UNIT 2:MEDICAL PATHOLOGIES OF EAR
pathology of oral and esophagus and invite the learners to follow the next lessons.
Teacher’s activity:
• Ask students to read the text and discuss the given questions.
• Engage students in working collectively the activity
• Help students with different problems
• Ask any four students to present their findings while others are following.
• Prepare trip field to nearest health facility in order to be familiar with Ear,
Nose and Throat (ENT) department equipment, and health assessment for
oral cavity disorders.
• Invite guest person who has specialty in Ear, Nose and Throat departmentdomain to teach the learners.
2.5. List of Lessons/sub-headings (including assessment)
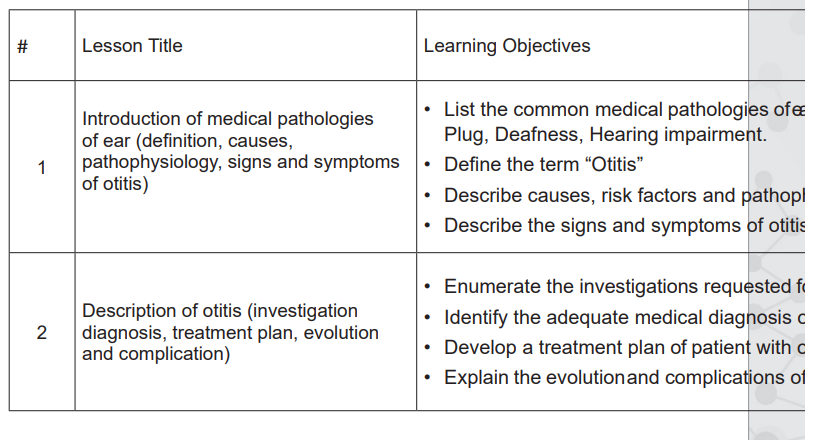
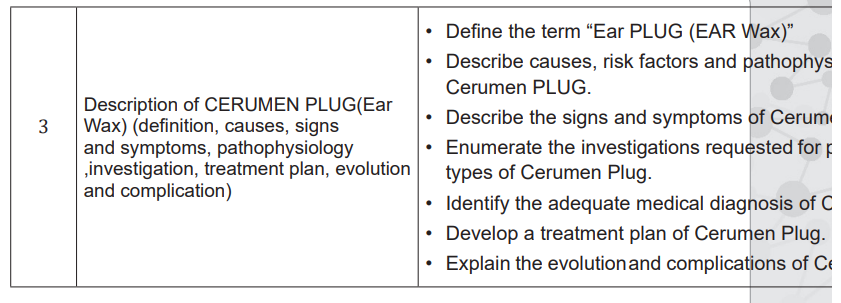
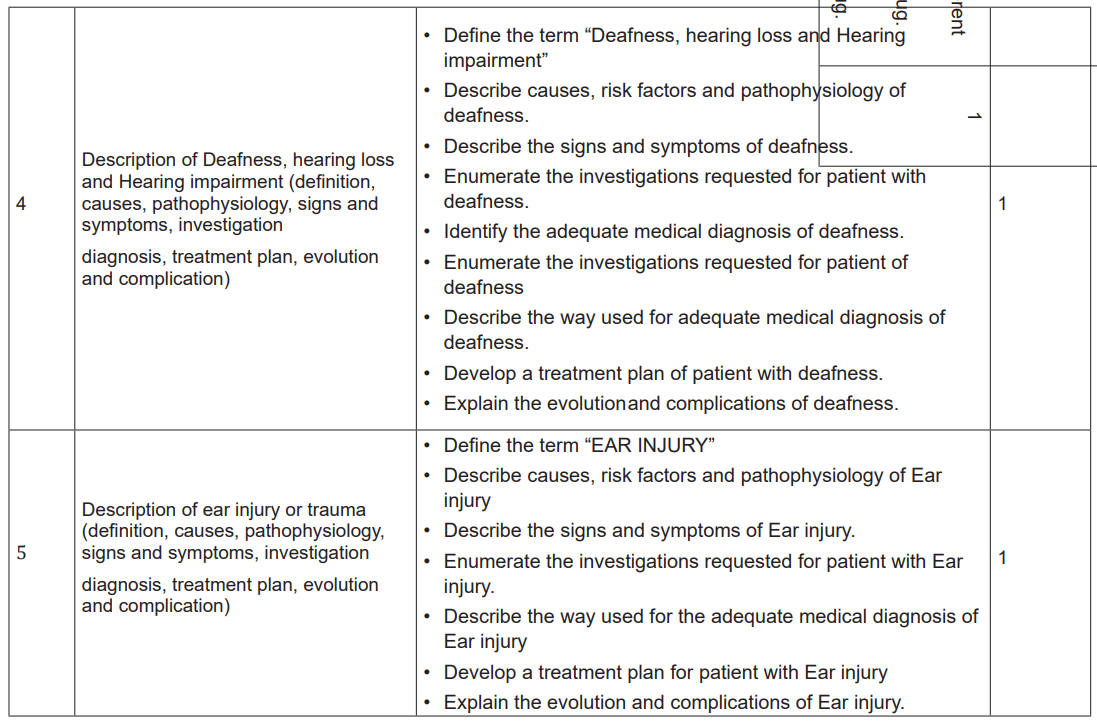

• Provide the necessary materials.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide their answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard, flipchart and whiteboard to take note of the main
students’ ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those, which are incomplete.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
Student‘s activity
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 2.1 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully.
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with the conclusion.
Expected answers to introductory activity 2.0
1. These persons are complaining with severe ear pain, itching and irritability of
the ear
2. Possible medical problems that the patients might complaint with otitis media,
ear trauma or injury.
Expected Answers to Questions from Learning Activity 2.1
1. The abnormal signs and symptoms that the patient was presenting are ear pain,
fever, drainage from the ear, trouble hearing, and inflammation of drum and
other surrounding membrane with the pus, body temperature of 38.5oc, White
Blood Cells (WBC) of 130000.
2. The medical problem of this patient was acute or chronic otitis
Lesson 2: Description of acute and chronic otitis (investigation
diagnosis, treatment plan, evolution and complication)
a) Prerequisite
This is the second lesson of the Second unit of medical pathologies of ear in sensory
organs. In this lesson, you will be dealing with the description of otitis such as its
investigation, medical diagnosis, treatment plan, evolution and complications. The
first thing to do before starting teaching is to remind learners that they have learnt
about lesson one of acute and chronic otitis.
b) Learning objectives
After completion of this lesson, the student will be able to:
• Enumerate the investigations requested for patient with acute and chronic
otitis
• Identify the adequate medical diagnosis of acute and chronic otitis
• Develop a treatment plan of patient with acute and chronic otitis
• Explain the evolution and complications of acute and chronic otitis.
c) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the anatomical model of the normal ear and abnormal ear
whenever possible and ensure the students are able to interpret them. In addition,
the teacher should present to the students the library textbooks on medical-surgical
nursing especially ear related diseases and indicates the pages. All students must
have their student’s books. There is a need of black board and chalks or flipcharts
and markers. Algorithms about assessment and management of dental caries must
also be displayed.
d) Learning activities
Teacher’s activities and methodology
• Ask learners to do individually activity 2.1 in their student book and answer
the questions related.
• Provide the necessary materials.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide their answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard the main student’s ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those, which are incomplete.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
• Use brainstorming while collecting the answers from different learners.• Judge the answers from learners by confirming the right responses.
Student’s activities
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 2.1 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with conclusion.
• Attempt to answer the self-assessment questions 2 .1
The expected answers from Questions of learning activity 2.1
1. Full Blood Count (FBC).
2. Treatment plan involved the use of Antibiotic like Amoxicillin 500mg TDS 7/7,
Paracemol 500mg tds3/7 and Ibuprofen 400mg TDS 4/7 for pain relief.
3. Swollen gums indicating gingivitis to dental caries
The expected answers from Questions of self-assessment 2.1
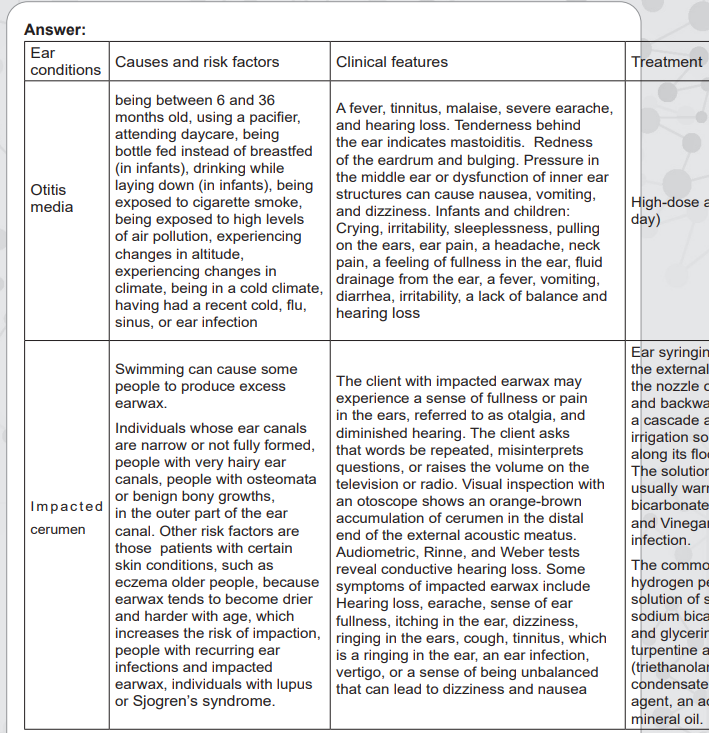
1. The signs and symptoms of acute and chronic otitis includes a fever, tinnitus,
malaise, severe earache, and hearing loss. Tenderness behind the ear indicates
mastoiditis. Redness of the eardrum and bulging. Pressure in the middle ear or
dysfunction of inner ear structures can cause nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. If
the tympanic membrane perforates, fluid drains into the external acoustic canal
and pain is relieved. Infants and children may have one or more of the following
symptoms: Crying, irritability, sleeplessness, pulling on the ears, ear pain, a
headache, neck pain, a feeling of fullness in the ear, fluid drainage from the ear,
a fever, vomiting, diarrhea, irritability, a lack of balance and hearing loss.
2. The causes and risk factors of otitis media includes being between 6 and 36
months old, using a pacifier, attending daycare, being bottle fed instead of
breastfed (in infants), drinking while laying down (in infants). Other risk factors
are exposure to cigarette smoke, high levels of air pollution, experiencing
changes in altitude, experiencing changes in climate, being in a cold climate,having had a recent cold, flu, sinus, or ear infection.
3. The most complications of acute otitis media include meningitis, brain abscesses,
epidural abscesses, mastoiditis, permanent sensorineural hearing loss, and
death.
4. The 5 elements to be monitored during otoscope examination includes redness,
swelling, blood, pus, air bubbles, fluid in the middle ear, perforation of theeardrum.
Lesson 3: Description of CERUMEN PLUG (Ear Wax) (definition,
causes, signs and symptoms, pathophysiology, investigation,treatment plan, evolution and complication)
a) Prerequisites
This is the Third lesson of the Second unit of medical pathologies of ear in sensory
organs. In this lesson, you will be dealing with the description of different causes
and risk factors of acute and chronic otitis, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms,
investigation, management, evolution and complications. The first thing to do
before starting teaching is to remind learners what they have learnt about the
anatomy and physiology of the sensory organs (Ear), health assessment of ear
from fundamentals of nursing. The students will discuss the questions from the
case study from learning activity 2.2 so that they can prepare themselves for this
lesson.
b) Learning objectives:
After completion of this lesson, the student will be able to:
• Define the term “Cerumen Plug (Ear wax)”
• Describe causes, risk factors and pathophysiology of Cerumen Plug (Earwax).
• Describe the signs and symptoms of Cerumen Plug (Earwax).
• Enumerate the investigations requested for patient different types of Cerumen
Plug (Earwax).
• Identify the adequate medical diagnosis of Cerumen Plug (Earwax).
• Develop a treatment plan of Cerumen Plug (Earwax).
• Explain the evolution and complications of Cerumen Plug (Earwax).
c) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the ear anatomical model and otoscope ensure the students
are able to use them. In addition, the teacher should present to the students the
library textbooks on medical-surgical nursing especially ear diseases and indicates
the pages. All students must have their student’s books. There is need of black
board and chalks or flipcharts and markers. Algorithms about assessment andmanagement of conjunctivitis must also be displayed.
d) Learning activities
Teacher’s activities and methodology
• Ask learners to do individually activity 2.2 in their student book and answer
the questions related.
• Provide the necessary materials.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide they answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard the main student’s ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those, which are incomplete.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
• Use brainstorming while collecting the answers from different learners.
• Judge the answers from learners by confirming the right responses.
Student’s activities
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 2.2 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with conclusion.
• Attend the library for reading related book of oral candidiasis conditions
• Attempt to answer the self-assessment questions 2.2
The expected answers from Questions of learning activity 2.2
1. Signs and symptoms that the patient was presenting are a fever, tinnitus,
malaise, severe earache hearing loss, tenderness behind the ear, redness of the
eardrum and bulging, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. In infant and children:
Crying, irritability, sleeplessness, pulling on the ears, ear pain, a headache, neck
pain, a feeling of fullness in the ear, fluid drainage from the ear, a fever, vomiting,diarrheas', irritability, a lack of balance and hearing loss.
2. The medical problem from those signs and symptoms are Otitis media
3. The otoscope examination was performed
4. The clinical management includes sodium bicarbonate eardrops and earirrigation.
The expected answers from Questions of self-assessment 2.2
1. The client with impacted earwax may experience a sense of fullness or pain in the
ears, referred to as otalgia, and diminished hearing. The client asks that words
be repeated, misinterprets questions, or raises the volume on the television or
radio. Visual inspection with an otoscope shows an orange-brown accumulation
of cerumen in the distal end of the external acoustic meatus. Audiometric, Rinne,
and Weber tests reveal conductive hearing loss. Some symptoms of impacted
earwax include Hearing loss, earache, sense of ear fullness, itching in the ear,
dizziness, ringing in the ears, cough, tinnitus, which is a ringing in the ear, an
ear infection, vertigo, or a sense of being unbalanced that can lead to dizziness
and nausea
2. The causes of cerumen plug are swimming for some people, individuals whose
ear canals are narrow or not fully formed people with very hairy ear canals, and
people with osteomata or benign bony growths in the outer part of the ear canal.
In addition, those with certain skin conditions, such as eczema, older people,
because earwax tends to become drier and harder with age, which increases
the risk of impaction, people with recurring ear infections and impacted earwax,
individuals with lupus or Sjogren’s syndrome.
3. The diagnosis of cerumen impaction is made by direct visualization with an
otoscope. Common symptoms include hearing loss, feeling of fullness in the ear,
itching, otalgia, tinnitus, cough, and, rarely, a sensation of imbalance. Hearing
loss from cerumen impaction can cause reversible cognitive impairment in older
persons. Some patients are unable to accurately convey symptoms, such as
those with dementia or developmental delay; nonverbal patients with behavioral
changes; and young children with fever, speech delay, or parental concerns. In
these patients, cerumen should be removed when it limits examination
4. Ear syringing techniques consists of pulling the external ear up and back, and
aiming the nozzle of the syringe slightly upwards and backwards so that the
water flows as a cascade along the roof of the canal. The irrigation solution flows
out of the canal along its floor, taking wax and debris with it. The solution used to
irrigate the ear canal is usually warm water, normal saline, sodium bicarbonate
solution, or a solution of water and Vinegar to help prevent secondary infection.
5. The common cerumen softeners include urea hydrogen peroxide (6.5%) and
glycerine, a solution of sodium bicarbonate in water, or sodium bicarbonate
(sodium bicarbonate and glycerine), Cerumol (peanut oil, turpentine and
dichlorobenzene), cerumenex (triethanolamine), polypeptides and oleate
condensate), docusate, an emulsifying agent, an active ingredient found inlaxatives, mineral oil.
6. Some of the complications of earwax includes ear infections if a person does not
get treatment. Very rarely, the infection may spread to the base of the skull andcause meningitis or cranial paralysis.
Lesson 4: Description of deafness, hearing loss, and hearingimpairment
(Definition, causes and risk factors, Pathophysiology, signs and symptoms,investigation, diagnosis, treatment plan, evolution and complication)
a) Prerequisites
This is the fourth lesson of the Second unit about medical pathologies of the ear.
In this lesson, you will be dealing with the definition, causes and risk factors,
Pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, investigation, diagnosis, treatment plan,
evolution and complication of deafness. The first thing to do before starting teaching
is to remind learners what they have learnt about the anatomy and physiology of
the sensory organs (ear), health assessment of oral cavity from fundamentals of
nursing. The students will discuss the questions from the case study from learning
activity 2.3 so that they can prepare themselves for this lesson.
b) Learning objectives:
After completion of this lesson, the student will be able to:
• Define the term “Deafness, hearing loss and Hearing impairment”
• Describe causes, risk factors and pathophysiology of deafness.
• Describe the signs and symptoms of deafness.
• Enumerate the investigations requested for patient with deafness.
• Identify the adequate medical diagnosis of deafness.
• Enumerate the investigations requested for patient of deafness
• Describe the way used for adequate medical diagnosis of deafness.
• Develop a treatment plan of patient with deafness.
• Explain the evolution and complications of deafness.
c) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the oral cavity anatomical model and otoscope and ensure
the students are able to use them. In addition, the teacher should present to the
students the library textbooks on medical-surgical nursing especially deafness and
indicates the pages. All students must have their student’s books. There is need
of black board and chalks or flipcharts and markers. Algorithms about assessmentand management of conjunctivitis must also be displayed.
d) Learning activities
Teacher’s activities and methodology
• Ask learners to do individually activity 2.3 in their student book and answer
the questions related.
• Provide the necessary materials.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide they answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard the main student’s ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones that are incorrect and try
again to complete those which are incomplete.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
• Use brainstorming while collecting the answers from different learners.
• Judge the answers from learners by confirming the right responses.
Student’s activities
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 2.3 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with conclusion.
• Attend the library for reading related book of oral cavity condition• Attempt to answer the self-assessment questions 2.3
The expected answers from Questions of learning activity 2.3
1. The signs and symptoms presented by the patient were difficulty understanding
words, especially against background noise or in a crowd, trouble hearing
consonants, He frequently asking others to speak more slowly, clearly and
loudly, He needs to turn up the volume of the television or radio while listening
to the radio and television’
2. The medical problem could be deafness, hearing loss, and hearing impairment
3. Laboratory, Full blood accounts (FBC); Imageries: Chest x- ray, otoscopic
examination and audiometric tests complement each other for the diagnosis
of hearing loss. Objective tests measure the hearing loss at some specific
frequencies
4. Hearing aids, Behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aids, In-the-canal (ITC) hearing
aids, completely in the canal (CIC) hearing aids, Bone conduction hearing aids,
Cochlear implants.
♦ Answers for Self-Assessment 2.3
1. The causes of loss of hearing in adult are the diseases of outer and middle ear,
the presence of wax in the ear canal, the congenital defects in the outer or middle
ear. In addition, defect and damage to the outer or middle ear, upper respiratory
tract infections, neglect of care of ears and oral cavity (mouth) contribute to the
conductive hearing loss. Moreover, the damage or disease of the inner ear or
auditory nerve, the infectious diseases like measles, mumps, meningitis and
Tuberculosis can cause the sensorineural hearing loss.
Some conditions that may cause congenital sensorineural hearing loss includes
hereditary childhood deafness, Rh incompatibility, premature birth (birth before due
time), and birth Asphyxia (lack of oxygen supply to the newborn due to inability to
breathe. Other causes of sensorineural hearing loss are Viral infections in pregnancy,
exposure to X–rays in the first trimester of pregnancy (taking X–ray within the first
three months), harmful drugs of variety e.g. streptomycin, and acoustic neuroma
(Tumor of the auditory nerve).
1. The physician will talk to the patient and ask several questions regarding the
symptoms, including when they started, whether or not they have gotten worse,
and whether the individual is feeling pain alongside the hearing loss. On physical
examination, the doctor will look into the ear using an otoscope
2. Treatment plan of Hearing Loss includes hearing aids, Behind-the-ear (BTE)
hearing aids, In-the-canal (ITC) hearing aids, completely in the canal (CIC)
hearing aids, Bone conduction hearing aids, Cochlear implants
3. The complications for hearing include conversation difficult, some people
experience feelings of isolation. Hearing loss is also associated with cognitive
impairment and decline, cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease, clinicaldepression, diabetes, falls among the elderly, heart diseases.
Lesson 5: Description of ear injury or Trauma (definition causes,
pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, investigation, treatment plan,evolution and complication)
a) Prerequisite
This is the fifth lesson of the Second unit about medical pathologies of the ear.
In this lesson, you will be dealing with the definition, causes and risk factors,
Pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, investigation, diagnosis, treatment plan,
evolution and complication of ear injury or trauma. The first thing to do before
starting teaching is to remind learners what they have learnt about the anatomy
and physiology of the sensory organs (ear), health assessment of oral cavity from
fundamentals of nursing. The students will discuss the questions from the case
study from learning activity 2.4 so that they can prepare themselves for this lesson.
b) Learning objectives
After completion of this lesson, the student will be able to:
• Define the term “EAR INJURY”
• Describe causes, risk factors and pathophysiology of Ear injury
• Describe the signs and symptoms of Ear injury.
• Enumerate the investigations requested for patient with Ear injury.
• Describe the way used for the adequate medical diagnosis of Ear injury
• Develop a treatment plan for patient with Ear injury
• Explain the evolution and complications of Ear injury.
c) Teaching resources
The teacher could avail the oral cavity anatomical model and otoscope and ensure
the students are able to use them. In addition, the teacher should present to the
students the library textbooks on medical-surgical nursing especially deafness and
indicates the pages. All students must have their student’s books. There is need
of black board and chalks or flipcharts and markers. Algorithms about assessmentand management of conjunctivitis must also be displayed.
d) Learning activities
Learning activities should be directly related to the learning objectives of the course
and provide experiences that will enable students to engage in practice and gain
feedback on specific progress towards those objectives. The various learning
activities will be carried out such as: taking notes, course work and reading textbook
related to the lesson, group assignment and summarize the content, engagementin debate and other clinical learning activities such as case study.
Teacher’s activity:
• Ask learners to do individually activity 2.4 in their student book and answer
the questions related.
• Provide the necessary materials to the students.
• Move around in silence to monitor if they are having some problems
• Remember to assist those who are weak but without giving them the
knowledge.
• Invite any five students to provide their answers
• Ask other students to follow carefully the answers provided by students
• Note on the blackboard the main student’s ideas.
• Tick the correct responses and correct those ones, which are incorrect and try
again to complete those which are incomplete.
• Use brainstorming while collecting the answers from different learners.
• Judge the answers from learners by conforming the right responses.
• Harmonize and conclude on the learned knowledge and still engage student
in making that conclusion.
Student’s activities
• The students answer the questions individually in learning activity 2.4 in their
student book
• The students ask the problems that may be raised from the provided activity
if any in order to get clarification
• Some students present the findings from the learning activity while others are
following carefully
• Summarize the content with the teacher and coming up with conclusion.
• Attend the library for reading related book of esophagus condition
• Attempt to answer the self-assessment questions 2.4
The expected answers from Questions of learning activity 2.4
1. Ear pain, dizziness, headache, hearing loss, bleeding from the same ear, tinnitus
sensation after falling down from motorcycle after road traffic accident
2. The medical problem for this case suggests ear injury or trauma
3. Complete Blood Count (CBC) ,Hemoglobin ,An otoscope exam and tympanometry
were performed
4. A sterile dry wound dressing was applied and Paracetamol 500mg TDS 3/7 as
well as cloxacillin 500mg TDS
The expected answers from Questions of self-assessment 2.4
1. Accidents, loud noises, changes in air pressure, trauma from contact sports and
foreign objects in the ear can cause injuries, causes of ear ruptures also include
getting hit in the ear, sustaining an injury during sports, falling on your ear, car
accidents
2. The signs and symptoms of ear injury includes Ear pain (earache), which can
be severe, dizziness and balance problems, headache, hearing loss, pus or
bleeding from the ear, tinnitus (buzzing or ringing in the ear).
3. The investigations that can help the doctor to confirm the diagnosis of ear injury
are the fluid sample test, and an otoscope exam to look the ear canal. In addition,
an audiology exam allows the doctor to test the hearing range and eardrum
capacity. Other investigations include tympanometry to test the eardrum’s
response to pressure changes.
4. Eardrum repair such as myringoplasty, Tympanoplasty
2.6 Summary of the unit
Medical pathology is a branch of medical science primarily concerning with the
diseases affecting different human organs such as respiratory tract organs, cardio
vascular organs, digestive organs, urino-genetal organs, sensory organs etc. This
unit of medical pathologies of the ear described the most common ear conditions
that are frequently observable in Rwanda such as acute and chronic otitis media,
Cerumen plug (ear wax), deafness (Hearing loss, hearing impairment), Ear injury or
Trauma. This unit describes the ear medical conditions by providing their definition,
clinical features, causes and risk factors, pathophysiology, investigation, treatment
plan, evolution and complications. The student who will be complete this content
will be able to take appropriate decision on different common medical pathologies
affecting the ear in terms of diagnosing, treatment and prevent the complication ofotitis, Cerumen, deafness and ear trauma.
END OF UNIT 2 ASSESSMENT ANSWERS
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions
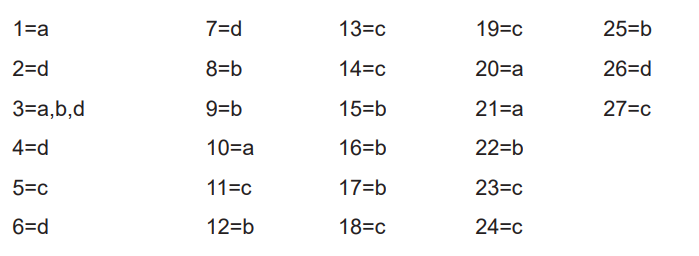
Section B: Essay Questions
1. Answer: The first priority is to kill the insect. This can be accomplished in many
ways. Asphyxiation is probably best. The use of lidocaine gel or solution not
only will suffocate the bug, but also may help to provide some anesthetic to the
ear canal, aiding with later removal. Contact medical control to discuss your
options...Once the bug has stopped buzzing/moving your patient will be much
more cooperative.
2. Answer: Hematomas of the outer ear will cause breakdown of the cartilage if
they are not treated with an incision and expression of clot, then a pressure
dressing. Cartilage breakdown will lead to the ‘cauliflower ear’ often seen in
boxers (and would-be boxers).
3. Answer: As before, lacerations to the cartilage of the ear can lead to severe
cosmetic defects unless the cartilage laceration is repaired.
4. Answer: The purpose of the Eustachian tube is to ventilate the middle ear, to
maintain air pressure within the ear and to drain infections. The primary function
of the Eustachian tube is to ventilate the middle ear space, ensuring that its
pressure remains at near normal ambient air pressure. The secondary function
of the Eustachian tube is to drain any accumulated secretions, infection, or debris
from the middle ear space. Several small muscles located in the back of the throat
and the palate control the opening and closing of the tube. Swallowing and
yawning cause contractions of these muscles and help to regulate Eustachian
tube function. If it were not for the Eustachian tube, the middle ear cavity would
be an isolated air pocket inside the head that would be vulnerable to every
change in air pressure, and lead to an unhealthy ear.
5. Answer: Bottle-feeding. Bottle feeding is a risk factor for otitis media in infants.
Breastfeeding passes immunity to the child that helps prevent acute otitis media.
The position of the breastfeeding child is better than the bottle feeding position
for Eustachian tube function. If a child needs to be bottle-fed, hold the infant
instead of allowing the child to lie down with the bottle is best. A child should not
take the bottle to bed. In addition to increasing the chance for acute otitis media,falling asleep with milk in the mouth increases the incidence of tooth decay.
6. Answer: Ear infection symptoms generally include trouble hearing and fever;
fluid drainage and dizziness and congestion in the ear. The hallmark of
an acute ear infection is sudden, piercing pain in the ear. The pain may be
worse when lying down, making it difficult to sleep. Other symptoms include
difficulty hearing, fever, fluid drainage from the ears, dizziness, and congestion.
Young children with otitis media may be irritable, fussy, or have problems feeding
or sleeping. Older children may complain about pain and fullness in the ear
(earache). Fever may be present in a child of any age. These symptoms are
often associated with signs of upper respiratory infection such as a runny or
stuffy nose, or a cough.
7. Answer: Hearing loss may occur as a result of an ear infection because pus
buildup dampens ear drum vibrations. Temporary hearing loss may occur during
an ear infection because the buildup of pus within the middle ear causes pain,and dampens the vibrations of the eardrum.
SECTION C: Questions to answer by True or False
1. Answer: True. Acute otitis media (ear infection) describes inflammation of the
middle ear, or tympanum. During an ear infection, there is fluid in the middle ear
accompanied by signs or symptoms of ear infection including a bulging eardrum
usually accompanied by pain; or a perforated eardrum, often with drainage of
pus (purulent material).
2. Answer: A: False. An ear infection itself is not contagious. Ear infections are
often the result of a previous infection of the throat, mouth, or nose that has
relocated and settled in the ears.
3. Answer: True. Untreated ear infections can lead to more serious complications,
including mastoiditis (a rare inflammation of a bone adjacent to the ear),
hearing loss, scarring and/or perforation of the eardrum, meningitis, speech and
language development problems, facial nerve paralysis, and possibly -- in adults
- Meniere’s disease.
Note: Meniere’s disease is likely a disorder of the flow of fluids of the inner with
symptoms that include vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss
4. Answer: False. Remember that the common cold is a key cause of ear infections.
Because of the highly contagious nature of the common cold, one strategy
for prevention of the cold itself and subsequent ear infections is to keep cold
viruses at bay. The most effective way to do this is frequent and meticulous hand
washing. Other strategies to prevent acute ear infections are to ensure a child
is vaccinated. Ensuring that a child receives an annual flu vaccine and is up to
date with his/her pneumococcal vaccine are excellent strategies used to prevent
the most common causes of ear infections. Other lines of defense against ear
infections include avoiding second hand smoke and breastfeeding your baby forthe first year of life.
2.7 Additional Information
Common additional information
Otitis Externa
Otitis externa is an inflammation of the tissue in the outer ear. Otitis externa means
that the inflammation is confined to the external part of the ear canal and does notgo further than the eardrum.
Pathophysiology and etiology
Inflammation usually is caused by an overgrowth of pathogens. The microorganisms
tend to follow trauma to the lining of the ear, or their growth is supported by retained
moisture from swimming. Another possibility is that a hair follicle becomes infected,causing a furuncle or an abscess to develop.
Several factors may predispose patients to the development of acute otitis externa.
One of the most common predisposing factors is swimming, especially in fresh
water. Other factors include skin conditions such as eczema and seborrhea, trauma
from cerumen removal, use of external devices such as hearing aids, and cerumen
buildup. These factors appear to work primarily through loss of the protective
cerumen barrier, disruption of the epithelium, inoculation with bacteria, and increasein the pH of the ear canal.
Signs and symptoms
The tissue in the external ear looks red. Sometimes it is difficult to see the tympanic
membrane because of swelling. Clients describe discomfort that increases with
manipulation during the examination. Hearing is reduced because of swelling. In
severe infections, a fever develops and the lymph nodes behind the ear enlarge.
Otoscopic examination reveals diffuse or confined inflammation, swelling, and pus.A culture of drainage identifies the specific pathogen.
Acute otitis externa presents with the rapid onset of ear canal inflammation, resulting
in otalgia, itching, canal edema, canal erythema, and otorrhea, and often occurs
following swimming or minor trauma from inappropriate cleaning.
Treatment Plan
Treatment includes warm soaks, analgesics, and antibiotic ear medication, oftenwith corticosteroid medication, such as neomycin/polymyxin/hydrocortisone otic
solution.
The nurse instructs the client to carry out the medical treatment and provides health
teaching to prevent recurrence. For example, he or she advises swimmers to wear
soft plastic ear plugs to prevent trapping water in the ear. If chewing produces or
potentiates discomfort, the nurse encourages the client to temporarily eat soft foods
or consume nourishing liquids. Above all, the nurse advises the client to avoid the
use of non-prescription remedies unless they have been approved by the physician
and to contact the physician if symptoms are not relieved in a few days.
A young woman comes in the clinic complaining of severe pain of her left ear; it
hurts to touch it. She says that she swims at least 3 days a week. She is diagnosed
with otitis externa. The nurse practitioner prescribes analgesics and application of
heat to the affected ear and also tells the client to avoid swimming for 2 weeks.
Because this client swims regularly for exercise, what further instructions can the
nurse provide to prevent future problems?
What actions would the nurse perform while administering ear drops to remove
excessive cerumen? Select all that apply.
a. Avoid inserting the irrigating syringe too deeply.
b. Boil the solution once.
c. Direct the flow of the ear drops toward the eardrum.
d. Direct the flow of the ear drops toward the roof of the canal.
e. Shake the ear drops container vigorously.
f. Warm the ear drops by holding the container in the hand for a few minutes.
A client arrives at the emergency department after an insect has entered the ear.
Which of the following solutions would the nurse instill into the client’s ear to smother
the insect?
a. Carbamide peroxide
b. Hot water
c. Mineral oil
d. Triethanolamine
Which is the best evidence that the antibiotic the nurse is administering for the
treatment of acute otitis media is having a therapeutic effect?
a. Ear discomfort is relieved.
b. Ear drainage is thin and watery.c. Ringing sounds within the ear stop.
d. The ear feels less warm to the touch.Cerumen-Softening Agents for Cerumen Removal
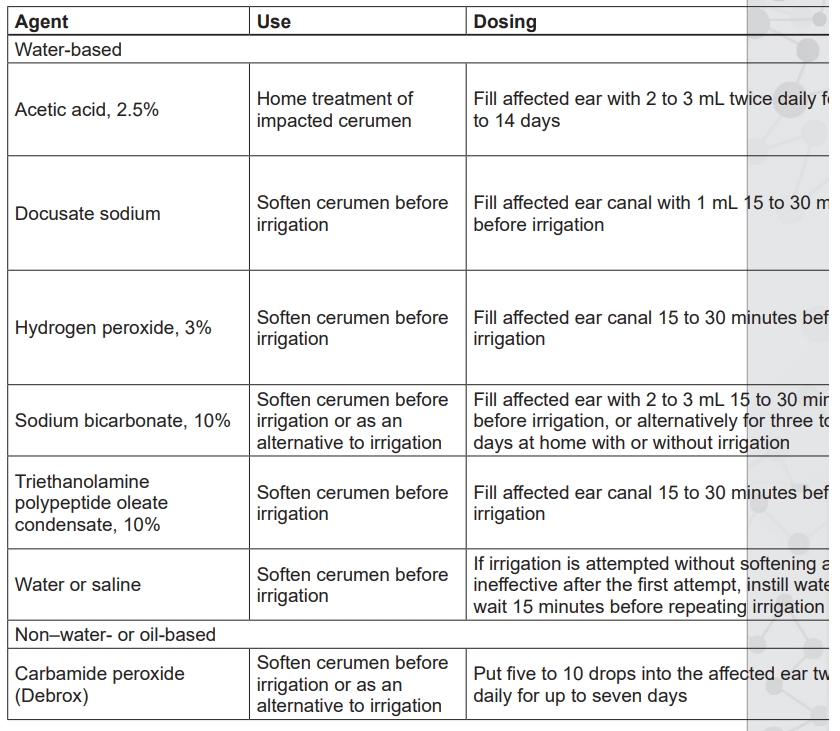
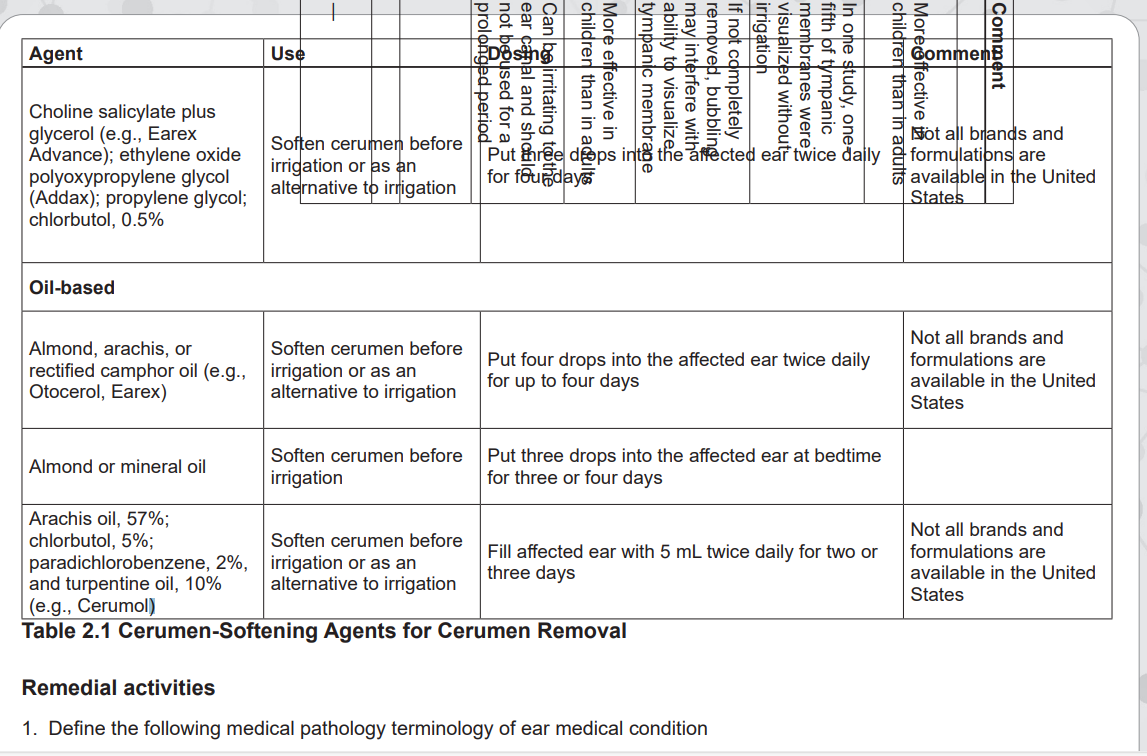





on the lowest settings and head tilting to remove water from the ear canal, and
avoidance of self-cleaning or scratching the ear canal. Acetic acid 2% (Vosol) otic
solutions are also used, either two drops twice daily or two to five drops after water
exposure.
6. What is ototoxicity and enumerate the factors that are related to it?
Answer:
Ototoxicity describes the detrimental effect of certain medications on the eighth
cranial nerve or hearing structures. Signs and symptoms of ototoxicity include tinnitus
and sensorineural hearing loss. Vestibular toxicity includes signs and symptoms of
light-headedness, vertigo, nausea, and vomiting. Drugs associated with ototoxicity
include salicylates, loop diuretics, quinidine, quinine, and aminoglycosides.
7. Which is the most ototoxicity among the following antimalarial
drugs?
a. Coartem
b. Artesunate
c. Quinine
d. Chroloquine
Answer: c
8. Changes in the ear that occur with aging may include:
a. atrophy of the tympanic membrane.
b. increased hardness of the cerumen.
c. degeneration of cells at the base of the cochlea.
d. all of the above
Answer: d
9. The most common fungus associated with ear infections is:
a. Staphylococcus albus.
b. Staphylococcus aureus.
c. Aspergillus.d. Pseudomonas
Answer:c
10. Nursing instructions for a patient suffering from external otitis
should include the:
a. application of heat to the auricle.
b. avoidance of swimming.
c. ingestion of over-the-counter analgesics, such as aspirin.
d. all of the above.
Answer: d
11. A tympanoplasty, the most common procedure for chronic otitis
media, is surgically performed to:
a. close a perforation.
b. prevent recurrent infection.
c. reestablish middle ear function.
d. accomplish all of the above
Answer: d
12. A symptom that is not usually found with acute otitis media is:
a. aural tenderness.
b. rhinitis.
c. otalgia.
d. otorrhea
Answer:a
13. An incident of otitis media is usually associated with:
a. ear canal swelling.
b. discharge.
c. intense ear pain.d. prominent localized tenderness.
Answer:c
14. A myringotomy is performed primarily to:
a. drain purulent fluid.
b. identify the infecting organism.
c. relieve tympanic membrane pressure.
d. accomplish all of the above
Answer:d
15. Postoperative nursing assessment for a patient who has had a
mastoidectomy should include observing
for facial paralysis, which might indicate damage to which cranial nerve?
a. First
b. Fourth
c. Seventh
d. Tenth
Answer:c
16. A facial nerve neuroma is a tumor on which cranial nerve?
a. Third
b. Fifth
c. Seventh
d. Eighth
Answer:c
3.1 Key unit competence
Demonstrate understanding of the appropriate management of different common
Medical Pathologies of the Nose
3.2 Prerequisite (Knowledge, skills, attitude and values)
To achieve the above competence the associate nurse student needs to have learnt
the following subjects:
• Human body anatomy and physiology: Sensory organs mainly Nose and
Throat
• Fundamental of Nursing: Vital signs and parameters measurements and
interpretation, Drugs administration (PO, inhalations, spray and injectable),
History taking, Complete health assessment from head to toes through
interview and Physical assessment regarding nose and throat.
• Ethics and professional code of conduct: Respect of principles of ethics
during management of a patient with all medical diseases. The Associate
Nurse student should demonstrate good behaviors while interacting with the
patient.
• Pharmacology: drugs acting on sensory system (NSAIDs, cortico-steroids,
anti-histamines drugs, antibiotics, etc.) with their posology and their mode of
administration.
3.3. Cross-cutting issues to be addressed
Standardization culture
All health care facilities must use same standard and accurate equipment and
techniques in the management of the medical conditions. During the field trips, the
teacher should ensure the availability of standard medical equipment and technics
before selecting the health care facility to use. The learners have to learn the use
of those standards equipment and technics in the management of patients with
sensory diseases.
3.3.1. Inclusive education
All students should participate in all activities without discrimination of a student
with any disability. This may be challenging to students with special educational
needs especially those with disabilities, slow learners, those with low self-esteem,
etc. However, the teacher can make some arrangements like:
• Grouping students: Students with special educational needs are grouped
with others and assigned the roles basing on individual student’s abilities.
Providing procedure/checklists or protocols earlier before the practical work
so that students get familiar with them. They can be written on the chalkboard
or printed depending on available resources. If you have, students with low
vision remember to print in appropriate fonts. In addition, you are supposed
to pay attention to all categories of learners.
• Every important point is written and spoken. The written points help students
with hearing impairment and speaking aloud helps students with visual
impairment.• Remember to repeat the main points of the lessons.
3.3.2. Gender education
Emphasize to learners that anybody irrespective of their gender can be a health
care professional. The teacher must present some role models of people who have
been successful in medical and nursing professions in the area where the learners
come from. Make sure that during practical work both boys and girls shares and
participate equally in practices, arranging and proper hygiene after procedures.
3.4 Guidance on the introductory activity
During the introductory activity 3.0, learners will observe all images illustrated and
the abnormal features from those images, and will remember the anatomy and
physiology of sensory system mainly nose and throat learnt in the unit of biology
and parts of sensory assessment learnt in unit of fundamentals of nursing. From all
these prerequisites, learners will be requested to observe the picture illustrated and
be able to list all abnormal features they see and list all medical conditions that can
lead to those abnormal features mentioned.
Teacher’s activity
• Using brainstorming: Every learner is given opportunity to observe the image
and answer the questions related to the image illustrated.
• Teacher writes on whiteboard the correct answers from the learners.
The expected answers to introductory activity 3.01) The observations about what the persons illustrated are
