UNIT 1: COMPUTER SECURITY
Introductory activity
Jane is an accountant in charge of payroll preparation in the Ministry of
Finance of Rwanda. She has a computer which, two months ago was
working quickly and properly. Every day she uses internet connection for
operating some online transactions, she also used a flash disk to share
her work with different workmates. Today her computer is no longer
responding quickly as before, when connecting a flash disk on her
computer some data are lost others hidden, some data are duplicated,
disorganized and most of the time her computer restarts itself while sheis working.
Discuss the main different causes of the above-mentioned issues of Jane's computer
identify the risks of an unsecured computer
Describe how this computer can be secured
Describe how data stored in a computer can be protectedActivity 1.1
What do you understand by security of the computer?
1. How a computer user can protect data and information stored in that computer?
2. What will happen if a user leaves his/her computer without switching it off?
1.1.1 Computer security
Computer security means techniques developed to safeguard information stored
on a computer. It is also the protection of computer systems and information
from harm, theft, and unauthorized use. The standard for a good security tells us
that 10% of security safeguards are technical, 90% of security safeguards rely
on the computer user to adhere to good computing practices.
Computer security is everyone’s responsibility; this means that everyone who
uses a computer or mobile device needs to understand how to keep their
computers, devices and data secure.
1.1.2. Computer security related terms
Security: This is a state of feeling safe and protected. Something that provides
a sense of protection against attack, harm or loss is security.
Malware: It is a file or code, typically delivered over a network, that infects,
explores, steals or conducts virtually any behavior an attacker wants. And
because malware comes in so many variants, there are numerous methods to
infect computer systems.
Spyware: Spyware is software with malicious behavior that aims to gather
information about a person or organization and send it to another entity in a
way that harms the user. It installs itself on your computer and starts covertly
monitoring your online behavior without your permission.
Trojan horse : A trojan horse, is a type of malware that conceals its true content
to fool a user into thinking it’s a harmless file.
Worm: A computer worm is a program containing malicious code that attacks
host computers and spreads via a network. Network worms exploit security
vulnerabilities in various applications. Due to the availability of the internet, they
can spread all over the world within a few hours of their release.
Adware : Adware (or advertising software) is the term used for various pop-up
advertisements that show up on your computer or mobile device. Adware have
the potential to become malicious and harm your device by slowing it down,
hijacking your browser and installing viruses and spyware.
Authentication: This is a process used to identify individuals based on
username and password. This process establishes whether; Someone or
something is in fact who or what is declared to be. Authentication ensures that
the individual is who he or she claims to be but nothing about access rights ofan individual.
Authorisation: This is permission to perform action.
Username: A username is a name that uniquely identifies someone on a
computer system. For example, a computer may be setup with multiple accounts,
with different usernames for each account.
Password: A Password is a word, phrase, or string of characters intended
to differentiate an authorized user or process (for the purpose of permitting
access) from an unauthorized user. A password is used to prove one’s identity,or authorize access to a resource.
Username is almost always paired with a password. This username/password
combination is referred to as a login, and is often required for users to log in
to computer or websites. For example, to access the e-mail via the Web, it is
required to enter the username and password. Once, it is done the usernamemay appear on the screen but the password is kept secret.
Application activity 1.1
1. Explain the meaning of the term Computer security.
2. Identify consequences of security violation
3. What is the role of applying password and username to login to a page?
1.2 Importance of computer security
Activity 1.2
The school accountant, wanted to make a payroll, but was unable to find
the final updated list of school employees on his/her computer. He/she
remembered that some days ago, she/he gave the same computer to the
school secretary to write a letter.
The school accountant decided to use any list found on his/her computer.
1. Discuss the impacts that may arise when the School Accountant
uses any list found on his/her computer
2. In pairs, discuss what can be the solution for the next time for not
losing either the letters or the list
3. Apart from the School Accountant and Secretary, who else has the
responsibility to protect the computer? Support your answer withpositive impacts of protecting a computer in different ways
The importance of computer security is to protect the computer and its data as
well as its user’s identity. The data and information that most users store on their
hard drives are often far more valuable than the computers themselves. Broadly,
the importance of computer security lies in how harmful it can be if that data islost.
Companies often store a lot of very sensitive information electronically, including
trade secrets, customer lists and extensive corporate documents, both finished
and those in progress. The importance of computer security is obvious in these
contexts. It is perhaps less obvious for home computer users, but it is no lessessential.
When computer hackers gain access to a computer, they can often see
everything that is stored there. This might include bank information, tax
identification documents and sensitive health information, along with
more ordinary files such as Word Processing documents and family
photos. Cyber criminals can use personally identifiable information to stealidentities and perpetrate fraud.
The importance of computer security also extends to larger network security.
A compromised computer can be manipulated and made into an agent of a
cyber crime ring. As one example viruses and malware are often designed tohijack and exploit email address books. They can sometimes also turn home
computers into bots, which are computers that have been taken over and are
made to network with others all over the world to perpetrate crime. Computers
that have fallen victim to bot networks are not fully used by their owners, often
they run very slowly and constantly their memory space is diverted to runningmalicious scripts.
Security of computer should help protect the confidential and important data
stored on a hard disk storage.
The major importance of computer security is:
Protect the computer
Protect data
Protect user’s identification.
This is mainly because data present in the computer can be misused by
unauthorised intrusions.
• Purpose of computer security is to:
• Keep your information on computer protected
• Maintain your computer’s overall health
• Help prevent viruses and malware
• Help programs run more smoothlyGenerally, computer security helps keep information safe
Application activity 1.2
1. Give the major importance of computer security
2. Discuss different kinds of data to be protected.
3. Discuss and write a brief report on the importance of computersecurity at your school, in financial institutions and in education field.
1.3 Computer threats
Activity 1.3
A consultant in the finance field joined her office as usual in the morning, after
switching on her computer, she realized that it goes slowly, some data on the
hard disk were unavailable, and faced complications of saving document on
the hard disk, yet the computer was before operating properly for long time ago.
– Describe the reasons of the above issues and propose what could bethe solution.
1.3.1 Threats
A threat, in the context of computer security, refers to anything that has the
potential to cause serious harm to a computer system. A threat is an activity,
attack, situation that may happen, with the potential to cause serious damage.Threats can lead to attacks on computer systems, networks and more.
1.3.2 Threat categories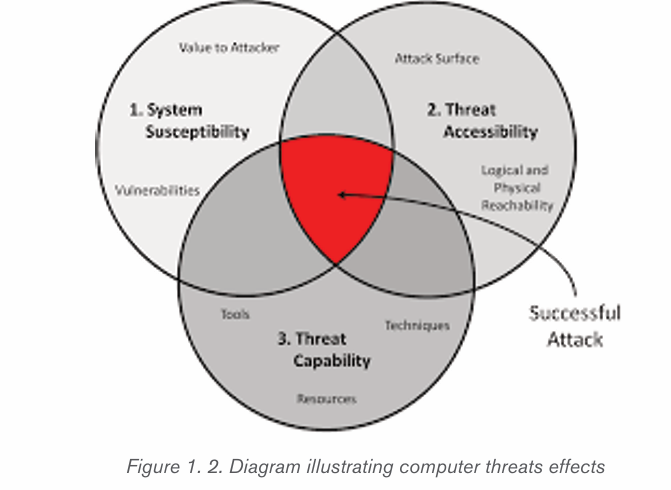
Knowing how to identify computer security threats is the first step in protecting
a computer. The threats could be intentional, accidental or caused by natural
disasters. Computer threats can be physical or logical.
• Physical threats
• Logical threats.
a) Physical threats
Digital storage media and hardware are subject to numerous internal and
external forces that can damage or destroy their readability. Below are some
cases of physical threats :
• Improper storage environment with high temperature, humidity, light, dust
• Over use mainly for physical contact media,
• Natural disaster such as fire, flood, earthquake
• Inadequate hardware maintenance,
• Hardware malfunction
b) Logical threats
Logical threats are events or attacks that remove, corrupt, deny access, allow
access, or steal information from a computer without physical presence of
somebody. These include viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, adware, SQLinjection etc.
1.3.3. Difference between logical threat and physical threats
Physical threats may include theft, vandalism and environmental damage
while logical threats are those that may damage your software systems, data, or
network without damaging your hardware.
General threats to information systems can cause the following:
Hardware failure: A malfunction within the electronic circuits or
electromechanical components (disks, tapes) of a computer system. Example:
a CPU socket damaged.
Software failure : The inability of a program to continue processing due to
erroneous logic. Example: A crash of a computer program.
Electrical problems: Are faults caused by electricity like a low-resistance
connection between two points in an electric circuit through which the current
tends to flow rather than along the intended path.
User errors: Is an error made by the human user of a computer system in
interacting with it. Example: A system file deleted unintentionally by a user.
Program changes ; modifications made to program. Example: a simple
modification in a program can affect the whole software.
Theft of data, software, services and equipment. When a physical or
logical component of a system is stolen, the whole system stops. Example:A computer cannot run without a RAM or cannot run with corrupted software.
Application activity 1.3
1. Discuss the difference between logical and physical threats
2. In the school computer lab, take one computer and remove all
available RAMs in the computer. Discuss what happens to the
functioning of the system.
3. Conduct a diagnostic of the school computer lab. From the diagnosis
enumerate the different threats found in the computers.4. Discuss the effect of both logical threats and physical threats
1.4 Computer virus
Activity 1.4
n the school computer lab, when one student inserted a flash disk in one
computer, all files are immediately deleted and the flash disk becomes
empty. Another student discovers that when he/she opens a document in
my Ms Word, the content is displayed in unknown characters.
In groups, discuss what should be the causes for such problems.
1.4.1 Definition
Computer viruses are unwanted software programs or pieces of code that
interfere with the functioning of the computer. They spread through contaminated
files, data, and insecure networks. Once it enters your system, it can replicate
to produce copies of itself to spread from one program to another program and
from one infected computer to another computer. Viruses are self-replicating
computer programs that interfere with the functioning of the computer byinfecting files, data, programs, etc.
1.4.2 Types of Computer Virus
1. Overwrite Virus
It is the simplest computer virus that overwrites the code of the host computer
system’s file with its own malicious code. The content of the infected file is
replaced partially or completely without changing the size of the file. Thus, it
destroys the original program code by overwriting it with its defective code. The
infected files must be deleted or replaced with a new copy as this virus cannotbe removed or disinfected.
2. Append Virus
As the name suggests, this virus appends its malicious code to the end of the
host program’s file. After that, it alters the file’s header in a way that the file’s
header is redirected to the start of the malicious code of the append virus. Thus,
this code is executed each time the program runs. However, it does not destroy
the host program; rather, it modifies it in a way that it holds the virus code andenables the code to run itself.
3. Macro Virus
Macro virus alters or infects the macros of a document or data file. It is embedded
as a macro in a document and adds its codes to the macros of the document.
The virus spreads when infected documents or data files are opened in othercomputers.
It also spreads through software programs, which execute macros such as Ms
Word, Ms Excel. Each time a document is opened using these programs, otherrelated documents will also get infected.
4. Boot Virus
The first macro virus, which was named concept, spread through emails with
attached Ms Word documents. It infected MsWord 6.0 and Ms Word 95
documents, which were saved using Save as option. Fortunately, it did notcause any harm, except for displaying a message on the screen.
Boot virus or boot sector virus alters the boot sector program stored in the
hard disk or any other storage device such as floppy disks. It replaces the boot
sector program with its own malicious version. It infects the computer only when
it is used to boot up the computer. If it enters after the boot-up process, it will
not infect the computer. For example, if someone forgets to remove the infected
floppy disk when the computer is turned off and then turns on this computer, itruns the infected boot sector program during the booting process.
Usually, it enters into the system through corrupt media files, infected storage
devices, and insecure computer networks. The spread of this virus is very rare
these days due to the decline in the use of floppy disk and use of boot-sectorsafeguards in the present-day operating systems.
5. Resident Virus
The resident virus stays permanently in the primary memory (RAM) of the
computer. When the computer is turning on, this type of virus becomes activeand corrupts the files and programs running on the computer.
6. Multipartite Virus
Multipartite virus spreads and infects in multiple ways. It infects both the boot
sector and the executable files stored on the hard drive simultaneously. When
the computer is turning on, the boot sector virus is triggered as it latches on
to the hard drive, which has the data for starting up the computer. Once it istriggered, the program files also get infected.
7. File Infector Virus
It is one of the commonly found computer viruses. It mainly infects the executable
files; the files with .com or .exe extensions. The virus becomes active when the
infected file is executed. The active virus overwrites the file partially or completely.Thus it may destroy the original file partially or completely.
8. Computer Worm
Computer worm is similar to a virus but is technically different from the virus. It
can replicate and spread like a virus, but unlike viruses, it does not need a host
program to spread. Being able to self-replicate it can produce multiple copies
of itself. It spreads through networks such as an email sent to an infected emailid can infect your system with a computer worm.
9. Trojan Horse
Trojan horse is a malware like a virus or a worm, but it is technically different from
both. It can’t replicate like virus and worm. Trojan horse hides itself in a program.
Once you install any such program, the trojan horse enters into your computer.
It can provide unauthorized access to a computer, send files to other computersand may delete files or can make other unwanted changes in a computer.
10. Cavity virus
It is also known as a spacefiller virus. As the name suggests, this virus tends to
install itself by occupying the empty sections of a file. It is not easy to detect thisvirus as it fills the empty spaces without changing the size of the file.
11. CMOS Virus
It infects the CMOS, which stands for complementary metal-oxide semiconductor
and is a memory chip that contains the system configuration. This virus canerase or reset the system configuration.
12. Companion Virus
It resides itself in a file whose name is similar to another program file, which is
executed normally. When the program file is executed, the virus gets activated
and performs malicious steps such as deleting the files on a computer harddrive. Globe virus is a first known companion virus, which was found in 1992.
13. Encrypted Virus
It encrypts its payload to make its detection more difficult. It comprises two
parts: An encrypted virus body and a decryptor, which decrypts the virus when
it is executed. After decryption, the virus can execute itself in order to replicate
and become a resident. Furthermore, it is different from cryptolocker, which is acomputer virus that encrypts the hard drive data and holds it for ransom.
14. Executable Virus
It is a non-resident computer virus, which resides in an executable file. Wheneverthe infected file is executed, it infects the other files.
15. Polymorphic Virus
It creates its thousands of copies itself; in each copy, it changes the sequence
and byte values to evade detection by antivirus software. Even the best
antiviruses may not be able to detect this virus. Polymorphic viruses affect data
types and functions and generally spread through spam, infected sites, andwhile using other malware.
16. Rabbit Virus
It is also known as wabbit, a fork bomb. It is capable of creating new processes,
and each of the new process further creates new processes. This process
continues until this virus utilizes all the available resources in the system and
system falls short of resources. It may cause the target system to slow down and
crash. For example, it is like an infinite loop that repeatedly creates processesthat consume lots of CPU cycles and operating system resources.
17. Stealth Virus
It is a hidden computer virus, which specifically attacks operating system
processes. It usually hides itself in partitions, files or boot sectors and is capable
of going unnoticed during antivirus or anti-malware scans making it capable ofintentionally avoiding detection.
18. Web Scripting Virus
The web scripting virus is a kind of computer security vulnerability through
websites which breaks our web browser security. This virus allows the attackers
to inject client-side scripting into the web page. It can steal our information from
the web browser. This type of viruses is usually used to attack the sites with alarger population such as social networking, e-mail, etc.
1.4.3 Characteristics of a Virus
Following are a couple of characteristics of any virus that infects computers.
• They reside in a computer’s memory and activate themselves while the
program that is attached starts running. For example: They attach
themselves to the explorer.exe in windows OS because it is the
process that is running all the time.
• They modify themselves after the infection phase making it so hard for
an antivirus to detect them.
• They always try to hide themselves in the operating systems by
encrypting themselves into cryptic symbols and decrypting themselves
when they replicate or execute.
1.4.4 Symptoms of a Computer Virus
There are many warning signs or symptoms which show that a computer is
infected with a virus, some of which are as follows:
• Slow computer performance: The computer may work slowly. The
result for this is that it will take more time to open or shut down, to open
a file, a document or a computer application, etc. The operating system
and internet speed may also slow down.
• Frequent pop-ups: A virus may cause unusual frequent window pop-ups.
• Hard drive issue: The hard drive may exhibit unusual high activity
even when it is not in use. It may cause unwanted changes to the hard
drive and may freeze or crash this device.
• Frequent crashes : One may experience frequent sudden system
crashes while playing games, watching videos, or doing some other
work using the infected system. A blue screen appears when it crashes.
• Unknown programs: Unwanted programs may open or start
automatically when the computer is turning on. These programs are
found in computer’s list of active applications. Sometimes, the window
shuts down unexpectedly without any reason.
• Unusual activities: The computer may perform differently, such as
not being able to log into accounts. The hardware, software, or OS may
start malfunctioning leading to crashing the system abruptly.
• Network issue : Sometimes, there is a high network activity even if the
computer is not connected to the internet and vice versa.
• Unnecessary advertisement: It is normal that sometimes
advertisements may come to the computer screen while browsing, but
when it comes when not browsing, it may indicates a virus on that
computer.
• Affected applications : Some viruses are developed to affect
specific applications. Consequently, some applications may not work if
the computer is infected.
• Blocked by antivirus sites: An antivirus site may deny access to a
computer that is infected by a virus.
• Dialog boxes : Many dialog boxes keep appearing suddenly on a
computer screen.
• Printer issues : A printer attached to an infected computer may print
documents without getting any command or in an inappropriate manner.
• Changed Homepage: A home page may get changed without being
done by the user.
• Strange messages: One may see strange error messages on a
computer such as «cannot rename the folder as a folder with the samename already exists»
1.4.5 Anti-virus installation
• In this case Kaspersky 2017 is going to be used as an example of how
to install an antivirus. Before the installation of Kaspersky 2017 on a
computer, the following preparation has to be made:
• Make sure that the software is on external storage device or on another
computer which is on the network;
• Check if the computer meets the requirements of Kaspersky Anti-Virus 2017;
• Make sure no antivirus software of Kaspersky Lab or other vendors is
installed on your computer;
• Check if there is any incompatible software and remove it;
• Close all running applications;
• Check if it is Kaspersky Anti-Virus 2017 installation under Windows10, then click on the Desktop tile on the start screen.
Standard Installation:
1. Download the installation file from Kaspersky Lab website and run it.
Then, the user follows the instructions given by the system.
2. If the antivirus Kaspersky installation file is saved in another computer
on the same network, connect to that computer and run the executive
file from it or move it using a removable storage. The instructions will be
followed as in the point above
3. Insert the disc into the CD/DVD drive if it contains the Kaspersky
installation file. If the installation does not start automatically, run theinstallation file manually. Click Install.
1.Read the License Agreement in the window that appear afterward by
clicking on the respective link. Accept its terms to install the application.
Respond to other windows that may display as the installation continues
2.Wait until the installation is complete. Make sure the Start Kaspersky
Anti-Virus check box is selected, then click Finish
Note: A virus scan is the process of using anti-virus software to scan and
identify viruses in a computing device. It is recommended to scan any external
storage connected to computer before using it.
Application activity 1.4
1. Explain clearly what will happen If a computer is infected by virus
that shows the following signs or symptoms:
ii) Slow computer performance
iii) Frequent pop-ups
iv) Hard Drive issue
v) Frequent crashes
vi) Unknown programs
2. Give the difference between resident virus and non-resident virus3. What do you understand by executable virus?
1.5 Computer attacks
Activity 1.5
One day, an ICT teacher found the messages belowon some computers in
computer lab.
1. Discuss which kind of messages they are
2. Explain the reason why some computers may display the above
messages
3. Give the solution that can help the ICT teacher avoid those types ofmessages in computers
A Computer attack is any attempt to gain unauthorized access to a computer,
or computing system with the intent to cause damage. Computer attacks aim
to disable, disrupt, destroy or control computer systems or to alter, block, delete, manipulate or steal the data.
1.5.1 Ways of computer attacks
1. Virus
Viruses spread when the software or documents they get attached to are
transferred from one computer to another using a network, a disk, file sharing
methods, or through infected e-mail attachments. Some viruses use differentstealth strategies to avoid their detection from anti-virus software.
2. Trojans
A Trojan horse, or Trojan, is a type of malicious code or software that looks
legitimate but can take control of your computer. A Trojan is designed to
damage, disrupt, steal, or in general inflict some other harmful action on yourdata or network. A Trojan acts like a genuine application or file to trick you.
3. Worms
A computer worm is a program containing malicious code that attacks
host computers and spreads via a network. Network worms exploit security
vulnerabilities in various applications. Due to the availability of the Internet, theycan spread all over the world within a few hours of their release.
4. Website Hacking
Attackers can run code, install malware, steal or modify data by exploiting
vulnerabilities. Typically, hackers snoop around and crawl websites to identify
underlying vulnerabilities and weaknesses and accordingly, orchestrate attacksand data breaches.
5. Cybercrime
Hacking is identifying and exploiting weaknesses in computer systems and/or
computer networks. Cybercrime is committing a crime with the aid of computersand information technology infrastructure.
6. Unwanted content
Unwanted content can come in various different forms and can have a negative
impact on how things are perceived. It is generally personal information that
is displayed on a computer when connected to the internet without the user’sconsent.
7. Attacks through computer network
Actions taken through the use of computer networks to disrupt, deny, degrade,
or destroy information resident in computers and computer networks, or thecomputers and networks themselves.
Examples :
Unauthorized access.Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
8. Attacks by means of removable media
Data can be lost or sensitive data can be leaked. In many cases this data loss
comes at a high price both in reputational damage and financial loss. Another
security risk in the use of removable media is the introduction of malware fromone device to another.
Denial of Services attack
A denial-of-service attack is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator seeks to
make a computer or network resource unavailable to its intended users bytemporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to a network.
Application activity 1.5
1. Explain different ways of how a computer can be attacked.
2. What is a computer attack?
3. Identify any 5 examples of computer attacks
4. Visit you school computer laboratory and detect whether there aresome computers which have been attacked or not.
1.6Threats protection
Activity 1.6
A group of O’level students went to do a research in computer laboratory
and found that some computers have those messages as shown on the
images below. They tried to close those messages but still the computersdid not work properly.
1. Explain why those messages were displayed on the computer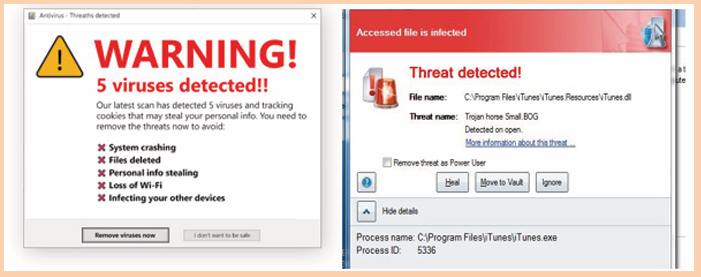
screens.2. Explain can be done in order to make those computers work properly
1.6.1 Computer antivirus
There are many antiviruses, which are programs that can help to protect a
computer from viruses. It scans the system and cleans the viruses detected
during the scan. Some of the popular antiviruses include Avast, Quickheal,
McAfee, Kaspersky, etc
• Basic functions of Antivirus Engines:This is the core of any antivirus
product. All antivirus engines have three components to function
accordingly. It is important to understand these functions because it
will help for better manual cleaning of viruses.
• Scanning: When a new virus is detected in the cyberspace, antivirus
producers start writing programs (updates) that scans for similar
signature strings.
• Integrity checking: This method generally checks for manipulated
files in OS from the viruses.
• Interception: This method is used basically to detect Trojans and it
checks the request made by the operating system for network access.
The following image shows the schema for an antivirus engines functionality.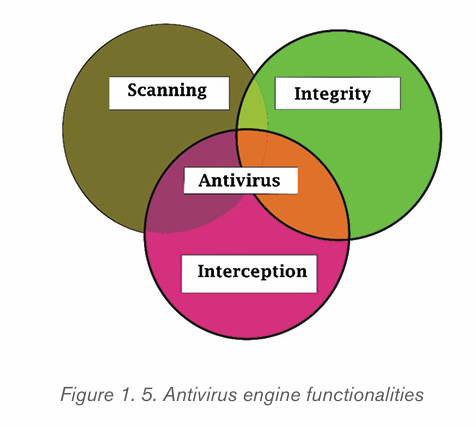
Types of anti virus
1. Free Antivirus Software
The free versions of anti-viruses have nearly identical malware detection scores
to the paid versions produced by the same company, but the commercial
antivirus makes a small difference in the performance of security. Examples
of such antiviruses are Avast Antivirus, AVG Antivirus, Panda Antivirus,
Bitdefender Antivirus, and Microsoft Security Essentials. When the
computer to be installed is a server, there will be a need to have a commercial version
2. Commercial Antivirus
These are the ones that are got after paying a fee. The buyer then gets a key
that will be entered when the antivirus is being installed. Note also that all the
producers of the free antiviruses offer their commercial versions. Some of
the commercial antiviruses are: Kaspersky Anti-Virus, McAfee AntiVirus Plus,
Webroot Secure Anywhere Antivirus, and Bitdefender Antivirus Plus Theseantiviruses can be downloaded as free trials from the maker’s websites.
The Kaspersky Antivirus has an excellent score in anti-phishing and gives a
useful bonus in security tools like credit card protection in computers. McAfee
Antivirus Plus can protect all the operating systems like Windows, Mac OS,
Android, and iOS devices and has very good malicious URL blocking and anti
phishing. Webroot SecureAnywhere Anti virus has features like recovery of files
encrypted by ransomware, very fast scan, handles unkown malware and usessmall amount of disk space.
When using the above type of antivirus, modified, replaced or deleted files and
the shared libraries should also be checked. They generally infect executable
program files with extension like .EXE, .DRV, .SYS, .COM, .BIN. Malwares
changes extension of genuine files, for example: File.TXT to File.TXT.VBS.
For the system administrator of a webserver, be aware of another form of malware
which is called webshell. It generally is in a .php extension but with strange file
names and in an encrypted form.When those types of file are detected from any
computer, they must be deleted.• Detecting a Computer Error from a Virus Infection
This section explains how to detect a computer or OS fault from a virus because
sometimes people and system administrators mix the signs.
The following events are most likely not caused by a malware:
• Error while the system is booting in bios stage, like Bios’s battery cell
display, timer error display.
• Hardware errors, like beeps RAM burn, HDD, etc.
• If a document fails to start normally like a corrupted file, but the other
files can be opened accordingly.
• Keyboard or mouse doesn’t respond to any commands
• Monitor switching on and off too often, like blinking or vibrating, this isa hardware fault.
On the other hand, the following signs in a computer system are caused by malware:
• The computer shows a pop-up or error tables.
• Freezes frequently.
• It slows down when a program or process starts.
• Third parties complain that they are receiving invitation in social media
or via email by computer user.
• Files extensions changes appear or files are added to the system
without computer user consent.
• Internet Explorer freezes too often even though the internet speed is
very good.
• Hard disk space is full all the time, even when there seem to be few files
and folders in the computer.
• Files and program sizes changes comparing to its original version.• Installation of an antivirus
To install an antivirus program on a computer, follow the steps below:
Insert the CD or DVD into the computer’s disc drive. The installation process
should start automatically, with a window opening to guidance through theinstallation process.
• If the antivirus program is downloaded from the Internet, find the
downloaded file on computer. If the downloaded file is a zip file, unzip
the file to extract and access the installation files. Look for a file named
setup.exe, install.exe, or something similar, then double-click that file.
The installation process should start, with a window opening to helpguide through the install process.
1.6.2 Anti-Spyware
Anti-spyware is a type of software that is designed to detect and remove
unwanted spyware programs. Spyware is a type of malware that is installed on
a computer without the user’s knowledge in order to collect information about
them. This can pose a security risk to the user, but more frequently spyware
degrades system performance by taking up processing power, installing
additional software, or redirecting users’ browser activity.
Anti-spyware is an antivirus software primarily utilized to scan a hard disk
for viruses, worms, and Trojan horses, and removes, fixes, or isolates any
threats that are found. Antispyware software scans the hard disk and registry for
traces of spyware and adware to removes them or prompt the user to removethem.
For preventing a computer to be affected by spywares the installation of an anti
spyware is needed. Such anti spyware are: TotalAV, Outbyte PC Repair, Restoro,Advanced SystemCare, Iolo System Mechanic, Malwarebytes Adwcleaner, etc
Applying antispyware
The computer user can download and install a free or commercial AntiSpyWare
then run it and scan the computer as it was done for antivirus to remove foundspyware.
1.6.3 Firewalls
Firewall is a network security device that monitors and filters incoming and
outgoing network traffic based on an organization’s previously established
security policies. It can be a At its most basic, a firewall is essentially the barrierthat sits between a private internal network and the public internet.
A firewall can be a hardware or a software. Afirewall can help protect a network
by acting as an intermediary between the internal network and outside traffic. It
monitors attempts to gain access to the operating system and blocks unwanted
incoming traffic and unrecognized sources. The Benefits of a firewall include
among others preventing hackers and remote access, protecting data, networkmonitoring, protecting against Trojan and other malicious software, etc.
Firewalls are also categorized based on how they operate. Based on theirmethod of operation, below are different types of firewalls:
3. Packet Filtering Firewalls
Packet filtering firewalls are the oldest, most basic type of firewalls. Operating
at the network layer, they check a data packet for its source IP and destination
IP, the protocol, source port, and destination port against predefined rules to
determine whether to pass or discard the packet. Packet filtering firewalls are
essentially stateless, monitoring each packet independently without any track
of the established connection or the packets that have passed through that
connection previously. This makes these firewalls very limited in their capacityto protect against advanced threats and attacks.
Packet filtering firewalls are fast, cheap, and effective. But the security theyprovide is very basic.
4. Circuit level gateways
Circuit-level gateways verify established Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
connections and keep track of the active sessions. They are quite similar to
packet filtering firewalls in that they perform a single check and utilize minimal
resources. Primarily, they determine the security of an established connection.
When an internal device initiates a connection with a remote host, circuit-level
gateways establish a virtual connection on behalf of the internal device to keepthe identity of the internal user hidden.
5. Stateful Inspection Firewalls
They verify and keep track of established connections to perform packet inspection
to provide better, more comprehensive security. They work by creating a kind of
table with source computer addresses, destination computer address, source
computer port and destination computer port once a connection is established.
They create their own rules dynamically to allow expected incoming network
traffic instead of relying on a static set of rules based on this information. Theytherefore drop data packets that do not belong to a verified active connection.
6. Application level Gateways
Also called Proxy Firewalls, application-level gateways are implemented
at the application layer via a proxy device. Instead of an outsider accessing
your internal network directly, the connection is established through the proxy
firewall. The external client sends a request to the proxy firewall. After verifying
the authenticity of the request, the proxy firewall forwards it to one of the internal
devices or servers on the client’s behalf. Alternatively, an internal device may
request access to a webpage, and the proxy device will forward the requestwhile hiding the identity and location of the internal devices and network.
1.6.4 Access control
Every computer user needs access to a password that is shared with them.
The user makes a request to access the password. The request is sent to thedesignated administrator(s) for approval.
1. Main category of users
• Administrator
An administrator is someone who can make changes on a computer that will
affect other users of the computer. Administrators can change security settings,
install software and hardware, access all files on the computer, and make
changes to other user accounts.
• Local user
Local user accounts are stored locally on the server. These accounts can be
assigned rights and permissions on a particular server, but on that server only.
Local user accounts are security principals that are used to secure and manage
access to the resources on a standalone or member server for services or users.
To create a new user account in Windows 10, follow these steps:
1. Right-click the Windows Start menu button.
2. Select Control Panel
3. Select User Accounts .
4. Select Manage another account .
5. Select Add a new user in PC settings .
6. Click on “I don’t have this person’s sign-in information”
7. Click on Add a user without a Microsoft accountAfter following all these steps, the following window will be displayed :
1. On the above window, enter the username and the password the new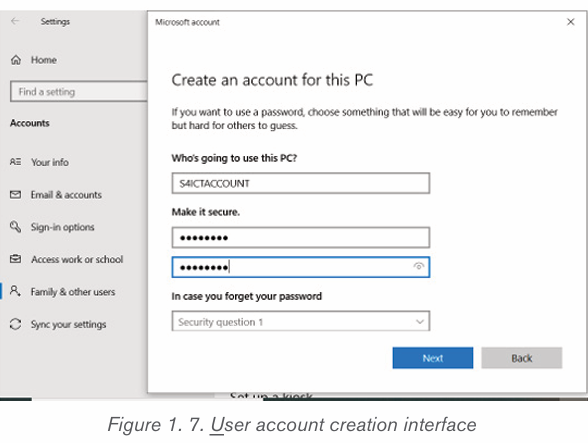
user will use to login.
2. Choose and answer the questions which help in recovering an account
when the password is forgetten.
3. After clicking on Next, a new user account will be created.
Note: The Administrator account is the first account that is created during
the Windows installation. The Administrator account has full control of the
files, directories, services, and other resources on the local computer. The
Administrator account can create other local users, assign user rights, andassign permissions.
Application activity 1.6
1. Describe different functions of an anti virus
2. Differentiate AVG anti virus to Microsoft security essentials
3. Briefly differentiate the types of firewall
4. a) At your school, the anti-virus used or installed in computers is for
how many users ?
5. b) Suppose that, the anti-virus keys are stolen by someone else to
use it on network. What can be the consequences for that anti-virus
users in that school ?6. c) How the computer users can avoid that illegal action ?
Activity 1.7
In the school computer laboratory, to enter in a secured computer with
password, someone needs to be given that password. If it has been
forgotten, it becomes impossible to work with that computer. Answer the
following questions :
1. What is the importance of login to computer with password ?
2. List other security measures that can be used to protect a computer.3. Explain how data stored in computer can be protected from damage ?
1.7 Threat prevention
Computer viruses can easily spread through the internet and email, causing
potential harm to a computer’s data, files and hard drive. Viruses are commonly
disguised as hyperlinks, pop-ups or email attachments of images, greeting cards,
audio or video files. Use the following instructions to help keep the computersafe from viruses, hackers and other malicious attacks.
1. Use Strong Passwords
It is very necessary to keep data safe by creating unique, complex passwords.
The best passwords include a mix of numbers, letters, and symbols and are atleast 8 characters long.
2. Keep everything up to date
Another basic step to take is to make sure you have the latest versions of all
software installed on your devices. The importance of this is because software
updates include features designed to withstand the latest security threats.
Microsoft, Oracle, and other makers regularly update their software to eliminate
“bugs” that hackers could exploit.
If a computer has an operating a system from many years ago, it’s defenseless
against any viruses or malware recently developed. Make it a habit to install allnew software updates as soon as they become available.
1. Use Antivirus Software
Antivirus software acts as a “vaccine” against virtual viruses. It can identify andeliminate the threat that could harm a computer.
2. Use a Firewall
Using antivirus programs doesn’t automatically mean that there is a firewall in a
computer. Macs computers come with pre-installed firewall software. Make sureit’s enabled to provide an extra layer of protection from viruses and malware.
3. Install a popup blocker
Many attacks happen through browsers, during everyone’s daily activities.
Hackers can gain access to any computer from one innocent click on the wrong
ad or link. An ad or popup blocker is essential to protecting any computer’s
data. It will prevent any unwanted pages from opening automatically. Never clickon, open, or download anything unless its source is known.
4. Beware of Email Phishing Scams
These appear in email form under the guise of a legitimate company. The goal is
to get the computer user to enter his/her personal information or to click on aninfected link that allows access to the computer.
Some companies will have their own domain name for emails. If an email address
claims to be from Paypal or Netflix but ends with @gmail.com, it’s a scam.Other
signs include misspellings, poor grammar, and suspicious attachments, buttons,
or links. A legitimate company will never invite you via email to log in and providepersonal or billing information.
5. Know the signs of infection
There are different signs which may make one think about a computer being
onfected such as repeated error messages, unexpected shutdowns, a sudden
slowing down of a computer, a computer taking too long to shut down or restart,
new unknown toolbars, etc. Any of these signs could mean that the computeris infected.
6. Consider additional security features
At the very least, it is better to perform weekly or even daily backups of all
important data. Store it securely in the cloud or on a separate hard drive.
That way, if the virus come accidentaly the vital information won’t be lost or
compromised. For extra protection, it is good to consider advanced security
measures like endpoint security. This protects not just not only the computerbut also the whole network.
Application activity 1.7
1. In group of 4 discuss the best practices that every user of the
computer should apply as routine in order to keep an installed
antivirus stronger.
2. Install an available antivirus in the computer lab, update it and scan
the full computer then report you observed during the whole process
up to the end.
3. Discuss the necessary recommendations to prevent viruses and
spywares from the computer4. Outline the signs of a computer which has been infected by virus
End of unit assessment 1
Part 1. Written
a) What is computer security ?
b) What is the purpose of computer security ?
c) With an example, explain how you can protect a computer from
physical threats ?
d) By using examples, explain access control in authorization
e) Which type of attack that enable a computer user to access his/
her e-mail address ?
f) Identify consequences of security violation in computer security
context
g) Discuss and write a brief report on the importance of computer
security at your school, in financial institutions and in education field
h) With an example differentiate the physical threats to logical threats
i) Explain the term “Executable virus”
j) It is heard that some web site become hacked by unknown
people. Which strategies can be used to avoid young Rwandan
programmers to engage in that action ?
k) Using an arrow match the following in Group A with their
corresponding in Group B
Part 2. Written
In school computer lab, every student takes a computer and do the following
activities :
i) Create a user name and password to enter in that particular computer
ii) Add a new user on the computeriii) Update the anti-virus found on the computers
To set a paragraph spacing follow these steps:
2. Type the list, pressing Enter once to insert another bullet. When fini
shed, simply press Enter twice.
i) To create a numbered list in Microsoft Word, follow the steps below.
1. Position the cursor where the numbered list will be inserted.
2. In the Home tab, click the Numbering tool. A number One should appear.
