UNIT 6: Human rights and ethics
Key Unit Competence: To use language learnt in the context of human rights
and ethics.Introductory activity
Picture observation and interpretation

After observing the picture above, answer the following questions:
1. What do you understand by the human rights?
2. What does 10th December remind you of?
3. Explain the difference between Equality and Equity.
4. How do you understand by ethics?
5. List at least five human rights respected in your community.6.1. Describing rights of accountants
6.1.1 Learning activities: Reading and text analysisActivity 1
Observe the picture below and then answer the questions related to it.

A. Reading comprehension
Activity 2
Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow.

An Accountant
Upon first glance, accounting might seem like a fairly straightforward
profession—it’s just crunching numbers, right? While it’s true that working
with financial data is a substantial part of the job, accounting is a critical
business function that involves much more problem solving than you may
think. For instance, leveraging assets, managing budgets, achieving
financial efficiencies, and maximizing investments are just some operations
of accounting and finance management that go beyond what most people
consider the profession to be.So, what does an accountant actually do on a daily basis? Here, we’ll discuss
the roles and responsibilities, important skills, and career outlook for
accountants, as well as current trends impacting the field.An accountant is a professional who is responsible for keeping and interpreting
financial records. Most accountants are responsible for a wide range of
finance-related tasks, either for individual clients or for larger businesses and
organizations employing them.Several other terms are often discussed in conjunction with the phrase
“accountant,” which can lead to confusion on what this career actually entails.
For example, “accountant” and “bookkeeper” are phrases that are sometimes
used interchangeably, yet there are several key differences between these
job titles.Typically, bookkeepers will have earned at least an associate degree and
focus on recording financial transactions. Accountants, on the other hand,
will have typically earned at least a bachelor’s degree in accounting, and
are tasked with interpreting financial information rather than simply gathering
it. In short, accountants can be bookkeepers but not all bookkeepers are
accountants.Additionally, a certified public accountant (CPA) is an accountant who has
passed the CPA exam and has met state licensing requirements. So, all
CPAs are accountants, but not all accountants are CPAs. Accounting
is a broad term that encompasses multiple different job titles and roles
within organizations. There are three main types of accountants—public
accountants, management accountants, and government accountants—all
of which focus on different aspects of the profession. Internal and external
auditors are also closely related.Adapted from: (Miller, 2019)
Comprehension questions
1. According to the passage, who is an accountant?
2. What are three types of accountant conferring to the passage?
3. What does a certified public accountant (CPA) mean?
4. Explain the difference between “accountant” and “bookkeeper.”
5. State the roles and responsibilities of an account.B. Vocabulary
Activity 3
Using dictionary find out the meaning of the following words and phrases as
they bolded in the passage
6.1.2 Application activities
Activity 1
Read the passage bellow and complete the gaps with the following words
Requirements, professionals, duties, reports, operations, degrees,
individuals, non-profits, background, professionals, public, dutiesAccountants are financial _____1_____ who take charge of a series of
accounts—either private or _____2_____. These accounts may be owned
by either a corporation or _____3_____. As such, they may find work with
corporations of different sizes—small to large—governments, different
organizations like _____4_____ or they may set up their own private practice
and work with individuals who enlist their services.They perform multiple accounting _____5_____ which vary based on
where they work. Accountants perform account analysis, review financial
statements, documents, and other _____6_____ to ensure they are accurate,
conduct routine and annual audits, review financial _____7_____ prepare
tax returns, advice on areas that require more efficiencies and cost-savings,
and provide risk analysis and forecasting.An accountant’s _____8_____ often depend on the type of educational
_____9_____ and designation they receive. Most _____10_____ in the field
possess bachelor’s _____11_____ and—if employed by a corporation—may
require certification to move up within the firm. Certification requirements
vary, with some roles requiring additional educational _____12_____ above
the bachelor’s degree and successful completion of rigorous examinations.
Accountants can have more than one designation.Activity 2
Writing skills
In not more than 4oo words discuss the advantages and disadvantages of
being an accountant.6.2 Describing ethics in accounting practices
6.2.1 Learning activities: Reading and text analysisActivity 1
Reading comprehension
Read the following passage, then answer the questions that followAccounting Ethics
Accounting Ethics is the basic requirement which is to be followed by the
accountant while doing accounts of an entity. It is like guidelines that are to
be followed and it has been set by the government authorized bodies.The accountant should follow the accounting ethics to take precaution from
any misuse of the financial statements. The accounting ethics are mandatorily
to be followed by each and every accountant and if they fail to follow then it
may attract financial punishments.Accounting ethics began from the year 1494. The government used to
form a body of persons to look after the same for the companies but it has
become difficult for them to do so. Therefore, some private organizations
were qualified to perform the task for the companies but under the wings of
the government.These private organizations are required to follow the norms and rules set by
the government any new rule should be passed by the government officials
to get enacted. In the United States of America, the accounting system has
taken a reform by the year 1905.The government started taking accounting bodies seriously and formed the
Association of Government accountants. These accountants were learned
and have a hold on the subject then after that Institute of Internal Auditors
were formed.The Institute of Internal Auditors was formed to check that the companies are
maintaining proper books of accounts or not? The report was later published
to the government. Therefore by these changes today we are getting a proper
system of accounting designed.Adapted from: (Jha, 2015)
A. Comprehension questions
1. According to the passage, what is Accounting Ethics?
2. When did Accounting ethics begin?
3. State the importance of Accounting ethics as mentioned in the passage.
4. Explain the reason why accounting ethics are mandatorily to be followed
by each and every accountant.B. Vocabulary
Activity 2
Match the following terms with their meaning
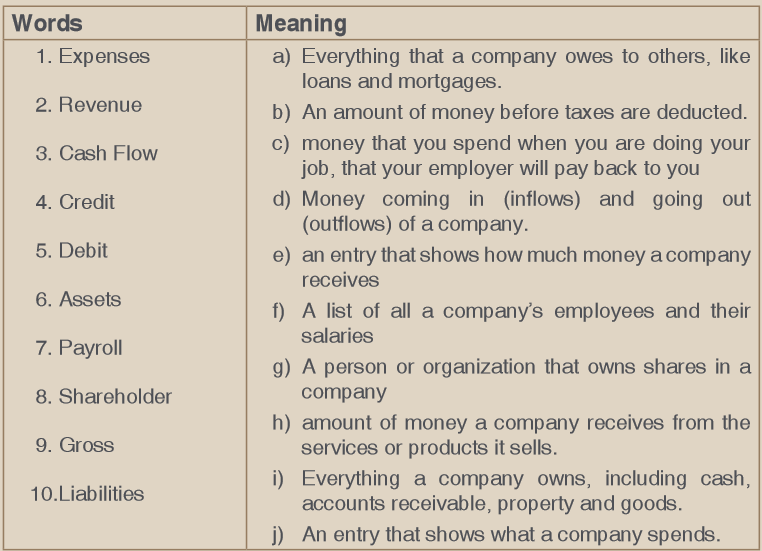
6.2.2 Application activities
Activity 1
Read the following sentences and complete the gaps with the following
terms.debit, credits, assets, net, liabilities, profit, capital, bookkeeper,
financial statements, auditors1. The companies _____________ were easy to calculate, but it was
difficult to quantify the value of the employees’ expertise.2. __________ are recorded on the right side of the balance sheet,
while assets are listed on the left.
3. She recorded the purchase of the new laptops as an __________
entry.
4. She realized that the total debits didn’t equal the total __________,
so she had to check each entry all over again.
5. She couldn’t tell me her __________ salary because she didn’t
know all the taxes she was paying; moreover, salaries are not
transparent in her company.
6. In order to decide if the company was worth investing in, they
wanted to look at the __________ it had been making over the
previous year.
7. He couldn’t start a business because he didn’t have enough
__________, so he decided to work as a freelancer for the time
being.
8. The accountants were all busy working on the__________ as the
company was planning to refinance its loans.
9. She was training to become an accountant, but in the meantime she
had a part-time job as a __________.
10. When the __________ asked for additional information about the
financial statements, our accountants complied without delay.Activity 2
Writing skills
In not more than 300 word discuss the advantages of accounting ethics.6.3 Fighting abuses
6.3.1 Learning activities: Reading and text analysisActivity 1
Reading comprehension
Read the following passage, then answer the questions that follow
Child Abuse
When we were young, no one ever told us about our rights. Most children
were badly beaten, denied food and education which every child should
have. It didn’t matter which offence you committed to be given such brutal
and harsh punishments.I remember the countless number of offences we were beaten for. One could
be beaten for crying when you are beaten, they would beat you if you were
punished and never cried. They would say you were a bad boy or a bad
girl. You could be punished if you stood when elders were sitting; beaten
for sitting when elders were standing. They would punish you if you ate with
visitors. Refusing to eat with visitors would lead to being punished too. We
were beaten for almost everything and nothing we did.During those days, the child belonged to the community. Everyone in the
community had the right to punish you. I remember one day as we came
from school; I was in primary five, when boys drew a line across the road and
challenged me with another boy that whoever crossed the line would be a
“man”. We stood on opposite sides and waited to see who would cross first.
Because the other boy was older and bigger, he decided to cross first. No
sooner had the fight begun than an old man we didn’t know arrived. What he
did to us I have not forgotten till now.The worst part is that when I reached home, I found the news already
received and sticks were waiting for me. Today as an adult, I feel sometimes
I was punished unfairly yet did nothing to stop it. Now that you know your
rights, knowledge is our strongest weapon. In the fight against child abuse,
knowledge is our strongest weapon. The more you know about it, the more
you can do to help those who have already been victimized and to prevent it
from happening again.You are encouraged to learn more about child abuse and the programmes
in your community and to pass that information on to those around you,
remind whoever wants to punish you that you have rights and they should be
respected. This does not mean you misbehave. It is your responsibilities to
fight for your rights as a child.Comprehension questions
1. List at least three children’s rights not respected in the passage.
2. According to the passage, which offences would children be beaten for?
3. State the cause that pushed the two boys in the story to fight?
4. Explain the consequences of their fighting?
5. What is your opinion of this community?6.3.2 Application activity
Activity 1
Give a synonym and opposite of the words below
a) committed
b) punishments
c) offences
d) misbehave
e) responsibilitiesActivity 2
Writing skills
Write a speech you would give during community works in your society,
sensitizing people about children’s rights violations.6.4 Language structure: Modal verbs and passive voice
6.4.1 Modal verbs: should, would, could, can, should, may, be
able toModal verbs
Definition: A Modal verb is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to convey
ideas like talking about ability, asking permission, making requests, talking about
things which are desired and so on. This verb can never stand alone in the sentence.
It is always with the main.Examples:
1. You must do your homework every day.
2. We must remember our history to plan for the future.
Note: Must can be replaced by have to, or had to (past tense).Uses of modal verbs
a) How to use the modal verb can
Can is used when talking about someone’s skill or general abilities. It is also used
to make offers, ask and give permission.Examples:
1. Rodgers is patient and humble, he can adapt to any situation. (Ability)
2. If children’s rights are recognized, a child can follow a career he likes.
(Permission)
3. I can play for you a nice piece of music about children’s rights if you like.
(Offer)b) How to use modal verb should
Should is used when giving a piece of advice, a recommendation or a suggestion.Very often, should is used instead of must to make rules, orders or instructions
sound more polite.Examples:
1. If we are to live peacefully with others, we should avoid prejudices.
(Advice, recommendation, suggestion).2. We should experience a united community since people now respect each
other’s beliefs. (Likely situation).3. As tolerance is encouraged in our communities, we should have a more
peaceful generation in the future. (Prediction).c) How to use modal verb might and may
Might is used to talk about possibilities in the present, past and future. It has the
same meaning as may but may is used when one is a bit more sure, while might
expresses some doubts. Therefore, “may” and “might” can be used:i) To show possibility
Examples:
1. There might be life on Mars, we never know. (In this sentence, the
degree of certainty is low)
2. There may be life on Mars. Since they found there water and
microorganisms.
(In this sentence, the degree of certainty is a bit higher for water and
microorganisms are signs of life)ii) To ask for or give permission:
Examples:
1. You may go now.
2. You may come at eleven if you wish.iii) To express polite offers, request or suggestions.
Examples:
1. May I borrow the car tomorrow?
2. May we come a bit later?iv) How to use be able to
We use “was/were able to” to describe successful completion of a specific
action or “am/is/are able to” for the ability that we have to do something now.Examples:
1. ANC was able to fight against apartheid in South Africa.
2. Even though I am a woman, I am able to driveActivity 1. Fill in the blanks with appropriate modal auxiliary verbs.
1. I ___________ arrange the flowers for the bouquet. (may/can)
2. ___________ I borrow this pen from you? (may/might)
3. The teacher ___________ ask you to bring the homework. (might/can)
4. According to the weather forecast, it ___________ snow heavily tomorrow.
(may/shall)
5. Raj hasn’t studied well. He ___________ fail his exam. (might/shall)
6. You ___________ follow the traffic rules. (may/must)
7. It ___________ be difficult to live amidst war. (should/must)
8. My mother ___________ cold me if I don’t go back on time. (will/may)
9. We ___________ take care of our parents. (ought to/ could)
10. I ___________ visit the local grocery store soon. (shall/can)
11. You ___________ be punctual. (should/ought)
12. One ___________ repay all their debts. (must/ought to)
13. ___________ you show me the road to the market? (could/might)
14. The child ___________ be taken to hospital immediately. (must/might)
15. ___________ you have hot chocolate? (shall/will)Passive voice
What is a passive voice?
Passive voice is a form or set of forms of a verb in which the subject undergoes
the action of the verbe.g. 1. They were killed by thieves.
How do we make the passive?
The passive voice in English is composed of the following elements:
The auxiliary be is conjugated in all tenses. The main verb is always the past
participle. The agent is the original “doer” of the action.Look at some examples:
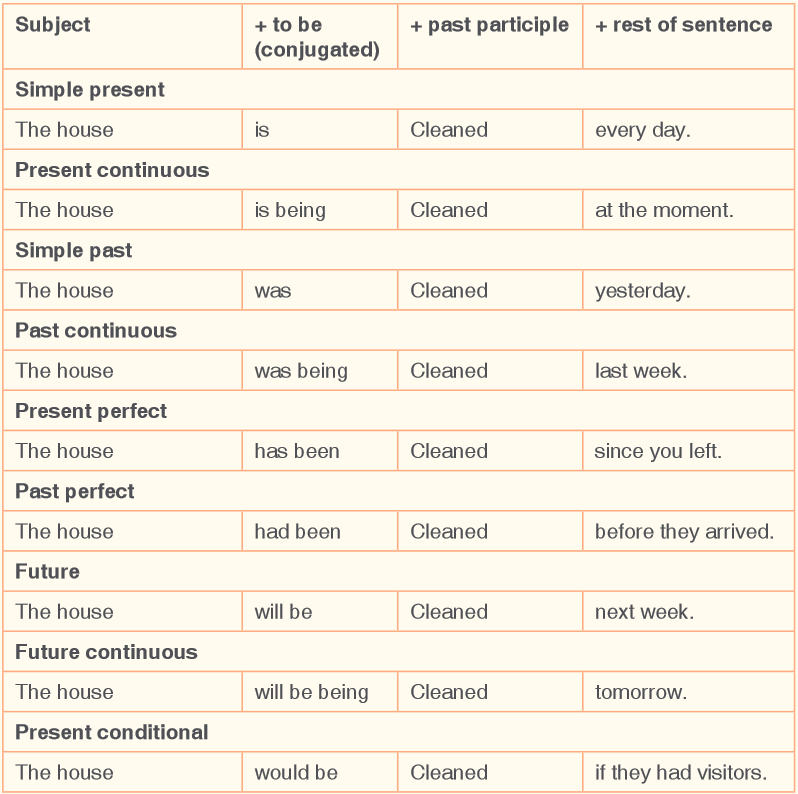
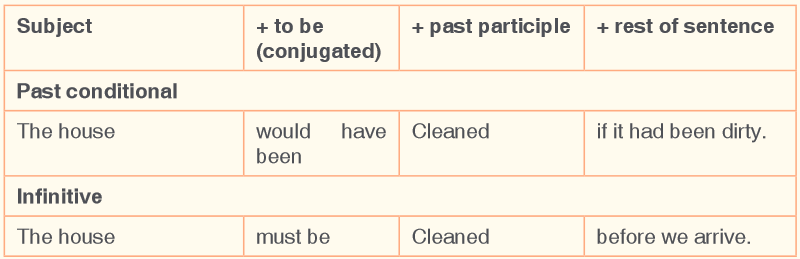
Activity 1. Change the sentences to passive voice.
1. The Browns have built the large house.
2. A jellyfish stung her while she was swimming.
3. They gave her a nice present.
4. Jane is singing the new song.
5. The storm destroyed the house.
6. People spent a lot of Monday on the first shopping Saturday.
7. How do you write that word?
8. She watered the flowers every day.
9. The headmaster called his parents to the office.
10. Ben will direct the show.6.6 End unit assessment
Activity 1
Look at the following sentences and choose the correct answer. Sometimes,
there’s more than one correct answer.
1. They had to hire a__________ because Jane was not qualified
to produce all the documents for the audit in June.
A. auditor B. accountant C. bookkeeper2. The __________ is an important accounting document showing a
company’s assets, liabilities and the owner’s equity.
A. cash flow statement B. balance sheet C. income statement.3. He was hoping to be able to raise enough __________ to set up his
own business in five years’ time.
A. assets B. capital C. equity4. As she was calculating the company’s liabilities, she realized she
forgot to include the __________.
A. accounts payable B. accounts receivable5. They wanted to resort to __________ in order to convince investors
of their company’s high profitability, but then they realized that the
auditors that worked for the investors would see right through it.
A. bookkeeping B. accounting C. creative accounting
6. He had been trying to pass his exams in order to become
a__________, but in the end he gave up and decided to charge a
higher fee for his bookkeeping services in order to make ends meet.
A. chartered accountant B. shareholder C. investor7. The auditor was looking at the financial statements that the
company presented him when he realized he was actually
interested in a different __________. He then had to ask for a
different set of financial statements.
A. income statement B. payroll C. accounting period8. She was considering giving up working as an accountant for that
company and becoming a self-employed freelancer because the
__________ she had to pay was lower. She also had the expertise
to file her own tax return, which was an additional advantage.
A. income tax B. Value Added Tax9. The idea of becoming a shareholder seemed really bad now that the
__________ was lower than in any other previous year.
A. share price B. return on investment10. Their __________ was too high during the past few months, so they
have been thinking of either not giving their employees any bonuses
this year or investing less in advertising.
A. overhead B. appreciation C. depreciationActivity 2
Fill in the blanks with an appropriate modal auxiliary verb.
1. ___________ you mind posting this letter for me?
a) Could b) would c) should2. ___________ you lend me your bicycle?
a) Shall b) will c) may3. You ___________ not come to my door again.
a) Will b) shall c) would4. You regret this.
a) Shall b) may c) can5. What ___________ we do now?
a) Will b) shall c) can6. Parents ___________ teach their children to be honest.
a) Shall b) should c) would7. He ___________ take rest if he is tired.
a) Would b) can c) shall8. You __________ have told me before borrowing my car.
a) Would b) should c) might9. The students asked if they __________ o home early.
a) Would b) could c) can10. I __________ run faster when I was younger.
a) Would c) should b) couldActivity 3
Complete the sentences below with either passive or active voice where
applicable.
1. It is not clear how many human rights (abuse) ______1______ by
criminals.
2. It may be possible to tell whether a person (violate) ______2______
the rights of others after the criminal (investigate) ______3______
3. These days, many cyber-criminal (use) ______4______ the internet
to disturb the privacy of others. This (do) ______5______ by
hacking emails and websites and getting information or blocking
them.
4. If you (tell) ______6______ that you have won money you did not
compete for, know it is the first step to (rob) ______7______.
5. Sometimes money (steal) ______8______ from people’s bank
accounts using computers. If you (ask) ______9______ to give your
account number to people you don’t know, please don’t do it.
6. Some people (deny) ______10______ their freedom of speech.
They (tell) ______11______ to shut their mouths in case they try to
report abuses.
7. Many human right abuses (not/report) ______12______. This is
because people (not/inform) ______13______ about their rights.
8. In Rwanda, training is (give) ______14______ by many
organisations and people (start) ______15______ to know how to
protect their rights.Activity 4
Writing skills
In not more 300 discuss the rules and responsibilities of an account.
