UNIT 2: BUSINESS PLAN FOR AN ENTERPRISE
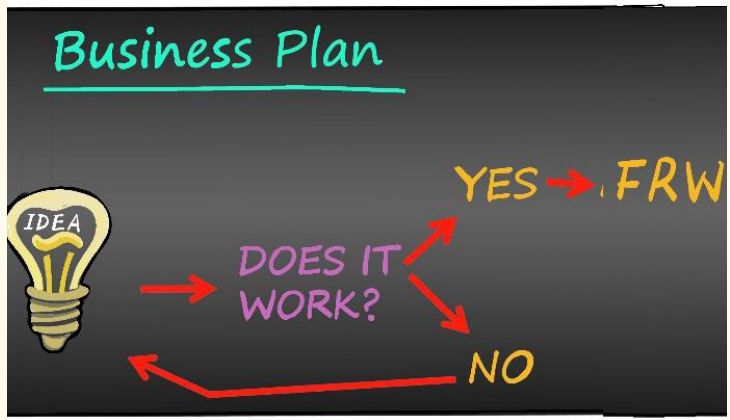
Key unit competence: To be able to prepare a business plan for an enterprise
Introductory activity
Munezero and Kabera are twin brothers and Accounting graduates. They have always had a dream of being self-employed. Munezero wanted to start a restaurant and Kabera wanted to start a piggery project. Both had knowledge of entrepreneurship from school, secured financing from their parents as well as personal savings accumulated while at school.
Munezero starts immediately and after a few months the business started doing well but later before the year ended, he was in a great loss and decided to close down.
Kabera took his time to discover and learn about the business he intended to start and devised/developed a plan and laid strategies on how to put the plan in action. He started later after five months, but a few challenges came his way though he never gave up. He now has over 100 pigs and has recently secured a sausage making machine and obtained enough market in Kigali and outside the country to supply her products.
Questions
a) According to the above case, what do you think is the secret of Kabera’s success?
b) Why do you think it is important for an entrepreneur to plan before undertaking any business venture?
c) Suggest the elements that you would put into consideration while preparing a business plan?
Questions
a) According to the above case, what do you think is the secret of Kabera’s success?
b) Why do you think it is important for an entrepreneur to plan before undertaking any business venture?
c) Suggest the elements that you would put into consideration while preparing a business plan?
2.1. Introduction to Business plan
Learning Activity 2.1
Case study Mugabo had a business idea of buying and selling boiled eggs in his village where many people were doing poultry farming. He negotiated a loan with a nearby Umurenge Sacco. During his loan application process, the Sacco requested him to bring a document detailing how his business will be started and run over at least 5 years to come. He finally secured a loan of 60,000FRW from Umurenge Sacco and bought eggs, boiled them and started selling them but unfortunately, he didn’t find any customers to buy his eggs. After two days, all eggs were damaged and he lost his capital.
i) Use the case above to fill in the following statements with appropriate words/sentences:
a) A business plan is…………………………………………….over a given period of time.
b) Financial institutions are one of the users of …………………………
ii) Describe other stakeholders that may be in need of Mugabo’s business plan.
2.1.1. Meaning of a business plan
The business plan is a detailed document detailing how the business will be started and operated over a given period of time. It is a written document of an entrepreneur’s proposed business venture highlighting its goals and objectives, and his skills, abilities and requirements to implement it.
It helps the owner to make judgments and decisions on opportunities and threats by providing a framework to assess the options. A business plan describes how the business operates, how it is managed, how it interacts in the marketplace, how it functions financially and what its strengths and weaknesses are.
2.1.2. Users of a business plan
Business plan provides essential information to a range of users. Users of a business plan include but are not limited to the following:
a. Business owners/Entrepreneurs The entrepreneur needs a business plan for various reasons which include the following:
• To create a new business. This helps the entrepreneur to mobilize and coordinate needed resources.
• Better understanding of competition.
• Better understanding of business customers.
• To assess the feasibility of the venture. That is to determine if the business is profitable on not
• To document the business revenue model. Documenting the revenue model helps to address challenges and assumptions associated with the model.
• To determine business financial needs. This process is essential for raising capital for business and for effectively employing the capital.
• To reduce the risk of pursuing the wrong opportunity. Writing the business plan helps to assess the attractiveness of this particular opportunity versus other opportunities.
• To help you research and really know your market.
• To plot your course and focus your efforts. The business plan provides a roadmap from which to operate, and to look for direction in times of doubt.
• To position your brand. Creating the business plan helps to define your company’s role in the marketplace.
• To judge the success of your business. A formal business plan allows you to compare actual operational results versus the business plan itself.
b. Government agents
• The business plan made by entrepreneur helps the government to assess the viability of a business to determinate specific incentives like tax exemptions, credit guarantees and subsidies that the government may give to the entrepreneur.
• The business plan helps the government to plan for infrastructures and other services that it may want to put up.
• With business plan, the government determines a relevant tax for the business.
• In some cases, the entrepreneur may want to borrow money from financial institutions like, banks; such loans require the government to guarantee basing on how good a business plan is.
c. Managers
• Business planning is important to managers because the whole point of management is to allow a business to operate more efficiently and to be able to achieve its goals.
• Business plan helps managers allocate scarce resources appropriately.
• It enables managers to control the different aspects of their projects and processes to ensure each task stays on course.
• Business plan also provides the framework for measuring the progress of the different processes and tasks.
d. Employees
• The business plan helps the workers to determine production targets that they have to achieve within set periods.
• The business plan gives the employees assurance about the duration of their employment. It gives them job security because they know the expected life cycle of the business.
• The organizational plan helps define tasks and responsibilities of each of the workers and so helps reduce conflict.
• The business plan helps employees to know the mission and vision of the enterprise.
e. Financial institutions
• Most financiers will closely look and verify the following parts of your business plan: The balance sheet is probably the first thing your loan officer will turn to. The balance sheet records your assets, liabilities and capital.
• Along with the balance sheet, they will look very carefully at the profit or loss and the cash flow, which should be very closely related to the balance sheet and to each other.
• Bankers will also look for hard evidence of founders and managers who know their business.
f. Investors
A business plan attracts investors. The business plan answers investors’ questions such as:
– Is there a need for this product/service (is there a target market)?
– What are the financial projections? What is the company’s growth or exit strategy?
Application activity 2.1
Think of a feasible business of your interest and identify who will be the users of your business plan and explain how they will use it.
2.2. Importance of a business plan
Learning Activity 2.2
As a student of senior 5; you have acquired some initiation and management knowledge. What do you think is the importance of a business plan?
The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. In more details, the business plan helps:
• To attract investors: Whether you want to shop your business to venture capitalists, or attract angel investors, you need to have a solid business plan. A poor presentation may anger their interest, but they will need a well-written document they can take away and study before they will be prepared to make any investment commitment.
• To test the feasibility of a business idea: Writing a business plan is the best way to test whether or not an idea for starting a business is feasible or not. In this sense, the business plan is your safety net.
• To secure funding such as bank loans: Having a business plan gives a business person the chance of getting the money needed to start, keep operating or expand the business. This money can be sourced from banks, donors, government which require the business plan as a prerequisite to disburse their money.
• To make business planning manageable and effective: A business plan is essential when the entrepreneur is thinking of starting a business, but it is also an important tool for established businesses.
Application activity 2.2
Kanyange has had a dream to start a business ever since she started studying entrepreneurship subject in secondary schools. After completing her secondary education, she visited her colleague Kanzayire who was operating a successful small coffee shop in her home trading centre. Kanyange wanted to start the same business and asked her friend for advice. Kanzayire advised her to prepare a business plan before starting to which Kanyange ignored as useless. Kanyange copied her colleague’s business model and started it immediately in her village without any prior study. 6 months later, the business collapsed.
Questions:
i) What should Kanyange have done to succeed in her business?
ii) Advise Kanyange on the importance of preparing a business plan before starting any business venture.
2.3 Components of a business plan
Learning Activity 2.3
Assume that you are selected by Educate! Rwanda, an NGO aiming at entrepreneurship promotion, to train youths on business planning start-up and development. Explain what will be entailed in your training presentation as the main elements of a business plan
Business plans differ in content depending on the purpose, but the basic format remains the same. There is no exact number of sections to include in a business plan. The sections to include in a business plan depends on the size and nature of the business.
2.3.1. General business description
The business description outlines vital details about a business, such as:
i) The name of a business: This is the official name of your business as registered in the country where you do business.
ii) Contact address: This is the contact anyone can use to ask some information about your business. It may be a phone number, email, website, fax and the location address of the business, etc.
iii) Legal form: A legal form of business refers to businesses allowed by the government to be run by business entrepreneurs. The business owner must choose the legal structure of his business. e. g. sole proprietorship, partnership, company, cooperative, etc.
iv)Types of business: The type of business refers to the nature of business like agribusiness, manufacturing; trading, service, etc.
v) Description of the business idea and market:
This section includes the following;
– Information about the owner: The first item in a plan should be written in the description of business owner background, including name, address, email, phone number, education, family status, sex etc.
– Mission statement: A clear mission statement that represent the purpose of your business. E.g.: To provide uncompromised quality product to our customers
– Objectives: An outline of what you want to accomplish in the mediate future based on the data in the rest of the business plan as well as future growth goals. E.g.: To increase the market share by 13% by the end of 2021
– Vision statement: About how you envision the future of the company, e.g.: Transforming the livelihood of the population. – Business location: Where is the business / company and its headquarters?
– Business history: When did the business start or when do you plan to start if it is a new business. What inspires you to start the business?
– Products or services and target market: A brief overview of what you plan to sell and to whom.
– Description of market: Which include geographical area, type of customers, size of total market, description of the competitors, market share for the new business, etc.
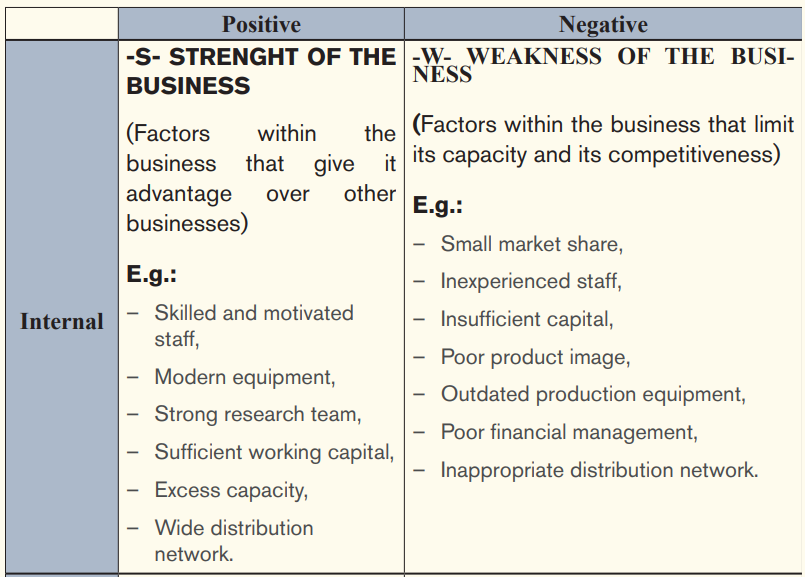
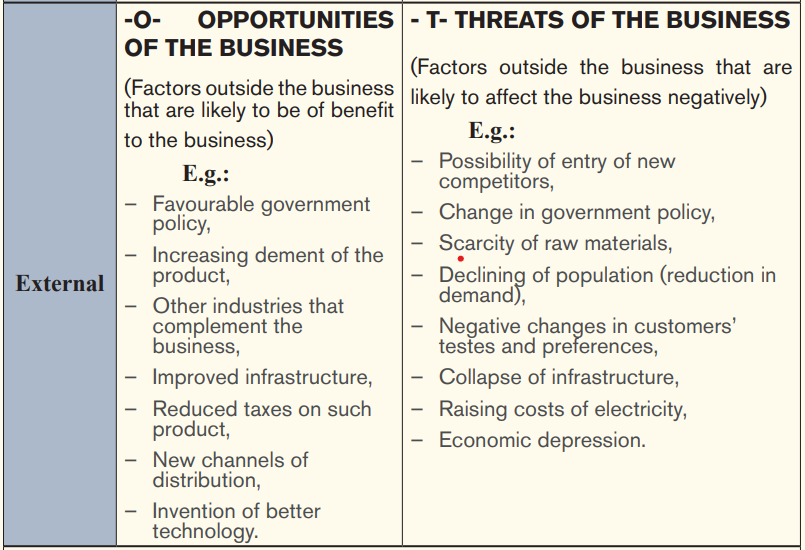
– SWOT analysis: The analysis of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the business.
Exercise 2.1
Think of any business you intend to start after graduating from accounting profession. Prepare its sound general business description
2.3.2. Statement of vision, mission, goals and objectives
• Vision and mission statements
Assume you have started your business and everything is going according to your plan. What would your business look like in five years? How would you describe it in one sentence? The vision statement is a description of the company based on best results, i.e. assuming all goes well. The vision statement should motivate and inspire you to work towards it. It should therefore be short and inspirational.
Example of vision statement: “To be the leading quality beverage provider in East African region”
On the other hand, the mission statement explains why your business exists. Example of mission statement: “To produce quality and nutritious fruit juices” • Goals and objectives
Goals are the targets that the entrepreneur wants to achieve with the company in the medium and long term. The goals are certainly based on the mission statement of the company. Objectives are specific goals that an entrepreneur sets that allow them to move towards achieving their goals and ultimately mission. An entrepreneur can develop multiple goals from his mission and multiple goals from each goal.
An example of a goal statement may be: “To increase production capacity by 7% per year over a period of 4 years”.
You should always be mindful that business activities are derived from the objectives of the business. The business activities are core part of the action plan.
Exercise 2.2
Set the vision, mission, goals and objectives of the business you intended to start in exercise 1
2.3.3. Action plan
An action plan is the careful lay out of the sequenced steps towards achieving the business goals. The main purpose of the action plan is to guide the entrepreneur as a time table during the business plan, and to help him/her become and remain focused on the implementation of his/her business.
The action plan in particular will help the entrepreneur to:
• Find road blocks in advance or expected challenges so as to take appropriate steps to solve them.
• Locate sources of information and resources needed for the business.
• Obtain feedback on the progress towards enterprise established.
• Coordinate efficient use of resources for the business.
• Implement planned activities.
• Specify how workers’ responsibilities and tasks are traced and allocated.
• Monitor and evaluate work progress.
• Discover business challenges and how to solve them.
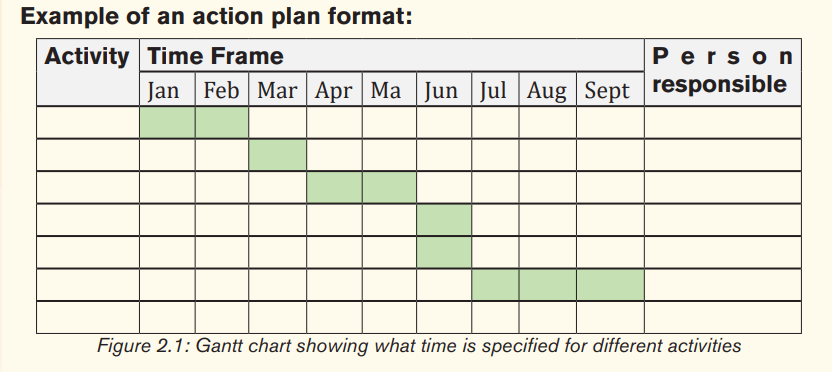
Exercise 2.3
Prepare an action plan of the business you intended to start in exercise 1 and whose vision, mission, goals and objectives are set in exercise 2.
2.3,4, Organization plan
This part describes the form of business ownership, the lines of authority and accountability for members of the new venture.
It includes items such as:
• Form of ownership
• Identification of business partners or principal shareholders.
• Authority of principals.
• Management team and background.
• Roles and responsibilities of members of the organization.
• Decisions on the numbers or types of workers that are required to operate the proposed business.
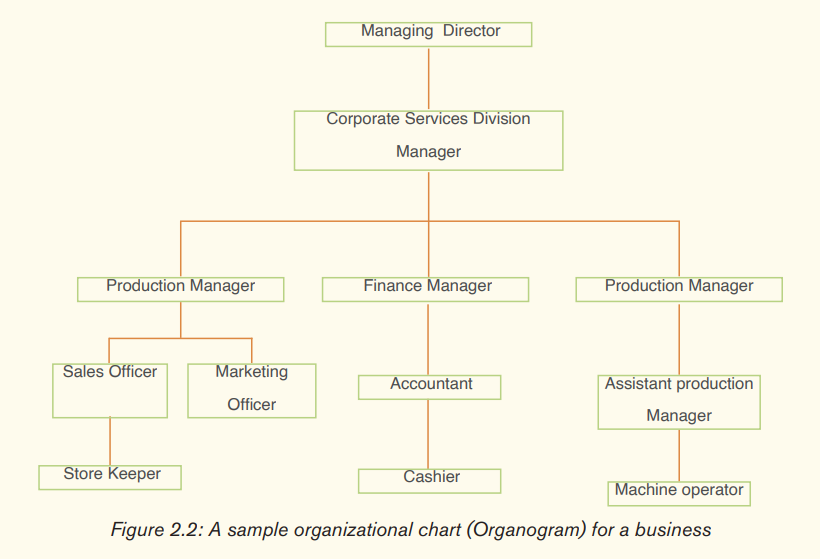
Organizational structure:
This is the systematic arrangement of human resources in an organization so as to achieve common business objectives. The following is an example of an organization structure which is also known as “Organogram”
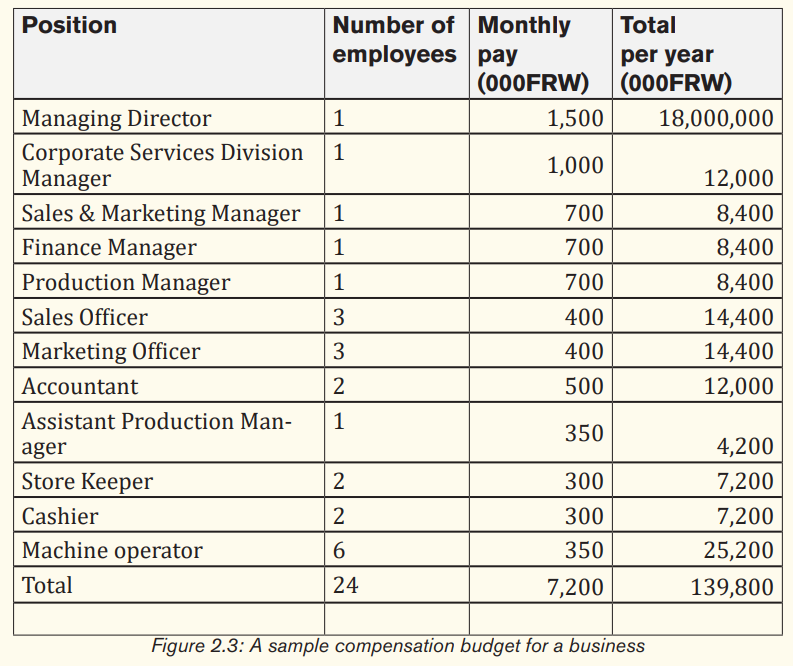
Compensation budget i.e. salary, bonuses, etc.
Exercise 2.4
With the same business you decided to start in exercise 1, outline at least 10 key activities that should be performed for the first year. Using the business key activities outlined, prepare the action plan for your business.
2.3.5. Production plan
This consists of projected needs for manufacturing the proposed product. It is then necessary to assess whether production at this scare is technically feasible.
The production plan mainly focuses on:
• Location of the business,
• Sources of raw materials,
• Production staff,
• Quality control,
• Production utilities required,
• Packaging materials
• A description of the product and what it does, manufacturing process,
• Product innovation, suppliers of raw materials, quality control, nature of packaging, production staff,
• Machinery, equipment and techniques used,
• Product development and substitution,
• Intangible assets and protection.
Factors to consider in deciding the location of the business include:
1. Distance to your customers and suppliers:
Transportation costs are usually a large component of total supply chain costs. Generally, the further you are from your customers and suppliers, the higher the transportation costs will be.
2. Access to the transportation network.
Operating an effective supply chain is contingent upon having good access to your transportation network. This may include alternate transportation methods.
3. Security.
The location of a business can increase the probability of being affected by insecurities. So, it is better to choose a location which is more secure and safe for your business.
4. Labour availability.
Understanding the labour market situation in the area will assist in determining projected labour costs and the availability of workers with the skills you require. In addition, transportation access to your facility for your staff is very important.
Exercise 2.5
Keeping in mind the nature of the business you decided to start in exercise 1, prepare its production plan.
2.3.6. Marketing plan
A marketing plan is a business document outlining market strategy and tactics. It is often focused on a specific period of time (for instance 12 months) and covers a variety of marketing related details, such as costs, goals and action steps. The marketing plan is built from the results of the market research and the specific value proposition of the product or a service.
The right marketing plan should basically identify the following:
• Your target customers;
• How you will reach and retain them;
• How much are customers willing to pay?
• Product description, current production, distribution channel that will be used;
• What are competitors’ prices?
• Forms of advertisement, pricing strategies to be used, and how the price will be determined?
The key elements of any successful marketing plan include:
a) Product description: A portion of a marketing plan should describe the type of business you run, including a list of the products and services you offer to potential customers. It is a detailed description of the product or service. It includes the denomination specification (size, colour, quality) of the product, packaging and after sales service.
b) Customer description, demand/ need for the product, competition
i)Customer description: Before you can begin marketing your product or service, you have to know the type of customers you are trying to attract to your business. Outline your target market by listing characteristics such as age, income, education level, geographic local, marital status, lifestyle, hobbies and interests. This information can help you pinpoint the most effective media to use when you are marketing to your target clients.
v) ii)Demand/Need for the product: This entails uniqueness of the business from existing businesses. It looks at the extent to which a particular business is different from the others. The most important item in this section is a description of why your product or service is better than or is likely to be better than that of its competitors.
iii) Competition: Regardless of the size of the business, you likely have competitors who offer products and services that are similar to what your business provides. There is a need for every entrepreneur to identify who their competitor is, by name, listing the types of products and services they offer, the types of customers they target and take note of the tactics they use to attract and retain customers. This information will help him/her to develop his/her own marketing strategies and tactics.
c) Current production: In this section, you compare the quantity that you can produce to the market and to your competitors (your capacity to produce all products or services needed to the market). This section includes: Capacity to produce, What quantity you plan to produce in order to satisfy the market and compare to competitors;
d) Price: The pricing strategy portion of the marketing plan involves determining how you will price your product or service; the price you charge has to be competitive but still should allow you to make a reasonable profit. You can charge any price you want to, but for every product or service there is limit to how much the consumer is willing to pay. Your pricing strategy must consider the last amount the customer is willing to pay.
e) Sales forecast for next 12 months: Generally, the primary goal of the marketing plan is to get people to buy your products or services. The sales and distribution part of the marketing plan details the following;
f) Promotion: Promotion includes a description of the planned actions to inform customers about the opening of new business (e.g. printed information, brochures, posters, newspapers articles, radio advertisements, opening ceremony, etc.).
Exercise 2.6
Now that you have prepared essential plans (from exercise 1 above) of the business you intended to start, you are required to develop a marketing plan for your business.
2.3.7. Financial plan
The financial plan section of the business plan covers all of the business’ financial needs and forecasts. It shows what the company expects to spend and earn. This section draws its information from other sections of the business plan. So it is done when all the other sections of the business plan are done. For example, you cannot prepare the income statement before you have prepared the management plan because you receive salaries and wages from the management plan that go into the income statement.
• It is important to keep your statements current and to refer to them on a monthly basis.
• You should include the following financial plans with projections for three to five years:
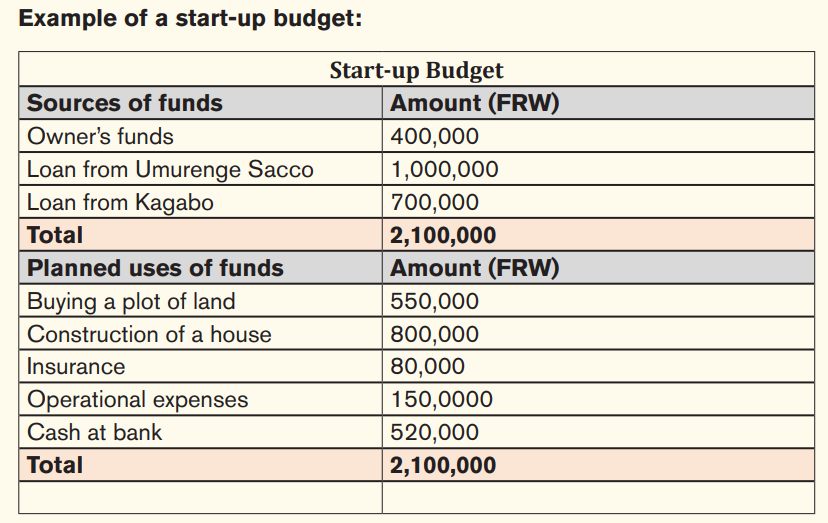
i) Start-up budget: A start-up budget is an itemized list of income and expenses for a new business, which often covers the period up to commencing operations and perhaps a small amount of time after operations have commenced.
ii) Forecasted income statement: While planning for your business, you should forecast the statement of profit and loss of the business for some years to come.
Example of a forecasted income statement:
iii) Cash flow projections: An entrepreneur should show projection of cash movement in his/her business plan i.e. cash inflows and cash out flows for a given period of time.
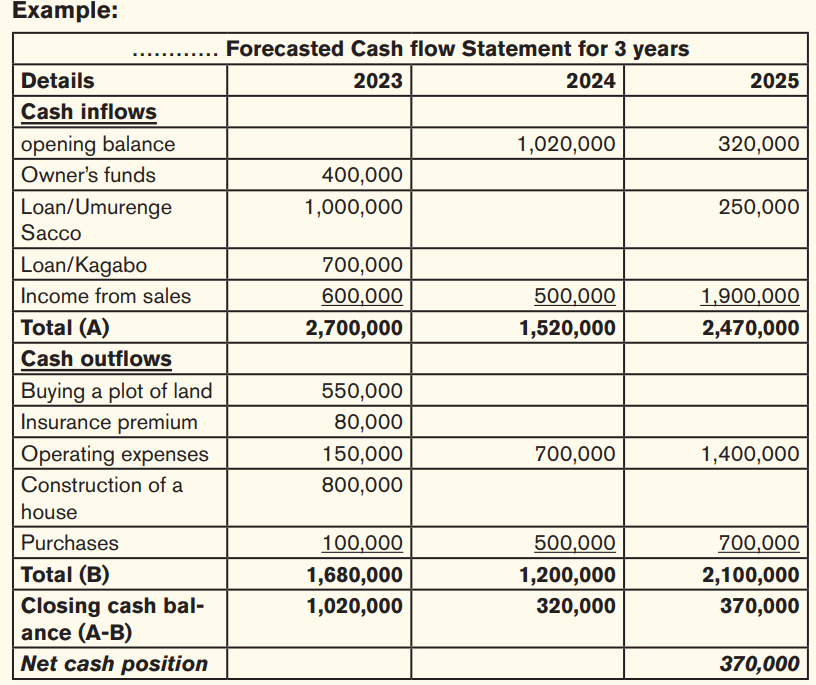
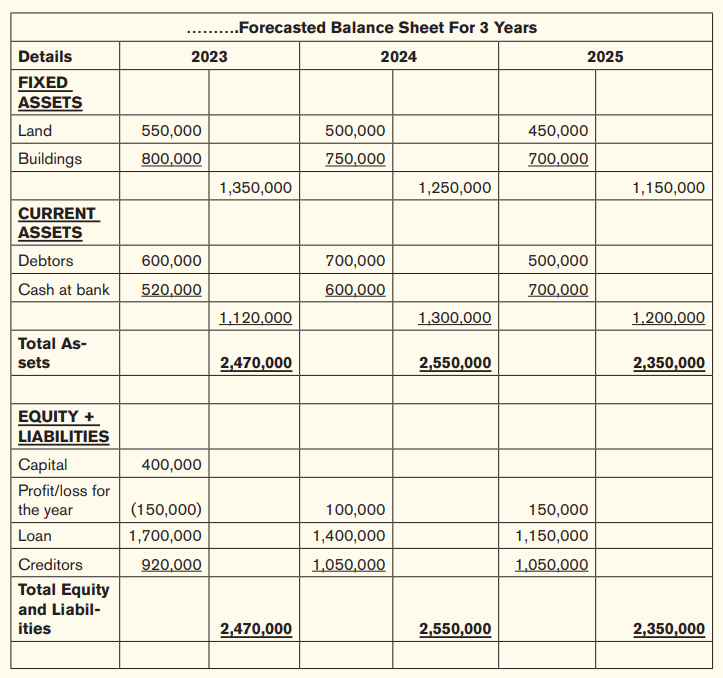
iv)Projected balance sheet: this is also referred to as a pro forma balance sheet. It shows the estimation of the total assets and total liabilities of any business. A pro forma balance sheet is a tabulation of future projections. As a result, it will help your business manage your assets now for better results in the future.
Example of a forecasted balance sheet:
Other elements of the financial plan include:
• A breakeven point analysis (BEP): this is an investment appraisal technique to determine at what point a company, a new product or service will be profitable. It is a financial calculation used to determine the number of products or services you must sell to at least cover your production costs. At break-even point, total revenues are equal to total costs.
Example:
Using the balance sheet above, let us use the following additional information to determine the break-even analysis: – Price: 20 FRW/unit – Total Fixed Cost: 180,000 FRW – Variable cost/Unit: 8 FRW
Required: Determine the break-even point in both quantity and revenue.
Solution:
Profit=TR-TC
Profit= P*Q-(FC+VC*Q), where P: Price, TR: Total Revenue, VC: Variable
Cost, Q: Quantity and TC: Total Costs
20Q-(180,000+8Q) =0
20Q-180,000-8Q =0
12Q=180,000
Q=180,000/12
Q=15,000 Units, hence Break-even quantity is 15,000 Units. This means that the business has to sell 15,000 units to cover the total cost incurred.Break-even in revenue= 15,000 units*20FRW= 300,000FRW
We may ask ourselves how much the business will have to sell in 2024 to make a profit of 100,000FRW ceteris paribus.
Let us do it,
Profit= P*Q-(FC+VC*Q)
100,000FRW=20*Q-(180,000+8Q)
100,000FRW=20*Q-180,000FRW-8Q
100,000FRW+180,000FRW=12Q
280,000FRW=12Q
Q=280,000/12
Q= 23,333.33333 units
Proof:
P*Q-(FC+VC*Q) = Profit
20*Q-180,000FRW-8Q
20*23,333.33333-(180,000+8*23,333.33333)
466,666.6667 – (180,000 +186,666.6667) = 100,000FRW
• Payback period (PBP): this is the length of time it takes a business to recover the cost of investment using its projected cash inflows.
Let us determine the payback period for our business in examples above:
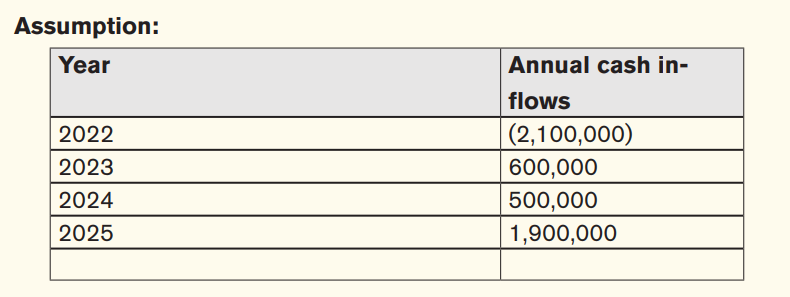
Year 1: 2,100,00FRW-600,000FRW=1,500,000FRW
Year 2: 1,500,000FRW-500,000FRW=1,000,000FRW
Year 3: (1,000,000FRW*12)/1,900,000FRW= 6 months
The payback period is 2 years and 6 months or 2.6 years. This means that the business will recover its investment of 2,100,000FRW in 2 years and 6 months.
Decision criteria: the shorter payback period, the better investment project.
There are other investment appraisal techniques that can be used such as:
• Return on Investment (ROI),
• Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
• Net present value (NPV),
• Internal rate of return (IRR)
• Modified internal rate of return (MIRR)
• Profitability index (PI), etc.
Note: When making financial projections, it is important to explain how you determined the figures you used. If you are looking for financial assistance, lenders will want to know where you will get financing for your business and how you will spend the money.
Exercise 2.7
Congratulations! You have covered one of the most important parts of a business plan which shows whether your financial capacity fits the business financial requirements. Now, Prepare the financial plan for your business taking into consideration all the previous sections you have covered so far
2.3,8 Contingency plan/Risk management
Understanding a risk is critical as you start, run and grow your business. The process of identifying risks, assessing them, and developing strategies to manage them is known as risk management. A risk management plan is an essential part of any business as it helps to understand potential risks to your business and identify ways to mitigate them or recover from their effects.
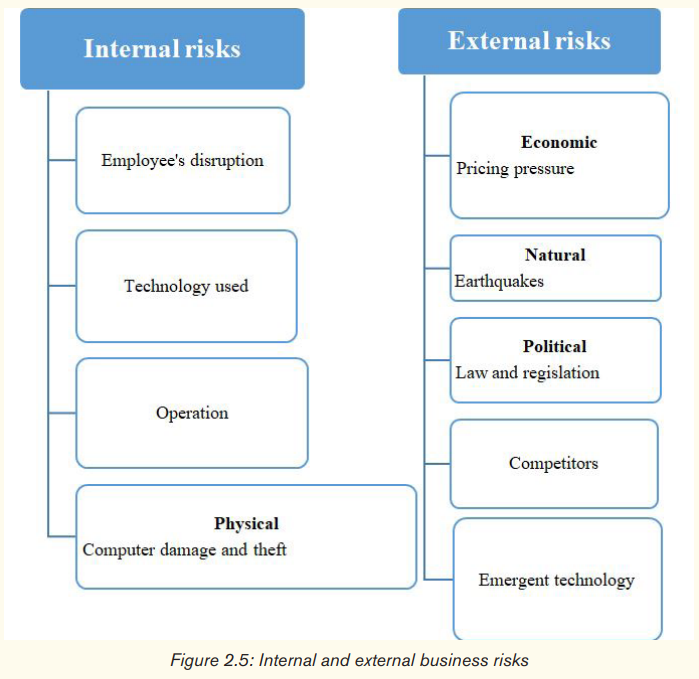
• Broad categories of risks in business:
a) Internal risks
These are internal factors which affect the business but are within a company’s control and sometimes occur as a result of improper systems put in place or the lack thereof. The hidden costs of transportation delays, warehousing and misaligned strategies among business partners can often hinder the major cost benefits of global sourcing.
Generally, internal risks are easier to identify and manage while external risks are more elusive.
b) External risks
External risks are outside the control of the project team and its host organization. Because of this, external risks are generally more difficult to predict and control. Factors such as a key vendor going bankrupt, economic upheaval, wars, crime, earthquake, floods and other events may directly impact the business’ effectiveness.
• Procedure strategies to reduce/avoid the risks
There are different techniques that an entrepreneur can apply to address risks that his/her business faces. Those techniques may include, but are not limited to the following:
i) Select a business structure that limits personal liability: Change your business structure from a sole proprietorship in which you are personally liable for business operations to a limited liability company where you have limited liability.
ii) Transfer risk to insurance companies: Insure against major risks such as damage to your facilities, product liability, injuries to customers or suppliers and death or incapacity of company principals.
iii) Perform a risk analysis: evaluate the consequences of risky activities, the likelihood of the consequences occurring and the benefits of the risky activities. Avoid risk by not carrying out activities that have severe and likely consequences and low benefits.
iv) Transfer the risk of activities with severe and likely consequences but high benefits to other parties: Create a new, independent company to carry out these activities or assign them to suppliers or partners.
v) Reduce risk from product failure and warranty claims: implement a quality assurance program. Develop a system of reporting from customer service to identify problems. Structure the quality assurance program to document production tasks and product testing. Link the problems reported by customer service to specific failures in production or testing procedures and institute corrective action.
vi) Reduce risk of surprises in operating results: keep accurate records and instituting effective controls. Put in place a system that limits who can authorize specific actions and how much they can spend. Implement a reporting system that gives you key information about company performance. Evaluate the controls and reporting system by comparing actual practice and performance to the control procedures and the reported information.
vii) Reduce financial risks: manage your accounts receivable to minimize outstanding balances and identify poor credit risks. Implement credit and payment standards, specifying which credit scores and payment records are acceptable. Evaluate customer payments and ask for advance payment from customers who don’t meet the standards.
Guidelines to create a business risk management plan:
No matter how well you plan and prepare for every aspect of your business operation, you cannot predict everything that you, your employees and your business partners will experience over time. Creating a proper risk management plan for your business is all about making sure your business is able to survive any type of unforeseen circumstance and surprise that comes its way.
• -Defining business risks for your risk management plan template: The first step in creating a quality risk management plan for your organization is to define your business risks. A business risk is a circumstance, event or occurrence that has the potential to adversely affect your business.
• Identify your business risks: The first step you must take in creating an effective risk management plan is to systematically look at the types of risk your organization faces. This not only allows you to get a good picture of the potential issues you may be facing, but also to assess how serious those risks are and understand what you need to do to mitigate them.
• Evaluate your business risks: Once you have identified all of your risks, it is time to assess them to determine which risks are more dangerous than others. There are two things to consider when assessing your risks; how likely they are and what impact they could potentially have on your business.
• Determine how to deal with your business risks: This part of the process of creating a risk management plan involves deciding how to prepare your organization to manage those risks. In most cases, you will have to avoid, reduce, accept, and transfer risks as strategies to implement for almost any potential business risk.
• Monitor the effectiveness of your business risk management plan: Once you have a risk management plan for your business that you are happy with, the next step is to regularly check that it is working and that it is working.
When evaluating your business risks in your initial risk management plan and revisiting them, focus on two things in particular: • How your risks have evolved over time?
• How effective your chosen strategies for dealing with them have been.
Exercise 2.8
Remember, you have selected a business of your interest at the beginning of your business plan. Identify all possible risks that may occur in your business, and develop risks management plan to mitigate those risks.
2.3.9.Executive summary
The executive summary should be the first section of a business plan after the table of contents to give the reader an insight of what the entire business plan talks about. However, it is typically written/ prepared last after all the other sections since all other information (other parts ) are clear to the face of an entrepreneur.
An executive summary discusses the following items:
• Business name, address and contact person.
• Business idea and goals: This section provides an overview of the business project, what product or service is being sold and what the entrepreneur’s goals are. It also indicates where the business expects to be in a year’s time and later.
• Legal form: e.g. sole proprietorship, partnership, company.
• Marketing: This part looks at how the products or services of business will be sold. Who will be the main target markets (customer groups)? And what are the main elements of the proposed advertising and promotion strategy for the firm?
• Operations: This is concerned with where the business will be located. How many staff will be needed and how they will be managed.
• Finances: How much money is required to finance the plan, where will such capital be obtained from and how it will be repaid. How much profit the firm is expected to make by the end of the business plan time period?
Application activity 2.3
Using the different business plan sections you have prepared from exercise 1 to exercise 8, you are required to:
i) Prepare the executive summary and
ii) Compile your business plan document.
Skills Lab 2
Think about the project you plan to start in your business club. Prepare its business description and marketing plan that must be presented and submitted to the teacher and the club leadership committee for further consideration.
End of unit assessment
1. After your studies, you have a dream to start a small business and you have just started writing your business plan. Describe how financial institutions can use that business plan.
2. You have just established a mushroom growing business in your home area. You intend to launch your business to create community awareness.
Required: Describe any three risks that a new enterprise might face and propose the possible measures to mitigate them.
3. Discuss the term “marketing mix” as used in business planning.
