UNIT5:HEMORRHOIDS
Key Unit competence:Take appropriate decision on Hemorrhoids
Introductory activity 5.0
The images below from A to E illustrate the structures of the cross section ofsigmoid and anus. Observe them and respond to the attached questions.
1) What are the physiological changes would reflect these changes in the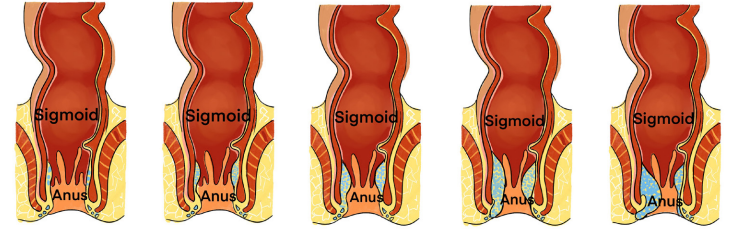
intestines?
2) What are the manifestations of such abnormalities in the human body?
3) How can health personnel identify or notice these abnormalities?4) How can these abnormalities be corrected?
5.1. Description of Hemorrhoids
Learning Activity 5.1
N.A is a 37-year-old pregnant woman consults the hospital with pain in the rectum
during and after passing stools. She said that he saw blood on the toilet paper
that she used. She also mentioned that she has been having hard stool since
some weeks and itching. The medical doctor put the patient on the left lateral
decubitus with the N. A’s knees flexed toward the chest, he inspected the anus
and performed anal digital examination. A bulging mucosa was observed duringinspection and palpated confirming external hemorrhoids.
Questions related to the case study
1) What is the medical history of N.A described in the case study?
2) Do you think that this history has something to do with the haemorrhoids?
Explain your response.3) Describe the signs and symptoms presented in the case study
5.1.1. Definition of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are a very common anorectal condition defined as the symptomatic
enlargement and distal displacement of the normal anal cushions.
5.1.2. Causes and pathophysiology of hemorrhoids
The exact pathophysiology of hemorrhoidal development is poorly understood.
For years the theory of varicose veins, which postulated that hemorrhoids were
caused by varicose veins in the anal canal, had been popular but now it is obsolete
because hemorrhoids and anorectal varices are proven to be distinct entities.
Today, the theory of sliding anal canal lining is widely accepted. This proposes that
hemorrhoids develop when the supporting tissues of the anal cushions disintegrate
or deteriorate. Hemorrhoids are therefore the pathological term to describe the
abnormal downward displacement of the anal cushions causing venous dilatation
and increase in pressure in the veins.
Some of the risk factors of hemorrhoids include pregnancy, prolonged sitting or
standing position, obesity and chronic constipation. Portal hypertension related to
liver disease may also be a factor.
5.1.3 Signs and symptoms of Hemorrhoids
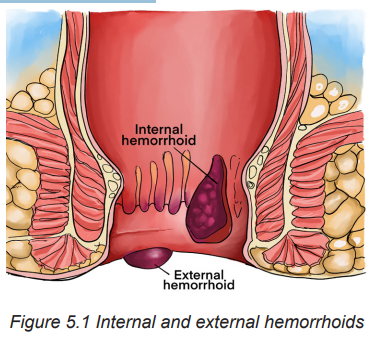
Internal hemorrhoids (Fig 5.1) are usually not painful unless they prolapse. They
may bleed during bowel movements. External hemorrhoids (Fig 5.1) cause itching
and pain when inflamed and filled with blood (thrombosed). Inflammation and
edema occur with thrombosis, causing severe pain and possibly infarction of theskin and mucosa over the hemorrhoid
5.1.4 Diagnostic measures
The Hemorrhoids can be diagnosed through a complete history, physicalexamination; (lubricated finger, gently inserted into the anal canal while asking the
patient to bear down the resting tone of the anal canal). Internal hemorrhoids are
generally not palpable on digital examination, anoscopy is performed. Hemorrhoidal
bundles will appear as bulging mucosa and anoderm within the open portion of the
anoscope. Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy can also be used. A complete blood cell
(CBC) count may be useful as a marker for infection. Anemia due to hemorrhoidalbleeding is possible.
Self-assessment 5.1
1) Briefly explain the pathophysiology of Hemorrhoids?2) Identify other diseases that would mimic the symptoms of Hemorrhoids?
5.2. The management of Hemorrhoids
Learning Activity 5.2
…Continuation of N.A case study
After physical exam, the medical doctor confirmed that Madam N.A is suffering
from Hemorrhoids. Regarding the treatment, Mr. S.D has received antiinflammatory drugs and advice on how to change her lifestyle
Questions related to the case study.
1) What is the surgical treatment plan adopted by the medical doctor for this
patient?
2) In group, discuss the different medication prescribed to this patient.3) List potential complications which may happen to Madam N.A.
5.2.1. The treatment plan of Hemorrhoids
Treatment is aimed at preventing constipation, avoiding straining during
defecation, maintaining good personal hygiene, and making lifestyle changes to
relieve hemorrhoid symptoms and discomfort .Lifestyle modification use of anti
inflammatory and surgery are the treatment of hemorrhoids
5.2.2. Associate nurse decision making
In the hospital, the associate nurse will perform tasks that are delegated by
registered nurses. The primary focus of care for haemorrhoids disease is educatingpatients. Encourage patient and caregiver to share concerns about lifestyle.
5.2.3. Complications of Hemorrhoids
The most common and serious complications of haemorrhoids include perianal
thrombosis and incarcerated prolapsed internal haemorrhoids with subsequent
thrombosis. They are characterised by severe pain in the perianal region possibly
with bleeding. In a short history of the perianal thrombosis, acute surgical incisionor excision is indicated, which can result in rapid relief of the painful symptoms
Self-assessment 5.2
Mr. K.M a patient on your department unit, has a Hemorrhoids. His wife runs to
the nursing station and says that you need to help her husband, he is in pain.
4) What additional data would you gather to confirm the statement of her
wife?5) What emotional support would you offer to Mrs. SM?
5.3 End unit assessment
End of unit assessment
1) Following a hemorrhoidectomy, what should the nurse advise the patient
to do?
a) Use daily laxatives to facilitate bowel emptying.
b) Use ice packs to the perineum to prevent swelling.
c) Avoid having a bowel movement for several days until healing occurs.
d) Take warm sitz baths several times a day to promote comfort and
cleaning.
2) A patient is scheduled for a hemorrhoidectomy at an ambulatory day
surgery center. An advantage of performing surgery at an ambulatory
center is a decreased need for
a) laboratory tests and perioperative medications.
b) preoperative and postoperative teaching by the nurse.
c) psychologic support to alleviate fears of pain and discomfort.
d) preoperative nursing assessment related to possible risks and
complications.
3) Apart from digital examination, what are other diagnostic tests indicated
in the case of hemorrhoids?
4) Changing life style is one way to prevent and treat hemorrhoids. What
are the lifestyle modifications would you recommend a patient with
haemorrhoids?
5) What is the role of medications in the treatment of haemorrhoids?The
goals of pharmacotherapy are to reduce pain and constipation in patients
with haemorrhoids.
6) What is the role of pregnancy in the aetiology of haemorrhoids?Pregnancy
clearly predisposes women to symptoms from haemorrhoids, although
the aetiology is unknown. Notably, most patients revert to their previously
asymptomatic state after delivery. The relationship between pregnancy
and haemorrhoids lends credence to hormonal changes or direct pressure
as the culprit.
7) What is the role of blood studies in the workup of hemorrhoids? A complete
blood cell (CBC) count may be useful as a marker for infection. Anemia
due to hemorrhoidal bleeding is possible
8) What is the role of colonoscopy in the workup of hemorrhoids?
Colonoscopy, virtual colonoscopy, and barium enema are reserved forcases of bleeding without an identified anal source.
