UNIT 14: AUDIT REPORT
Key unit competence: To be able to prepare an appropriate report
Introductory activity
In modern world, organizations are required to report concerning the general
performance to their stakeholders on regular basis. In this regard, different
reports such as audit reports, activity reports, and financial reports are being
prepared and submitted timely to concerned stakeholders. Some of those
reports are statutory and some are not. Those reports are therefore used by
different stakeholders to make informed decisions.
Question: How do you call the document prepared by the auditor at the end ofaudit process which contains his conclusion, opinion and recommendations?
14.1. Auditor’s report
Learning activity 14.1
After observing pictures above, identify the documents related to the audit
work?
14.1.1. Meaning of audit report
An audit report is a document that expresses an auditor’s opinion on a company’s
financial performance and compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles (GAAP).An audit report is a written opinion of an auditor regardingan entity’s financial statements.
An audit report is a document from the auditor of a company that is the end result
of the audit process. It states the auditor’s opinion on whether the company’s
financial statements are in compliance with the Generally Accepted AccountingPrinciples (GAAP) and if they are free from material misstatement.
The audit report is the end-product of the external audit process. It is the
document in which the auditor expresses his/her professional judgment onwhether the financial statements present a ‘true and fair view’.
Is a document prepared by an auditor at the end of auditing process that
consolidates all of his/her findings and observations about a company’s financialstatements.
14.1.2. Basic elements of an audit report
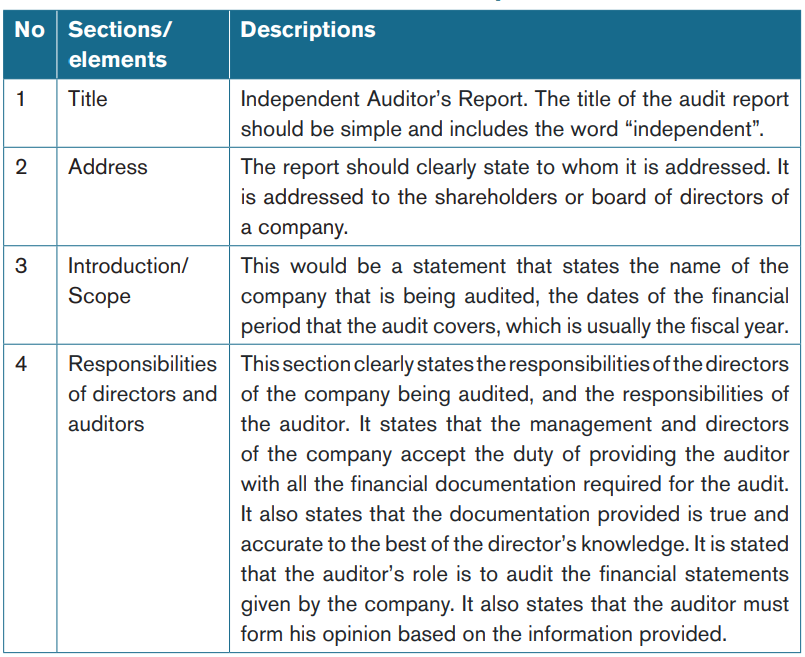
a) Example of audit report
An example of an unmodified audit report is set out below.
INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT
(Appropriate addressee)
Report on the financial statements
We have audited the accompanying financial statements of BATAMU Ltd
Company, which comprise the statement of financial position as at 31
December 2021, and the statement of comprehensive income, statement of
changes in equity, and statement of cash flows for the year then ended, and asummary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory information.
Management’s responsibility for the financial statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these
financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting
Standards, and for such internal control as management determines is
necessary to enable the preparation of financial statements that are free frommaterial misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
Auditor’s responsibility
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements
based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with International
Standards on Auditing. Those standards require that we comply with ethical
requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assuranceabout whether the financial statements are free from material misstatement.
An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about
the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. The procedures
selected depend on the auditor’s judgment, including the assessment of
the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due
to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, the auditor considers
internal control relevant to the entity’s preparation and fair presentation of the
financial statements in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate
in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the
effectiveness of the entity’s internal control. An audit also includes evaluating
the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of
accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overallpresentation of the financial statements.
We believe that the audit evidence that we have obtained is sufficient andappropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Opinion
In our opinion, the financial statements give a true and fair view (or present
fairly, in all material respects,) of the financial position of BATAMU Ltd
Company as at 31 December 2021, and of its financial performance and itscash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial
Reporting Standards.
(Auditor’s signature)
(Date of the report)
(Auditor’s address)
b) Qualities of a good audit report
Qualities of a good audit report are:
• It should not be biased to any party with financial stake in the business.
• It should be forceful.
• It should be based on constructive criticism/ideas.
• It should offer constructive and timely suggestions to the managementso as to solve problems highlighted in the report.
• It should be clear and concise.
c) Importance of audit report
For the audited company
• Helps to reveal a true and fair view of the company’s financial statements
• Reveals errors and frauds committed or inherent in the company’sbooks of accounts
• Traces the strength and weaknesses of the internal control system
• Shows if the internal auditing function is working properly
• Helps to ensure if the company fulfils legal requirements
For the shareholders or associates
• Helps them to ensure if their shares are earning interest by the companyand if it is profitable to continue to invest in the company
• Helps to know if the statutory requirements are being implemented bythe company
For the tax authorities
• The audit report ensures to the government if the taxes due by the
company are properly given by the company
• Ensures if other legal requirements like social security contributions are
being implemented
• Ensures that the company respects accounting principles, company’s
Act and other regulations in application
• Ensures if the public funds are being used properly by governmentinstitutions and other private institutions
For the thirds parties
• For employees audit report helps them to ensure the continuity of the
company’s activities so as to ensure their job security and continuity of
employment
• For the customers they are proud of their relationships with their
supplier (audited company) if good management and fair and true
image are revealed by the audit report
• For suppliers, they ensure their market with the audited company if true
and fair view is revealed by the auditor’s report
• For banks and financial institutions, they ensure refund of their loansgranted to the audited company
14.1.3. The auditor’s report on financial statements
The auditor is required to produce an audit report at the end of the audit which
sets out his/her opinion on the truth and fairness of the financial statements. The
report contains a number of consistent elements so that users know the audithas been conducted according to recognized standards
The audit report refers to financial statements and you need to know what theseare. They consist of the following:
• The statement of financial position (or balance sheet).sss
• The statement of profit or loss ( Income statement )
• The statement of changes in equity.
• The cash flow statement.
• The notes to the account
ISA 700 Forming an opinion and reporting on financial statements establishes
standards and provides guidance on the form and content of the auditor’s
report issued as a result of an audit performed by an independent auditor on the
financial statements of an entity. It states that the auditor shall form an opinion
on whether the financial statements are prepared, in all material respects, inaccordance with the applicable financial reporting framework.
In order to form the opinion, the auditor needs to conclude as to whether
reasonable assurance has been obtained that the financial statements are free
from material misstatement. The auditor’s conclusion need to consider thefollowing.
• Whether sufficient appropriate audit evidence has been obtained (ISA
330)
• Whether uncorrected misstatements are material (ISA 450)
• Whether the financial statements adequately disclose the significant
accounting policies selected and applied
• Whether the accounting policies selected and applied are consistent
with the applicable financial reporting framework and are appropriate
• Whether accounting estimates made by management are reasonable
• Whether the information in the financial statements is relevant, reliable,
comparable and understandable
• Whether the financial statements provide adequate disclosures to
allow users to understand the effect of material transactions and events
on the information presented in the financial statements
• Whether the terminology used in the financial statements is appropriate
• The overall presentation, structure and content of the financial
statements
• Whether the financial statements represent the underlying transactions
and events so as to achieve fair presentation
• Whether the financial statements adequately refer to or describe theapplicable financial reporting framework
Application activity 14.1
1. John is a member of ABX ltd Company. Help him to understand the
importance of audit report.2. What are the qualities of a good audit report?
14.2. Unmodified auditor’s report and Modified opinions
Learning activity 14.2

Read the words on the picture above and give it opposite
Now we are going to look at the types of audit report that exist. First and simplestis the unmodified audit report.
14.2.1. Unmodified audit’s report
Definition of unmodified audit report
An unmodified audit report is an audit report containing an audit opinion not
modified in any way – either by changing the unmodified opinion or by adding
an extra paragraph such as an ‘emphasis of matter’ or ‘other matters’ paragraphafter the opinion paragraph.
An unmodified opinion is the opinion expressed by the auditor when the auditor
concludes that the financial statements are prepared, in all material respects, inaccordance with the applicable financial reporting framework.
If the auditor concludes that the financial statements as a whole are not free from
material misstatement or cannot obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence to
make this conclusion, the auditor must modify the opinion in accordance withISA 705 Modifications to the opinion in the independent auditor’s report.
We discuss modifications to the opinion in the following sub heading.
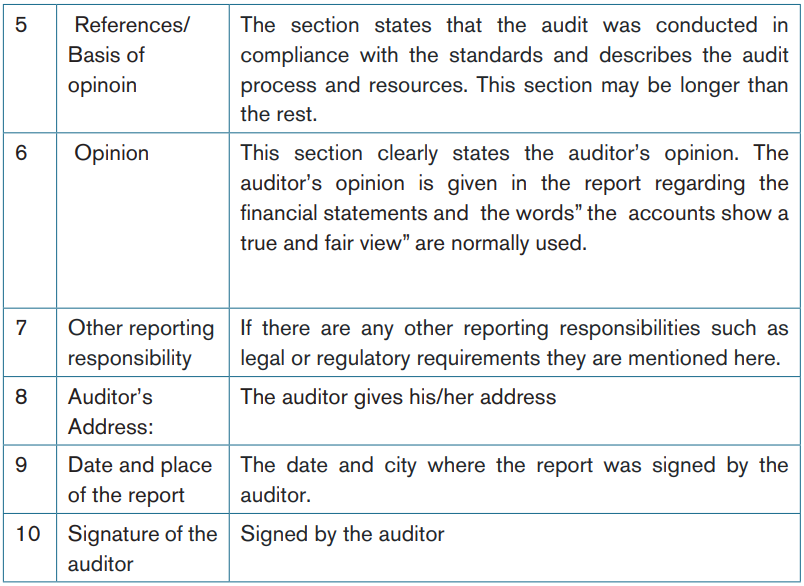
14.2.2. Modified opinions
A modified opinion is required when:
The auditor concludes that the financial statements as a whole are not free from
material misstatements or the auditor cannot obtain sufficient appropriate audit
evidence to conclude that the financial statements as a whole are free frommaterial misstatement.
Types of modifications
There are three types of modified opinions:
a. A qualified opinion
b. An adverse opinionc. A disclaimer of opinion
Qualified opinion
A qualified opinion must be expressed in the auditor’s report in the followingtwo situations:
1. The auditor concludes that misstatements are material, but not pervasive tothe financial statements.
Material misstatements could arise in respect of:
• The appropriateness of selected accounting policies
• The application of selected accounting policies
• The appropriateness or adequacy of disclosures in the financialstatements
2. The auditor cannot obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence on which
to base the opinion but concludes that the possible effects of undetectedmisstatements, if any, could be material but not pervasive.
The auditor’s inability to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence is alsoreferred to as a limitation on the scope of the audit and could arise from:
• Circumstances beyond the entity’s control (e.g. accounting recordsdestroyed)
• Circumstances relating to the nature or timing of the auditor’s work
(e.g. the timing of the auditor’s appointment prevents the observationof the physical inventory count)
• Limitations imposed by management (e.g. management prevents
the auditor from requesting external confirmation of specific accountbalances)
Adverse opinion
An adverse opinion is expressed when the auditor, having obtained sufficient
appropriate audit evidence, concludes that misstatements are both material andpervasive to the financial statements.
Disclaimers of opinion
An opinion must be disclaimed when the auditor cannot obtain sufficient
appropriate audit evidence on which to base the opinion and concludes that
the possible effects on the financial statements of undetected misstatements, ifany, could be both material and pervasive.
Summary of modifications and impact on the auditor’s report
The following table summarizes the different types of modified opinions that canarise:
14.2.3. Emphasis of matter and other matter paragraphs in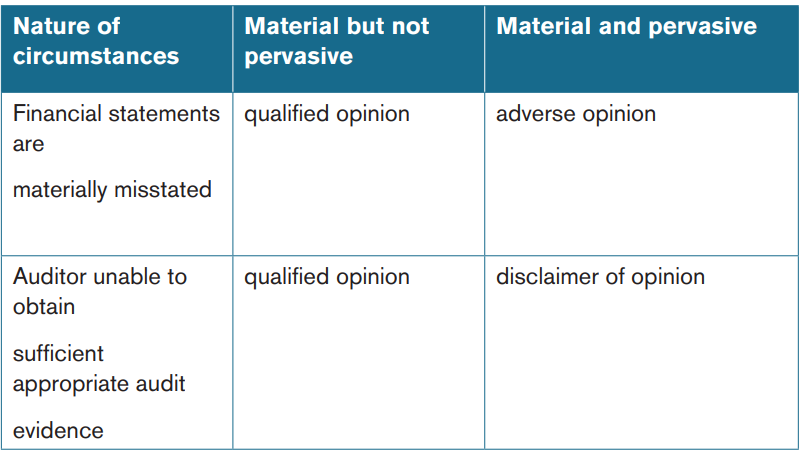
the auditor’s report
a) Emphasis of matter paragraphs
An emphasis of matter paragraph is a paragraph included in the auditor’s report
that refers to a matter appropriately presented or disclosed in the financial
statements that, in the auditor’s judgment, is of such importance that it isfundamental to users’ understanding of the financial statements.
Emphasis of matter paragraphs are used to draw readers’ attention to a matter
already presented or disclosed in the financial statements that the auditor feels
is fundamental to their understanding, provided that the auditor has obtainedsufficient appropriate audit evidence that the matter is not materially misstated.
b) Other matter paragraphs
Other matter paragraphs are used where the auditor considers it necessary to
draw readers’ attention to a matter that is relevant to their understanding of theaudit, the auditor’s responsibilities or the auditor’s report.
The other matter paragraph must be included immediately after the opinion
paragraph and any emphasis of matter paragraph, or elsewhere in the auditor’sreport if the content of it is relevant to the other reporting responsibilities section.
The content of the other matter paragraph must reflect clearly that the other
matter is not required to be presented and disclosed in the financial statements,
and does not include information that the auditor is prohibited from providing
by law and regulations or other standards, or information that is required to beprovided by management.
Application activity 14.2
1. Explain unmodified auditor’s report.
2. Identify three (3) types of modified auditor’s opinions.
Skills lab activity 14
In learning group, teacher presents to their students an unmodified audit
report in which some elements are missing, ask them to discuss about it.
Through discussions, the students must discover the missing elementsand rewrite the appropriate report.
End unit 14 assessment
1. What is the importance of audit report to audited company?
2. Explain two main types of audit report.
3. Explain the basic elements of an audit report
4. Define the term audit report
5. Explain emphasis of matter paragraphs.
6. Outline the qualities of a good audit report.
7. What are the auditable finanancial statementsReferences
1. International, E. W. (2015). Audit and Assurance . Berkshire- United
Kingdom: Emile Woolf International.
2. MANAS’SEH, P. N. (2000). PRINCIPLES OF AUDITING . NAIROBI:
McMore Accounting Books.
3. MEDIA, B. L. (2009). AUDIT AND ASSURANCE (INTERNATIONAL).
London: BPP Learning Media Ltd.
4. MEDIA, B. L. (2019). Audit and Assurance . London: BPP Learning Media
Ltd .
5. MEDIA, B. L. (2020). Audit and Assurance . London : BPP Learning Media.
6. Sagwa, P. N. (2015). Auditing and Assurance . Nairobi-Kenya: Manifested
Publishers Ltd.
7. SALEEMI, N. A. (1997). AUDITING SIMPLIFIED . NAIROBI, KENYA: Uni-Trade Printers Ltd
