UNIT 8 :ICT TOOLS IN ACCOUNTING
Introductory activity
Kamali’s grandfather worked in a bank in 1980. He narrates that at that time
when a customer came to the bank, a bank staff had to get his/her booklet,
locate his/her information sheet which was kept in a box with other clients’
information sheets and bring it to the teller. When a transaction was done
the information about that transaction was kept both in the booklet and the
customer information sheet. The teller had to count the money by hand and
give it to the customer. The bank’s staff had then to take back the customer
information sheet and put it again in its appropriate place.
Visit the nearest bank of your home or school, and request to branchmanager some information about:
a. How the bank process was done in the years 1980
b. What are the dangers presented in that banking process stated in question 1?
c. What are the common ICT tools used at banks in these days?
d. How the current banking system corrected the problems that
were in the old banking system.
8.1 Counting machines
Activity 8.1
Kamanzi is a company owner whose activities are carried out in East Africa
and China. At the end of the day the company’s headquarter have to count
the received money and deposit it to the company’s accounts.
1) If at the end of the day this company has hundreds of millions to
count, what are the tools that they will use to ease this task?
2) State the process of using the tool given in questions 1)
3) Give at least the parts of the tool you have given.
A counting machine or more precisely a currency counting machine is a machine
that counts money. They are in different types namely bank note only counters,
banknote and coin counters, coin sorters, coin counters. All these machines
have many advantages including among others saving time and resources,
fighting counterfeited notes, increased accuracy in accounting and facilitatingthe keeping book of accounts.
8.1.1.Banknotes only counters
These are devices which can count bank notes only. Most of the counters need
to be fed with sorted notes for counting to be properly done meaning that they
can count only same value bills at the same time. However more advanced
counters can identify different bill and provide a total currency value of mixedbanknotes, including those that are upside down.
NB: There are devices which can count both coins and banknotes. These are
called Banknotes and coins counters.
A. Parts of a banknote counter
Apart from the external frame, a banknote counter has different part which areseen from outside of which are not visible as they are encased inside.
B. Using a counter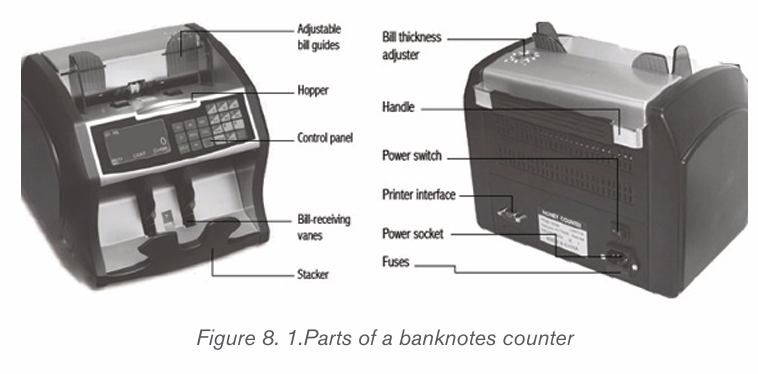
A billing machine is used in the following process :
• The billing machine has first to be plugged to the power source using
its powercable then switched on. If the billing machine has a battery, it
can be operated without being plugged to the power source.
• Select the function that the counter will perform
• Place the bank notes in the appropriate tray
• Press the start button for the counting operation to start
i). Some of a counter’s functions
A counter has functions which facilitate how it is utilized by a user. Some of the
basic functions are:
Currency Code: After the machine is turned on, the currency kind is displayed
on the screen. To change the current currency press “CURRENCY” key to
choose a new currency.
Counting Mode: There are different counting mode which are selected by
pressing the MODE button. One example of counting is batch in which the user
specifies the number of notes to count say 100 notes.
ii). Counter basic maintenance
A counter may have slight problems that don’t need deep competences in order
to sort them out. Those problems can be prevented in this way:
• Clean regularly the counter for optimal performance. This cleaning
includes that of the hopper and stacker which has to be done using a brush
• Clean the banknote pathway using a soft brush or a dry soft lint free cloth
• Occurrence of error during banknotes counting can be solved by doing
one of these depending on the kind of error: Removing the banknote,cleaning the counter’s sensors.
8.1.2.Coin sorters and coin counters
Coin sorters are devices used to arrange coins into separate groups according
to their denominations. These devices are commonly specific for coins of specific
countries as the size of coins may vary depending on countries. Some sorters
have screens which show the number of the coins that passed through it.
As its name suggest, a coin counter on the other hand is used to count the value
of coins. However some of these devices both sort and count coins at the same
time or count only presorted coins that are all the same size. Most counters use
bowl with flat spinning disks at the bottom of the bowl to distribute the coins
around the bowl perimeter. At the bottom of that bowl there is an opening which
allows the passing of one coin at a time. These coins then pass through a light
beam counter or are pushed through a spring loaded cam that accepts only onecoin at a time.
Application activity 8.1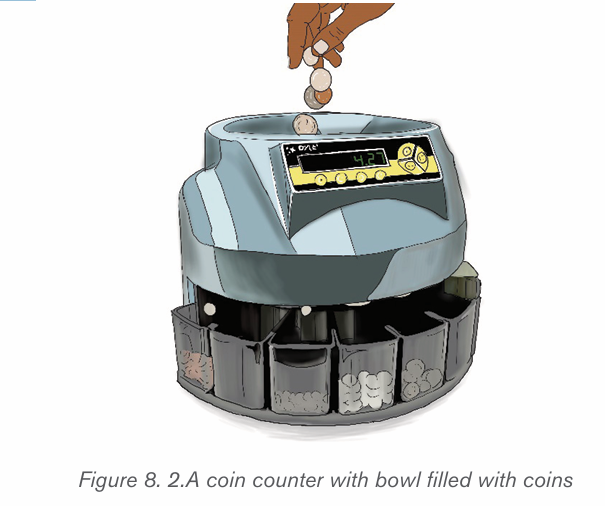
1) What is a banknotes counter?
2) What are the different parts of a banknotes counter?
3) By doing a research identify the internal parts of a banknote only counter
4) By doing a research on the internet find at least 5 different banknotes
counters and their specifications. The specifications should at leastinclude the counting speed, hopper capacity, stacker capacity, weight.
8.2.3 Billing machines
Activity 8.2
Isimbi, a student in was doing a research about billing machines used in
Rwanda. She visited one supermarket to ask questions to the owner, clients
and the supermarket staff. Suggest the answers she will get about the
following questions:
1) Which machines are used to make bills in a supermarket?
2) How does the supermarket staff proceed in order to make a bill for
a customer?
3) Which type of information is found on a bill?
4) What are the advantages of the billing system in a supermarket in
regard to:
a) Stock management?b) Paying taxes?
These are machines that are used in entering in a system of customer informationand purchased goods so as to come up with invoices or bills.
For these machines to print bills they use a thermal printing process by which
images are produced by selectively heating coated thermochromic paper when
it passes over the thermal print head. The coating becomes black in the areas
where it is heated, producing an image. Two-color direct thermal printers can
print both black and an additional color (often red) by applying heat at two
different temperatures.
Bill printers print by direct contact between the thermal head which generates
heat and thermal paper which is thermally coated to be sensitive to heat. The
paper rolls available are sensitive to the heat and thus when the heat is produced
it can easily initiate the process of printing. It can print more than just a single
color by setting the printer to different temperatures.
The world is becoming more digital and this require that stores acquire billing
machines as every business is required to issue receipts generated using billing
machines. Billing machines reduce the chances of error, once the required
information is entered into the system, it automatically updates each new billwithout any additional effort.
8.2.1.Main parts of a billing machine
Billing machine systems, like most electronic devices, consist of different parts
which play different roles grouped into three categories namely inputting data,
processing and printing bills. The first part is the keyboard which is used
to feed information like goods names in the billing machine. The second part
can be considered to be the processor and all parts working with it like memory
and motherboard. The third part is the printer which plays the role of helping
get hard copy bills. Also in the same third category is a screen which displays
information that a billing machine user can understand. Note that some billing
machines may have additional parts which help in payments like a weighingscale.
8.2..2.Operating a billing machine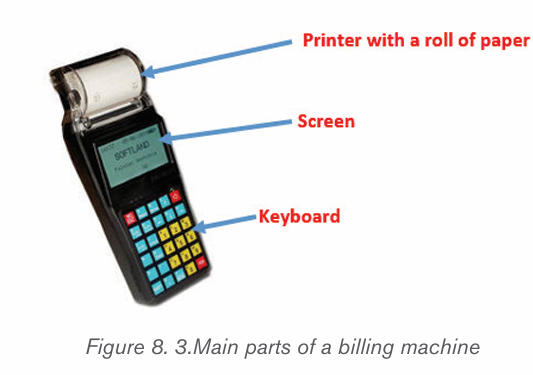
Producing a bill by a billing machine requires the presence the information to
appear on the bill. That information can be fed to the billing machine’s printer
from different sources namely the database on which the billing machine is
connected through internet or a local network, the billing machine’s permanent
memory or temporary memory. The temporay memory of this machine keeps
information which is immediately fed to it by using its keyboard or any otherinput device
Before using a billing machine make sure the following is met :
• It is properly connected to a power source or that its battery has enough
power,
• It is properly connected to a local network or internet by the use of a
cable or wireless network. This is necessary when the machine gets or
submits data to a database stored at another location
• All the peripherals to a billing machine are properly connected
• Make sure that as a user, you have the right access credential if the
machine is password protected
When a billing machine is ready follow the following steps to use it:
• Log in to the machine. Some may need a username and password
while some need a swiping card accompanied by a password.
• Enter the billing information by using the keyboard. This information
is about the client details, purchased goods details and amount to be
paid. Most of the time the price of each item purchase is got from
the machine’s database and the total price to pay is automatically
calculated.
• Print the bill by pressing the key for printing
Note that:
Some billing machines may not require login depending on how their
setting were configured. There exist typically three types of user on a
billing machine namely Clerk who can only generate invoice, the Admi
nistrator who can generate Invoice and Reports, add or modify items and
their price, change print settings and the Supervisor who has access
to all that the administrator can do and more to that have access to
System settings, Erase Memory/Bills, Create different users and assign
password.
Billing machines allow users to get different reports. Depending on the
available functionalities, these machines can provide daily, weekly oryearly reports.
8.2.3.Billing machines in Rwanda
Rwanda through the Rwanda Revenue Authority (RRA) adopted the use of
billing machines from 2013. These machines which are known as Electronic
Billing Machines (EBM) are devices which receive information from the user like
bought items and generate a bill which is then printed. These devices come with
software installed by the manufacturer or the vendor and the user can not easily
remove or add a new software.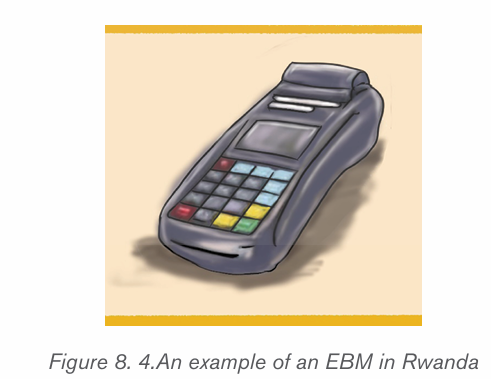
In 2017 Rwanda Revenue Authority adopted a new version of EBM which
is known as EBM version 2 (EBM ver2.0) which is a software installed on
a computer allowing then to have access to the central database. With this
software installed, after logging in the user has access to different functionalities
including among others item management, customer management, sales
management, purchase management. This EBM also allows the printing of aninvoice to be given to the customer.
8.2.4.Types of billing machines
There are machines which are dedicated to be billing machines. With these ma
chines the software which make them operate is installed by the manufacturer or the
vendor and these devices cannot play another role other than the one they were made
for. On another hand, billing machine functionalities are implemented in a software
which can then be installed on electronic devices like computers, ipad, smart phones
and therefore acting as billing machines.The different types of dedicated billing machines are outlined below :
A. Portable machines
Billing machines that can be moved from place to place are referred to as
portable machines. The handheld machines or the bus ticketing machines areexamples of such machines.
Among portable machines are card swipe machines which are devices that
read the magnetic stripe on a card and takes the information from it. The most
common card swipe machine is a credit card reader that is used with a cash
register. These machines come with a keypad for the customer to enter the PINof the card, a display bar and a swipe slot for swiping the card.
B. Automatic machines
These are machines come with software and algorithms inbuilt in it to add up the
taxes and deduct the rebates automatically. No additional manual instructionsare required for such type of machines.
C. POS machines
The POS or the Point of Sale is a billing technology used in supermarkets to
keep track on the sales of goods. This system uses bar-code technology to
perform tasks like review sales or prepare the next fresh lot of products that
need to be replaced with the sold-out ones.
Normally a POS system is referred to as a cash register at a store. While this is
still true today’s modern POS systems accepts payments even when customers
are away from the POs system. What is needed in this case is a POS app and
an internet-enabled device, like a tablet or phone.
Hardware parts of a POS system
POS system uses POS software. However in the case of an online store the
POS system does not need to have the hardware. In this case of an online store
all of the sales happen on a website, so the business owner does not need POShardware to help accept payments.
Register: this helps calculate and process a client’s transaction.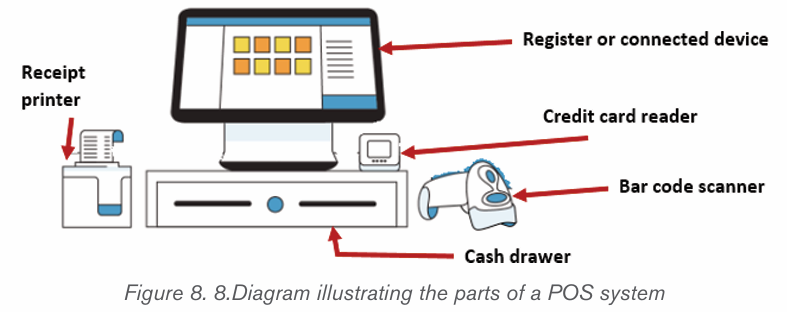
Connected device, like an iPad or other tablet: These are devices
equipped with a monitor allowing the user to view a list of items and
interact with the system Credit card reader: A card reader lets a customer pay by credit card
while in the store.
Cash drawer: This is a place where cash can be kept in case the
store accepts payments in cash. POS software that’s connected to a
cash drawer can minimize fraud by tracking exactly when the drawer is
opened.
Receipt printer: A paper receipt shows customers exactly when and
what they purchased and how much they paid.
Bar code scanner: A bar code scanner reads an item’s product de
tails so you can ring it up. It can also be a quick way to double-checkthe price, stock level, and other details.
Application activity 8.2
1) What is the technology used by billing machines in printing the bills?
2) What are the 3 main parts of a billing machine?3) What is EBM version 2
8.3 Note detector
Activity 8.3
1) Suppose you are a teller at a new bank which features will you check
in a note in order to discover counterfeited notes
2) Which device will your bank buy in order to detect fake notes easily?
3) What are the advantages that using the device stated in question 2 has?
A note detector is a device which is designed to sort identify a fake note which
does not have all the attributes of a nation’s notes. Fake notes can be identified
by using hands and eye, a counterfeit detector pen, or a machine known as anote detector.
i) The Counterfeit Detector Pen
Counterfeiters don’t use expensive special inks to try to closely duplicate paper
currency. They instead try to create a bill that looks like the authentic one by using
their available means which include wood-based paper. However, their bills would
not raise any initial suspicion when used in an everyday purchase.
One of the simplest tools used for counterfeit detection is a Counterfeit
Detector Pen. This pen contains an iodine solution that reacts with the starch
in wood-based paper to create a black, marker-like stain. When the solution
found in this pen is applied to the fiber-based paper used in authentic bills there
is no change in color and no stain appears. This tool is useful for identifying
amateur counterfeit currency. However, when dealing with more sophisticatedcounterfeit bills, utilizing a more complex detector is be necessary.
ii) Fake notes detection by a counter
Some banknote counters can also detect counterfeit notes by using one of the
following methods:
• Magnetic counterfeit bill detection: This is a method by which the
specialized magnetic ink which is found in bills is read by currency
counters with magnetic detection capabilities to identify counterfeited
bills from genuine ones.
Magnetic inks are ones with pigments containing magnetic material typically
iron oxide similar to what is used in the coatings of audio and video tape. These
inks are employed by most countries in the printing of paper currencies.
There are different methods and devices used in detecting the magnetic
properties in currency such as hand-held units and single-bill readers that
require the user to rub or slide the bill across a sensor. This device then emits
an audible signal to indicate the presence of the magnetic properties in the
bill. These devices are easy to use and are effective but they are impractical
for banks and big businesses with big amounts of cash to verify. There are
also more effective and quick modern money counters equipped with magnetic
counterfeit technology which can scan hundred or even thousands of bills per
minute.
• UV counterfeit detection: This is a method in which detection
devices use ultra-violet light to detect fake notes. With this method the
counterfeit detector works by detecting the UV fluorescent phosphors
used on authentic bills. This phosphor produces a reaction when
placed under the UV light but remains hidden when viewed under
normal lighting conditions. The UV ink changes its appearance and can
then be easily seen by the human eye under UV light.
Apart from banknotes detectors which have fake notes detection functionalities,
there are note detectors which have the sole functionality of detecting fake
money by using the ultraviolet light or the magnetic detection method. To use
these devices the user places suspicious notes in the appropriate place and thedevice detects its authenticity

Application activity 8.3
1) Explain the methods used by a note detector to identify fake notes2) By doing a research on the internet, identify the parts of a note detector.
8.4 Automatic Teller Machine
Activity 8.4
You have at least once visited banks in Rwanda.
1) Explain how the process of withdrawing and depositing money at a
bank is done
2) Give the name of a machine that can do the task of a human teller?
3) Explain how withdrawing and depositing money using the machinestated in 2) is done.
An ATM known in full letters as an Automated Teller Machine, is a specialized
computer device that is used by bank customers to perform transactions on their
bank accounts. With these devices customers can check account balances,
withdraw or deposit money, transfer funds from one account to another, print astatement of account activities.
ATMs can be found in financial institutions like banks. However there are also
ATMs that can be displaced and found at other places like airports, shopping
malls where there may be many people needing cash. ATMs started being usedas a response to labor cost and request to get cash even after working hours.
8.4.1.Parts of an ATM
Like other computers and most electronic devices, an Automatic Teller Machinehas two parts namely hardware and software.
A. Hardware
The hardware parts of an ATM work together in order to make a transaction
possible. An ATM has parts that are visible by the client that can be considered
as an interface and other parts which are visible by the bank administrators.
Although each ATM offers various features other than basic services, all the
devices contain the same components. The parts of ATM are detailed below :
Card Reader
A card reader is a device that can decode the information contained in a credit
or debit card’s magnetic strip or microchip. In finance, this term refers to the
technologies used to detect the account number, cardholder information, and
authorization code contained on a credit card. When a customer inserts a card
in the machine, a card reader reads the account details of the clients then verifythe provided information and process the transaction.
Keypad
A keypad for electronic devices is an input unit which enters data in that device.
Keypads have keys which are mostly numeric and letter keys. When the bank
card holder has put it in the ATP slot, he/she is prompted to enter a password,
choose among different options, etc and this is done using the keys found onthe keypad
Cash Dispenser
A cash dispenser is the part that contains cash. Cash dispensers are connected
with a safe that contains cash. Through cash dispensers, customers receivebanknotes in return to the transaction they made.
Printer
An ATM printer has the role of printing a receipt of the performed transaction.
The printed receipts include all the details of the transaction for cash withdrawal.
It further shows the total balance that a cardholder has in their bank account.
Screen
The display screen in ATM shows the cardholder all the details. It prompts the
customer through each step of the transaction process. Nowadays advanced
ATM screens may be touchscreens whereby instead of using the physical keythere is a virtual keypad laying under the screen.
SpeakerThe speaker provides feedback in form of audio when a particular key is pressed.
Vaults: This is a house to which store the parts of the machinery requiring restricted
access.
Note also that, like other computers, ATMs have most hardware parts found
inside a computer like processors and motherboards to support the whole
circuitry. Moreover they have sensors and indicators and cameras. One of the
functions of a sensor is to measure if the thickness of the bill is normal in order to
avoid that two bills may pass at the same time which would result in a customerreceiving more money than requested.
A. Software
Like any other electronic device that performs complex tasks, an ATM has an
operating system. Today, the vast majority of ATMs worldwide use Microsoft
Windows among which a big number runs on Windows XP (95% in 2014).
There are also a small number of ATMs which are still running older versions
of Windows such as Windows NT, Windows CE or Windows 2000. Some
others use newer operating systems such as Windows 8.1, Windows 10 andWindows 11.
Windows is not the only operating system for ATMs because in these days
Linux is also finding some ground like in Brazil where the Banrisul bank’s ATMsrun on Linux.
8.4.2.Withdrawing and depositing from an ATM
The process of withdrawing cash from an ATM machine has to go through a
number of steps starting by insertion of the bank card and a withdrawal of thatsame card. Those steps are outlined below:
Step 1: Insert an ATM Card in the card slot
Step 2: Select the language from the language options appearing on the display
screen
Step 3: Enter ATM Pin using the keypad. For most ATMs PIN are in 4 digits.
Do not ever share your ATM Pin with anyone even with bank staff. Ensure that
nobody is watching you, while you enter the Pin. Make sure you enter a right pin
as entering a wrong one may lead to the blockage of the ATM card.
Step 4: Select the type of transaction which can be withdrawal, deposit or
transfer.
Step 5: Select your type of account: As an individual banker, you should be
choosing a savings account, as current accounts are a special type of accounts
used by businesses. Some ATMs offer you a choice to add a line of credit to
your account. This can help a banker when they need excessive money in an
emergency.
Step 6: Enter the withdrawal amount. The withdrawal amount should not be
more than the balance in your account.
Step 7: Collect the cash from the ATM cash slot
Step 8: Take the receipt which is produced by the ATM printer. Making the
printer produce a receipt is done by prompting the ATM to print it. If you choosenot to have a receipt, it will not be produced.
A. ATM malfunction errors
The hardware components specifically the ones which move may wear out or
get old therefore resulting in a faulty equipment
• Faulty dispenser
When the dispenser has problems, customers insert their ATM cards in the slot,
enter their password or PIN, select the cash withdraw option and fill the cash
amount but when it arrives at the steps of counting and dispensing the cash
everything halts yet the customer’s account has already been to the full amount.
Another scenario is that ATM may fail to provide the full requested amount.
When such errors happen, the customer will have to apply for payment and the
bank manager will verify that application.
• Worn out card reader
Bank cards have a dark magnetic stripe on the back which contains specific
details about the card and its owner. When the bank card is inserted in an ATM,
the reader verifies the information on the card before it authorizes the transaction.
As a card is used again and again, the ATM card reader wears it out therefore
making the reading of information on the card impossible. If this happen, obviously
the transaction the customer wanted to carry out will not be done.
• Broken Keypad
The keypad which is used as an interface between a custom and the ATM may
be broken or one key may stick or may be unresponsive. If among the keys that
the customer needs have such problems, a transaction will not be possible.
• Receipt Malfunctions
The ATM printer may not give a receipt due to different reasons such as when
the machine has run out of paper, the printer has run out of paper, there is a
paper jam or any other problem with the ATM printing system. Since the receipt
contains vital information about the ATM transaction, it’s imperative that any
issues with printing receipts is handled quickly.
• Software glitches
ATM have different software whose technology never ceased to advance. Many
ATMs now have touch screen and other technology that relies on computer
software to function. Like other machines that run on computer software, ATMs
can have software glitches. When such problem happens, a transaction in not
possible.
Application activity 8.4
1) By doing a research on the internet, identify the internal parts of an
Automatic Teller Machine
2) Can an ATM be hacked? If yes explain the likely consequences of this hacking.
Skills Lab 7
Use different ICT tools in Accounting you have learnt to perform the
following activities:
a) Counting money
b) Detecting fake money
c) Withdrawing using ATM cards
End of unit assessment 8
1) What are the benefits of using ICT tools in Accounting
2) Describe the ICT tools you have seen in this unit
3) Using the internet do a research on the software tools used inAccounting
REFERENCES
1. MINEDUC, (2013), Education Sector Strategic Plan, Kigali.
2. MINEDUC, (2014), ICT in Education Policy, Kigali: MINEDUC.
3. MYICT, (2011), National ICT strategy and plan NICI III-2015, Kigali.
4. Herman Oduor, 2014, Senior Secondary Certificate Computer Science
for Rwanda student’s book 4, East African Publisher, Kigali
5. National Curriculum Development Centre(NCDC), (2010), computer
science curriculum for computer science economics and mathematics
option & mathematics physics and computer science option, Kigali,
Rwanda
6. www.sumup.co.uk/invoices/dictionary/quotation/ 27/03/2022
7. www.umucyo.gov.rw/ 27/03/2022
8. https://www.reviews.in/best-billing-machine.html
9. http://mybillmachine.com/ visited on 27/03/2022
10. https://carnation-inc.com/ visited on 28/03/2022
11. https://tax-handbook.rra.gov.rw/handbook/explanation-of-ebms/ visited
on 30/03/2022
12. https://squareup.com/us/en/townsquare/what-pos-system visited on
31/03/2022
13. https://en.wikipedia.org/ visited on 01/04/2022
14. https://www.tutorialspoint.com
15. https://www.tutorialandexample.com16. https://www.tutorialandexample.com
