UNIT 05 : DATABASE MANAGEMENT WITH ACCESS
Introductory activity
The management of TERIMBERE Sacco cooperative located in GICUMBI
District, would wish to hire a qualified consultant in ICT who will design an
efficient Database which will help them to shift from a tradictional paper
based data recording to a Computerized database management system.
Below are some main services offered and transactions performed by
different concerned staff:
a. Creation of a new customs account using cooperative customer form
b. Money-deposit by customer using cooperative customer bookc. withdraw money from customer account using cooperative customer book
As a student in ICT in Accounting, you are requested to :
i. Suggest different ways that can be used to keep the above information.
ii. What is the benefit of keeping that information in a computerdatabase compared to keeping it on a paper?
iii. Which Office program to use to create that database?
5.1 Understanding database
Activity 5.1
1) What do you understand by the term Databaseb) Give examples of databases you know in the society you live in.
In our information society, record keeping and data processing using data
base has become an important aspect of every organization such as Hospital,
School, Universities and Governments. Databases are used all the time, often
without knowing it. For example, withdrawing money from the Bank’s ATM
requires the existence of a database where information about clients and theirbalance is kept.
5.1.1. Database concepts
A. Definitions
a) Database
A database is an organized collection of related data so that its contents can
easily be accessed, managed, and updated. It is considered to be organizedbecause the data is stored in categories that are accessible in a logical manner.
b) Data
Data are unprocessed raw facts that include text, number, images, audio, and
video. The data are useless for decision-makers until they have been processedor refined in some manner.
c) Information
Information is data that has been processed, refined and given in the format that
is suitable for decision making or other organizational activities.
For example: Report about student fee paid is useful information for financesection.
d) Database management
Database management refers to a set of activities performed on the database.Some of these activities are :
Insertion of new records in tables are,
Deletion of unnecessary records,
Updating records if the information is changed,
Searching for records according to the given criteria whenever needed.
e) Database Management System (DBMS)
The Database Management System (DBMS) is an application software that
enables users to define, create, and maintain the database and which provides
controlled access to this database.
The DBMS receives requests (queries) encoded in SQL and translates those
queries into actions on the database.
A database system comprises of five major components :
1. Data: The database contains both the operational data and the meta
data (the data about data).
2. Hardware: this consists of the secondary storage (hard disk) on which
the database resides together with the associated devices.
3. Software: Software refers to the collection of programs used within
the database system. It includes the DBMS software the application
programs, together with the operating system, including network software
if the DBMS is being used over a network. The application programs that
allow users to store information in an ordered manner for timely and quick
retrieval is called Database Management System (DBMS).
4. Procedures: These are the instructions and rules that govern the design
and use of the database. This may include instructions on how to log on
the DBMS, make backup copies of the database, and how to handle
hardware or software failures.
5. People (users): This includes the database designers, database
administrators (DBAs), application programmers and end users.
Databases are useful. For example many computing applications deal with large
amounts of information; they have become an essential component of everyday
life in this modern society. Database systems give a set of tools for storing,searching and managing this information.
A. Importance of database
– A database enables to put data on the disposition of users for consulting
or updating
– The database should manage the privileges granted to its users.
– A database can be local in one machine just used by one user or
distributed in many machines accessible by many users through a
network (sharing of data).
– The main advantage of using database is its possibility to be used
simultaneously by many users as per the image below :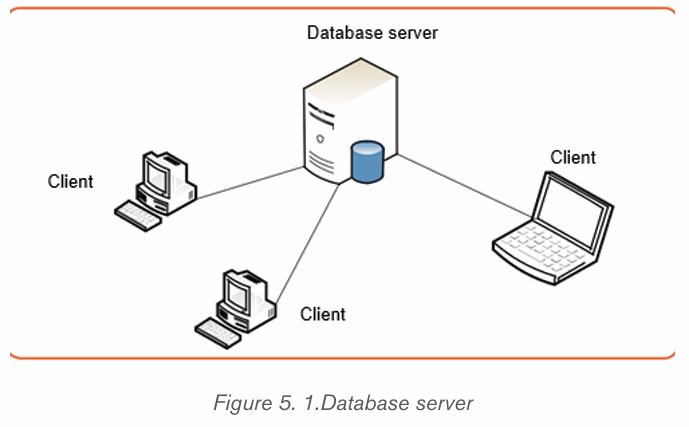
5.1.2. Database Approaches
A. Paper based database
This is a kind of database where information is kept on papers. Keeping a
database on papers makes its management difficult and the size of paperscumbersome.
Paper based database presents the following disadvantages:
Papers can be lost, damaged over time or due to calamities like fire and flood
If there is change in the stored information the hard copies are hard to update
or may even rewriting the information on a new copy having the new updates.
Compared to information kept in a computer, paper-based databases aredifficult to copy and search.
A. Computerized database
When a database is stored electronically on a computer and can be manipulated
using a computer, it is called a computerized database. Computerized databasescan be of different types:
a) Traditional File Processing Systems (TFPS) approach
This is an approach which was used before the invention of modern Database
Management Systems (DBMS) but this approach was difficult to use as
It required advanced knowledge and to use it one had to have advanced
programming knowledge which was not easy for a common user. Users had
to write application programs to store data in form of files on the computer
permanent storage device (Hard Disk) and each application program written by
a user had to define and manage its own data.
Compared to manual management of information, the Traditional File Processing
presents the following advantages:
• Simplicity: the design of file processing is more simple than designing
a database
• Efficiency: file processing cost less and can be more speedy than
database
• Customization: you can customize file processing more easily and
efficiently than database because files are related with the application
and it has all the data needed for that application.
In File-based processing, for each database there is a separate application
program as shown by the following figure: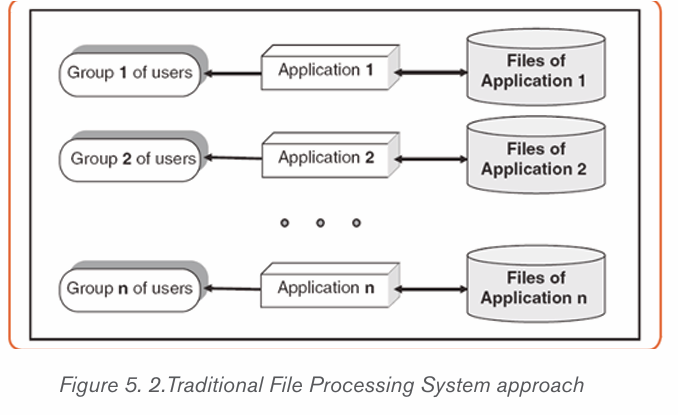
Traditional File Processing System presents the following disadvantages :
• Separation and isolation of data : as data is isolated in many files,
it is not easy to have access to data.
• Duplication of Data : because of the decentralized management,
data may be scattered on different computers and this has as
consequences a misuse of storage space as data is repeatedly stored
in different locations (This is known as Data Redundancy) and a loss
of data integrity as data is stored in different locations and the different
copies may be slightly different.
• Wastage of storage space: Duplication of data leads to wastage
of storage space. If the storage space is wasted it will have a direct
impact on cost. The cost will increase.
• Loss of data integrity : Data integrity means data consistency.
Duplication of data can also lead to loss of data integrity; the data are
no longer consistent.
• Data dependence: in traditional file processing, the structure of data
files is embedded in the application programs, so any changes to the
structure of a file may require changing all programs that access this file.
Therefore, data dependence means the application program depends
on the data. This means that if some modifications have to be made on
data, then the application program has to be rewritten.
• Incompatible file formats: the structure of files is embedded in the
application programs and therefore structures are dependent on the
application programming language.
The many difficulties attached to using Traditional File Processing Systems
prompted researchers to invent another way to use in order to make data
management more effective. This came up with another approach which is
DATABASE and Database Management System (DBMS)
ii) Database Management System (DBMS) approach
DBMS is a software that provides a set of primitives for defining, accessing,
and manipulating data. In DBMS approach, the same data are being shared by
different application programs. As a result, data redundancy is minimized. TheDBMS approach structure is shown in the following figure.
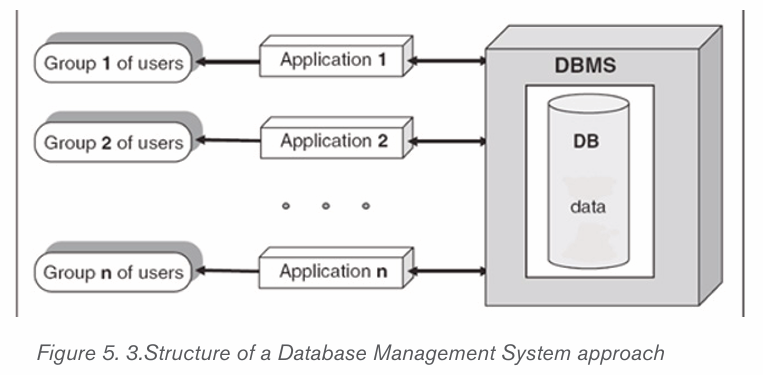
Advantages of DBMS
There are many advantages of database management system.
• Centralized Data Management : In DBMS all files are integrated into
one system thus reducing redundancies and making data management
more efficient. One user can know data in another department without
moving from one department to another. This is called data integration.
• Data Independence : Data independence means that programs are
isolated from changes in the way the data are structured and stored.
• Data consistency : In DBMS, data inconsistency is avoided. Data
inconsistency means different copies of the same data will have
different values.
For example : Consider a person working in a branch of an organization. The
details of the person will be stored both in the branch office as well as in the
main office. If that particular person changes his address, then the “change of
address” has to be maintained in the main office as well as the branch office. In
case the “change of address” is maintained in the branch office but not in the
main office, then the data about that person is inconsistent. DBMS is designed
to have data consistency which makes DBMS have the quality of increased dataintegrity.
• Data sharing : Due to the fact that data is centralized, many different
users from different locations can share data.
• Data recovery after a crash : After a break down, DBMS allows to
recover data after a crash. The crash may be caused by power failure
or hardware failure.
• Concurrent transaction control : A transaction means a collection
of operations that perform a single action in a database. Example :Transferring money from one account to another.
Concurrent transactions mean that many transactions are being done
simultaneously or concurrently.
Concurrent transaction problem occurs when multiple users want to access
data in the database at the same time like for example when someone wants
to withdraw money from his/her account while at that time there is someone
else who is using ATM card to withdraw money from the same account. DBMS
ensures that many users are accessing data and these problems are controlled.
Increased Data security and safety: DBMS allows data to be highlyprotected against unauthorized access.
Application activity 5.1
1. Differentiate paper-based database from a computerized database
and give examples
2. Outline advantages of DBMS
3. List any thre3 examples of DBMS
5.2. Key terms used in Database
Activity 5.2
By doing a research explain the term database and identify the keyterms that are used in the database field and explain them
5.2.1 Relational Database
There are different types of database but the most common type is the one that
use tables commonly known as Relational Database.
A relational database is the one having one or many Relations which are the
mathematical concept representing physically a table
In this kind of database, the table also known as an Entity may have two or many
columns also known as Attributes or Fields and details on items are stored in
rows also known as Tuples or records. A certain column has some values that
is allowed to accept and those are called Domain.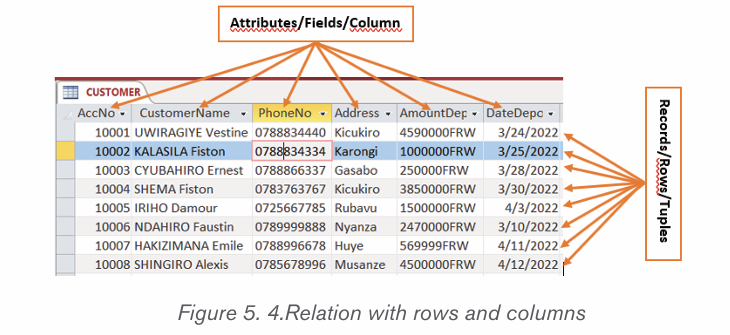
Cardinality refers to the number of rows in a table. In the above table cardinality
is 6
Degree of a relation (table) equals to the number of its attributes (columns/
properties/fields). For example, in the above table, degree is 5.
Properties of Relations in a relational database
• A table (relation) in a relational database has properties which have to be met
• The relation has a name that is distinct from all other relation names in
the database
• Each cell of the relation contains exactly one atomic (single) value
• Each attribute has a distinct name
• The values of an attribute are all from the same domain. The domain is
the type of data acceptable in a column. For example, Name column
should not accept only numbers data
• Each tuple is distinct; there are no duplicate tuples The order of
attributes and tuples has no significance
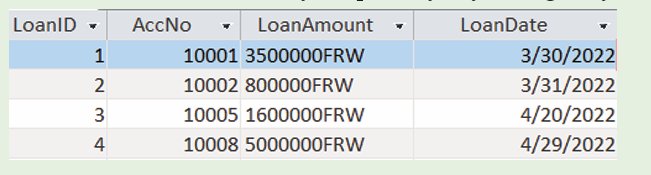
A. Primary Key
In a database table, a primary key is a column or combination of columns that
uniquely identifies table records. This column does not accept null values and all
its values are unique. The primary key column can be created by the database
manager or can be generated by the database according to the defined sequence.
A table can have only one primary key, which may consist of single or multiple
fields. When multiple fields are combined and used as a primary key, they are
called a composite key. If the primary key is already defined, it is not possible
to have two records having the same value in that field.
The figure below shows an Access table in which an AccNo column plays
the role of a primary key. The values in that column are unique, no value is like
another and no cell is empty (no null values).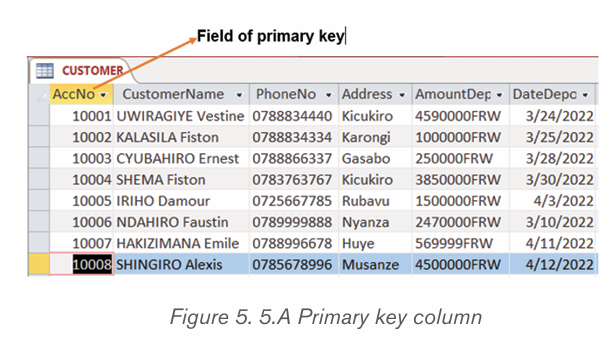
A. Foreign Key
A foreign key is a field or collection of fields in one table that refers to the
primary key in another table. The table containing the foreign key is called the
child table, and the table containing the candidate key is called the referenced
table, parent table or master table.
The image below shows a table with a unique value column whose values are
those from the master table, the AccNo is the primary key of the CUSTOMER
table while in the LOANS table the AccNo is the foreign key. All values in the
Master table don’t need to be in the child table.
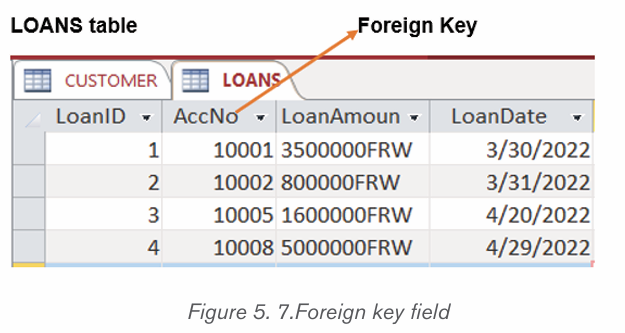
D. Candidates keys
All attributes that can uniquely identify an entity are called candidates keys. They
are never NULL and cannot allow duplication of values. When multiple possibleidentifiers exist, each of them is a candidate key.
5.2.2 Relational Database Management System (RDBMS),
RDBMS serves as an interface between the database and end users or
application programs to make sure that data is well organized and remainseasily accessible.
DBMS helps provide concurrency, security, data integrity and uniform data
administration procedures. Advanced query languages such as SQL are used
along with the DBMS package to interact with a database.
Some DBMS examples include MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, dBASE, FoxPro,Access, etc
A. Table
Tables are database objects that contain all the data in a database. In tables,
data is logically organized in a row-and-column format similar to a spreadsheet.
Each row represents a unique record, and each column represents a field in the
record.
B. Record
A record is simply a set of data stored in a table, for example, a customer
record. A record in a database is an object that can contain one or more values.
Groups of records are then saved in a table; the table defines the data that each
record may contain.
Below is the CUSTOMER table: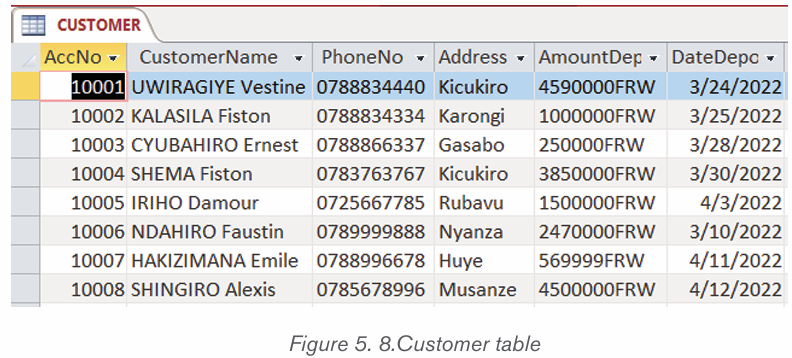
A. Field
Field is the component that provides structure for a table. A table without fields
does not exist. For instance, a database creator can create an empty table thathas fields defined but no rows (records).
A. Data type
A data type is a description of the kind of data in a table column. Each database
system recognises its own set of datatypes, although some are common to many.
Table 5.1 Data type descriptionsBelow are different data types of table CUSTOMER in design view:
A. Relationship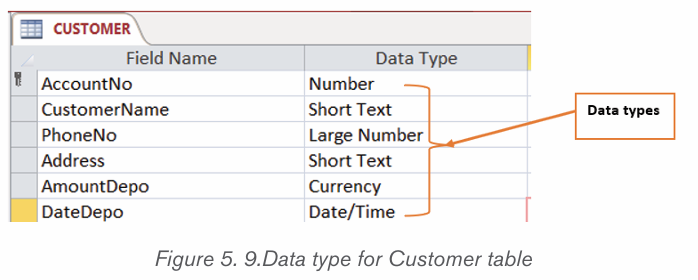
Database relationships are associations between tables that are createdusing join statements to retrieve data.
• Types of relationship
There are three types of relationships between the data that are likely to encounter
at this stage in the design : one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many. To be
able to identify these relationships, it is needed to examine the data and have anunderstanding of what business rules apply to the data and tables.
a) One-to-one (1-1)
A one-to-one relationship is a link between the information in two tables,
where each record in each table only appears once.
Another example, there might be a one-to-one relationship between employees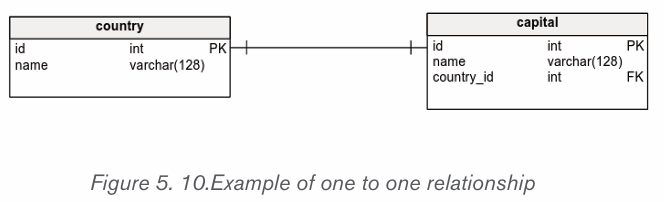
and the cars they drive, because only one driver can drive a car.
a) One-to-many (1-M)
In a relational database, a one-to-many relationship exists when one row in
table A may be linked with many rows in table B, but one row in table
B is linked to only one row in table A. It is important to note that a one
to-many relationship is not a property of the data, but rather of the relationshipitself.
Note : One customer can make many orders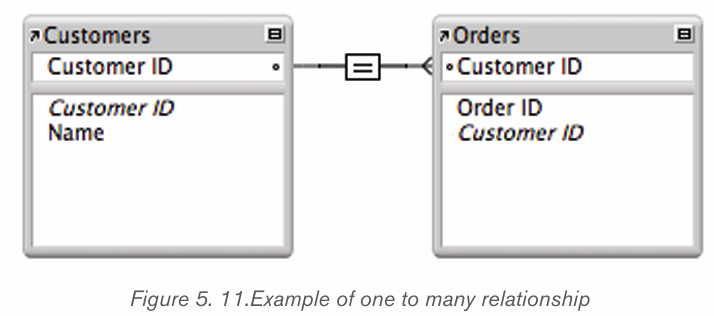
a) Many-to-many (M-M)
A many-to-many relationship refers to a relationship between tables in a
database when a parent row in one table contains several child rows in thesecond table, and vice versa.
5.2.3 Structured Query Language (SQL)
SQL is a programming language used for managing data in a relational database
SQL can be used to create a database and tables inside that database, insert
and delete data in tables, query the database and whatever other task to bedone on a database.
SQL statements look like ordinary English though the words may appear straight
or are in a shortened form. Below is a statement in Access that displays allinformation from the table CUSTOMER.
When the SQL statement above is run, it displays all the records in the table
CUSTOMER.
Application activity 5.2
1. What do you understand by the relational Database
2. Explain the following terms:
a) Field
b) Table
3. Differentiate candidate key from foreign key
4.By using examples, distinguish the types' of data relationship
5.Enumerate the properties of relation in relational database6. Given the table below; identify the primary key, foreign key and records
5.3. Database design process
Activity 5.3
1. Having hired as a database designer at your school,
explain different steps you will go through to design
a database that will manage your school library.
2. Discuss the benefits for your school when students,
teachers and librarian will start using the newcomputerized database of the library.
The most important thing to do to start designing a database is to plan ahead.
When a case that needs a database creation is presented, before switching on
a computer and starting creating the database it is better to think about the type
of information to work with and the types of questions that the database should
answer, what information needs to be stored and what specifically are the links
between them. The next phases are to verify all requirements specifications, torepresent the data with diagram, and to plan the database.
When data is more complex, there are more needs to plan. Even the simplest
database should be thought thoroughly on paper before being created usingDatabase Management System such as Microsoft Access, SQL, MySQL, etc.
A well-designed database performs well and adapts to future needs by giving
users access to essential information. Poor planning often results in a database
that fails to meet the current needs or the needs that may arise in the future
cannot easily be integrated in the existing database
In planning the database, regardless of its size and complexity, the following
basic steps are used :
• Gathering information (investigation)
• Identify the objects (Important Entities and their Attributes).
• Model the objects.
• Identify the types of information for each object.
• Identify the relationships between objects.
• Database optimization through normalization.
• Data entry and manipulation
5.3.1. Gathering information
Before creating a database, there is a need to understand the problem that
the database is expected to solve. If the database is to replace the traditional
method, file based approach method, then the existing system will give most of
the information needed.
In this step there is a need to work with everyone involved in the existing system
which can be a paper based database, an old database or no database at
all. Gathering techniques include collecting copies of customer information,
management reports, and any other documents that are part of the existing
system or interviewing staff who are familiar of the work done in that institution,
the staff who are expected to use the new database or who use the old one.
This step is useful in designing the database and the interfaces.
The output of this step is information on how the business of an institution is
carried out and this can be analyzed to derive the different tables (entities) that
will be needed.
5.3.2. Identifying the important entities and their attributes
During the process of gathering information, the key objects or entities that will
be managed by the database must be identified. The object can be a tangible
thing such as a person (for example student, employee, and patient), a product,
or it can be a more intangible item, such as a department in an institution, a
Combination in a school. Each distinct item in the database should have acorresponding table for which column titles are attributes of the entity.
5.3.3. Identifying the Relationship between entities
It is good to relate or associate information about various items in a database.
Identifying the relationship between entities in the design process requires
looking at the entities and determining how they are logically related and adding
relational columns (foreign key) that establish a link from one table to another.
After identifying the relationship between entities an Entity Relationship (E-R)Diagram is created using appropriate symbols.
5.3.4. Modeling the objects
As the objects in the system and their attributes are identified, they are recorded
in a way that represents the system visually. They are recorded using Relationalmodel and Entity Relational model.
5.3.5. Identifying the types of information for each object
After identifying the primary objects/entities in the database as candidates for
tables, the next step is to identify the types of information that must be storedfor each object.
These are the columns in the table of the object. Fields/columns should be kept
simple, the more atomic are the fields the more flexible will be the database.
For example, in a database of names and addresses, it is better to keep eachpart of the person’s name as a separate field.
5.3.6. Database optimization through normalization
One of the most important step to consider when designing a database
is database definition. If tables are not set up properly, it can cause a lot of
headaches at the time of extracting/retrieving required data.
Normalizing a database eliminates redundancy, and other anomalies that may
arise as the database is being used. Redundancy means that the same data issaved more than once in a database.
Those anomalies are: insertion anomalies, deletion anomalies and updation
anomalies. Normalization will be developed in details in the subsequent sections.
Update anomalies: If data items are scattered and are not linked to each
other properly, then it could lead to strange situations where one row is updated
but others are left with old values leading to inconsistency in database.
Deletion anomalies: As data may be scattered somewhere else, in a database
that is not normalized when one record is deleted, other related records mayremain in the database.
Insert anomalies: In a very long table which is not normalized, one may need
to insert some values but may not have values to insert for some columns which
may lead to tables in which some cells are filled while others are empty.
Normalization is a method to remove all these anomalies and bring the database
to a consistent state.
A Properly normalized design allows to use storage space efficiently, eliminate
redundant data, reduce or eliminate inconsistent data and ease the databasemaintenance
5.3.7. Data entry and manipulation
When the database is completely designed the last step is using it by putting
in it the data. Data can be manually entered from hard copy forms or it can be
imported from other files like excel or other files supported by the current one.
While entering data or importing it from other files make sure the data is valid
because if the database has strong validation rules, which is an ideal, it will notaccept those data.
Application activity 5.3
1. Explain clearly the role of gathering information before desing a
database2.What do you understand by database normalization?
3.With an example, differentiate update and deletion anomalies in Database optimization.
5.4. Creating, Saving, Closing and Opening a database
Activity 5.4
Create a database to manage the stock of your school kitchen:
1. Create the following three tables:
a. Foods
b. StockIn
c. StockOut
2. Identify for each table the name of the column that will have unique
values (values that don’t resemble and no duplicate values in thewhole column and that cannot contain null values)
Activity 5.4
Create a database to manage the stock of your school kitchen:
1. Create the following three tables:
a) Foods
b) StockIn
c) StockOut
2. Identify for each table the name of the column that will have unique
values (values that don’t resemble and no duplicate values in thewhole column and that cannot contain null values)
5.4.1 Database creation
A database is a collection of information. In Access, every database is stored in
a single file and has to have a name and different objects.
Different objects in an Access database are tables, queries, forms, reports,
macros, and modules.• Tables : They store information. A database can have as many tables
as are needed.
• Queries : They let database users perform actions on tables which canbe data definition queries or data manipulation queries.
• Forms : Those are attractive windows created by the database user
and provide a way to view or change information in a table
• Reports : They are summary of the information contained in different
tables which have a common characteristic.
To create an Access database first start Microsoft Office Access by clicking on
the start button then on Access 2019, in the window that will appear write thedatabase name and click on Create.
The new database is now created but has no table.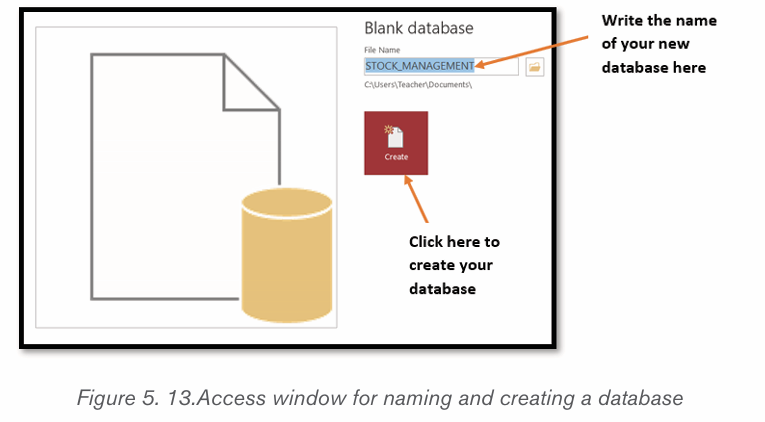
Tables can be created using one of the available options : Datasheet view, Design View
i) Creating a table in Datasheet view
When the database is created, the default option to create tables is using the
Datasheet view. The Datasheet view is the option which allows to view many
rows in a table at the same time. This option also allows to filter and sort data
using the built in sorting and filtering options. This view is also useful for quickly
viewing the details of many records, adding new records and deleting records
from a table.
To create a table in Datasheet view, do the following :
Click on Create menu then on the table icon. New table with two columns andone row appears.
• To add new columns to the existing table in the image above click on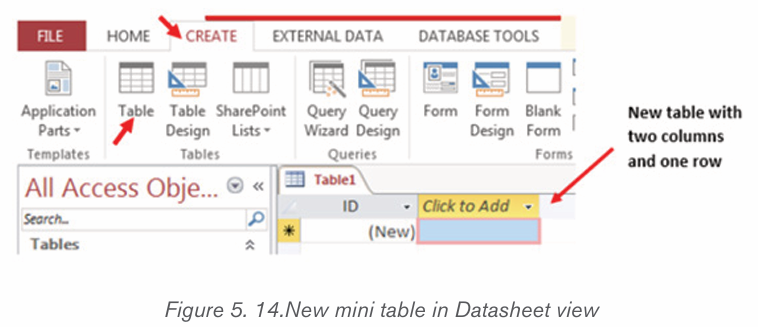
the drop down arrow next to Click to Add. In the list of data types that
will appear choose one suitable to the information to be kept in the column.
• Write the name of the new column. Repeat the same steps of choosing
the data type and renaming the column up to when you have all the
needed columns.
• Save the table by clicking on the save icon write the table name andclick on OK.
ii) Creating a table in Design view
A table can also be created in Design view and this provides additional options
compared to the Datasheet view like adding/changing the primary key and
changing the column data type. In Design view, the table structure is createdbut entering data requires using the Datasheet view
To create a table in Design view go through these steps :• On the Create tab, in the Tables group, click Table Design or in the
Views group click on the View tab then choose Design View.
• In the new window that will appear, specify the field names, Data types
and the descriptions of the fields (optional) and set the primary key by
selecting the field name then clicking on the Key icon. The primary key
column will then have a key icon in front of it
• Save the new table by clicking on the save icon and specifying thename.
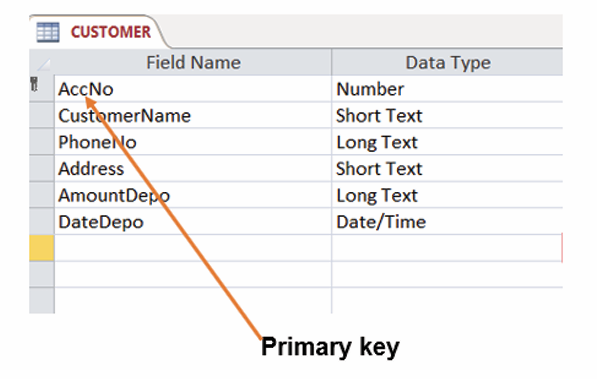
Figure 5. 15.Window to create a table in Design View
5.4.2 Opening and closing a database
A database created can be closed by clicking on the close icon of the Access
window in which it is opened. This same database can also be opened by first
opening Microsoft Office Access then going to the File tab then choosing the
Open option and browsing the database to open.
Once the database is opened, it will show its different objects (Tables,Queries, Forms, Report), choose the one you want to have access
Application activity 5.4
1. Using Access, create a database named “Payroll“ and save it on
the desktop.
2) a. Create two tables which will keep respectively Staff identification
and their Salary.b. Indicate the primary key for each table.
5.5. Creation of tables relationship
Activity 5.5
1. What do you understand by relationship in relational database?
2. With examples, explain different types of tables relationship
Table relationship is the backbone of database management as it helps in
making the many tables seem one. Without this option it would not be possible
to retrieve data from different tables at the same time but every table would be
taken as a separate entity.
For tables to be logically related they have to have a common column which
binds them; this is the foreign key.
A relationship is established between two tables when one table uses a foreign
key that references the primary key of another table. This is the basic conceptbehind the term relational database.
Here is in brief why table relationships are needed:
As most of the time a database has more than one table to work while running
queries it is necessary that tables be related as the query works by matching
the values in the primary key field of the first table with a foreign key field in the
second table.
While designing a form or a report, MS Access uses the information it gathers
from the table relationships already defined to present you with informed choices
and to prepopulate property settings with appropriate default values.
These foreign key-primary key pairings form the basis for table relationships andmulti-table queries.
A. Different relationships
There are three main relationships in database tables namely one to one, one tomany (or many to one) and many to many.
i) One to one (1:1)
In a one to one relationship one record in one table can be related to only one
other record in the other table. This kind of relationship can be implemented in a
single table and therefore does not use a foreign key which is needed only whentwo tables are to be related.
This kind of relationship is not so common as the data stored in table B could
just have easily been stored in table A. However, there are some valid reasons
for using this relationship type like security purposes, the need to diminish the
number of columns in a table and slash it into smaller tables, and various otherspecific reasons.
These are examples of One to One relationships in real life:
• In a marriage, each spouse has only one other spouse.
• A son has only one mother
• A car can be driven by one driver at a time• A President and a country
ii) One to many /many to one (1:M / M:1)
A one-to-many relationship allows a single record in table A to be related to
multiple records in table B but a record in table B can have only one matching
record in table A. This is the most common type of relationship and it is used torelate one record from the ‘primary’ table with many records in the ‘related’ table.
Examples :
Consider a business with a database that has Customers and Orders tables. A
single customer can purchase multiple orders, but a single order could not belinked to multiple customers.
• A mother can have many children
• A businessman can have many cars• One federate country can have more than one state
iii) Many to many (M:M)
Two tables have a many-to-many relationship when a single record in the first
table can be related to one or more records in the second table and a single
record in the second table can be related to one or more records in the first table.
Briefly two tables A and B are said to have a many-to-many relationship when A
record in Table A can have many matching records in Table B, and a record inTable B can have many matching records in Table A.
Examples :
The relationship between TEACHER entity and STUDENT entity is an example
of many-to-many relationship. One teacher teaches many students and one
student is taught by many teachers.• Many students are taught by many teachersCUSTOMER table• Many customers may buy many products
The CUSTOMER table will have 6 columns namely IDcustomer, Lname, Lname,
PhoneNo, Address and Gender. The data types for all the columns is Short Text.The Sex column will allow only two values: male and female.
The IDcustomer field does not need to be too long, that is why we specify its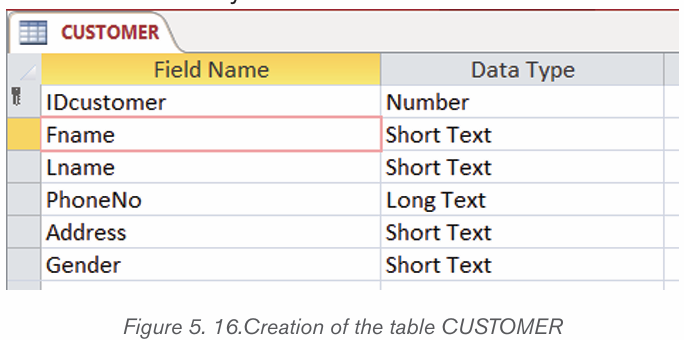
length as Long Integer. The length of a field is specified in the Field Propertiesshown in the image below which is the part of the window for fields definition.
Using this same Field Properties window, one can specify different properties
of the table fields like a customized error message when wrong data type isentered in a table and validation rules.
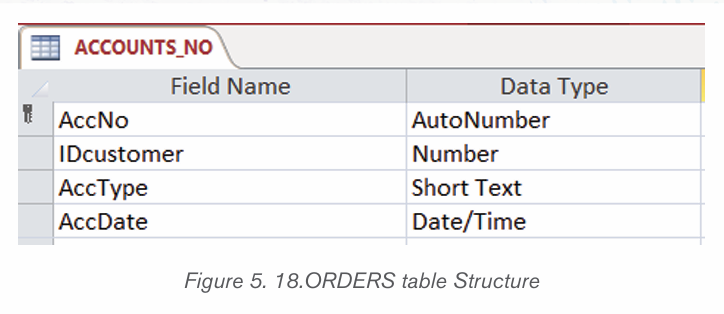
ACCOUNT_NO table
This table will contain information about Customers account number.
The values of Idcustomer column will be those that exist in the CUSTOMER
table Idcustomer column while those in the AccNo column are those that existin the ACCOUNT_NO table AccNo column.
The DEPOSIT table
The DEPOSIT table has 4 rows namely IDDeposit which uniquely identify everyCustomer deposit (primary key), the AccoNo, Amount and DateDeposit.
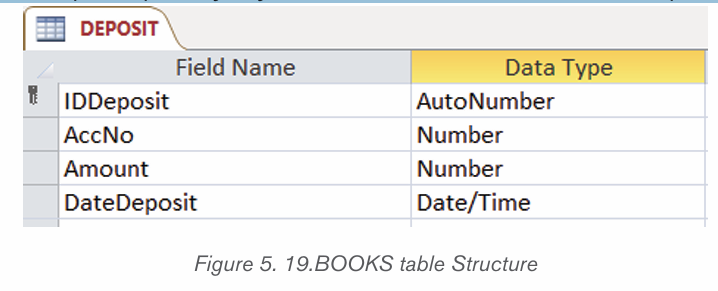
WITHDRAW table
The WITHDRAW table has 4 columns namely IDwithdraw which uniquely identifyevery Customer withdraw (primary key), the AccoNo, Amount and Datewithd.
LOANS table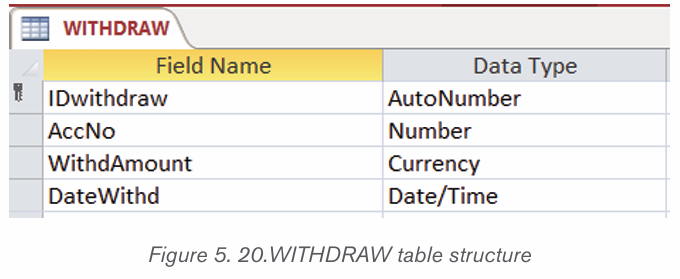
The LOANS table has 4 columns namely LoanID which uniquely identify everygiven loan to a customer (primary key), the AccoNo, LoanAmount and LoanDate.
BALANCE table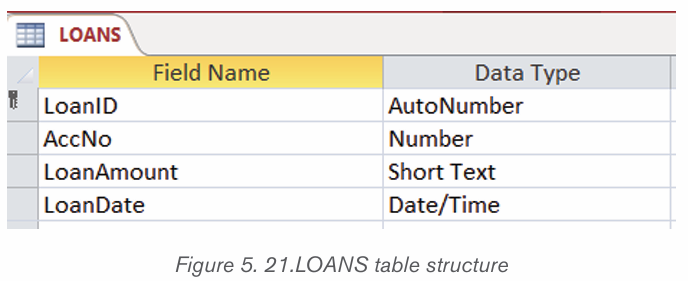
The BALANCE table has 4 columns namely IDBalance which uniquely identify
customer balance (primary key) whenever he/ or she deposits or withdrawsmoney, the IDdeposit, IDwithdraw and Balance.
B. Creating relationships
As it has been seen tables which are not normalized present many anomalies
which make such a database very bad. When database is normalized, its tables
are broken down into smaller tables which help eliminate redundancy but there
must be a mechanism to link those tables so that they can be queried as one.The mechanism used is to relate different tables by using foreign keys.
A relationship between tables is built like this :
• Under the Database Tools tab click on Relationships tool , drag and
, drag and
drop the tables between which to create a relationship from the leftpane to the relationships area. Tables are dragged.
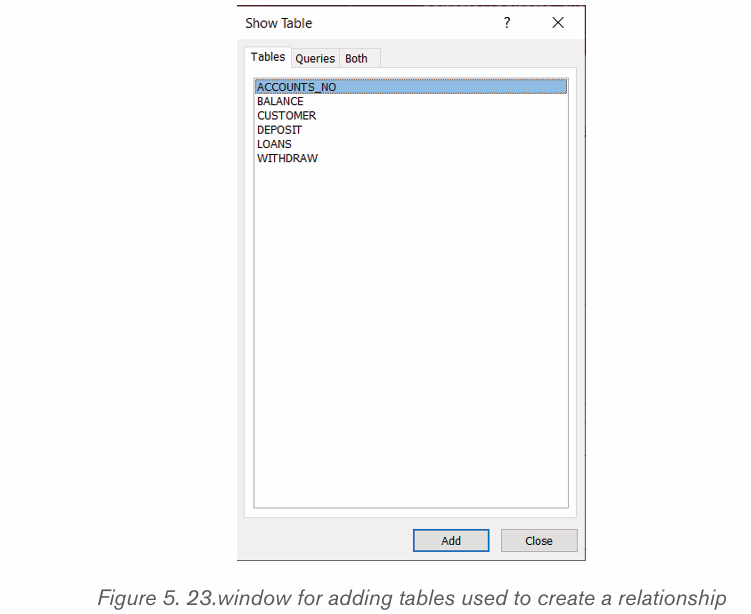
• Arrange the tables properly so as to make an easy to read diagram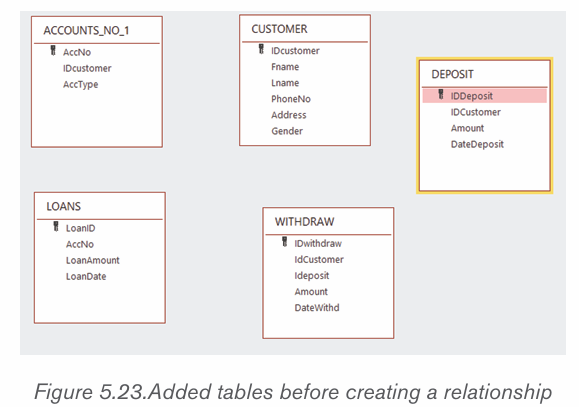
once the relationship is created.
• Click and hold down the column name from which the relationship is
to be established and move the cursor (from left to right) to the other
related column in the other table. The window below that will appearwill help in editing the relationship.
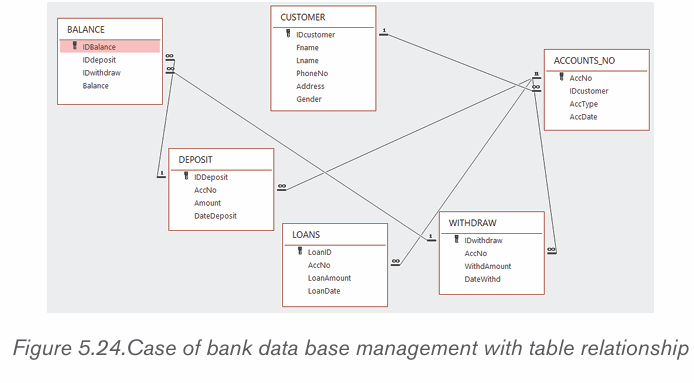
• Continue the process in the above bullets until all the tables to be linked are linked.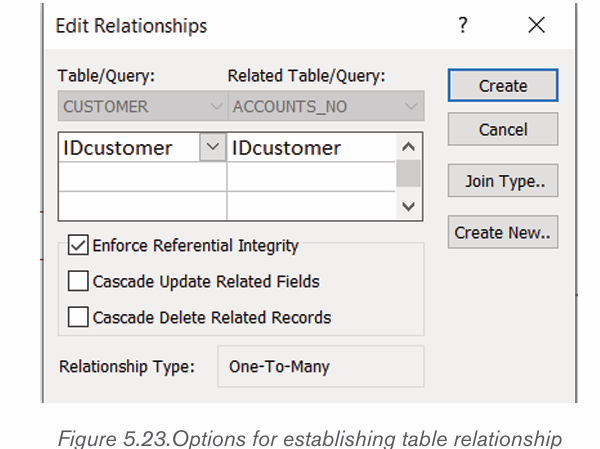
Note that the columns to link have to be of the same data type and of the same
length if not so the attempt to create a relationship will result in an error.
After linking all the tables, the relationships between the library database tableswill look like in the image below:
Application activity 5.5
1. Create a database with the following tables then create a relationship:
a. ITEMS (Iditem, itemname)
b. ORDER (Idorder, Iditem, quantity,dateorder)
c. STOCKIN (Idstockin, Idorder, quantity, datestockin)d. STOCKOUT (Idstockout, quantity,datestickout)
5.6. Adding Data to a database
Activity 5.6
1. Using your own words, explain what is data entry in database
2. Differentiate back-end from front-end
3. Discuss different ways that can be used to add data to an Access databaseAdding Data to a database (Data Entry)
Data entry is a direct input of data in the appropriate data fields of a database
through the use of a human data-input device such as a keyboard, mouse, or
touch screen, or through speech recognition software.
Before doing a data entry be aware of fields to enter and the validation rules
associated with those fields. This will help in avoiding to enter a wrong data type
in a field and knowing that the database will not accept that data type, it will take
time to figure out the right data to enter. Know which fields get data from other
fields (lookup), fields that have specific values (like yes/no). In short, study the
table/form before entering data.
Adding data to an Access database can be done in 3 main ways :
• Data entry through a front end interface
• Entering data in a Datasheet view table• Entering data using an Access form
5.6.1 Data entry through a front end interface
In programming and development, a front-end is a term that describes a user
interface that is used to interact with the database instead of working directly
with the database.
For example, a website front-end developer
handles the visual aspects of how the web page looks and responds to the
visitor. The front end interacts with the back end (database) which may be on
the local computer or remotely placed on a server.
The front end provides forms which are developed using different languages
like HTML (HyperText Markup Language), HTML5 and programming languages
to link the webpages to the database like PHP.
The forms provided by the front end has different fields which correspond to
the fields in the database and alert the data entry clerk whenever form validation
rules are not followed. They also provide a “submit” button on which to click for
sending data in the database.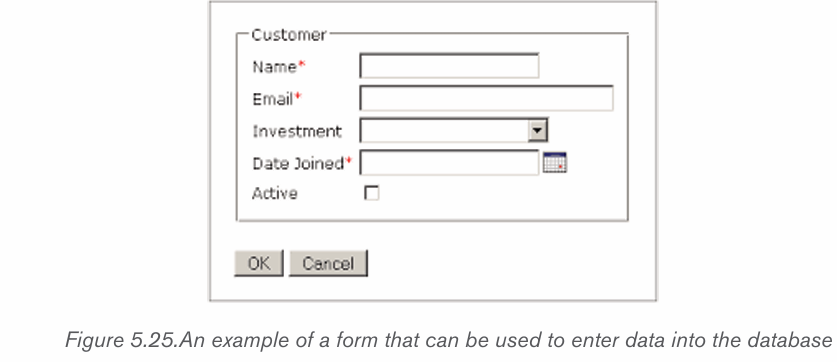
5.6.2 Entering data in a Datasheet view table
Datasheet view is one of the table viewing in Access which allows a user toenter directly data in a table.
To add records to a table in datasheet view in Access, click into this row and enter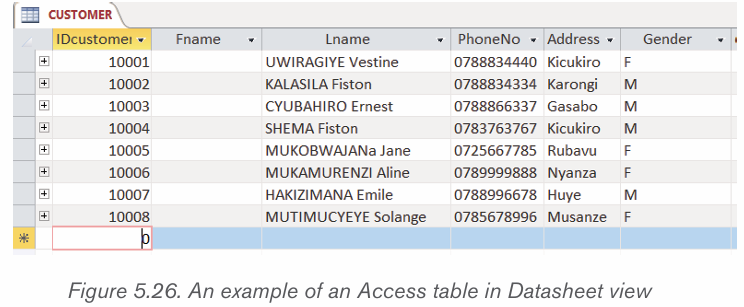
the new record. The asterisk will then change to a picture of a “pencil” as data is
being entered. The pencil will let know which record that is being edited. Another
new “New Record” row also appears once it is done with the current row.
While entering data in an Access table, it is necessary to follow the validation
rules of the table because when they are not respected, the data will not be
accepted.
5.6.3. Entering data using an Access form
Microsoft Access 2019 provides different objects the common ones being
tables, queries, forms and reports.
Access forms are accessed by clicking on the Create tab then select one of the
form options provided in the Forms group.
The Form tool is used to view table data in a form format and is accessed just
by opening the table and clicking on the Form tool
To navigate in the form’s data or to enter new data use the tools available on
Record tools group. By using the tools in this group one will be able to move to
the next row, move to the last row, empty the form so as to enter new data and
searching for a row containing specific text.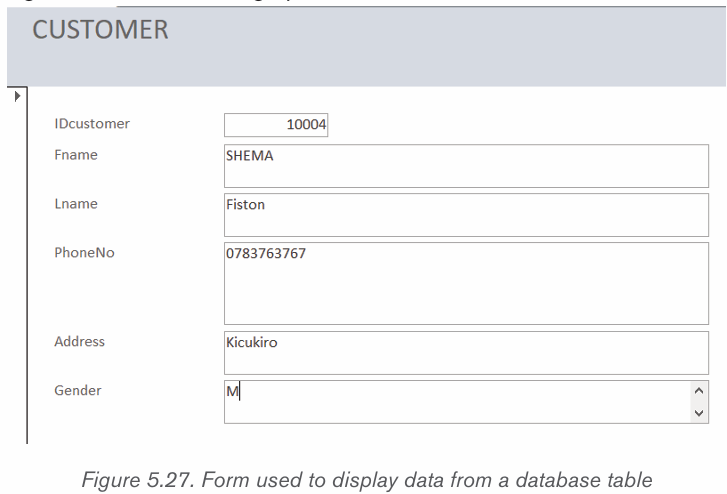

A. Designing a form from scratch
A form can also be designed from scratch and not created from an existing
table. The created form will then create a table to which it will be linked.
To create a form from scratch go through these steps :
• Under the Create tab click on the Form Design tool
• In the form area drag and drop the form design tool to use but before
this name your form by using the Title tool found in the header/footer
group. If needed also set the form’s logo.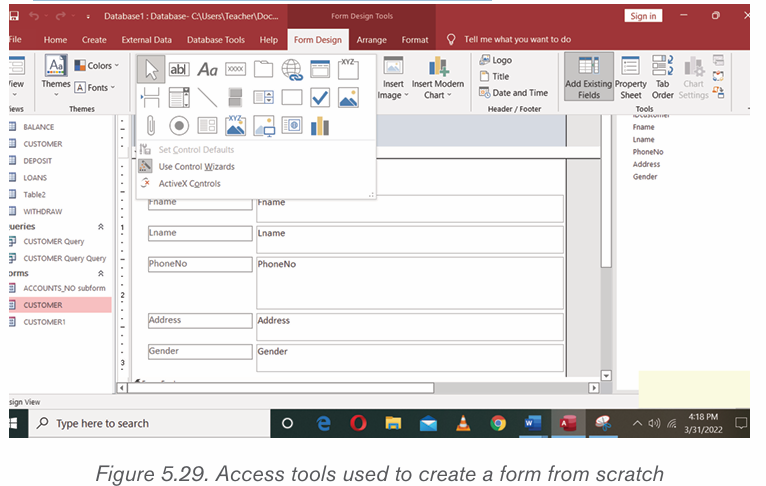
From left to right the different tools to choose from are: Select tool, Text Box,
Label, Button, Tab Control, Hyperlink, Web Browse Control, Navigation Control,
Option Group, Insert Page Break, Combo Box, Chart, Line, Toggle Button, List
Box, rectangle, Check Box, Unbound Object Frame, Attachment, Option Button,
Subform/Subreport, Bound Object Frame and Image.
B. School library form
Here is a form created from scratch which accepts data and submits it to the
database table. It has been created by taking the different tools available for
building a form. The different tools dragged from the Form Layout tool are: Logo,Title, Text Boxes, Option Group and Button.
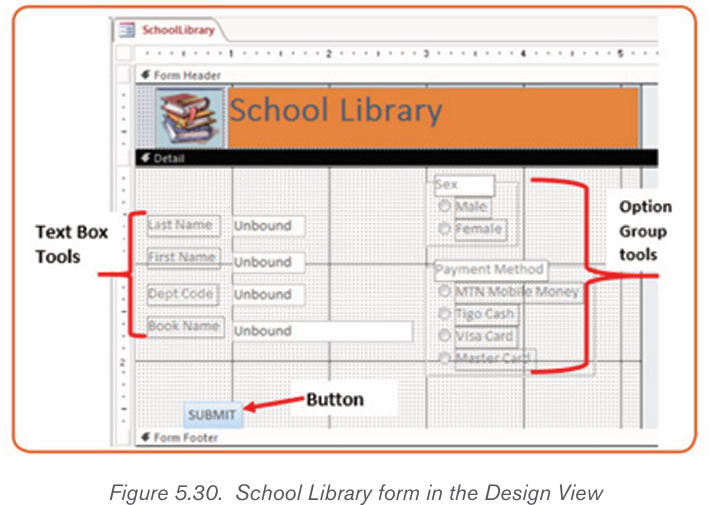
The above Form viewed in the Form view looks like this :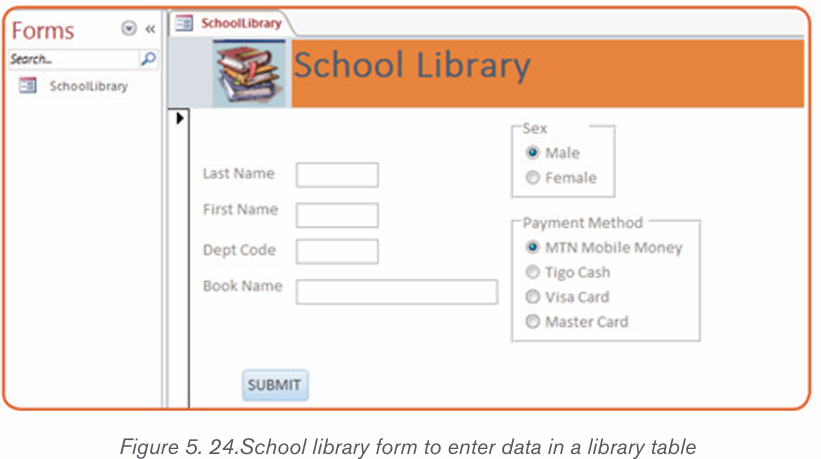
Application activity 5.6
1. Design the form below that can be used to enter student registrationinformation in the database.
a) Add your school logo.
b) Make sure the table/form is validated to accept only valid data.
5.7. Querying a Database in design view
Activity 5.7
a) Create the following ACCOUNTSNO table as below: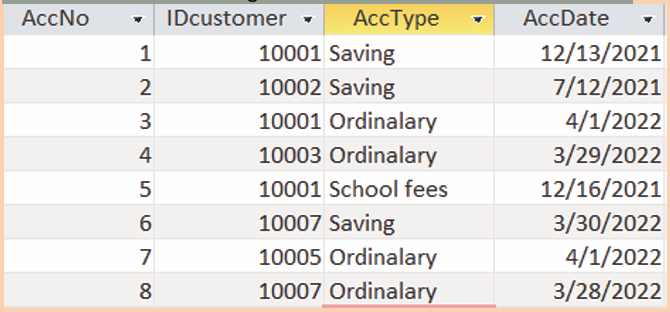
b) Display all accounts numbers which have been created in 2021.c) Display all customers accounts.
A query is a request for data results, and for action on data. A query can be used
to answer a simple question, to perform calculations, to combine data from
different tables, or even to add, change, or delete table data.
A query is a request to the database tables for data results or for action on
data. This query can help answer a question, combine data from multiple tables,
perform calculations, change or delete table data.
In Access, querying a database can be done in two ways: by writing a
query in a language that is understandable to the database that is known as
SQL query or by designing or by using the Design View approach. This section
is going to talk about querying an Access database in Design view.
5.7.1 Benefits of using queries
The benefits of using queries are so multiple :
• As the table increases in size and may have thousands of records, it is
so difficult to spot one record by scrolling through the database. The
query approach solves this problem by spotting the needed records
and performing needed actions on them
• A query can help in applying a filter on table’s data and get only what
is needed
• When one same action is to be performed on many records, it would
be a loss of time to repeat every action on every record. Doing itautomatically in a query quickens the process
5.7.2 Types of queries in Access
There are mainly two types of queries in Access:
• Select queries which are used to display data from tables or to perform
calculations
• Action queries which are used to add, change or delete data
A. Select queries
A select query is the one which displays records from one or more tables of a
database The SQL SELECT statement returns a result set of records from one
or more tables. A SELECT statement retrieves zero or more rows from one or
more database tables or database views basing on the selection criteria if there
is one.A select query on one table
To design a select query, do the following:
• Under the Create tab click on Query Design
• In the “Show Table” window that will appear choose the table on which
the query is to be run and click on Add. In this case the table BOOKS was chosen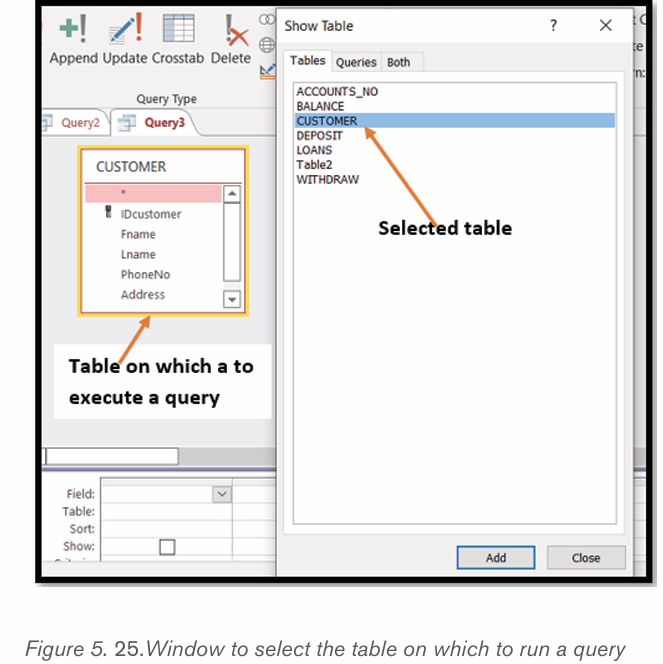
• After selecting the table click on Close to close the window
• In the table, select the columns to appear in the result. In this case onlythese columns were selected: Fname, Lname, Address, and PhoneNo.
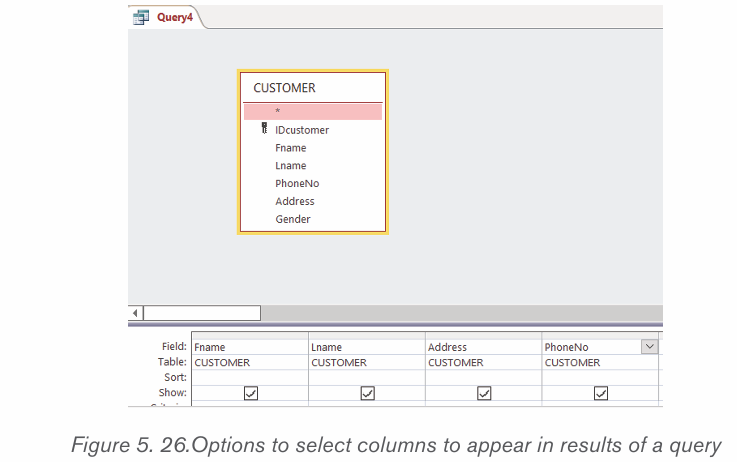
• If there is a criterion for selection specify it and if there is not one leave
the criteria field empty. In this case only books in the science category
are going to be displayed
• Click on Run to get the results of the query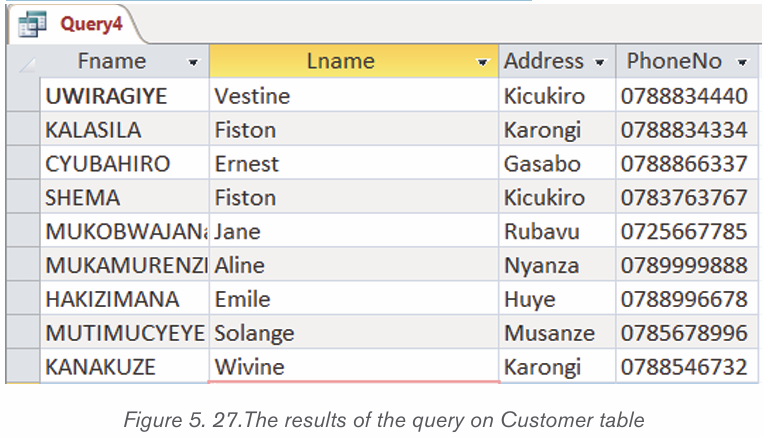
Select query on multiple tables
In a normalized database it is possible to link more than two table in order to get
a more revealing display (report). For example, in the table that have been used
one may need to know the names of students who borrowed science books and
their combinations.
To answer such a question requires to combine columns from three tables and
thanks to the foreign keys in the tables this combination is possible. The tables
to combine are: CUSTOMER, ACCOUNT_NO and DEPOSIT
To make such a query do the following :
• Under the Create tab click on Query Design
• Chose the table that are to be used in the new query. Here select all the
tables (CUSTOMER, ACCOUNT_NO and DEPOSIT)
• Select the columns that will appear in the results. Those columns are:
Fname, Lname, AccNo, Amount and DateDeposit.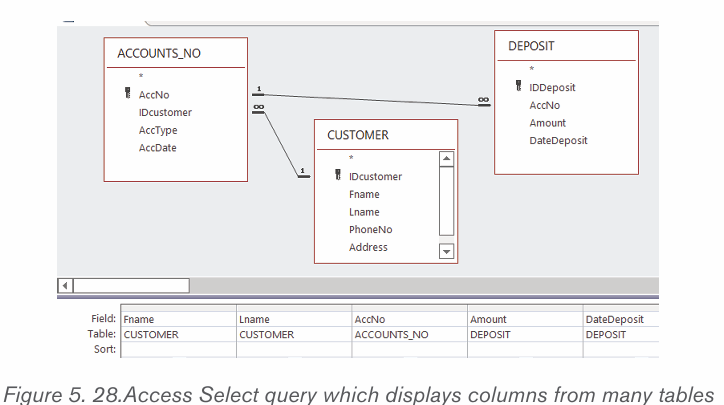
• Run the query by clicking on the Run tab which is found under the
Query Tools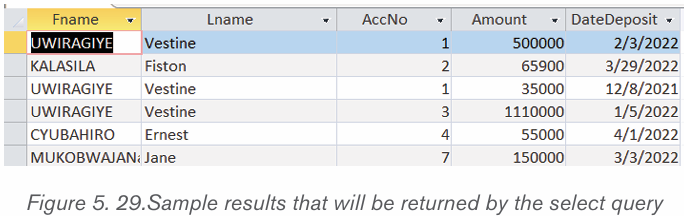
Note that this kind of query that combines many tables is possible only if tables
are related by the use of foreign key.
Application activity 5.7
Using the four tables (CUSTOMER, ACCOUNT_NO, DEPOSIT, and
LOANS) create queries in Design View that do the following:
d) Customers whose gender is Female
e) Customers whose name start with letter “M”
f) All loans that have been given to different customers in the year of 2022
End of unit assessment 5
Q1. Explain the following terms:
1. Database
2. Field
3. Table
4. Query
End of unit assessment 5
Q2. Give the difference between primary key and foreign key
Q3. Explain why it is necessary to have a normalized database
Q4. Outline the advantages of DBMS
Q5. Using the four tables (STUDENTS, BOOKS, ORDERS, and
COMBINATIONS) used through this section create queries in Design
View that do the following:
a) Students whose sex is Male
b) Students whose name start with letter “U”
c) Books which are in the Mathematics category
d)Students who study in MPC option in 2010
Q6. GIRUBUZIMA is the PHARMACY that orders, stores and sells drugs
to patients. You are requested to create the database throught doing the
following different activities:
a. Propose the name of database and create it
b. Identify and create the necessary tables(entities) and thier corres
poning fields, their primary keys and foreign keys.
c. Create a relationship between the tables
d. Create forms that will allow GIRUBUZIMA PHARMACY Pharmacist
to record all orders, to store and sell different kinds of drugs.
e. Write SQL query which displays all drugs in the stock that havebeen manufactured before end of the year 2020
Skills Lab 5
You are a business owner. Create a database that will help in the daily
management of that business. The database created should include at
least the following:
• Tables with primary keys and foreign keys
• Forms to provide interface
• Automatimatically produce reports• Has features like automatically calculating taxes, etc
