UNIT 1:FORECAST INCOME AND EXPENDITURE
Key unit competence: To be able to forecast an income and expenditure for an accounting period.

Accounting Management | Student Book | Senior Six
1.1.2.Definition of concepts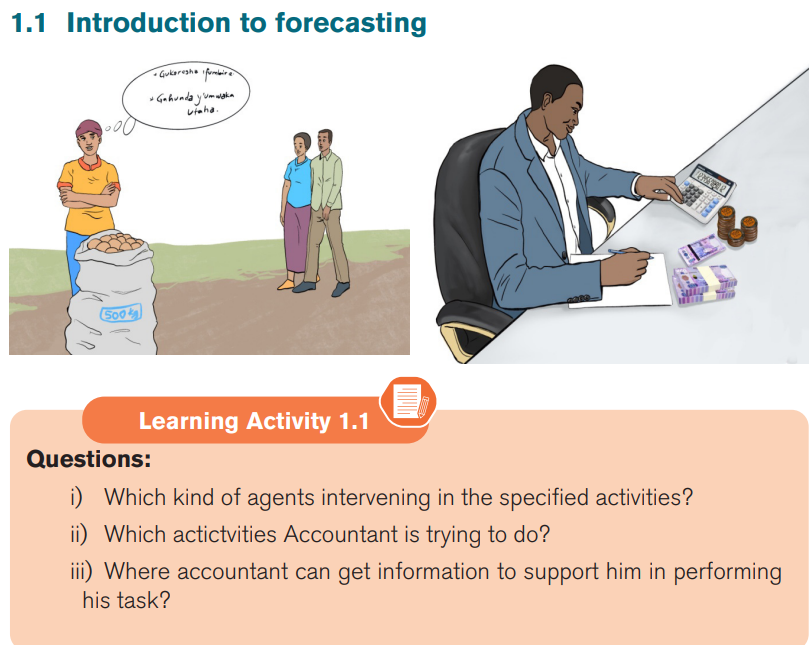
• Forecasting
It refers to the practice of predicting what will happen in the future by taking into
consideration events in the past and present. Basically, it is a decision-making
tool that helps businesses cope with the impact of the future’s uncertainty by
examining historical data and trends. It is a planning tool that enables businesses
to chart their next moves and create budgets that will hopefully cover whatever
uncertainties may occur.
• Financial forecasting
It is predicting a company’s financial future by examining historical performance
data, such as revenue, cash flow, expenses, or sales. This involves guesswork and
assumptions, as many unforeseen factors can influence business performance.
Common types of forecasts include cash flow forecast, projected profit and
loss and balance sheet forecast.
• Difference between Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting are both tools that help businesses plan for theirfuture. However, the two are distinctly different in many ways:
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
• Budgeting
It involves creating financial statements for a specific period, such as projected
revenue, expenses, cash flow and investments. It is usually conducted with input
from many different departments in order to come up with a holistic and detailed
report. Therefore, the budgeting process takes time to complete. The company
uses the budget to guide it in its financial activities. In other words, a budget is
a plan for a company’s future.
While budget are usually made for an entire year, forecasts are usually updated
monthly or quarterly. Through forecasting, a company can project where it’s
going, and it may adjust its budget and allocate more or less funds to an activity,
depending on the forecast. In summary, budgets depend on the forecast.
Forecasting is a common statistical task in business, where it helps to inform
decisions about the scheduling of production, transportation and personnel,
and provides a guide to long-term strategic planning. However, business
forecasting is often done poorly, and is frequently confused with planning and
goals. They are three different things.
• Forecasting
It is about predicting the future as accurately as possible, given all of available
the information , including historical data and knowledge of any future events
that might impact the forecasts.
Goals are what business would like to have happen. Goals should be linked to
forecasts and plans, but this does not always occur. Too often, goals are set
without any plan for how to achieve them, and no forecasts for whether they are
realistic.
Planning is a response to forecasts and goals. Planning involves determining
the appropriate actions that are required to make your forecasts match your
goals.
Forecasting should be an integral part of the decision-making activities of
management, as it can play an important role in many areas of a company.
Modern organizations require short-term, medium-term and long-term forecasts,
depending on the specific application.
1.1.2. Source of information in forecasting
The data used for forecasting methods can either come from primary sources
or secondary sources. Primary sources provide first-hand information, collected
directly by the person or organization that is doing the forecasting, Secondary
sources provide information that has already been gathered and processed byManagement Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
a third-party organization.
Collection of data is a first step in any statistical investigation. It is the basis
for any analysis and interpretations. Before collection of data, planner needs
to know the source in which you can get information. Below is key source of
information in forecasting
a) Market or industry data: Market or industry is Secondary source
supplying information that has been collected and published by other
entities. Examples of this type of information might be industry reports,
growth rate of economy, inflation, interest rate, tax incentives, etc. These
data are useful for predicting future. As this information has already been
compiled and analyzed, it makes the process quicker.
b) Competitors: A competitor is a person, business, team, or organization
that competes against you or your company. If somebody is trying to
beat you in a race, that person is your competitor. Information like sales
quantity, competitor’s price, market share, financial performance and
position will help business to predict future
c) Key customers: A customer is a person or business that buys goods
or services from another business. Customers are crucial because they
generate revenue. Without them, businesses would cease to operate.
Any decision and forecast that business need to make it is necessary to
first look at customer’s capacity to pay, quality needed, volume needed.
For example, in forecasting sales volume you need to know how much
customer is willing and able to buy.
d) Suppliers: A supplier is a person, company, or organization that sells or
supplies something such as goods or equipment to you. In forecasting
any company needs to gather information from suppliers to know how
many resources you are going to receive, the willingness of suppliers to
continue to serve you and financial capabilities of supplier to continue to
serve in future.
e) Procurement department: Also called the purchasing or sourcing
department, the procurement department is where the procurement
process starts and finishes. This is the place where the procurement
manager discusses the time for procurement process, list of goods, list of
suppliers, products price levels and tender awarded should go with the
other team members. This is also where each member of the procurement
team does its respective assignments. That is why it is very important for
the company to do forecast after consulting procurement department.
f) Humana resource department: Human resources (HR) department is
the division of a business that is charged with finding, screening, recruiting,
and training job applicants. It also administers employee-benefit programs.Human resource department is key source of information for forecasting
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
the labor cost and the availability of human contribution. Leaves, needed
skills labor, capacity building cost, tasks and responsibilities, salaries and
wages, fringe benefits, labor turnover, labor contracts.... )
g) Financial goal and objectives: Financial objectives are the goals or
targets related to the financial performance of a business. There are six
types of financial objectives: revenue objectives, cost objectives, profit
objectives, cash flow objectives, investment objectives and capital
structure objectives. Those objectives offer information to budgetingdepartment to be based on in forecasting future.
Application activity 1.1
1. Define the following concepts:
A. Forecasting.
B. Budgeting
C. Financial Forecasting
2. Manager of XYZ Ltd has planned to forecast future sales but he
is unsure on where he can get reliable information to be based on
while making prediction. Advise him five key sources of informationfor forecasting.
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
1.1.Forecasting Methods for income and expenditure
Learning Activity 1.2

i) What are two variables shown on above image?
ii) What come to your mind once you see image above?
There are two primary categories of forecasting: quantitative and qualitative.N = Total number of periods
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
A.Quantitative Methods
When producing accurate forecasts, business leaders typically turn to
quantitative forecasts, or assumptions about the future based on historical data.
1.1.1.Straight Line
The straight-line method assumes a company’s historical growth rate will
remain constant. Forecasting future revenue involves multiplying a company’s
previous year’s revenue by its growth rate. Although straight-line forecasting is
an excellent starting point, it doesn’t account for market fluctuations or supply
chain issues.
For arriving to the forecasted future revenue or cost the following step will be
followed:
1. The first step in straight-line forecasting is to determine the sales/cost
growth rate that will be used to calculate future revenues.
2. To forecast future revenues, take the previous year’s figure and multiply
it by the growth rate.
For example, Total income of Akeza Ltd for year ended 31 December 2021 and
2022 is Frw 24,000,000 and Frw 30,000,000 respectively. Compute growth
rate and forecast revenue for the year ended 2023if the calculated will continueto grow by same growth.
Solution:
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
future. This method involves more closely examining a business’s high or low
demands, so it’s often beneficial for short-term forecasting. For example, you
can use it to forecast next month’s sales by averaging the previous quarter.
Moving average forecasting can help estimate several metrics. While it’s most
commonly applied to future stock prices, it’s also used to estimate future
revenue.
To calculate a moving average, use the following formula:
A1 + A2 + A3 … / N
Formula breakdown:
A = Average for a period
N = Total number of periods
1.1.3.Time series
This is a sequence of variable values like sales or production that change over a
uniform set of time. The variable values represent statistical data while time can
be in seconds, hours, days, weeks, etc.
Time series analysis is a specific way of analyzing a sequence of data points
collected over an interval of time. In time series analysis, analysts record data
points at consistent intervals over a set period of time rather than just recording
the data points intermittently or randomly.
All-time series contain at least one of the following four components:
1. Secular trend: The general underlying tendency of the time series data
to increase, decrease or remain constant for a long period of time.
2. Seasonal variations: Are periodic movements of the data where the
duration is less than a year. The factors that mainly cause these variations
are:
a) Climatic changes
b) The customs and habits that people follow at different times
3. Cyclical variations: Are periodic movements within the time series
data where the duration is more than a year. They are not as regular as
the seasonal variations but their sequence of change is the same. The
causes of the cyclical variations are the four phases of an economic cycle
which include: the boom/peak, decline/downturn, depression/trough and
recovery/upswing.4. Random/ irregular erratic variations: These are completely
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
unpredictable variations within the data caused by unpredictable events
like sickness, machine breakdown, weather conditions, strikes etc. They
are non-recurring influences which cannot be mathematically captured
yet they have profound consequences on a time series.The equation for trend is:
Y = a+ bx
Formula breakdown:
Y= Dependent variable (the forecasted number)
b = line’s slopex = Independent variable (time numbered from 0 upwards)
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
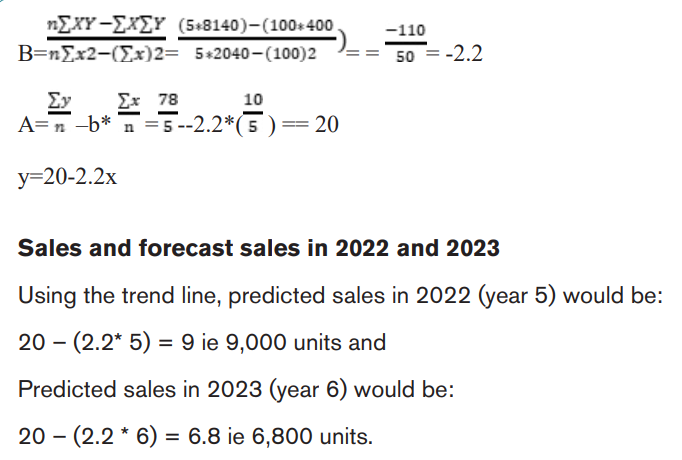
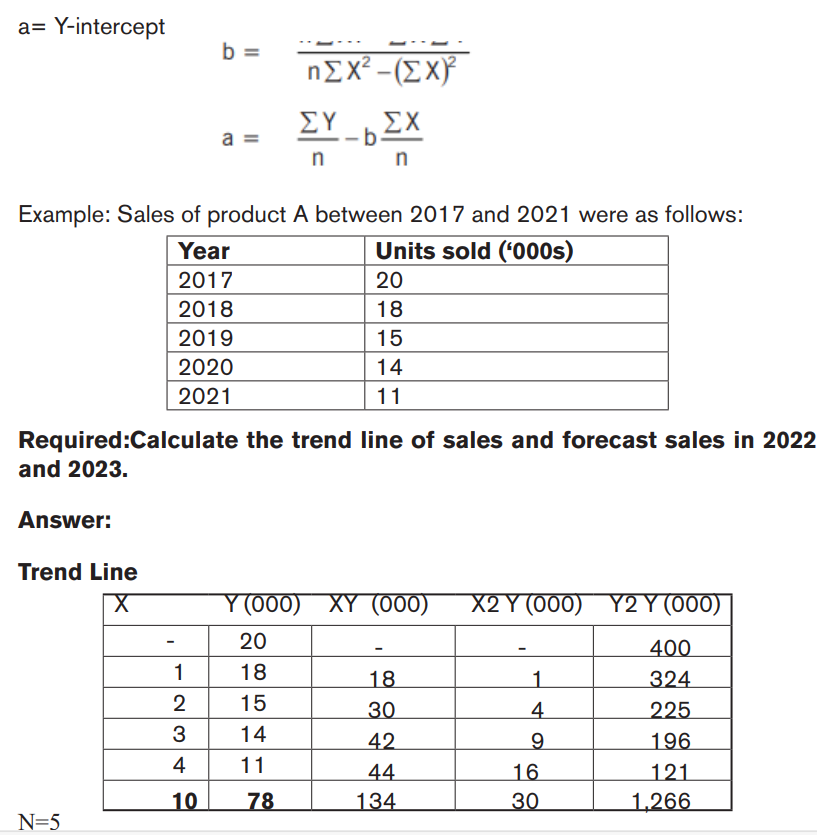
1.1.4.Simple Linear Regression/least squares method
Linear regression analysis (the least squares method) is one technique for
estimating a line of best fit. Once an equation for a line of best fit has been
determined, forecasts can be made. Simple linear regression forecasts metrics
based on a relationship between two variables: dependent and independent. The
dependent variable represents the forecasted amount, while the independent
variable is the factor that influences the dependent variable.The equation for simple linear regression is:
Y = a+ bx
Formula breakdown:
Y = Dependent variable (the forecasted number)
b = Regression line’s slope
x = Independent variable
a= Y-intercept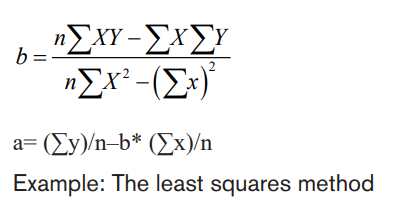
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six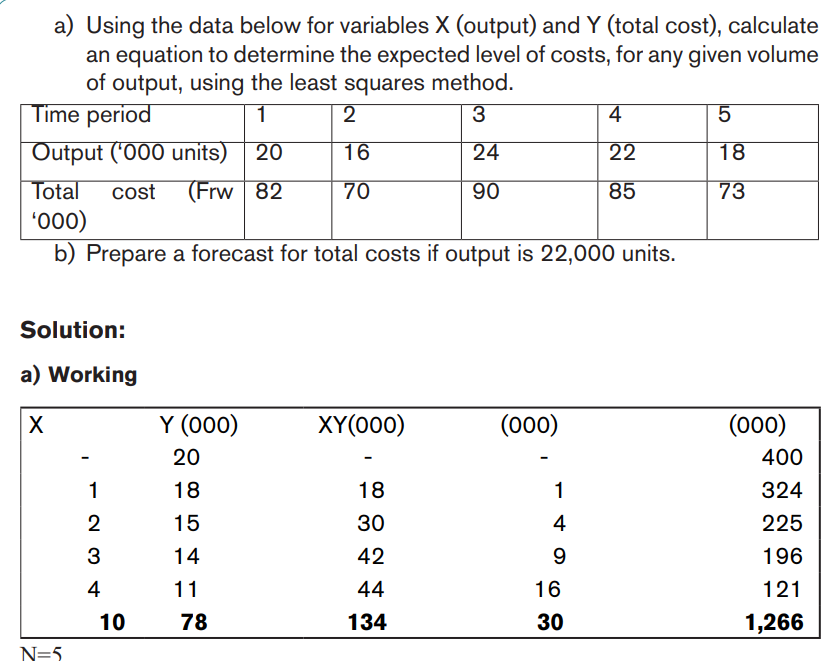

Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
Qualitative forecasting relies on experts’ knowledge and experience to predict
performance rather than historical numerical data.
These forecasting methods are often called into question, as they’re more
subjective than quantitative methods. Yet, they can provide valuable insight into
forecasts and account for factors that can’t be predicted using historical data.
1.1.5.Market Research
Market research is essential for organizational planning. It helps business leaders
obtain a holistic market view based on competition, fluctuating conditions,
and consumer patterns. It’s also critical for start-ups when historical data isn’t
available. New businesses can benefit from financial forecasting because it’s
essential for recruiting investors and budgeting during the first few months of
operation.
When conducting market research, begin with a hypothesis and determine
what methods are needed. Sending out consumer surveys is an excellent way
to better understand consumer behavior when you don’t have numerical data to
inform decisions.
1.1.6. Delphi Method
This method incorporates both judgmental and subjective factors. It is an
iterative process that allows experts to make an objective forecast. There are 3
groups of participants involved namely:
1. Decision makers: group usually consists of 5 - 10 experts who will be
making the actual forecast.
2. Staff personnel: assist the decision makers by preparing, distributing,
collecting and summarizing a series of questionnaires and survey results.
3. Respondents: The respondents are a group of people whose views
and judgments are valued and are being sought. This group provides
input to the decision makers before the forecast is made. In this method,
it is crucial to select participants from different functional fields due to the
following reasons:
– To get diverse opinions
– To have diversity of ideas and experience
– To reduce prediction error– To improve on quality of final results
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
1.2. Forecasting Models for income and expenditure
Application activity 1.2
Alex Mugabo is Budget manager of MG factory a company based in Kigali to
produce and sales furniture to household. The following table shows the actualunits sold from 2010 to 2016 by MG factory
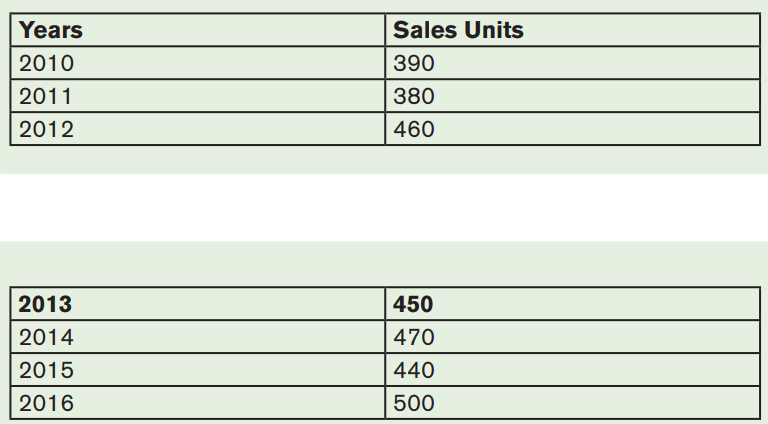
Required
d) Take a moving average of the annual sales over a period of three
yearse) Based on calculated moving value in a) Advice Alex on future sales
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
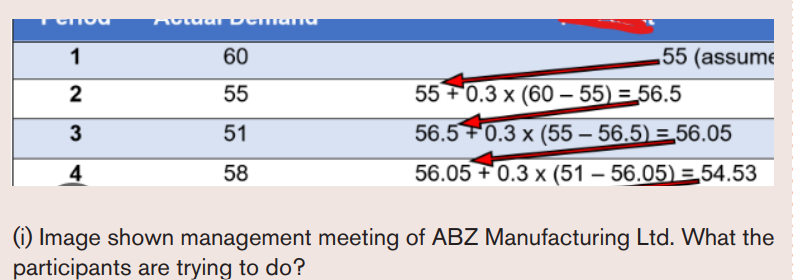
vi. Based on knowledge acquired from previous methods of forecasting
what is method identified in the image above?vii.What the participants in this image trying to do?
Forecasting models are one of the many tools’ businesses use to predict
outcomes regarding sales, supply and demand, consumer behavior and more.
These models are especially beneficial in the field of sales and marketing. There
are several forecasting methods businesses use that provide varying degrees
of information. From the simple to the complex, the appeal of using forecasting
models comes from having a visual reference of expected outcomes.
There are numerous ways to forecast business outcomes; there are four main
types of models that companies use to predict revenue and expenditure in the
future.
1.2.1. Time Series Model
This type of model uses historical data as the key to reliable forecasting. You’ll
be able to visualize patterns of data better when you know how the variables
interact in terms of hours, weeks, months or years. Time series has four main
components which are trend, seasonal variations, cyclical variations and random
variations.
1.2.2. Econometric Forecasting ModelEconometric forecasting models are systems of relationships between variables
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
such as GNP, inflation, exchange rates etc. Their equations are then estimated
from available data, mainly aggregate time series. Econometric models attempt to
quantify the relationship between the parameter of interest (dependent variable)
and a number of factors (explanatory variables) that affect the dependent
variable. A simple example of an econometric model is one that assumes that
monthly spending by consumers is linearly dependent on consumers’ income in
the previous month.
1.2.3. Judgmental forecasting Model
Various forecasting models of the judgmental kind utilize subjective and intuitive
information to make predictions. For instance, there are times when there is no
data available for reference. Launching a new product or facing unpredictable
market conditions also creates situations in which judgmental forecasting
models prove beneficial.
Product life cycle and market knowledge: Management should know that,
most products have a limited product life cycle which will show different sales
and profitability patterns at different stages of the life cycle.
In time series method, analysis makes the assumption that the sales figures
will continue to change in line with the trend. Such statistical projections are
helpful in forecasts but a manager should not ignore knowledge of the market
or product itself.
The trend will not continue unchanged in practice as most products have a
limited product life cycle which will show different sales and profitability patterns
at different stages of the life cycle.
The product life cycle is generally thought to split naturally into five separate
stages: Development, Launch, Growth, Maturity and Decline.
So, a business has to consider not only its products’ sales trends but also
the stage of the life cycle of each product and the state of the market for that
product.
However, the analysis could go even further, into the general state of the
environment in which the business operates. This can often be efficiently done
by carrying out a PEST analysis. This examines the following factors: Political,Economic, Social, And Technological.
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
1.2.4. Delphi Model
This method is commonly used to forecast trends based on the information
given by a panel of experts. It assumes that a group’s answers are more useful
and unbiased than answers provided by one individual. The total number of
rounds involved may differ depending on the goal of the company or group’s
researchers.
These experts answer a series of questions in continuous rounds that ultimately
lead to the “correct answer” a company is looking for. The quality of information
improves with each round as the experts revise their previous assumptions
following additional insight from other members in the panel.
Application activity 1.3
Most products have a limited product life cycle which will show different
sales and profitability patterns at different stages of the life cycle.
Required :List and explain four cycles of products
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
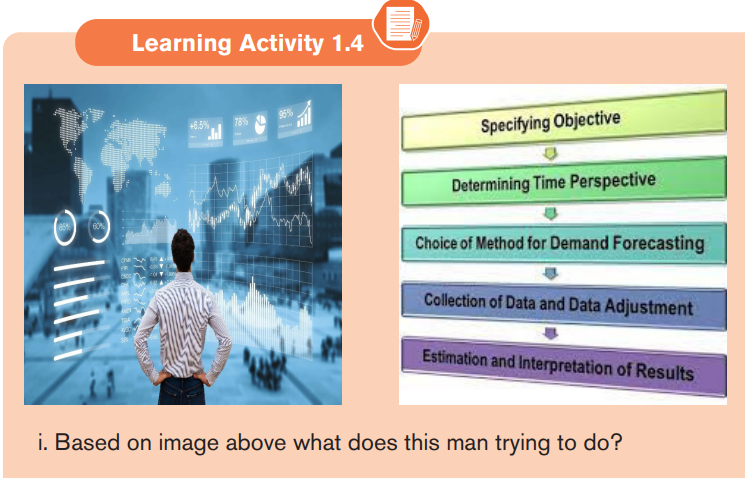
1.3. The Process /Step of Forecasting
Management of institutions/ company needs to follow carefully the process in
order to get accurate results. Below is the process for forecasting
1.3.1. Determine what the forecast is for
The first step in the process is to determine what kind of forecast you need to
make. Remember that forecasts are made in order to plan for the future. To do
so, we have to decide what forecasts are actually needed. This is not as simple
as it sounds. For example, do we need to forecast sales or demand? These
are two different things, and sales do not necessarily equal the total amount of
demand for the product. Both pieces of information are usually valuable.
1.3.2. Select the items for the forecast.
This step involves identifying what data are needed and what data are available.
This will have a big impact on the selection of a forecasting model. For example,
if you are predicting sales for a new product, you may not have historical sales
information, which would limit your use of forecasting models that require
quantitative data.
1.3.3. Select the time horizon.
A time horizon is a fixed point of time in the future at which point certain
processes will be evaluated or assumed to end. Forecasts in Business are
classified according to period, time and use. There are long term forecasts and
short-term forecasts. Operation managers need long range forecast for making
strategic decisions related to products, processes and facilities. They also need
short term forecasts to assist them in making decisions about production issues
that span, only few weeks. Forecasting forms an integral part of planning thatwhy production managers must be aware about the horizon of forecasts.
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
1.3.4. Select the forecast model, type and method.
Based on what you want to forecast for, you should select appropriate model
and type that will give you reliable results, there are number of factors that
will influence you in choosing right forecasting model, amount and types of
available data, degree of accuracy required, forecast time horizon and kind
of data. Appropriate method of sales forecasting is selected by the company
taking into account all the relevant information, purpose of forecasting and the
degree of accuracy required.
1.3.5. Gather data to be input into the model
There are generally two kinds of information available for forecasting: statistical
data which is generally historic numerical data and the accumulated judgment and
expertise of key personnel. Also, other relevant data such as the time and length
of any significant production downtime due to equipment failure or industrial
disputes may prove useful and therefore may also be collected in gathering
data they will consider primary source of information (information collected
from internals) and secondary source of information (information collected from
externals) all that information will give required data in forecasting.
1.3.6. Make the forecast.
Perform initial analysis of the data to see if it is usable. Check trends and patterns
shown in the data to see if they are helpful. Cut out any unwanted data. Using
your chosen model, run the data, analyze it, and make the forecast.
1.3.7. Verify and Implement the results
Every step is checked, refinements and modifications are made at the end you
will get outcomes from the forecasting model and plan accordingly. Forecasting
isn’t a measure just to get the business up and running. Successful companies
use their market forecast to calculate their progress and use it as a managementtool to run the business better.
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
Application activity 1.4
The General Manager of AOB Limited is planning to launch a new product
Urwiwacu which is new product to Rwanda market and the rest of east Africa
but is unsure on profitability of Urwiwacu. CEO convening meeting with
chief operation Manager, Sales Manager and budget manager to discuss
the feasibility of the proposal to launch Urwiwacu. The following concerns
were raised by the participants: the budget manager has concern of timing
the launch of Urwiwacu due to the lack of sufficient information related to
the cost, revenue and profitability. He has concern over the method that
AOB can use to estimate the profit expected from Urwiwacu. The Chief
Operation Manager tells the meeting that the raw materials needed for
production will be available at a high cost and this is due to the lack of local
supplier. The sales manager says that the department has been trying to
collect data related to Urwiwacu and tells the participants that the product
is needed on market and customer will be happy to buy product but he was
not sure of price to be charged in order to cover cost and remain with profit.
General manager requests all participants to take one month and come up
with forecasted revenue and cost from Urwiwacu product.
Required: You have completed senior six and you are hired by AOB ltd in
department of budgeting. Referring to the case above Apply first 4 steps offorecasting
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
1.4. Challenges to forecasting
Learning Activity 1.5
a) What do you think about the problems this man would have after
looking above photo?
Every large businesses or medium perform financial forecasting for various
reasons such as projecting future sales, understanding working capital needs,
launching new product and more. With accurate financial forecasting, businesses
can easily achieve both their short-term and long-term goal but forecasting has
its challenge:
a) Forecasting Time Period
Shorter the period more is the accurate financial forecasting. Longer the period
less is the accurate and difficult financial forecasting. Mostly, less difficulty
comes for a short span and more difficulty comes for a long span. In simple
words, we say the shorter forecasting period will always be more accurate as
compared to the larger prediction time.
b) Data Collections
Collecting and gathering all the business finance data to proceed further can
never be easy. This task can take a week to weeks to gather all the information
to build the cash flow projection and revenue forecast. Collecting these data for
forecasting is one of the huge financial forecasting problems.
c) Problems with the Input data
Forecasts using linear analysis can be common, but this type of forecasting
fails to account for the uncertainty in the future. In statistics, the assumptionof linearity is necessary when certain assumptions are made about the future.
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
However, there is no assurance that a relationship between two variables
will continue in the future. Many factors come into play when you’re making
a forecast, especially when it’s on an important matter. Human error which is
common can mean the difference in wrong predictions.
d) Unforeseeable Events
Another financial forecasting problem is unforeseeable. In spite of the businesses
achieve the quantitative and qualitative forecasting techniques to make their
prediction accurate, unforeseeable can never be achieved. These components
can vary inherently, and reach the risks of forecasting. For example, let us take
an example of supermarket that opens the store with the pillar financial growth.
It leads to affecting the other supermarket in the particular area. It can never be
forecasted.
e) Accuracy of past data
Financial forecasting is performed based on past business data to predict the
future. Take an instant that your business average growth as 10% as a stable
one for the past 4 years, you could predict your business finance for the next 4
years as 10%. While you use this kind of system wider, then you are on the way
to financial forecasting problems.
If a company has variable results year over year, using the previous period data
is worthless. Additionally, the financial data will not be available for the startups,
as they should go by approximate estimation without any accurate idea.
Note, Apart from the above-mentioned challenges there are many other
challenges such as Social changes, Technological advances, Environmental
changes, Political and economic changes, No easy way to capture forecast
assumptions of all managers, Lack of tools to analyze historical trends, etc.
Application activity 1.5
You are employed by ABZ company as sales officer. Budget department
sent to you target sales value for first quarter but you are not sure if you will
achieve target.
You know that forecasts are subject to error, but the likely errors vary from
case to case due to:
a) The further into the future the forecast is for; the more unreliable it is
likely to be.
b) The less data available on which to base the forecast, the less reliable
the forecast.
c) The pattern of trend and seasonal variations cannot be guaranteed to
continue in the future.
d) There is always the danger of random variations upsetting the patterns.Required: Explain 3 main challenges of forecasting.
Skills Lab 1
The students visit one of the nearest manufacturing industries. Let us take
MUTEXRWA Industry as our case study.
Let us approach production departmental manager and share us the
methods used in forecasting their production volume and the challenges
they face with. We have selected one kind of products they produce
which is Uniforms clothes for secondary schools. The Sales departmental
manager is about sharing how forecasting is most useful in their prediction
of production sales level. “We collect forecasting information from Ministry
of education to know school calendar year and new schools are about
opening.
We mostly use time series method based on the calendar year set by
Ministry of Education as it is the key determinant of our uniform clothes
demand, this where the method of time series comes as the time series has
a component called seasonal variation,
For previous academic terms we have much data recorded in our financial
statements and their trend analysis report is there, we base on the above
historical trends data and we use time series mathematical calculations to
predict the production demand for the future.
Let Sales production manager also tells us about the challenges
MUTEXRWA faces in forecasting,
“There are less data available to be based on, this lead less reliability on
forecast because in our sector the demand of uniform clothes is limited,
the many customers demand diversity design of clothes, We also meet
with challenges of Technology changes, here I want to mean that the past
is not a reliable indication of likely future events. For example, the availability
of faster machinery may make it difficult to use current output levels as the
basis for forecasting future production output, there many other factors out
of our control such Economical and political factors
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
Also as in forecasting uncertainty future events there are many assumptions
used, this become challenge to our company because each manager has
his/ her own assumption. Apart from the above challenges, I would like to
conclude by saying that forecasting is the useful tool in company as it is
used to predict company future operations” Said by MUTEXRWA Sales
departmental manager.
Before leaving this industry, let us also have a short interview with
MUTEXRWA Production departmental Manager. Let us ask him whether
forecasting is the recommendable basing on its result to their industry.
“Yes, forecasting is highly recommendable to all companies as it helps of
predicting what will happen in the future by taking into consideration events
in the past and present and this enables businesses to predict their next
moves and create budgets that will hopefully cover whatever uncertaintiesmay occur” said by Production departmental manager.
End of unit assessment 1
Question 1
Time series is method for forecasting where independent variable is time.
What do you understand by time series? Give examples of time series.
Question2
If manager wants to forecast; he will need to collect information to be based
on, those collected information are either primary source or Secondary
source.
Advise him 5 sources of forecasting information and specify whether that
source is primary or secondary.
Question 3
The data below shows the monthly sales (Frw million) made by Mukungwa
ltd. for the year 2020.Month
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
Required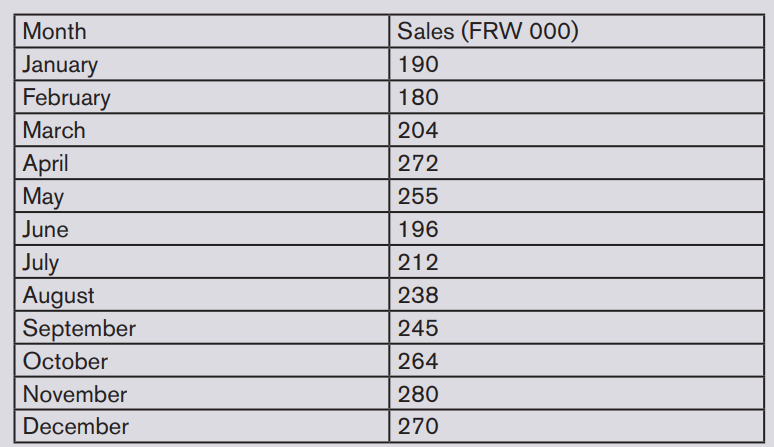
c) Calculate the moving average of order 3
Question 4
Methods for forecasting are classified into Quantitative and Qualitative.
Explain 2 qualitative methods.
Question5
Most of time forecast and actual results differ significantly. Elaborate clearly
3challenges of forecasting.
Question 6
In forecasting steps there is time horizon, Explain three forecasting timehorizons in forecasting
Management Accounting | Experimental Version | Student Book | Senior Six
