methods of contraception.
• Coitus interruptus can be used by couples who are waiting to get another
alternative method immediately but find themselves in need of sexual
intercourse without having obtained that method.
• Couples who need a temporary method while they wait the start of another
method may choose to use coitus interruptus.
• Couples who do sex infrequently can choose coitus interruptus method.
ii) Contra-indication
• Coitus interruptus must not be the method of choice if a man has premature
ejaculation issues.
• The method is also not appropriate for women with conditions that make
pregnancy an unacceptable risk because of the relatively high risk of
failure of coitus interruptus.
• This method is not allowed to couples who are not cooperative.
iii)Mode of action
When the man feels close to ejaculating, he must immediately remove his penis
from his female partner’s vagina to ejaculate outside and keeping his semen away
from her vulva. If man has ejaculated recently, before penetrating the female partner
again, he must urinate and clean the tip of his penis to remove any sperm that may
be remaining on his penis. The man should feel confident he can use withdrawal
correctly whenever he is engaged in the act of sex with his partner.Self-assessment 1.3.6
i) How does coitus interruptus method work?
ii) Who would you recommend to not use coitus interruptus and why?
iii) Describe how a male partner may pull out his penis from the vagina if thecouple is using coitus interruptus.
Maternal Child Health - Student Book - Senior 6
End unit assessment
1. Explain briefly the principles of family planning?
2. What are the signs that can make a woman to be conscious that is in her
fertile period with the help of cervical mucus?
3. Discuss any factors that may affect Mrs. Lina’s use of cycle bead
successfully.
4. Discuss the factors that can influence the use Lactational Amenorrhea
Method.
5. How does coitus interruptus method work?
6. The couple X have chosen to use Standard Days Method as their
preferred family planning method. The woman’s cycle in the last three
months had been between 28 and 32 days. The woman had seen her
periods on 5th April.
Draw a cycle bead and guide this couple on how they can use this method to
avoid unplanned pregnancy.
7. You are sent to the community and meet a group of women on Umuganda
day. The village head requests you to offer an educational session about
natural family planning.
Explain how you will educate the above group on different methods of natural
family planning focusing on different methods’ mode of action, indications, andcontraindications.
